Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
|
|
|
- Clementine Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the figure below to the right, suppose the method of constant stimuli was used to measure the perceived lightness of the shaded bright patch (labeled B ) compared to the unshaded bright patch. On each trial, the intensity at B varied and the subject was asked whether B looked brighter or darker than the unshaded bright patch. Suppose the subject generated the psychometric function on the right. Unshaded bright patch Shaded bright patch Ac cording to this data, what intensity of patch B best matched the perceived intensity of the unshaded bright patch? a. 70 d. 50 b. 60 e. 65 c Which of the following sensory dimensions has an expansive power function for magnitude estimation? a. lifted weight c. sound intensity b. electric shock d. light intensity 3. The highest density of cones are found in a. the periphery. c. the optic nerve. b. the blind spot. d. the fovea. 4. In normal humans, the left LGN receives inputs from a. only cones c. only the contralateral eye b. only rods d. both eyes 5. Which best describes receptive fields of LGN neurons? a. orientation selective d. center/surround b. argumentative e. simple c. complex 6. The advantage of many rods converging to few ganglion cells is: a. better light sensitivity c. better color vision b. better spatial resolution d. better frequency discrimination 1
2 Name: 7. Photoreceptors in the eye adapt to higher light levels by a. decreasing their proportion of isomerized retinal molecules b. depleting their supply of neurotransmitters c. switching over to the cone system d. decreasing their convergence to ganglion cells 8. A neuron signals an increase in stimuls intensity by increasing the of the spikes. a. frequency c. sensitivity b. amplitude d. velocity 9. An increase in neural activity leads to a local a. decrease in blood oxygenation. c. increase in receptive field size. b. decrease in receptive field size. d. increase in blood oxygenation. 10. Which of the following is not evidence of orientation selective cells? a. the Hermann grid illusion c. the tilt illusion b. orientation selective adaptation d. the tilt aftereffect 11. The cortical magnification factor occurs in humans because a. a small area in the fovea accounts for a large areas on the cortex. b. the lens accommodates so that the image is focused on the retina. c. a small area in the peripheral retina accounts for a large area on the cortex. d. the area of the optic disk accounts for a large area on the cortex. 12. The ratio station KEXP in Seattle cannot be detected by our visual system because a. visible light adapts the radio waves emitted by the broadcast tower. b. radio waves have much longer wavelengths than visible light. c. we do not know what music would look like. d. light and radio signals are unrelated phenomena. 13. Visual information from the left travels to the hemisphere of the brain a. left eye; left c. left half of the visual field; right b. left half of the visual field; left d. left eye; right 14. In which psychophysical method does the experimenter select several stimuli in the vicinity of threshold and present them in random order? a. magnitude estimation d. method of adjustment b. method of constant magnitude e. method of limits c. method of constant stimuli 15. What is the range of wavelenghts that we perceive as light? a nanometers d speedometers b micrometers e meters c millimeters 16. Presbyopia a. causes the farthest distance at which one can see to move out. b. is due to a decreased ability to accommodate. c. is due to a decreased ability to adapt. d. is caused by the cornea becoming non-spherical. 17. The contrast sensitivity function shows that normal observers are most sensitive to a. middle spatial frequencies. c. high spatial frequencies. b. low spatial frequencies. d. high and low spatial frequencies. 2
3 Name: 18. The receptive field of a neuron in the visual system is a. the set of post-synaptic neurons. b. the set of neurons connected to its dendrites. c. the region of the visual field in which stimulation affects the cell s response. d. the cell body. e. shaped like a giant cone. 19. People with a primary visual cortex are more likely to have visual acuity thresholds. a. retinotopic; oriented c. large; high b. large; small d. oriented; normal 20. Most light entering the eye is a. adapted. c. reflected off of the cornea. b. reflected off of something. d. coming directly from a light source. 21. If you penetrate an electrode vertically down through the LGN, you ll find evidence of a. eye-dominance, magnocellular and parvocellular layers. b. bias in orientation selectivity toward vertical and horizontal. c. a retinotopic map. d. cortical magnification. 22. Which of the following brain imaging technique has the best spatial resolution? a. TMS c. BLT b. EEG d. fmri 23. In the simultaneous contrast illusion, gray squares of equal intensities are surrounded by either a dark background or lighter background. The square on the dark background looks the square on the lighter background. a. the same as c. more colorful than b. lighter than d. darker than 24. Retinotopic maps can be found a. both in the LGN and in V1. c. in V1 but not in the LGN. b. in the LGN but not in V1. d. in the Geology department. 25. Hubel and Wiesel first measured orientation selectivity a. in the primary visual cortex of the cat. b. in the primary visual cortex of the monkey. c. in the LGN of the cat. d. in the LGN of the monkey. 26. After being exposed to light, a dissected frog retina becomes _ over time. a. more responsive c. faster b. lighter d. darker 27. The blind spot a. is most common in older individuals. b. is caused by the optic nerve leaving the eye. c. is in the fovea. d. is caused by elevated pressure in the eye. 28. When you focus from a far distance to an object up close, the ciliary muscles which causes the lens to. a. tighten; thicken c. relax; thicken b. relax; become thinner d. tighten; become thinner 3
