Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering
|
|
|
- Jonas Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering 1
2 Introduction Plots are a very useful tool for presenting information. MATLAB has many commands that can be used for creating different types of plots. These include standard plots with linear axes, plots with logarithmic bar and stairs plots, polar plots, three-dimensional contour surface and mesh plots, and many more. The plots can be formatted to have a desired appearance. The line type (solid, dashed, etc.), color, and thickness can be prescribed, line markers and grid lines can be added, as can titles and text comments. Several graphs can be created in the same plot, and several plots can be placed on the same page. 2
3 Introduction 3
4 5.1 THE plot COMMAND The plot command is used to create two-dimensional plots. The simplest form of the command is: The arguments x and y are each a vector (one-dimensional array). The two vectors must have the same number of elements. When the plot command is executed, a figure is created in the Figure Window. The figure has a single curve with the x values on the horizontal axis and the y values on the vertical axis. If only one vector is entered as an input argument in the plot command (for example: plot (y)) then the figure will show a plot of the values of the elements of the vector ( y(l), y(2), y(3),... ) versus the element number ( 1, 2, 3,... ). 4
5 5.1 THE plot COMMAND 5
6 5.1 THE plot COMMAND The plot command has additional, optional arguments that can be used to specify the color and style of the line and the color and type of markers, if any are desired. 6
7 5.1 THE plot COMMAND Line Specifiers: optional, can be used to define the style and color of the line and the type of markers. 7
8 5.1 THE plot COMMAND 8
9 5.1 THE plot COMMAND Notes about using the specifiers: The specifiers are typed inside the plot command as strings. Within the string the specifiers can be typed in any order. The specifiers are optional. This means that none, one, two, or all three types can be included in a command. 9
10 5.1 THE plot COMMAND Property Name and Property Value: Properties are optional and can be used to specify the thickness of the line, the size of the marker, and the colors of the marker's edge line and fill. 10
11 For example, the command: 5.1 THE plot COMMAND creates a plot that connects the points with a magenta solid line and circles as markers at the points. The line width is 2 points and the size of the circle markers is 12 points. The markers have a green edge line and yellow filling. 11
12 5.1 THE plot COMMAND A note about line specifiers and properties: The three line specifiers, which indicate the style and color of the line, and the type of the marker can also be assigned with a PropertyName argument followed by a PropertyValue argument. 12
13 5.1.1 Plot of Given Data 13
14 5.1.1 Plot of Given Data 14
15 5.1.2 Plot of a Function As an example, the plot command is used to plot the function y = x cos (6x) for -2 x 4. 15
16 5.1.2 Plot of a Function 16
17 5.1.2 Plot of a Function In the last example a small spacing of 0.01 produced the plot of the function. If larger spacing is used, for example, 0.3, the plot gives a distorted picture of the function. 17
18 5.2 THE fplot COMMAND The fplot command plots a function with the form y = f(x) between specified limits. The command has the form: 18
19 5.2 THE fplot COMMAND 19
20 5.2 THE fplot COMMAND 20
21 5.2 THE fplot COMMAND 21
22 5.3 PLOTTING MULTIPLE GRAPHS IN THE SAME PLOT There are three methods to plot multiple graphs in one figure. One is by using the plot command, the second is by using the hold on and hold off commands, and the third is by using the line command Using the plot Command Two or more graphs can be created in the same plot by typing pairs of vectors inside the plot command. The command: plot(x,y,u,v,t,h) creates three graphs y vs. x, v vs. u, and h vs. t all in the same plot. The vectors of each pair must be of the same length. It is also possible to add line specifiers following each pair. For example the command: plot(x,y, '-b',u,v, '--r', t,h, 'g:') 22
23 Sample Problem 5-1: Plotting a function and its derivatives Plot the function y = 3x 3-26x + 10, and its first and second derivatives, for -2 x 4, all in the same plot. Solution The first derivative of the function is: y = 9x The second derivative of the function is: y = 18x. 23
24 Sample Problem 5-1: Plotting a function and its derivatives 24
25 5.3.2 Using the hold on and hold off Commands To plot several graphs using the hold on and hold off commands, one graph is plotted first with the plot command. Then the hold on command is typed. This keeps the Figure Window with the first plot open including the axis properties and formatting. Additional graphs can be added with plot commands that are typed next. Each plot command creates a graph that is added to that figure. The hold off command stops this process. It returns MATLAB to the default mode, in which the plot command erases the previous plot and resets the axis properties. 25
26 5.3.2 Using the hold on and hold off Commands 26
27 5.3.3 Using the line Command With the line command additional graphs (lines) can be added to a plot that already exists. The properties are optional, and if none are entered MATLAB uses default properties and values. For example, the command: line(x,y, 'linestyle', '--','color', 'r', 'marker', 'o') will add a dashed red line with circular markers to a plot that already exists. 27
28 5.3.3 Using the line Command The major difference between the plot and line commands is that the plot command starts a new plot every time it is executed, while the line command adds lines to a plot that already exists. To make a plot that has several graphs, a plot command is typed first and then line commands are typed for additional graphs. (If a line command is entered before a plot command, an error message is displayed.) 28
29 5.4.1 Formatting a Plot Using Commands The xlabel and ylabel commands: 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT The title command: The text command: The text command places the text in the figure such that the first character is positioned at the point with the coordinates x, y (according to the axes of the figure). The gtext command places the text at a position specified by the user. When the command is executed, the Figure Window opens and the user specifies the position with the mouse. 29
