Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
|
|
|
- Leonard Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
2 Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ perception: the organization, identification, and interpretation of a sensation in order to form a mental representation transduction: what takes place when many sensors in the body convert physical signals from the environment into encoded neural signals sent to the central nervous system
3 Psychophysics and Measuring Thresholds psychophysics: methods that measure the strength of a stimulus and the observer s sensitivity to that stimulus absolute threshold: the minimal intensity needed to just barely detect a stimulus threshold: boundary Weber s law: the just noticeable difference of a stimulus is a constant proportion despite variations in intensity just noticeable difference (JND): the minimal change in a stimulus that can just barely be detected
4 Signal Detection and Sensory Adaptation signal detection theory: an approach to psychophysics, the response to a stimulus depends both on a person s sensitivity to the stimulus in the presence of noise and on a person s decision criterion examples: memories, moods + sights, noise sensory adaptation: sensitivity to prolonged stimulation tends to decline over time as an organism adapts to current conditions (very useful!)
5 Illusions
6 Light Visible Light - The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see Light waves Length - Distance between peaks, determines hue Amplitude - Height of peak, determines brightness Purity - # of wavelengths, determines saturation
7 The Human Eye
8 Phototransduction in the Retina Photoreceptor cells - contain light sensitive pigments which transduce light into neural impulses Cones - Detect color in daylight, focus on detail (6 million) Rods - Active in low light, sense shades of grey (120 million)
9 Phototransduction in the Retina Photoreceptor cells send signals to Bipolar cells which then transmit signals to Retinal Ganglion Cells (RGCs) The axons of the RGCs form the optic nerve which exits through a hole in the retina (leaving a blind spot)
10 Color
11 Color Mixing Reflection Absorption
12 The Visual Brain Area V1 Primary visual cortex Edge orientation Ventral stream Shape and identity Dorsal stream location and motion
13 Attention Binding Problem: phenomenon that links features together to allow us to see distinct objects instead of random disjointed shapes Illusory Conjunction: a perceptual mistake where features or shapes are incorrectly combined
14 Feature Integration Theory States that attention IS NOT required to notice factors about a stimulus but attention IS required to piece them together properly and without errors Attention is the glue that connects features together to prevent illusory conjunction Parietal lobe is necessary to this process
15 Perceptual Consistency Even when a major change occurs in something you are familiar with, you can still recognize it Recognition centers in the temporal lobe may be optimized for recognizing faces (modular view v. distributed representation)
16 Gestalt Perceptual Grouping Rules
17 Monocular Depth Cues Ames Room
18 Binocular Depth Cues Uses disparity between images received by the eyes
19 Motion and Change Humans are very sensitive to motion Brain subtracts your motion from the eye s images Waterfall effect: when you look at something moving down for a while, then look away, everything appears to be moving up Sensors analogous to color sensors cause waterfall effect
20 Apparent Motion Rapid, successive stationary images appear to be moving Used in signs, movies, and TV
21 Change and Inattentional Blindness Change Blindness is where people fail to notice changes in the visual details of a scene Inattentional Blindness is where people fail to notice things that do are not in their focal area
22 Audition
23 Audition
24 The Body Senses Haptic perception results from our active exploration of the environment by touching and grasping objects with our hands
25 Touch The left half of the body is represented by the right side of the brain More of the brain is devoted to parts of the skin surface that have greater spatial resolution Distinction between what and where system
26 Pain Pain is important! Pain receptors are not only on the skin, but also inside of our bodies. It indicates damage or potential damage to the body
27 Pain Referred pain is when sensory information from internal and external areas converge on the same nerve cell in the spinal cord Gate control theory: signals arriving from pain receptors in the body can be stopped by interneurons in the spinal cord via feedback from two directions
28 Body Position, Movement and Balance Vestibular system is responsible for balance -three fluid filled semi-circular canals and adjacent organs located next to the cochlea in each inner ear
29 The chemical senses: Smell Smell - Flavour: a perceptual experience - Olfactory Epithelium is a mucous membrane where odors travel from to the Olfactory Bulb - Contains Olfactory Receptor Neuroms (ORNs) that initiate the sense of smell
30 Smell - Oflaction (smell) is associated with memory - Pheromones: odorants emitted by other members of certain species - Affects the behaviour/physiology of the animal - E.g: parents can smell own children from others and vise versa (infants can detect mothers breast) - Some discourse about human pheromones
31 Taste - Papillae, taste buds, taste receptor cells, microvilli - Microvilli have tasting molecules that respond to food - Many people lose most by age 20 - Five primary taste sensations: salt, sour, bitter, sweet, umami - Umami is least common
32
33
34
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
 1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6
 Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
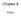 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Unit 4. Sensation and. Perception. 6-8% (7-9% in past) College Board - Acorn Book Course Description. Unit IV. Sensaton and.
 Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception
 Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Sensation and perception. Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
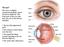 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, Wednesday, 8 January, 14
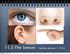 11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Unit IV Sensation Perception
 Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 10. Neurophysiology
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Feeding human senses through Immersion
 Virtual Reality Feeding human senses through Immersion 1. How many human senses? 2. Overview of key human senses 3. Sensory stimulation through Immersion 4. Conclusion Th3.1 1. How many human senses? [TRV
Virtual Reality Feeding human senses through Immersion 1. How many human senses? 2. Overview of key human senses 3. Sensory stimulation through Immersion 4. Conclusion Th3.1 1. How many human senses? [TRV
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Definitions Sensation Sensation and perception Perception
 Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
Lecture 14. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017
 Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Frequencies and Color
 Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Capturing Light in man and machine. Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al.
 Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
