Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
|
|
|
- Curtis Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos
2 Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece, occular, tube lens) Robert Hooke ca 1670 olympusmicro.com
3 Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece, occular, tube lens) Compound microscope, zeiss-campus.magnet.fsu.edu
4 Object F objective Objective F eyepiece Primary image Fundamentals of light Eyepiece The objective forms a magnified image of the object near (or in) the eyepiece The intermediate image is examined by the eyepiece and eye forming a real image on the retina Virtual image seen by eye
5 illumination light path four aperture planes Iris image-forming light path four field planes Retina Bio 407 Fundamentals of light Conjugate focal planes Primary image Back focal plane Sample plane Aperture diaphragm Field diaphragm Lamp filament
6 Fundamentals of light Köhler illumination
7 Fundamentals of light Magnification: What is the maximal magnification? Is there a limit in useful magnification? => Why is there a limit in resolution? Compound microscope, Robert Hooke ca 1670
8 Resolution Limit Wavelength Object 1 mm MRI, CT Why is there a limit in resolution? Radio Human eye 100 m Properties of light Cells Infrared 10 m Red blood cells Visible Light microscope Ultraviolet 1 m Bacteria 100 nm Mycoplasma Viruses 10 nm Proteins x, -rays 1 nm Amino acids Electron microscope Bio nm Atoms
9 Why is there a limit in resolution? Properties of light
10 Why is there a limit in resolution? Light interactions with matter
11 Why is there a limit in resolution? Diffraction and interference
12 Why is there a limit in resolution? Aperture angle single-slit diffraction pattern
13 Diffraction image of a point source of light The image of a self-luminous point in a microscope is a pattern created by interference in the image plane The pattern is a central bright spot surrounded by a series of rings The central spot contains 84% of light The image is called: Airy disk (after Sir George Airy ( )) cambridgeincolour.com
14 Image formation in the light microscope Diffraction patterns in the back focal plane Generation of an image by interference requires collection of two adjacent orders of diffracted light! a,b: no image is formed c: image is formed d: image with high definition due to multiple diffracted orders collected
15 Resolution and refractive index The objective aperture must capture light from a wide angle for maximum resolution (diffracted or emitted light) NA = n sin α α: half angle of the cone of specimen light accepted by the objective n: refractive index of medium between lens and specimen
16 Why is there a limit in resolution? Resolution and aperture angle Aperture of objective determines the resolution, not the magnification!
17 Why is there a limit in resolution? Resolution and aperture angle Objective with high aperture (NA 1.25) Aperture of objective determines the resolution, not the magnification! Objective with low aperture (NA 0.3)
18 Resolution and Rayleigh criterion Resolving power of microscope: 0.61 λ Concept: an image of an extended object consists of a pattern of overlapping diffraction spots Resolution: the larger the NA of the objective, the smaller the diffraction spots (airy disks).
19 Amplitude and phase objects: only amplitude objects can be seen by eye! Bright field Phase contrast Phase contrast
20 Amplitude and phase objects: only amplitude objects can be seen by eye! Phase contrast
21 Phase contrast
22 Bright Field Microscopy Phase Contrast Microscopy Objective Objective with Phase Ring Condenser Condenser Phase Ring Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture: close max 20% Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture fully open Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Adjust correct phase rings
23 Differential interference (DIC)
24 Bright Field Microscopy Differential Interference Microscopy Phase Contrast Microscopy Polarizer Wollaston Prism Objective Objective Objective with Phase Ring Condenser Condenser Condenser Wollaston Prism Polarizer Phase Ring Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture: close max 20% Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture: close max 20% Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Adjust polarizers and wollaston prisms Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture fully open Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Adjust correct phase rings
25 Bio 407 Fluorescence
26 Fluorescence
27 Bio 407 Fluorescence
28 Bio 407 Fluorescence
29 Fluorescence
30 Bio 407 Fluorescence
31 Setup Light microscopes Bright Field Microscopy (including DIC / Phase Contrast) Fluorescence Microscopy Ocular Fluorescence Light Source Polarizer Wollaston Prism Condenser Wollaston Prism Phase Ring Polarizer Light Source Objectives Sample Plane Z Focus Fluorescence Filter Cube
