Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
|
|
|
- Erin Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basics of End Mills
2 Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
3 Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
4 What is Cutting? What is Cutting? Making products having desired surface shape by... putting and moving a cutting tool on a work piece, and separating unnecessary parts as chips by breaking with internal stress. a) Cutting work piece by chisel Image drawing Plastic deformation on both sides of the cutting part Need big force to pushing in Image drawing b) Scraping an edge of work piece by cutting tool Plastic deformation occurs only to cutting chips Work piece itself does not deform Material of work piece Metals, woods, plastics, etc. Features Higher accuracy than chip-less processing Rapid progress and diversification of cutting technology Systematic understanding to phenomena is important to use cutting process effectively!
5 Tool bit Tools for Cutting Tool bit Chip Milling cutter A rotary cutting tool having many cutting edges on the periphery or an end face of a cylinder and a cone. (Cutting image by tool bit) A cutting tool for lathe, planer, shaper, boring machine, etc. Reamer Shank Work piece Drill A tool for drilling. Cutting edges are only on a top. End mill A cutting tool for making inside wall of a drilled hole smooth and accurate. Features of each tool A multi-functional tool which has cutting edges on the periphery and an end face. Side milling, curved surface milling and drilling are possible only by one tool. With few cutting edges...inexpensive production and re-grinding With many cutting edges...high cutting efficiency Understanding of features of each tool and also cutting actions are important for economical & efficient processing!
6 Cutting Related Parts and Names Cutting tool Instrument for cutting Also called simply Tool Rake face Tool surface in contact with cutting chip Cutting chip Removed unnecessary part Cut surface Surface before cut Work piece Finished surface Cut surface Relief face Opposite side of rake face Cutting edge Intersection of rake face and relief face on tool point
7 Work Material vs. Tool Material Comparison of Hardness Vickers hardness Rockwell hardness ex. TiSiN based coat. ex. AlCrN based coat. TiN Coating Tool materials need more than 3 or 4 times the hardness of work material in Vickers Hardness. Cemented carbide tool can process work materials up to 30HRC. Processing 40HRC is a little difficult. High-speed steel tool is not possible to process hardened steels ~ HRC 60HRC 50HRC 40HRC 30HRC Highhardness hardened materials Mediumhardness hardened materials CrN Coating Cemented carbide (WC-Co) High speed steel Coating (Cover the hardness of tool material) If coated tools need x4 harder than work material... 40HRC Hardened steels >>> Tool materials need 1600Hv CrN (Little difficult) TiN (Available) 50HRC Hardened steels >>> Tool materials need 2000Hv TiN (Actually difficult) AlCrN (Available) 65HRC Hardened steels >>> Tool materials need 3300Hv TiSiN based coating is available
8 Coating Purpose of Coating To improve tool life and cutting ability... Apply coating technology Tool obtains new characteristics by covering tool surface with coating. Coating is expected to have... Hardness Heat resistance Toughness Lubricity to make cutting edge stand on work piece not to change in quality under high temperature during cutting to stop chipping of cutting edge to control friction during cutting Coating methods PVD method (Physical Vapor Deposition) Coating method by reacting evaporated metal and reaction gas. Process temperature is relatively low ( 500 C). CVD method (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Coating method by thermochemical reaction. Able to deposit on complicated shape, but cannot apply to some materials because of high treatment temperature ( C).
9 Coating Actual Use of Coating Types of coating Ceramic-base coating Highly hard and heat resistant. Characteristic can be changed by adding other elements. Diamond coating Excellent hardness and anti-welding ability toward non-ferrous metals. (Coatings constructed by carbon atoms is not suitable for ferrous materials.) DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coating Carbon based coating which is excellent in smoothness and lubricity, but not as hard as diamond. Multi-layer coating Work piece High-hardness and high-lubricity layer High-toughness layer High adhesion layer Achieved high-performance coating by piling up a plurality of coating which has various characteristics. Understanding of characteristics & uses of coatings >>>Improvement of tool life and cutting ability
10 Summary What is Cutting? Machining method which puts a hard cutting tool on a part near a edge of a work piece and separates cutting chips by causing plastic deformation. Advantages of cutting Application for various work materials Relatively high machining accuracy Cutting and tools Understanding features of each tools and appropriate use are important for economical & efficient processing. Tools need to be more than 3 times harder than a work material.
11 Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
12 Types of End Mill Processing Slotting Side milling Tapering Profiling Contouring Pocket milling Ribbing Spot facing
13 Processing Method Down Cutting vs. Up Cutting Basically down cutting is recommended. Generally down cutting is recommended for the whole range of metal processing considering direction of deflection and finished surface quality. For resin materials, up cutting sometimes makes better finished surface. Down cutting Remaining: Allowance for rework Up cutting Too much cut: Recovery is impossible Target finished surface Direction of deflection Feeding direction Feeding direction Direction of deflection
14 Up Cutting Impact to contact material. Small >> Small chipping toward black surface of material High milling temperature because of slip phenomenon >>X Large relief face wearing Slip phenomenon Milling area Cutting chip Thickness of cutting chip Slip phenomenon: a cutting edge does not cut but rub a work piece because of too small cutting depth Direction of rotation Feeding direction
15 Down Cutting Low milling temperature because of no slip >> Small rake face wearing Large impact at a time of biting >>X Large chipping toward materials with black rust Cutting chip Impact Milling area Thickness of cutting chip Feeding direction Direction of rotation
16 Right/Left Cutting Edge Direction of rotation differs in direction of cutting edge Cross-section of end mill Right cutting edges Left cutting edges Direction of cross-sectional observation Direction of rotation Direction of rotation Clockwise Counter-clockwise A tool rotates clockwise is called Right cutting edge. A tool rotates counter-clockwise is called Left cutting edge. Ordinary end mills are Right cutting edge and Left cutting edge are very rare.
17 Right/Left Twisted Blades Direction of chip evacuation differs in direction of Helix. Right cutting edges & right Helix Right cutting edges & left Helix Direction of cutting chip flow Direction of cutting chip flow Raised upward Lowered downward Right edges & right Helix: cutting chips are evacuated upward Right edges & left Helix: cutting chips are evacuated downward Ordinary end mills are right edges & right Helix and right edges & left Helix are very rare.