4 Name: 29. As you move from the fovea to the periphery, the number of rods per square millimeter. a. decreases c. increases b. incerases and then decreases d. decreases and then increases 30. Between a dark night and a bright day, light levels range over orders of magnitude. Iin a given lighting condision, light ranges over about orders of magnitude. a. 9; 2 c. 9; 9 b. 2; 2 d. 2; Which of the following is NOT a way the visual system deals with a broad range of light levels. a. Having rods for night vision, cones for day vision b. Pupil dialation c. Adaptation of photoreceptors d. Accomodation of the lens 32. True or false: sensory action potentials can occur in the absence of a physical stimulus: a. True b. False 33. Which is an example of the oblique effect? a. Lines do not look parallel in the Cafe wall illusion. b. The visual system is more sensitive in the fovea than the periphery. c. The visual system is more sensitive to vertical and horizontal orientations than to oblique orientations. d. The rods are most sensitive at night. 34. If you record from neurons with an electrode as it penetrates straight down into the cortex (perpendicular to the surface), neurons will a. have receptive fields at roughly the same location. b. change from rod to cone vision. c. have peferred occular dominance that alternates from eye to eye d. have preferred orientations that change systematically. 4
5 Name: Short Answer (3 points each) 35. What is it about the retina of the Octopus that makes it unnecessary for it to have a blind spot?. 36. Describe Hubel and Wiesel s Cube Model of the primary visual cortex. Draw a diagram if it helps.. 5
6 Name: 37. Plot your estimate of the amount of orientation content present in the image below. You may plot it as a Cartesian graph (with orientation on the x-axis), or as a polar plot as shown in lecture. 6
7 Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: B 3. ANS: D 4. ANS: D 5. ANS: D 6. ANS: A 7. ANS: A 8. ANS: A 9. ANS: D 10. ANS: A 11. ANS: A 12. ANS: B 13. ANS: C 14. ANS: C 15. ANS: A 16. ANS: B 17. ANS: A 18. ANS: C 19. ANS: B 20. ANS: B 21. ANS: A 22. ANS: D 23. ANS: B 24. ANS: A 25. ANS: A 26. ANS: B 27. ANS: B 28. ANS: A 29. ANS: B 30. ANS: A 31. ANS: D 32. ANS: A 33. ANS: C 34. ANS: A 1
8 SHORT ANSWER 35. ANS: Our photoreceptors point away from the light and lie in the back of the retina. We have a blind spot at the optic disc where the nerve fibers leave the eye because there is no room for photoreceptors there. Photoreceptors in the Octopus retina point toward the light away from the back of the retina, so there is room for them on top of the optic disc. 36. ANS: Orientation columns in one dimension, ocular dominance columns in the other. 37. ANS: 2
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night.
 Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
The best retinal location"
 How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Outline. The visual pathway. The Visual system part I. A large part of the brain is dedicated for vision
 The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
Visual Perception. Readings and References. Forming an image. Pinhole camera. Readings. Other References. CSE 457, Autumn 2004 Computer Graphics
 Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes
 Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
CS 534: Computer Vision
 CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
Biological Vision. Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University
 Biological Vision Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines How do we see: some historical theories of vision Biological vision: theories and results from psychology and cognitive
Biological Vision Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines How do we see: some historical theories of vision Biological vision: theories and results from psychology and cognitive
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September ) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this
 Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Vision and Color. Reading. The lensmaker s formula. Lenses. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
CS510: Image Computation. Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018
 CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
Fundamentals of Computer Vision B. Biological Vision. Prepared By Louis Simard
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision 308-558B Biological Vision Prepared By Louis Simard 1. Optical system 1.1 Overview The ocular optical system of a human is seen to produce a transformation of the light
Fundamentals of Computer Vision 308-558B Biological Vision Prepared By Louis Simard 1. Optical system 1.1 Overview The ocular optical system of a human is seen to produce a transformation of the light
Eye. Eye Major structural layer of the wall of the eye is a thick layer of dense C.T.; that layer has two parts:
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
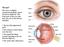 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Reading. Lenses, cont d. Lenses. Vision and color. d d f. Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp
 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology.
 This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
VISUAL NEURAL SIMULATOR
 VISUAL NEURAL SIMULATOR Tutorial for the Receptive Fields Module Copyright: Dr. Dario Ringach, 2015-02-24 Editors: Natalie Schottler & Dr. William Grisham 2 page 2 of 36 3 Introduction. The goal of this
VISUAL NEURAL SIMULATOR Tutorial for the Receptive Fields Module Copyright: Dr. Dario Ringach, 2015-02-24 Editors: Natalie Schottler & Dr. William Grisham 2 page 2 of 36 3 Introduction. The goal of this
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
CS 544 Human Abilities
 CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15
 Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN. No Thing to See. Copyright Worth Publishers 2013 NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
 3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
Prof. Greg Francis and the eye PSY 310 Greg Francis The perceptual process Perception Recognition Processing Action Transduction Lecture 03 Why does my daughter look like a demon? Stimulus on receptors
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
ensory System III Eye Reflexes
 ensory System III Eye Reflexes Quick Review from Last Week Eye Anatomy Inside of the Eye choroid Eye Reflexes Eye Reflexes A healthy person has a number of eye reflexes: Pupillary light reflex Vestibulo-ocular
ensory System III Eye Reflexes Quick Review from Last Week Eye Anatomy Inside of the Eye choroid Eye Reflexes Eye Reflexes A healthy person has a number of eye reflexes: Pupillary light reflex Vestibulo-ocular
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing
 Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Cortical sensory systems
 Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016
 Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Lecture 8. Lecture 8. r 1
 Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Review, the visual and oculomotor systems
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
