Introduction to Color Theory
|
|
|
- Abner Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. is a system of rules and guidance for mixing various colors. Color can be your most powerful design element if you learn to use it effectively. Being able to use colors consciously and harmoniously can help you create spectacular visualization and animation. How to calculate the color of a pixel? 1
2 3/25/2018 The Foundation of Color At its core, color is light. Light: electromagnetic phenomenon (different wavelength = different color). Light is composed of many different colors and the various mixtures of light compose the colors that we can see. Color: Interaction of light Color Wheel and eye-brain system. The Foundation of Color Primary Colors: Colors that can not be created by mixing other colors. Secondary Colors: Colors made by mixing primaries colors. Intermediate (Tertiary) Colors: Colors made by mixing primaries and secondary colors. Color Wheel 2
3 The Foundation of Color glbegin (GL_TRIANGLES); glcolor3f (1.0, 0.0, 0.0); // red glvertex2iv (p1); glcolor3f (0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // green glvertex2iv (p2); glcolor3f (0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // blue glvertex2iv (p3); glend ( ); An OpenGL Example Types of Color Theories Subtractive Theory The subtractive, or pigment theory deals with how white light is absorbed and reflected off of colored surfaces. Additive Theory The Additive, or light theory deals with radiated and filtered light. 3
4 Subtractive Black absorbs most light. White reflects most light. Colored Pigments absorb light and reflect only the frequency of the pigment color. All colors other than the pigment colors are absorbed so this is called subtractive color theory. The primary colors in Subtractive Theory are: Cyan ( C ) Magenta ( M ) Yellow ( Y ) Black ( K ) Used in Printing and Painting Additive Black radiates no light. White (sun) radiates all light. Video is the process of capturing and radiating light, therefore it uses Additive (Light) Theory not Subtractive (Pigment) Theory. The primary colors in Additive Theory are: Red ( R ) Green ( G ) Blue ( B ) The primary colors add together to make white. Light Theory is also called Additive Theory. Used in Television, theater lighting, computer monitors, and video production 4
5 The Color Wheel Colors on the wheel can be described using three parameters: Hue: degrees from 0 to 360 Saturation: brightness or dullness Value: lightness or darkness Hue The Color Wheel Hue or Spectral Color is represented as an angle to distinguish the dominant color (frequency). Primary Colors: 0 = Red 120 = Green 240 = Blue Secondary Colors: 60 = Yellow 180 = Cyan 300 = Magenta Angle Color 0 60 Red Yellow Green Cyan Blue Magenta 5
6 3/25/2018 The Color Wheel Saturation Saturation or Chroma is the intensity of a color; i.e. defines the purity (vibrancy) of the color to indicate if it is mixed with other colors. A highly saturated color is bright and appears closer to the edge of the wheel. A more unsaturated color is dull. A color with no saturation is achromatic or in the grey scale. The Color Wheel Value Value represents the luminescent contrast value between black and white. 6
7 The Color Wheel 3D Three parameters to describe a color: Hue Chroma Value Tone = Shade + Tint What is the Tone? 7
8 Color Schemes Systematic ways of selecting colors Monochromatic Complementary Analogous Warm Cool Color Schemes Monochromatic One Hue (Color) and its values of Tint and Shade 8
9 Color Schemes Complementary (note spelling--not complimentary) Colors that are opposite on the wheel. Two colors when mixed produce white (gray in general). High Contrast Color Schemes Analogous A selection of colors that are adjacent. Minimal Contrast 9
10 Color Schemes Warm Right half of the wheel gives warmer colors. Warm colors make objects look closer in a painting or drawing. The warm colors found in fire and the Sun. Color Schemes Cool Left half of the wheel gives cooler colors. Cool colors make objects tend to recede in a composition. The cool colors found in snow and ice. 10
