Fundamentals of Computer Vision
|
|
|
- Candace Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012)
2 What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer see.! The complexity of this task is enormous!! It is about understanding visual input and making inferences about the visual world.! What you see is NOT necessarily what is there!!
3 Visual illusions!
4 Visual illusions!
5 Visual illusions!
6 What do you see?!
7 Is it clearer now?!
8 Bregman B s!
9 Why study computer vision?! Scene reconstruction! Object recognition and identification! Object modeling! Robot navigation! Medical imaging! Image-guided neurosurgery!
10 Aspects of computer vision! Early vision: receptive fields, biological vision systems.! Linear systems, signal processing, convolution.! Edge detection, feature detection.! Projective geometry and camera modeling.! Stereo vision.!
11 Aspects of computer vision! Shape from shading and texture.! Optical flow and motion analysis.! Object representation and recognition.! Graph-theoretic methods.! PDEs in vision.! Applications.!
12 Brain Mechanisms of Vision!
13 Brain Mechanisms of Vision!
14 Brain Mechanisms of Vision!
15 Cerebral Cortex! It is the outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres. Approx. 2mm thick, 1.5 square feet, highly folded, 10 billion neurons!! Most sensory and motor areas of the cortex contain systematic 2D maps of the world represented. These maps are NOT spatially uniform. Much more cortex is dedicated to the fingers than to the rear-end. In vision the fovea has a representation which is approx. 35 more times more detailed than the periphery.! Visual pathways cross so that the left half of the visual world projects to the right cerebral cortex and vice-versa.! Operations in the visual cortex are LOCAL. In a deep sense this drives the local to global transition in computational vision.!
16 Visual Pathway! Messages from the light-sensitive elements, the rods and cones, traverse a few layers involving other retinal cell types (bipolar, horizontal, amacrine) before arriving at the retinal ganglion cells [See Nalwa, Chapter 1.] The rods facilitate night vision and the cones are responsible for color vision.! 125 million rods and cones, so compaction is involved.! The axons of the ganglion cells comprise about a million nerve fibers which are bundled together in the optic nerve.! The optic nerve feeds to the lateral geniculate nuclei (LGN s),with partial crossing in the optic chiasm.! The right halves of the retina project to the right LGN and right cortex, which represent the left part of the visual world (and vice-versa for the left halves of the retina).!
17 A Receptive Field! The mapping of the response of a neuron as a function of the amount of light incident on a retinal patch.! Single cell recording paradigm:! Stimulate! the retina! with a pattern! of light! and probe! the!!! neuron with! a microelectrode.!!!!!!!! Find the! optimal! pattern by! trial and! error and! proceed!!! to test hundreds! of cells.!!!!!!!!!!! Analogy to the impulse response of a linear time invariant system.! Proceed from the fibers to the LGN to the primary visual cortex to deduce function from structure.! A receptive field is an abstraction.! Retinotopic maps.!
18 Receptive Field Types! Center-Surround!!!!!!!!! -! +!! +! -!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Both retinal ganglion cells and LGN cells respond best to light of a particular size in a particular location of the retina.! LGN feeds into the lower part of layer IV (where the cells have the same receptive fields). LGN cells are monocular, with information from the left and right eyes kept separate.! Simple-Cells!!!!!!!!!!Cells outside layer IV behave like line! +! -!! - +!! detectors. They are orientation and location!!!sensitive but are still monocular.!
19 Receptive Field Types! Complex Cells!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! +! -!! + -!! +!-!! + -!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Not! sensitive! to exact! location.! Hence,! they! are involved!! in the processing!! of visual! motion.! Some! stereo! behavior! is!!!!!not sensitive to exact location. now observed.! Hence, they are!!!!!!!
20 Orientation Columns! Approximately 10 degree shifts in orientation preference with an oblique penetration. No change in orientation preference or location for a vertical penetration (but change in size).!
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 Ocular Dominance Columns! Vertical penetrations reveal columns which receive most of their input from one eye, but not the other. Staining techniques have confirmed the anatomy.!