18 Terms Used for Parameters 1 Parameter Conventional expression Recommended expression Unit Velocity V V c m/min Spindle Speed N n min -1 Revolutions per min Meaning Moving distance of an optional point on the circumference per unit (1min) Feed Rate F V f mm/min Moving distance in direction of feed per unit (1min) Feed per tooth Sz f z mm/t Lateral moving distance from one tooth comes to another does Feed f f mm/rev Lateral feed rate (moving distance) per one rotation Number of flutes Z Z - Number of tool flutes Axial depth Ad a p mm Axial cutting amount Radial depth Rd a e mm Radial cutting amount Pick feed Pf P f mm Moving distance of tool Example of side milling Example of slope milling Feed Rate V f Velocity V c Spindle Speed n Radial depth a e Pick feed P f Axial depth a p Work piece Number of flutes Z Pick feed P f Axial depth a p Radial depth a e
19 Terms Used for Parameters 2 1. Velocity (peripheral speed) Vc [Unit: m/min] Moving distance of an optional point on the circumference per unit (1 minute) Related values Diameter D [mm] Twice of the distance from the rotational center (radius) Spindle Speed n [min -1 ] The circular constant = 3.14 (Unit: Nil) Revolution per minute [Number of revolutions / min.] [min -1 ]=[rpm: revolutions per minute] Circumferential length = Diameter x = D [mm] Velocity (peripheral speed) Vc: Moving distance per minute = Circumferential length x Spindle rotation speed Vc = x D [mm] x n [min -1 ] 1 [min] [mm/min] Unit conversion: 1mm=1/1000 m D [mm]=d/1000 [m] therefore... D Vc = x D [mm] x n [min -1 ] 1000 x 1 [min] [m/min]
20 Terms Used for Parameters 3 2. Feed per tooth fz [Unit: mm/t] Related Values Feed Rate Vf [mm/min] Spindle Speed n [min -1 ] Number of flutes z [t] Moving distance (of machine axis) in direction of feed per minute Revolutions per minute [Number of revolutions / min.] [min -1 ]=[rpm: revolutions per minute] Number of flutes The amount of feed per rotation f [mm/rev] is as below. (rev=revolution: rotation) Vf [mm/min] Vf mm min f= = [ ] [ ] n [rev/min] n min rev Vf = [mm/rev] n The amount of feed per tooth fz [mm/t] is... calculated by dividing the amount of feed per rotation by number of tooth (flutes) which contributes for milling. fz= f [mm/rev] z = Vf n z [mm/t] In case of 2 flutes Feeding Direction Direction of rotation f=f/z =f/2 [mm/t] f=fz 2 [mm/rev] The other items used for parameters Radial depth : a e Axial depth : a p
21 Contents 1. Cutting and Cutting Tools 2. Processing by End Mills 3. Cutting Action and Phenomena during Cutting
22 Cutting Action Model diagram of cutting action Cutting chip Cutting direction Procedure of cutting Cutting edge moves forward Share surface Cutting tool Rake face compresses a part to be chipped off and share occurs Cut surface Finished surface Cutting chips are evacuated following rake face of cutting edge (Work piece) A state of cutting a part close to an edge of a work piece. Plastic deformation occurs only on cutting chips and there is almost no deformation on a work piece. Shape of cutting chips changes by cutting conditions.
23 Measure Reason Characteristic Schematic diagram Shape of Cutting Chips Flow shape Share shape Tear shape Crack shape Tool Workpiece Cutting chips continuously flow on a rake face. Load on cutting edge is constant and a smooth surface is obtained. Most desirable shape. Deformation of cutting chips repeat Sharing Finished surface is not good as Flow shape. Cutting chips pile up on a tool and finally large tear is caused. A finished surface has scars and remarkably bad. Crack occurs during deformation of cutting chips and they become crack shape. Crack makes finished surface remarkably worse. Note: Too long cutting chips disturb cutting instead. need Breaking cutting chips in certain length (by tool geometry, coolant, etc.). - Fragile of work piece Low thermal conductivity High ductility Fragile of work piece - Increase cutting speed Decrease cutting depth and increase cutting speed Increase cutting speed and decrease feed per tooth Shape of cutting chips is information source of cutting situation.
24 < Cutting temperature > Shape of Cutting Chips Heat Generation & Cutting Temperature Tool Color of cutting chips Power for cutting Ex. of chips by milling Conversion Heat energy (Cutting heat) Work material Cutting chips 800 C High Cutting chip Frictional heat generated between tool and cutting chip Generation of heat by plastic deformation on a share surface Work Material Tool Frictional heat generated between a tool and a finished surface 700 C 600 C Cutting chips change color by cutting temperature. > By change of chip color, cutting temperature can be estimated. Cutting heat is a very important element for tool life! 200 C Low
25 Difference of Tool Shape & Cutting Chips 2-flute type CFB/CFLB Wide Ideal shape Wide Comp. A Comp. E Narrow X Compressive deformation Narrow X Curled
26 Setting of Milling Condition How to increase milling efficiency while reducing tool damage... Velocity (Spindle Speed) Feed per tooth Axial depth a p Radial depth a e Which should be adjusted? Velocity (Spindle Speed) Feed (Work piece) (Direction of rotation) (Work piece) Axial depth a p Feed per tooth Radial depth a e Study case Tool: HMS ( 10 x Length of cut: 22) Work material: SKH51 (63HRC) Coolant: Air blow Details: Side milling
27 Optimization of HMS Milling Condition for SKH51 Condition Cutting chips n min -1 Velocity m/min Vf mm/min Feed per tooth mm/t a p mm a e mm Efficiency mm 3 /min
28 Optimization of HMS Milling Condition for SKH51 Tools after milling on each condition Condition1-3: Tools after 9000mm 3 milling Condition 4-6: Tools after 50000mm 3 milling (20min milling with No.5) Condition Radial relief face Rake face Cutting chips Efficiency [mm 3 /min]
29 Phenomena during Cutting Build-up Edge Various phenomena during cutting become obstacles to processing. Build-up edge...a phenomenon that a part of cutting chips covers a cutting edge and exhibits cutting function instead of the cutting edge. Formation cycle of build-up edge A part of cutting chips adheres to a tooth part and covers a cutting edge (formation of build-up edge). Tool Growth Tool Adhered substances grow gradually while exhibiting cutting function instead of the original cutting edge. >>Surface roughness becomes worse. Build-up edge (A flow of work materials and cutting chips) Tool Build up edge drops off at a certain size. >>Tool life decreases. Measures Increase cutting speed and raise temperature Provide high lubricity cutting fluid
30 Phenomena during Cutting Chattering Various phenomena during cutting become obstacles to process. Chattering Phenomenon On cutting processing, resonance occurs among a work piece, a tool and a machine and stripes appear on a finished surface. Influence Surface roughness becomes worse and tool life decreases. Sometimes difficult to continue because of chattering. Measures Adjust clumping of a work piece and a tool (overhang) and a movement component of a machine. Adjust quantity of cutting motion such as cutting speed, Feed Rate, axial/radial depth, etc.. Stripes appeared on a work piece by chattering
