Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
|
|
|
- Lorena Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Human Vision
2 SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses
3 SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
4 SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT Limitations of the Senses 4 Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish Spatially Imprecise source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
5 VISUAL ORIENTATION 3-D Neurobehavioral Model 5 Focal Extrapersonal (object recognition) Ambient Extrapersonal Action Extrapersonal (navigation) Peripersonal (reaching) Peripersonal Ambient Extrapersonal (Spatial orientation) Action Extrapersonal Focal Extrapersonal Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
6 VISUAL ORIENTATION The Two Visual System Hypothesis 6 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
7 VISUAL ORIENTATION The Two Visual System Hypothesis 7 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Focal Mode Object recognition ( What? ) Processes fine visual details Confined to central visual field Conscious processing (attention demanding) Synthetic spatial orientation
8 VISUAL ORIENTATION The Two Visual System Hypothesis 8 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Focal Mode Object recognition ( What? ) Processes fine visual details Confined to central visual field Conscious processing (attention demanding) Synthetic spatial orientation
9 VISUAL ORIENTATION 9 Alterations of The Ambient Visual Frame Distortion -- The Ames Room Absence -- The Black Hole Approach This image is in the public domain. Source: Wikipedia. Distortion -- Memory Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Original Remembered source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
10 VISUAL ORIENTATION 10 Ambient Visual Effects (Self-Motion) Characteristics of Vection Requires large retinal area (including periphery) More dependent on background visual field Relies on moving textures (sluggish response, low frequency) Can occur with optically degraded stimuli Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
11 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Effects (Self-Position) 11 Characteristics of Field-Dependence Similar visual requirements as vection (e.g., reliance on background field, can tolerate optical degradation) Tilted scenes produces changes in perceived visual vertical, gravitational vertical and posture Other position effects (luminance gradients, depth) Rod-and-frame
12 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Effects (Self-Position) 12 Characteristics of Field-Dependence Similar visual requirements as vection (e.g., reliance on background field, can tolerate optical degradation) Tilted scenes produces changes in perceived visual vertical, gravitational vertical and posture Other position effects (luminance gradients, depth) Rod-and-frame
13 VISUAL ORIENTATION 13 Ambient Visual Effects (Self-Position) Characteristics of Field-Dependence Similar visual requirements as vection (e.g., reliance on background field, can tolerate optical degradation) Tilted scenes produces changes in perceived visual vertical, gravitational vertical and posture Other position effects (luminance gradients, depth) Rod-and-frame Postural Effects source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
14 VISUAL ORIENTATION 14 Ambient Visual Effects (Self-Position) Characteristics of Field-Dependence Similar visual requirements as vection (e.g., reliance on background field, can tolerate optical degradation) Tilted scenes produces changes in perceived visual vertical, gravitational vertical and posture Other position effects (luminance gradients, depth) Rod-and-frame source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see Postural Effects Optokinetic-Cervical Reflex
15 VISUAL ORIENTATION 15 Ambient Luminance Gradients Luminance Gradients Light-to-Dark Gradient Important in Judging Visual Vertical Gradient Inversions Caused by Low Sun Angles Clouds Terrain Shadowing Lunar Reflections Can Result in Inversion Illusions source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
16 VISUAL ORIENTATION 16 Ambient Luminance Gradients Luminance Gradients Light-to-Dark Gradient Important in Judging Visual Vertical Gradient Inversions Caused by Low Sun Angles Clouds Terrain Shadowing Lunar Reflections, etc. Can Result in Inversion Illusions source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
17 VISUAL ORIENTATION 17 Ambient Luminance Gradients Luminance Gradients Light-to-Dark Gradient Important in Judging Visual Vertical Gradient Inversions Caused by Low Sun Angles Clouds Terrain Shadowing Lunar Reflections, etc. Can Result in Inversion Illusions Inverted source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
18 VISUAL ORIENTATION 18 Ambient Luminance Gradients Luminance Gradients Light-to-Dark Gradient Important in Judging Visual Vertical Gradient Inversions Caused by Low Sun Angles Clouds Terrain Shadowing Lunar Reflections, etc. Can Result in Inversion Illusions Upright source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
19 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Cues to Depth 19 Ambient Depth Cues Linear perspective/foreshortening Gradient of texture Motion parallax Illumination Aerial perspective Image courtesy of Patrick M. on Flickr. Linear perspective Image courtesy of Cameron Chamberlain on Flickr. Aerial perspective Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Motion parallax
20 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Cues to Depth 20 Linear Perspective & Gradient of Texture Linear perspective Aerial perspective Image courtesy of Patrick M. on Flickr. Motion parallax
21 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Cues to Depth 21 Ambient Depth Cues Linear perspective/foreshortening Gradient of texture Motion parallax Illumination Aerial perspective Image courtesy of Patrick M. on Flickr. Linear perspective Image courtesy of Cameron Chamberlain on Flickr. Aerial perspective Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Motion parallax
22 VISUAL ORIENTATION 22 Ambient Visual Cues to Depth Motion Parallax Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
23 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Cues to Depth 23 Ambient Depth Cues Linear perspective/foreshortening Gradient of texture Motion parallax Illumination Aerial perspective Image courtesy of Patrick M. on Flickr. Linear perspective Image courtesy of Cameron Chamberlain on Flickr. Aerial perspective Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Motion parallax
24 VISUAL ORIENTATION Ambient Visual Cues to Depth 24 Aerial Perspective Image courtesy of Cameron Chamberlain on Flickr.
