Scien&fic and Large Data Visualiza&on 8 November 2017 Visual Percep&on. Massimiliano Corsini Visual Compu,ng Lab, ISTI - CNR - Italy
|
|
|
- Warren Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scien&fic and Large Data Visualiza&on 8 November 2017 Visual Percep&on Massimiliano Corsini Visual Compu,ng Lab, ISTI - CNR - Italy
2 Intro Our Eye Overview Recep&ve Field Model, CSF, Mach Bending, Cornsweet effect.. What we really see PreaPen&ve Process Gestalt Laws Percep&on of lines and areas
3 Human Visual System (HVS) The Human Visual System (HVS) is subdivided into two parts: Op,cal part à our eye. Visual Percep,on à our brain (visual cortex).
4 Our Eye
5 The Re,na The re-na is composed by a large number of photoreceptors (rods and cones). 100 millions of rods, 6 millions of cones. Cones are concentrated in the fovea (1.5-2 degrees). Re,nal ganglion cells send informa,on, through the op,c nerve, to the brain.
6 Rods and Cones Distribu,on
7 Visual Acuity Points 1 minute of arc. Gra,ngs 1-2 minutes of arc. LeTer 5 minutes of arc. Vernier acuity (the ability to see if two segments are colinear) 10 seconds of arc.
8 Snellen Chart Visual Acuity
9 Visual Acuity Figure by Vanessa Ezekowitz under CC-SA-BY 3.0.
10 Contrast Sensi,vity Func,on (CSF) Our percep,on is sensi,ve to patern contrast, frequency and orienta,on. Also color influences the CSF. Figure by Martin Reddy.
11 Contrast Sensi,vity Func,on (CSF)
12 Visual Cortex LGN (Lateral Geniculate Nucleus) forwards pulses to V1. It is also connected with V2 and V3. V1 is the primary visual cortex. It performs edge detec,on and global organiza,on (inputs from V2, V3).
13 Visual Cortex V2 handles depth, foreground, illusory contours. V3 supports global mo,on understanding. V4 recognizes simple geometric shape. V5/MT: mo,on percep,on integra,on and eye movements guidance.
14 Recep,ve Field (in the re,na) The recep-ve field of a cell is the visual area over which a cell responds to light. Re,nal ganglion cells are organized with circular recep,ve fields. S,mulated on-center they are excited, s,mulated off-center they are inhibited.
15 Recep,ve Field (in the re,na) Excita&on Inhibi&on - - A good mathema&cal model is the Difference of Gaussians (DoG):
16 Difference of Gaussians (DoG)
17 Difference of Gaussians (DoG) S&mulus for sigma = 5 pixels
18 Difference of Gaussians (DoG) S&mulus for sigma = 10 pixels
19 Difference of Gaussians (DoG)
20 Simultaneous Brightness Contrast Figure from the Perception course by Prof. David Heeger.
21 Mach Banding Do you remember the problem of costant shading? This perceptual effect is called Mach Banding. Abrupt changes are strongly perceived.
22 Mach Banding Figure from Perception course by Prof. David Heeger.
23 Hermann Grid Illusion
24 Hermann Grid (stronger s,mulus)
25 Hermann Grid Illusions Classical explana,ons: Other experiments demonstrate that this theory is insufficient. An alterna,ve theory is that the illusion is due to the S1 type simple cells.
26 The Chevreul Illusion One a sequence of uniform bands is shown, such bands appear darker at one edge.
27 Greyscale Maps These visual effects can result in large errors when reading quan,ta,ve informa,on map displayed using a greyscale map. Use greyscale maps to represent few values (!)
28 Cornsweet Illusion Lateral inhibi,on can be considered part of an edge detec,on process in a scene under viewing. Pseudo-edges can be seen depending on the s,mulus. The brain does perceptual interpola,on so that regions affected by such edges can appear lighter or darker. This is called Cornsweet illusion (also known as the Craik O'Brien Cornsweet illusion).
29 The Cornsweet Effect Figure by Fibonacci user (Wikipedia) under CC-SA-BY 3.0.
30 Cornsweet Effect The Cornsweet effect can be used to highlight bounded regions. Figure from Information Visualization Perception for Design by Colin Ware.