31 Cutting Resistance Each Component Cutting resistance...reaction force caused when a cutting tool is pushed into a work piece. It is considered as three force components. Feed force Horizontal force component in a feed direction. It determines a magnitude of feed power for cutting. Direction of rotation Work piece Feeding direction Cutting force Force component acts in a direction vertical to feed force. It affects heating value during cutting. In addition, power requirement during cutting is calculated by a magnitude of cutting force. (ex. In case of round cutting by a lathe) Thrust force Axial force component. It becomes force to deform a work piece and a tool, and decreases accuracy when it is large. P = F x v 60 x 102 x η P: Cutting power requirement (kw) F: Cutting force (kgf) v: Velocity (m/min) η: Mechanical efficiency
32 Cutting Resistance Magnitude and Changing Factor Cutting force is especially important among three force components (because it is a factor determining power requirement and heat generation ). Generally cutting force is sometimes referred to cutting resistance. Cutting resistance (cutting force) changes according to cutting conditions. Factors which may change cutting force (general tendency) Cutting resistance (cutting force) Small Large Note Work material Soft Hard Tooth part geometry (Rake angle) Milling area (Cutting depth x Feed Rate) Large rake angle Small Small rake angle Large Velocity Fast Slow Cutting force decreases when rake angle is up to about 30. Sometimes cutting force decreases by reducing cutting depth and increasing Feed Rate. Cutting force does not change so much in velocity over certain high speed.
33 Cutting Fluid Functions Cutting fluid is supplied to a cutting area to obtain fine surface and extend tool life on cutting processing. 3 functions of cutting fluid Lubrication Prevention of friction among cutting edges, cutting chips and a finished surface Prevention of occurrence of build-up edge Tool Work piece Cutting fluid Cutting chips Cooling Cleaning Prevention of chipping and scars on a finished surface by washing away cutting chips Extension of tool life by cooling tool Prevention of size deviation by temperature rise of a work piece
34 Cutting fluid Cutting Fluid Characteristics Requirements to cutting fluid Be harmless to humans Do not erode a work piece, a machine and paints Has a low risk of ignition and smoking Be small in putrefaction, degeneration, etc. No cutting fluid can satisfy all of there requirements. Appropriate cutting fluid differs depending on which is important among tool life, finished surface and efficiency. Types and characteristics of cutting fluid Water-soluble: Fine cooling Elements determining a capacity of non water-soluble cutting fluid Viscosity: Low High cleaning & cooling function High High lubrication function Non water-soluble: Fine lubricity Additive: Contained Cutting ability improves (but there is a possibility of corrosion of a work piece or fluid supplying equipment and outbreak of toxic gas during hightemperature milling) Fatty oil: Contained Prevention of occurrence of build-up edge Improvement of lubrication function
35 Cutting Fluid MQL Processing MQL (Minimum Quantity Lubrication)...Milling method using only very small quantity of cutting fluid. Problems of using cutting fluid Cost: Expense for cutting fluid and an electric bill to work a pump Environmental load: Treatment of used waste liquid, mass consumption of electrical energy Wish to decrease the use amount of cutting fluid MQL Processing, which atomizes small quantity (2-10ml/hour) of cutting fluid by high pressure air, attracts attention. (There is a case that reduces energy cost by 25% and cutting fluid cost by 95% by adoption of MQL.) Function of cutting fluid on MQL Processing Cooling function by evaporation Tool Entering a rake face of a tool and forming lubricant film >>Reduce frictional resistance Minimum quantity of cutting fluid is supplied to a cutting point by vacuum suction >>Continuation of lubrication function Work piece MQL is a effective method using lubrication function of cutting fluid at the most! (Cooling might be insufficient on processing with large heating value.)
36 Tool Wear Forms of Wear A cutting edge wears when continuous milling is performed. Tool wear shows various forms according to its factor. Notable examples are as follows. Mechanical wear Welding wear A part of welded work piece Tool Workpiece Hard particles in a work piece scratch and shave off a cutting edge. A part of work piece is welded on a rake face, and takes a part of the tool away when the welded piece peels off. Diffusional wear Chemical wear Cutting fluid Oxygen Mutual diffusion occurs between a work piece and a tool, and a soft compound is formed. Compound is made by reaction between a tool and other materials (cutting fluid, oxygen in the air, etc.) and removed.
37 Direction of cutting Work piece Tool Wear Part of Wear Wear of an edge part is called as below depending on where it occurs. Cutting chip Enlarge Rake face wear (Crater) Rake face Cutting edge Chipping Tool Relief face wear Crater is -concavity that occurs near a cutting edge by rake face wear. -likely to occur on high-speed milling of steels by cemented carbide tools. When wear occurs and progresses, re-pointing of an edge part or changing cutting tool is needed. >>End of tool life
38 Tool Life Standard & Judgment Breakage and wear of an edge part Standard for judgment Increase of cutting resistance Bad finished surface quality Re-pointing of the edge part or changing cutting tool is needed = End of tool life Shiny stripes occur on a finished surface Change of finished size or roughness of a finished surface reaches a certain value Thrust force or feed force of cutting resistance increases quickly Cutting force of cutting resistance increases by a certain value compared to a beginning of milling Wear of an edge part reaches a certain value Width of relief face wear w (mm) Standard for judgment of cemented carbide tool life Max. depth of crater t (mm) Application Accurate light milling Finishing of non-ferrous alloys, etc Milling of alloy steels, etc General milling of cast iron, steels, etc Roughing of gray cast iron, etc.
39 Tool Life Factors Determining Tool Life Tool life equation (F. W. Taylor) V c T m = C T = C V c 1 m V c : Velocity (m/min) T: Tool life m: Constant C: Constant From the equation above... Increase of velocity (V c ) Decrease of tool life (T) (because of increase of cutting heat by increase of speed on a tool end) Selection of heat-resistant tool material Ingenuities to reduce cutting heat (adjustment of milling condition and appropriate use of cutting fluid) are important! (Recently, there are almost no tools that are directly applicable to the equation above because of advances in coated cemented carbide tools for improving heat resistance. In addition, intermittent cutting such as processing by end mills shows tendency different from the equation above.)
