UC Berkeley Green Manufacturing and Sustainable Manufacturing Partnership
|
|
|
- Annabella Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UC Berkeley Green Manufacturing and Sustainable Manufacturing Partnership Title Development of a micro-drilling burr-control chart for PCB drilling Permalink Journal Precision Engineering, 38(1) Authors Bhandari, Binayak Hong, Young-Sun Yoon, Hae-Sung et al. Publication Date 2014 escholarship.org Powered by the California Digital Library University of California
2 Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Precision Engineering jou rn al hom epage: Technical note Development of a micro-drilling burr-control chart for PCB drilling Binayak Bhandari a, Young-Sun Hong a, Hae-Sung Yoon a, Jong-Seol Moon a, Minh-Quan Pham a, Gyu-Bong Lee b, Yuchu Huang c, Barbara S. Linke c, D.A. Dornfeld c, Sung-Hoon Ahn a, a School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul , Republic of Korea b Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH), Cheonan-si , Republic of Korea c Laboratory for Manufacturing and Sustainability, University of California, Berkeley, CA , United States a r t i c l e i n f o Article history: Received 17 April 2012 Received in revised form 11 July 2013 Accepted 29 July 2013 Available online 7 August 2013 Keywords: Micro drilling PCB Drilling burr control Taguchi method Burr classification S/N ratio a b s t r a c t A drilling burr-control chart (DBCC), based on experimental results, is a tool for the prediction and control of drilling burrs for a large range of drilling parameters. A micro-drilling burr-control chart (M-DBCC) was developed for a standard double-sided copper-clad laminated (CCL) printed circuit board (PCB) with laminated fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) substrate. This chart will assist in the selection of favorable drilling parameters for predicting and achieving preferred types of burrs. Burr classification was carried out according to the burr geometric characteristics, burr formation mechanisms, burr height, and drill bit breakage while drilling. The design of experiment (DOE) technique based on the Taguchi method was used to find the most significant drilling parameter affecting burr height. The results show that the drill diameter makes a statistically significant contribution to burr-height variation Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction A printed circuit board (PCB) is a thin plate made of one or more layers of insulating board (also known as substrate), which supports electronic components and connects them electrically, using conductive pathways, tracks, or signal traces [1]. PCBs are found in almost every kind of electronic device, ranging from toys to sophisticated radar systems. There are three major types of PCB construction: single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layered. In single-sided construction, all components are placed on one side of the board. Double-sided PCBs are used when the number of components is too large to allow single-sided construction within the designated space. A multilayered board has several printed circuit layers separated by layers of insulation. The electronic components on the surface are connected through plated holes drilled down to the appropriate circuit layer, which simplifies the circuit. The most common substrate used for PCBs is made of glassfiber-reinforced epoxy resin with copper foil bonded to the surface (single- or double-sided). Drilling provides the holes for the electronic components to be placed on PCB surfaces. Burrs are thereby created on both the Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: ahnsh@snu.ac.kr (S.-H. Ahn). entrance and exit surfaces of a PCB [2]. In engineering, a burr refers to a raised edge on a metal part, and appears in many contexts, including filed wires, raised portions of a surface, etc. In the PCB manufacturing industry, most of the operations are automatically controlled by computer programs, except for the drilling operation, which is usually the bottleneck station [3]. Micro-drilling in PCBs presents greater problems, since coolant-fed drills cannot be used. In general, high spindle speed and high infeed are recommended for PCB drilling operations. However, this might not be always cost-effective, because a large amount of time must be devoted to deburring operations after drilling. A multitude of ideas [4 7] have been proposed by researchers and engineers to achieve burrless drilling, but thus far, these efforts have met with only partial success. In the drilling process, burrs are produced on both the entrance and exit surfaces of the workpiece. However, the formation mechanisms are different. Entrance burrs are formed via plastic flow, while exit burrs are formed as the material extends off the exit surface of the workpiece [8]. Generally, exit burrs are larger than entrance burrs, and are undesirable because they cause most burrrelated problems, such as interference with the assembly of parts, which leads to jamming and misalignment, reduces the fatigue life of the parts, and acts as a crack initiation point and safety hazard. Deburring is often required, but in the case of micro-drilling, manual removal of burrs is not practical, and sometimes even impossible /$ see front matter 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
3 222 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Table 1 Parameters affecting burr formation while drilling. Category Parameters Drill geometry Point geometry, point angle, helix angle, relief angle Drill bit material Hardness, strain-hardening characteristics, ductility, toughness, thermal properties Cutting conditions Cutting speed, spindle speed, infeed, lubrication, use of coolant, retract rate, chip load Others Tool wear, machined material, built-up-edge, entry materials, exit materials, dwell time between drill hits, drill bit clogging, temperature Several earlier burr-related studies [6,9] have been based on experiments rather than analytical methods, due to the complex burr-formation mechanism, which is further influenced by a number of parameters, including drill geometry, workpiece material, drilling conditions and environmental factors. Watanabe et al. [10] studied the influence of the radial run-out of micro-drills on the hole quality. Hinds and Treanor [11] used finite element methods to analyze the stresses occurring in micro-drills. They used threedimensional models of the drills, and performed experimental tests to determine the drill loading. Furthermore, many published studies of drilling burrs [6,8] have been concerned with isotopic and tensile materials, such as various steels. Our study focuses on the development of a micro-drilling burrcontrol chart (M-DBCC) for PCB board substrates, which are made of composite material and are brittle in nature. A drilling burr-control chart (DBCC) is a tool developed on the basis of experimental results for predicting and controlling drilling burrs under a wide range of drilling conditions [12]. This chart also assists in selecting the cutting parameters to obtain a preferred type of burr. 2. Burr formation mechanisms There is no generally accepted analytical model for controlling and predicting the mechanisms of burr formation. This is mainly because the drilling mechanism itself is a complicated phenomenon, affected by many parameters, which are listed in Table 1. It is even more complicated in the case of layered composite drilling (e.g., PCB drilling), since additional phenomena such as delamination are caused by heat built-up while drilling. However, the present paper focuses on burr formation, without taking heat generation during the drilling process into account. The thrust force of the drilling process is affected by the ratio of the feed (infeed (mm/s)/spindle speed (rev/s)) to the drill diameter ( m). The plastic deformation of the exit surface, which influences the burr formation, is determined by the thrust force. Increased feed while drilling increases the thrust force. A correlation between the feed and the thrust force with varying drill diameters can be approximated using the orthogonal cutting model described in [8]. The cutting edge of the drill is assumed to be divided into many segments, and an orthogonal cutting model is applied to each segment, as shown in Fig. 1. Where, Res is the resultant force, F is friction force, N is normal force to friction, F s is shear force, F n is normal force to shear and F c is the cutting force. The thrust force exerted on each segment is represented as F t = kf sin sin ( ) 2 sin ϕ cos(ϕ + ) W (1) W = ( i+1 i )R sin for i = 1, 2,..., n (2) is the relative radius r/r, which is the ratio of the distance, from the drill center to the segment, to the drill radius. f/2 sin F N Res F s Chip Workpiece Fig. 1. Orthogonal cutting model. N Res F F c Tool For the chisel edge of a split point twist drill, a constant rake angle can be assumed and therefore the total thrust force F t is given by n F t = ( F t,chisel edge + F t,cutting edge) (3) F t = i=1 n (k f R f n (ϕ ı h )) (4) i=1 where k is the shear strength of the workpiece material, f n is a function of (ϕ,, ı, h, ), f is the feed (mm/rev), 2 is the point angle of the drill, is the friction angle, is the tool rake angle, ϕ is the shear plane angle, R is drill radius, ı is the ratio of the web thickness to the drill diameter, and h is the helix angle. The burr formation mechanism is influenced by stress and resultant strain. The effective stress can be represented as follows: = F t A F t d 2 (5) where F t is the thrust force, which is a function of the feed rate (f), diameter (d), drill bit, and workpiece material. = f d.f n(material(k, ), Geometry(ϕ, ı, h, )) (6) For a given drill geometry and workpiece material, burr formation is determined solely by f/d, which is the dimensionless feed parameter (F n ) in the M-DBCC. The cutting speed parameter (S) is defined as the product of the drill diameter ( m) and spindle speed (N), and its units are m/min. F n = f d S = K d N (8) where N = spindle speed (min 1 ), d = drill bit diameter ( m), f = feed (mm/rev), and K is a constant that makes the orders of the two equations equal. N, d, and f are the parameters of the M-DBCC. 3. Classification of burr types There are three types of burrs, depending on location: (a) entrance burrs, (b) interlayer burrs, and (c) exit burrs. An entrance burr is created on the side of the workpiece where the drill enters. This type of burr is usually very small, and may be removed without much difficulty by chamfering the hole. Interlayer burrs occur at the junction of two layers of a PCB, and depend on the combination of materials in the upper and the lower layers, as well as the F t (7)
