Maps and map interpretation An introduction for geoscientists
|
|
|
- Gertrude Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Maps and map interpretation An introduction for geoscientists Produced by the University of Derby in conjunction with UKOGL
2 Aims This teaching package provides an introduction to maps and how to identify landforms using contours and cross-sections It is designed primarily for A-Level and first year undergraduate geology and geography students who may have little experience of topographic maps, or for those who haven t worked with them recently
3 Contents Part 1 - Introduction to maps Title Key (sometimes called legend or explanation) Scales Contours Part 2 Map interpretation Contour patterns Cross-sections
4 Part 1 - Introduction to maps Maps are a 2-D representation of a 3-D world. They are a bird s eye view as if the viewer is flying above the land surface and looking down on it They show how objects are distributed and their relative size Maps are a very useful way of visualizing all sorts of data and they are a key tool for geoscientists
5 The same map outline can be used to show different information, so it is important to identify the map title, key, scale and orientation N N Key North Point Scale Title UK Bedrock Geology UK Annual Mean Wind Speed
6 Maps show how objects are distributed and their relative size This is the area north of Derby that we will be focusing on later N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service.
7 Scales Show the distance on the map compared to the distance on the ground It is important to choose an appropriate map scale for the task you are undertaking Common scales include: 1: (e.g. world map or atlas) 1: (e.g. country map) 1: (e.g. regional map) 1: (e.g. local map) A map scale of 1: means: 1mm on the map represents mm or 50m or 0.05km on the ground
8 Scales with large numbers (e.g. 30 million) produce maps covering a large area in little detail
9 In contrast, on a 1: map, individual buildings, minor roads and contours are evident N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. 1 km
10 The scale bar shows a measurement on the map and the specific distance it represents on the ground N Cowers Lane to Shottlegate is about 1 km Galway to Dublin is about 200 km N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. 1 km 200 km
11 Contours Contours are lines joining points of equal value. This value on topographic maps is height (or elevation/altitude) above mean sea level (MSL) Each successive contour represents an increase or decrease in constant value. Often every 5 th contour will be in bold to help identification Contours are normally associated with changes in height, but they can represent any parameter (e.g. thickness, pressure, rainfall). They can also be called iso-lines (e.g. isopachs, isobars, isohyets)
12 Contours show the distribution and relative size of any measured value Surface air pressure is measured in millibars and is shown here as isobars
13 Contours can show the distribution and relative size of any measured value This map shows the thickness of the Earth s crust (in kms) This map shows rainfall data for Australia (in mm)
14 Let s return to topographic maps - on the map the land surface looks flat, but the contours indicate otherwise X View from Point X towards the SW, showing a valley and a hill in the distance N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. 1 km
15 Contours never cross and will at some point close, although this may be off the map. Topographic contours that close in concentric patterns delineate hills or depressions 1 km
16 Contours are drawn perpendicular to the maximum slope, with the spacing between contours indicating the steepness of the slope 1 km
17 Based on the shape of contours, landforms such as valleys and ridges can be recognised Valley and stream Ridge 1 km
18 This image highlights the real shape of two hills and how they are shown on a contour map 40m 30m 20m 10m 0 MSL Image from OS Map reading made easy.
19 You can watch a video explaining how to read contour lines on an Ordnance Survey map Click here to play The Ordnance Survey website has further information on all aspects of maps and map reading, including how to work out grid references and take compass bearings
20 Practical exercise 1 Drawing contours
21 970m 1100m 975m 900m 920m 875m 900m 835m 835m 880m 800m 800m 950m 900m 700m 1070m 800m 900m
22 The easiest way to draw a contour map based on spot heights is to simply interpolate between the known values. As you interpolate between points make sure you label the new values, as it quickly becomes very confusing if you don t! Then join identical values with smooth curves to create contours that simulate topography 800m 800m Start by interpolating between individual points, labelling new values as you go. 700m 750m 750m 700m 750m 750m 800m Then join up all the original and interpolated points of equal value to form contours. 800m 850m 900m
23 970m 1100m 975m 900m 920m 875m 900m 835m 835m 880m 800m 800m 900m 950m 700m 1070m 800m 900m
24 Completing the contouring exercise Based on the contour map you have created: Where is the highest ground? Where is the lowest area? Describe the major landforms Mark on the most likely course of a stream and determine in which direction it is flowing
25 970m 1100m 975m 900m m 875m 900m m 835m 880m 800m 800m 900m 950m 700m 1070m 800m 900m
26 Part 2 Map interpretation Contour patterns can be used to recognise distinctive landforms such as ridges, valleys and hills Contours may appear as black or coloured lines on maps, and are often supported by colour shading to give an impression of relief Cross-sections provide a useful way of visualizing the shape of the land surface, but care needs to be taken in their construction, particularly in terms of vertical exaggeration
27 Previously we looked at the topography in this area let s take a closer look at the contours N 1 km Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service.
28 The contour interval is 10m with bold lines every 50m 150m contour N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. What is the contour interval? Locate the 150m contour between Shottle and Blackbrook 1 km
29 150m contour N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. If you walked along this contour, what would your route be like? Flat, as long as you remain on the 150m contour
30 200m contour 150m contour Downhill 100m contour N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. Which direction is downhill from the 150m contour?
