Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
|
|
|
- Claude Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
2 Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain s integration of sensory information Top-Down Processing information processing guided by higher-level mental processes as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
3 Sensation- Basic Principles Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological experience of them Light- brightness Sound- volume Pressure- weight Taste- sweetness
4 Sensation- Thresholds Absolute Threshold minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time Difference Threshold minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time just noticeable difference (JND)
5 Sensation- Thresholds Signal Detection Theory predicts how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise) assumes that there is no single absolute threshold detection depends partly on person s experience expectations motivation level of fatigue
6 Sensation- Thresholds Percentage of correct detections Subliminal stimuli Subliminal When stimuli are below one s absolute threshold for conscious awareness 0 Low Absolute threshold Medium Intensity of stimulus
7 Sensation- Thresholds Weber s Law- to perceive as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage light intensity- 8% weight- 2% tone frequency- 0.3% Sensory adaptation- diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
8 Vision Transduction conversion of one form of energy to another in sensation, transforming of stimulus energies into neural impulses Wavelength the distance from the peak of one wave to the peak of the next
9 Vision Hue dimension of color determined by wavelength of light Intensity amount of energy in a wave determined by amplitude brightness loudness
10 The spectrum of electromagnetic energy
11 Vision- Physical Properties of Waves Short wavelength=high frequency (bluish colors, high-pitched sounds) Great amplitude (bright colors, loud sounds) Long wavelength=low frequency (reddish colors, low-pitched sounds) Small amplitude (dull colors, soft sounds)
12 Vision Pupil- adjustable opening in the center of the eye Iris- a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape to focus images on the retina
13 Vision
14 Vision Accommodation- the process by which the eye s lens changes shape to help focus near or far objects on the retina Retina- the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
15 Vision Acuity- the sharpness of vision Nearsightedness- condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because distant objects in front of retina Farsightedness- condition in which faraway objects are seen more clearly than near objects because the image of near objects is focused behind retina
16 Retina s Reaction to Light- Receptors Rods peripheral retina detect black, white and gray twilight or low light Cones near center of retina fine detail and color vision daylight or well-lit conditions
17 Retina s Reaction to Light Optic nerve- nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain Blind Spot- point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a blind spot because there are no receptor cells located there Fovea- central point in the retina, around which the eye s cones cluster
18 Vision- Receptors Receptors in the Human Eye Number Location in retina Sensitivity in dim light Color sensitive? Cones 6 million Center Low Yes Rods 120 million Periphery High No
19 Pathways from the Eyes to the Visual Cortex
20 Visual Information Processing Feature Detectors nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features shape angle movement Cell s responses Stimulus
21 How the Brain Perceives
22 Visual Information Processing Parallel Processing simultaneous processing of several aspects of a problem simultaneously
23
24 Color-Deficient Vision People who suffer red-green blindness have trouble perceiving the number within the design
25 Opponent Process- Afterimage Effect
26 Visual Information Processing Color Constancy Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even if changing illumination alters the wavelengths reflected by the object
27 Audition Audition the sense of hearing Frequency the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time Pitch a tone s highness or lowness depends on frequency
28 The Intensity of Some Common Sounds
29
30 Audition- The Ear Middle Ear chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea s oval window Inner Ear innermost part of the ear, contining the cochlea, semicurcular canals, and vestibular sacs Cochlea coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which
31 Audition Place Theory the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea s membrane is stimulated Frequency Theory the theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch
32 How We Locate Sounds
33 Audition Conduction Hearing Loss hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea Nerve Hearing Loss hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea s receptor cells or to the auditory nerve
34 Touch Skin Sensations pressure only skin sensation with identifiable receptors warmth cold pain
35 Pain Gate-Control Theory theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological gate that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain gate opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers gate closed by activity in larger fibers or by information coming from the brain
36 Taste Taste Sensations sweet sour salty bitter Sensory Interaction the principle that one sense may influence another as when the smell of food influences its taste
37 Smell Olfactory nerve Olfactory bulb Nasal passage Receptor cells in olfactory membrane
38 Body Position and Movement Kinesthesis the system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts Vestibular Sense the sense of body movement and position including the sense of balance
39 Perception Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
40 Perceptual Illusions
41 Perceptual Illusions
42 Perceptual Organization: Gestalt Visual Capture tendency for vision to dominate the other senses Gestalt--an organized whole tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes
43 Perceptual Organization: Gestalt Grouping the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups Grouping Principles (Pg. 237) proximity--group nearby figures together similarity--group figures that are similar continuity--perceive continuous patterns closure--fill in gaps connectedness--spots, lines, and areas are seen as unit when connected
44 Perceptual Organization Figure and Ground--organization of the visual field into objects (figures) that stand out from their surroundings (ground)
45 Perceptual Organization: Depth Perception Depth Perception ability to see objects in three dimensions allows us to judge distance Binocular cues retinal disparity images from the two eyes differ closer the object, the larger the disparity convergence neuromuscular cue two eyes move inward for near objects
46 Perceptual Organization: Depth Perception Visual Cliff
47 Perceptual Organization: Depth Perception Monocular Cues ( ) relative size smaller image is more distant interposition closer object blocks distant object relative clarity hazy object seen as more distant texture coarse --> close fine --> distant
48 Perceptual Organization: Depth Perception Monocular Cues (cont.) relative height higher objects seen as more distant relative motion closer objects seem to move faster linear perspective parallel lines converge with distance relative brightness closer objects appear brighter
49 Perceptual Organization: Depth Perception Illusory Depth
50 Perceptual Constancy Perceptual Constancy perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal image change color shape size
51 Perceptual Organization- Brightness Contrast
52 Perceptual Interpretation Perceptual Adaptation (vision) ability to adjust to an artificially displaced visual field prism glasses Perceptual Set a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
53 Perceptual Set: Schemas What you see in the center is influenced by perceptual set
54 Perceptual Set: Schemas Flying Saucers or Clouds?
55 Perception and the Human Factor Human Factors Psychology explores how people and machines interact explores how machine and physical environments can be adapted to human behaviors
56 Is There Extrasensory Perception? Extrasensory Perception controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input telepathy clairvoyance precognition Parapsychology the study of paranormal phenomena ESP psychokinesis
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6
 Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
 1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
Unit IV Sensation Perception
 Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Chapter 6: Perception
 Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Perception. Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Cocktail Party Effect
 Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception
 Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and perception. Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Unit 4. Sensation and. Perception. 6-8% (7-9% in past) College Board - Acorn Book Course Description. Unit IV. Sensaton and.
 Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
zmacdonald zmacintosh zmackerel zmacrame zmachine
 Sensation Sensation Sensation Objectives: 1. Contrast the processes of sensation and perception. 2. Distinguish between absolute and difference thresholds, and discuss research findings on subliminal stimulation.
Sensation Sensation Sensation Objectives: 1. Contrast the processes of sensation and perception. 2. Distinguish between absolute and difference thresholds, and discuss research findings on subliminal stimulation.
Definitions Sensation Sensation and perception Perception
 Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception
 Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter Introduction. Chapter Wrap-Up. and the Eye
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Sound Light Chapter Wrap-Up Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye How do sound and light waves travel and interact with matter? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Sound Light Chapter Wrap-Up Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye How do sound and light waves travel and interact with matter? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
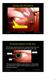 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Why is blue tinted backlight better?
 Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
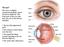 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
5. According to the philosopher, we learn to perceive the world. A) Locke B) Kant C) Gibson D) Walk E) Neisser
 Bryant-Taneda: AP Psychology Test Bank Perception (Chapter 6) 1. If two objects are assumed to be the same size, the object that casts the smaller retinal image is perceived to be: A) more coarsely textured.
Bryant-Taneda: AP Psychology Test Bank Perception (Chapter 6) 1. If two objects are assumed to be the same size, the object that casts the smaller retinal image is perceived to be: A) more coarsely textured.
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Sensation & Perception. Chapter 6 Perception. Myers PSYCHOLOGY. Attention: Theoretical Issues. Perception Outline
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY C6:1 Sensation & Perception C6:2 Chapter 6 Perception Sensation - Process by which sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energy (+1) Perception - Process
Myers PSYCHOLOGY C6:1 Sensation & Perception C6:2 Chapter 6 Perception Sensation - Process by which sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energy (+1) Perception - Process
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Chapter 6 Human Vision
 Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
March 9. Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion?
 March 9 EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion? Agenda: 1. Perception Theories 2. Brain Games Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. Table of Contents: 87. March 9 & 10 88.
March 9 EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion? Agenda: 1. Perception Theories 2. Brain Games Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. Table of Contents: 87. March 9 & 10 88.
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness )
 Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE
 Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