30 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT The legend command: 30
31 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT Formatting the text within the xlabel, ylabel, title, text and legend commands: The formatting can be used to define the font, size, position (superscript, subscript), style (italic, bold, etc.), and color of the characters, the color of the background, and many other details of the display. The formatting can be done either by adding modifiers inside the string, or by adding to the command optional PrapertyName and PrapertyValue arguments following the string. 31
32 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT Formatting the text within the xlabel, ylabel, title, text and legend commands: Subscript and superscript: A single character can be displayed as a subscript or a superscript by typing_ (the underscore character) or ^ in front of the character, respectively. Several consecutive characters can be displayed as a subscript or a superscript by typing the characters inside braces { } following the_ or the ^. 32
33 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT Formatting the text within the xlabel, ylabel, title, text and legend commands: Greek characters: 33
34 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT Formatting the text within the xlabel, ylabel, title, text and legend commands: Formatting of the text can also be done by adding optional PropertyName and PropertyValue arguments following the string inside the command. 34
35 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT The axis command: The grid command: 35
36 5.4 FORMATTING A PLOT 36
37 5.4.2 Formatting a Plot Using the Plot Editor 37
38 5.5 PLOTS WITH LOGAJUTHMIC AXES Line specifiers and Property Name and Property Value arguments can be added to the commands (optional) just as in the plot command 38
39 5.5 PLOTS WITH LOGAJUTHMIC AXES 39
40 5.5 PLOTS WITH LOGAJUTHMIC AXES 40
41 5.6 PLOTS WITH ERROR BARS An error bar is typically a short vertical line that is attached to a data point in a plot. It shows the magnitude of the error that is associated with the value that is displayed by the data point. 41
42 5.6 PLOTS WITH ERROR BARS Symmetric error bar: the error bar extends the same length above and below the data point The lengths of the three vectors x, y, and e must be the same. The length of the error bar is twice the value of e. At each point the error bar extends from y(i)-e(i) to y(i)+e(i). 42
43 5.6 PLOTS WITH ERROR BARS 43
44 Non-symmetric error bars: 5.6 PLOTS WITH ERROR BARS The lengths of the four vectors x, y, d, and u must be the same. At each point the error bar extends from y(i)-d(i) to y(i)+u(i). 44
45 5. 7 PLOTS WITH SPECIAL GRAPHICS 45
46 5. 7 PLOTS WITH SPECIAL GRAPHICS 46
47 5. 7 PLOTS WITH SPECIAL GRAPHICS 47
48 5.8 HISTOGRAMS Histograms are plots that show the distribution of data. The overall range of a given set of data points is divided into subranges (bins), and the histogram shows how many data points are in each bin. 48
49 5.8 HISTOGRAMS The following data points are the daily maximum temperature (in F) during the month of April:
50 5.8 HISTOGRAMS The smallest value in the data set is 48 and the largest is 93, which means that the range is 45 and the width of each bin is 4.5. The range of the first bin is from 48 to 52.5 and contains two points. The range of the second bin is from 52.5 to 57 and contains three points, and so on. Two of the bins (75 to 79.5 and 84 to 88.5) do not contain any points. 50
51 5.8 HISTOGRAMS The number of bins can be defined to be different than 10. This can be done either by specifying the number of bins, or by specifying the center point of each bin: 51
52 5.8 HISTOGRAMS 52
53 5.8 HISTOGRAMS 53
54 5.8 HISTOGRAMS Fig The vector n shows that the first bin has two data points, the second bin has three data points, and so on. 54
55 5.8 HISTOGRAMS 55
56 5.9 POLAR PLOTS Polar coordinates, in which the position of a point in a plane is defined by the angle θ and the radius (distance) to the point, are frequently used in the solution of science and engineering problems. 56
57 5.9 POLAR PLOTS To plot a function r = f(θ) in a certain domain, a vector for values of θ is created first, and then a vector r with the corresponding values of is created using element-by-element calculations. 57
58 5.10 PUTTING MULTIPLE PLOTS ON THE SAME PAGE Multiple plots can be created on the same page with the subplot command, which has the form: The command divides the Figure Window into mxn rectangular subplots. The subplots are arranged like elements in an mxn matrix where each element is a subplot. The subplots are numbered from 1 through m*n. The command subplot(m,n,p) makes the subplot p current. For example, the command subplot(3,2,1) creates six areas arranged in three rows and two columns as shown, and makes the upper left subplot current. 58
Contents. An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users
 An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users (Using Two-Dimensional Plots) Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional
An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users (Using Two-Dimensional Plots) Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB
 Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Plot (2D) plot(x,y, -mo, LineWidth,2, markersize,12, MarkerEdgeColor, g, markerfacecolor, y ) Plot (2D) Plot of a Function As an example, the plot command
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Plot (2D) plot(x,y, -mo, LineWidth,2, markersize,12, MarkerEdgeColor, g, markerfacecolor, y ) Plot (2D) Plot of a Function As an example, the plot command
MATLAB - Lecture # 5
 MATLAB - Lecture # 5 Two Dimensional Plots / Chapter 5 Topics Covered: 1. Plotting basic 2-D plots. The plot command. The fplot command. Plotting multiple graphs in the same plot. MAKING X-Y PLOTS 105
MATLAB - Lecture # 5 Two Dimensional Plots / Chapter 5 Topics Covered: 1. Plotting basic 2-D plots. The plot command. The fplot command. Plotting multiple graphs in the same plot. MAKING X-Y PLOTS 105
MATLAB 2-D Plotting. Matlab has many useful plotting options available! We ll review some of them today.