31 N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. What else about the contours help to determine the direction of slope? The contour values are perpendicular to the slope, with the bottom of the number on the downhill side
32 A B N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. What does the hillside look like if you stand at Point A and look towards Point B? It would go downhill to the stream and then uphill again to Point B 1 km
33 A useful technique to visualise landforms is to draw a cross-section. This one is between Points A and B on the previous map No vertical exaggeration Contour value (metres) A B Valley with stream This image shows a similar valley in the area, confirming the gentle slope angles Distance (metres) The X axis represents distance and the Y axis height
34 When drawing cross-sections it is important to be aware how the scales affect your perception of slope angle Contour value (metres) x vertical exaggeration A B Valley with stream Distance (metres) The purpose will dictate the scales you use. If the crosssection is to highlight relative changes in topography then a vertical exaggeration is fine, despite the fact that it increases the angles of all sloping lines If there is a need to add subsurface geology or calculate true slope angles, then there should be no vertical exaggeration
35 Compare the effects of vertical exaggeration on the same cross-section Notice how the change in vertical exaggeration affects the angles of slope Bear this in mind when drawing your own crosssections and decide how much (if any) vertical exaggeration is required
36 Uphill N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. You now know how to identify a sloping valley by the shape of the contours. They form a V-shape that points uphill
37 Arrows indicate downhill direction of valleys N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. There are lots of valleys on the map; mark them with an arrow pointing in the downhill direction
38 Arrows indicate downhill direction of valleys N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. Notice that all the rivers are in valleys, but not all the valleys have a river. Why is this the case?
39 N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. What feature do the contours in the red area represent? A broad, N-S trending ridge
40 Axis of ridge C D We can draw a cross-section to confirm our idea N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. It may help if you imagine you are standing at Point C on the 150m contour, looking towards Point D. Would you be able to see Point D?
41 Cross-section showing the broad, gentle ridge between Points C and D 2x vertical exaggeration Contour value (metres) C D Ridge Standing at Point C you would be unable to see Point D because the crest of the ridge is higher than Point D Here some vertical exaggeration is appropriate because the relief is very subtle Distance (metres)
42 Practical exercise 2 Constructing cross-sections
43 We will now draw our own crosssection between Cowers Lane (A) and Chevinside (A ) Before constructing a crosssection, look at the contours and try to imagine what the surface topography looks like Narrower range of contours between m indicate a relatively flat hill top A A Widely spaced contours showing less steep slopes compared to those in the east Closely spaced contours showing a steep slope
44 Use graph paper to mark on every time a contour crosses the chosen line of section Label each contour height and plot the value directly onto the Y-axis of the cross-section 200m A A m 100m 50m
45 Once all the contour heights along the section have been plotted the land surface can be added This surface should be drawn free hand to give a natural shape that honours the contours 200m A A 50m 100m 50m 4x vertical exaggeration
46 A completed cross-section between A-A The vertical scale has been exaggerated in order to show the subtle relief. To calculate the vertical exaggeration, divide the horizontal scale (1cm to 200m) by the vertical scale (1cm to 50m) So, 200/50 = 4x vertical exaggeration 200m A 4x vertical exaggeration A 50m 100m 50m 0 West 1 km 2 km 3 km Scale 1: East
47 Comparison between a vertically exaggerated section and a true scale cross-section 200m 4x vertical exaggeration 150m 100m 50m 0 No vertical exaggeration 200m 0 The vertically exaggerated section provides a clearer representation of subtle landforms, the other a true representation of slope angles
48 Learning outcomes You have now been introduced to the basic elements of topographic maps You have used contours to identify common landforms and begun to visualise them in 3-D You can now construct cross-sections and understand the concept of vertical exaggeration
49 Handouts required for the practicals Slide 50: print out at A4, in B/W, portrait format Slide 51: print out at A4, in colour, portrait format Slide 52: print out at A4, in colour, portrait format Graph paper for constructing the cross-section
50 970m 1100m 975m 900m 920m 875m 900m 835m 835m 880m 800m 800m 950m 900m 700m 1070m 800m 900m
51 N Crown Copyright/database right An Ordnance Survey/EDINA supplied service. 1 km
52 A A
53
Earth Sciences 089G Short Practical Assignment #4 Working in Three Dimensions
 Earth Sciences 089G Short Practical Assignment #4 Working in Three Dimensions Introduction Maps are 2-D representations of 3-D features, the developers of topographic maps needed to devise a method for
Earth Sciences 089G Short Practical Assignment #4 Working in Three Dimensions Introduction Maps are 2-D representations of 3-D features, the developers of topographic maps needed to devise a method for
Module 2: Mapping Topic 3 Content: Topographic Maps Presentation Notes. Topographic Maps
 Topographic Maps 1 Take a few moments to study the map shown here of Isolation Peak, Colorado. What land features do you notice? Do you thinking hiking through this area would be easy? Did you see the
Topographic Maps 1 Take a few moments to study the map shown here of Isolation Peak, Colorado. What land features do you notice? Do you thinking hiking through this area would be easy? Did you see the
ENVI.2030L Topographic Maps and Profiles
 Name ENVI.2030L Topographic Maps and Profiles I. Introduction A map is a miniature representation of a portion of the earth's surface as it appears from above. The environmental scientist uses maps as
Name ENVI.2030L Topographic Maps and Profiles I. Introduction A map is a miniature representation of a portion of the earth's surface as it appears from above. The environmental scientist uses maps as