4 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Fig. 2. Classification of burr types: (a) uniform burr and (b) transient burr (redrawn from [8]). thickness of the sealant between the layers (if any) and the process parameters. In the presence of a thick sealant, exit burrs are fully developed from the upper layer. Exit burrs are larger than entrance burrs, and hence the exit burrs of a PCB stack are mainly considered for study [13]. Depending on their nature, and based on size, we have classified PCB burrs into (a) uniform burrs and (b) transient burrs. Uniform burrs have relatively small and unvarying heights around the periphery of a drilled hole. As the drill approaches the exit surface, the material under the chisel edge begins to deform. The distance from the exit surface to the point where the deformation begins depends mainly on the thrust force while drilling. As the drill advances, the plastic deformation zone expands from the center to the edge of the drill. Finally, an initial fracture occurs at the end of the cutting edge. When the drill exits, a small portion of the material is bent and pushed out ahead to create a uniform burr, as shown in Fig. 2(a). In a transient burr, a higher thrust force, due to higher infeed, causes a large portion of the drill exit surface to be pushed out, resulting in a large material flow from the exit surface. In PCB drilling, transient burrs are larger, irregular, and non-uniformly Table 2 Specifications of the drill bits. Helix angle 35 Point angle 130 1st relief angle 15 2nd relief angle 30 distributed. The formation mechanism of a transient burr is shown in Fig. 2(b). 4. Experiments 4.1. Micro-drill bit Due to the trend toward highly efficient, low-cost, and downsized electric parts, there is an increasing demand for micromachining [14], and for drills that are smaller in diameter and capable of drilling a wider variety of materials. The diameter of the smallest drill in use today is only about 50 m, which is about the thickness of a human hair. In our experiments, split-point twist drills with tungsten carbide (WC) tips and high-speed steel Fig. 3. (a) Copper-clad laminated double-sided PCB with GFRP substrate, (b) PCB stacking for drilling, and (c) cross-section of the PCB stack.
5 224 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Table 3 Experimental parameters and their levels. Factors Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Infeed (mm/s) Spindle speed (min 1 ) 90,000 60,000 30,000 Drill diameter ( m) III, the experiments were conducted by varying the drilling parameters until bit breakage occurred. New drill bits were used in every set of experiments. A field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) was used to measure the burr height. 5. Design of experiment 5.1. Fractional factorial design A fractional matrix of experiments was used instead of a full matrix to reduce the number of experiments. The design of experiment (DOE) technique was performed, in which the following three cases were considered for each drill bit size (400 m, 600 m, and 800 m). Case I: Varying spindle speed (min 1 ), constant infeed (mm/s). Case II: Varying infeed (mm/s), constant spindle speed (min 1 ). Case III: Varying infeed (mm/s) and spindle speed (min 1 ). Fig. 4. Drilling experimental setup. (HSS) shanks were used, having diameters of 400 m, 600 m, and 800 m. The micro-drill bits used in the experiments were manufactured by Neo Technical System Co., Ltd., Korea, and their specifications are listed in Table Experimental setup Three stacks of double-sided copper-clad laminated (CCL) PCBs were used in the experiments. The lower part of a stack was supported by a wooden backup board, and an aluminum entry board was placed on the top of the stack for heat dissipation (a standard procedure in PCB drilling). These were clamped together, as shown in Fig. 3(b). Fig. 3(c) shows a cross-section of the PCB stack. A three-axis stage (Justek Inc., Korea) and a high-speed spindle (D1733, Westwind Air Bearings, United Kingdom) were used in the drilling experiments. The experimental setup is shown in Fig. 4. Three drilling trials were conducted for each set of designed experiments. The experiments were performed at standard room temperature (22 C), and natural convection was allowed, without application of any external cooling to the workpiece. In Cases I and From the above DOE, the significance of the experimental parameters and their relevance to the experiment were easily understood. The current standard drilling conditions in the PCB industry for a 400- m drill are a spindle speed (N) of 90,000 min 1 and an infeed of 40 mm/s. The designed experimental conditions included the standard conditions Taguchi design The effects of many different parameters on performance characteristics can be concisely examined using the orthogonal array experimental design proposed by Genichi Taguchi. This DOE can be used to estimate the main effects using only a few experimental cases. The infeed (mm/s), spindle speed (min 1 ), and drill diameter ( m) were chosen as controllable parameters affecting the burr size. Altogether, three levels were selected for each parameter, and an L9 (3 3 ) orthogonal array (OA) of experiments was performed. L9 means that the array required 9 runs, and 3 3 indicates that the design estimated up to three main effects at 3 levels each. Table 3 lists the experimental parameters (viz., infeed, spindle speed, and drill diameter) and their levels. A spindle speed of 90,000 min 1 and an infeed of 40 mm/s are standard practice for a 400- m drill diameter in the PCB industry. As the diameter of the drill bit increases, the spindle speed and feed rate decrease. All parameters were varied in two directions from the standard machining conditions, except for the 400- m drill diameter. The parameter levels were selected for ease of comparison, and to find a correlation between the parameters and the burr size. Table 4 Drill bit conditions for Case I (varying spindle speed of 90, min 1 and constant infeed of 30 mm/s), and the corresponding S and F n values. Drill diameter ( m) Spindle speed (min 1 ) Infeed (mm/s) Drill bit condition Burr chart functions 400, 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , OK Broken (dia) S (400) F n(400) S (600) F n(600) S (800) F n(800) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (800) (400, 600) (800) (800)
6 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Table 5 Drill bit conditions for Case II (constant spindle speed of 90,000 min 1 and varying infeed of mm/s), and the corresponding S and F n values. Drill diameter ( m) Spindle speed (min 1 ) Infeed (mm/s) Drill bit condition Burr chart functions 400, 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , OK Broken (dia) S (400) F n(400) S (600) F n(600) S (800) F n(800) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) Table 6 Drill bit conditions for Case III (varying spindle speed of 90, min 1 and varying infeed of mm/s), and the corresponding S and F n values. Drill diameter ( m) Spindle speed (min 1 ) Infeed (mm/s) Drill bit condition Burr chart functions 400, 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , , 600, , OK Broken (dia) S (400) F n(400) S (600) F n(600) S (800) F n(800) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (all) (800) (400, 600) (800) Results and discussion 6.1. Drill bit condition There are two different types of drill-bit breakage: deflected breakage and twisted breakage. The former is caused by radial force, and the breakage is at the end of flute, whereas the latter is caused by high torque, and the breakage is normally in the middle of the flute. In our experiments, all drilling parameters were gradually varied. The spindle speed was initially set at 90,000 min 1, and was gradually reduced to 10,000 min 1 in 10,000 min 1 steps. The infeed was gradually increased from 30 mm/s in steps of 10 mm/s until the drill bit broke. The main reason for performing drilling experiments that continue until bit breakage occurs is to determine the various combinations of parameters leading to breakage. The smaller drill bits (with diameters of 400 m and 600 m) broke at 10,000 min 1 for an infeed of 30 mm/s (Case I) and an infeed of 110 mm/s (Case III), verifying that the lower spindle speed plays a greater role in micro-drill-bit breakage than infeed. For the 800- m drills, the spindle speed was further reduced, as shown in Tables 4 and 6, until the bits broke. No drill bits were reported broken in the experiment with a constant spindle speed of 90,000 min 1 and varying infeed (30 90 mm/s), as Table 5 indicates. The experimental results obtained under the drill bit conditions of Cases I III with 400- m, 600- m, and 800- m drills, and the corresponding burr chart functions calculated via Eqs. (7) and (8) are listed in Tables Drilling burr shape In PCB drilling, the burr shape is important, since the quality of the hole and the burr size can be approximated from it. Thus, before taking an FESEM image of a burr, each drilled PCB was carefully placed in a sonicator (Mujigae Analog SD-80H, Korea) with an ultrasonic frequency of 40 khz for 5 10 s to remove the debris produced during PCB drilling. All the burrs considered in this study are from the exit surfaces of the third layer. Fig. 5 shows the FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with a constant infeed of 30 mm/s and varying spindle speed (Case I). As the figures indicate, all workpieces had small, uniform burrs around the periphery of the drilled hole. Hence, all of the burrs fell into the uniform category. Fig. 6 shows the FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with a constant spindle speed of 90,000 min 1 and varying infeed (Case II). All workpieces but one (Fig. 6(a)) had large, irregular, non-uniformly distributed burrs, which placed them in the transient burr category. Fig. 7 shows the Fig. 5. FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with a constant infeed of 30 mm/s and varying spindle speed.