 Class15 MATLAB 2-D Plotting Matlab has many useful plotting options available! We ll review some of them today. help graph2d will display a list of relevant plotting functions. Plot Command Plot command
Class15 MATLAB 2-D Plotting Matlab has many useful plotting options available! We ll review some of them today. help graph2d will display a list of relevant plotting functions. Plot Command Plot command
Two-Dimensional Plots
 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Plots are a very useful tool for presenting information. This is true in any field, but especially in science and engineering where MATLAB is mostly used. MATLAB has many
Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Plots are a very useful tool for presenting information. This is true in any field, but especially in science and engineering where MATLAB is mostly used. MATLAB has many
Computer Programming: 2D Plots. Asst. Prof. Dr. Yalçın İşler Izmir Katip Celebi University
 Computer Programming: 2D Plots Asst. Prof. Dr. Yalçın İşler Izmir Katip Celebi University Outline Plot Fplot Multiple Plots Formatting Plot Logarithmic Plots Errorbar Plots Special plots: Bar, Stairs,
Computer Programming: 2D Plots Asst. Prof. Dr. Yalçın İşler Izmir Katip Celebi University Outline Plot Fplot Multiple Plots Formatting Plot Logarithmic Plots Errorbar Plots Special plots: Bar, Stairs,
Plotting. Aaron S. Donahue. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140
 Plotting Aaron S. Donahue Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140 A. S. Donahue (University of Notre Dame) Lecture 4 1 / 15
Plotting Aaron S. Donahue Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140 A. S. Donahue (University of Notre Dame) Lecture 4 1 / 15
MATLAB: Plots. The plot(x,y) command
 MATLAB: Plots In this tutorial, the reader will learn about obtaining graphical output. Creating a proper engineering plot is not an easy task. It takes lots of practice, because the engineer is trying
MATLAB: Plots In this tutorial, the reader will learn about obtaining graphical output. Creating a proper engineering plot is not an easy task. It takes lots of practice, because the engineer is trying
Two-dimensional Plots
 Two-dimensional Plots ELEC 206 Prof. Siripong Potisuk 1 The Plot Command The simplest command for 2-D plotting Syntax: >> plot(x,y) The arguments x and y are vectors (1-D arrays) which must be of the same
Two-dimensional Plots ELEC 206 Prof. Siripong Potisuk 1 The Plot Command The simplest command for 2-D plotting Syntax: >> plot(x,y) The arguments x and y are vectors (1-D arrays) which must be of the same
CSCD 409 Scientific Programming. Module 6: Plotting (Chpt 5)
 CSCD 409 Scientific Programming Module 6: Plotting (Chpt 5) 2008-2012, Prentice Hall, Paul Schimpf All rights reserved. No portion of this presentation may be reproduced, in whole or in part, in any form
CSCD 409 Scientific Programming Module 6: Plotting (Chpt 5) 2008-2012, Prentice Hall, Paul Schimpf All rights reserved. No portion of this presentation may be reproduced, in whole or in part, in any form
Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting
 PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB for Engineers, Third Edition Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting Copyright 2010. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. This work is only for non-profit use by instructors
PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB for Engineers, Third Edition Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting Copyright 2010. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. This work is only for non-profit use by instructors
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by. Introduction to Matlab
 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by Mohamed Hussein Lecture 5 Introduction to Matlab More on XY Plotting Other Types of Plotting 3D Plot (XYZ Plotting) More on XY Plotting Other XY plotting commands are axis ([xmin
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by Mohamed Hussein Lecture 5 Introduction to Matlab More on XY Plotting Other Types of Plotting 3D Plot (XYZ Plotting) More on XY Plotting Other XY plotting commands are axis ([xmin
Making 2D Plots in Matlab
 Making 2D Plots in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Plotting with Matlab Overview Plotting in Matlab Plotting (x, y) data
Making 2D Plots in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Plotting with Matlab Overview Plotting in Matlab Plotting (x, y) data
Attia, John Okyere. Plotting Commands. Electronics and Circuit Analysis using MATLAB. Ed. John Okyere Attia Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999