Topographic Maps. Contour Lines
 Topographic Maps Our first task today will consist of locating ourselves with the help of a topographic map. GPS units that can tell you the location of any Dunkin' Donuts within a five mile radius. Paper
Topographic Maps Our first task today will consist of locating ourselves with the help of a topographic map. GPS units that can tell you the location of any Dunkin' Donuts within a five mile radius. Paper
Surveying & Measurement. Detail Survey Topographic Surveying
 Surveying & Measurement Detail Survey Topographic Surveying Introduction Mapping surveys are made to determine the relief of the earth s surface and locate critical points on it. to determine the locations
Surveying & Measurement Detail Survey Topographic Surveying Introduction Mapping surveys are made to determine the relief of the earth s surface and locate critical points on it. to determine the locations
CONTOURS SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- Ishik University / Sulaimani Civil Engineering Department 12/7/2017. Ishik University / Sulaimani
 Civil Engineering Department SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- CONTOURS 1 2 1 3 4 2 PURPOSE OF CONTOURING Contour survey is carried out at the starting of any engineering project such as a road, a railway,
Civil Engineering Department SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- CONTOURS 1 2 1 3 4 2 PURPOSE OF CONTOURING Contour survey is carried out at the starting of any engineering project such as a road, a railway,
BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 Build an Island INTRODUCTION For this assignment, you will be creating a topographic map and three-dimensional model of a fictional island that you have designed. You will start by exploring some basic
Build an Island INTRODUCTION For this assignment, you will be creating a topographic map and three-dimensional model of a fictional island that you have designed. You will start by exploring some basic
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contours and Form DEFINITION
 1 DEFINITION A clear understanding of what a contour represents is fundamental to the grading process. Technically defined, a contour is an imaginary line that connects all points of equal elevation above
1 DEFINITION A clear understanding of what a contour represents is fundamental to the grading process. Technically defined, a contour is an imaginary line that connects all points of equal elevation above
Lab #4 Topographic Maps and Aerial Photographs
 Lab #4 Topographic Maps and Aerial Photographs Purpose To familiarize you with using topographic maps. Visualizing the shape of landforms from topographic maps is an essential skill in geology. Proficiency
Lab #4 Topographic Maps and Aerial Photographs Purpose To familiarize you with using topographic maps. Visualizing the shape of landforms from topographic maps is an essential skill in geology. Proficiency
PRE-LAB for: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Ch. 3)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: PRE-LAB for: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Ch. 3) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler.
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: PRE-LAB for: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Ch. 3) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler.
Lab #8: Topographic Map Lab
 NAME: LAB TIME: TA NAME: Lab #8: Topographic Map Lab Topography is the shape of the land. Topographic maps are used to aid in the visualization of the shape of the land. Topographic maps include the accurate
NAME: LAB TIME: TA NAME: Lab #8: Topographic Map Lab Topography is the shape of the land. Topographic maps are used to aid in the visualization of the shape of the land. Topographic maps include the accurate
Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 3)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 3) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Objectives:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 3) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Objectives:
AutoCAD 2016 for Civil Engineering Applications
 Introduction to AutoCAD 2016 for Civil Engineering Applications Learning to use AutoCAD for Civil Engineering Projects Nighat Yasmin Ph.D. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Introduction to AutoCAD 2016 for Civil Engineering Applications Learning to use AutoCAD for Civil Engineering Projects Nighat Yasmin Ph.D. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Slope analysis & Grading. Earth shape and earthwork Topographic map Slope form Slope analysis Grading
 6 Slope analysis & Grading Earth shape and earthwork Topographic map Slope form Slope analysis Grading 81 Topographic Map Topographic Contour map Topographic contour map are composed of a series of line
6 Slope analysis & Grading Earth shape and earthwork Topographic map Slope form Slope analysis Grading 81 Topographic Map Topographic Contour map Topographic contour map are composed of a series of line
Land Navigation / Map Reading
 Land Navigation / Map Reading What is the Field Manual for map reading and land navigation? FM 3-25.26 What are the basic colors of a map, and what does each color represent? Black - Indicates cultural
Land Navigation / Map Reading What is the Field Manual for map reading and land navigation? FM 3-25.26 What are the basic colors of a map, and what does each color represent? Black - Indicates cultural
Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 7, 9 th edition) or (chapter 3, 8 th edition)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 7, 9 th edition) or (chapter 3, 8 th edition) For this assignment you will require:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Introduction to Aerial Photographs and Topographic maps (Chapter 7, 9 th edition) or (chapter 3, 8 th edition) For this assignment you will require:
1 : 5,000 1cm to 100m
 4.1.1 Scales and Converting Scales In Hong Kong maps, there are 2 types of scales: 1. 1:5000 (Black and white with no color) 2. 1:20000 (With color) If there is no unit in a representative fraction scale,
4.1.1 Scales and Converting Scales In Hong Kong maps, there are 2 types of scales: 1. 1:5000 (Black and white with no color) 2. 1:20000 (With color) If there is no unit in a representative fraction scale,
TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS A NEW WAY TO VIEW THE WORLD!
 TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS A NEW WAY TO VIEW THE WORLD! http://courtneyjennings.weebly.com/unit-4---weathering-erosiontopo-maps-past.html A topographic map, simply put, is a two-dimensional representation of a portion
TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS A NEW WAY TO VIEW THE WORLD! http://courtneyjennings.weebly.com/unit-4---weathering-erosiontopo-maps-past.html A topographic map, simply put, is a two-dimensional representation of a portion
Topography and Contouring Teaching Assistant Guide
 Topography and Contouring Teaching Assistant Guide Learning Objectives: At the end of the exercise the students will be able to read a contour map contour data draw a topographic profiles Getting Started
Topography and Contouring Teaching Assistant Guide Learning Objectives: At the end of the exercise the students will be able to read a contour map contour data draw a topographic profiles Getting Started
Engineering Surveying -1 CE212 Contouring Lectures. Lecture 2016, November 29 th Muhammad Noman
 Engineering Surveying -1 CE212 Contouring Lectures Lecture 2016, November 29 th Muhammad Noman Contour An Imaginary line on the ground surface joining the points of equal elevation is known as contour.
Engineering Surveying -1 CE212 Contouring Lectures Lecture 2016, November 29 th Muhammad Noman Contour An Imaginary line on the ground surface joining the points of equal elevation is known as contour.
Shoe Box Activity Constructing a Topographic Map
 Shoe Box Activity Constructing a Topographic Map Background Information All maps are models of some feature of the real world. The kind of map oen used by scientists is called a contour or topographic
Shoe Box Activity Constructing a Topographic Map Background Information All maps are models of some feature of the real world. The kind of map oen used by scientists is called a contour or topographic
Contour An imaginary line on the ground surface joining the points of equal elevation is known as contour.
 Contour An imaginary line on the ground surface joining the points of equal elevation is known as contour. In other words, contour is a line in which the ground surface is intersected by a level surface
Contour An imaginary line on the ground surface joining the points of equal elevation is known as contour. In other words, contour is a line in which the ground surface is intersected by a level surface
Line Graphs. Name: The independent variable is plotted on the x-axis. This axis will be labeled Time (days), and
 Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #6 DRAWING A CONTOUR MAP FROM A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #6 DRAWING A CONTOUR MAP FROM A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL INTRODUCTION Since land distances and elevations on the earth's surface can be very great it is necessary to
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #6 DRAWING A CONTOUR MAP FROM A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL INTRODUCTION Since land distances and elevations on the earth's surface can be very great it is necessary to
1. The topographic map below shows a depression contour line on Earth's surface.
 1. The topographic map below shows a depression contour line on Earth's surface. Points A, B, C, and D represent surface locations. Contour line elevations are in feet. Which profile best shows the topography
1. The topographic map below shows a depression contour line on Earth's surface. Points A, B, C, and D represent surface locations. Contour line elevations are in feet. Which profile best shows the topography
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
A contour line is a line that passes through points having the same elevation.* Definition
 Contour Lines A contour line is a line that passes through points having the same elevation.* Definition Eleven (11) characteristics of contour lines 1. Contour lines are continuous. 2. Contour lines are
Contour Lines A contour line is a line that passes through points having the same elevation.* Definition Eleven (11) characteristics of contour lines 1. Contour lines are continuous. 2. Contour lines are
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 206 Land Navigation TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a military topographic map, protractor, and objective,
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 206 Land Navigation TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a military topographic map, protractor, and objective,
i Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date b(hdt(h LfiR i Using Graphing Skills me ntroduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. t is used to
Name Class Date b(hdt(h LfiR i Using Graphing Skills me ntroduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. t is used to
Title: How steep are those hills? Engineering Grade: Estimated Time: 3 hours (2 days) Groups: 3 to 4 students
 Title: How steep are those hills? Engineering Grade: 10-12 Estimated Time: 3 hours (2 days) Groups: 3 to 4 students Synopsis: Students will be able to understand the concept of surveying and mapping ground
Title: How steep are those hills? Engineering Grade: 10-12 Estimated Time: 3 hours (2 days) Groups: 3 to 4 students Synopsis: Students will be able to understand the concept of surveying and mapping ground
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Time required: 30 minutes Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Time required: 30 minutes Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in
Ch. 1.3: Topographic Maps
 Ch. 1.3: Topographic Maps StudentS will be able to Explain what are topographic maps Read a topographic map Create a topographic map "Geologists don't dislike classical music, they just prefer rock." Topographic
Ch. 1.3: Topographic Maps StudentS will be able to Explain what are topographic maps Read a topographic map Create a topographic map "Geologists don't dislike classical music, they just prefer rock." Topographic
31, The following isoline map shows the variations in the relative strength of Earth's magnetic field from 1 (strong) to 11 (weak).
