OIML R 46-3 RECOMMENDATION. Edition 2013 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION
|
|
|
- Meagan Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 46-3 Edition 2013 (E) Active electrical energy meters. Part 3: Test report format Compteurs actifs d'énergie électrique. Partie 3: Format du rapport d essais OIML R 46-3 Edition 2013 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE MÉTROLOGIE LÉGALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF LEGAL METROLOGY
2
3 Contents Foreword Information Meter specification Test values General Requirements checklist Timing requirements for interval and multi-tariff meters (3.4) Storage period for interval and multi-tariff data (3.4) Meter markings (3.5) Validation procedure (protection of metrological properties) (4.3; 3.6) Tests for maximum permissible error Initial intrinsic error for positive and negative flow (6.2.1) Reverse energy flow (6.2.1) Self heating (6.2.2) Starting current (6.2.3) Test of no-load condition (6.2.4) Meter constants (6.2.5) Tests for influence quantities Temperature dependence (6.3.2; Table 3) Load balance (6.3.3) Voltage variation (6.3.4) Frequency variations (6.3.5) Harmonics in voltage and current (6.3.6) Tilt (6.3.7) Severe voltage variations (6.3.8) One or two phases interrupted (6.3.9) Sub-harmonics in the AC current circuit (6.3.10) Harmonics in the AC current circuit (6.3.11) Reversed phase sequence (any two phases interchanged) (6.3.12) Continuous (DC) magnetic induction of external origin (6.3.13) Magnetic field (AC, power frequency) of external origin (6.3.14) Radiated, radio frequency (RF), electromagnetic fields ( ) Imm to conducted disturbances, induced by radiofrequency fields ( ) DC in the AC current circuit (6.3.16) High-order harmonics (6.3.17) Test for disturbances Critical change value (6.4.1 a); ) Magnetic field (AC, power frequency) of external origin (6.4.2) Electrostatic discharge (6.4.3) Fast transients (6.4.4) Voltage dips and interruptions (6.4.5) Radiated, radio frequency (RF), electromagnetic fields (6.4.6) Surges on AC mains power lines (6.4.7) Damped oscillatory waves imm test (6.4.8) Short-time overcurrent (6.4.9)
4 6.10 Impulse voltage (6.4.10) Earth fault (6.4.11) Operation of auxiliary devices (6.4.12) Vibrations ( ) Shock ( ) Protection against solar radiation (6.4.14) Protection against ingress of dust (6.4.15) Extreme temperatures - Dry heat ( ) Extreme temperatures - Cold ( ) Damp heat, steady-state (non-condensing), for humidity class H1 ( ) Damp heat, cyclic (condensing), for humidity class H2 and H3 ( ) Water test ( ) Durability (6.4.17)
5 Foreword The International Organization of Legal Metrology (OIML) is a worldwide, intergovernmental organization whose primary aim is to harmonize the regulations and metrological controls applied by the national metrological services, or related organizations, of its Member States. The main categories of OIML publications are: International Recommendations (OIML R), which are model regulations that establish the metrological characteristics required of certain measuring instruments and which specify methods and equipment for checking their conformity. OIML Member States shall implement these Recommendations to the greatest possible extent; International Documents (OIML D), which are informative in nature and which are intended to harmonize and improve work in the field of legal metrology; International Guides (OIML G), which are also informative in nature and which are intended to give guidelines for the application of certain requirements to legal metrology; International Basic Publications (OIML B), which define the operating rules of the various OIML structures and systems; and OIML Draft Recommendations, Documents and Guides are developed by Project Groups linked to Technical Committees or Subcommittees which comprise representatives from OIML Member States. Certain international and regional institutions also participate on a consultation basis. Cooperative agreements have been established between the OIML and certain institutions, such as ISO and the IEC, with the objective of avoiding contradictory requirements. Consequently, manufacturers and users of measuring instruments, test laboratories, etc. may simultaneously apply OIML publications and those of other institutions. International Recommendations, Documents, Guides and Basic Publications are published in English (E) and translated into French (F) and are subject to periodic revision. Additionally, the OIML publishes or participates in the publication of Vocabularies (OIML V) and periodically commissions legal metrology experts to write Expert Reports (OIML E). Expert Reports are intended to provide information and advice, and are written solely from the viewpoint of their author, without the involvement of a Technical Committee or Subcommittee, nor that of the CIML. Thus, they do not necessarily represent the views of the OIML. This publication - reference OIML R 46-3, edition 2013 (E) was developed by OIML TC 12 Instruments for measuring electrical quantities. It was approved for final publication by the International Committee of Legal Metrology at its 48th meeting in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam, in October OIML Publications may be downloaded from the OIML web site in the form of PDF files. Additional information on OIML Publications may be obtained from the Organization s headquarters: Bureau International de Métrologie Légale 11, rue Turgot Paris - France Telephone: 33 (0) Fax: 33 (0) biml@oiml.org Internet: 5
