Color Outline. Color appearance. Color opponency. Brightness or value. Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Color appearance
|
|
|
- Irma Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically different lights evoke the same responses in the 3 cones then the two lights will look the same (metamers). Explains when two lights will look the same, not what they will look like. Color appearance Color opponency: appearance depends on the differences between cone responses (R-G and B-Y). Chromatic adaptation: color appearance also depends on context because the each cone adapts (like light and dark adaptation) to the ambient illumination. Color constancy: visual system infers surface color, despite changes in illumination. Color appearance Brightness or value Color opponency
2 Color opponency Hue cancellation experiment Hue cancellation experiment
3 Hue cancellation Cancellation intensity Blue curve, wavelengths that appear blue were cancelled by adding yellow light. Likewise for red and green. Why is the curve red below 475nm as well as above 580nm? Hurvich & Jameson (1957) Color opponency neural computation L-M L+M-S L+M+S Color opponency Will a 650nm light look redish or greenish? What about a 500 nm light? What monochromatic light will appear neither redish nor greenish? What color will it appear to have?
4 Some retinal ganglion cell types midget small bistratified parasol Ganglion cell mosaics Field et al., Nature (2010) Blue/yellow pathway Cones Bipolars cones B/Y ganglion B/Y ganglion cell
5 S-cone (cross section) S-cone sampling mosaic Bistratified ganglion cell Dendritic tree of bistratified ganglion cell branches in two separate layers of the retina. Inner tree avoids S cone bipolar cells. Inner tree Outer tree has synapses with every S cone bipolar cell. S cone bipolar cell Outer tree Ganglion cell
6 Blue/yellow pathway S cone bipolar terminals Bistratified ganglion cells Color and pattern S-cones have low resolution
7 Monochrome MTF Increasing contrast Increasing spatial frequency Chromatic MTF Light and dark adaptation
8 Surface luminance levels Sunlight: 10 5 candelas/meter 2 (cd/m 2 ) Approx photons/m 2 /sec 3%-90% of photons are reflected as luminance 3% for black surfaces, 90% for white surfaces Only some of the reflected photons enter the pupil of eye Indoor lighting, CRTs: 10 2 cd/m 2 Moonlight: 10-1 cd/m 2 Starlight: 10-3 cd/m 2 The eye can adjust to changes in light level by a factor of 100,000,000! Yet firing rates only typically range from 0-400Hz. Dark adaptation Threshold (log intensity) Time in the dark (min) Mechanisms of light/dark adaptation 1. Pupil size 2. Switchover between rods and cones 3. Bleaching/regeneration of photopigment 4. Feedback from horizontal cells to control the responsiveness of photoreceptors
9 Contrast mean = 1 contrast = 50% Intensity mean = 1 contrast = 100% contrast = amp of modulation mean mean = 2 contrast = 50% Time or space Responses increase with contrast Responses increase with contrast low stimulus contrast high
10 Chromatic adaptation Chromatic adaptation
11
12 Asymmetric color matching Memory matching Dichoptic matching Von Kries theory of chromatic adaptation (change of gain) G L 0 G M 0 G S Von Kries (1905) Von Kries theory of chromatic adaptation (change of gain) Adaptation scale factors Photoreceptor responsivity Input SPD Canonical context cone absorptions
13 What determines the gain Neural computation with coloropponency and adaptation Simultaneous color contrast
14 Lightness constancy Surface reflectance light light 90% reflected 10% reflected White paper: 10% absorbed Black paper: 90% absorbed 10, perceived brightness? reflects 90% reflects 10%
15 10, reflects 90% reflects 10% Ratios black = 1/5 white = 9/ Ratios black = 1/5 white = 9/ Simultaneous brightness contrast Color constancy
16 Color signaling Surface-illuminant equations R(λ) E(λ) S(λ) 0 0 Cameras do not have color constancy daylight flourescent light
17 Daylight illumination examples Blue sky Disk of sun Principles Psychophysics is part psycho and part physics. Theory: linear systems. Methodology: matching. Computation: linear summation, static nonlinearity, adaptation. Principle of univariance. Parallel pathways. Perceptual constancy (lightness, color, size, etc.), adaptation, and visual illusions (e.g., aftereffects).