40 Summary Cutting action Repeating moving of a cutting edge, plastic deformation and chip evacuation continuously. Cutting chips Cutting condition, tool material & heat generation are reflected to chip form. Information source to know a state of cutting Phenomena during cutting Build-up edge Chattering Influence on tool life and a finished surface Measures to prevent occurrence are needed. Cutting resistance Changes according to sharpness of a tool, cutting conditions, etc.. (Relationship to a condition of cutting, power and cutting heat) Cutting fluid Need to understand functions of cutting fluid and select suitable one in accordance with the type of cutting. Tool life Use of a tool Deterioration of tool condition by wear, etc. Deterioration of finished surface quality Pay attention to determining tool life and making a fine finished surface Prolong tool life and improve cutting performance by coating technology
Metal Cutting - 5. Content. Milling Characteristics. Parts made by milling Example of Part Produced on a CNC Milling Machine 7.
 Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Materials Removal Processes (Machining)
 Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Lecture 15. Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes. Turning
 Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
Metal Cutting (Machining)
 Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING
 Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING SUMMARY MILLING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a milling cutter 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Select
Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING SUMMARY MILLING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a milling cutter 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Select
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes.
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making
 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
4/5/6RFH 4/5/6RFH NEW. High Efficiency Roughing End Mill for Difficult-to-Cut Material
 For Difficult-to-Cut Material High Efficiency Roughing End Mill 4/5/6RFH High Efficiency Roughing End Mill for Difficult-to-Cut Material 4/5/6RFH NEW High Efficiency Machining of Difficult-to-Cut Material
For Difficult-to-Cut Material High Efficiency Roughing End Mill 4/5/6RFH High Efficiency Roughing End Mill for Difficult-to-Cut Material 4/5/6RFH NEW High Efficiency Machining of Difficult-to-Cut Material
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting. By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar
 Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Cutting with broach. You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1
 Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON
 GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON Electromagnetic Iron can be readily machined when proper tool angles are used. Tools should be ground to more acute cutting edge angles than are
GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON Electromagnetic Iron can be readily machined when proper tool angles are used. Tools should be ground to more acute cutting edge angles than are
A H M 531 The Civil Engineering Center
 Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
Thread Mills. Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
Various other types of drilling machines are available for specialized jobs. These may be portable, bench type, multiple spindle, gang, multiple
 Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
The role of inclination angle, λ on the direction of chip flow is schematically shown in figure which visualizes that,
 EXPERIMENT NO. 1 Aim: To study of Orthogonal & Oblique Cutting on a Lathe. Experimental set up.: Lathe Machine Theoretical concept: It is appears from the diagram in the following figure that while turning
EXPERIMENT NO. 1 Aim: To study of Orthogonal & Oblique Cutting on a Lathe. Experimental set up.: Lathe Machine Theoretical concept: It is appears from the diagram in the following figure that while turning
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba
 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Special reamers. Figure N 1 Reamer with descending cutting edges in carbide (Cerin)
 Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
11/15/2009. There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate
 s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
Solid Carbide Tools. Composite Tools. Performance by Design. ISO 9001 Certified Company
 Solid Carbide Tools Composite Tools Performance by Design ISO 9001 Certified Company As one of the world s largest manufacturers of solid carbide rotary cutting tools, SGS Tool Company has pioneered some
Solid Carbide Tools Composite Tools Performance by Design ISO 9001 Certified Company As one of the world s largest manufacturers of solid carbide rotary cutting tools, SGS Tool Company has pioneered some
Typical Parts Made with These Processes
 Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill
 New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing
 SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
PRODUCT INFORMATION CBN-SXR CBN-LN-SXR CBN-SXB CBN-LN-SXB. CBN End Mill Series
 PRODUCT INFORMATION CBN-LN-SXR CBN-LN-SXB CBN End Mill Series The helical flutes are changing the CBN end mills! Highly Appealing OSG CBN End Mill Series Are you bothered by these issues? The work material
PRODUCT INFORMATION CBN-LN-SXR CBN-LN-SXB CBN End Mill Series The helical flutes are changing the CBN end mills! Highly Appealing OSG CBN End Mill Series Are you bothered by these issues? The work material
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting
 Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
Design for machining
 Multiple choice questions Design for machining 1) Which one of the following process is not a machining process? A) Planing B) Boring C) Turning D) Forging 2) The angle made between the rake face of a
Multiple choice questions Design for machining 1) Which one of the following process is not a machining process? A) Planing B) Boring C) Turning D) Forging 2) The angle made between the rake face of a
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Kalpakjian Schmid Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1
 CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
Indexable Milling Tools
 Tools Difference and selection between down milling and up milling X Vf Vf Y B Up milling magnified X Dowm milling magnified Y Climb milling (also called down milling): the feed direction of workpiece
Tools Difference and selection between down milling and up milling X Vf Vf Y B Up milling magnified X Dowm milling magnified Y Climb milling (also called down milling): the feed direction of workpiece
3AFK 3AFK. For Aluminum Machining. 3-Flute End Mill for High Efficiency and Precision. Solid End Mill
 Solid End Mill For Machining 3-Flute End Mill for High Efficiency and Precision High Efficiency with 3-Flutes. Excellent Precision Machining Stable Machining due to sharp edge for Anti-chattering Performance
Solid End Mill For Machining 3-Flute End Mill for High Efficiency and Precision High Efficiency with 3-Flutes. Excellent Precision Machining Stable Machining due to sharp edge for Anti-chattering Performance
TURNING BORING TURNING:
 TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
Machining Strenx and Hardox. Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling
 Machining and Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling and are registered trademarks. These steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB. high strength steel and wear plate are steel grades
Machining and Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling and are registered trademarks. These steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB. high strength steel and wear plate are steel grades
TOOLS NEWS B228G. Ceramic End Mills. CERAMIC Corner Radius End Mills. Ultra high productivity for nickel based heat resistant alloys CERAMIC
 Ceramic End Mills TOOLS NEWS B228G CERAMIC Corner Radius End Mills Ultra high productivity for nickel based heat resistant alloys CERAMIC CERAMIC End Mill Series From difficult-to-cut to easy-to-cut! Generation
Ceramic End Mills TOOLS NEWS B228G CERAMIC Corner Radius End Mills Ultra high productivity for nickel based heat resistant alloys CERAMIC CERAMIC End Mill Series From difficult-to-cut to easy-to-cut! Generation
New. Products2013.