31 Recap Use Grayscale Wisely Does not use for maps or to compare many values. Use to highlights: Bounded regions Important items (by reduce luminance contrast of unimportant items) Adjust background luminance to obtain beter readability
32 Eye Movements Saccadic movements: ballis,c movements of the eyes that change the point of fixa,on. They can be voluntary or s,mulus-elicited. Smooth-pursuit movements: slow tracking movements of the eyes to keep a moving s,mulus on the fovea. Vergence movements: align the fovea of each eye to a target according to its distance. Ves-bulo-ocular movements: stabilize the eyes compensa,ng for head movements.
33 Saccadic Movements and Fixa,ons
34 Saccadic Movements and Fixa,ons Saccade takes ms. Both eyes move in the same direc,on. The movement may be not a simple linear trajectory. A fixa,on is composed of slower and fine movements (microsaccades, tremor and drih) that help the eye align with the target. A fixa,on varies between ms. Typical movements during reading: 2 degrees. Typical movements (in general): 2-5 degrees. > 20 degrees à head movement is required.
35 Eye Tracking System Tobii Pro 2 Tobii Lab
36 PreaTen,ve Processes Count the number of 8s
37 PreaTen,ve Processes Count the number of 8s J
38 PreaTen,ve Processes Some visual s,mulus pop up from their surroundings. Ini,ally, researchers thinked that they happened before aten,on (erroneous). ATen,on is a part of the process.
39 PreaTen,ve Processes When a visual s,mulus is preaten,ve? Response time # distractors
40 PreaTen,ve Processes Visual features that are preaten,vely processed: Orienta,on ; Curvature ; Shape ; Size ; Color ; Light/Dark ; Enclosure ; Concavity/Convexity ; Addi,on Some of them are not symmetric. Visual features that are not preaten,vely processed: Juncture ; Parallelism
41 PreaTen,ve Features Orienta,on
42 PreaTen,ve Features Shape
43 PreaTen,ve Features Color
44 PreaTen,ve Features Light/Dark
45 PreaTen,ve Features Curvature
46 PreaTen,ve Features Length
47 PreaTen,ve Process Asymmetry Some preaten,ve process are not simmetric: Adding marks is more efficient than removing marks. Increase sharpness is more efficients than decrease sharpness. A big object surrounded by small objects is more efficient than a small object surrounded by big objects.
48 Asymmetric Processes Marks
49 Asymmetric Processes Size Ra,o
50 Asymmetric Processes Sharpness
51 Combina,on of PreaTen,ve Features Note that the combina,ons of preaten,ve visual features may not be preaten,ve. Examples: Shape + Color Size + Color Shape + Mo,on
52 Combina,on of PreaTen,ve Features Where is the red circle? Figure from Perception in Visualization by Christopher G. Healey, North Carolina State University.
53 Combina,on of PreaTen,ve Features Where is the red circle? Figure from Perception in Visualization by Christopher G. Healey, North Carolina State University.
54 Gestalt Laws From Gestalt School of Psychology (founded in 1912 by Max Westhemer, Kurt Koqa and Wolfgang Koheler). The first serious atempt to understand patern percep,on. The neural mechanisms proposed do not pass the test of the,me.... BUT the laws have proven to be valid.
55 Gestalt Laws Proximity Similarity Connectedness Con,nuity Symmetry Closure Common fate Figure-ground
56 Proximity Objects close to each other are perceived to form a group.
57 Similarity Similar objects are perceived to from a group.
58 Connectedness Connected objects are perceived as related. Connec,ng different objects with a line is a powerful way to express that there is some rela,onship between them.
59 Con,nuity We expect that a line or an edge con,nue to follow its direc,on and does not deviate from it. is perceived as not as
60 Con,nuity
61 Simmetry Objects arranged simmetrically are perceived as forming a visual whole instead of being preceived as separated en,,es. Simmetry is best perceived for horizontal and ver,cal axes.