 Attia, John Okyere. Plotting Commands. Electronics and Circuit Analysis using MATLAB. Ed. John Okyere Attia Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999 1999 by CRC PRESS LLC CHAPTER TWO PLOTTING COMMANDS 2.1 GRAPH
Attia, John Okyere. Plotting Commands. Electronics and Circuit Analysis using MATLAB. Ed. John Okyere Attia Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999 1999 by CRC PRESS LLC CHAPTER TWO PLOTTING COMMANDS 2.1 GRAPH
Worksheet 5. Matlab Graphics
 Worksheet 5. Matlab Graphics Two dimesional graphics Simple plots can be made like this x=[1.5 2.2 3.1 4.6 5.7 6.3 9.4]; y=[2.3 3.9 4.3 7.2 4.5 6.1 1.1]; plot(x,y) plot can take an additional string argument
Worksheet 5. Matlab Graphics Two dimesional graphics Simple plots can be made like this x=[1.5 2.2 3.1 4.6 5.7 6.3 9.4]; y=[2.3 3.9 4.3 7.2 4.5 6.1 1.1]; plot(x,y) plot can take an additional string argument
Plotting in MATLAB. Trevor Spiteri
 Functions and Special trevor.spiteri@um.edu.mt http://staff.um.edu.mt/trevor.spiteri Department of Communications and Computer Engineering Faculty of Information and Communication Technology University
Functions and Special trevor.spiteri@um.edu.mt http://staff.um.edu.mt/trevor.spiteri Department of Communications and Computer Engineering Faculty of Information and Communication Technology University
Plots Publication Format Figures Multiple. 2D Plots. K. Cooper 1. 1 Department of Mathematics. Washington State University.
 2D Plots K. 1 1 Department of Mathematics 2015 Matplotlib The most used plotting API in Python is Matplotlib. Mimics Matlab s plotting capabilities Not identical plot() takes a variable number of arguments...
2D Plots K. 1 1 Department of Mathematics 2015 Matplotlib The most used plotting API in Python is Matplotlib. Mimics Matlab s plotting capabilities Not identical plot() takes a variable number of arguments...
Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting and Model Building
 PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB 7 for Engineers Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting and Model Building Copyright 2005. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB 7 for Engineers Chapter 5 Advanced Plotting and Model Building Copyright 2005. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Week 2: Plotting in Matlab APPM 2460
 Week 2: Plotting in Matlab APPM 2460 1 Introduction Matlab is great at crunching numbers, and one of the fundamental ways that we understand the output of this number-crunching is through visualization,
Week 2: Plotting in Matlab APPM 2460 1 Introduction Matlab is great at crunching numbers, and one of the fundamental ways that we understand the output of this number-crunching is through visualization,
Outline. 1 File access. 2 Plotting Data. 3 Annotating Plots. 4 Many Data - one Figure. 5 Saving your Figure. 6 Misc. 7 Examples
 Outline 9 / 15 1 File access 2 Plotting Data 3 Annotating Plots 4 Many Data - one Figure 5 Saving your Figure 6 Misc 7 Examples plot 2D plotting 1. Define x-vector 2. Define y-vector 3. plot(x,y) >> x
Outline 9 / 15 1 File access 2 Plotting Data 3 Annotating Plots 4 Many Data - one Figure 5 Saving your Figure 6 Misc 7 Examples plot 2D plotting 1. Define x-vector 2. Define y-vector 3. plot(x,y) >> x
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert
 Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB
 GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB Contents 1 Preview: Programming & Experiments Goals 2 2 Homework Assignment 3 3 Measuring The
GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB Contents 1 Preview: Programming & Experiments Goals 2 2 Homework Assignment 3 3 Measuring The
Introduction to Matplotlib
 Lab 5 Introduction to Matplotlib Lab Objective: Matplotlib is the most commonly-used data visualization library in Python. Being able to visualize data helps to determine patterns, to communicate results,
Lab 5 Introduction to Matplotlib Lab Objective: Matplotlib is the most commonly-used data visualization library in Python. Being able to visualize data helps to determine patterns, to communicate results,
Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets
 Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets
 Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
NCSS Statistical Software
 Chapter 147 Introduction A mosaic plot is a graphical display of the cell frequencies of a contingency table in which the area of boxes of the plot are proportional to the cell frequencies of the contingency
Chapter 147 Introduction A mosaic plot is a graphical display of the cell frequencies of a contingency table in which the area of boxes of the plot are proportional to the cell frequencies of the contingency
Examples: Find the domain and range of the function f(x, y) = 1 x y 2.