11 Color Spaces (or Models) The RGB Color Space - Computer Displays The HSV Color Space The HLS Color Space The HSB Color Space A color space is a method by which we can specify, create and visualize color. The CIE Color Space Color Standard The CMY Color Space - Printing The YIQ, YUV, YCrCb Color Space Television Opponent Colors Biological The color space is a 3D space; hence, any color can be defined as a 3D vector where each element in the vector represents one color component. RGB Color Spaces (or Models) Used in Video and computer graphics It is represented as the cube shown with Cartesian coordinates. Each of the three axes represents a primary color. Each point on or inside the cube represents a color where the coordinates of this point represent the components of the primary colors that contribute to the current color. Each component should have a value from 0 to 255 (or from 0.0 to 1.0). The grayscale from 0,0,0 to 255,255,255 (0,0,0 to 1,1,1) represents the shades of gray from black to white. 11
12 HSV Color Spaces (or Models) HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) Saturation and Value are represented in % or within a range. Value represents the brightness of the color. Value is represented as the centerline of the cone. Value 0.0 (0) (black) is at the lower tip of the cone. Value 1.0 (100) (white) is at the center point of the upper circle. Shades of gray are represented along this line between black and white. The HSV color space is quite similar to the way in which humans perceive color, which is not always the case with RGB. RGB to HSV Transformation The conversion from a RGB to a HSV model is described by these formulas: v = max = max (r,g,b) min = min(r,g,b) s = c/v where: c = chroma = max (r,g,b) - min (r,g,b) h = depends on which of r,g,b is the maximum The meaning of the variables: r,g,b the red, green, blue components of the RGB model h,s,v - the hue, saturation, value components of HSV model The components of the RGB model (r,g,b), saturation (s) and value (v) should have values in the range [0,1], while the hue (h) should have values in the range [0,360] 12
13 HSV to RGB Transformation The conversion from a HSV to RGB a model is described by these formulas: The meaning of the variables: h,s,v - the hue, saturation, value components of HSV model r,g,b the red, green, blue components of the RGB model c - chroma m - the RGB component with the smallest value x - an intermediate value used for computing the RGB model The components of the RGB model (r,g,b), saturation (s) and value (v) should have values in the range [0,1], while the hue (h) should have values in the range [0,360] Gamma Correction A typical CRT has a non-linear voltage-to-light transfer function with a power law usually denoted by gamma. Power-Law Transformations Gamma Correction I = c * I 1/γ γ < 1 Useful for enhancing details in the darker regions of the image at the expense of detail in the brighter regions. γ > 1 Useful for enhancing details in the brighter regions of the image at the expense of detail in the darker regions. 13
14 Gamma Correction Original γ = 0.6 γ = 0.4 γ = 0.3 Gamma Correction Original γ = 3.0 γ = 4.0 γ =
15 Digital Image A digital image is composed of pixels which can be thought of as small dots on the screen. A digital image is an instruction of how to color each pixel. In the general case we say that an image is of size m- by-n if it is composed of m pixels in the vertical direction and n pixels in the horizontal direction. Let us say that we have an image on the format 512-by pixels. This means that the data for the image must contain information about pixels. Digital Image Color images have 3 values per pixel; monochrome images have 1 value per pixel. grid of squares, each of which contains a single color each square is called a pixel (for picture element) 15
16 Digital Image Pixel A digital image, I, is a mapping from a 2D grid of uniformly spaced discrete points, {p = (r,c)}, into a set of positive integer values, {I( p)}, or a set of vector values}. At each column location in each row of I there is a value. The pair ( p, I( p) ) is called a pixel (for picture element). Digital Image Pixel p = (r,c) is the pixel location indexed by row, r, and column, c. I( p) = I(r,c) is the value of the pixel at location p. If I( p) is a single number then I is monochrome. If I( p) is a vector (ordered list of numbers) then I has multiple bands (e.g., a color image). 16