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50 ^l ^ n ^v α
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Lecture 5. The Visual Cortex. Cortical Visual Processing
 Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Lecture 5 The Visual Cortex Cortical Visual Processing 1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) LGN is located in the Thalamus There are two LGN on each (lateral) side of the brain. Optic nerve fibers from eye
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
CS510: Image Computation. Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018
 CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Fundamentals of Computer Vision B. Biological Vision. Prepared By Louis Simard
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision 308-558B Biological Vision Prepared By Louis Simard 1. Optical system 1.1 Overview The ocular optical system of a human is seen to produce a transformation of the light
Fundamentals of Computer Vision 308-558B Biological Vision Prepared By Louis Simard 1. Optical system 1.1 Overview The ocular optical system of a human is seen to produce a transformation of the light
Outline. The visual pathway. The Visual system part I. A large part of the brain is dedicated for vision
 The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
The Visual system part I Patrick Kanold, PhD University of Maryland College Park Outline Eye Retina LGN Visual cortex Structure Response properties Cortical processing Topographic maps large and small
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
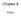 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
CS 534: Computer Vision
 CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Cortical sensory systems
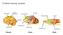 Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
Cortical sensory systems Motorisch Somatosensorisch Sensorimotor Visuell Sensorimotor Visuell Visuell Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Olfaktorisch Auditorisch Mensch Katze Ratte Primary Visual Cortex
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Biological Vision. Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University
 Biological Vision Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines How do we see: some historical theories of vision Biological vision: theories and results from psychology and cognitive
Biological Vision Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines How do we see: some historical theories of vision Biological vision: theories and results from psychology and cognitive
A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision
 A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision Guest&Lecture:&Marius&Cătălin&Iordan&& CS&131&8&Computer&Vision:&Foundations&and&Applications& 27&October&2014 detection recognition
A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision Guest&Lecture:&Marius&Cătălin&Iordan&& CS&131&8&Computer&Vision:&Foundations&and&Applications& 27&October&2014 detection recognition
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
1/21/2019. to see : to know what is where by looking. -Aristotle. The Anatomy of Visual Pathways: Anatomy and Function are Linked
 The Laboratory for Visual Neuroplasticity Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School to see : to know what is where by looking -Aristotle The Anatomy of Visual Pathways: Anatomy and Function
The Laboratory for Visual Neuroplasticity Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School to see : to know what is where by looking -Aristotle The Anatomy of Visual Pathways: Anatomy and Function
A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision
 A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision Guest Lecture: Marius Cătălin Iordan CS 131 - Computer Vision: Foundations and Applications 27 October 2014 detection recognition
A Primer on Human Vision: Insights and Inspiration for Computer Vision Guest Lecture: Marius Cătălin Iordan CS 131 - Computer Vision: Foundations and Applications 27 October 2014 detection recognition
Frog Vision. PSY305 Lecture 4 JV Stone
 Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
Large Scale Imaging of the Retina. 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina
 Large Scale Imaging of the Retina 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina understand the language used by the eye to send information about the visual world to the brain use techniques
Large Scale Imaging of the Retina 1. The Retina a Biological Pixel Detector 2. Probing the Retina understand the language used by the eye to send information about the visual world to the brain use techniques
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN. No Thing to See. Copyright Worth Publishers 2013 NOT FOR REPRODUCTION
 3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
3 THE VISUAL BRAIN No Thing to See In 1988 a young woman who is known in the neurological literature as D.F. fell into a coma as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning at her home. (The gas was released
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes
 Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
Structure and Measurement of the brain lecture notes Marty Sereno 2009/2010!"#$%&'(&#)*%$#&+,'-&.)"/*"&.*)*-'(0&1223 Neural development and visual system Lecture 2 Topics Development Gastrulation Neural
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Vision III. How We See Things (short version) Overview of Topics. From Early Processing to Object Perception
 Vision III From Early Processing to Object Perception Chapter 10 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Beyond the retina: 2 pathways to V1 Subcortical structures (LGN & SC) Object & Face recognition Primary
Vision III From Early Processing to Object Perception Chapter 10 in Chaudhuri 1 1 Overview of Topics Beyond the retina: 2 pathways to V1 Subcortical structures (LGN & SC) Object & Face recognition Primary
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
Neural basis of pattern vision
 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE 2000 Macmillan Reference Ltd Neural basis of pattern vision Visual receptive field#visual system#binocularity#orientation selectivity#stereopsis Kiper, Daniel Daniel C.