62
63 Closure We tend to perceive the complete appearance of an object. Our brain fills the gap in case of missing parts.
64 Illusory Contour
65 Common Fate We tend to perceive as a group objects that moves in the same direc,on.
66 Figure-Ground This perceptual effect regards the forma,on of a figure from the background.
67
68 Müller-Lyer Illusion These two lines have equal length but we perceive that they have different length. Two explana,ons: Perspec,ve explana,on Centroid explana,on
69 Wundt Illusion Wilhelm Wundt ( ) ( father of experimental psychology ). Not completely explained.
70 Hering Illusion Another similar illusion (inverted effect of Wundt illusion). Possible explana,ons: Lateral inhibi,on Perspec,ve effect Temporal delays in visual processing
71 Horizontal Ver,cal Illusion Another simple illusion discovered by Wundt. The ver,cal line is perceived 30% more length than the horizontal line. Cross-cultural (small) differences have been no,ced. This is true also for intersec,ng lines.
72 Comparing Area Comparing area is difficult (remember the area of circles just men,oned). When we compare areas the propor,ons are underes,mated (worst for volumes). Flannery (1970) proposed to compensate the percep,on by applying a perceptual scaling factor. Tuhe, in his famous The Visual Display of Quan-ta-ve Informa-on (2001), opposed to anything but absolute scaling, i.e. to excludes compensa,on for human perceptual failings. J. J. Flannery, The Relative Effectiveness of Some Common Graduated Point Symbols in the Presentation of Quantitative Data, Symposium on the Influence of Map User on Map Design, 1970.
73 Flannery s Perceptual Scaling
74 Comparing Area Perceptual scaling may be insufficient. Things are more complex from a perceptual point of view à Heidenberg illusion.
75 Weber s Law Ernst Heinrich Weber ( ) conducted studies on the percep,on of physical s,mulus by human senses (vision, hearing, taste, touch and smell). Weber s Law: Just No,ceable Difference (JND) S,mulus
76 Weber s Law Percep,on depends by the ini,al s,mulus. Ra,os are more important than absolute values.
77 What about color? We will see something about color in the next lesson...
78 Summary Visual designers take in great considera,on visual percep,on à the same has to be done for data visualiza,on. Grayscale should be used wisely. PreaTen,ve processes are powerful to drive the aten,on and to avoid confused visualiza,on. Gestalt Laws are powerful allies (to group elements, to show rela,onships, to make paterns comparison, in an effec,ve way).
79 Ques&ons?
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Color and Perception
 Color and Perception Why Should We Care? Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Some errors
Color and Perception Why Should We Care? Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Some errors
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
The human visual system
 The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Optics, perception, cognition. Multimedia Retrieval: Perception. Human visual system. Human visual system
 Multimedia Retrieval: Perception Remco Veltkamp Optics, perception, cognition Be aware of human visual system, perception, and cognition Human visual system Human visual system Optics: Rods for b/w Cones
Multimedia Retrieval: Perception Remco Veltkamp Optics, perception, cognition Be aware of human visual system, perception, and cognition Human visual system Human visual system Optics: Rods for b/w Cones
Chapter 6: Perception
 Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition
 BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition We want to understand
BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition We want to understand
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Why Should We Be Interested In Visualization. Intro to Human Visual System and Displays. Basic Pathways. Perceptual versus Cultural A B C D
 Intro to Human Visual System and Displays Fundamental Optics Fovea Perception These slides were developed by Colin Ware, Univ. of New Hampshire Why Should We Be Interested In Visualization Hi bandwidth
Intro to Human Visual System and Displays Fundamental Optics Fovea Perception These slides were developed by Colin Ware, Univ. of New Hampshire Why Should We Be Interested In Visualization Hi bandwidth
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
 1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Objec&ve % Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics.
 Objec&ve 102.01 15% Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. Part 1: Elements of Design q Color q Line q Shape q Texture Color q Helps iden&fy objects in a design. q Creates visual flow
Objec&ve 102.01 15% Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. Part 1: Elements of Design q Color q Line q Shape q Texture Color q Helps iden&fy objects in a design. q Creates visual flow
Objec&ve % Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics.