7 226 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Fig. 6. FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with a constant spindle speed of 90,000 min 1 and varying infeed. Fig. 7. FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with varying infeed spindle speed. Fig. 8. Burr height measured by FESEM (600- m drill bit, Case III). FESEM images from the 400- m drilling experiments with varying infeed and spindle speed (Case III). As in the previous case, all burrs except those of Fig. 7(a) fell into the transient burr category. All of these images (Figs. 5 7) were exit burrs taken with the workpiece inclined at 45 relative to the horizontal plane Drilling burr height Prior to taking the FESEM images, fine grinding was applied to each PCB edge, as close as 500 m from the burr surface, for clear imaging. The workpiece was then subjected to 5 10 s of sonication to remove the debris produced during grinding, following which sputtering was performed. Each workpiece was placed vertically in the FESEM chamber, and an FESEM image was taken. Figs. 8 and 9 show the drilling burr heights (Case III) for the 600- m and 800- m drilling experiments, respectively. It can be inferred from these figures that under the same machining conditions, the burr heights were greater for a smaller drilling diameter Taguchi experimental results Taguchi experiments were performed to determine the relationship between the drilling parameters and the burr height. The three independent variables in the Taguchi experiments were spindle speed (min 1 ), infeed (mm/s), and drill diameter ( m); the dependent variable was burr height ( m). Three drilling trials were Fig. 9. Burr height measured by FESEM (800- m drill bit, Case III).
8 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Table 7 L9 (3 3 ) Taguchi orthogonal array. S. no. Infeed (mm/s) Spindle speed (min 1 ) Drill dia ( m) S F n Drill bit condition 1 1 (30) 1 (90,000) 1 (400) (30) 2 (60,000) 2 (600) (30) 3 (30,000) 3 (800) (40) 1 (90,000) 2 (600) (40) 2 (60,000) 3 (800) (40) 3 (30,000) 1 (400) (50) 1 (90,000) 3 (800) (50) 2 (60,000) 1 (400) (50) 3 (30,000) 2 (600) Burr Height (µm) Taguchi Experiments (No.) Fig. 10. Average burr heights from the Taguchi experiments, plotted with error bars. conducted for each set of experiments. New drill bits were used for every set of experiments. Table 7 shows the L9 (3 3 ) Taguchi orthogonal array, containing the infeed, spindle speed, drill diameter, burr chart functions, and drill bit condition. No drill-bit breakage was reported for any of the experiments. The reported burr height was the average of the maximum burr heights for the three trials. The corresponding error bars are shown in Fig. 10. Multiple regression tests were performed to analyze the results of the OA experiments, and to determine the burr-height variation contributed by each parameter. Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS 19) was used for the analysis. A p-value of 0.05 was chosen as the significance level. Table 8 summarizes the results of the regression tests. The probability values (p-values) for the drill diameter were less than 0.05, indicating that the drill diameter made a statistically significant contribution to the burr-height variation. Contrary to general intuition, the smaller drill bits produced larger burrs. Standardized multiple regression coefficients (beta coefficients) are estimates resulting from an analysis of variables that have been standardized so that their variances are 1. In a multiple regression analysis, standardization is usually carried out to answer the question of which independent variable has a greater effect on the dependent variable, when the variables are measured in different units. Comparison of the standardized coefficient (beta) values indicated that the drill diameter (beta = 0.726) had the greatest effect on the burr height, followed by the spindle speed (beta = 0.296) and infeed (beta = 0.110). Table 8 Standardized beta values and p-values, indicating the statistically significant parameter. Model Parameters Beta p value 1 Drill diameter ( m) * 2 Drill diameter ( m) * Spindle speed (min 1 ) Drill diameter ( m) * Spindle speed (min 1 ) Infeed (mm/s) Correlation between burr height, spindle speed, drill diameter, and feed rate Using the results of the multi-variable regression analysis, a correlation between the burr height, spindle speed (N, min 1 ), drill diameter (d, m), and infeed rate (f, mm/s) was obtained for PCB drilling. The equation can be expressed as follows: Burr height = N d f, R 2 = (9) In the above equation, the slope with respect to the spindle speed is Analysis of the S/N ratio To determine the effect of each variable on the output, experimental results are transformed into a signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio. In the Taguchi method, the term signal and noise represents the desirable value and undesirable value for the output characteristics. Taguchi recommends the use of the S/N ratio to measure the quality characteristics deviating from the desired values. There are three cases of S/N ratios, nominal the better characteristics, smaller the better characteristics and bigger the better characteristics. Eqs. (10) (12) are used for above cases respectively. SN i = 10 log ȳ2 i s 2 y i (10) SN i = 10 log 1 n SN i = 10 log 1 n ( ) y 2 i ( ) 1 y 2 i (11) (12) ȳ i is the mean value of the observations, s 2 y i is the variance of y, n is the number of observations and y is the observed data. The objective of the experiment is to minimize the burr-height of PCB drilling, thus the smaller the better characteristics of the S/N ratio formula is used for analysis. Table 9 shows the mean and S/N ratios for each level. Table 9 Experiment results for S/N ratio. Experiment no. Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Mean SN ratio
9 228 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) Fig. 11. M-DBCC chart showing burr types under various drilling conditions. Table 10 Response table with the ranking of parameters influencing the drill burr height. Level Infeed Spindle speed Drill dia = Max Min Ranking height measurement was needed. However, the boundary between uniform and transient burrs was not clearly distinguishable, and good judgment was required to distinguish between uniform and transient burrs that were close to the boundary. As described above, smaller drill bits produced larger burrs, while larger drill bits produced smaller burrs under the same drilling conditions. The preferred burrs (i.e., uniform burrs with minimal heights) are indicated in the diagram by the dark oval region. In addition, response of each parameter on the burr-height was studied. The response of each parameter is shown in Table 10. The response table is created by calculating an average SN value for each factor using Eq. (13). From Table 10, it can be seen that drill diameter has the largest effect on the burr height. SN SN parameter,level = (13) NoL SN is the sum of SN values corresponding to the parameter and level considered in the Taguchi orthogonal array. NoL is the number of levels. For example, SN diameter,1 = (SN 1 + SN 6 + SN 8 )/3 or SN infeed,3 = (SN 7 + SN 8 + SN 9 )/3. 7. Micro-drilling burr-control chart Numerous parameters affect burr formation during drilling operations, as Table 1 indicates. The workpiece material is selected according to product requirements, while the tool material and geometry are usually standardized. The cutting speed and infeed are significant parameters, and are included in most drilling research. Based on our experimental results and burr classifications, a new M-DBCC was developed for micro-drilling on CCL double-sided PCBs. A complete burr chart can be used to predict the type of burr produced by various values of the drill diameter, infeed, and spindle speed for a given type of workpiece material. Fig. 11 shows the newly developed M-DBCC chart. For each experiment performed, the parameters F n and S were plotted as the abscissa and ordinate, respectively, of the burr chart. In accordance with the classification of burr shape, burr height, and tool breakage, the regions in the burr chart are classified into uniform burr, transient burr, preferred burr, drill breakage, and critical burr-height regions. The thick line denotes the boundary between uniform and transient burr types. The Matlab function convhull was used to plot the critical burrheight region. Critical burr height is defined as a burr height greater than 20 m, irrespective of burr type. The drill-bit breakage region was easily distinguished, since neither burr classification nor burr 8. Conclusions DOE was used to develop a micro-drilling burr-control chart for a double-sided PCB with a laminated fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) substrate. The classification of burrs and burr formation mechanisms into uniform and transient types was explained. The uniform burr region, transient burr region, preferred burr region, drill-bit breakage region, and critical burr-height region were plotted in the M-DBCC according to various classifications of PCB drilling burrs. The term critical burr height was defined to indicate the region of greater burr height, irrespective of burr type. This M-DBCC can be used to predict and control burrs for a large range of cutting parameters. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the Brain Korea 21 project at Seoul National University, and the KITECH project funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (No TD ) References [1] Bhandari B, Hong Y-S, Yoon H-S, Lee J-C, Moon J-S, Dornfeld DA, et al. Development of micro drilling burr control chart based on Taguchi methods for PCB drilling. In: Asian Symposium for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology [2] Nakao Y, Watanabe Y. Measurement and evaluations of drilling burr profile. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2006;220: [3] Chang P-C, Hsieh J-C, Wang C-Y. Adaptive multi-objective genetic algorithms for scheduling of drilling operation in printed circuit board industry. Applied Soft Computing 2007;7: [4] Wang X, Wang LJ, Tao JP. Investigation of thrust in vibration drilling of fiber-reinforced plastics. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2004;148: [5] Takeyama H, Kato S. Burrless drilling by means of ultrasonic vibration. Annals of the CIPR 1991;41:83 6. [6] Ko S-L, Chang J-E, Yang G-E. Burr minimizing scheme in drilling. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2003;140: [7] Chung I-Y, Kim J-D, Kang K-H. Ablation drilling of invar alloy using ultrashort pulsed laser. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 2009;10:11 6.
