Pre-Calculus. Riemann Sums. Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163. Slide 3 / 163. Slide 4 / 163. Slide 5 / 163. Slide 6 / 163. Intro to Integrals
|
|
|
- Kenneth McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 Pre-alculus Intro to Integrals Slide 3 / 163 Table of ontents Riemann Sums Trapezoid Rule ccumulation Function & efinite Integrals Fundamental Theorem of alculus rea etween urves Volume: Shell Method click on the topic to go to that section Slide 4 / 163 Riemann Sums Return to Table of ontents Slide 5 / 163 Slide 6 / 163 onsider the following velocity graph: 30 mph ut we seldom travel at a constant speed. 50 mph 5 hrs How far did the person drive? The area under the velocity graph is the total distance traveled. Integration is used to find the area. 5 hrs The area under this graph is still the distance traveled but we need more than multiplication to find it.
2 Slide 7 / 163 Slide 8 / 163 George Riemann (Re-mon) studied making these curves into a series of rectangles. Riemann Sums, or Rectangular pproximation Method (RM), is calculated by drawing rectangles from the x-axis up to the curve. The question is: What part of the "top" of the rectangle should be used to determine the height of the rectangle? So the area under the curve would be the sum of areas of the rectangles, this is called Riemann Sums. The right hand corner. (RRM) The left hand corner. (LRM) The middle. (MRM) Slide 9 / 163 Slide 10 / 163 Example: Find the area between y = x 2, the x-axis, and [0,1] using Riemann Sums and 4 partitions. LRM Example: Find the area between y = x 2, the x-axis, and [0,1] using Riemann Sums and 4 partitions. RRM 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1 Found the width of the rectangle: (b-a)/n= (1-0)/4 = 1/4 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1 Is this approximation an overestimate or an underestimate? Is this approximation an overestimate or an underestimate? Slide 11 / 163 Slide 12 / 163 Example: Find the area between y = x 2, the x-axis, and [0,1] using Riemann Sums and 4 partitions. MRM *NOTE: MRM LRM + RRM 2 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1 This value falls between LRM and RRM.
3 Slide 13 / 163 Slide 14 / When finding the area between and the x-axis [1,3] using four partitions, how wide should each interval be? Slide 15 / 163 Slide 16 / Find the area between and the x-axis [1,3] using four partitions and LRM. 3 Find the area between and the x-axis [1,3] using four partitions and RRM. Slide 17 / 163 Slide 18 / When finding the area between and the x-axis [1,3] using four partitions and MRM, when in the third rectangle, what x should be used to find the height? 5 Find the area between and the x-axis [1,3] using four partitions and MRM.
4 Slide 19 / 163 Slide 20 / 163 We can write the four areas using Selected Rules for Sigma where a k is the area of the k th rectangle. It is just another way of writing what we just did. # is the Greek letter sigma and stands for the summation of all the terms evaluated at starting with the bottom number and going through to the top. Slide 21 / 163 Slide 22 / st n integers: Equivalent Formulas 6 1 st n squares: 1 st n cubes: Slide 23 / 163 Slide 24 / 163 7
5 Slide 25 / 163 Slide 26 / 163 Trapezoid Rule Return to Table of ontents Slide 27 / 163 Slide 28 / 163 Example: Find the area y = x 2 and the x-axis [0,1] using 4 partitions. Example: Find the area y = x 2 and the x-axis [0,1] using 4 partitions and the trapezoids. Trapezoids 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1 Why were areas found using RM only estimates? How could we draw lines to improve our estimates? What shape do you get? 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1 Slide 29 / 163 *NOTE: Trapezoid pproximation = LRM + RRM 2 Slide 30 / The area between and the x-axis [1,3] is approximated with 4 partitions and trapezoids. What is the height of each trapezoid? We could make our approximation even closer if we used parabolas instead of lines as the tops of our intervals. This is called Simpson's Rule but this is not on the P alc exam.
6 Slide 31 / 163 Slide 32 / The area between and the x-axis [1,3] is approximated with 4 partitions and trapezoids. What is the area of the 4 th trapezoid? 12 The area between y = and the x-axis [1,3] is approximated with 4 partitions and trapezoids. What is the approximate area? Slide 33 / 163 Slide 34 / What is the approximate area using the trapezoids that are drawn? 14 What is the approximate fuel consumed using the trapezoids rule for this hour flight? Time (minutes) Rate of onsumption (gal/min) Slide 35 / 163 In the last 2 responder questions, the partitioned intervals weren't uniform. The P will use both. So don't assume. Slide 36 / 163 So far we have been summing areas using #. Gottfried Leibniz, a German mathematician, came up with a symbol you're going to see a lot of: #. It is actually the German S instead of the Greek. It still means summation. s a point of interest, we use the German notation in calculus because Leibniz was the first to publish. Sir Isaac Newton is now given the credit for unifying calculus because his notes predate Leibniz's.