32 Bright Field Microscopy Differential Interference Microscopy Phase Contrast Microscopy Fluorescence Microscopy Polarizer Wollaston Prism Fluorescence Cube Objective Objective Objective with Phase Ring Objective Condenser Condenser Condenser Wollaston Prism Polarizer Phase Ring Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture: close max 20% Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture: close max 20% Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Adjust polarizers and wollaston prisms Alignment: Köhler illumination Condenser aperture fully open Field aperture: illuminaton of field of view Adjust correct phase rings Alignment: Correct alignment of fluorescence lamp
33 Widefield Bio 407 Confocal laser scanning
34 Confocal laser scanning Increase signal to noise ratio Widefield Higher Z-resolution Less out-of-focus blur Confocal
35 Theory Reality 0.1 µm bead focal plane Bio 407 Confocal laser scanning Spatial resolution in x,y and z Objects are 3 dimensional The resulting image will also be a 3D image in the image space an image of an extended object consists of a pattern of overlapping diffraction spots Crossection 1 µm
36 Confocal laser scanning Spatial resolution in x,y and z Objects are 3 dimensional The resulting image will also be a 3D image in the image space an image of an extended object consists of a pattern of overlapping diffraction spots In widefield the out of focus information is increasing the background and results in low contrast images
37 focal plane Theory 0.2 µm or smaller structure Bio 407 Confocal laser scanning Spatial resolution in X,Y and Z 1 µm Reality Crossection d = 0.61 λ / NA Imaging EGFP in living cells has a resolution of approximately 200 (XY) and 500 nanometers (Z)
38 Confocal laser scanning Increase signal to noise ratio Higher Z-resolution Less out-of-focus blur Only small volume at once Large volumes need long acquisition times
39 Confocal laser scanning Sample is excited by point focus laser Emitted fluorescent from focus is focus at pinhole and reaches detector Emitted fluorescent from out-of-focus is also out-offocus at pinhole and largely excuded from detector
40 Confocal laser scanning
41 Confocal laser scanning
42 Confocal laser scanning Select fluorochromes according to laser lines
43 Confocal laser scanning X-Y Galvoscanner
44 Confocal laser scanning Photomultiplier (PMT)
45 Bio 407 Confocal laser scanning 3D + Time
46 Confocal laser scanning Widefield vs laser scanning confocal microscope
47 Confocal laser scanning Widefield vs laser scanning confocal microscope
48 Confocal laser scanning Widefield vs laser scanning confocal microscope
49 Confocal laser scanning Widefield vs laser scanning confocal microscope
50 Confocal laser scanning Widefield vs laser scanning confocal microscope
51 Confocal laser scanning Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching FRAP
52 Glutamate Receptor movement in NMJ of drosophila Bio 407 Confocal laser scanning Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching FRAP Füger et al., Nature Protocols 2, (2007)
53 Confocal laser scanning Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching FRAP
54 Confocal laser scanning Fluorescence resonance energy transfer FRET Emission spectrum donor overlapping Excitation spectrum acceptor Förster distance range 10 nm Gines and Davidson Florida State University
55 Spinning disk Increase acquisition speed
56 Spinning disk Increase acquisition speed Gines, Rainey and Davidson Florida State University
57 Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy SPIM 4D imaging Light-sheet-imaging technique Better signal-to-noise ratio Low photodamage Huisken et al., Science 305, (2004)
58 Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy SPIM Widefield compared with SPIM Widefield SPIM Huisken et al., Science 305, (2004)
59 Total internal refletion fluorescence TIRF Signal to noise ratio Fellers and Davidson, Florida State University Ross and Schwartz Nikon Instruments
60 TIRF Signal to noise ratio Nanometer range Evanescent wave excites only fluorophores near the glass farther away from the interface are not excited Refractive index between glass and sample Critical angle to produce evanescent field Axelrod, Long and Davidson Univ Michigan and Florida State University
61 TIRF Prism method Objective lens method Fellers and Davidson, Florida State University Ross and Schwartz Nikon Instruments
62 Bio 407 Multiphoton Imaging deep into tissue
63 Multiphoton Imaging deep into tissue
64 Multiphoton Two photons that arrive simultaneously at a molecule combine their energies to promote the molecule to an excited state, and leads to fluorescence emission.