25 VISUAL ORIENTATION Focal Visual Effects 25 Size and Shape Constancies Rigidity is considered to be a fundamental property of objects; therefore, deviations in the size and shape of ground objects are perceived as changes in our orientation relative to the ground Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. (a) (a) (b) (b) (c) (c) Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Size Constancy Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Shape Constancy
26 VISUAL ORIENTATION Focal Visual Effects 26 Size and Shape Constancies Rigidity is considered to be a fundamental property of objects; therefore, deviations in the size and shape of ground objects are perceived as changes in our orientation relative to the ground Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. (a) (a) (b) (b) (c) (c) Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Size Constancy Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Shape Constancy
27 VISUAL ORIENTATION Focal Visual Effects 27 Size and Shape Constancies Rigidity is considered to be a fundamental property of objects; therefore, deviations in the size and shape of ground objects are perceived as changes in our orientation relative to the ground Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. (a) (a) (b) (b) (c) (c) Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Size Constancy Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Shape Constancy
28 Contents 28 Introduction Contrast & Frequency Visual Pathway, Visual Image Receptive Fields, Gestalt Color, Color deficits, after images Size of objects
29 Spatial Frequency and Contrast 29 Contrast amplitude Spatial frequency of grid This image is in the public domain. For more examples:
30 Optic nerve - from eye to brain 30 Left visual field -> right brain side Right visual field -> left brain side Left visual field Right visual field Number of cells Rods: 125 * 10 6 Cones: Ganglion: Optic nerv: Optic nerv: 6 * * * * 10 6 Primary visual cortex: 250 * 10 6 Retina 11cm 2 Optic nerve diameter 2mm Temporal Nasal Temporal Optic chiasm convergence receptors ->ganglion Pulvinar nucleus Lateral geniculate nucleus Superior colliculus divergence optic nerv -> visual cortex Optic radiation Primary visual cortex Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
31 Rod and cone density 31 Blind spot Fovea Image of rods and cones removed due to copyright restrictions. Number/mm 2 Rods Rods Cones 50 o 70 o 30 o 10 o 0 Distance across retina 10 o 30 o 50 o 70 o 90 o Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. On average 120 rods converge on 1 ganglion cell On average 6 cones converge on 1 ganglion cell
32 Image properties 32 source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see Image quality created by retina is not homogenous Color vision mainly in fovea Resolution decreases in periphery Best resolution for color in the fovea Best resolution for b/w 20 parafovela
33 Questions 33 How come that we perceive such a nice and homogenous image of our surrounding? What happened to the blind-spot hole? Why do we perceive color in the periphery?
34 Receptive Fields On Off Light-dot On Off Light-dot On Off Light-dot On Off Light-dot On-center Fields Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. _ + + _ + Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
35 Filling the blind spot 35 X X X Close your left eye and fixated with the right eye the X. Which number is missing? What is the color pattern at the psotion of the missing number? The blind spot is filled with the surrounding pattern.
36 Figure and background 36 The total visual input is organized into figures and background. The Gestalt-laws describe principles how figure and ground are separated. Figures are in front, have a border, connected, things. The background is behind the figure, withour border, uninterrupted, homogenous.