Color Perception. Color, What is It Good For? G Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney. perceptual organization. perceptual organization
 G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
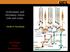 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Lecture 4. Opponent Colors. Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space
 Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Lecture 4 Opponent Colors Hue Cancellation Experiment HUV Color Space 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100 120 50 100 150 200 250 20 40 60 80 100
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
What is Color. Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception.
 Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
Color What is Color Color is a fundamental attribute of human visual perception. By fundamental we mean that it is so unique that its meaning cannot be fully appreciated without direct experience. How
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night.
 Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
The best retinal location"
 How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Additive. Subtractive
 Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing
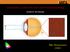 Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Visual optics, rods and cones and retinal processing Andrew Stockman MSc Neuroscience course Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Rods and cones Univariance Trichromacy Chromatic
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Frequencies and Color
 Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine. Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al.
 Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Color Perception. This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
 Color Perception This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County Characteristics of Color Perception Fundamental, independent visual process after-images
Color Perception This lecture is (mostly) thanks to Penny Rheingans at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County Characteristics of Color Perception Fundamental, independent visual process after-images
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Color Science. CS 4620 Lecture 15
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Color. University of Massachusetts, Amherst September 15, 2014 Instructor: Subhransu Maji
 CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Color University of Massachusetts, Amherst September 15, 2014 Instructor: Subhransu Maji Slides by D.A. Forsyth 2 Color is the result of interaction between light in the environment
CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Color University of Massachusetts, Amherst September 15, 2014 Instructor: Subhransu Maji Slides by D.A. Forsyth 2 Color is the result of interaction between light in the environment
excite the cones in the same way.
 Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Humans have 3 kinds of cones Color vision Edward H. Adelson 9.35 Trichromacy To specify a light s spectrum requires an infinite set of numbers. Each cone gives a single number (univariance) when stimulated
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region.
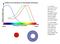 In a centersurround cell of any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region. + _ In a chromatic center-surround field, each in innervated by one class
In a centersurround cell of any kind, you have two receptive fields, one the small center region, the other the surround region. + _ In a chromatic center-surround field, each in innervated by one class
CS6640 Computational Photography. 6. Color science for digital photography Steve Marschner
 CS6640 Computational Photography 6. Color science for digital photography 2012 Steve Marschner 1 What visible light is One octave of the electromagnetic spectrum (380-760nm) NASA/Wikimedia Commons 2 What
CS6640 Computational Photography 6. Color science for digital photography 2012 Steve Marschner 1 What visible light is One octave of the electromagnetic spectrum (380-760nm) NASA/Wikimedia Commons 2 What
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
12/02/2017. From light to colour spaces. Electromagnetic spectrum. Colour. Correlated colour temperature. Black body radiation.
 From light to colour spaces Light and colour Advanced Graphics Rafal Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge 1 2 Electromagnetic spectrum Visible light Electromagnetic waves of wavelength
From light to colour spaces Light and colour Advanced Graphics Rafal Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge 1 2 Electromagnetic spectrum Visible light Electromagnetic waves of wavelength
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Color Science. What light is. Measuring light. CS 4620 Lecture 15. Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD)
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Vision and Color. Reading. The lensmaker s formula. Lenses. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading. Lenses, cont d. Lenses. Vision and color. d d f. Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp
 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
CGT 511 Perception. Facts. Facts. Facts. When perceiving visual information
 CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
Question From Last Class
 Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Visibility, Performance and Perception. Cooper Lighting
 Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
Visibility, Performance and Perception Kenneth Siderius BSc, MIES, LC, LG Cooper Lighting 1 Vision It has been found that the ability to recognize detail varies with respect to four physical factors: 1.Contrast
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Color Image Processing. Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6
 Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Color Image Processing Gonzales & Woods: Chapter 6 Objectives What are the most important concepts and terms related to color perception? What are the main color models used to represent and quantify color?