 T u n g a l o y www.tungaloy.com Company Overview Providing Complete Tooling Solutions for the Metal Removal and Industrial Product Sectors TUNGALOY is one of the world s leading manufacturers of carbide
T u n g a l o y www.tungaloy.com Company Overview Providing Complete Tooling Solutions for the Metal Removal and Industrial Product Sectors TUNGALOY is one of the world s leading manufacturers of carbide
Improved Efficiency for Slot Milling with Deep Depths of Cut
 TOOLS NEWS B230G Corner Radius End Mill for High Efficiency Titanium Alloy Machining New Product Improved Efficiency for Slot Milling with Deep Depths of Cut Corner Radius End Mill for High Efficiency
TOOLS NEWS B230G Corner Radius End Mill for High Efficiency Titanium Alloy Machining New Product Improved Efficiency for Slot Milling with Deep Depths of Cut Corner Radius End Mill for High Efficiency
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT III THEORY OF METAL CUTTING Broad classification of Engineering Manufacturing Processes. It is extremely difficult to tell the exact number of various manufacturing processes
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT III THEORY OF METAL CUTTING Broad classification of Engineering Manufacturing Processes. It is extremely difficult to tell the exact number of various manufacturing processes
地址 : 中国湖南株洲市天元区黄河南路 Address: Huanghe Southern Road, Tianyuan Zone,Zhuzhou, Hunan Province, China 邮编 (Postcode): 电话 (Tel):
 地址 : 中国湖南株洲市天元区黄河南路 Address: Huanghe Southern Road, Tianyuan Zone,Zhuzhou, Hunan Province, China 邮编 (Postcode): 412007 电话 (Tel): 0731-22882430 22889474 22889477 22889468 22887814 22880853 22882725 22882431
地址 : 中国湖南株洲市天元区黄河南路 Address: Huanghe Southern Road, Tianyuan Zone,Zhuzhou, Hunan Province, China 邮编 (Postcode): 412007 电话 (Tel): 0731-22882430 22889474 22889477 22889468 22887814 22880853 22882725 22882431
Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning
 You are here: Home > Handout > Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Contents 1. Introduction 2. Center Lathe 3. Cutting Tools 4. Basic Matel Cutting Theory 5. Tool Angles
You are here: Home > Handout > Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Contents 1. Introduction 2. Center Lathe 3. Cutting Tools 4. Basic Matel Cutting Theory 5. Tool Angles
Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes. Materials Processing. Hole Making Processes. MET Manufacturing Processes
 MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
Quick Change Carbide & Steel Boring Bar Instructions Manual
 Workpiece Rigidity 1 Work holding Use the proper chuck and jaws to hold the work-piece, to assure that the part is held with maximum rigidity and stability under cutting force. 2 Steady Rest Support When
Workpiece Rigidity 1 Work holding Use the proper chuck and jaws to hold the work-piece, to assure that the part is held with maximum rigidity and stability under cutting force. 2 Steady Rest Support When
Grade/Chip breaker. Contents. Grades. Chip breakers A02 A03 A04. Korloy grades system Grade selection system The feature of korloy grades A06 A08 A09
 Grade/Chip breaker Contents Korloy grades system Grade selection system The feature of korloy grades A02 A03 A04 For For For A06 A08 A09 >>> /Chipbreakers Korloy grades system Uncoated P For steel ST05
Grade/Chip breaker Contents Korloy grades system Grade selection system The feature of korloy grades A02 A03 A04 For For For A06 A08 A09 >>> /Chipbreakers Korloy grades system Uncoated P For steel ST05
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1
 MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
Figure N 1- Characteristic angles of a drill
 Basic of drill In these technical descriptions for simplicity we use the term drill instead of the more complete name twist drill bits. The drill is the tool universally used to make holes in any material.
Basic of drill In these technical descriptions for simplicity we use the term drill instead of the more complete name twist drill bits. The drill is the tool universally used to make holes in any material.
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
TRAINING MANUAL. Part INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS
 PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice. By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR
 Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
Hybrid TAC Mill Series Next generation TAC endmills allow one tool for various types of machining
 No.011-USA April 2009 Small diameter endmills able to handle various machining modes Hybrid TAC Mill Series Next generation TAC endmills allow one tool for various types of machining Hybrid TAC Mills provide
No.011-USA April 2009 Small diameter endmills able to handle various machining modes Hybrid TAC Mill Series Next generation TAC endmills allow one tool for various types of machining Hybrid TAC Mills provide
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS
 Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
ROOP LAL Unit-6 (Milling) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
FMA 2000 / 5 FMA 63 / 5 FM 1000 / FM 25 / Copy Milling Program Tool Contents. Milling Cutters Identification System Arbor
 Copy Milling Program Tool Contents FM Style 1 Toroid Cylindrical End Milling Cutter 42/43 FM Style 2 Toroid Taper End Milling Cutter 42/43 FMA Arbor Style Milling Cutter 42/43 Insert ata 44/45 Cutting
Copy Milling Program Tool Contents FM Style 1 Toroid Cylindrical End Milling Cutter 42/43 FM Style 2 Toroid Taper End Milling Cutter 42/43 FMA Arbor Style Milling Cutter 42/43 Insert ata 44/45 Cutting
Copy Milling Program Tools
 Millstar face mills are equally useful on newer high velocity machines and older slower equipment and will optimize milling performance of all your machine tools. The hardened tool bodies can be run at
Millstar face mills are equally useful on newer high velocity machines and older slower equipment and will optimize milling performance of all your machine tools. The hardened tool bodies can be run at
Implementation and Analysis on Carbide Boring Tool for Increasing Tool Life
 Implementation and Analysis on Carbide Boring Tool for Increasing Tool Life Prathamesh Vishwas Waghmare 1, Parag Arun Yeshi 2 Omkar Suresh Thakur 3, Amol Parshuram Khairnar 4 Deepak Padmakar Patil 5 1,2,3,4,5
Implementation and Analysis on Carbide Boring Tool for Increasing Tool Life Prathamesh Vishwas Waghmare 1, Parag Arun Yeshi 2 Omkar Suresh Thakur 3, Amol Parshuram Khairnar 4 Deepak Padmakar Patil 5 1,2,3,4,5
MASTER CATALOGUE. Beyond EADE Solid Ceramic End Mills.