 Multivariate Functions In this chapter, we will return to scalar functions; thus the functions that we consider will output points in space as opposed to vectors. However, in contrast to the majority of
Multivariate Functions In this chapter, we will return to scalar functions; thus the functions that we consider will output points in space as opposed to vectors. However, in contrast to the majority of
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
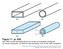 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design. Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph
 Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph Step 1: Set up the variables X axis for AB Design Enter X axis label
Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph Step 1: Set up the variables X axis for AB Design Enter X axis label
Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor As we studied last section points may be described in polar form or rectangular form. Likewise an equation may be written using either
Precalculus Lesson 9.2 Graphs of Polar Equations Mrs. Snow, Instructor As we studied last section points may be described in polar form or rectangular form. Likewise an equation may be written using either
How to define Graph in HDSME
 How to define Graph in HDSME HDSME provides several chart/graph options to let you analyze your business in a visual format (2D and 3D). A chart/graph can display a summary of sales, profit, or current
How to define Graph in HDSME HDSME provides several chart/graph options to let you analyze your business in a visual format (2D and 3D). A chart/graph can display a summary of sales, profit, or current
PASS Sample Size Software. These options specify the characteristics of the lines, labels, and tick marks along the X and Y axes.
 Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Engineering Department Professionalism: Graphing Standard
 Engineering Department Professionalism: Graphing Standard Introduction - A big part of an engineer s job is to communicate. This often involves presenting experimental or theoretical results in graphical
Engineering Department Professionalism: Graphing Standard Introduction - A big part of an engineer s job is to communicate. This often involves presenting experimental or theoretical results in graphical
Creating Nice 2D-Diagrams
 UseCase.0046 Creating Nice 2D-Diagrams Keywords: 2D view, z=f(x,y), axis, axes, bitmap, mesh, contour, plot, font size, color lookup table, presentation Description This use case demonstrates how to configure
UseCase.0046 Creating Nice 2D-Diagrams Keywords: 2D view, z=f(x,y), axis, axes, bitmap, mesh, contour, plot, font size, color lookup table, presentation Description This use case demonstrates how to configure
Lab 4 Projectile Motion
 b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x x v v v o ox ox v v ox at 1 t at a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally or an
b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x x v v v o ox ox v v ox at 1 t at a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally or an
Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity)
 Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity) Importing Data into MATLAB Change your Current Folder to the folder where your data is located. Import
Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity) Importing Data into MATLAB Change your Current Folder to the folder where your data is located. Import
Engineering Fundamentals and Problem Solving, 6e
 Engineering Fundamentals and Problem Solving, 6e Chapter 5 Representation of Technical Information Chapter Objectives 1. Recognize the importance of collecting, recording, plotting, and interpreting technical
Engineering Fundamentals and Problem Solving, 6e Chapter 5 Representation of Technical Information Chapter Objectives 1. Recognize the importance of collecting, recording, plotting, and interpreting technical
Description cabiplot caprojection Remarks and examples References Also see
 Title stata.com ca postestimation plots Postestimation plots for ca and camat cabiplot caprojection Remarks and examples References Also see The following postestimation commands are of special interest
Title stata.com ca postestimation plots Postestimation plots for ca and camat cabiplot caprojection Remarks and examples References Also see The following postestimation commands are of special interest
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
PASS Sample Size Software
 Chapter 945 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a histogram. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Chapter 945 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a histogram. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Why Should We Care? Everyone uses plotting But most people ignore or are unaware of simple principles Default plotting tools are not always the best
 Elementary Plots Why Should We Care? Everyone uses plotting But most people ignore or are unaware of simple principles Default plotting tools are not always the best More importantly, it is easy to lie
Elementary Plots Why Should We Care? Everyone uses plotting But most people ignore or are unaware of simple principles Default plotting tools are not always the best More importantly, it is easy to lie
User s Manual ❿ Drawings-Detailing
 User s Manual ❿ Drawings-Detailing 2 CONTENTS I. THE NEW UPGRADED INTERFACE of SCADA Pro 4 1. UNITS 5 1.1 Drawings-Detailing 5 I. Files 6 II. Drawing 25 III. Formworks 30 IV. Edit 45 V. View 58 VI. Layers
User s Manual ❿ Drawings-Detailing 2 CONTENTS I. THE NEW UPGRADED INTERFACE of SCADA Pro 4 1. UNITS 5 1.1 Drawings-Detailing 5 I. Files 6 II. Drawing 25 III. Formworks 30 IV. Edit 45 V. View 58 VI. Layers
Using Figures - The Basics
 Using Figures - The Basics by David Caprette, Rice University OVERVIEW To be useful, the results of a scientific investigation or technical project must be communicated to others in the form of an oral
Using Figures - The Basics by David Caprette, Rice University OVERVIEW To be useful, the results of a scientific investigation or technical project must be communicated to others in the form of an oral
Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1
 Objective: Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1 This Matlab Project is an extension of the basic correlation theory presented in the course. It shows a practical application
Objective: Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1 This Matlab Project is an extension of the basic correlation theory presented in the course. It shows a practical application
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis
 Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
Graph of the Sine Function
 1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
Purpose. Charts and graphs. create a visual representation of the data. make the spreadsheet information easier to understand.