 31, The following isoline map shows the variations in the relative strength of Earth's magnetic field from 1 (strong) to 11 (weak). 33. The following four temperature field maps represent the same region
31, The following isoline map shows the variations in the relative strength of Earth's magnetic field from 1 (strong) to 11 (weak). 33. The following four temperature field maps represent the same region
MAKE A CO NTO U R MAP
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Student Version MAKE A CO NTO U R MAP How does a
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop Student Version MAKE A CO NTO U R MAP How does a
CHAPTER 3 MARGINAL INFORMATION AND SYMBOLS
 CHAPTER 3 MARGINAL INFORMATION AND SYMBOLS A map could be compared to any piece of equipment, in that before it is placed into operation the user must read the instructions. It is important that you, as
CHAPTER 3 MARGINAL INFORMATION AND SYMBOLS A map could be compared to any piece of equipment, in that before it is placed into operation the user must read the instructions. It is important that you, as
Markville Secondary School Geography Department
 Markville Secondary School Geography Department CGC1D1 Geography of Canada PERFORMANCE TASK - UNIT 1 AND 2 DUE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2011 Parent Signature: CONTOUR MAP AND MODEL The performance task for Geography
Markville Secondary School Geography Department CGC1D1 Geography of Canada PERFORMANCE TASK - UNIT 1 AND 2 DUE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2011 Parent Signature: CONTOUR MAP AND MODEL The performance task for Geography
Following are the geometrical elements of the aerial photographs:
 Geometrical elements/characteristics of aerial photograph: An aerial photograph is a central or perspective projection, where the bundles of perspective rays meet at a point of origin called perspective
Geometrical elements/characteristics of aerial photograph: An aerial photograph is a central or perspective projection, where the bundles of perspective rays meet at a point of origin called perspective
Appendix C: Graphing. How do I plot data and uncertainties? Another technique that makes data analysis easier is to record all your data in a table.
 Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Important Questions. Surveying Unit-II. Surveying & Leveling. Syllabus
 Surveying Unit-II Important Questions Define Surveying and Leveling Differentiate between Surveying and Leveling. Explain fundamental Principles of Surveying. Explain Plain and Diagonal Scale. What is
Surveying Unit-II Important Questions Define Surveying and Leveling Differentiate between Surveying and Leveling. Explain fundamental Principles of Surveying. Explain Plain and Diagonal Scale. What is
Markville Secondary School Geography Department
 Markville Secondary School Geography Department CGC1D1 Geography of Canada PERFORMANCE TASK - UNITS 1 AND 2 February 2012 DUE DATE: Parent Signature: CONTOUR MAP AND MODEL The performance task for the
Markville Secondary School Geography Department CGC1D1 Geography of Canada PERFORMANCE TASK - UNITS 1 AND 2 February 2012 DUE DATE: Parent Signature: CONTOUR MAP AND MODEL The performance task for the
3.2 Exercises. rise y (ft) run x (ft) Section 3.2 Slope Suppose you are riding a bicycle up a hill as shown below.
 Section 3.2 Slope 261 3.2 Eercises 1. Suppose ou are riding a biccle up a hill as shown below. Figure 1. Riding a biccle up a hill. a) If the hill is straight as shown, consider the slant, or steepness,
Section 3.2 Slope 261 3.2 Eercises 1. Suppose ou are riding a biccle up a hill as shown below. Figure 1. Riding a biccle up a hill. a) If the hill is straight as shown, consider the slant, or steepness,
East Bay Municipal Utility District. Study Guide for Survey Technician I
 East Bay Municipal Utility District Study Guide for Survey Technician I Summer 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction... 1 Scoring... 1 Visual Perception... 2 Sample Questions 1-2... 2 Reading and Interpreting
East Bay Municipal Utility District Study Guide for Survey Technician I Summer 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction... 1 Scoring... 1 Visual Perception... 2 Sample Questions 1-2... 2 Reading and Interpreting
Level Curves, Partial Derivatives
 Unit #18 : Level Curves, Partial Derivatives Goals: To learn how to use and interpret contour diagrams as a way of visualizing functions of two variables. To study linear functions of two variables. To
Unit #18 : Level Curves, Partial Derivatives Goals: To learn how to use and interpret contour diagrams as a way of visualizing functions of two variables. To study linear functions of two variables. To
Beach monitoring with GPS William F Price Department of Civil Engineering, University of Brighton, BRIGHTON, BN1 4GJ, UK
 Beach monitoring with GPS William F Price Department of Civil Engineering, University of Brighton, BRIGHTON, BN1 4GJ, UK Abstract In common with many other countries that have an extended coastline, sea
Beach monitoring with GPS William F Price Department of Civil Engineering, University of Brighton, BRIGHTON, BN1 4GJ, UK Abstract In common with many other countries that have an extended coastline, sea
Patterns and Graphing Year 10
 Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Watershed Topography
 Watershed Topography Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity. Creek Connections, Allegheny College, Meadville, Pennsylvania, 16335 Topography in Watersheds Grade Level: Basic to intermediate.
Watershed Topography Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity. Creek Connections, Allegheny College, Meadville, Pennsylvania, 16335 Topography in Watersheds Grade Level: Basic to intermediate.
AIM. What is-a contour map? 23-
 .. '; AIM 23- What is-a contour map?.,,.,, I. There are many different kinds of maps. The maps we use most often are surface maps. A surface map is a drawing. It shows all or part of the earth's surface.
.. '; AIM 23- What is-a contour map?.,,.,, I. There are many different kinds of maps. The maps we use most often are surface maps. A surface map is a drawing. It shows all or part of the earth's surface.