17 Digital Image A D 1D E 0C 0A 0A 0A B A 08 0B 0A 0D 0B 0B 0C F 0B E 0C A 0A 0B 0F 0A 0C B 07 0B 05 0B E 0C A A A C 0B 0A A 0C 0A 0A 08 0A 0A A B 14 0F 0F 0D 0A 0E 0A 0C 0C 0E 0A 0C 0B 09 0A 09 0A 0A 09 0B 0B 05 0C 0C 0A B 10 0A 0D 0D 0B 0D 0C 0B 0B 0C 0D 0B 0B 0A 0A 0A 0B 0C C 15 0D E C 0D 0C 0C 0A 0B 0B 09 0C 0F D 07 0B D D 0A F 0E B 0C 0F 0F 0E 0C 10 0D E 3F A 09 0A C B 10 0F 0C D 0F 0D 0D 0B 25 7A 7F 79 6D 80 6E 54 0C 0D 09 0A F 0D 12 0E 10 0E 0F F E 8C 73 7A 5C 1E 05 0A 0F 0E 0C F 15 0D D B A 12 0A 0B E 1A F 7D C 7F 6F 5F 0B D 0C D E 36 5B 29 2C F AF BC AF AB 9E A F AE AD A E 0A 0C B B 1A 1A 2B 1B 2A C 1B 26 4C 40 BA BB B5 AE A 8A 9A B9 BB AD 9C 8A B 0D 0F 0B A 18 1C 1E D 3F 4E B 1B AF AB B1 AC A AA 9F AD 7F 0C 0B 0E 0B 0C 0C C 24 2E B B 2B A1 AB AC B2 A6 A6 A F 10 1C F 0C 0F A C F 33 1F B 4D A3 A5 99 8D 7A 4E 0E 1B F 0F B 01 1D 1F 2B F 40 2F 2D 2A 25 2B 2C E 55 5E 62 6D 6D 6E 68 5E 43 0D A F 2A B 45 2E 3A D 2F 1F 1E 1B C 3F 3C D 0B 0E 11 1E 23 1B D 10 0F 12 0F A 1B 35 4A 1D 20 2C 2F 1F 1F 3B 34 1A 2A E 0C 0C 06 0C B B 0E 10 0D 0D 0F D 1E C E 0E 1A A 18 2C 2E 19 0F 0D 10 0E 0E 14 0D B 1E 17 1C 1F 1F 1F 1C C 2F B D D A 1D 1F 1D 1B 1E 1B B 22 1A 1E 1B C 0D 11 0E 12 0D C 2E E 20 1F 1F 1D 1B 1C B 1E 15 1A A E 1D B 1B A 4C 33 1C E A E Digital Image 17
18 Digital Image Digital Image Representing Digital Images The representation of an M N numerical array as a0,0 a0,1... a0, N 1 a1,0 a1,1... a 1, N 1 A = am 1,0 am 1,1... am 1, N 1 18
19 Digital Image Representing Digital Images The representation of an M N numerical array as f (0,0) f (0,1)... f (0, N 1) f (1,0) f (1,1)... f (1, N 1) f ( x, y) = f ( M 1,0) f ( M 1,1)... f ( M 1, N 1) Image File Header Format Fixed Format Fixed fields sequence. Predefined items Fixed size Field 1 Field 2 Field n 19
20 Image File Header Format Tagged Format Variable sequence of fields. Variable number of items Unlimited field size Variable size Tags have fixed size/format Tag 1 Field 1 Tag 2 Field 2 Tag i Field i... Image File Format There are a number of file formats in which one may store the images in files and retrieve them from files. These are known as image file format standards. Here we will present some of the most popularly used Image file format standards. Tagged Image Format (.tif,.tiff): The.tif format is a very broad format, which can handle anything from bitmaps to compressed color palette images. The tiff format supports several compression schemes, but is often used for uncompressed images as well. This format is popular, relatively simple, and allows color. 20
21 Image File Format JPEG (.jpg): It is the most widely used as a standard and includes a variable lossy encoding as part of the standard. Most images you find on the Internet are JPEG-images MPEG (.mpg): This format is extensively used throughout the Web and is used only for motion images. This uses compression, yielding only lossy videos. Graphics Interchange Format (.gif): This format supports 8-bit color palette images and is not very popular among the image processing researchers. Postscript (.ps,.eps,.epsf): This image format is mainly used while introducing images or figures in a book and for printing. In postscript format, gray level images are represented by decimal/hex numerals encoded in ASCII. Intensity image This is the equivalent to a "grayscale image". It represents an image as a matrix where every element has a value corresponding to how bright/dark the pixel at the corresponding position should be colored. There are two ways to represent the number that represents the brightness of the pixel: The double class (or data type). This assigns a floating number ("a number with decimals") between 0 and 1 to each pixel. The value 0 corresponds to black and the value 1 corresponds to white. The other class is called uint8 which assigns an integer between 0 and 255 to represent the brightness of a pixel. The value 0 corresponds to black and 255 to white. Binary image Image File Format This image format also stores an image as a matrix but can only color a pixel black or white (and nothing in between). It assigns a 0 for black and a 1 for white. In that sense, any pixel may be stored in 1 bit only. 21
22 Image File Format RGB image This is another format for color images. It represents an image with three matrices of sizes matching the image format. Each matrix corresponds to one of the colors red, green or blue and gives an instruction of how much of each of these colors a certain pixel should use. Therefore, a pixel requires 24 bits to store its color. (Hence comes the term 24- bit image.) The number of different colors that can be represented by one pixel is 224 = different colors. Multiframe image In some applications we want to study a sequence of images. This is very common in biological, medical imaging, and animation. For these cases, the multiframe format is a convenient way of working with a sequence of images. Image File Format Indexed image This is a practical way of representing color images. An indexed image stores an image as two matrices. The first matrix has the same size as the image and one number for each pixel. The second matrix is called the color map (Look-Up Tables - LUT) and its size may be different from the image. The numbers in the first matrix is an instruction of what number to use in the color map matrix. For example, 8-bit Color Images in which the color at each pixel is represented using an 8-bit integer. This means that the maximum number of different colors that is associated with the pixel is 256. For each pixel, an index number is stored (in 8 bits). This introduces additional complexity into the image format as the LUT is usually attached to the image. When the image colors are altered, it will be required to generate a new LUT. 22