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Color. Bilkent University. CS554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu
 1 Color CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) λ is wavelength
1 Color CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) λ is wavelength
Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision
 Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision Andrew Stockman Revision Course in Basic Sciences for FRCOphth. Part 1 Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Refractive
Fundamental Optics of the Eye and Rod and Cone vision Andrew Stockman Revision Course in Basic Sciences for FRCOphth. Part 1 Outline The eye Visual optics Image quality Measuring image quality Refractive
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
19. Vision and color
 19. Vision and color 1 Reading Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Watt, Chapter 15. Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, pp. 45-50 and 69-97,
19. Vision and color 1 Reading Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Watt, Chapter 15. Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, pp. 45-50 and 69-97,
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Color. Color. Colorfull world IFT3350. Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Vision and color. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell
 Vision and color University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Watt, Chapter 15. Brian Wandell. Foundations
Vision and color University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Watt, Chapter 15. Brian Wandell. Foundations
Color Assimilation and Contrast near Absolute Threshold
 This is a preprint of 8292-2 paper in SPIE/IS&T Electronic Imaging Meeting, San Jose, January, 2012 Color Assimilation and Contrast near Absolute Threshold John J. McCann McCann Imaging, Belmont, MA 02478
This is a preprint of 8292-2 paper in SPIE/IS&T Electronic Imaging Meeting, San Jose, January, 2012 Color Assimilation and Contrast near Absolute Threshold John J. McCann McCann Imaging, Belmont, MA 02478
A World of Color. Session 4 Color Spaces. OLLI at Illinois Spring D. H. Tracy
 A World of Color Session 4 Color Spaces OLLI at Illinois Spring 2018 D. H. Tracy Course Outline 1. Overview, History and Spectra 2. Nature and Sources of Light 3. Eyes and Color Vision 4. Color Spaces
A World of Color Session 4 Color Spaces OLLI at Illinois Spring 2018 D. H. Tracy Course Outline 1. Overview, History and Spectra 2. Nature and Sources of Light 3. Eyes and Color Vision 4. Color Spaces
1 Human Color Vision
 1 Human Color Vision Color appearance models aim to extend basic colorimetry to the level of specifying the perceived color of stimuli in a wide variety of viewing conditions. To fully appreciate the formulation,
1 Human Color Vision Color appearance models aim to extend basic colorimetry to the level of specifying the perceived color of stimuli in a wide variety of viewing conditions. To fully appreciate the formulation,
The Photoreceptor Mosaic
 The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics
 University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Color 2 Week 10, Fri 7 Nov 2003 Tamara Munzner 1 Readings Chapter 1.4: color plus supplemental reading: A Survey of Color for Computer Graphics,
University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Color 2 Week 10, Fri 7 Nov 2003 Tamara Munzner 1 Readings Chapter 1.4: color plus supplemental reading: A Survey of Color for Computer Graphics,
Images. CS 4620 Lecture Kavita Bala w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Fall 2015 Lecture 38
 Images CS 4620 Lecture 38 w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 1 Announcements A7 extended by 24 hours w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Color displays Operating principle: humans are trichromatic match
Images CS 4620 Lecture 38 w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 1 Announcements A7 extended by 24 hours w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Color displays Operating principle: humans are trichromatic match
Color. Phillip Otto Runge ( )
 Color Phillip Otto Runge (1777-1810) What is color? Color is a psychological property of our visual experiences when we look at objects and lights, not a physical property of those objects or lights (S.
Color Phillip Otto Runge (1777-1810) What is color? Color is a psychological property of our visual experiences when we look at objects and lights, not a physical property of those objects or lights (S.
Color and Perception. CS535 Fall Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Color and Perception CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Elements of Color Perception 2 Elements of Color Physics: Illumination Electromagnetic spectra; approx.
Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
Light as a stimulus for vision. Electromagnetic spectrum. Radiant Energy (Electromagnetic) Spectrum. Solar Radiation Spectrum
 Light as a stimulus for vision The physics of light: Light is considered both as a propagating electromagnetic wave and as a stream of individual particles (photons). In Vision Science, both of these aspects
Light as a stimulus for vision The physics of light: Light is considered both as a propagating electromagnetic wave and as a stream of individual particles (photons). In Vision Science, both of these aspects
Color. Fredo Durand Many slides by Victor Ostromoukhov. Color Vision 1
 Color Fredo Durand Many slides by Victor Ostromoukhov Color Vision 1 Today: color Disclaimer: Color is both quite simple and quite complex There are two options to teach color: pretend it all makes sense
Color Fredo Durand Many slides by Victor Ostromoukhov Color Vision 1 Today: color Disclaimer: Color is both quite simple and quite complex There are two options to teach color: pretend it all makes sense
Today. Color. Color and light. Color and light. Electromagnetic spectrum 2/7/2011. CS376 Lecture 6: Color 1. What is color?
 Color Monday, Feb 7 Prof. UT-Austin Today Measuring color Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
Color Monday, Feb 7 Prof. UT-Austin Today Measuring color Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE III: COLOR IN IMAGE & VIDEO DR. OUIEM BCHIR
 1 LECTURE III: COLOR IN IMAGE & VIDEO DR. OUIEM BCHIR 2 COLOR SCIENCE Light and Spectra Light is a narrow range of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic waves have the properties of frequency and wavelength.
1 LECTURE III: COLOR IN IMAGE & VIDEO DR. OUIEM BCHIR 2 COLOR SCIENCE Light and Spectra Light is a narrow range of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic waves have the properties of frequency and wavelength.
Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance
 Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance Sumanta N. Pattanaik 1 Mark D. Fairchild 2 James A. Ferwerda 1 Donald P. Greenberg 1 1 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University,
Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance Sumanta N. Pattanaik 1 Mark D. Fairchild 2 James A. Ferwerda 1 Donald P. Greenberg 1 1 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University,
The human visual system
 The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
The human visual system Vision and hearing are the two most important means by which humans perceive the outside world. 1 Low-level vision Light is the electromagnetic radiation that stimulates our visual
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Color April 16 th, 2015
 Color April 16 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Today Measuring color Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
Color April 16 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Today Measuring color Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
Color. April 16 th, Yong Jae Lee UC Davis
 Color April 16 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Measuring color Today Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
Color April 16 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Measuring color Today Spectral power distributions Color mixing Color matching experiments Color spaces Uniform color spaces Perception of color Human photoreceptors
Appearance at the low-radiance end of HDR vision: Achromatic & Chromatic
 This is a preprint of Proc. IS&T Color Imaging Conference, San Jose, 19, 186-190, November, 2011 Appearance at the low-radiance end of HDR vision: Achromatic & Chromatic John J. McCann McCann Imaging,
This is a preprint of Proc. IS&T Color Imaging Conference, San Jose, 19, 186-190, November, 2011 Appearance at the low-radiance end of HDR vision: Achromatic & Chromatic John J. McCann McCann Imaging,
icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance
 icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance Jiangtao Kuang, Mark D. Fairchild, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New York Abstract A new image appearance model, designated as icam06, has been developed
icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance Jiangtao Kuang, Mark D. Fairchild, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New York Abstract A new image appearance model, designated as icam06, has been developed
History of Computer Vision and Human Vision System
 History of Computer Vision and Human Vision System 簡韶逸 Shao-Yi Chien Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall 2018 1 History of Computer Vision 2 1960s--1970s In 1966, Minsky
History of Computer Vision and Human Vision System 簡韶逸 Shao-Yi Chien Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall 2018 1 History of Computer Vision 2 1960s--1970s In 1966, Minsky
Modeling Blue shift in Moonlit Scenes by Rod Cone Interaction Paper ID: paper_0151 Saad Masood Khan Sumanta N. Pattanaik University of Central Florida
 Modeling Blue shift in Moonlit Scenes by Rod Cone Interaction Paper ID: paper_0151 Saad Masood Khan Sumanta N. Pattanaik University of Central Florida Abstract Moonlit night scenes have a tinge of blue.
