This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology.
|
|
|
- Cathleen Richards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology. Pages , in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings of the 28th Workshop/Conference of the Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE), 403 pages. Compilation copyright 2007 by the Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE) ISBN All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the copyright owner. Use solely at one s own institution with no intent for profit is excluded from the preceding copyright restriction, unless otherwise noted on the copyright notice of the individual chapter in this volume. Proper credit to this publication must be included in your laboratory outline for each use; a sample citation is given above. Upon obtaining permission or with the sole use at one s own institution exclusion, ABLE strongly encourages individuals to use the exercises in this proceedings volume in their teaching program. Although the laboratory exercises in this proceedings volume have been tested and due consideration has been given to safety, individuals performing these exercises must assume all responsibilities for risk. The Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE) disclaims any liability with regards to safety in connection with the use of the exercises in this volume. The focus of ABLE is to improve the undergraduate biology laboratory experience by promoting the development and dissemination of interesting, innovative, and reliable laboratory exercises. Visit ABLE on the Web at:
2 Mini Workshop 311 Visual Sensory Physiology Robert A. Linsenmeier 1 and Roberta W. Ellington 2 1 Dept. of Biomedical Engineering 2145 Sheridan Road Northwestern University Evanston, Il r-linsenmeier@northwestern.edu 2 Dept. of Biological Sciences 2205 Tech Drive (2-100) Northwestern University Evanston, Il r-ellington@northwestern.edu Abstract: This lab exercise teaches students about the location and size of the blind spot as well as the location in the visual field of the ability to do color discrimination. The exercise can be completed within a two-hour lab period and is suitable for students in High School AP Biology through the college sophomore level. Materials are inexpensive and can be reused. Introduction Part 1: Size of the Blind Spot/Optic Nerve Head The back of the eye is lined with retina, except in one region. This region is the area where blood vessels enter the eye to nourish the retina, and where axons of retinal ganglion cells leave the eye to travel to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus and other parts of the brain. This region is located at the end of the optic nerve and is often called the optic nerve head. Since it is round, it is also called the optic disc. There are no photoreceptors or other neurons in this region, therefore it is blind, and is also called the blind spot. In some retinal diseases, loss of retinal neurons causes other regions to be blind as well; these are called scotomas but we all have this one natural blind spot. What is remarkable is that under normal conditions, even when we only use one eye, the blind region causes us no problems and is basically undetectable. Interestingly, people with retinal disease often do not notice that they have scotomas either, unless the scotomas are large or in the central part of the visual field. The optic nerve head can be located in your own eye and you can determine its size and location in the visual field. This is the goal of this exercise. Measurements in the visual field are generally made in degrees of visual angle, rather than distance. We first need to define the visual axis. If you look straight ahead, you will naturally bring your eye into a particular alignment. Suppose you fixate on the period at the end of this sentence. The visual axis is the line between your eyeball and this fixation point. Extending the line into the eyeball, it will hit the fovea, the part of the retina with the largest concentration of photoreceptors and the most acute vision. We can measure visual angle relative to this axis, using the cornea as the vertex of the visual angle, as shown in Figure 1. (The actual vertex is inside the eye a bit.) The advantage of dealing in visual angle, rather than distance in cm across
3 312 ABLE 2006 Proceedings Vol. 28 the visual field, is that an image that hits a certain point on the retina will always be at a certain angle from the visual axis, whereas the distance in cm will depend on how far away the object is from you. Our visual field extends to about + and - 90 degrees of visual angle (actually the nose gets in the way and makes the nasal visual field smaller.) Figure 1. The visual angle using the cornea as the vertex of the angle. Part 2: Color Vision We often think that the cones in the retina are there so that we can see color. There are three types of cone receptors; each is sensitive to a different range of wavelengths (short, middle and long wavelength, or blue, green, and red); and the comparison in the retina of the signals from the three does allow color vision. Color vision is a nice feature of cone vision in people, some primates, and some other animals (birds and some fish). However, many animals (such as dogs and cats) have cones, but have terrible color vision, in that they are very poor at discriminating among different colors. Cones are present fundamentally to allow you to see under conditions of bright illumination where rod signals are saturated. Rods are very good at dim illumination, but overwhelmed by bright light. This experiment is to determine the region on the retina where you have good color vision, that is, where you can discriminate among colors. There are two things you may want to know in order to help interpret your findings, although you will probably not be able to arrive at completely definitive conclusions. First, the receptive fields of ganglion cells are not the same size across the retina. They are smallest in the central visual field and larger in the periphery. Second, the cone density (cones/mm 2 of retinal surface) also varies. The cones are most concentrated in the central retina, as shown in Figure 2, which represents the sum of the three cone types.