6 1 Information 1.1 Meter specification Application no.: Meter manufacturer: Meter model: Serial number(s): Meter type (electromechanical/static): Accuracy class: A B C D Nominal voltage, U nom : Nominal frequency, f nom : Maximum current, I max : Transitional current, : Minimum current, I min : Starting current, I st : V Hz A A A A Direct-connected Current transformer Current and voltage transformers Connection mode (phases, wires, elements): Alternative connection mode(s): Direction of energy flow / registers: Single-register, bi-directional Two-register, bi-directional Register multiplier: Meter constant: Specified clock frequencies: Indoor / Outdoor: IP Rating: Terminal arrangement (e.g: BS, DIN): Insulation protection class: Single-register, positive direction only Single-register, uni-directional (include units of measurement) (include units of measurement) Lower specified temperature: 55 C 40 C 25 C 10 C +5 C Upper specified temperature: +30 C +40 C +55 C +70 C Humidity class: H1 H2 H3 Tilt / Mounting position: Mounting position specified Any position is allowed Hardware version(s): Software version(s): 1.2 Test values When ranges of values are specified by the manufacturer, the values used for testing shall be specified below. Test voltage: V Test frequency: Hz Test connection mode: 6
7 2 General 2.1 Requirements checklist Clause Description Remarks 3.1 Units of measurement Valid units of measurement (Wh, kwh, MWh, GWh) 3.2; Table 1 Rated operating conditions (Table 1) Check I max / ratio complies Check I max /I min ratio complies Check I max /I st ratio complies 3.4 Requirements for interval and multi-tariff meters For interval meters, the summation of interval data shall equate to the cumulative register value over the same period One and only one register (in addition to the cumulative register) shall be active at any time The summation of values recorded in each multi-tariff register shall equate to the value recorded in the cumulative register Checking facility event record Check any checking facility for sufficient room for events and that it is of the first-in-first-out type Readability of result Indicating device is easy to read Height of characters of measurement result 4 mm All decimal fractions are clearly indicated Able to display all data relevant for billing purposes All registers relevant for billing can store and display energy = (4000 U nom I max n) Wh, where n is the number of phases. (4000 h). For mechanical registers All decimal fraction drums are marked differently For auto-sequencing displays Each register for billing purposes is retained for 5 s For multi-tariff meters The register which reflects the active tariff is indicated It is possible to read each tariff register locally and each register is clearly identified For electronic registers Retention time for results for a disconnected meter is 1 year Electronic indicating devices are provided with a display test Testability The meter is equipped with a test output The wavelength of radiated signals is between 550 nm to 1000 nm. The radiation strength E T complies with limits at on and off conditions. 7
8 2.2 Timing requirements for interval and multi-tariff meters (3.4) Limits shall be determined from IEC based on clock type. Test Temperature ( C) Duration Result (s/day) Limit (s/day) Mains operation days High temperature: hours Low temperature: hours Operation reserve: - 36 hours Check that each result limit 2.3 Storage period for interval and multi-tariff data (3.4) Specify storage period Remarks 2.4 Meter markings (3.5) Description Markings are indelible, distinct and legible from outside the meter Serial number affixed in position not readily disassociated from meter Remarks Meter marking Manufacturer Nominal voltage U nom Maximum current I max Transitional current Minimum current I min Approval mark(s) Serial number Number of phases Number of wires Register multiplier (if other than ) Meter constant(s) Year of manufacture Accuracy class Directionality of energy flow (if required) Meter type Temperature range Humidity and water protection information Impulse voltage protection information Nominal frequency f nom The connection mode(s) for which the meter is specified Connection terminals uniquely identified to distinguish between terminals Valid marking on meter? Yes No Remarks 8