7 Slide 37 / 163 Slide 38 / 163 ccumulation Function ccumulation Function V (m/s) nother way we can calculate area under a function is to use geometry. t (sec) What's happening during t=0 to t=3? What is the area of t=0 to t=3? What does the area mean? What is the acceleration at t=3? Return to Table of ontents What is happening during t=3 to t=6? What is the area of t=3 to t=6? What does this area mean? Where is the object at t=6 in relation to where it was at t=0? Slide 39 / 163 Slide 40 / 163 ccumulation Function The symbol notation for the area from zero to 3: "The area from t=0 to t=3 is the integral from 0 to 3 of the velocity function with respect to t." In general: Slide 41 / 163 Slide 42 / 163 ccumulation Function When solving an accumulation function: (direction)(relation to x-axis)(area) ccumulation Function 15 semicircle
8 Slide 43 / 163 Slide 44 / 163 ccumulation Function ccumulation Function 16 (round to two decimal places) 17 (round to two decimal places) semicircle semicircle Slide 45 / 163 Slide 46 / 163 ccumulation Function 18 semicircle Slide 47 / 163 Slide 48 / 163 rea under the curve of f(x) from a to b is & efinite Integrals We have been using geometry to find. The antiderivative of f(x) can also be used. Return to Table of ontents
9 Slide 49 / 163 Slide 50 / 163 Properties of efinite Integrals 20 Slide 51 / 163 Slide 52 / Slide 53 / 163 Slide 54 / ntiderivative Rules Why +?
10 Slide 55 / 163 Slide 56 / 163 Slide 57 / 163 Slide 58 / Slide 59 / 163 Slide 60 /
11 Slide 61 / 163 Slide 62 / Slide 63 / 163 Slide 64 / Slide 65 / 163 Slide 66 / 163 The graphing calculator also has a built-in integration function. MTH -> 9:fnInt( depending on the version of the operating system: fnint( or For example, integrate x 2-3 from 1 to 4 with respect to x. fnint(x 2-3,x,1,4) Fundamental Theorem of alculus Return to Table of ontents
12 Slide 67 / 163 Slide 68 / 163 Fundamental Theorem of alculus Fundamental Theorem of alculus (F.T..) Part 2 If F(x) is continuous at every point of [a,b] then has a derivative at every point on [a,b],and Slide 69 / 163 Slide 70 / 163 Fundamental Theorem of alculus Fundamental Theorem of alculus Example: 31 It looks easy, but be aware. When the derivative of the bounds in anything other that 1, need to multiply f(x) by the derivative. Slide 71 / 163 Slide 72 / 163 Fundamental Theorem of alculus Fundamental Theorem of alculus 32 33
13 Slide 73 / 163 Slide 74 / 163 Fundamental Theorem of alculus 34 HINT Return to Table of ontents Slide 75 / 163 Slide 76 / 163 Just like with differentiation, there are many integrals that are more complicated to evaluate. In situations like these, we use the to turn a difficult integral into a much simpler one. Slide 77 / 163 Slide 78 / 163 Ex: Ex: Let Let
14 Slide 79 / 163 Slide 80 / What is the value of u? 36 What will the integral be after the substitution is made? Slide 81 / 163 Slide 82 / Evaluate the integral The If you have a definite integral, you have two options for plugging in the bounds to get the final answer. 1. Plug a and b into the integrated function FTER you have re-substituted the x's back into the function 2. Plug a and b into to create two new bounds, and plug these into the integrated function Slide 83 / 163 Slide 84 / 163 Ex: 38 What is the value of u? Let
15 Slide 85 / What is the new upper bound? Slide 86 / What is the new lower bound? Slide 87 / 163 Slide 88 / What will the integral be after the substitution is made? 42 What is the value of the integral? Slide 89 / 163 Slide 90 / What is the value of u? 44 What is the new upper bound?
16 Slide 91 / 163 Slide 92 / What is the new lower bound? 46 What will the integral be after the substitution is made? Slide 93 / 163 Slide 94 / What is the value of the integral? rea etween urves Return to Table of ontents Slide 95 / 163 Slide 96 / 163
17 Slide 97 / 163 Slide 98 / 163 rea etween urves rea etween urves 48 When finding the area between and, what is the left bounds of x? 49 When finding the area between and, what is the right bounds of x? Slide 99 / 163 Slide 100 / 163 rea etween urves rea etween urves 50 When finding the area between and, what is integral used? 51 What is the area between and? Slide 101 / 163 Slide 102 / 163
18 Slide 103 / 163 Slide 104 / 163 Slide 105 / 163 Example: Find the area between the curves in the first quadrant. Notice that the lower function isn't the same for the entire region. We could find the area in terms of y or divide the region into 2 separate integrals and add their areas. rea etween urves 55 Slide 106 / 163 When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what would be the area to the left of the y-axis? Slide 107 / 163 Slide 108 / 163 rea etween urves 56 When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what is the left bounds of h(x) - f(x)? rea etween urves 57 When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what is the right bound of h(x) - f(x)?