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE 2000 Macmillan Reference Ltd Neural basis of pattern vision Visual receptive field#visual system#binocularity#orientation selectivity#stereopsis Kiper, Daniel Daniel C.
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
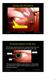 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Color. Color. Colorfull world IFT3350. Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3350 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
An Engineer s Perspective on of the Retina. Steve Collins Department of Engineering Science University of Oxford
 An Engineer s Perspective on of the Retina Steve Collins Department of Engineering Science University of Oxford Aims of the Talk To highlight that research can be: multi-disciplinary stimulated by user
An Engineer s Perspective on of the Retina Steve Collins Department of Engineering Science University of Oxford Aims of the Talk To highlight that research can be: multi-disciplinary stimulated by user
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
2/3/2016. How We Move... Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Sensory Processing.
 How We Move Sensory Processing 2015 MFMER slide-4 2015 MFMER slide-7 Motor Processing 2015 MFMER slide-5 2015 MFMER slide-8 Central Processing Vestibular Somatosensation Visual Macular Peri-macular 2015
How We Move Sensory Processing 2015 MFMER slide-4 2015 MFMER slide-7 Motor Processing 2015 MFMER slide-5 2015 MFMER slide-8 Central Processing Vestibular Somatosensation Visual Macular Peri-macular 2015
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
8.2 IMAGE PROCESSING VERSUS IMAGE ANALYSIS Image processing: The collection of routines and
 8.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we will study and discuss some fundamental techniques for image processing and image analysis, with a few examples of routines developed for certain purposes. 8.2 IMAGE
8.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we will study and discuss some fundamental techniques for image processing and image analysis, with a few examples of routines developed for certain purposes. 8.2 IMAGE
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
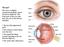 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
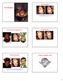 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
VISION. John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00
 VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00 Objectives Purposes of vision Problems that the visual system has to overcome Neural organization of vision Human Perceptual Abilities Detect a candle, 30 miles
VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00 Objectives Purposes of vision Problems that the visual system has to overcome Neural organization of vision Human Perceptual Abilities Detect a candle, 30 miles
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Modeling cortical maps with Topographica
 Modeling cortical maps with Topographica James A. Bednar a, Yoonsuck Choe b, Judah De Paula a, Risto Miikkulainen a, Jefferson Provost a, and Tal Tversky a a Department of Computer Sciences, The University
Modeling cortical maps with Topographica James A. Bednar a, Yoonsuck Choe b, Judah De Paula a, Risto Miikkulainen a, Jefferson Provost a, and Tal Tversky a a Department of Computer Sciences, The University
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology.
 This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Maps in the Brain Introduction
 Maps in the Brain Introduction 1 Overview A few words about Maps Cortical Maps: Development and (Re-)Structuring Auditory Maps Visual Maps Place Fields 2 What are Maps I Intuitive Definition: Maps are
Maps in the Brain Introduction 1 Overview A few words about Maps Cortical Maps: Development and (Re-)Structuring Auditory Maps Visual Maps Place Fields 2 What are Maps I Intuitive Definition: Maps are
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY
 OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Uniformity of Monkey Striate Cortex: A Parallel Relationship between Field Size, Scatter, and Magnification Factor
 Uniformity of Monkey Striate Cortex: A Parallel Relationship between Field Size, Scatter, and Magnification Factor DAVID H. HUBEL AND TORSTEN N. WIESEL Drpccrtmmt of Nezcrobzobgy, Huructrd Mtdzccil School,
Uniformity of Monkey Striate Cortex: A Parallel Relationship between Field Size, Scatter, and Magnification Factor DAVID H. HUBEL AND TORSTEN N. WIESEL Drpccrtmmt of Nezcrobzobgy, Huructrd Mtdzccil School,
Coarse hairs that overlie the supraorbital margins Functions include: Shading the eye Preventing perspiration from reaching the eye
 SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
The Photoreceptor Mosaic
 The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
The Photoreceptor Mosaic Aristophanis Pallikaris IVO, University of Crete Institute of Vision and Optics 10th Aegean Summer School Overview Brief Anatomy Photoreceptors Categorization Visual Function Photoreceptor
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Review, the visual and oculomotor systems
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