9 3 Validation procedure (protection of metrological properties) (4.3; 3.6) The two applicable validation procedures are as follows: AD: Analysis of the documentation and validation of the design. VFTSw: Validation by functional testing of software functions. Clause Requirements Validation description Software identification (AD + VFTSw) Specify software identification and means of identification Validate the presentation or display of the software identification Validate that the software identification is inextricably linked to the software Prevention misuse (AD + VFTSw) Validate that possibilities of misuse are minimal Fraud protection (AD + VFTSw) Validate that legally relevant software is secured against modification, loading or changes Validate that only clearly documented functions can be activated by the user interface Validate protection/sealing that makes unauthorised access impossible or evident Parameter protection (AD + VFTSw) Validate that legally relevant characteristics are secured against unauthorised modification. The following are considered as modifications to (legally relevant) device-specific parameters. Zeroing or changing the register for total energy Zeroing or changing the event record of a checking facility Validate that the meter stops registering energy when modifying a (legally relevant) device-specific parameter Validate (where applicable) a facility to record adjustments to device-specific parameters Separation of electronic devices and sub-assemblies (AD) Identify the legally relevant part(s) of the meter Validate the separation. Metrologically critical parts of an electricity meter whether software or hardware parts shall not be inadmissibly influenced by other parts of the meter Separation of software (AD) Identify and validate legally relevant software Identify and validate the interface between legally relevant software and other software parts Identify and validate documented interface commands and statement of completeness Storage of data, transmission via communication systems (AD + VFTSw) Refer to clause for applicability of these requirements. Validate that measurement values stored or transmitted are accompanied by all information necessary for future legally relevant use 9
10 Clause Requirements Validation description Data protection with respect to time of measurement (AD + VFTSw) Validate that software data protection with respect to time of measurement Automatic storing (AD + VFTSw) Validate automatic storage of data. Validate sufficient permanency and memory for storage of data Validate deletion of stored data Transmission delay (AD + VFTSw) Validate that measurement is not inadmissibly influenced by a transmission delay Transmission interruption (AD + VFTSw) Validate measurement data is not lost due to unavailability of network services Time stamp (AD + VFTSw) Validate that time stamps are read from the clock of the device Validate that setting of the clock is protected as a legally relevant parameter Maintenance and re-configuration (AD) Identify and validate the implementation for software updates 10
11 4 Tests for maximum permissible error 4.1 Initial intrinsic error for positive and negative flow (6.2.1) If a meter is specified with alternate connection modes, this test shall be made for all specified connection modes. Connection mode: I X : test point specified by the national authority between and I max : Value of most inductive power factor in test: Value of most capacitive power factor in test: Positive energy flow Test Current Power Factor I min I X I max (most inductive) I X I max I X I max Negative energy flow I max I max (most capacitive) (most inductive) Error (%) with test current from Low to high High to low Mean error 1 (%) Base mpe (%) (most capacitive) I max Note 1: Mean error is the mean of the error with increasing and decreasing currents for each test point. Check that each mean error base mpe 11
12 4.2 Reverse energy flow (6.2.1) Calculation for test time for reverse flow I min I max a) Time that the test output would register ten pulses in the forward energy flow direction (minutes): b) Time that the primary register would register 2 units of the least significant digit in the forward energy flow direction (minutes): c) 1 minute: 1 1 Test time is the maximum of a), b) and c): Test Current Power Test Time Change in register Number of test pulses factor (minutes) Measured Limit Measured Limit I min 0 1 I max Check that there is no change in the energy registered in the primary register. Check that the number of test pulses emitted 1. 12