Computers and Imaging
 Computers and Imaging Telecommunications 1 P. Mathys Two Different Methods Vector or object-oriented graphics. Images are generated by mathematical descriptions of line (vector) segments. Bitmap or raster
Computers and Imaging Telecommunications 1 P. Mathys Two Different Methods Vector or object-oriented graphics. Images are generated by mathematical descriptions of line (vector) segments. Bitmap or raster
Colors in Images & Video
 LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO
 MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
Color Theory and Mixing
 MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
Dr. Shahanawaj Ahamad. Dr. S.Ahamad, SWE-423, Unit-06
 Dr. Shahanawaj Ahamad 1 Outline: Basic concepts underlying Images Popular Image File formats Human perception of color Various Color Models in use and the idea behind them 2 Pixels -- picture elements
Dr. Shahanawaj Ahamad 1 Outline: Basic concepts underlying Images Popular Image File formats Human perception of color Various Color Models in use and the idea behind them 2 Pixels -- picture elements
COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT
 COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 8 Color Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 8 Color Processing 1 COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING COLOR IMAGE PROCESSING Color Importance Color is an excellent descriptor Suitable for object Identification and Extraction
Color Theory. Additive Color
 Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Images and Colour COSC342. Lecture 2 2 March 2015
 Images and Colour COSC342 Lecture 2 2 March 2015 In this Lecture Images and image formats Digital images in the computer Image compression and formats Colour representation Colour perception Colour spaces
Images and Colour COSC342 Lecture 2 2 March 2015 In this Lecture Images and image formats Digital images in the computer Image compression and formats Colour representation Colour perception Colour spaces
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image Perception & 2D Images
 Image Perception & 2D Images Vision is a matter of perception. Perception is a matter of vision. ES Overview Introduction to ES 2D Graphics in Entertainment Systems Sound, Speech & Music 3D Graphics in
Image Perception & 2D Images Vision is a matter of perception. Perception is a matter of vision. ES Overview Introduction to ES 2D Graphics in Entertainment Systems Sound, Speech & Music 3D Graphics in
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle.
 The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Color Image Processing. Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6
 Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red.
 Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing 1 Corners Corners (interest points) Unlike edges, corners (patches of pixels surrounding the corner) do not necessarily correspond
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Corner Detection & Color Processing 1 Corners Corners (interest points) Unlike edges, corners (patches of pixels surrounding the corner) do not necessarily correspond
Color & Compression. Robin Strand Centre for Image analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 Color & Compression Robin Strand Centre for Image analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline Color Color spaces Multispectral images Pseudocoloring Color image processing
Color & Compression Robin Strand Centre for Image analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline Color Color spaces Multispectral images Pseudocoloring Color image processing
Brief Introduction to Vision and Images
 Brief Introduction to Vision and Images Charles S. Tritt, Ph.D. January 24, 2012 Version 1.1 Structure of the Retina There is only one kind of rod. Rods are very sensitive and used mainly in dim light.
