A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night.
|
|
|
- Roy Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges over only about two orders of magnitude. Dark night Indoor lighting Seattle day Sunny day If we were sensitive to this whole range all the time, there wouldn t be able to discriminate lightness levels in a typical scene.
2 The visual system solves this problem by restricting the dynamic range of its response to match the current overall or ambient light level. Dark night Indoor lighting Seattle day Sunny day Dark night Indoor lighting Seattle day Sunny day
3 Three Mechanisms for Light/Dark adaptation 1. The pupil ranges in diameter from about 2mm to 8mm. This factor of 4 means that the amount of eye ranges over a factor of 16, or just about one order of magnitude. We still have 8 orders of magnitude to go!
4 Mechanisms of Light/Dark adaptation 2. Rods vs Cones. We essentially have two visual systems in the eye.
5 3. Rods and Cones adapt. Both rods and cones become less sensitive as light levels increase.
6 Psychophysical Measurement of Dark Adaptation Measure detection thresholds as function of time in the dark. Experiment for rods and cones Observer looks at fixation point but pays attention to a test light to the side
7 The dark adaptation curve Threshold Time in the dark (minutes)
8 The dark adaptation curve Rod monochromat only has rods in the retina Threshold Cones detect the light at first until rods take over Time in the dark (sec)
9 The dark adaptation curve
10 Demonstration of dark adaptation: Dark spots unisomerized molecules in a cone (ready for a photon) Photon of light
11 Demonstration of dark adaptation: Dark spots unisomerized molecules in a cone (ready for a photon)
12 Demonstration of dark adaptation: Dark spots unisomerized molecules in a cone (ready for a photon) In the dark, all retinal molecules are ready for a photon The photoreceptor is very sensitive to light Sensitivity This is a good state to be in for walking around in the dark. But not if you walk outside.
13 Demonstration of dark adaptation: Dark spots unisomerized molecules in a cone (ready for a photon) Bright spots: isomerized molecules In bright light, nearly all molecules are isomerized. The photoreceptor is not sensitive to light Sensitivity Now you re not overexposed outside, but you can t see in the dark.
14 Demonstration of dark adaptation: Back in the dark, the molecules slowly recover and are ready to receive photons again. The cone recovers its sensitivity over time. Sensitivity
15 Light adaptation in the frog retina Time in the light Figure 2.25 A frog retina was dissected from the eye in the dark and then exposed to light. (a) This picture was taken just after the light was turned on. The dark red color is caused by the high concentration of visual pigment in the receptors. As the pigment bleaches, the retina becomes lighter, as shown in (b) and (c).
16 With digital cameras and software, you can combine pictures with different exposures to expand the dynamic range. You get detail at all light levels. Underexposed Overexposed Combined
17 With digital cameras and software, you can combine pictures with different exposures to expand the dynamic range. You get detail at all light levels.
18 Spectral Sensitivity of Rods and Cones Sensitivity of rods and cones to different parts of the visual spectrum Use monochromatic light to determine threshold at different wavelengths Threshold for light is lowest in the middle of the spectrum 1/threshold = sensitivity, which produces the spectral sensitivity curve
19 Figure 2.26 (a) The threshold for seeing a light versus wavelength. (b) Relative sensitivity versus wavelength -- the spectral sensitivity curve.