65 Multiphoton Two photons that arrive simultaneously at a molecule combine their energies to promote the molecule to an excited state, and leads to fluorescence emission. Helmchen and Denk, Nature Methods 2005
66 Multiphoton Imaging in scatter tissue All fluorescent photons provide useful signal. Helmchen and Denk, Nature Methods 2005
67 Multiphoton Deep tissue two-photon Helmchen and Denk, Nature Methods 2005
68 Bio 407 Multiphoton
69 Bio 407 Multiphoton laser scanning microscope
70 Multiphoton
71 Super resolution Beyond the diffraction limit d = 0.61 λ / NA Imaging EGFP in living cells has a resolution of approximately 200 (XY) and 500 nanometers (Z)
72 Super resolution Beyond the diffraction limit d = 0.61 λ / NA Imaging EGFP in living cells has a resolution of approximately 200 (XY) and 500 nanometers (Z)
73 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Superresolution Resolution depends on: wavelength and opening angle of objetives Diffraction limit (Abbe, 1873) Lateral (XY) 200nm Axial (Z) 500nm Abbe, E. Arch. Mikrosk. Anat. Entwicklungsmech. 1873
74 Superresolution
75 Superresolution
76 222nm Superresolution
77 222nm Superresolution
78 Superresolution Resolution limit, defined as the minimum distance that two point-source objects have to be in order to distinguish the two sources from each other 222nm
79 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Superresolution Structured illumination José María Mateos
80 Superresolution Structured illumination
81 Superresolution Structured illumination Sample structure Illumination pattern Image (Moiré) Algorithm (calculation of sample structure) Gustafsson 2005
82 Superresolution Structured illumination
83 Superresolution Structured-illumination Superresolution white paper SR-SIM Zeiss
84 Superresolution Structured illumination Advantages Uses standard epifluorescence microscope No special fluorophores required Live cell imaging possible Large field of view 3D-possible (but decreased speed, etc.) Disadvantages Resolution ~100 nm
85 In STED, an initial excitation pulse is focused on a spot. The spot is narrowed by a second, donutshaped pulse that prompts all excited fluorophores in the body of the donut to emit (this is the emission depletion part of STED). This leaves only the hole of the donut in an excited state, and only this narrow hole is detected as an emitted fluorescence. Bio 407 Super resolution Stimulated emission depletion STED Abbott Nature 459, (2009)
86 Super resolution Stimulated emission depletion STED
87 Super resolution Stimulated emission depletion STED Based on confocal Hell et al.,
88 Super resolution Confocal Stimulated emission depletion STED Based on confocal STED Sample courtesy Martin Engelke, Urs Greber, Institute of Zoology, University of Zurich
89 Advantages Standard fluorescent proteins and fluorophore tagged antibodies can be used High frame rate for live cell imaging Resolution: x, y ~20 nm, z ~50 nm 3D possible Bio 407 Super resolution Stimulated emission depletion STED Disadvantages Special lasers required/desired (supercontinuum laser) Small field of view (confocal imaging pixel size)
90 Imaging single molecules Bio 407 Super resolution Statistical STORM Stochastic optical reconstruction Position of a single molecule can be localized to 1 nm accuracy or better if enough photons are collected and there are no other similarly emitting molecules within ~200 nm (Heisenberg 1930, Bobroff 1980). PALM Photoactivated localization GSD Ground state depletion
91 Super resolution Photoactivated localization PALM single-molecule techniques stochastic photoswitching where most of the molecules remain dark llippincott-schwartz Nature 459, (2009)
92 Super resolution Photoactivated localization PALM single-molecule techniques stochastic photoswitching where most of the molecules remain dark Price and Davidson Florida State University
93 Super resolution Photoactivated localization PALM single-molecule techniques stochastic photoswitching where most of the molecules remain dark Price and Davidson Florida State University
94 Super resolution Photoactivated localization PALM single-molecule techniques stochastic photoswitching where most of the molecules remain dark Price and Davidson Florida State University
95 Advantages Large field of view (imaging with CCD camera) Resolution: x, y ~25 nm, z ~ 65 nm 3D possible Disadvantages Photoactivatable proteins/fluorophores required (EosGFP etc.) Slow for high accuracy/resolution Special lasers may be required Live-cell difficult (illumination, bleaching, time) Bio 407 Super resolution Photoactivated localization PALM
96 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Superresolution Structured illumination José María Mateos
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Imaging with light / Overview of techniques Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Imaging with light / Overview of techniques Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
5/4/2015 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT. Image formation in a nutshell. Overview of techniques
 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Invitation for a walk through microscopy. Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner
 Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging
 Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy (an overview) Microscopy with light Components of a light microscope 1. Light source 2. Objective 3. Sample or specimen holder
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy (an overview) Microscopy with light Components of a light microscope 1. Light source 2. Objective 3. Sample or specimen holder