 Purpose Charts and graphs are used in business to communicate and clarify spreadsheet information. convert spreadsheet information into a format that can be quickly and easily analyzed. make the spreadsheet
Purpose Charts and graphs are used in business to communicate and clarify spreadsheet information. convert spreadsheet information into a format that can be quickly and easily analyzed. make the spreadsheet
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2924: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan. Figure 50.1
 50 Polar Coordinates Arkansas Tech University MATH 94: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan Up to this point we have dealt exclusively with the Cartesian coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is
50 Polar Coordinates Arkansas Tech University MATH 94: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan Up to this point we have dealt exclusively with the Cartesian coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is
Math 148 Exam III Practice Problems
 Math 48 Exam III Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 48 Exam III Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Why Should We Care? More importantly, it is easy to lie or deceive people with bad plots
 Elementary Plots Why Should We Care? Everyone uses plotting But most people ignore or are unaware of simple principles Default plotting tools (or default settings) are not always the best More importantly,
Elementary Plots Why Should We Care? Everyone uses plotting But most people ignore or are unaware of simple principles Default plotting tools (or default settings) are not always the best More importantly,
MATH 259 FINAL EXAM. Friday, May 8, Alexandra Oleksii Reshma Stephen William Klimova Mostovyi Ramadurai Russel Boney A C D G H B F E
 MATH 259 FINAL EXAM 1 Friday, May 8, 2009. NAME: Alexandra Oleksii Reshma Stephen William Klimova Mostovyi Ramadurai Russel Boney A C D G H B F E Instructions: 1. Do not separate the pages of the exam.
MATH 259 FINAL EXAM 1 Friday, May 8, 2009. NAME: Alexandra Oleksii Reshma Stephen William Klimova Mostovyi Ramadurai Russel Boney A C D G H B F E Instructions: 1. Do not separate the pages of the exam.
Appendix C: Graphing. How do I plot data and uncertainties? Another technique that makes data analysis easier is to record all your data in a table.
 Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 A) Even B) Odd C) Neither
 Assignment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 1) A)
Assignment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 1) A)
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing. 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane
 Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Module 2.1, 2.2 Review. EF101 Analysis & Skills Module 2.3. Sketched Features and Operations. On-line Help Two Locations
 EF101 Analysis & Skills Module 2.3 Engineering Graphics Revolved Features Placed Features Work Features Module 2.1, 2.2 Review What are the three types of operations for adding features to the base feature?
EF101 Analysis & Skills Module 2.3 Engineering Graphics Revolved Features Placed Features Work Features Module 2.1, 2.2 Review What are the three types of operations for adding features to the base feature?
266&deployment= &UserPass=b3733cde68af274d036da170749a68f6
 Sections 14.6 and 14.7 (1482266) Question 12345678910111213141516171819202122 Due: Thu Oct 21 2010 11:59 PM PDT 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 14.6.012. [1289020] Find the directional derivative, D u f, of
Sections 14.6 and 14.7 (1482266) Question 12345678910111213141516171819202122 Due: Thu Oct 21 2010 11:59 PM PDT 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 14.6.012. [1289020] Find the directional derivative, D u f, of
 http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective
 Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective The objective is to teach students a basic digital communication
Wireless Communication Systems Laboratory Lab#1: An introduction to basic digital baseband communication through MATLAB simulation Objective The objective is to teach students a basic digital communication
Extrema Tutorial. Customizing Graph Presentation. Cohen et al. NP_A395(1983) Oset et al. NP_A454(1986) Rockmore PR_C27(1983) This work
 Extrema Tutorial Customizing Graph Presentation 16 O( 10 4 π +,π - π + ) Cohen et al. NP_A395(1983) Oset et al. NP_A454(1986) Rockmore PR_C27(1983) This work 10 3 10 2 10 1 180 200 220 240 260 280 300
Extrema Tutorial Customizing Graph Presentation 16 O( 10 4 π +,π - π + ) Cohen et al. NP_A395(1983) Oset et al. NP_A454(1986) Rockmore PR_C27(1983) This work 10 3 10 2 10 1 180 200 220 240 260 280 300
Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES:
 Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES: 1. To learn how to present data in graphical form manually (paper-and-pencil) and using computer software. 2. To learn how to interpret graphical data by, a. determining the
Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES: 1. To learn how to present data in graphical form manually (paper-and-pencil) and using computer software. 2. To learn how to interpret graphical data by, a. determining the
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934)
 HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet
 Name: Date: Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet Directions Using our class datasheets, we will analyze additional scatterplots, using Microsoft Excel to make those plots. To get started,
Name: Date: Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet Directions Using our class datasheets, we will analyze additional scatterplots, using Microsoft Excel to make those plots. To get started,
Chapter 3. Graphical Methods for Describing Data. Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing Data 1 Frequency Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer to the
Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing Data 1 Frequency Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer to the
Lab 4 Projectile Motion
 b Lab 4 Projectile Motion Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: 1 x = x o + voxt + at o ox 2 at v = vox + at at 2 2 v 2 = vox 2 + 2aΔx ox FIGURE 1 Linear FIGURE Motion Linear Equations Motion Equations
b Lab 4 Projectile Motion Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: 1 x = x o + voxt + at o ox 2 at v = vox + at at 2 2 v 2 = vox 2 + 2aΔx ox FIGURE 1 Linear FIGURE Motion Linear Equations Motion Equations
This tutorial will lead you through step-by-step to make the plot below using Excel.