10 B. Bhandari et al. / Precision Engineering 38 (2014) [8] Kim J, Min S, Dornfeld DA. Optimization and control of drilling burr formation of AISI 304L and AISI 4118 based on drilling burr control charts. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 2001;41: [9] Gillespie LK. Burrs Produced by Drilling. Bendix Corporation Unclassified Topical Report; [10] Watanabe H, Tsuzaka H, Masuda M. Microdrilling for printed circuit boards (PCBs) influence of radial run-out of microdrills on hole quality. Precision Engineering 2008;32: [11] Hinds BK, Treanor GM. Analysis of stresses in micro-drills using the finite element method. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 2000;40: [12] Dornfeld D, Lee D. Precision Manufacturing. New York: Springer; [13] Aurich JC, Dornfeld D, Aeeazola PJ, Franke V, Leitz L, Min S. Burrs-analysis, control and removal. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology 2009;58: [14] Kang H-J, Ahn S-H. Fabrication and characterization of microparts by mechanical micromachining: precision and cost estimation. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2007;221:
An experimental study on the burr formation in drilling of aluminum channels of rectangular section
 5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India An experimental study on the burr formation
5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India An experimental study on the burr formation
OPTIMIZATION OF CUTTING TOOL GEOMETRIC PARAMETERS IN MILLING OF CFRP LAMINATES
 21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 OPTIMIZATION OF CUTTING TOOL GEOMETRIC PARAMETERS IN MILLING OF CFRP LAMINATES S. Waqar 1, Y. He 2*, C.A. Abbas 3, and
21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 OPTIMIZATION OF CUTTING TOOL GEOMETRIC PARAMETERS IN MILLING OF CFRP LAMINATES S. Waqar 1, Y. He 2*, C.A. Abbas 3, and
Development of an Integrated Drilling, Chamfering and Deburring Tool
 Development of an Integrated Drilling, Chamfering and Deburring Tool Peter Stringer UCD School of Electrical, Electronic and Mechanical Engineering Scoil na hinnealtóireachta Leictrigh, Leictreonaigh agus
Development of an Integrated Drilling, Chamfering and Deburring Tool Peter Stringer UCD School of Electrical, Electronic and Mechanical Engineering Scoil na hinnealtóireachta Leictrigh, Leictreonaigh agus
Prediction Of Thrust Force And Torque In Drilling On Aluminum 6061-T6 Alloy
 Prediction Of Thrust Force And Torque In Drilling On Aluminum 6061-T6 Alloy P. Kishore Kumar 1 ; Dr. K. Kishore 2 ; Prof. P. Laxminarayana 3 ; Anurag group of Institutions Vasavi College of Engineering
Prediction Of Thrust Force And Torque In Drilling On Aluminum 6061-T6 Alloy P. Kishore Kumar 1 ; Dr. K. Kishore 2 ; Prof. P. Laxminarayana 3 ; Anurag group of Institutions Vasavi College of Engineering
Investigation of Interlayer Burr Formation in the Drilling of Stacked Aluminum Sheets
 Investigation of Interlayer Burr Formation in the Drilling of Stacked Aluminum Sheets A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Cody Hellstern In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Investigation of Interlayer Burr Formation in the Drilling of Stacked Aluminum Sheets A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Cody Hellstern In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Metal Cutting (Machining)
 Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.V.R. and J.C. College of Engineering, Chowdavaram, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India 2
 Overview on Burr Formation, Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Burr size based on Taguchi Design of Experiments during Drilling of Alluminium 7075 Alloy Reddy Sreenivasulu 1 and Chalamalasetti
Overview on Burr Formation, Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Burr size based on Taguchi Design of Experiments during Drilling of Alluminium 7075 Alloy Reddy Sreenivasulu 1 and Chalamalasetti
Burr Size Analysis in Drilling Process for Different Alloys Using Image Processing Technique
 Burr Size Analysis in Drilling Process for Different Alloys Using Image Processing Technique Prof. G. M. Dhote, Ankit J. Wagh, Palash Chopde, Lokesh Bhatri, Nikita Khelkar Professor, Dept. of Mechanical
Burr Size Analysis in Drilling Process for Different Alloys Using Image Processing Technique Prof. G. M. Dhote, Ankit J. Wagh, Palash Chopde, Lokesh Bhatri, Nikita Khelkar Professor, Dept. of Mechanical
VIBRATION ASSISTED DEEP HOLE MICRO-DRILLING: A PRELIMINARY EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
 DOI: 10.2507/27th.daaam.proceedings.119 VIBRATION ASSISTED DEEP HOLE MICRO-DRILLING: A PRELIMINARY EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Todić Rajko, Bartulović Ante This Publication has to be referred as: Todic, R[ajko]
DOI: 10.2507/27th.daaam.proceedings.119 VIBRATION ASSISTED DEEP HOLE MICRO-DRILLING: A PRELIMINARY EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Todić Rajko, Bartulović Ante This Publication has to be referred as: Todic, R[ajko]
CHAPTER 6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
 159 CHAPTER 6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Composite materials are widely used in different fields due to their excellent properties. CFRP composite plates are used in many applications such as aerospace, defense,
159 CHAPTER 6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Composite materials are widely used in different fields due to their excellent properties. CFRP composite plates are used in many applications such as aerospace, defense,
Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Micro Grooving
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol.68, No.1, March 2008 Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Micro Grooving by Osamu OHNISHI *, Hiromichi ONIKURA **, Seung-Ki MIN *** Muhammad Aziz
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol.68, No.1, March 2008 Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Micro Grooving by Osamu OHNISHI *, Hiromichi ONIKURA **, Seung-Ki MIN *** Muhammad Aziz
Assessment of the Exit Defects in Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Plates Caused by Drilling
 Key Engineering Materials Vols. 96 () pp. - Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Assessment of the Exit Defects in Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Plates Caused by Drilling Houjiang Zhang, Wuyi Chen, Dingchang
Key Engineering Materials Vols. 96 () pp. - Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Assessment of the Exit Defects in Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Plates Caused by Drilling Houjiang Zhang, Wuyi Chen, Dingchang
An experimental investigation into the orthogonal cutting of unidirectional fibre reinforced plastics
 International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 43 (2003) 1015 1022 An experimental investigation into the orthogonal cutting of unidirectional fibre reinforced plastics X.M. Wang, L.C. Zhang School
International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 43 (2003) 1015 1022 An experimental investigation into the orthogonal cutting of unidirectional fibre reinforced plastics X.M. Wang, L.C. Zhang School
The shape of the cone of the twist drills
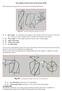 The shape of the cone of the twist drills With reference to figure N 1 we can give the following definitions: Fig. N 1- Some characteristic angles of twist drill ε : Helix angle; it is formed by the tangent
The shape of the cone of the twist drills With reference to figure N 1 we can give the following definitions: Fig. N 1- Some characteristic angles of twist drill ε : Helix angle; it is formed by the tangent
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SINGLE POINT CUTTING TOOL
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SINGLE POINT CUTTING TOOL Poonam D. Kurekar, S. D. Khamankar 2 M-Tech Student, Mechanical Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Research Technology, MH, India
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SINGLE POINT CUTTING TOOL Poonam D. Kurekar, S. D. Khamankar 2 M-Tech Student, Mechanical Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Research Technology, MH, India