20 Figure 2.27 Spectral sensitivity curves for rod vision (left) and cone vision (right).
21 Spectral Sensitivity of Rods and Cones - continued Rod spectral sensitivity shows: More sensitive to short-wavelength light Most sensitivity at 500 nm Cone spectral sensitivity shows: Most sensitivity at 560 nm Purkinje shift - enhanced sensitivity to short wavelengths during dark adaptation when the shift from cone to rod vision occurs
22 Demonstration of Purkinje Shift Cone vision (day) Rod vision (night)
23 Demonstration of Purkinje Shift Cone vision (day) Rod vision (night)
24
25 Normally, we have three cone types, with pigments that absorb best at 419nm, 532nm, & 558nm. More on that later when we get to color vision (Chapter 7)
26 Crash course on basic neurophysiology Key components of neurons: Cell body Dendrites Axon or nerve fiber Receptors - specialized neurons that respond to specific kinds of energy
27 There are many kinds of neurons
28 Sequence of Events for Neuronal Communication 1. Membrane permeability changes. 2. Sodium rushes in. 3. Voltage inside gets more positive. 4. Critical Value reached and action potential occurs. 5. Potassium flows out. 6. Action potential travels down the axon and stimulates synaptic vesicles. 7. Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse that influence the permeability of the next neuron. Voltage (mv) Time (ms)
29 At rest, there are is a higher concentration of Na+ (Sodium) molecules outside, and K+ (Potassium) molecules inside the cell.
30 When a neuron receives input from another neuron, the permeability of the cell membrane changes, allowing sodium (Na+) to rush in and potassium (K+) to rush out. The influx of positively charged Na+ increases the potential (voltage) inside the cell, and then the outflow of the K+ decreases the voltage back to resting level. Voltage inside cell relative to outside (mv) Na+ in K+ out -70 time When the potential gets positive enough to reach a critical value (about -55 mv), it FIRES and produces what is called an ACTION POTENTIAL.
31
32 2 mv injected Voltage (mv) spikes mv injected Voltage (mv) spikes mv injected Voltage (mv) Voltage (mv) mv injected spikes 13 spikes
33 Three important facts about these processes: 1. Action potentials are ALL-OR-NONE. 2. There s a REFRACTORY PERIOD after an action potential during which another action potential cannot occur. 3. There is a SPONTANEOUS, background level of firing even in the absence of stimulation. 16 mv injected Voltage (mv)
34 Action potentials and intensity of stimulation Pressure applied Soft pressure Time Medium pressure Strong pressure Spontaneous (background) rate of firing
35 5 spikes/sec Time (sec) 20 spikes/sec Time (sec) 75 spikes/sec Time (sec)
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
Color Outline. Color appearance. Color opponency. Brightness or value. Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Color appearance
 Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
The best retinal location"
 How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
The Eye. Morphology of the eye (continued) Morphology of the eye. Sensation & Perception PSYC Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D
 Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D The Eye The Eye The function of the eyeball is to protect the photoreceptors The role of the eye is to capture an image of objects that we
Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D The Eye The Eye The function of the eyeball is to protect the photoreceptors The role of the eye is to capture an image of objects that we
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September ) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this
 Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
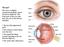 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Retina. last updated: 23 rd Jan, c Michael Langer
 Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
Color Perception. Color, What is It Good For? G Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney. perceptual organization. perceptual organization
 G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine. Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al.
 Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision
 Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision Andrew Stockman Revision Course in Basic Sciences for FRCOphth. Part 1 Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Refractive
Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision Andrew Stockman Revision Course in Basic Sciences for FRCOphth. Part 1 Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Refractive
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Lab #9: Compound Action Potentials in the Toad Sciatic Nerve
 Lab #9: Compound Action Potentials in the Toad Sciatic Nerve In this experiment, you will measure compound action potentials (CAPs) from an isolated toad sciatic nerve to illustrate the basic physiological
Lab #9: Compound Action Potentials in the Toad Sciatic Nerve In this experiment, you will measure compound action potentials (CAPs) from an isolated toad sciatic nerve to illustrate the basic physiological
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Frequencies and Color
 Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Visibility, Performance and Perception. Cooper Lighting
 Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY
 OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
BIOPHYSICS OF VISION GEOMETRIC OPTICS OF HUMAN EYE. Refraction media of the human eye. D eye = 63 diopter, D cornea =40, D lens = 15+
 BIOPHYSICS OF VISION THEORY OF COLOR VISION ELECTRORETINOGRAM Two problems: All cows are black in dark! Playing tennis in dark with illuminated lines, rackets, net, and ball! Refraction media of the human
BIOPHYSICS OF VISION THEORY OF COLOR VISION ELECTRORETINOGRAM Two problems: All cows are black in dark! Playing tennis in dark with illuminated lines, rackets, net, and ball! Refraction media of the human
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
What determines data speed?
 PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
Visual Imaging and the Electronic Age Color Science
 Visual Imaging and the Electronic Age Color Science Grassman s Experiments & Trichromacy Lecture #5 September 5, 2017 Prof. Donald P. Greenberg Light as Rays Light as Waves Light as Photons What is Color
Visual Imaging and the Electronic Age Color Science Grassman s Experiments & Trichromacy Lecture #5 September 5, 2017 Prof. Donald P. Greenberg Light as Rays Light as Waves Light as Photons What is Color
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
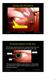 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Unit 1 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS
 Unit 1 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS What Is Digital Image? An image may be defined as a two-dimensional function, f(x, y), where x and y are spatial (plane) coordinates, and the amplitude of f at any pair
Unit 1 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS What Is Digital Image? An image may be defined as a two-dimensional function, f(x, y), where x and y are spatial (plane) coordinates, and the amplitude of f at any pair
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Reading. Lenses, cont d. Lenses. Vision and color. d d f. Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp
 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
How We See Color And Why CRI Matters
 Let s talk color; but first, how do we see color? The human eye gives us the sense of sight; from which, we can interpret colors, shapes and dimensions of the world around us by processing light reflecting
Let s talk color; but first, how do we see color? The human eye gives us the sense of sight; from which, we can interpret colors, shapes and dimensions of the world around us by processing light reflecting
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Introduction. Chapter Aim of the Thesis
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Aim of the Thesis The main aim of this investigation was to develop a new instrument for measurement of light reflected from the retina in a living human eye. At the start of
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Aim of the Thesis The main aim of this investigation was to develop a new instrument for measurement of light reflected from the retina in a living human eye. At the start of
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital image processing is based on. Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis
 Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Mastery. Chapter Content. What is light? CHAPTER 11 LESSON 1 C A
 Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
SEEING. Seeing lecture 2 The retina and colour vision. Dr John S. Reid Department of Physics University of Aberdeen
 SEEING Seeing lecture 2 The retina and colour vision Dr John S. Reid Department of Physics University of Aberdeen 1 The retina Forming an image on the back of the eye is the easy part. Seeing the image
SEEING Seeing lecture 2 The retina and colour vision Dr John S. Reid Department of Physics University of Aberdeen 1 The retina Forming an image on the back of the eye is the easy part. Seeing the image
Why is blue tinted backlight better?
 Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
 1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
Vision and Color. Reading. The lensmaker s formula. Lenses. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Special Senses: The Eye
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Light as a stimulus for vision. Electromagnetic spectrum. Radiant Energy (Electromagnetic) Spectrum. Solar Radiation Spectrum
 Light as a stimulus for vision The physics of light: Light is considered both as a propagating electromagnetic wave and as a stream of individual particles (photons). In Vision Science, both of these aspects
Light as a stimulus for vision The physics of light: Light is considered both as a propagating electromagnetic wave and as a stream of individual particles (photons). In Vision Science, both of these aspects
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
Pupil Lumens and their impact on the choice of lighting
 Pupil Lumens and their impact on the choice of lighting A warehouse facility recently upgraded its lighting. Before the lighting improvement project it was illuminated by low CRI HPS lamps which were replaced
Pupil Lumens and their impact on the choice of lighting A warehouse facility recently upgraded its lighting. Before the lighting improvement project it was illuminated by low CRI HPS lamps which were replaced
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
CGT 511 Perception. Facts. Facts. Facts. When perceiving visual information
 CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing
 Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