Brief Introduction to Vision and Images Charles S. Tritt, Ph.D. January 24, 2012 Version 1.1 Structure of the Retina There is only one kind of rod. Rods are very sensitive and used mainly in dim light.
Digital Image Processing Color Models &Processing
 Digital Image Processing Color Models &Processing Dr. Hatem Elaydi Electrical Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza Fall 2015 Nov 16, 2015 Color interpretation Color spectrum vs. electromagnetic
Digital Image Processing Color Models &Processing Dr. Hatem Elaydi Electrical Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza Fall 2015 Nov 16, 2015 Color interpretation Color spectrum vs. electromagnetic
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #12
 Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
Lecture #12 Image Correlation (example) Color basics (Chapter 6) The Chromaticity Diagram Color Images RGB Color Cube Color spaces Pseudocolor Multispectral Imaging White Light A prism splits white light
Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester
 Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester Lecture 8: Color Image Processing 04.11.2017 Dr. Mohammed Abdel-Megeed Salem Media
Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester Lecture 8: Color Image Processing 04.11.2017 Dr. Mohammed Abdel-Megeed Salem Media
Images and Graphics. 4. Images and Graphics - Copyright Denis Hamelin - Ryerson University
 Images and Graphics Images and Graphics Graphics and images are non-textual information that can be displayed and printed. Graphics (vector graphics) are an assemblage of lines, curves or circles with
Images and Graphics Images and Graphics Graphics and images are non-textual information that can be displayed and printed. Graphics (vector graphics) are an assemblage of lines, curves or circles with
CHAPTER 3 I M A G E S
 CHAPTER 3 I M A G E S OBJECTIVES Discuss the various factors that apply to the use of images in multimedia. Describe the capabilities and limitations of bitmap images. Describe the capabilities and limitations
CHAPTER 3 I M A G E S OBJECTIVES Discuss the various factors that apply to the use of images in multimedia. Describe the capabilities and limitations of bitmap images. Describe the capabilities and limitations
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 4: Color Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Chap. 4 of Fundamentals of Multimedia Some reference from http://media.ee.ntu.edu.tw/courses/dvt/15f/ 1 Outline
Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 4: Color Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Chap. 4 of Fundamentals of Multimedia Some reference from http://media.ee.ntu.edu.tw/courses/dvt/15f/ 1 Outline
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations
 Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.3 Further Exploration 1 Li & Drew c Prentice Hall 2003 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.3 Further Exploration 1 Li & Drew c Prentice Hall 2003 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
NEWTONIAN COLOR THEORY
 THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
Hello, welcome to the video lecture series on Digital image processing. (Refer Slide Time: 00:30)
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with
 DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes.
 Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
CUT the wheel vertically IN HALF: WARM (right) AND COOL COLORS (left)
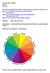 COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
Introduction. The Spectral Basis for Color
 Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing
 I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
2. Color spaces Introduction The RGB color space
 Image Processing - Lab 2: Color spaces 1 2. Color spaces 2.1. Introduction The purpose of the second laboratory work is to teach the basic color manipulation techniques, applied to the bitmap digital images.
Image Processing - Lab 2: Color spaces 1 2. Color spaces 2.1. Introduction The purpose of the second laboratory work is to teach the basic color manipulation techniques, applied to the bitmap digital images.
Introduction to Color Science (Cont)
 Lecture 24: Introduction to Color Science (Cont) Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley Empirical Color Matching Experiment Additive Color Matching Experiment Show test light spectrum on left Mix primaries
Lecture 24: Introduction to Color Science (Cont) Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley Empirical Color Matching Experiment Additive Color Matching Experiment Show test light spectrum on left Mix primaries
Fig Color spectrum seen by passing white light through a prism.
 1. Explain about color fundamentals. Color of an object is determined by the nature of the light reflected from it. When a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam of light is not
1. Explain about color fundamentals. Color of an object is determined by the nature of the light reflected from it. When a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam of light is not
The BIOS in many personal computers stores the date and time in BCD. M-Mushtaq Hussain
 Practical applications of BCD The BIOS in many personal computers stores the date and time in BCD Images How data for a bitmapped image is encoded? A bitmap images take the form of an array, where the
Practical applications of BCD The BIOS in many personal computers stores the date and time in BCD Images How data for a bitmapped image is encoded? A bitmap images take the form of an array, where the
Value. Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page.
 Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Color images C1 C2 C3
 Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II
 GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
UBT128X Colour theory
 UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition. Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout.
 The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
Computer Graphics. Si Lu. Fall er_graphics.htm 10/02/2015
 Computer Graphics Si Lu Fall 2017 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs447/cs447_547_comput er_graphics.htm 10/02/2015 1 Announcements Free Textbook: Linear Algebra By Jim Hefferon http://joshua.smcvt.edu/linalg.html/
Computer Graphics Si Lu Fall 2017 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs447/cs447_547_comput er_graphics.htm 10/02/2015 1 Announcements Free Textbook: Linear Algebra By Jim Hefferon http://joshua.smcvt.edu/linalg.html/
To discuss. Color Science Color Models in image. Computer Graphics 2
 Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
Properties of Color. Value: Tint: Shade: Tone: Intensity:
 Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
Image is a spatial representation of an object or a scene. (image of a person, place, object)
 Graphics & Images Table of Content 1. Introduction 2. Types of graphics 3. Resolution 4. Memory/Storage requirement 5. Types of images 6. Image colour schemes 7. Colour dithering 8. Image processing 9.
Graphics & Images Table of Content 1. Introduction 2. Types of graphics 3. Resolution 4. Memory/Storage requirement 5. Types of images 6. Image colour schemes 7. Colour dithering 8. Image processing 9.
Fundamentals of Multimedia
 Fundamentals of Multimedia Lecture 2 Graphics & Image Data Representation Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Black & white imags 1 bit images 8-bit gray-level images Image histogram Dithering
Fundamentals of Multimedia Lecture 2 Graphics & Image Data Representation Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Black & white imags 1 bit images 8-bit gray-level images Image histogram Dithering
Notes on colour mixing
 INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
Color Theory: Defining Brown
 Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
05 Color. Multimedia Systems. Color and Science
 Multimedia Systems 05 Color Color and Science Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan www.imranihsan.com Lectures Adapted From: Digital Multimedia
Multimedia Systems 05 Color Color and Science Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan www.imranihsan.com Lectures Adapted From: Digital Multimedia
Lecture 8. Color Image Processing
 Lecture 8. Color Image Processing EL512 Image Processing Dr. Zhu Liu zliu@research.att.com Note: Part of the materials in the slides are from Gonzalez s Digital Image Processing and Onur s lecture slides
Lecture 8. Color Image Processing EL512 Image Processing Dr. Zhu Liu zliu@research.att.com Note: Part of the materials in the slides are from Gonzalez s Digital Image Processing and Onur s lecture slides
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color
 Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
check it out online at
 check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing
 Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Chapter 3 Part 2 Color image processing Motivation Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image processing Full-color image processing: Component-wise Vector-based Recent and current work Spring 2002
Designing Flower Beds with Colors
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right
 COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
Figure 1: Energy Distributions for light
 Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Lecture 4: Colour The physical description of colour Colour vision is a very complicated biological and psychological phenomenon. It can be described in many different ways, including by physics, by subjective
Introduction to Multimedia Computing
 COMP 319 Lecture 02 Introduction to Multimedia Computing Fiona Yan Liu Department of Computing The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Learning Outputs of Lecture 01 Introduction to multimedia technology
COMP 319 Lecture 02 Introduction to Multimedia Computing Fiona Yan Liu Department of Computing The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Learning Outputs of Lecture 01 Introduction to multimedia technology
Hue Value Intensity tint shade Tones
 COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations
 Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats Li, Drew, & Liu 1 1 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats Li, Drew, & Liu 1 1 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia
12 Color Models and Color Applications. Chapter 12. Color Models and Color Applications. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 12-1
 Chapter 12 Color Models and Color Applications 12-1 12.1 Overview Color plays a significant role in achieving realistic computer graphic renderings. This chapter describes the quantitative aspects of color,
Chapter 12 Color Models and Color Applications 12-1 12.1 Overview Color plays a significant role in achieving realistic computer graphic renderings. This chapter describes the quantitative aspects of color,
Mahdi Amiri. March Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2014 Sharif University of Technology The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed ν is given by Physics of
RGB COLORS. Connecting with Computer Science cs.ubc.ca/~hoos/cpsc101
 RGB COLORS Clicker Question How many numbers are commonly used to specify the colour of a pixel? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 or more 2 Yellow = R + G? Combining red and green makes yellow Taught in elementary
RGB COLORS Clicker Question How many numbers are commonly used to specify the colour of a pixel? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 or more 2 Yellow = R + G? Combining red and green makes yellow Taught in elementary
In order to manage and correct color photos, you need to understand a few
 In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE
 IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Human visual system Color images Color quantization Colorimetric color spaces HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL
IMAGE PROCESSING >COLOR SPACES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Human visual system Color images Color quantization Colorimetric color spaces HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL SYSTEM HUMAN VISUAL
YIQ color model. Used in United States commercial TV broadcasting (NTSC system).