37 Gestalt-laws 37 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
38 Perceptual categories 38 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Square Diamond The shapes in-between are neither square nor diamond. Our perception is organized in categories, even if the stimuli are continuos.
39 Perceptual categories: Reproducing shapes 39 Figure in B is the drawing when the shape of the Figure A is given as a tactile stimulus (without vision). A B Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
40 Emergence 40 source unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see The dog is perceived as a whole, all at once. We do not construct the dog by first identifying its parts, e.g. combining feet, ears, nose, tail, etc.
41 Invariance 41 simple geometrical objects are recognized independent of rotation, translation, and scale, (and other deformations) Objects in A are immediately recognized as the same shape, are different from those in B, are the same as in C despite perspective and elastic deformations, and can be depicted using different graphic elements as in D. This image is in the public domain. Source: Wikipedia.
42 Reification 42 The perceived object can contain more information as given by the sensory input. (e.g. ball in C) Mostly for spatial information. This image is in the public domain. Source: Wikipedia.
43 Multistable perception 43 This image is in the public domain. Source: Wikipedia. Necker cube Rubin's Figure / Vase Ambiguous perceptual experiences (2 figures share a common border) lead to multistable perception. The experiences pop back and forth between two or more alternative interpretations.
44 What are the components? 44 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
45 Some of the combinations 45 Tasten Aufbau Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
46 Color 46 Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Original image can be viewed on Wikimedia. Wavelength - physics Color - perception Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Original image can be viewed on Wikimedia.
47 Color blindness 47 Normal color vision is trichormat, 3 cone types are used. Dichromacy, most common Red-Green color blindness lacking or reduced long-wavelength or medium-wavelength cones (4-8% of the male population!) includes: Protanopia (rare), Deuteranopia (1% m), Protanomaly (1% m), Deuteranomaly (6% m) Monochromacy, complete inability to distinguish any colors cone monochromacy (only 1 cone type) rod monochromacy (only rods) Human Factors Color codes (Maps, Signals, etc) Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Original image can be viewed on Wikimedia.
48 Color blindness - samples Trichormat (all cones) 48 Protanopia (L-cone) Deutanopia (M-cone) Tritanopia (S-cone) sources unknown. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license. For more information, see
49 Color vision - after images 1 49 Fixate center dot on flag for 1 minute, then look at a white surface
50 Color vision - after images 2 50
51 51 0,5 Grad MOON 3476 Kilometer Kilometer 0,5 Grad SUN 1,392 Million Kilometer 149,6 Million Kilometer Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
52 Perceived size How to estimate the distance of person? 52 Image Angel D P = D/S W = P *K P P W f Sinnesorgan f -1 Eye Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. S K
53 Additional Slides 53 Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
54 Major parts 54 Occipital lobe: visual perception system E.g., visuospatial processing, discrimination of movement and colour discrimination Adapted from Stangor, C. Introduction to Psychology. Flatworld Knowledge, Courtesy of Flatworld Knowledge.
55 Sensory Maps - Homunculus 55 Image of Homunculus removed due to copyright restrictions.
56 56 Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Original image can be viewed on Scientific American.
57 Figure 6.3 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, Preview image with Google Books.
58 Figure 6.8 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, Preview image with Google Books.
59 Figure 6.9 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, Preview image with Google Books.
60 Figure 6.12 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, 2008.
61 Figure 6.15 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, 2008.
62 Figure 6.16 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, 2008.
63 Figure 6.17 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, 2008.
64 Figure 6.17 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, 2008.
65 Figure 6.22 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, Preview image with Google Books.
66 Figure 6.23 removed due to copyright restrictions. Source: Proctor, Robert W., and Trisha Van Zandt. Human Factors in Simple and Complex Systems. CRC Press, Preview image with Google Books.