IAN HUMBY TEACHING. List of Hand-Outs. Levelling
 IAN HUMBY TEACHING List of Hand-Outs Levelling 6-1 Equipment List (Levelling) 11-1 to 11-3 Introduction to Levelling 11-4 Levelling Terminology 12-1 to 12-2 Measuring Height Change by Basic Methods 13-1
IAN HUMBY TEACHING List of Hand-Outs Levelling 6-1 Equipment List (Levelling) 11-1 to 11-3 Introduction to Levelling 11-4 Levelling Terminology 12-1 to 12-2 Measuring Height Change by Basic Methods 13-1
Question bank. Unit 1: Introduction
 Question bank Unit 1: Introduction 1. Define surveying. 2. State the objects of surveying 3. State and explain the principle of surveying 4. State and explain the classification of surveying 5. Differentiate
Question bank Unit 1: Introduction 1. Define surveying. 2. State the objects of surveying 3. State and explain the principle of surveying 4. State and explain the classification of surveying 5. Differentiate
Orthographic Projection 1
 Orthographic Projection 1 What Is Orthographic Projection? Basically it is a way a representing a 3D object on a piece of paper. This means we make the object becomes 2D. The difference between Orthographic
Orthographic Projection 1 What Is Orthographic Projection? Basically it is a way a representing a 3D object on a piece of paper. This means we make the object becomes 2D. The difference between Orthographic
Constructing Line Graphs*
 Appendix B Constructing Line Graphs* Suppose we are studying some chemical reaction in which a substance, A, is being used up. We begin with a large quantity (1 mg) of A, and we measure in some way how
Appendix B Constructing Line Graphs* Suppose we are studying some chemical reaction in which a substance, A, is being used up. We begin with a large quantity (1 mg) of A, and we measure in some way how
Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy
 Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy Vocabulary Data Table A place to write down and keep track of data collected during an experiment. Line
Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy Vocabulary Data Table A place to write down and keep track of data collected during an experiment. Line
Information for teachers
 Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
LONGITUDINAL PROFILE COMPLETION
 LONGITUDINAL PROFILE COMPLETION Vertical alignment of the ditch bottom determine using cross-sections plot (refer to fig. 0630) according to the chainage direction: ditch bottom on right side... dotted
LONGITUDINAL PROFILE COMPLETION Vertical alignment of the ditch bottom determine using cross-sections plot (refer to fig. 0630) according to the chainage direction: ditch bottom on right side... dotted
CHAPTER 3-LAB 1: A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 Name Teacher Period Date CHAPTER 3-LAB 1: A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP IN THREE DIMENSIONS Introduction A topographic map shows the shape ofthe land surface with contour lines. On page 29 you will find Figure 3-6,
Name Teacher Period Date CHAPTER 3-LAB 1: A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP IN THREE DIMENSIONS Introduction A topographic map shows the shape ofthe land surface with contour lines. On page 29 you will find Figure 3-6,
REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM
 REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM Be familiar with all materials covered in class, your class handouts and the notes you took in class, your homework assignments, test questions, formulas, tables, figures.
REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM Be familiar with all materials covered in class, your class handouts and the notes you took in class, your homework assignments, test questions, formulas, tables, figures.
Perspective Sketching
 Perspective Sketching Perspective Drawings A perspective drawing offers the most realistic three-dimensional view of all the pictorial methods, because it portrays the object in a manner that is most similar
Perspective Sketching Perspective Drawings A perspective drawing offers the most realistic three-dimensional view of all the pictorial methods, because it portrays the object in a manner that is most similar
A Visual Display. A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. Communicating with Graphs
 A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
Floods On The Minnesota River Planning For St. Peter
 Floods On The Minnesota River Planning For St. Peter Group Members Section: A B C D E In this lab, we will make a flood hazard map for the city of St. Peter. We will use the 100-year flood as the design
Floods On The Minnesota River Planning For St. Peter Group Members Section: A B C D E In this lab, we will make a flood hazard map for the city of St. Peter. We will use the 100-year flood as the design
Date Requested, 200_ Work Order No. Funding source Name of project Project limits: Purpose of the project
 Bureau of Engineering SURVEY DIVISION REQUEST FOR TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEY Date Requested, 200_ Work Order No. Funding source Name of project Project limits: Purpose of the project Caltrans involvement (must
Bureau of Engineering SURVEY DIVISION REQUEST FOR TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEY Date Requested, 200_ Work Order No. Funding source Name of project Project limits: Purpose of the project Caltrans involvement (must
NAVIGATION HANDBOOK Prepared for the HRCR Clubmans Rally Championship
 NAVIGATION HANDBOOK Prepared for the HRCR Clubmans Rally Championship INTRODUCTION This Rally Navigation Handbook has been prepared as a handy reference document, to give novice navigators an insight into
NAVIGATION HANDBOOK Prepared for the HRCR Clubmans Rally Championship INTRODUCTION This Rally Navigation Handbook has been prepared as a handy reference document, to give novice navigators an insight into
Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice
 Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice Name Date CP If an equation is linear, then there are three formats typically used to express
Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice Name Date CP If an equation is linear, then there are three formats typically used to express
Year 11 Graphing Notes
 Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
A To draw a line graph showing the connection between the time and cost
 Hire a coach In this activity you will use Excel to draw line graphs which show the connection between variables in real situations. You will also study how features of the graphs are related to the information
Hire a coach In this activity you will use Excel to draw line graphs which show the connection between variables in real situations. You will also study how features of the graphs are related to the information
How to make a line graph
 How to make a line graph Line graphs are powerful in science because of the relationship they show between two variables (showing how one variable changes as the other changes). Step One You need the topic
How to make a line graph Line graphs are powerful in science because of the relationship they show between two variables (showing how one variable changes as the other changes). Step One You need the topic
Name: Topographic Profiles Multiple Choice
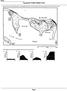 1. Base your answer to the following question on the topographic map below. Points A and B represent locations on the map. Elevations are shown in meters. Which diagram best represents the topographic
1. Base your answer to the following question on the topographic map below. Points A and B represent locations on the map. Elevations are shown in meters. Which diagram best represents the topographic
Tips & Tricks for Regional Maps
 Tips & Tricks for Regional Maps A Cartography Guild Tutorial by Torston Contents Drawing Top-Down Hills Page 1 Hand Drawn Mountains Page 2 Three Different Cliff Styles Page 3 Isometric Cliffs Page 4 How
Tips & Tricks for Regional Maps A Cartography Guild Tutorial by Torston Contents Drawing Top-Down Hills Page 1 Hand Drawn Mountains Page 2 Three Different Cliff Styles Page 3 Isometric Cliffs Page 4 How
Riches of the Earth Guidance Sheet 5
 Riches of the Earth Guidance Sheet 5 www.watershedlandscape.co.uk Recording individual features Several forms of recording are used to give as much information as possible about the feature being recorded.