19 rea etween urves 58 Slide 109 / 163 When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what would be the area to the right of the y-axis? rea etween urves Slide 110 / When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what is the right bound of h(x) - g(x)? Slide 111 / 163 Slide 112 / 163 rea etween urves 60 When finding the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1, what is the left bound of h(x) - g(x)? rea etween urves 61 Find the area between f(x) = x, g(x) = -1/2x, and h(x) =1/2x - 1. Slide 113 / 163 Slide 114 / 163 nother way to make a 3- object is to take a region and rotate it about an axis. Volume: isk Method When this rectangle is rotated a cylinder is formed. We could use geometry, but can we use calculus? Return to Table of ontents From the section on known cross sections: nd since the cross sections are circles:
20 Slide 115 / 163 Slide 116 / 163 Rotate about x-axis from x=1 to x=4. When rotating about a horizontal axis: When rotating about a vertical axis: Slide 117 / 163 Slide 118 / 163 Rotate about y=2 from x=1 to x=4. Since y=2 is a horizontal axis of rotation, integral is in terms of x. Rotate about y= -2 from x=1 to x=4. Since y=-2 is a horizontal axis of rotation, integral is in terms of x. y -2 r=2-y Why? From the x-axis to the curve is y and to axis of rotation is 2, we want upper minus lower. r=y- -2=y+2 Why? upper minus lower Slide 119 / 163 Slide 120 / Rotate y=2x 2 about the x-axis over [0,5]. What is the lower bound? 63 Rotate y=2x 2 about the x-axis over [0,5]. What is the upper bound?
21 Slide 121 / 163 Slide 122 / Rotate y=2x 2 about the x-axis over [0,5]. What is integral? 65 Rotate y=2x 2 about the x-axis over [0,5]. What is the volume? Slide 123 / 163 Slide 124 / Rotate y=2x 2 about the line x=4 over [0,5]. What is the lower bound? 67 Rotate y=2x 2 about the line x=4 over [0,5]. What is the upper bound? Slide 125 / 163 Slide 126 / Rotate y=2x 2 about the line x=4 over [0,5]. What is the radius? 69 Rotate y=2x 2 about the line x=4 over [0,5]. What is integral?
22 Slide 127 / Rotate y=2x 2 about the line x=4 over [0,5]. What is the volume? Slide 128 / 163 Rotate for x=0 to x=2 about the y-axis. Since this is a vertical axis,the problem should be rewritten in terms of y: Rotate for y=0 to y=16 about the y-axis. 16 Slide 129 / 163 Slide 130 / 163 Rotate for x=0 to x=2 about the x=2. Since this is a vertical axis, the problem should be rewritten in terms of y: 71 Rotate about the y-axis over. What is the lower bound? 16 Rotate for y=0 to y=16 about the x=2. Slide 131 / 163 Slide 132 / Rotate about the y-axis over. What is the upper bound? 73 Rotate about the y-axis over. What is the radius?
23 Slide 133 / 163 Slide 134 / Rotate about the y-axis over. What is integral? 75 Rotate about the y-axis over. What is the volume? Slide 135 / 163 Slide 136 / 163 Slide 137 / 163 Slide 138 / 163
24 Slide 139 / 163 Slide 140 / 163 Volume: Washer Method Return to Table of ontents Slide 141 / 163 Slide 142 / 163 For the washer method, there is a gap between the region being rotated and the axis. When rotating about a horizontal axis: Rotating this rectangle we get a tube, or a cylinder with a smaller cylinder taken away. Where R is the greater distance from the axis, not necessarily the upper function. When rotating about a vertical axis: Our cross section would be: R r *aution: # can be factored out but not the square. Slide 143 / 163 Slide 144 / 163 Find the volume when f(x) and g(x) are rotated about the x-axis [0,2]. Rotate the region bound by y=x 2, x=2, and y=0 about the y-axis. Since a vertical axis of rotation, integration is done in terms of y. (2,4) Hint
25 Slide 145 / 163 Slide 146 / 163 Rotate the region bound by x-axis, y=x 2, x=1, and x=2 about y= -1. Since y= -1 is horizontal integration is done in terms of x. 81 Rotate the region between and about the x-axis over [0,1]. What is the lower bound? r=1 R=x 2 +1 Slide 147 / 163 Slide 148 / Rotate the region between and about the x-axis over [0,1]. What is the upper bound? 83 Rotate the region between and about the x-axis over [0,1]. What is integral? Slide 149 / 163 Slide 150 / Rotate the region between and about the x-axis over [0,1]. What is the volume? 85 Rotate the region between and about the y-axis over [0,1]. What is integral?
26 Slide 151 / 163 Slide 152 / Rotate the region between and about the y-axis over [0,1]. What is the volume? 87 Rotate the region between and about the y=1 over [0,1]. What is R? Slide 153 / 163 Slide 154 / Rotate the region between and about the y=1 over [0,1]. What is integral? 89 Rotate the region between and about the y=1 over [0,1]. What is the volume? Slide 155 / 163 Slide 156 / Rotate the region between and about the x=-1 over [0,1]. What is integral? 91 Rotate the region between and about the x=-1 over [0,1]. What is the volume?