 CMY color model Each color is represented by the three secondary colors --- cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y ). It is mainly used in devices such as color printers that deposit color pigments. It is
CMY color model Each color is represented by the three secondary colors --- cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y ). It is mainly used in devices such as color printers that deposit color pigments. It is
Color image processing
 Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
Color Science. What light is. Measuring light. CS 4620 Lecture 15. Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD)
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
White light can be split into constituent wavelengths (or colors) using a prism or a grating.
 Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
IMAGES AND COLOR. N. C. State University. CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking. Fall Lecture # 10
 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 10 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture
IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 10 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture
Color Image Processing
 Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
CIE tri-stimulus experiment. Color Value Functions. CIE 1931 Standard. Color. Diagram. Color light intensity for visual color match
 CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
CIE tri-stimulus experiment diffuse reflecting screen diffuse reflecting screen 770 769 768 test light 382 381 380 observer test light 445 535 630 445 535 630 observer light intensity for visual color
Performance Analysis of Color Components in Histogram-Based Image Retrieval
 Te-Wei Chiang Department of Accounting Information Systems Chihlee Institute of Technology ctw@mail.chihlee.edu.tw Performance Analysis of s in Histogram-Based Image Retrieval Tienwei Tsai Department of
Te-Wei Chiang Department of Accounting Information Systems Chihlee Institute of Technology ctw@mail.chihlee.edu.tw Performance Analysis of s in Histogram-Based Image Retrieval Tienwei Tsai Department of
CHAPTER 2 - DIGITAL DATA REPRESENTATION AND NUMBERING SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 2 - DIGITAL DATA REPRESENTATION AND NUMBERING SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION Digital computers use sequences of binary digits (bits) to represent numbers, letters, special symbols, music, pictures, and videos.
CHAPTER 2 - DIGITAL DATA REPRESENTATION AND NUMBERING SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION Digital computers use sequences of binary digits (bits) to represent numbers, letters, special symbols, music, pictures, and videos.
The Visual Elements Part II. Lecture 3B
 The Visual Elements Part II Lecture 3B Lecture Overview: The 5 Main Visual Elements 1. Line /Shape 2 Space 3. Texture/Pattern 4. Time / Motion 5. Light / Color The language of art is the visual elements.
The Visual Elements Part II Lecture 3B Lecture Overview: The 5 Main Visual Elements 1. Line /Shape 2 Space 3. Texture/Pattern 4. Time / Motion 5. Light / Color The language of art is the visual elements.
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg
 Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
Elements and Principles
 Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Color Wheel. Warm Colors. Cool Colors
 Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
6 Color Image Processing
 6 Color Image Processing Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image
6 Color Image Processing Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline Color fundamentals Color models Pseudocolor image
Light. intensity wavelength. Light is electromagnetic waves Laser is light that contains only a narrow spectrum of frequencies
 Image formation World, image, eye Light Light is electromagnetic waves Laser is light that contains only a narrow spectrum of frequencies intensity wavelength Visible light is light with wavelength from
Image formation World, image, eye Light Light is electromagnetic waves Laser is light that contains only a narrow spectrum of frequencies intensity wavelength Visible light is light with wavelength from
Objective Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics.