 GES 131 Making Plots with Excel 1 / 6 This tutorial will lead you through step-by-step to make the plot below using Excel. Number of Non-Student Tickets vs. Student Tickets Y, Number of Non-Student Tickets
GES 131 Making Plots with Excel 1 / 6 This tutorial will lead you through step-by-step to make the plot below using Excel. Number of Non-Student Tickets vs. Student Tickets Y, Number of Non-Student Tickets
How to Make a Run Chart in Excel
 How to Make a Run Chart in Excel While there are some statistical programs that you can use to make a run chart, it is simple to make in Excel, using Excel s built-in chart functions. The following are
How to Make a Run Chart in Excel While there are some statistical programs that you can use to make a run chart, it is simple to make in Excel, using Excel s built-in chart functions. The following are
Basic Signals and Systems
 Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
NX 7.5. Table of Contents. Lesson 3 More Features
 NX 7.5 Lesson 3 More Features Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Completion of NX 7.5 Lessons 1&2 Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material
NX 7.5 Lesson 3 More Features Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Completion of NX 7.5 Lessons 1&2 Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material
Introduction to MATLAB 7 for Engineers. Add for Chapter 2 Advanced Plotting and Model Building
 Introduction to MATLAB 7 for Engineers Add for Chapter 2 Advanced Plotting and Model Building Nomenclature for a typical xy plot. The following MATLAB session plots y 0 4 1 8x for 0 x 52, where y represents
Introduction to MATLAB 7 for Engineers Add for Chapter 2 Advanced Plotting and Model Building Nomenclature for a typical xy plot. The following MATLAB session plots y 0 4 1 8x for 0 x 52, where y represents
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching
 Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Digital Video and Audio Processing. Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises
 Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Completed project drawing (dimensions added for reference)
 CHAPTER 5 Fundamentals IV PROJECT EXERCISE This project exercise provides point-by-point instructions for setting up the drawing with layers and then creating the objects shown in the accompanying figure.
CHAPTER 5 Fundamentals IV PROJECT EXERCISE This project exercise provides point-by-point instructions for setting up the drawing with layers and then creating the objects shown in the accompanying figure.
Descriptive Statistics II. Graphical summary of the distribution of a numerical variable. Boxplot
 MAT 2379 (Spring 2012) Descriptive Statistics II Graphical summary of the distribution of a numerical variable We will present two types of graphs that can be used to describe the distribution of a numerical
MAT 2379 (Spring 2012) Descriptive Statistics II Graphical summary of the distribution of a numerical variable We will present two types of graphs that can be used to describe the distribution of a numerical
Assignment 12 CAD Mechanical Part 2
 Assignment 12 CAD Mechanical Part 2 Objectives In this assignment you will learn to apply the hidden lines, isometric snap, and ellipses commands along with commands previously learned.. General Hidden
Assignment 12 CAD Mechanical Part 2 Objectives In this assignment you will learn to apply the hidden lines, isometric snap, and ellipses commands along with commands previously learned.. General Hidden
Advance Steel. Tutorial
 Advance Steel Tutorial Table of contents About this tutorial... 7 How to use this guide...9 Lesson 1: Creating a building grid...10 Step 1: Creating an axis group in the X direction...10 Step 2: Creating
Advance Steel Tutorial Table of contents About this tutorial... 7 How to use this guide...9 Lesson 1: Creating a building grid...10 Step 1: Creating an axis group in the X direction...10 Step 2: Creating
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink
 Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Physics 132 Quiz # 23
 Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
CONTENT INTRODUCTION BASIC CONCEPTS Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing DRAWING STROKES...
 USER MANUAL CONTENT INTRODUCTION... 3 1 BASIC CONCEPTS... 3 2 QUICK START... 7 2.1 Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing... 7 3 DRAWING STROKES... 15 3.1 Creating a group of strokes...
USER MANUAL CONTENT INTRODUCTION... 3 1 BASIC CONCEPTS... 3 2 QUICK START... 7 2.1 Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing... 7 3 DRAWING STROKES... 15 3.1 Creating a group of strokes...