27 Slide 157 / 163 Slide 158 / 163 Volume: Shell Method Volume: Shell Method Volume: Shell Method When rotating about a horizontal axis: Return to Table of ontents When rotating about a vertical axis: Slide 159 / 163 Slide 160 / 163 Volume: Shell Method Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the area between the graph of and about the y-axis. Slide 161 / 163 Slide 162 / 163 Volume: Shell Method 92 Find the volume of the solid generated by rotating the area under the graph of from about the y-axis.
28 Slide 163 / 163 Volume: Shell Method 93 Find the volume of the solid generated by rotating the area between the graphs of and about the y-axis.
33. Riemann Summation over Rectangular Regions
 . iemann Summation over ectangular egions A rectangular region in the xy-plane can be defined using compound inequalities, where x and y are each bound by constants such that a x a and b y b. Let z = f(x,
. iemann Summation over ectangular egions A rectangular region in the xy-plane can be defined using compound inequalities, where x and y are each bound by constants such that a x a and b y b. Let z = f(x,
Pre-Calc. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160. Slide 4 / 160. Slide 3 / 160. Slide 5 / 160. Slide 6 / 160.
 Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-alc onics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Slide 4 / 160 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas Intro to
Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-alc onics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Slide 4 / 160 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas Intro to
A General Procedure (Solids of Revolution) Some Useful Area Formulas
 Goal: Given a solid described by rotating an area, compute its volume. A General Procedure (Solids of Revolution) (i) Draw a graph of the relevant functions/regions in the plane. Draw a vertical line and
Goal: Given a solid described by rotating an area, compute its volume. A General Procedure (Solids of Revolution) (i) Draw a graph of the relevant functions/regions in the plane. Draw a vertical line and
Math 122: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
Exam Information Math 1: Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam will be given on Wednesday, December 1th from 8-1 am. The exam is cumulative and will cover sections 5., 5., 5.4, 5.5, 5., 5.9,.1,.,.4,.,
INTEGRATION OVER NON-RECTANGULAR REGIONS. Contents 1. A slightly more general form of Fubini s Theorem
 INTEGRATION OVER NON-RECTANGULAR REGIONS Contents 1. A slightly more general form of Fubini s Theorem 1 1. A slightly more general form of Fubini s Theorem We now want to learn how to calculate double
INTEGRATION OVER NON-RECTANGULAR REGIONS Contents 1. A slightly more general form of Fubini s Theorem 1 1. A slightly more general form of Fubini s Theorem We now want to learn how to calculate double
Pre-Calc Conics
 Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-Calc Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-Calc Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Pre-Calc. Slide 1 / 160. Slide 2 / 160. Slide 3 / 160. Conics Table of Contents. Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas
 Slide 1 / 160 Pre-Calc Slide 2 / 160 Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 160 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Slide 1 / 160 Pre-Calc Slide 2 / 160 Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 160 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
MATH 20C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM
 MATH 2C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM Name Please circle the answer to each of the following problems. You may use an approved calculator. Each multiple choice problem is worth 2 points.. Multiple
MATH 2C: FUNDAMENTALS OF CALCULUS II FINAL EXAM Name Please circle the answer to each of the following problems. You may use an approved calculator. Each multiple choice problem is worth 2 points.. Multiple
Pre Calc. Conics.