 Objective 102.01 Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. PART 1: ELEMENTS OF DESIGN o Color o Line o Shape o Texture o Watch this video on Fundamentals of Design. 2 COLOR o Helps identify
Objective 102.01 Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. PART 1: ELEMENTS OF DESIGN o Color o Line o Shape o Texture o Watch this video on Fundamentals of Design. 2 COLOR o Helps identify
Chapter 4. Incorporating Color Techniques
 Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
1 Li & Drew c Prentice Hall Li & Drew c Prentice Hall 2003
 Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.3 Further Exploration 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.3 Further Exploration 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia
3.1 Graphics/Image age Data Types. 3.2 Popular File Formats
 Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.1 Graphics/Image age Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia continues to proliferate.
Chapter 3 Graphics and Image Data Representations 3.1 Graphics/Image Data Types 3.2 Popular File Formats 3.1 Graphics/Image age Data Types The number of file formats used in multimedia continues to proliferate.
Sampling Rate = Resolution Quantization Level = Color Depth = Bit Depth = Number of Colors
 ITEC2110 FALL 2011 TEST 2 REVIEW Chapters 2-3: Images I. Concepts Graphics A. Bitmaps and Vector Representations Logical vs. Physical Pixels - Images are modeled internally as an array of pixel values
ITEC2110 FALL 2011 TEST 2 REVIEW Chapters 2-3: Images I. Concepts Graphics A. Bitmaps and Vector Representations Logical vs. Physical Pixels - Images are modeled internally as an array of pixel values
The Color Wheel. The color wheel shows relationships between the colors.
 Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
the eye Light is electromagnetic radiation. The different wavelengths of the (to humans) visible part of the spectra make up the colors.
 Computer Assisted Image Analysis TF 3p and MN1 5p Color Image Processing Lecture 14 GW 6 (suggested problem 6.25) How does the human eye perceive color? How can color be described using mathematics? Different
Computer Assisted Image Analysis TF 3p and MN1 5p Color Image Processing Lecture 14 GW 6 (suggested problem 6.25) How does the human eye perceive color? How can color be described using mathematics? Different
Computer Graphics. Rendering. Rendering 3D. Images & Color. Scena 3D rendering image. Human Visual System: the retina. Human Visual System
 Rendering Rendering 3D Scena 3D rendering image Computer Graphics Università dell Insubria Corso di Laurea in Informatica Anno Accademico 2014/15 Marco Tarini Images & Color M a r c o T a r i n i C o m
Rendering Rendering 3D Scena 3D rendering image Computer Graphics Università dell Insubria Corso di Laurea in Informatica Anno Accademico 2014/15 Marco Tarini Images & Color M a r c o T a r i n i C o m
Unit 8: Color Image Processing
 Unit 8: Color Image Processing Colour Fundamentals In 666 Sir Isaac Newton discovered that when a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam is split into a spectrum of colours The
Unit 8: Color Image Processing Colour Fundamentals In 666 Sir Isaac Newton discovered that when a beam of sunlight passes through a glass prism, the emerging beam is split into a spectrum of colours The
MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox
 MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Copyright: Mathworks 1998. The following is taken from the Matlab Image Processing Toolbox users guide. A complete online manual is availabe in the PDF form (about 5MB).
MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Copyright: Mathworks 1998. The following is taken from the Matlab Image Processing Toolbox users guide. A complete online manual is availabe in the PDF form (about 5MB).
Lecture Color Image Processing. by Shahid Farid
 Lecture Color Image Processing by Shahid Farid What is color? Why colors? How we see objects? Photometry, Radiometry and Colorimetry Color measurement Chromaticity diagram Shahid Farid, PUCIT 2 Color or
Lecture Color Image Processing by Shahid Farid What is color? Why colors? How we see objects? Photometry, Radiometry and Colorimetry Color measurement Chromaticity diagram Shahid Farid, PUCIT 2 Color or
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes
 Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color. Chapter 6. (colour) Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition
 Color (colour) Chapter 6 Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition What is color? Color is how our eyes perceive different forms of energy. Energy moves in the form of waves. What is a wave? Think of a fat guy (Dr.
Color (colour) Chapter 6 Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition What is color? Color is how our eyes perceive different forms of energy. Energy moves in the form of waves. What is a wave? Think of a fat guy (Dr.
Line. The path created by a point moving through space. i n. Horizontal Line. Thin Line. Thick Line
 Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