 MASTER CATALOGUE Beyond EADE Solid Ceramic End Mills Beyond EADE Solid Ceramic End Mill Primary Application EADE Solid Ceramic End Mills offer higher productivity and tool life in roughing nickel-based
MASTER CATALOGUE Beyond EADE Solid Ceramic End Mills Beyond EADE Solid Ceramic End Mill Primary Application EADE Solid Ceramic End Mills offer higher productivity and tool life in roughing nickel-based
In hall 4, stand A42, you can experience Intelligence in Production. The following trade show highlights can be seen at EMO:
 Guhring at EMO 2013 Intelligence in Production with precision tools from Guhring In the spirit of the motto of this year s EMO, from 16th to 21th September in Hanover, Guhring is introducing trendsetting
Guhring at EMO 2013 Intelligence in Production with precision tools from Guhring In the spirit of the motto of this year s EMO, from 16th to 21th September in Hanover, Guhring is introducing trendsetting
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING
 THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine
 CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
THE PROBLEM OF TOOL SELECTION FOR MILLING LARGE INTERNAL THREADS
 THE PROBLEM OF TOOL SELECTION FOR MILLING LARGE INTERNAL THREADS Mladen Bošnjaković Dragomir Moškun Marko Jerković M.Sc. Mladen Bošnjaković, Slavonski Brod University of Applied Science, Dr. M. Budaka
THE PROBLEM OF TOOL SELECTION FOR MILLING LARGE INTERNAL THREADS Mladen Bošnjaković Dragomir Moškun Marko Jerković M.Sc. Mladen Bošnjaković, Slavonski Brod University of Applied Science, Dr. M. Budaka
Drilling Tools. Common problems and solutions for drilling. Problem Cause Solution. Bend,distortion and slippage of machine and workpiece
 Drilling Tools for solid carbide drills C Common problems and solutions for drilling Problem Cause Solution Drill breakage Bend,distortion and slippage of machine and workpiece Increase the rigidity of
Drilling Tools for solid carbide drills C Common problems and solutions for drilling Problem Cause Solution Drill breakage Bend,distortion and slippage of machine and workpiece Increase the rigidity of
Jet-Stream Modular Carbide & Steel Boring Bar Instructions Manual
 Workpiece Rigidity 1 Work holding Use the proper chuck and jaws to hold the work-piece, to assure that the part is held with maximum rigidity and stability under cutting force. 2 Steady Rest Support When
Workpiece Rigidity 1 Work holding Use the proper chuck and jaws to hold the work-piece, to assure that the part is held with maximum rigidity and stability under cutting force. 2 Steady Rest Support When
Features. Special forms are possible
 Center Drill >> The is a trademark of Nine9, the developer of the first indexable center drill in the world.(patented) Offering an indexable insert system for the 1st time, Nine9 s design improves your
Center Drill >> The is a trademark of Nine9, the developer of the first indexable center drill in the world.(patented) Offering an indexable insert system for the 1st time, Nine9 s design improves your
Machining. Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling
 Machining Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling hardox and weldox are registered trademarks.these steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB Oxelösund AB. hardox wear plate and weldox extra-high
Machining Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling hardox and weldox are registered trademarks.these steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB Oxelösund AB. hardox wear plate and weldox extra-high
FMA 2000 / 5 FMA 63 / 5 FM 1000 / FM 25 / Copy Milling Program Tool Contents. Milling Cutters Identification System Arbor
 Copy Milling Program Tool Contents FM Style 1 Toroid Cylindrical End Milling Cutter 38/39 FM Style 2 Toroid Taper End Milling Cutter 38/39 FMA Arbor Style Milling Cutter 38/39 Insert ata 40/41 Cutting
Copy Milling Program Tool Contents FM Style 1 Toroid Cylindrical End Milling Cutter 38/39 FM Style 2 Toroid Taper End Milling Cutter 38/39 FMA Arbor Style Milling Cutter 38/39 Insert ata 40/41 Cutting
Optimum tool for finish machining
 Series Expansion Indexable Ball-nose End Mill for Finishing Indexable Corner Radius End Mill for Finishing 2011.2 Update B065E SRF/SRB SUF High accuracy indexable end mill Optimum tool for finish machining
Series Expansion Indexable Ball-nose End Mill for Finishing Indexable Corner Radius End Mill for Finishing 2011.2 Update B065E SRF/SRB SUF High accuracy indexable end mill Optimum tool for finish machining
INTRODUCTION TO GRINDING PROCESS
 GRINDING PART 2 Grinding Grinding is a material removal process accomplished by abrasive particles that are contained in a bonded grinding wheel rotating at very high surface speeds. The rotating grinding
GRINDING PART 2 Grinding Grinding is a material removal process accomplished by abrasive particles that are contained in a bonded grinding wheel rotating at very high surface speeds. The rotating grinding
DRA DRA. MagicDrill. High Efficiency Modular Drill. Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design. High Efficiency Modular Drill
 High Efficiency Modular Drill High Efficiency Modular Drill MagicDrill DRA Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design Optimal web thickness limits deflection Fine chip breaking and smooth
High Efficiency Modular Drill High Efficiency Modular Drill MagicDrill DRA Excellent hole accuracy with a low cutting force design Optimal web thickness limits deflection Fine chip breaking and smooth
Product Information Report Maximizing Drill Bit Performance
 Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
The shape of the cone of the twist drills
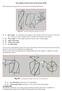 The shape of the cone of the twist drills With reference to figure N 1 we can give the following definitions: Fig. N 1- Some characteristic angles of twist drill ε : Helix angle; it is formed by the tangent
The shape of the cone of the twist drills With reference to figure N 1 we can give the following definitions: Fig. N 1- Some characteristic angles of twist drill ε : Helix angle; it is formed by the tangent
Chapter 25. Other Machining Processes. Materials Processing. MET Manufacturing Processes. Shaping Planing Broaching Sawing Filing
 MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 25 Other Machining Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Other Machining Processes Shaping
MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 25 Other Machining Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Other Machining Processes Shaping
Optimized flute design Better chip evacuation. Carbide substrate Higher heat resistance, higher speed.