Riches of the Earth Guidance Sheet 5 www.watershedlandscape.co.uk Recording individual features Several forms of recording are used to give as much information as possible about the feature being recorded.
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) platform. height 5 ft
 MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) Learning Objectives Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms of linear equations Write equations
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) Learning Objectives Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms of linear equations Write equations
PRELIMINARY PLAT CHECK LIST
 Name of Proposed Subdivision: The following items must be included with the initial submittal of a Preliminary Plat: Application, filled out completely Project Narrative Pre-application Conference Report
Name of Proposed Subdivision: The following items must be included with the initial submittal of a Preliminary Plat: Application, filled out completely Project Narrative Pre-application Conference Report
Google SketchUp TECHNICAL WORKSHOPS
 TECHNICAL WORKSHOPS Outcomes: -A reasonable technical understanding of OS referencing for accurately aligning contours to OS Cad bases -A general understanding of SkecthUp add-ons and their implications/
TECHNICAL WORKSHOPS Outcomes: -A reasonable technical understanding of OS referencing for accurately aligning contours to OS Cad bases -A general understanding of SkecthUp add-ons and their implications/
Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line
 ++ Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line Student Outcomes Students use similar triangles to explain why the slope is the same between any two distinct points on a non vertical
++ Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line Student Outcomes Students use similar triangles to explain why the slope is the same between any two distinct points on a non vertical
AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS
 AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Introduction to Statistics Read the introduction no written assignment 2 Bar Graphs Bar Graphs 3 Double Bar Graphs Double
AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Introduction to Statistics Read the introduction no written assignment 2 Bar Graphs Bar Graphs 3 Double Bar Graphs Double
Mapping The Study Area
 While on the beach you will need to take some measurements to show where the study area is relative to the rest of the world and to show what is inside the study area. Once the measurements have been taken,
While on the beach you will need to take some measurements to show where the study area is relative to the rest of the world and to show what is inside the study area. Once the measurements have been taken,
Gradient and Rate of Change
 Name: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the topographic map shown below. Letters A, B, C, and D represent locations on Earth s surface. The symbol marks the highest elevation on Patty
Name: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the topographic map shown below. Letters A, B, C, and D represent locations on Earth s surface. The symbol marks the highest elevation on Patty
7. Consider the following common offset gather collected with GPR.
 Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE213L Surveying & Introduction to GIS Lab SURVEYING LABORATORY NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY Center of Excellence in Higher Education The First Private University
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE213L Surveying & Introduction to GIS Lab SURVEYING LABORATORY NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY Center of Excellence in Higher Education The First Private University
Introduction Getting Started
 Introduction Getting Started 1. If you haven t done it already, download Google Earth TM 5.0 from earth.google.com and install it on your computer. 2. If you haven t done it already, download the Essentials_3E_Geotours.kmz
Introduction Getting Started 1. If you haven t done it already, download Google Earth TM 5.0 from earth.google.com and install it on your computer. 2. If you haven t done it already, download the Essentials_3E_Geotours.kmz
New Mexico Pan Evaporation CE 547 Assignment 2 Writeup Tom Heller
 New Mexico Pan Evaporation CE 547 Assignment 2 Writeup Tom Heller Inserting data, symbols, and labels After beginning a new map, naming it and editing the metadata, importing the PanEvap and CountyData
New Mexico Pan Evaporation CE 547 Assignment 2 Writeup Tom Heller Inserting data, symbols, and labels After beginning a new map, naming it and editing the metadata, importing the PanEvap and CountyData
Using Charts and Graphs to Display Data
 Page 1 of 7 Using Charts and Graphs to Display Data Introduction A Chart is defined as a sheet of information in the form of a table, graph, or diagram. A Graph is defined as a diagram that represents
Page 1 of 7 Using Charts and Graphs to Display Data Introduction A Chart is defined as a sheet of information in the form of a table, graph, or diagram. A Graph is defined as a diagram that represents
At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy
 7 Multiview Drawing OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy 1. explain the importance of mulitview drawing as a communication tool far
7 Multiview Drawing OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy 1. explain the importance of mulitview drawing as a communication tool far
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12. Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the. Externally set task 2017
 Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Chapter 2: Functions and Graphs Lesson Index & Summary
 Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
PASS Sample Size Software. These options specify the characteristics of the lines, labels, and tick marks along the X and Y axes.
 Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Leaving Certificate Technology
 Leaving Certificate Technology Core Module Resource: Communications and Graphics Media Communications and Graphics Media Resource Document Material and Layout Range of tasks exploring topics and learning
Leaving Certificate Technology Core Module Resource: Communications and Graphics Media Communications and Graphics Media Resource Document Material and Layout Range of tasks exploring topics and learning
History of Cartographic Landscape Representation
 History of Cartographic Landscape Representation Graphic representations Where is the observer? Here are the 2 most typical mapping situations: Above the surface with no perspective foreshortening Often
History of Cartographic Landscape Representation Graphic representations Where is the observer? Here are the 2 most typical mapping situations: Above the surface with no perspective foreshortening Often
n 4ce Professional Module
 n 4ce Fact Sheet n 4ce Professional Module For the discerning user with specialist needs, n 4ce Professional provides extra facilities in Design and 3D presentations. Using the same platform as Lite, extra
n 4ce Fact Sheet n 4ce Professional Module For the discerning user with specialist needs, n 4ce Professional provides extra facilities in Design and 3D presentations. Using the same platform as Lite, extra
MAPPING YOUR STREAM. TIME REQUIRED 50 minutes in Field 50 minutes in Classroom 50 minutes Homework
 OUR MAPPING YOUR STREAM STREAM ACTIVITY SUMMARY Students will draft a cross-sectional profile of the stream and measure the velocity of the current. They will use both of these to calculate the discharge
OUR MAPPING YOUR STREAM STREAM ACTIVITY SUMMARY Students will draft a cross-sectional profile of the stream and measure the velocity of the current. They will use both of these to calculate the discharge
Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide
 3-D formal drawing Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-927194-15-7 For individual student use only. No other use permitted. ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd,
3-D formal drawing Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-927194-15-7 For individual student use only. No other use permitted. ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd,
Lesson 10. Unit 2. Reading Maps. Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane
 Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
MEASURING SHAPES M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides. Level: GCSE Foundation Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Measuring Shapes Page 1 of 17 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier MEASURING SHAPES Version: 2.2 Date: 16-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Measuring Shapes Page 1 of 17 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier MEASURING SHAPES Version: 2.2 Date: 16-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
General Editor: Vince Russett
 YCCCART 2017/Y12 Terrain modelling compared with resistivity surveys off Ham Lane, Yatton. (Mr Simmons 1 & 2) YATTON, CONGRESBURY, CLAVERHAM AND CLEEVE ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH TEAM (YCCCART) General Editor:
YCCCART 2017/Y12 Terrain modelling compared with resistivity surveys off Ham Lane, Yatton. (Mr Simmons 1 & 2) YATTON, CONGRESBURY, CLAVERHAM AND CLEEVE ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH TEAM (YCCCART) General Editor:
Instructions for Figure Submission
 Instructions for Figure Submission Please double check that your figures meet ALL of the following criteria: 1. Authors should be pleased with the figure submission quality before submission. It is recommended
Instructions for Figure Submission Please double check that your figures meet ALL of the following criteria: 1. Authors should be pleased with the figure submission quality before submission. It is recommended
The knowledge and understanding for this unit is given below:
 WAVES AND OPTICS The knowledge and understanding for this unit is given below: Waves 1. State that a wave transfers energy. 2. Describe a method of measuring the speed of sound in air, using the relationship
WAVES AND OPTICS The knowledge and understanding for this unit is given below: Waves 1. State that a wave transfers energy. 2. Describe a method of measuring the speed of sound in air, using the relationship
Now we are going to introduce a new horizontal axis that we will call y, so that we have a 3-dimensional coordinate system (x, y, z).
 Example 1. A circular cone At the right is the graph of the function z = g(x) = 16 x (0 x ) Put a scale on the axes. Calculate g(2) and illustrate this on the diagram: g(2) = 8 Now we are going to introduce
Example 1. A circular cone At the right is the graph of the function z = g(x) = 16 x (0 x ) Put a scale on the axes. Calculate g(2) and illustrate this on the diagram: g(2) = 8 Now we are going to introduce
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS. Ms. Sicola
 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
Unit 5 Shape and space
 Unit 5 Shape and space Five daily lessons Year 4 Summer term Unit Objectives Year 4 Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line parallel to Page 106 one side (all sides parallel or perpendicular
Unit 5 Shape and space Five daily lessons Year 4 Summer term Unit Objectives Year 4 Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line parallel to Page 106 one side (all sides parallel or perpendicular
Building a Chart Using Trick or Treat Data a step by step guide By Jeffrey A. Shaffer
 Building a Chart Using Trick or Treat Data a step by step guide By Jeffrey A. Shaffer Each year my home is bombarded on Halloween with an incredible amount of Trick or Treaters. So what else would an analytics
Building a Chart Using Trick or Treat Data a step by step guide By Jeffrey A. Shaffer Each year my home is bombarded on Halloween with an incredible amount of Trick or Treaters. So what else would an analytics
LEVELING. Definitions
 Definitions An elevation of a point : The vertical distance between the point and the reference level surface ( datum ),the most commonly used datum is the mean sea level (MSL ). Leveling : The process
Definitions An elevation of a point : The vertical distance between the point and the reference level surface ( datum ),the most commonly used datum is the mean sea level (MSL ). Leveling : The process