Modeling Blue shift in Moonlit Scenes by Rod Cone Interaction Paper ID: paper_0151 Saad Masood Khan Sumanta N. Pattanaik University of Central Florida Abstract Moonlit night scenes have a tinge of blue.
Radiometry vs. Photometry. Radiometric and photometric units
 Radiometry vs. Photometry Radiometry -- the measurement and specification of the power (energy) of a source of electromagnetic radiation. total energy or numbers of quanta Photometry -- the measurement
Radiometry vs. Photometry Radiometry -- the measurement and specification of the power (energy) of a source of electromagnetic radiation. total energy or numbers of quanta Photometry -- the measurement
2 The First Steps in Vision: Seeing Stars
 2 The First Steps in Vision: Seeing Stars Outline What is light? Types of waves Dual nature of light: waves and particles Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation Intensity, wavelength, polarization, direction
2 The First Steps in Vision: Seeing Stars Outline What is light? Types of waves Dual nature of light: waves and particles Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation Intensity, wavelength, polarization, direction
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Radiometry vs. Photometry. Radiometric and photometric units
 Radiometry vs. Photometry Radiometry -- the measurement and specification of the power (energy) of a source of electromagnetic radiation.! total energy or numbers of quanta Photometry -- the measurement
Radiometry vs. Photometry Radiometry -- the measurement and specification of the power (energy) of a source of electromagnetic radiation.! total energy or numbers of quanta Photometry -- the measurement
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Announcements. Electromagnetic Spectrum. The appearance of colors. Homework 4 is due Tue, Dec 6, 11:59 PM Reading:
 Announcements Homework 4 is due Tue, Dec 6, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 3: Color CSE 252A Lecture 18 Electromagnetic Spectrum The appearance of colors Color appearance is strongly affected by (at least):
Announcements Homework 4 is due Tue, Dec 6, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 3: Color CSE 252A Lecture 18 Electromagnetic Spectrum The appearance of colors Color appearance is strongly affected by (at least):
Chapter 5: Color vision remnants Chapter 6: Depth perception
 Chapter 5: Color vision remnants Chapter 6: Depth perception Lec 12 Jonathan Pillow, Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 1 Other types of color-blindness: Monochromat:
Chapter 5: Color vision remnants Chapter 6: Depth perception Lec 12 Jonathan Pillow, Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 1 Other types of color-blindness: Monochromat:
Colour. Why/How do we perceive colours? Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!
 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing
 I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 18
 CSE 152 Lecture 18 Announcements Homework 5 is due Sat, Jun 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 3: Color Electromagnetic Spectrum The appearance of colors Color appearance is strongly affected by (at least):
CSE 152 Lecture 18 Announcements Homework 5 is due Sat, Jun 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 3: Color Electromagnetic Spectrum The appearance of colors Color appearance is strongly affected by (at least):
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September ) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this
 Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
Vision Science I Exam 1 23 September 2016 1) The plot to the right shows the spectrum of a light source. Which of the following sources is this spectrum most likely to be taken from? A) The direct sunlight
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
Biology 70, Lecture 4, Part II Fall 2007
 color another bad joke 1 2 from lecture outline: COLOR What s wrong here?????? 7. What property of light is responsible for color information? Under white light why does an opaque or translucent blue object
color another bad joke 1 2 from lecture outline: COLOR What s wrong here?????? 7. What property of light is responsible for color information? Under white light why does an opaque or translucent blue object
Using Color Appearance Models in Device-Independent Color Imaging. R. I. T Munsell Color Science Laboratory
 Using Color Appearance Models in Device-Independent Color Imaging The Problem Jackson, McDonald, and Freeman, Computer Generated Color, (1994). MacUser, April (1996) The Solution Specify Color Independent
Using Color Appearance Models in Device-Independent Color Imaging The Problem Jackson, McDonald, and Freeman, Computer Generated Color, (1994). MacUser, April (1996) The Solution Specify Color Independent
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference
 1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