4 Mini Workshop 313 Figure 2. Top view of the left eye and corresponding densities of rods and cones cross the retina. Taken from Visual Perception by T.N. Cornsweet, Academic Press, 1970
5 314 ABLE 2006 Proceedings Vol. 28 Student Outline Procedure for Part 1 The materials that you will need include a tape measure; calculator with trig functions; an index card; 2 pieces of printer paper, scotch taped together lengthwise; and an appropriate marker that has a white body and a dark colored ink so that the tip is dark relative to the paper but the body of the marker is the same color as the paper. The object is to have a marker in which the tip contrasts with the paper but the body does not. If you wear glasses, you may need to remove them before doing this exercise. Tape the paper to the wall so that the long axis is horizontal. Mark a fixation point at eye level with the marker on either the left or right end of the paper. It should be about one cm in diameter, but the exact size is not important. Stand at a length of arm s length from the paper, so that you can just write on the board. Fixate on the right-hand fixation spot with your left eye, or on the left-hand fixation spot with your right eye. Cover the other eye with an index card. Make sure that you keep your head straight and not tilted. Your partner can help here. The blind spot is approximately on a horizontal line from the fixation point. Knowing this, extend your arm toward the paper and slowly bring the tip of the marker across the visual field until it disappears. Move the marker slowly, starting away from the blind spot and moving into it. Mark the point at which the marker tip just disappears. Do this starting from different initial locations in the visual field. This will trace out the size of the blind spot. Make sure you keep fixating on the fixation point at all times. Careful mapping may become tiring. You can take a break, as long as you stay the same distance from the paper. If it is difficult for you to fixate and move the marker, you may have your partner move the marker slowly; you will say when it disappears. Repeat all of your determinations at least once after writing down the data asked for below. Your partner will do the same experiment. The distance from your eye to the fixation point is 57 cm (or arm s length). Measure the distance from the fixation point to the far edge and to the near edge of the blind spot in cm. Record these numbers on your data sheet. You should measure the horizontal and vertical components of the blind spot (measure the distance across the blind spot in cm). Note the shape of the blind spot. Procedure for Part 2 You will be using a piece of poster board with a fixation point near one edge, and lightly marked vertical lines showing distances of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, and 40 degrees. If your eye is 57 cm from the fixation point, it turns out that one cm on the poster board is one degree of visual angle, so the 5-40 degree lines can be drawn 5-40 cm from the fixation point. Obtain a bag of 8 sticks with three different colored tapes in bands at one end. 1. One partner (the subject) will look at the fixation point with one eye, covering the other eye with an index card. The eye should be arm s length or 57cm from the poster board, so that one cm on the board = 1 deg of visual angle. Measure the distance using your tape measure. If you are using your right eye, the poster board will extend to the right and if you are using your left eye, the poster board will extend to the left do not cross the field of vision.