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting. By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar
 Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Various other types of drilling machines are available for specialized jobs. These may be portable, bench type, multiple spindle, gang, multiple
 Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Experimental Studies on Perpendicularity of Drilling Operation using DOE
 Volume,Issue 3, April 24, e-issn: 2348-447, print-issn:2348-646 Experimental Studies on Perpendicularity of Drilling Operation using DOE B. P. Patel, Prof. (Dr.) P. M. George 2, Prof. (Dr.) V.J.Patel 3
Volume,Issue 3, April 24, e-issn: 2348-447, print-issn:2348-646 Experimental Studies on Perpendicularity of Drilling Operation using DOE B. P. Patel, Prof. (Dr.) P. M. George 2, Prof. (Dr.) V.J.Patel 3
UC Berkeley Consortium on Deburring and Edge Finishing
 UC Berkeley Consortium on Deburring and Edge Finishing Title Strategies for Preventing and Minimizing Burr Formation Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2239m1ns Author Dornfeld, David Publication
UC Berkeley Consortium on Deburring and Edge Finishing Title Strategies for Preventing and Minimizing Burr Formation Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2239m1ns Author Dornfeld, David Publication
Available online at ScienceDirect. 6th CIRP International Conference on High Performance Cutting, HPC2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 14 ( 2014 ) 389 394 6th CIRP International Conference on High Performance Cutting, HPC2014 High-Precision and High-Efficiency Micromachining
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 14 ( 2014 ) 389 394 6th CIRP International Conference on High Performance Cutting, HPC2014 High-Precision and High-Efficiency Micromachining
Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making
 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Characteristics of Grooving by Micro End Mills with Various Tool Shapes and Approach to Their Optimal Shape
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol.67, No., December 7 Characteristics of Grooving by Micro End Mills with Various Tool Shapes and Approach to Their Optimal Shape by Osamu OHNISHI
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol.67, No., December 7 Characteristics of Grooving by Micro End Mills with Various Tool Shapes and Approach to Their Optimal Shape by Osamu OHNISHI
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
Solid Carbide Tools. Composite Tools. Performance by Design. ISO 9001 Certified Company
 Solid Carbide Tools Composite Tools Performance by Design ISO 9001 Certified Company As one of the world s largest manufacturers of solid carbide rotary cutting tools, SGS Tool Company has pioneered some
Solid Carbide Tools Composite Tools Performance by Design ISO 9001 Certified Company As one of the world s largest manufacturers of solid carbide rotary cutting tools, SGS Tool Company has pioneered some
Reproducibility of surface roughness in reaming
 Reproducibility of surface roughness in reaming P. Müller, L. De Chiffre Technical University of Denmark, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark pavm@mek.dtu.dk ABSTRACT An investigation
Reproducibility of surface roughness in reaming P. Müller, L. De Chiffre Technical University of Denmark, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark pavm@mek.dtu.dk ABSTRACT An investigation
NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM)
 NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM) A machining process is called non-traditional if its material removal mechanism is basically
NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM) A machining process is called non-traditional if its material removal mechanism is basically
Development of Grinding Simulation based on Grinding Process
 TECHNICAL PAPER Development of Simulation based on Process T. ONOZAKI A. SAITO This paper describes grinding simulation technology to establish the generating mechanism of chatter and grinding burn. This
TECHNICAL PAPER Development of Simulation based on Process T. ONOZAKI A. SAITO This paper describes grinding simulation technology to establish the generating mechanism of chatter and grinding burn. This
Thread Mills. Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
ANN MODEL TO PREDICT BURR HEIGHT AND THICKNESS. A Thesis by. Nikethan Narigudde Manjunatha
 ANN MODEL TO PREDICT BURR HEIGHT AND THICKNESS A Thesis by Nikethan Narigudde Manjunatha Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering and Management, VTU, 2003 Submitted to the Department of Industrial
ANN MODEL TO PREDICT BURR HEIGHT AND THICKNESS A Thesis by Nikethan Narigudde Manjunatha Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering and Management, VTU, 2003 Submitted to the Department of Industrial
Technical Paper. Keywords: High speed drilling, Micro-holes, Flexible printed circuit board, Thrust force
 12 Technical Paper Experimental Study on Cutting Force of High-speed Micro-drilling Flexible Printed Circuit Board Xin Zhang, Chengyong Wang, Lijuan Zheng, Linfang Wang, Yuexian Song Guangdong University
12 Technical Paper Experimental Study on Cutting Force of High-speed Micro-drilling Flexible Printed Circuit Board Xin Zhang, Chengyong Wang, Lijuan Zheng, Linfang Wang, Yuexian Song Guangdong University
Design of intermediate die shape of multistage profile drawing for linear motion guide
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 24 (12) (2010) 2539~2544 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-010-0630-y Design of intermediate die shape of multistage profile drawing
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 24 (12) (2010) 2539~2544 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-010-0630-y Design of intermediate die shape of multistage profile drawing
APPLICATION OF DOE, ANOVA AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MACHINING FACTORS ON CHISEL EDGE WEAR IN DRILLING GFRP COMPOSITES
 APPLICATION OF DOE, ANOVA AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MACHINING FACTORS ON CHISEL EDGE WEAR IN DRILLING GFRP COMPOSITES Sathish Rao U., Akshay Mimani, Manjot Singh Dhillon, Sanjay S.
APPLICATION OF DOE, ANOVA AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MACHINING FACTORS ON CHISEL EDGE WEAR IN DRILLING GFRP COMPOSITES Sathish Rao U., Akshay Mimani, Manjot Singh Dhillon, Sanjay S.
Product Information Report Maximizing Drill Bit Performance
 Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
UC Berkeley Green Manufacturing and Sustainable Manufacturing Partnership
 UC Berkeley Green Manufacturing and Sustainable Manufacturing Partnership Title Burrs-Analysis, control and removal Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0zz4s5qb Journal CIRP Annals - Manufacturing
UC Berkeley Green Manufacturing and Sustainable Manufacturing Partnership Title Burrs-Analysis, control and removal Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0zz4s5qb Journal CIRP Annals - Manufacturing
Parametric Optimization of Ball Burnishing Process Parameter for Hardness of Aluminum Alloy 6061
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 Vol. 0, Issue 08 (August. 01), V PP 1-6 www.iosrjen.org Parametric Optimization of Ball Burnishing Process Parameter for Hardness
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 Vol. 0, Issue 08 (August. 01), V PP 1-6 www.iosrjen.org Parametric Optimization of Ball Burnishing Process Parameter for Hardness
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT PARAMETERS TOWARDS MILLING BURR MINIMIZATION AT WET CONDITION
 INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT PARAMETERS TOWARDS MILLING BURR MINIMIZATION AT WET CONDITION S.K.Singh 1, S.R.Dutta 2 1,2 Assistant Professor Department of ME, West Bengal University of Technology, India ABSTRACT
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT PARAMETERS TOWARDS MILLING BURR MINIMIZATION AT WET CONDITION S.K.Singh 1, S.R.Dutta 2 1,2 Assistant Professor Department of ME, West Bengal University of Technology, India ABSTRACT
Fig. N 1 The indexing error between two consecutive flutes: (this must be measured half way up the tooth) as indicated in figure N 2.