 Thread Mills Available for the first time, our solid thread mills are designed to be the highest quality thread milling solution. WIDIA-GTD Cut up to 63 HRC. Improved overall thread quality. Optimized
Thread Mills Available for the first time, our solid thread mills are designed to be the highest quality thread milling solution. WIDIA-GTD Cut up to 63 HRC. Improved overall thread quality. Optimized
Automotive. Tooling Solutions. Providing Optimal Tooling Solutions for Automotive Machining
 Automotive Tooling Solutions Providing Optimal Tooling Solutions for Automotive Machining Crankcase Cylinder Heads Crankshafts Camshafts Connecting Rods Valve Bodies Synchronizer Gears Main Shafts CVT
Automotive Tooling Solutions Providing Optimal Tooling Solutions for Automotive Machining Crankcase Cylinder Heads Crankshafts Camshafts Connecting Rods Valve Bodies Synchronizer Gears Main Shafts CVT
FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly NARRATION (VO): NARRATION (VO): NARRATION (VO): INCLUDING: METALS,
 Copyright 2002 Society of Manufacturing Engineers --- 1 --- FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly SCENE 1. CG: Plastics Machining white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape
Copyright 2002 Society of Manufacturing Engineers --- 1 --- FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly SCENE 1. CG: Plastics Machining white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape
Tungsten Carbide End Mills UNIMAX Series
 Tungsten Carbide End Mills UNIMAX Series Diamond Coated 2 Flute UDC Series NEW NEW UDCBF UDCLBF UDCB UDCLB UDCLRS High-grade Ball End Mills High-grade Long Neck Ball End Mills Ball End Mills Long Neck
Tungsten Carbide End Mills UNIMAX Series Diamond Coated 2 Flute UDC Series NEW NEW UDCBF UDCLBF UDCB UDCLB UDCLRS High-grade Ball End Mills High-grade Long Neck Ball End Mills Ball End Mills Long Neck
UNIT 4: (iii) Illustrate the general kinematic system of drilling machine and explain its working principle
 UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
Module 2. Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing. 1 Pepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta
 Module 2 Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing 1 Module Objectives: 1. Calculate the cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut 2. Recognize coordinate 3. Differentiate between Cartesian
Module 2 Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing 1 Module Objectives: 1. Calculate the cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut 2. Recognize coordinate 3. Differentiate between Cartesian
ROOP LAL Unit-6 Lathe (Turning) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 4 General urpose Machine Tools Lesson 24 Forces developing and acting in machine tools Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Identify the sources
Module 4 General urpose Machine Tools Lesson 24 Forces developing and acting in machine tools Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Identify the sources
Carbide Drill for Hardened Steel EHSE-TH. Epoch TH Hard Drill. New Product News No.405E
 Carbide Drill for Hardened Steel Epoch TH Hard Drill New Product News No.0E- 17-7 TH coating and guides with double margins make it last even longer. EDM, which is generally used for drilling hardend steel,
Carbide Drill for Hardened Steel Epoch TH Hard Drill New Product News No.0E- 17-7 TH coating and guides with double margins make it last even longer. EDM, which is generally used for drilling hardend steel,
DIE & MOLD MACHINING TOOL SOLUTIONS FOR INDUSTRIES DM18 HEAD OFFICE
 DM18 DIE & MOLD MACHINING TOOL SOLUTIONS FOR INDUSTRIES HEAD OFFICE 211, Sewolcheon-ro, Bupyeong-gu, Incheon, South Korea Phone : +82-32-526-0909 E-mail : yg1@yg1.kr www.yg1.kr Note The new address above
DM18 DIE & MOLD MACHINING TOOL SOLUTIONS FOR INDUSTRIES HEAD OFFICE 211, Sewolcheon-ro, Bupyeong-gu, Incheon, South Korea Phone : +82-32-526-0909 E-mail : yg1@yg1.kr www.yg1.kr Note The new address above
Features. High Positive Rake Angle. Multi-Side Grinding. High Speed, High Feed Rate. Economical
 Engraving This is a revolutionary new concept of engraving tools with indexable carbide inserts. They offer you the ability to produce HIGH QUAITY ENGRAVING in most materials. The latest coated carbide
Engraving This is a revolutionary new concept of engraving tools with indexable carbide inserts. They offer you the ability to produce HIGH QUAITY ENGRAVING in most materials. The latest coated carbide
AUTOMATED MACHINE TOOLS & CUTTING TOOLS
 CAD/CAM COURSE TOPIC OF DISCUSSION AUTOMATED MACHINE TOOLS & CUTTING TOOLS 1 CNC systems are used in a number of manufacturing processes including machining, forming, and fabrication Forming & fabrication
CAD/CAM COURSE TOPIC OF DISCUSSION AUTOMATED MACHINE TOOLS & CUTTING TOOLS 1 CNC systems are used in a number of manufacturing processes including machining, forming, and fabrication Forming & fabrication
APRIL 2009 / NEW-100 / PAGE 1 OF 13
 APRIL 2009 / NEW-100 / PAGE 1 OF 13 The standard UNIDEX line covers reaming applications from 5/16 to 1 1/4 diameter. The single indexable blade and high wear resistant carbide or cermet pads provide a
APRIL 2009 / NEW-100 / PAGE 1 OF 13 The standard UNIDEX line covers reaming applications from 5/16 to 1 1/4 diameter. The single indexable blade and high wear resistant carbide or cermet pads provide a
Understanding the basics of Spiral Pointed Taps. July 2017
 Understanding the basics the of Spiral Basics Pointed Taps of Spiral Pointed Taps July 2017 Understanding the Basics of Spiral Pointed Taps What is a spiral pointed taps? Cutting torque of spiral pointed
Understanding the basics the of Spiral Basics Pointed Taps of Spiral Pointed Taps July 2017 Understanding the Basics of Spiral Pointed Taps What is a spiral pointed taps? Cutting torque of spiral pointed
Kennametal Twist Drills KHSS Drill Dictionary
 Kennametal Twist KHSS Drill Dictionary shank diameter tang tang drive axis taper shank shank length neck straight shank point angle helix angle flutes flute length body overall length drill diameter lip
Kennametal Twist KHSS Drill Dictionary shank diameter tang tang drive axis taper shank shank length neck straight shank point angle helix angle flutes flute length body overall length drill diameter lip
CARBIDE END MILLS SPECIFICATIONS
 SPECIFICATIONS COATING GUIDE Material Hardness TiN TiCN TiALN Austentic Stainless Steel < 35 HRc * X Martinistic Stainless Steel < 35 HRc * X Martinistic Stainless Steel >= 35 HRc X PH Stainless Steel
SPECIFICATIONS COATING GUIDE Material Hardness TiN TiCN TiALN Austentic Stainless Steel < 35 HRc * X Martinistic Stainless Steel < 35 HRc * X Martinistic Stainless Steel >= 35 HRc X PH Stainless Steel
Cat.3a Super Power Drill Super Drill
 www.jic-tools.com.tw Cat.3a Super Power Drill Super Drill WE HAVE INVESTED RESOURCES IN THE DESIGN & MANUFACTURE OF INSERTED CUTTERS Cost Saving Our innovative tooling design upgrades productivity and
www.jic-tools.com.tw Cat.3a Super Power Drill Super Drill WE HAVE INVESTED RESOURCES IN THE DESIGN & MANUFACTURE OF INSERTED CUTTERS Cost Saving Our innovative tooling design upgrades productivity and
Lower Spindle Power Consumptionn
 ower Spindle Power Consumptionn > Five cutters for drilling Ø13~Ø50 mm. > One insert for all kind of materials. > The drilling is done by helical interpolation. (circular ramping milling) Nine9 NC Helix
ower Spindle Power Consumptionn > Five cutters for drilling Ø13~Ø50 mm. > One insert for all kind of materials. > The drilling is done by helical interpolation. (circular ramping milling) Nine9 NC Helix
Drilling. Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL.