 Objec&ve 102.01 15% Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. Part 1: Elements of Design q Color q Line q Shape q Texture Color q Helps iden&fy objects in a design. q Creates visual flow
Objec&ve 102.01 15% Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. Part 1: Elements of Design q Color q Line q Shape q Texture Color q Helps iden&fy objects in a design. q Creates visual flow
Cognition and Perception
 Cognition and Perception 2/10/10 4:25 PM Scribe: Katy Ionis Today s Topics Visual processing in the brain Visual illusions Graphical perceptions vs. graphical cognition Preattentive features for design
Cognition and Perception 2/10/10 4:25 PM Scribe: Katy Ionis Today s Topics Visual processing in the brain Visual illusions Graphical perceptions vs. graphical cognition Preattentive features for design
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Gestalt and Picture Organization
 Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Grouping by color Georgia O Keeffe Gestalt and Picture Organization Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Grouping, illusory contour
Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Grouping by color Georgia O Keeffe Gestalt and Picture Organization Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Grouping, illusory contour
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING (COM-3371) Week 2 - January 14, 2002
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING (COM-3371) Week 2 - January 14, 22 Topics: Human eye Visual phenomena Simple image model Image enhancement Point processes Histogram Lookup tables Contrast compression and stretching
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING (COM-3371) Week 2 - January 14, 22 Topics: Human eye Visual phenomena Simple image model Image enhancement Point processes Histogram Lookup tables Contrast compression and stretching
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015
 Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
Psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #10: Dec. 01 st 2014 Lecture plan: VISUAL ILLUSIONS THE STUDY OF VISUAL
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
CS 559: Computer Vision. Lecture 1
 CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Principles of Organiza1on. Claudia Jacques de Moraes Cardoso
 Principles of Organiza1on Claudia Jacques de Moraes Cardoso Structure of Art Components of Art - Analyzed by the Degrees of Representation Subject Matter Content Context Form Elements of Design Line Shape
Principles of Organiza1on Claudia Jacques de Moraes Cardoso Structure of Art Components of Art - Analyzed by the Degrees of Representation Subject Matter Content Context Form Elements of Design Line Shape
OPTICAL ILLUSIONS. Matyas Molnar
 OPTICAL ILLUSIONS Matyas Molnar More info, examples, sources Mohit Gupta: Understanding optical illusions https://www.eyebuydirect.com/understanding-perception-optical-illusions https://www.rd.com/culture/optical-illusions/
OPTICAL ILLUSIONS Matyas Molnar More info, examples, sources Mohit Gupta: Understanding optical illusions https://www.eyebuydirect.com/understanding-perception-optical-illusions https://www.rd.com/culture/optical-illusions/
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
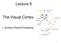 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 4. Opponent Colors. Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space
 Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
CS 544 Human Abilities
 CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping. Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016
 Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016 Foveal Resolution Resolution Limit for Reading at 18" The triangle subtended by a
Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016 Foveal Resolution Resolution Limit for Reading at 18" The triangle subtended by a
Visual Perception. Readings and References. Forming an image. Pinhole camera. Readings. Other References. CSE 457, Autumn 2004 Computer Graphics
 Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Analysis of Informa.on - III
 Analysis of Informa.on - III Efficiency of Graphic The efficiency of a graphic is determined as: To obtain a correct and complete answer to a given ques.on, all other things being equal, one graphic requires
Analysis of Informa.on - III Efficiency of Graphic The efficiency of a graphic is determined as: To obtain a correct and complete answer to a given ques.on, all other things being equal, one graphic requires
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Visual Perception. Martin Čadík. Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
 Visual Perception Martin Čadík Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Content HVS Visual Illusions, Form, Brightness Adaptation - HDRI Colour Vision Depth, Motion Image Quality Assessment