 Hob resharpening The accuracy of the hobbing process to a large extent on good hob resharpening and the performance of hob is very much affected by the type of resharpening carried out. If a hob is resharpened
Hob resharpening The accuracy of the hobbing process to a large extent on good hob resharpening and the performance of hob is very much affected by the type of resharpening carried out. If a hob is resharpened
Modeling and Optimizing of CNC End Milling Operation Utilizing RSM Method
 I Vol-0, Issue-0, January 0 Modeling and Optimizing of CNC End Milling Operation Utilizing RSM Method Prof. Dr. M. M. Elkhabeery Department of Production Engineering & Mech. design University of Menoufia
I Vol-0, Issue-0, January 0 Modeling and Optimizing of CNC End Milling Operation Utilizing RSM Method Prof. Dr. M. M. Elkhabeery Department of Production Engineering & Mech. design University of Menoufia
1272. Phase-controlled vibrational laser percussion drilling
 1272. Phase-controlled vibrational laser percussion drilling Chao-Ching Ho 1, Chih-Mu Chiu 2, Yuan-Jen Chang 3, Jin-Chen Hsu 4, Chia-Lung Kuo 5 National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Douliou,
1272. Phase-controlled vibrational laser percussion drilling Chao-Ching Ho 1, Chih-Mu Chiu 2, Yuan-Jen Chang 3, Jin-Chen Hsu 4, Chia-Lung Kuo 5 National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, Douliou,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July-2014 ISSN
 ISSN 2229-5518 724 Abstract Diamond core drilling is considered to be a cost effective method for making deep holes in advanced ceramics, composites, quartz, stone, glass etc. with superior surface finish.
ISSN 2229-5518 724 Abstract Diamond core drilling is considered to be a cost effective method for making deep holes in advanced ceramics, composites, quartz, stone, glass etc. with superior surface finish.
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING
 THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting
 Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
TWIST DRILL FOR DRILLING IN TO GREY GRAY CAST IRON GG 20 SVOČ FST 2011
 TWIST DRILL FOR DRILLING IN TO GREY GRAY CAST IRON GG 20 SVOČ FST 2011 Pavel Roud, Západočeská univerzita v Plzni, Univerzitní 8, 306 14 Plzeň Česká republika ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to present
TWIST DRILL FOR DRILLING IN TO GREY GRAY CAST IRON GG 20 SVOČ FST 2011 Pavel Roud, Západočeská univerzita v Plzni, Univerzitní 8, 306 14 Plzeň Česká republika ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to present
Internal Threads for Thin-Walled Sections
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 601-606 601 Internal s for Thin-Walled Sections
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 601-606 601 Internal s for Thin-Walled Sections
DRA DRA. MagicDrill. High Efficiency Modular Drill. Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design. High Efficiency Modular Drill
 High Efficiency Modular Drill High Efficiency Modular Drill MagicDrill DRA Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design Optimal web thickness limits deflection Fine chip breaking and smooth
High Efficiency Modular Drill High Efficiency Modular Drill MagicDrill DRA Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design Optimal web thickness limits deflection Fine chip breaking and smooth
The role of inclination angle, λ on the direction of chip flow is schematically shown in figure which visualizes that,
 EXPERIMENT NO. 1 Aim: To study of Orthogonal & Oblique Cutting on a Lathe. Experimental set up.: Lathe Machine Theoretical concept: It is appears from the diagram in the following figure that while turning
EXPERIMENT NO. 1 Aim: To study of Orthogonal & Oblique Cutting on a Lathe. Experimental set up.: Lathe Machine Theoretical concept: It is appears from the diagram in the following figure that while turning
warwick.ac.uk/lib-publications
 Original citation: Gupta, Aniruddha, Ascroft, Helen and Barnes, Stuart (216) Effect of chisel edge in ultrasonic assisted drilling of carbon fibre reinforced plastics (CFRP). In: 7th HPC 216 CIRP Conference
Original citation: Gupta, Aniruddha, Ascroft, Helen and Barnes, Stuart (216) Effect of chisel edge in ultrasonic assisted drilling of carbon fibre reinforced plastics (CFRP). In: 7th HPC 216 CIRP Conference
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL TOOL FOR SHEET METAL SPINNING OPERATION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL TOOL FOR SHEET METAL SPINNING OPERATION Amit Patidar 1, B.A. Modi 2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad, India Abstract-- The
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL TOOL FOR SHEET METAL SPINNING OPERATION Amit Patidar 1, B.A. Modi 2 Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad, India Abstract-- The
Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part I. Wear measurement and results
 Wear 250 (2001) 587 592 Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part I. Wear measurement and results Albert J. Shih a,, Jeffrey L. Akemon b a Department of Mechanical and
Wear 250 (2001) 587 592 Wear of the blade diamond tools in truing vitreous bond grinding wheels Part I. Wear measurement and results Albert J. Shih a,, Jeffrey L. Akemon b a Department of Mechanical and
Experimental Study of Influence of Drilling Tool Geometry for Hybrid Composite Materials
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VII (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental Study of Influence
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VII (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental Study of Influence
Rotary ultrasonic machining of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer: feasibility study
 This is the author s final, peer-reviewed manuscript as accepted for publication. The publisher-formatted version may be available through the publisher s web site or your institution s library. Rotary
This is the author s final, peer-reviewed manuscript as accepted for publication. The publisher-formatted version may be available through the publisher s web site or your institution s library. Rotary
8.6 Experimental Study of Micro-holes Position Accuracy on Drilling Flexible Printed Circuit Board
 8.6 Experimental Study of Micro-holes Position Accuracy on Drilling Flexible Printed Circuit Board L. J. Zheng 1, X.Zhang 1, C. Y. Wang 1,*, L. F. Wang 1, S. Li 1, Y. X. Song 1, L. Q. Zhang 2 1 Guangdong
8.6 Experimental Study of Micro-holes Position Accuracy on Drilling Flexible Printed Circuit Board L. J. Zheng 1, X.Zhang 1, C. Y. Wang 1,*, L. F. Wang 1, S. Li 1, Y. X. Song 1, L. Q. Zhang 2 1 Guangdong
MICRODRILLING AND MICROMILLING OF BRASS USING A 10 µm DIAMETER TOOL
 MICRODRILLING AND MICROMILLING OF BRASS USING A 10 µm DIAMETER TOOL EGASHIRA Kai and MIZUTANI Katsumi Kinki University, Uchita, Wakayama 649-6493, Japan Abstract The microdrilling and micromilling of brass
MICRODRILLING AND MICROMILLING OF BRASS USING A 10 µm DIAMETER TOOL EGASHIRA Kai and MIZUTANI Katsumi Kinki University, Uchita, Wakayama 649-6493, Japan Abstract The microdrilling and micromilling of brass
ENHANCING THE MACHINING PERFORMANCE OF HSS DRILL IN THE DRILLING OF GFRP COMPOSITE BY REDUCING TOOL WEAR THROUGH WEAR MECHANISM MAPPING
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 1, January 2017, pp. 120 131, Article ID: IJMET_08_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=1
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 1, January 2017, pp. 120 131, Article ID: IJMET_08_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=1
WIRTSCHAFTLICHES BOHREN UND FRÄSEN VON COMPOSITE VERBUNDWERKSTOFFEN