6 Mini Workshop The other partner (the experimenter) will hold a stick vertically at an eccentricity of 40 degrees, and ask the subject to name the colors from top to bottom. The experimenter will note on the data sheet whether the response was correct or not. (Some mark should be made whether the answer was right or wrong, because this will help the experimenter keep track of the total number of presentations.) The experimenter should move the stick into the desired position at moderate speed and then should hold it still. It could be brought in from the top, bottom or side, but be consistent. There is no partial credit - the subject either identifies all the colors correctly in order or not. The presentation of the colors in a research setting would ordinarily be brief. If the subject is taking more than a couple of seconds to respond, reject the trial and do another. 3. The experimenter will present the 8 different sticks at this location so that a meaningful % correct can be obtained. 4. The experimenter should occasionally remind the subject to look at the fixation point, and not at the sticks. 5. Repeat items 2 and 3 for all degrees of eccentricities listed in the data section. 6. After obtaining a complete set of data, partners should change roles and repeat the experiment. Data Section Part 1: Size of Blind Spot Distance from eye to fixation point: cm Distance from fixation point to far edge of blind spot: cm Distance from fixation point to near edge of blind spot: cm Distance across blind spot (diameter): cm Shape of blind spot: Part 2: Color Vision Degrees of Eccentricity Trial Mean % Correct
7 316 ABLE 2006 Proceedings Vol. 28 Lab Report 1. A brief (3-4 sentences) Introduction. What is the purpose of this lab? How does this lab relate to the sensory physiology concepts you learned in lecture? 2. Results: Hand in your data sheet, and show your answers and calculations for the following (use Figure 3 to help you): For Part 1: a. How far in degrees is the blind spot from the fixation point? (Convert the distance measured to visual angle, using the surface of the eye as the vertex of the angle as noted above.) b. Report the visual angle subtended by the diameter of the blind spot, in degrees. c. The eye is about 24 mm deep (of course this varies depending on whether you are nearsighted or farsighted, but we will ignore that). With this knowledge you can construct similar triangles inside the eye to the ones you are drawing outside the eye. Knowing the visual angles just calculated, determine how far it is across the optic nerve head (in mm) in the eye, and how far this is from the fovea. For Part 2: d. Graph the percentages correct as a function of eccentricity, for yourself or your lab partner. 3. Discussion: This section should include answers to the following questions: a. Blind Spot Experiment: The vertex of the visual angle is actually a little inside the eye. What does this mean about your estimates? What other sources of error can you think of in these measurements? b. Blind Spot Experiment: Why do you suppose that the blind spot is ordinarily not a blank spot in your visual field? It may help to realize that the board did not disappear in the area where the marker tip disappeared. c. Color Vision Experiment: Discuss at least one plausible hypothesis about the retina and visual system that would explain why the percent correct differs with different degrees of eccentricity. Figure 3. Diagram of the angles to aid students with calculations.
8 Mini Workshop 317 Instructor s Notes 1. If one partner is color blind, it may not be possible for that student to be either the experimenter or the subject in the color vision experiment. In this case, the student should obtain data to analyze from another member of the lab section or work as a group of three for this part of the lab exercise. 2. Arm s length or 57 cm can be used. But, there is a reason for the 57 cm. We are dealing with angles and tangents. The tangent of 1 degree is and 1/57 is Using arm s length gives comparable measurements and gives student individuality. 3. Materials Needed Per pair of students: Tape measure Lab marker taped with white tape so that it blends with the white printer paper Index card (3 x 5) for covering the eye Popsicle sticks (8), in plastic bag, wrapped with tape see chart below Printer paper 2 sheets scotch-taped together lengthwise White tape Graph paper Piece of poster board with a fixation point near one edge, and lightly marked vertical lines showing distances of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, and 40 degrees. These marks will each be 5 cm apart. 4. Students will need to bring a calculator with trig functions. 5. The popsicle-sticks: Each band should be about a cm high. The three bands will each be made from one of four colors, with each color used an equal amount across all sticks. If there are three bands per stick, and there are four colors to choose from (red, green, yellow, blue), with each color used only once per stick, the subject would be able to guess the order of the three colors on a stick with only about 4% probability [(1/4)*(1/3)*(1/2) = 1/24 = 0.04]. Each group receives eight sticks from the collection chosen at random. Place in a sandwich bag. No writing is on the sticks, only tape. The sticks will be taped in bands at one end only. There should be no space between the bands. 6. These supplies are used over and over again many times. The only supplies needing replenishing for each lab section are the 3 x 5 cards and the scotch-taped printer paper. 7. Purchasing the lab supplies: Popsicle-sticks are purchased from any crafts store. Poster paper is purchased from any supplier and cut in half. Rolls of red, blue, green, and yellow electric tape are purchased from any hardware store.