 1 Pre Calc Conics 2015 03 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections Parabolas Circles Ellipses Hyperbolas
1 Pre Calc Conics 2015 03 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections Parabolas Circles Ellipses Hyperbolas
Math 2321 Review for Test 2 Fall 11
 Math 2321 Review for Test 2 Fall 11 The test will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1-16.5 of chapter 16. These review sheets consist of problems similar to ones that could appear on the test. Some problems
Math 2321 Review for Test 2 Fall 11 The test will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1-16.5 of chapter 16. These review sheets consist of problems similar to ones that could appear on the test. Some problems
MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems
 Name: MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems 1. TRUE or FALSE, plus explanation. Give a full-word answer TRUE or FALSE. If the statement is true, explain why, using concepts and results from class to justify
Name: MATH 105: Midterm #1 Practice Problems 1. TRUE or FALSE, plus explanation. Give a full-word answer TRUE or FALSE. If the statement is true, explain why, using concepts and results from class to justify
Page 1 part 1 PART 2
 Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTERS 1 & Worksheet: 1(a, c), 2(a, c), 3a, 4, 5, 10a, 11b, (Solving inequalities)
 AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTERS 1 & 2 1. Worksheet: 1(a, c), 2(a, c), 3a, 4, 5, 10a, 11b, 12-15 (Solving inequalities) 2. Pg. 25-26: 1, 3, 7, 13, 14 (Functions. Abs. Val., Piece-wise) Pg. 59-62: 3, 7, 13, 19,
AP CALCULUS AB - CHAPTERS 1 & 2 1. Worksheet: 1(a, c), 2(a, c), 3a, 4, 5, 10a, 11b, 12-15 (Solving inequalities) 2. Pg. 25-26: 1, 3, 7, 13, 14 (Functions. Abs. Val., Piece-wise) Pg. 59-62: 3, 7, 13, 19,
MATH Exam 2 Solutions November 16, 2015
 MATH 1.54 Exam Solutions November 16, 15 1. Suppose f(x, y) is a differentiable function such that it and its derivatives take on the following values: (x, y) f(x, y) f x (x, y) f y (x, y) f xx (x, y)
MATH 1.54 Exam Solutions November 16, 15 1. Suppose f(x, y) is a differentiable function such that it and its derivatives take on the following values: (x, y) f(x, y) f x (x, y) f y (x, y) f xx (x, y)
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT. Name Period Date
 6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006
 Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006 October 31, 2006 The second midterm exam will take place: Monday, November 13, from 8:15 to 9:30 pm. It will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1 16.4,
Review Sheet for Math 230, Midterm exam 2. Fall 2006 October 31, 2006 The second midterm exam will take place: Monday, November 13, from 8:15 to 9:30 pm. It will cover chapter 15 and sections 16.1 16.4,
Practice problems from old exams for math 233
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Solids Washers /G. TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will be able to visualize the solid generated by revolving the region bounded between two function graphs and the vertical lines x = a and x = b about the x-axis. Students will
Math Objectives Students will be able to visualize the solid generated by revolving the region bounded between two function graphs and the vertical lines x = a and x = b about the x-axis. Students will
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
AREA See the Math Notes box in Lesson for more information about area.
 AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 233 March 30, 2009
 Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 2 March, 29 Midterm 2 covers material that begins approximately with the definition of partial derivatives in Chapter 4. and ends approximately with methods for calculating
Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 2 March, 29 Midterm 2 covers material that begins approximately with the definition of partial derivatives in Chapter 4. and ends approximately with methods for calculating
Estimating Areas. is reminiscent of a Riemann Sum and, amazingly enough, will be called a Riemann Sum. Double Integrals
 Estimating Areas Consider the challenge of estimating the volume of a solid {(x, y, z) 0 z f(x, y), (x, y) }, where is a region in the xy-plane. This may be thought of as the solid under the graph of z
Estimating Areas Consider the challenge of estimating the volume of a solid {(x, y, z) 0 z f(x, y), (x, y) }, where is a region in the xy-plane. This may be thought of as the solid under the graph of z
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Expressions
 Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions
Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions
Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle. Learning Objectives: Materials:
 Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle Lesson Information Written by Jonathan Schweig and Shira Sand Subject: Pre-Calculus Calculus Algebra Topic: Functions Overview: Students will explore some
Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle Lesson Information Written by Jonathan Schweig and Shira Sand Subject: Pre-Calculus Calculus Algebra Topic: Functions Overview: Students will explore some
Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities
 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
Math 118: Business Calculus Fall 2017 Final Exam 06 December 2017
 Math 118: Business Calculus Fall 2017 Final Exam 06 December 2017 First Name: (as in student record) Last Name: (as in student record) USC ID: Signature: Please circle your instructor and lecture time:
Math 118: Business Calculus Fall 2017 Final Exam 06 December 2017 First Name: (as in student record) Last Name: (as in student record) USC ID: Signature: Please circle your instructor and lecture time:
Title: Oct 9 8:27 AM (1 of 30)
 Applied Max and Min (Optimization) 1. If you have 100 feet of fencing and you want to enclose a rectangular area up against a long, straight wall, what is the largest area you can enclose? Title: Oct 9
Applied Max and Min (Optimization) 1. If you have 100 feet of fencing and you want to enclose a rectangular area up against a long, straight wall, what is the largest area you can enclose? Title: Oct 9
MITOCW ocw f07-lec25_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec25_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec25_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units (c) 2006 Correlated to: Utah Core Curriculum for Math (Grade 6)
 Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017
 Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017 Name: Instructions: Be sure to read each problem s directions. Write clearly during the exam and fully erase or mark out anything you do not want graded. You may use your
Calculus 3 Exam 2 31 October 2017 Name: Instructions: Be sure to read each problem s directions. Write clearly during the exam and fully erase or mark out anything you do not want graded. You may use your
Similarly, the point marked in red below is a local minimum for the function, since there are no points nearby that are lower than it:
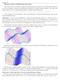 Extreme Values of Multivariate Functions Our next task is to develop a method for determining local extremes of multivariate functions, as well as absolute extremes of multivariate functions on closed
Extreme Values of Multivariate Functions Our next task is to develop a method for determining local extremes of multivariate functions, as well as absolute extremes of multivariate functions on closed
Maxima and Minima. Terminology note: Do not confuse the maximum f(a, b) (a number) with the point (a, b) where the maximum occurs.