67 MIT OpenCourseWare / Human Factors Engineering Fall 2011 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
VISION. John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00
 VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00 Objectives Purposes of vision Problems that the visual system has to overcome Neural organization of vision Human Perceptual Abilities Detect a candle, 30 miles
VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00 Objectives Purposes of vision Problems that the visual system has to overcome Neural organization of vision Human Perceptual Abilities Detect a candle, 30 miles
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Content removed due
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Creative Computing II
 Creative Computing II Christophe Rhodes c.rhodes@gold.ac.uk Autumn 2010, Wednesdays: 10:00 12:00: RHB307 & 14:00 16:00: WB316 Winter 2011, TBC Ambiguity Image Walter Ehrenstein (1899 1961) Zeitschrift
Creative Computing II Christophe Rhodes c.rhodes@gold.ac.uk Autumn 2010, Wednesdays: 10:00 12:00: RHB307 & 14:00 16:00: WB316 Winter 2011, TBC Ambiguity Image Walter Ehrenstein (1899 1961) Zeitschrift
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Visual Perception. Jeff Avery
 Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
2/3/2016. How We Move... Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Ecological View. Sensory Processing.
 How We Move Sensory Processing 2015 MFMER slide-4 2015 MFMER slide-7 Motor Processing 2015 MFMER slide-5 2015 MFMER slide-8 Central Processing Vestibular Somatosensation Visual Macular Peri-macular 2015
How We Move Sensory Processing 2015 MFMER slide-4 2015 MFMER slide-7 Motor Processing 2015 MFMER slide-5 2015 MFMER slide-8 Central Processing Vestibular Somatosensation Visual Macular Peri-macular 2015
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling
 Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Spatial coding: scaling, magnification & sampling Snellen Chart Snellen fraction: 20/20, 20/40, etc. 100 40 20 10 Visual Axis Visual angle and MAR A B C Dots just resolvable F 20 f 40 Visual angle Minimal
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness )
 Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Frog Vision. PSY305 Lecture 4 JV Stone
 Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
Frog Vision Template matching as a strategy for seeing (ok if have small number of things to see) Template matching in spiders? Template matching in frogs? The frog s visual parameter space PSY305 Lecture
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington Visual sensory physiology.
 This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
This article reprinted from: Linsenmeier, R. A. and R. W. Ellington. 2007. Visual sensory physiology. Pages 311-318, in Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching, Volume 28 (M.A. O'Donnell, Editor). Proceedings
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Meeting of Modern Science and School Physics: College for School Teachers of Physics in ICTP. 27 April - 3 May, Vision and illusions
 2234-19 Meeting of Modern Science and School Physics: College for School Teachers of Physics in ICTP 27 April - 3 May, 2011 Vision and illusions Alexandre Bouzdine University of Bordeaux France VISION
2234-19 Meeting of Modern Science and School Physics: College for School Teachers of Physics in ICTP 27 April - 3 May, 2011 Vision and illusions Alexandre Bouzdine University of Bordeaux France VISION
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
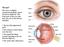 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Sensation, Part 4 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 20, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 From last time T. M. D'Zmura 2 Rod Transduction
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
Digital Image Processing IMAGE PERCEPTION & ILLUSION Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 What is color? Image perception Color matching Color gamut Color balancing Illusions What is Color? 3 Visual perceptual
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
CS 534: Computer Vision
 CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
CS 534: Computer Vision Spring 2004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Human Vision - 1 Human Vision Outline How do we see: some historical theories of vision Human vision: results
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
3D Space Perception. (aka Depth Perception)
 3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
Question From Last Class
 Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Question From Last Class What is it about matter that determines its color? e.g., what's the difference between a surface that reflects only long wavelengths (reds) and a surfaces the reflects only medium
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
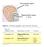 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Review, the visual and oculomotor systems
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2013 Review, the visual and oculomotor systems 1 Basic wiring of the visual system 2 Primates Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016
 Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Lecture 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Fall 2016 Contents Elements of visual perception Light and the electromagnetic spectrum Image sensing
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal. Victor Ostromoukhov - Université de Montréal
 IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
IFT3355 Victor Ostromoukhov Université de Montréal full world 2 1 in art history Mondrian 1921 The cave of Lascaux About 17000 BC Vermeer mid-xvii century 3 is one of the most effective visual attributes
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
TSBB15 Computer Vision
 TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
TSBB15 Computer Vision Lecture 9 Biological Vision!1 Two parts 1. Systems perspective 2. Visual perception!2 Two parts 1. Systems perspective Based on Michael Land s and Dan-Eric Nilsson s work 2. Visual
Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
Don t twinkle, little star!
 Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Lecture 16 Ch. 6. Optical instruments (cont d) Single lens instruments Eyeglasses Magnifying glass Two lens instruments Microscope Telescope & binoculars The projector Projection lens Field lens Ch. 7,
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