9 318 ABLE 2006 Proceedings Vol. 28 Literature Cited Cornsweet, T.N Visual Perception. New York: Academic Press. p.137. About the Authors Robert A. Linsenmeier is a professor of Neurobiology and Physiology and also of Biomedical Engineering at Northwestern University. He received his PhD from Northwestern University. He teaches upper level physiology classes. His research has covered many areas of retinal physiology. He is the past chair of the Biomedical Engineering Department and is the current Associate Director of the VaNTH Engineering Research Center for Bioengineering Educational Technologies. Roberta W. Ellington is a lecturer in Biological Sciences at Northwestern University. She received her MS from Loyola University Chicago. She is the Preparator for the Biology Labs and is the Lab Coordinator for the School of Continuing Studies (the Northwestern night school) Biology Labs. 2007, Northwestern University
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
The Eye and Vision. Activities: Linda Shore, Ed.D. Exploratorium Teacher Institute Exploratorium, all rights reserved
 The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
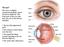 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Frog Vision. PSY305 Lecture 4 JV Stone
 Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Introduction. The Human Eye. Physics 1CL OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS AND THE EYE SPRING 2010
 Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Human Visual System. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
Human Visual System Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we discuss: - Structure of human eye - Mechanics of human visual system (HVS) - Brightness
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Retina. last updated: 23 rd Jan, c Michael Langer
 Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
Retina We didn t quite finish up the discussion of photoreceptors last lecture, so let s do that now. Let s consider why we see better in the direction in which we are looking than we do in the periphery.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, Wednesday, 8 January, 14
 11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
11.5 The Senses Tuesday January 7, 2014. TEST ON ALL OF HOMEOSTASIS (FOCUS ON REPRODUCTIVE AND NERVOUS SYSTEM) ON FRIDAY. Structure of the Eye Eye Anatomy and Function http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=0hzwmldldhi&feature=related
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
LO - Lab #06 - The Amazing Human Eye
 LO - Lab #06 - In this lab you will examine and model one of the most amazing optical systems you will ever encounter: the human eye. You might find it helpful to review the anatomy and function of the
LO - Lab #06 - In this lab you will examine and model one of the most amazing optical systems you will ever encounter: the human eye. You might find it helpful to review the anatomy and function of the
Aspects of Vision. Senses
 Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
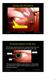 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
The best retinal location"
 How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
How many photons are required to produce a visual sensation? Measurement of the Absolute Threshold" In a classic experiment, Hecht, Shlaer & Pirenne (1942) created the optimum conditions: -Used the best
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE
 Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
Chapter 11 Lesson 4 THE EYE Eye Openers Museum of Vision You need a couple blank sheets of paper. Label each side #1 How We See #2 Binocular Vision #3 Optical Illusions #4 Persistence of Vision On Packet
What determines data speed?
 PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
PHY385-H1F Introductory Optics Class 12 Outline: Section 5.7, Sub-sections 5.7.1 5.7.6 Fibre-Optics The Human Eye Corrective Lenses Pinhole Camera Camera Depth of Field What determines data speed? Broadband
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception
 Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Lecture 15 End Chap. 6 Optical Instruments (2 slides) Begin Chap. 7 Visual Perception Mar. 2, 2010 Homework #6, on Ch. 6, due March 4 Read Ch. 7, skip 7.10. 1 2 35 mm slide projector Field lens is used
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1
 Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
Low Vision Assessment Components Job Aid 1 Eye Dominance Often called eye dominance, eyedness, or seeing through the eye, is the tendency to prefer visual input a particular eye. It is similar to the laterality
Handout G: The Eye and How We See
 Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
CS 534: Computer Vision
 CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15
 Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY
 OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Color Perception. Color, What is It Good For? G Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney. perceptual organization. perceptual organization
 G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
G892223 Perception October 5, 2009 Maloney Color Perception Color What s it good for? Acknowledgments (slides) David Brainard David Heeger perceptual organization perceptual organization 1 signaling ripeness
Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert
 University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
10.2 Color and Vision
 10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE
 LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE Overview: By dissecting a mammalian eye, students will learn how the lens in the eye focuses light to form an image of an object. They will also learn the main parts of
LESSON 5 - THE OPTICS OF THE EYE Overview: By dissecting a mammalian eye, students will learn how the lens in the eye focuses light to form an image of an object. They will also learn the main parts of
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night.
 Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Nervous System Lab Make up Reflexes, Sensory Receptors, and Reaction Time
 Nervous System Lab Make up Reflexes, Sensory Receptors, and Reaction Time Purpose: To explore the body s reflexes, sensory receptors and reaction times and relate the findings to our study of the nervous
Nervous System Lab Make up Reflexes, Sensory Receptors, and Reaction Time Purpose: To explore the body s reflexes, sensory receptors and reaction times and relate the findings to our study of the nervous
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Mastery. Chapter Content. What is light? CHAPTER 11 LESSON 1 C A
 Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Handout 1: Color Survey
 Handout : Color Survey Have you ever thought about whether everyone sees colors in the same way? Here s your chance to find out! Your teacher will display crayons or slides. Categorize each of the 5 colors
Handout : Color Survey Have you ever thought about whether everyone sees colors in the same way? Here s your chance to find out! Your teacher will display crayons or slides. Categorize each of the 5 colors
Biology 9 Senses Lab
 Biology 9 Senses Lab Objectives: To understand the anatomy and physiology of several of our senses both through observation and by means of some simple experiments and examinations. PART 1: The Eye 1.
Biology 9 Senses Lab Objectives: To understand the anatomy and physiology of several of our senses both through observation and by means of some simple experiments and examinations. PART 1: The Eye 1.
Optics. Experiment #4
 Optics Experiment #4 NOTE: For submitting the report on this laboratory session you will need a report booklet of the type that can be purchased at the McGill Bookstore. The material of the course that
Optics Experiment #4 NOTE: For submitting the report on this laboratory session you will need a report booklet of the type that can be purchased at the McGill Bookstore. The material of the course that
Inquiry Unit for CT State Science Standard 5.2
 Inquiry Unit for CT State Science Standard 5.2 Hope Pardee hpardee@milforded.org Marilyn Odell scinco@snet.net Christina Holth cholth@salem.cen.ct.gov Inquiry Institute Classroom Applications Summer 2007
Inquiry Unit for CT State Science Standard 5.2 Hope Pardee hpardee@milforded.org Marilyn Odell scinco@snet.net Christina Holth cholth@salem.cen.ct.gov Inquiry Institute Classroom Applications Summer 2007
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016
 Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Lecture 8. Lecture 8. r 1
 Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision
 The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
The Human Eye Nearpoint of vision Rochelle Payne Ondracek Edited by Anne Starace Abstract The human ability to see is the result of an intricate interconnection of muscles, receptors and neurons. Muscles
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
EXAMINATION OF THE CENTRAL VISUAL FIELD AT
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 408 EXAMINATION OF THE CENTRAL VISUAL FIELD AT A READING DISTANCE*t BY V. N. HIGHMAN Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London THIS investigation was started in an attempt
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 408 EXAMINATION OF THE CENTRAL VISUAL FIELD AT A READING DISTANCE*t BY V. N. HIGHMAN Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London THIS investigation was started in an attempt
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
The Eye. Morphology of the eye (continued) Morphology of the eye. Sensation & Perception PSYC Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D
 Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D The Eye The Eye The function of the eyeball is to protect the photoreceptors The role of the eye is to capture an image of objects that we
Sensation & Perception PSYC420-01 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D The Eye The Eye The function of the eyeball is to protect the photoreceptors The role of the eye is to capture an image of objects that we
13. Optical Instruments*
 13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