 10-11-2010 HW: 14.7: 1,5,7,13,29,33,39,51,55 Maxima and Minima In this very important chapter, we describe how to use the tools of calculus to locate the maxima and minima of a function of two variables.
10-11-2010 HW: 14.7: 1,5,7,13,29,33,39,51,55 Maxima and Minima In this very important chapter, we describe how to use the tools of calculus to locate the maxima and minima of a function of two variables.
Now we are going to introduce a new horizontal axis that we will call y, so that we have a 3-dimensional coordinate system (x, y, z).
 Example 1. A circular cone At the right is the graph of the function z = g(x) = 16 x (0 x ) Put a scale on the axes. Calculate g(2) and illustrate this on the diagram: g(2) = 8 Now we are going to introduce
Example 1. A circular cone At the right is the graph of the function z = g(x) = 16 x (0 x ) Put a scale on the axes. Calculate g(2) and illustrate this on the diagram: g(2) = 8 Now we are going to introduce
Exam 2 Review Sheet. r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t)
 Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
2.3: The Human Cannonball
 2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions
 6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing. 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane
 Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
14.2 Limits and Continuity
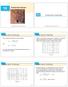 14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
Math 2411 Calc III Practice Exam 2
 Math 2411 Calc III Practice Exam 2 This is a practice exam. The actual exam consists of questions of the type found in this practice exam, but will be shorter. If you have questions do not hesitate to
Math 2411 Calc III Practice Exam 2 This is a practice exam. The actual exam consists of questions of the type found in this practice exam, but will be shorter. If you have questions do not hesitate to
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Geometry. Practice Pack
 Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms
 NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
VECTOR CALCULUS Julian.O 2016
 VETO ALULUS Julian.O 2016 Vector alculus Lecture 3: Double Integrals Green s Theorem Divergence of a Vector Field Double Integrals: Double integrals are used to integrate two-variable functions f(x, y)
VETO ALULUS Julian.O 2016 Vector alculus Lecture 3: Double Integrals Green s Theorem Divergence of a Vector Field Double Integrals: Double integrals are used to integrate two-variable functions f(x, y)
Graphing Guidelines. Controlled variables refers to all the things that remain the same during the entire experiment.
 Graphing Graphing Guidelines Graphs must be neatly drawn using a straight edge and pencil. Use the x-axis for the manipulated variable and the y-axis for the responding variable. Manipulated Variable AKA
Graphing Graphing Guidelines Graphs must be neatly drawn using a straight edge and pencil. Use the x-axis for the manipulated variable and the y-axis for the responding variable. Manipulated Variable AKA
MAT187H1F Lec0101 Burbulla
 Spring 17 What Is A Parametric Curve? y P(x, y) x 1. Let a point P on a curve have Cartesian coordinates (x, y). We can think of the curve as being traced out as the point P moves along it. 3. In this
Spring 17 What Is A Parametric Curve? y P(x, y) x 1. Let a point P on a curve have Cartesian coordinates (x, y). We can think of the curve as being traced out as the point P moves along it. 3. In this
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Practice problems from old exams for math 233
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III January 14, 2010 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III January 14, 2010 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Review #Final Exam MATH 142-Drost
 Fall 2007 1 Review #Final Exam MATH 142-Drost 1. Find the domain of the function f(x) = x 1 x 2 if x3 2. Suppose 450 items are sold per day at a price of $53 per item and that 650 items are
Fall 2007 1 Review #Final Exam MATH 142-Drost 1. Find the domain of the function f(x) = x 1 x 2 if x3 2. Suppose 450 items are sold per day at a price of $53 per item and that 650 items are
F13 Study Guide/Practice Exam 3
 F13 Study Guide/Practice Exam 3 This study guide/practice exam covers only the material since exam 2. The final exam, however, is cumulative so you should be sure to thoroughly study earlier material.
F13 Study Guide/Practice Exam 3 This study guide/practice exam covers only the material since exam 2. The final exam, however, is cumulative so you should be sure to thoroughly study earlier material.