Visual Perception Martin Čadík Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Content HVS Visual Illusions, Form, Brightness Adaptation - HDRI Colour Vision Depth, Motion Image Quality Assessment
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Contrast, Luminance and Colour
 Contrast, Luminance and Colour Week 3 Lecture 1 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Some of these slides have been borrowed and adapted from Maureen Stone and Colin Ware What is gray? Colour space is 3 dimensions 1 achromatic
Contrast, Luminance and Colour Week 3 Lecture 1 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Some of these slides have been borrowed and adapted from Maureen Stone and Colin Ware What is gray? Colour space is 3 dimensions 1 achromatic
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
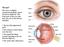 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and perception. Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 10. Neurophysiology
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
S. Rinzivillo DATA VISUALIZATION AND VISUAL ANALYTICS
 S. Rinzivillo rinzivillo@is/.cnr.it DATA VISUALIZATION AND VISUAL ANALYTICS TAXONOMY OF VISUAL VARIABLES Cleveland McGill [1984] Cleveland & McGill: graphical encodings Angle Area Color Hue Color Satura/on
S. Rinzivillo rinzivillo@is/.cnr.it DATA VISUALIZATION AND VISUAL ANALYTICS TAXONOMY OF VISUAL VARIABLES Cleveland McGill [1984] Cleveland & McGill: graphical encodings Angle Area Color Hue Color Satura/on
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference
 1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Presentation Design Principles. Grouping Contrast Proportion
 Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object Text Object Object Object Object
Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object Text Object Object Object Object
Foundations for Art, Design & Digital Culture. Observing - Seeing - Analysis
 Foundations for Art, Design & Digital Culture Observing - Seeing - Analysis Paul Martin Lester (2006, 50-51) outlined two ways that we process communication: sensually and perceptually. The sensual process,
Foundations for Art, Design & Digital Culture Observing - Seeing - Analysis Paul Martin Lester (2006, 50-51) outlined two ways that we process communication: sensually and perceptually. The sensual process,
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
This is due to Purkinje shift. At scotopic conditions, we are more sensitive to blue than to red.
 1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Occlusion. Atmospheric Perspective. Height in the Field of View. Seeing Depth The Cue Approach. Monocular/Pictorial
 Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Motion illusion, rotating snakes
 Motion illusion, rotating snakes Previous classes Computer vision overview Mathematics of pinhole camera Sensors and light Recap: projection X t x K R 1 1 0 0 0 1 33 32 31 23 22 21 13 12 11 0 0 z y x t
Motion illusion, rotating snakes Previous classes Computer vision overview Mathematics of pinhole camera Sensors and light Recap: projection X t x K R 1 1 0 0 0 1 33 32 31 23 22 21 13 12 11 0 0 z y x t
the human chapter 1 the human Overview Perception Limitations of poor interface design Why do we need to understand users?
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
Presentation Design Principles. Grouping Contrast Proportion R.I.T. S. Ludi/R. Kuehl p. 1 R I T. Software Engineering
 Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion S. Ludi/R. Kuehl p. 1 Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Object Text Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object
Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion S. Ludi/R. Kuehl p. 1 Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Object Text Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Digital Image Processing Lec 02 - Image Formation - Color Space
 DIP-AMA, Fall 2018 Digital Image Processing Lec 02 - Image Formation - Color Space Zhu Li Dept of CSEE, UMKC Office: FH560E, Email: lizhu@umkc.edu, Ph: x 2346. http://l.web.umkc.edu/lizhu p.1 Outline Recap
DIP-AMA, Fall 2018 Digital Image Processing Lec 02 - Image Formation - Color Space Zhu Li Dept of CSEE, UMKC Office: FH560E, Email: lizhu@umkc.edu, Ph: x 2346. http://l.web.umkc.edu/lizhu p.1 Outline Recap
Computa(onal Vision Introduc(on and Overview. Lecture 1: Introduc(on Hamid Dehghani Office: UG38
 Computa(onal Vision Introduc(on and Overview Lecture 1: Introduc(on Hamid Dehghani Office: UG38 Schedule 1 Lecture / week 9 am, Fridays@ Nuffield G13 1 Lab / week 11 am Fridays, @ UG04, CS Modules webpages
Computa(onal Vision Introduc(on and Overview Lecture 1: Introduc(on Hamid Dehghani Office: UG38 Schedule 1 Lecture / week 9 am, Fridays@ Nuffield G13 1 Lab / week 11 am Fridays, @ UG04, CS Modules webpages
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Visual Rules. Why are they necessary?
 Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