Quasi-static Contact Mechanics Problem
 Type of solver: ABAQUS CAE/Standard Quasi-static Contact Mechanics Problem Adapted from: ABAQUS v6.8 Online Documentation, Getting Started with ABAQUS: Interactive Edition C.1 Overview During the tutorial
Type of solver: ABAQUS CAE/Standard Quasi-static Contact Mechanics Problem Adapted from: ABAQUS v6.8 Online Documentation, Getting Started with ABAQUS: Interactive Edition C.1 Overview During the tutorial
ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES. Types of Graphs. Bar Graphs
 ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES Types of Graphs Bar Graphs Bar graphs are used to present and compare data. There are two main types of bar graphs: horizontal and vertical. They are
ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES Types of Graphs Bar Graphs Bar graphs are used to present and compare data. There are two main types of bar graphs: horizontal and vertical. They are
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Lab 1: FFT, Spectral Leakage, Zero Padding Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz
Digital Signal Processing Lab 1: FFT, Spectral Leakage, Zero Padding Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial
 AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory
 Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Chapter Displaying Graphical Data. Frequency Distribution Example. Graphical Methods for Describing Data. Vision Correction Frequency Relative
 Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing 3.1 Displaying Graphical Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer
Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing 3.1 Displaying Graphical Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer
AutoCAD Tutorial First Level. 2D Fundamentals. Randy H. Shih SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
IDEA Connections. User guide
 IDEA Connections user guide IDEA Connections User guide IDEA Connections user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 4 1.1 Installation guidelines... 4 2 User interface... 5 2.1 3D view in the main
IDEA Connections user guide IDEA Connections User guide IDEA Connections user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 4 1.1 Installation guidelines... 4 2 User interface... 5 2.1 3D view in the main
Princeton ELE 201, Spring 2014 Laboratory No. 2 Shazam
 Princeton ELE 201, Spring 2014 Laboratory No. 2 Shazam 1 Background In this lab we will begin to code a Shazam-like program to identify a short clip of music using a database of songs. The basic procedure
Princeton ELE 201, Spring 2014 Laboratory No. 2 Shazam 1 Background In this lab we will begin to code a Shazam-like program to identify a short clip of music using a database of songs. The basic procedure
SDC. AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial. Randy H. Shih. Schroff Development Corporation Oregon Institute of Technology
 AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
Pictorial Drawings. DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor
 DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor Pictorial Drawings Geisecke s textbook for reference: 14 th Ed. Ch. 15: p. 601 Ch. 16: p. 620 15 th Ed. Ch. 14: p. 518 Ch. 15: p. 552 Update:
DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor Pictorial Drawings Geisecke s textbook for reference: 14 th Ed. Ch. 15: p. 601 Ch. 16: p. 620 15 th Ed. Ch. 14: p. 518 Ch. 15: p. 552 Update:
Chapter 2: Diode Applications
 Chapter 2: Diode Applications Islamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik Load-Line Analysis (graphical solution) The analysis of diode can follow one of two paths: using the actual characteristics or applying
Chapter 2: Diode Applications Islamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik Load-Line Analysis (graphical solution) The analysis of diode can follow one of two paths: using the actual characteristics or applying
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor User Interface Student Manual MODEL WINDOW
 Emmett Wemp EDTECH 503 Introduction to Autodesk Inventor User Interface Fill in the blanks of the different tools available in the user interface of Autodesk Inventor as your instructor discusses them.
Emmett Wemp EDTECH 503 Introduction to Autodesk Inventor User Interface Fill in the blanks of the different tools available in the user interface of Autodesk Inventor as your instructor discusses them.
Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors. N r k. is the time shift applied to r k
 DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise section
DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise section
ARC By default AutoCAD will draw an ARC through three selected points. Options can be set at the start and within the command.
 DFTG 1309 Final Review Notes I. Draw commands: LINE (draws a series of lines) Valid input: Pick button Cartesian coordinates Absolute (2,3) Relative rectangular (@2,3) Relative polar (@ 2
DFTG 1309 Final Review Notes I. Draw commands: LINE (draws a series of lines) Valid input: Pick button Cartesian coordinates Absolute (2,3) Relative rectangular (@2,3) Relative polar (@ 2
Study of Analog Phase-Locked Loop (APLL)
 Laboratory Exercise 9. (Last updated: 18/1/013, Tamás Krébesz) Study of Analog Phase-Locked Loop (APLL) Required knowledge Operation principle of analog phase-locked-loop (APLL) Operation principle of
Laboratory Exercise 9. (Last updated: 18/1/013, Tamás Krébesz) Study of Analog Phase-Locked Loop (APLL) Required knowledge Operation principle of analog phase-locked-loop (APLL) Operation principle of
General Functions and Graphs
 General Functions and Graphs Section 7 Functions Graphs and Symmetry Functions can be represented both as algebraic expressions and as graphs. So far we have concentrated on algebraic operations related
General Functions and Graphs Section 7 Functions Graphs and Symmetry Functions can be represented both as algebraic expressions and as graphs. So far we have concentrated on algebraic operations related
2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your answer or you must explain how you obtained your answer.
 Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
Math 259 Winter Recitation Handout 6: Limits in Two Dimensions
 Math 259 Winter 2009 Recitation Handout 6: its in Two Dimensions As we have discussed in lecture, investigating the behavior of functions with two variables, f(x, y), can be more difficult than functions
Math 259 Winter 2009 Recitation Handout 6: its in Two Dimensions As we have discussed in lecture, investigating the behavior of functions with two variables, f(x, y), can be more difficult than functions