Investigation Optimization of Perimeter, Area, and Volume Activity #1 Minimum Perimeter
 Investigation Optimization of Perimeter, Area, and Volume Activity #1 Minimum Perimeter 1. Choose a bag from the table and record the number from the card in the space below. Each member of your group
Investigation Optimization of Perimeter, Area, and Volume Activity #1 Minimum Perimeter 1. Choose a bag from the table and record the number from the card in the space below. Each member of your group
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide Section 8.2 and 8.3-1
 8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
MATH CIRCLE, 10/13/2018
 MATH CIRCLE, 10/13/2018 LARGE SOLUTIONS 1. Write out row 8 of Pascal s triangle. Solution. 1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1. 2. Write out all the different ways you can choose three letters from the set {a, b, c,
MATH CIRCLE, 10/13/2018 LARGE SOLUTIONS 1. Write out row 8 of Pascal s triangle. Solution. 1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1. 2. Write out all the different ways you can choose three letters from the set {a, b, c,
MATH Review Exam II 03/06/11
 MATH 21-259 Review Exam II 03/06/11 1. Find f(t) given that f (t) = sin t i + 3t 2 j and f(0) = i k. 2. Find lim t 0 3(t 2 1) i + cos t j + t t k. 3. Find the points on the curve r(t) at which r(t) and
MATH 21-259 Review Exam II 03/06/11 1. Find f(t) given that f (t) = sin t i + 3t 2 j and f(0) = i k. 2. Find lim t 0 3(t 2 1) i + cos t j + t t k. 3. Find the points on the curve r(t) at which r(t) and
Section 15.3 Partial Derivatives
 Section 5.3 Partial Derivatives Differentiating Functions of more than one Variable. Basic Definitions In single variable calculus, the derivative is defined to be the instantaneous rate of change of a
Section 5.3 Partial Derivatives Differentiating Functions of more than one Variable. Basic Definitions In single variable calculus, the derivative is defined to be the instantaneous rate of change of a
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW
 PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
PREREQUISITE/PRE-CALCULUS REVIEW Introduction This review sheet is a summary of most of the main topics that you should already be familiar with from your pre-calculus and trigonometry course(s), and which
Functions of more than one variable
 Chapter 3 Functions of more than one variable 3.1 Functions of two variables and their graphs 3.1.1 Definition A function of two variables has two ingredients: a domain and a rule. The domain of the function
Chapter 3 Functions of more than one variable 3.1 Functions of two variables and their graphs 3.1.1 Definition A function of two variables has two ingredients: a domain and a rule. The domain of the function
Volumes of Revolution
 Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
5.4 Transformations and Composition of Functions
 5.4 Transformations and Composition of Functions 1. Vertical Shifts: Suppose we are given y = f(x) and c > 0. (a) To graph y = f(x)+c, shift the graph of y = f(x) up by c. (b) To graph y = f(x) c, shift
5.4 Transformations and Composition of Functions 1. Vertical Shifts: Suppose we are given y = f(x) and c > 0. (a) To graph y = f(x)+c, shift the graph of y = f(x) up by c. (b) To graph y = f(x) c, shift
Math 65A Elementary Algebra A Exam II STUDY GUIDE and REVIEW Chapter 2, Sections 3 5, and Chapter 3, Sections 1-3
 Exam II STUDY GUIDE and REVIEW Chapter 2, Sections 5, and Chapter, Sections 1 - Exam II will be given on Thursday, April 10. You will have the entire class time for the exam. It will cover Chapter 2, Sections
Exam II STUDY GUIDE and REVIEW Chapter 2, Sections 5, and Chapter, Sections 1 - Exam II will be given on Thursday, April 10. You will have the entire class time for the exam. It will cover Chapter 2, Sections
DeltaCad and Your Cylinder (Shepherd s) Sundial Carl Sabanski
 1 The Sundial Primer created by In the instruction set SONNE and Your Cylinder Shepherd s Sundial we went through the process of designing a cylinder sundial with SONNE and saving it as a dxf file. In
1 The Sundial Primer created by In the instruction set SONNE and Your Cylinder Shepherd s Sundial we went through the process of designing a cylinder sundial with SONNE and saving it as a dxf file. In
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook
 Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Chapter 3, Part 4: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions
 Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Test Yourself. 11. The angle in degrees between u and w. 12. A vector parallel to v, but of length 2.
 Test Yourself These are problems you might see in a vector calculus course. They are general questions and are meant for practice. The key follows, but only with the answers. an you fill in the blanks
Test Yourself These are problems you might see in a vector calculus course. They are general questions and are meant for practice. The key follows, but only with the answers. an you fill in the blanks
Mathematics 205 HWK 19b Solutions Section 16.2 p750. (x 2 y) dy dx. 2x 2 3
 Mathematics 5 HWK 9b Solutions Section 6. p75 Problem, 6., p75. Evaluate (x y) dy dx. Solution. (x y) dy dx x ( ) y dy dx [ x x dx ] [ ] y x dx Problem 9, 6., p75. For the region as shown, write f da as
Mathematics 5 HWK 9b Solutions Section 6. p75 Problem, 6., p75. Evaluate (x y) dy dx. Solution. (x y) dy dx x ( ) y dy dx [ x x dx ] [ ] y x dx Problem 9, 6., p75. For the region as shown, write f da as
KSF selected problems Student
 3 point problems 1. Andrea was born in 1997, her younger sister Charlotte in 2001. The age difference of the two sisters is therefore in any case. (A) less than 4 years (B) at least 4 years (C) exactly
3 point problems 1. Andrea was born in 1997, her younger sister Charlotte in 2001. The age difference of the two sisters is therefore in any case. (A) less than 4 years (B) at least 4 years (C) exactly
10.1 Curves defined by parametric equations
 Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
 CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
CHAPTER 11 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 1. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES A) Definition: A function of two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) in a set D a unique real number