 WIRTSCHAFTLICHES BOHREN UND FRÄSEN VON COMPOSITE VERBUNDWERKSTOFFEN WIRTSCHAFTLICHES BOHREN UND FRÄSEN VON COMPOSITE VERBUNDWERKSTOFFEN You looking forward to receive a economic and safe working solution
WIRTSCHAFTLICHES BOHREN UND FRÄSEN VON COMPOSITE VERBUNDWERKSTOFFEN WIRTSCHAFTLICHES BOHREN UND FRÄSEN VON COMPOSITE VERBUNDWERKSTOFFEN You looking forward to receive a economic and safe working solution
11/15/2009. There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate
 s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
Materials Removal Processes (Machining)
 Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
A Study on the Micro Tool Fabrication using Electrolytic In-process Dressing
 A Study on the Micro Tool Fabrication using Electrolytic In-process Dressing Hyunwoo Lee 1, Jaeyoung Choi 1, Haedo Jeong 1 Seokwoo Lee 2, Honzong Choi 2 1 Department of Precision Mechanical Engineering,
A Study on the Micro Tool Fabrication using Electrolytic In-process Dressing Hyunwoo Lee 1, Jaeyoung Choi 1, Haedo Jeong 1 Seokwoo Lee 2, Honzong Choi 2 1 Department of Precision Mechanical Engineering,
Special reamers. Figure N 1 Reamer with descending cutting edges in carbide (Cerin)
 Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Trade of Toolmaking. Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2. Published by. Trade of Toolmaking Phase 2 Module 3 Unit 9
 Trade of Toolmaking Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 9 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction... 4
Trade of Toolmaking Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 9 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction... 4
3-D FEA OF HARD TURNING: INVESTIGATION OF PCBN CUTTING TOOL MICRO- GEOMETRY EFFECTS
 3-D FEA OF HARD TURNING: INVESTIGATION OF PCBN CUTTING TOOL MICRO- GEOMETRY EFFECTS Yiğit Karpat and Tuğrul Özel Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Rutgers University Piscataway, New Jersey
3-D FEA OF HARD TURNING: INVESTIGATION OF PCBN CUTTING TOOL MICRO- GEOMETRY EFFECTS Yiğit Karpat and Tuğrul Özel Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Rutgers University Piscataway, New Jersey
Feasibility study of the ultrasonic vibration assisted drilling of Inconel superalloy
 International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 47 (27) 1988 1996 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijmactool Feasibility study of the ultrasonic vibration assisted drilling of Inconel superalloy Y.S. Liao
International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 47 (27) 1988 1996 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijmactool Feasibility study of the ultrasonic vibration assisted drilling of Inconel superalloy Y.S. Liao
TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE
 TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE CONTENTS 4.1 Tool wear During the cutting operation, the cutting edge is stressed mechanically and thermally until it becomes completely blunt and unable to cut, 100 % wear occurs
TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE CONTENTS 4.1 Tool wear During the cutting operation, the cutting edge is stressed mechanically and thermally until it becomes completely blunt and unable to cut, 100 % wear occurs
Analytical model for predicting the surface profile of a work piece in round-to-2 R and square-to-2 R oval groove rolling
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 4 (11) () 89~95 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI.7/s16--91-7 Analytical model for predicting the surface profile of a work piece in round-to- R and
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 4 (11) () 89~95 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI.7/s16--91-7 Analytical model for predicting the surface profile of a work piece in round-to- R and
Experimental Investigation of Process Parameters Using Molybdenum Wire on Tungsten Carbide in Wire Cut EDM
 International Journal of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Volume 1, Number 1 (2015), pp. 47-53 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Investigation of Process
International Journal of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Volume 1, Number 1 (2015), pp. 47-53 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Investigation of Process
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill
 New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
ANALYSIS OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS WITH VARIATION IN SHEAR AND RAKE ANGLE
 ANALYSIS OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS WITH VARIATION IN SHEAR AND RAKE ANGLE Sirajuddin Elyas Khany 1, Mohammed Hissam Uddin 2, Shoaib Ahmed 3, Mohammed Wahee uddin 4 Mohammed Ibrahim 5 1 Associate Professor,
ANALYSIS OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS WITH VARIATION IN SHEAR AND RAKE ANGLE Sirajuddin Elyas Khany 1, Mohammed Hissam Uddin 2, Shoaib Ahmed 3, Mohammed Wahee uddin 4 Mohammed Ibrahim 5 1 Associate Professor,
Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06
 Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06 (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) Today we are going to discuss about
Advanced Machining Processes Professor Vijay K. Jain Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 06 (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) Today we are going to discuss about
EFFECT OF RESIN AND GRAPHITE OF THE BRONZE-BONDED DIAMOND COMPOSITE TOOLS ON THE DRY GRINDING BK7 GLASSES
 16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFFECT OF RESIN AND GRAPHITE OF THE BRONZE-BONDED DIAMOND COMPOSITE TOOLS ON THE DRY GRINDING BK7 GLASSES Shenq-Yih Luo, Tseng-Yi Wang, Tsung-Han Yu
16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFFECT OF RESIN AND GRAPHITE OF THE BRONZE-BONDED DIAMOND COMPOSITE TOOLS ON THE DRY GRINDING BK7 GLASSES Shenq-Yih Luo, Tseng-Yi Wang, Tsung-Han Yu
Hard turning of interrupted surfaces using CBN tools
 journal of materials processing technology 195 (2008) 275 281 journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmatprotec Hard turning of interrupted surfaces using CBN tools Anselmo Eduardo Diniz, Adilson José
journal of materials processing technology 195 (2008) 275 281 journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmatprotec Hard turning of interrupted surfaces using CBN tools Anselmo Eduardo Diniz, Adilson José
Numerical Simulation and Analysis of Friction Drilling Process for Alumina Alloy using Ansys
 Numerical Simulation and Analysis of Friction Drilling Process for Alumina Alloy using Ansys 1Dr. A. Gopichand, Professor & HOD, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Swarnandhra college of Engineering
Numerical Simulation and Analysis of Friction Drilling Process for Alumina Alloy using Ansys 1Dr. A. Gopichand, Professor & HOD, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Swarnandhra college of Engineering
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR REAMERS FLUTE STYLES
 BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
CAD based Predictive Models of the Undeformed Chip Geometry in Drilling
 CAD based Predictive Models of the Undeformed Chip Geometry in Drilling Panagiotis Kyratsis, Dr. Ing. Nikolaos Bilalis, and Dr. Ing. Aristomenis Antoniadis Abstract Twist drills are geometrical complex
CAD based Predictive Models of the Undeformed Chip Geometry in Drilling Panagiotis Kyratsis, Dr. Ing. Nikolaos Bilalis, and Dr. Ing. Aristomenis Antoniadis Abstract Twist drills are geometrical complex
Metal Cutting - 5. Content. Milling Characteristics. Parts made by milling Example of Part Produced on a CNC Milling Machine 7.
 Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Effect of Initial Deflection of Diamond Wire on Thickness Variation of Sapphire Wafer in Multi-Wire Saw
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PRECISION ENGINEERING AND MANUFACTURING-GREEN TECHNOLOGY Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 117-121 APRIL 2015 / 117 DOI: 10.1007/s40684-015-0015-x ISSN 2288-6206 (Print) / ISSN 2198-0810 (Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PRECISION ENGINEERING AND MANUFACTURING-GREEN TECHNOLOGY Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 117-121 APRIL 2015 / 117 DOI: 10.1007/s40684-015-0015-x ISSN 2288-6206 (Print) / ISSN 2198-0810 (Online)
A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate and Surface Roughness for SS 202 Material During Face Milling Operation
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate
Kennametal Twist Drills KHSS Drill Dictionary
 Kennametal Twist KHSS Drill Dictionary shank diameter tang tang drive axis taper shank shank length neck straight shank point angle helix angle flutes flute length body overall length drill diameter lip
Kennametal Twist KHSS Drill Dictionary shank diameter tang tang drive axis taper shank shank length neck straight shank point angle helix angle flutes flute length body overall length drill diameter lip
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 7, July-2017 ISSN
 86 Optimization Of End Milling Process Parameters On Surface Roughness Using Taguchi Method Tasleem Ahmad,Noor Zaman Khan, Zahid A. Khan Abstract Present study investigated the optimization of CNC End
86 Optimization Of End Milling Process Parameters On Surface Roughness Using Taguchi Method Tasleem Ahmad,Noor Zaman Khan, Zahid A. Khan Abstract Present study investigated the optimization of CNC End
Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
 Basics of End Mills Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting
Basics of End Mills Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting
Optimization of Milling Process Parameters of HSS Using Taguchi Parameter Design Approach
 Optimization of Milling Process Parameters of HSS Using Taguchi Parameter Design Approach Dr.Ch.S.Naga Prasad Professor & Principal, Department of Mechanical Engineering, GIITS Engineering College, Aganampudi,
Optimization of Milling Process Parameters of HSS Using Taguchi Parameter Design Approach Dr.Ch.S.Naga Prasad Professor & Principal, Department of Mechanical Engineering, GIITS Engineering College, Aganampudi,
Design and Optimization of Ultrasonic Vibration Mechanism using PZT for Precision Laser Machining
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011) 258 264 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology Design and Optimization of Ultrasonic Vibration
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011) 258 264 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology Design and Optimization of Ultrasonic Vibration
EFFECT OF CRYOGENICALLY TREATED WIRE ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN WIRE EDM PROCESS
 I J A M R Serials Publications 9(1) 2017 : January-June pp. 9-14 EFFECT OF CRYOGENICALLY TREATED WIRE ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN WIRE EDM PROCESS KULTAR SINGH SAINI 1 AND PARLAD KUMAR GARG 2* 1 Research Scholar,
I J A M R Serials Publications 9(1) 2017 : January-June pp. 9-14 EFFECT OF CRYOGENICALLY TREATED WIRE ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN WIRE EDM PROCESS KULTAR SINGH SAINI 1 AND PARLAD KUMAR GARG 2* 1 Research Scholar,
Milling of Glass Fiber-Reinforced Plastics and Influence of Cutting Process Parameters on Cutting Forces
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering: F Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume Issue Version. Year Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering: F Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume Issue Version. Year Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Ultrasonic Machining. 1 Dr.Ravinder Kumar
 Ultrasonic Machining 1 Dr.Ravinder Kumar Why Nontraditional Processes? New Materials (1940 s) Stronger Tougher Harder Applications Cut tough materials Finish complex surface geometry Surface finish requirements
Ultrasonic Machining 1 Dr.Ravinder Kumar Why Nontraditional Processes? New Materials (1940 s) Stronger Tougher Harder Applications Cut tough materials Finish complex surface geometry Surface finish requirements
DIAMOND TOOLING FOR COMPOSITE MATERIALS P.B.S. DIAMOND TOOLING PCD TOOLING FLEXIBLE DIAMOND TOOLING
 DIAMOND FOR COMPOSITE MATERIALS P.B.S. DIAMOND PCD FLEXIBLE DIAMOND P.B.S. DIAMOND First patented by Abrasive Technology in 1975, this original brazed bonding process chemically bonds superabrasive crystals
DIAMOND FOR COMPOSITE MATERIALS P.B.S. DIAMOND PCD FLEXIBLE DIAMOND P.B.S. DIAMOND First patented by Abrasive Technology in 1975, this original brazed bonding process chemically bonds superabrasive crystals
User s Guide. Silent Tools. turning products
 User s Guide Silent Tools turning products Introduction This guide will help you to use dampened boring bars (Silent Tools) to achieve the best possible results in internal turning. Silent Tools dampened
User s Guide Silent Tools turning products Introduction This guide will help you to use dampened boring bars (Silent Tools) to achieve the best possible results in internal turning. Silent Tools dampened
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON LASER BENDING OF METAL SHEETS USING PARABOLIC IRRADIATIONS
 5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON LASER BENDING
5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON LASER BENDING
Effect of Peak Current on the Performance of WEDM
 Effect of Peak Current on the Performance of WEDM Rajeev Kumar 1 1 (Mechanical Engineering Department, MMU Sadopur, India) ABSTRACT : WEDM process is used extensively where the conventional machining process
Effect of Peak Current on the Performance of WEDM Rajeev Kumar 1 1 (Mechanical Engineering Department, MMU Sadopur, India) ABSTRACT : WEDM process is used extensively where the conventional machining process
Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes
 Introduction Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes Drawing is a process in which the material is pulled through a die by means of a tensile force. Usually the constant cross section is circular (bar,
Introduction Unit IV Drawing of rods, wires and tubes Drawing is a process in which the material is pulled through a die by means of a tensile force. Usually the constant cross section is circular (bar,
Effect of Tool Geometry Special Features on Cutting Forces of Multilayered CFRP Laminates
 Effect of Tool Geometry Special Features on Cutting Forces of Multilayered CFRP Laminates J-F. CHATELAIN and I. ZAGHBANI Mechanical Engineering Department Université du Québec (École de technologie supérieure)
Effect of Tool Geometry Special Features on Cutting Forces of Multilayered CFRP Laminates J-F. CHATELAIN and I. ZAGHBANI Mechanical Engineering Department Université du Québec (École de technologie supérieure)
Why gundrills? Dr. Viktor P. Astakhov, Independent Consultant
 Why gundrills? Dr. Viktor P. Astakhov, Independent Consultant Gundrilling, one of the basic and frequently performed material removal processes in the automotive, die and mold, and turbine industries,
Why gundrills? Dr. Viktor P. Astakhov, Independent Consultant Gundrilling, one of the basic and frequently performed material removal processes in the automotive, die and mold, and turbine industries,
Acoustic emission based drill condition monitoring during drilling of glass/phenolic polymeric composite using wavelet packet transform
 Materials Science and Engineering A 412 (2005) 141 145 Acoustic emission based drill condition monitoring during drilling of glass/phenolic polymeric composite using wavelet packet transform A. Velayudham
Materials Science and Engineering A 412 (2005) 141 145 Acoustic emission based drill condition monitoring during drilling of glass/phenolic polymeric composite using wavelet packet transform A. Velayudham
Drill for Wheel Hubs. Solid Carbide Drill MHE
 . Update B3G Expanded New Grade Solid Carbide Drill Uniue design provides superior hole accuracy for shallow hole drilling. Effective drilling of hub bolt holes can be achieved. Additional new grade DP30
. Update B3G Expanded New Grade Solid Carbide Drill Uniue design provides superior hole accuracy for shallow hole drilling. Effective drilling of hub bolt holes can be achieved. Additional new grade DP30
PRO LIGNO Vol. 13 N pp
 STUDY REGARDING THE INFLUENCE OF THE TOOL GEOMETRY AND FEED RATE ON THE DRILLING QUALITY OF MDF PANELS Mihai ISPAS Transilvania University of Brasov, Faculty of Wood Engineering Str. Universitatii nr.
STUDY REGARDING THE INFLUENCE OF THE TOOL GEOMETRY AND FEED RATE ON THE DRILLING QUALITY OF MDF PANELS Mihai ISPAS Transilvania University of Brasov, Faculty of Wood Engineering Str. Universitatii nr.
Cutting with broach. You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1
 Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
A guide to. effective composite machining for aerospace components
 A guide to effective composite machining for aerospace components Introduction Demands to reduce aircraft fuel consumption and minimise the greenhouse gas emissions associated with air travel is driving
A guide to effective composite machining for aerospace components Introduction Demands to reduce aircraft fuel consumption and minimise the greenhouse gas emissions associated with air travel is driving
MACHINING FORCES FOR ELLIPTICAL VIBRATION-ASSISTED MACHINING 1
 MACHINING ORCES OR ELLIPTICAL VIBRATION-ASSISTED MACHINING 1 D. E. Brehl, M.A. Cerniway, T.A. Dow,and N. Negishi Precision Engineering Center North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina, USA
MACHINING ORCES OR ELLIPTICAL VIBRATION-ASSISTED MACHINING 1 D. E. Brehl, M.A. Cerniway, T.A. Dow,and N. Negishi Precision Engineering Center North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina, USA
DETECTION AND SIZING OF SHORT FATIGUE CRACKS EMANATING FROM RIVET HOLES O. Kwon 1 and J.C. Kim 1 1 Inha University, Inchon, Korea
 DETECTION AND SIZING OF SHORT FATIGUE CRACKS EMANATING FROM RIVET HOLES O. Kwon 1 and J.C. Kim 1 1 Inha University, Inchon, Korea Abstract: The initiation and growth of short fatigue cracks in a simulated
DETECTION AND SIZING OF SHORT FATIGUE CRACKS EMANATING FROM RIVET HOLES O. Kwon 1 and J.C. Kim 1 1 Inha University, Inchon, Korea Abstract: The initiation and growth of short fatigue cracks in a simulated
INVESTIGATION OF PROCESS-RELATED DAMAGE DURING THERMAL PIERCING OF A THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS INVESTIGATION OF PROCESS-RELATED DAMAGE DURING THERMAL PIERCING OF A THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE N.W.A. Brown 1,2 *, C.M. Worrall 1, A. Kapadia 1,
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS INVESTIGATION OF PROCESS-RELATED DAMAGE DURING THERMAL PIERCING OF A THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE N.W.A. Brown 1,2 *, C.M. Worrall 1, A. Kapadia 1,