Microscopy Live Animal Imaging
 Microscopy Live Animal Imaging A collaborative environment that provides the knowledge, instruments, and expertise needed to visualize life at scales ranging from single molecules to entire animals. Project
Microscopy Live Animal Imaging A collaborative environment that provides the knowledge, instruments, and expertise needed to visualize life at scales ranging from single molecules to entire animals. Project
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY
 CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY 11.01.16-15.01.2016 CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY 25.01.16-29.01.2016 PhD Course - University of Copenhagen Department of Biomedical Sciences
CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY 11.01.16-15.01.2016 CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY 25.01.16-29.01.2016 PhD Course - University of Copenhagen Department of Biomedical Sciences
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV,
 EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Practical Flatness Tech Note
 Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Tissue Preparation ORGANISM IMAGE TISSUE PREPARATION. 1) Fixation: halts cell metabolism, preserves cell/tissue structure
 Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
Microscopy. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 2, 2017 Ron Dror
 Microscopy CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 2, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Microscopy: the basics Fluorescence microscopy Resolution limits The diffraction limit Beating the diffraction limit 2 Microscopy:
Microscopy CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 2, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Microscopy: the basics Fluorescence microscopy Resolution limits The diffraction limit Beating the diffraction limit 2 Microscopy:
Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope
 Summary of the PhD thesis Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope Author: Dudás, László Supervisors: Prof. Dr. Szabó, Gábor and Dr.
Summary of the PhD thesis Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope Author: Dudás, László Supervisors: Prof. Dr. Szabó, Gábor and Dr.
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
Microscopy Training & Overview
 Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
Microscopy. Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University
 Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging. October 15, 2010
 Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Systems Biology. Optical Train, Köhler Illumination
 McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
Imaging Introduction. September 24, 2010
 Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches
 Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL MICROSCOPY
 Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
BASICS IN BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens. Compound Light Micros
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
The Compound Microscope. Brightfield: Köhler Illumination
 Outline History of Microscopy The Magnifying Glass The Compound Microscope Brightfield: Köhler Illumination Microscopy µικροσ (mikros): small σκοπειν (skopein): to observe History of Microscopy Well :
Outline History of Microscopy The Magnifying Glass The Compound Microscope Brightfield: Köhler Illumination Microscopy µικροσ (mikros): small σκοπειν (skopein): to observe History of Microscopy Well :
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
CCAM Microscope Objectives
 CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution
 Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
 Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
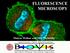 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll. Dept. of Applied Physics. 12 September Optical Microscopy. Supervisor s signature:...
 Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope
 2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
6/3/15. The Anatomy of a Digital Image. Representative Intensities. Specimen: (molecular distribution)
 2015 LMIC Imaging Workshop Sidney L. Shaw Technical Director An introduction of concepts for Super-Resolution Light Microscopy The Anatomy of a Digital Image Representative Intensities Specimen: (molecular
2015 LMIC Imaging Workshop Sidney L. Shaw Technical Director An introduction of concepts for Super-Resolution Light Microscopy The Anatomy of a Digital Image Representative Intensities Specimen: (molecular
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small.
 Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
Script Bio 407 Applied Microscopy Light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Dr. José María Mateos Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Winterthurerstrasse 190 CH-8057 Zurich Phone 044 635 98 20 mateos@zmb.uzh.ch www.zmb.uzh.ch Script
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Dr. José María Mateos Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Winterthurerstrasse 190 CH-8057 Zurich Phone 044 635 98 20 mateos@zmb.uzh.ch www.zmb.uzh.ch Script
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences
 Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY. Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University
 OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
CCAM s Selection of. Zeiss Microscope Objectives
 CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD
 MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um. Red Blood Cells = mm 1500 um. Width of penny Pearson Education, Inc.
 Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um Red Blood Cells 1.5mm 1500 um Width of penny = 1500 Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some representative objects within those ranges)
Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um Red Blood Cells 1.5mm 1500 um Width of penny = 1500 Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some representative objects within those ranges)
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程. Spot light 長庚大學
 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
Application Note. The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack
 The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM
 More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Image analysis. Intensity measurements Size measurements Organelle localization Colocalization Cell mobility Distance measurements FRAP, FLIP, FRET
 Dr. Kees Straatman Image analysis Imaris Volocity ImageJ/Fiji Huygens deconvolution NIS-Elements (incl. deconvolution in RKCSB) ScanR analysis CellR analysis Cell Profiler FV1000/LAS Image analysis Intensity
Dr. Kees Straatman Image analysis Imaris Volocity ImageJ/Fiji Huygens deconvolution NIS-Elements (incl. deconvolution in RKCSB) ScanR analysis CellR analysis Cell Profiler FV1000/LAS Image analysis Intensity
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Optical Design of. Microscopes. George H. Seward. Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88. SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA
 Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal
 Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Microscopic Structures
 Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY
 STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Questions for Lab Report 1. How do you define a resolution in STORM imaging? If you are given a STORM setup, how
STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Questions for Lab Report 1. How do you define a resolution in STORM imaging? If you are given a STORM setup, how
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain. Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology
 Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Microscopy. Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II Herbert Gross. Winter term
 Microscopy Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II 212-1-22 Herbert Gross Winter term 212 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary time schedule 2 No Date Main subject Detailed topics Lecturer 1 15.1. Optical
Microscopy Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II 212-1-22 Herbert Gross Winter term 212 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary time schedule 2 No Date Main subject Detailed topics Lecturer 1 15.1. Optical
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture. 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker
 Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Precision-tracking of individual particles By Fluorescence Photo activation Localization Microscopy(FPALM) Presented by Aung K.
 Precision-tracking of individual particles By Fluorescence Photo activation Localization Microscopy(FPALM) Presented by Aung K. Soe This FPALM research was done by Assistant Professor Sam Hess, physics
Precision-tracking of individual particles By Fluorescence Photo activation Localization Microscopy(FPALM) Presented by Aung K. Soe This FPALM research was done by Assistant Professor Sam Hess, physics
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
The Nature of Light. Light and Energy
 The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
Advanced Optical Microscopy
 Nanosystems I - Seminar TU München 8th December 2008 1 Introduction to Classical Optical Microscopy Denitions in Optical Microscopy Contrast and Contrast Enhancement 1 Introduction to Classical Optical
Nanosystems I - Seminar TU München 8th December 2008 1 Introduction to Classical Optical Microscopy Denitions in Optical Microscopy Contrast and Contrast Enhancement 1 Introduction to Classical Optical
Compound Light Microscopy. Microscopy. Things to remember... 1/22/2017. This is what we use in the laboratory
 Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy
 Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy Instrumentation Light Sources: One-photon and Multi-photon Excitation Applications in Cells Lifetime Imaging Figures acknowledgements: E.D. Salmon
Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy Instrumentation Light Sources: One-photon and Multi-photon Excitation Applications in Cells Lifetime Imaging Figures acknowledgements: E.D. Salmon
Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging
 Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Nikon. King s College London. Imaging Centre. N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING KING S COLLEGE LONDON
 N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
Shaping light in microscopy:
 Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
Lecture 4 to 5 MICROSCOPY-PRINCIPLES AND TYPES
 Lecture 4 to 5 MICROSCOPY-PRINCIPLES AND TYPES Microorganisms are too small to be seen by our unaided eyes and the microscopes are of crucial importance as they help to view the microbes. A microscope
Lecture 4 to 5 MICROSCOPY-PRINCIPLES AND TYPES Microorganisms are too small to be seen by our unaided eyes and the microscopes are of crucial importance as they help to view the microbes. A microscope