Double Integrals over More General Regions
 Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
Jim Lambers MAT 8 Spring Semester 9-1 Lecture 11 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1. in Stewart and Sections 5.3 and 5.4 in Marsden and Tromba. ouble Integrals over More General Regions We have
Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 A) Even B) Odd C) Neither
 Assignment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 1) A)
Assignment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the function is even, odd, or neither. 1) f(x) = 8x4 + 7x + 5 1) A)
Activity overview. Background. Concepts. Random Rectangles
 by: Bjørn Felsager Grade level: secondary (Years 9-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview What variables characterize a rectangle? What kind of relationships exists between
by: Bjørn Felsager Grade level: secondary (Years 9-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview What variables characterize a rectangle? What kind of relationships exists between
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
14.7 Maximum and Minimum Values
 CHAPTER 14. PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 115 14.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Definition. Let f(x, y) be a function. f has a local max at (a, b) iff(a, b) (a, b). f(x, y) for all (x, y) near f has a local min at
CHAPTER 14. PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 115 14.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Definition. Let f(x, y) be a function. f has a local max at (a, b) iff(a, b) (a, b). f(x, y) for all (x, y) near f has a local min at
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
VectorPlot[{y^2-2x*y,3x*y-6*x^2},{x,-5,5},{y,-5,5}]
![VectorPlot[{y^2-2x*y,3x*y-6*x^2},{x,-5,5},{y,-5,5}] VectorPlot[{y^2-2x*y,3x*y-6*x^2},{x,-5,5},{y,-5,5}]](/thumbs/88/116610289.jpg) hapter 16 16.1. 6. Notice that F(x, y) has length 1 and that it is perpendicular to the position vector (x, y) for all x and y (except at the origin). Think about drawing the vectors based on concentric
hapter 16 16.1. 6. Notice that F(x, y) has length 1 and that it is perpendicular to the position vector (x, y) for all x and y (except at the origin). Think about drawing the vectors based on concentric
ANSWER KEY. (a) For each of the following partials derivatives, use the contour plot to decide whether they are positive, negative, or zero.
 Math 2130-101 Test #2 for Section 101 October 14 th, 2009 ANSWE KEY 1. (10 points) Compute the curvature of r(t) = (t + 2, 3t + 4, 5t + 6). r (t) = (1, 3, 5) r (t) = 1 2 + 3 2 + 5 2 = 35 T(t) = 1 r (t)
Math 2130-101 Test #2 for Section 101 October 14 th, 2009 ANSWE KEY 1. (10 points) Compute the curvature of r(t) = (t + 2, 3t + 4, 5t + 6). r (t) = (1, 3, 5) r (t) = 1 2 + 3 2 + 5 2 = 35 T(t) = 1 r (t)
Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A
 Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A Name: ID: Circle your instructor and lecture below: Jankowski-001 Jankowski-006 Ramakrishnan-013 Read all of the following information
Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A Name: ID: Circle your instructor and lecture below: Jankowski-001 Jankowski-006 Ramakrishnan-013 Read all of the following information
JMG. Review Module 1 Lessons 1-20 for Mid-Module. Prepare for Endof-Unit Assessment. Assessment. Module 1. End-of-Unit Assessment.
 Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016
 THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
Math 259 Winter Recitation Handout 9: Lagrange Multipliers
 Math 259 Winter 2009 Recitation Handout 9: Lagrange Multipliers The method of Lagrange Multipliers is an excellent technique for finding the global maximum and global minimum values of a function f(x,
Math 259 Winter 2009 Recitation Handout 9: Lagrange Multipliers The method of Lagrange Multipliers is an excellent technique for finding the global maximum and global minimum values of a function f(x,
This early Greek study was largely concerned with the geometric properties of conics.
 4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
Sect Linear Equations in Two Variables
 99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review
 Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB
 Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
4.3. Trigonometric Identities. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Adding & Subtracting Decimals. Multiplying Decimals. Dividing Decimals
 1. Write the problem vertically, lining up the decimal points. 2. Add additional zeroes at the end, if necessary, to make the numbers have the same number of decimal places. 3. Add/subtract as if the numbers
1. Write the problem vertically, lining up the decimal points. 2. Add additional zeroes at the end, if necessary, to make the numbers have the same number of decimal places. 3. Add/subtract as if the numbers
Math 5BI: Problem Set 1 Linearizing functions of several variables
 Math 5BI: Problem Set Linearizing functions of several variables March 9, A. Dot and cross products There are two special operations for vectors in R that are extremely useful, the dot and cross products.
Math 5BI: Problem Set Linearizing functions of several variables March 9, A. Dot and cross products There are two special operations for vectors in R that are extremely useful, the dot and cross products.
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
Math Review Questions
 Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2
 MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
Bronze. Instructions. Information
 Bronze Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer ALL questions. Answer the questions in the spaces
Bronze Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer ALL questions. Answer the questions in the spaces
Definitions and claims functions of several variables
 Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Exam 2 Summary. 1. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputes of the function and the range is the set of all outputs.
 Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