 Drilling Machine Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling
Drilling Machine Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling
Lecture 18. Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing
 Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE
 TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE CONTENTS 4.1 Tool wear During the cutting operation, the cutting edge is stressed mechanically and thermally until it becomes completely blunt and unable to cut, 100 % wear occurs
TOOL WEAR AND TOOL LIFE CONTENTS 4.1 Tool wear During the cutting operation, the cutting edge is stressed mechanically and thermally until it becomes completely blunt and unable to cut, 100 % wear occurs
Machining vs. Grinding
 University of Connecticut Machining vs. Grinding -- Towards High Efficiency Machining Bi Zhang Mechanical Engineering zhang@engr.uconn.edu Presentation Sequence Introduction High Speed Machining High Speed
University of Connecticut Machining vs. Grinding -- Towards High Efficiency Machining Bi Zhang Mechanical Engineering zhang@engr.uconn.edu Presentation Sequence Introduction High Speed Machining High Speed
Router Section 2018 Master Catalog
 Router Section 2018 Master Catalog For more than 95 years, M.A. Ford has been at the cutting edge of tooling design and manufacturing and has developed an enviable global reputation for performance and
Router Section 2018 Master Catalog For more than 95 years, M.A. Ford has been at the cutting edge of tooling design and manufacturing and has developed an enviable global reputation for performance and
The Catalogue of Nomura Tool Works Co., Ltd. Tool manufacturing since 1954 Bent Shank Taps Nib Taps Nut Taps
 The Catalogue of Nomura Tool Works Co., Ltd. Tool manufacturing since 1954 Bent Shank Taps Nib Taps Nut Taps Introduction In today's highly developed machine industry, a tap is a cutting tool that requires
The Catalogue of Nomura Tool Works Co., Ltd. Tool manufacturing since 1954 Bent Shank Taps Nib Taps Nut Taps Introduction In today's highly developed machine industry, a tap is a cutting tool that requires
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
 Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
Up to 5 3 from 5 to 10 4 from 10 to 18 6 from 18 to 35 8
 Reamers They are the most used tools for the finishing holes. Can be divided into various categories, such as hand-reamers and those used in machine tools, reamers in highspeed steel, in carbide; inserted
Reamers They are the most used tools for the finishing holes. Can be divided into various categories, such as hand-reamers and those used in machine tools, reamers in highspeed steel, in carbide; inserted
Investigation And Optimization Of Various Machining Parameters Affecting The Effectiveness Of Turning: A Review
 Investigation And Optimization Of Various Machining Parameters Affecting The Effectiveness Of Turning: A Review 1 S B Chikalthankar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government
Investigation And Optimization Of Various Machining Parameters Affecting The Effectiveness Of Turning: A Review 1 S B Chikalthankar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government
Features. Excellent Repeatability >> Applications >>
 Chamfer Mill 45 >> Nine9 chamfer mill is designed for chamfering and countersinking with an indexable insert. The insert is a specifically designed for use in high speed machining ; the multiple flutes
Chamfer Mill 45 >> Nine9 chamfer mill is designed for chamfering and countersinking with an indexable insert. The insert is a specifically designed for use in high speed machining ; the multiple flutes
Abrasive Machining Processes. N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT Kanpur
 Abrasive Machining Processes N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT Kanpur Introduction Abrasive machining involves material removal by the action of hard, abrasive particles. The use of abrasives
Abrasive Machining Processes N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT Kanpur Introduction Abrasive machining involves material removal by the action of hard, abrasive particles. The use of abrasives
Makrolon Solid Polycarbonate Sheets
 1. General remarks Tools sheets can be machined using the standard tools commonly used for metal and woodworking. We recommend carbide-tipped tools. Above all, it is important to use sharp cutting tools
1. General remarks Tools sheets can be machined using the standard tools commonly used for metal and woodworking. We recommend carbide-tipped tools. Above all, it is important to use sharp cutting tools
Drill for Wheel Hubs. Solid Carbide Drill MHE
 . Update B3G Expanded New Grade Solid Carbide Drill Uniue design provides superior hole accuracy for shallow hole drilling. Effective drilling of hub bolt holes can be achieved. Additional new grade DP30
. Update B3G Expanded New Grade Solid Carbide Drill Uniue design provides superior hole accuracy for shallow hole drilling. Effective drilling of hub bolt holes can be achieved. Additional new grade DP30
Application and Technical Information Thread Milling System (TMS) Minimum Bore Diameters for Thread Milling
 Inserts Application and Technical Information Minimum Bore iameters for Thread Milling UN-ISO-BSW tpi 48 3 4 0 16 1 10 8 7 6 5 4.5 4 Technical ata Accessories Vintage Cutters Widia Cutters Thread Milling
Inserts Application and Technical Information Minimum Bore iameters for Thread Milling UN-ISO-BSW tpi 48 3 4 0 16 1 10 8 7 6 5 4.5 4 Technical ata Accessories Vintage Cutters Widia Cutters Thread Milling
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR REAMERS FLUTE STYLES
 BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