13 4.3 Self heating (6.2.2) Voltage circuits energized for time: (At least 1 hour for Class A, 2 hours for all other classes.) The test shall be carried out for at least 1 hour, and in any event until the variation of error over any 20-minute period does not exceed 10 % of base maximum permissible error. Time at I Power factor max (minutes) I max Unity Intrinsic error Error (%) Base mpe (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) Has the error shift levelled out? If no, continue test according to (a) or (b) below. (a) If the load can be changed in less than 30 seconds, then: I max Power factor 0.5 inductive Intrinsic error (%) Error (%) Base mpe (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) (b) Else, allow meter to return to its initial temperature and repeat test for power factor 0.5 inductive. Voltage circuits energized for time: Time at I Power factor max (minutes) I max 0.5 inductive Intrinsic error (At least 1 hour for Class A, 2 hours for all other classes.) Error (%) Base mpe (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) Check that each error base mpe Check that each error shift limit 13
14 4.4 Starting current (6.2.3) Determine the error at the starting current based on the rate of test pulses (or revolutions if no test output). Expected time between pulses, τ = ( m k U nom I st ) seconds: Power factor Meter started (Yes/No) Error (%) Base mpe (%) Unity Check that the error base mpe 4.5 Test of no-load condition (6.2.4) Minimum test period, 3 t ( b k m Unom Imin ) Test period Δt (hours) For meters with a test output Number of Limit pulses emitted No current 1 For electromechanical meters Rotor revolutions Limit Less than a complete revolution For meters with a test output, check if the number of pulses emitted 1. For electromechanical meters, check that the rotor does not make a complete revolution. 14
15 4.6 Meter constants (6.2.5) Does the meter have multiple registers or pulse outputs under legal control? (Yes/No) If yes, is there a system in place to guarantee identical behaviour of meter constants? (Yes/No) If yes, specify the system, otherwise all registers and pulse outputs must be tested. Register and test output tested: Apparent resolution of basic energy register, R expressed in Wh: Minimum energy to be passed through, Emin = 1000 R b expressed in Wh: Power factor Unity Energy measured by Register (r) Test output (t) Count of test output pulses Relative difference (%) t r ( ) r Limit (%) (10 % of base mpe) Check that each relative difference limit 15
16 5 Tests for influence quantities 5.1 Temperature dependence (6.3.2; Table 3) The mean temperature coefficient, c, is calculated by c = ( eu el ) ( tu tl ). Temperature intervals shall span at least 15 K and no more than 23 K. The set of intervals must span the entire specified operating range (intervals may overlap). A temperature coefficients table must be completed for each temperature interval. Temperature coefficients table Temperature interval (t l to t u ): t l ( C): t u ( C): Test Current Power factor Error (%) Mean temperature coefficient (%/K) e l e u c Limit 10 I max 0.5 inductive 10 I max Check that each c limit. 16
17 5.2 Load balance (6.3.3) This test is only for poly-phase meters and for single-phase three-wire meters. Reference voltages shall be applied to all voltage circuits Power factor Load Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Balanced Current in L1 only Current in L2 only Current in L3 only I max Balanced Current in L1 only Current in L2 only Current in L3 only inductive Balanced Current in L1 only Current in L2 only Current in L3 only I max 0.5 inductive Balanced Current in L1 only Current in L2 only Current in L3 only Check that each error shift limit. 17
18 5.3 Voltage variation (6.3.4) If several U nom values are stated, the test shall be repeated for each U nom value. U nom (V): Power factor Voltage variation Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (U nom ) 0.9 U nom 1.1 U nom inductive Reference (U nom ) 0.9 U nom 1.1 U nom Check that each error shift limit. 5.4 Frequency variations (6.3.5) If several f nom values are stated, the test shall be repeated for each f nom value. f nom (Hz): Power factor Frequency variation Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (f nom ) 0.98 f nom 1.02 f nom inductive Reference (f nom ) 0.98 f nom 1.02 f nom Check that each error shift limit. 18
19 5.5 Harmonics in voltage and current (6.3.6) Determine the error shift, relative to the error at reference conditions (with no harmonics), when the quadriform waveform (Table 11), is applied to both voltage and current circuits. Determine the error shift, relative to the error at reference conditions (with no harmonics), when the peaked waveform (Table 12), is applied to both voltage and current circuits. Power factor Harmonics applied to both voltage and current circuits 10 Reference (f nom ) Quadriform waveform Peaked waveform Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) Check that each error shift limit. 19
20 5.6 Tilt (6.3.7) This test is only for electromechanical meters or meters of other constructions that may be influenced by the working position. Operating position specified by manufacturer: Define or illustrate perpendicular orientations corresponding to forward, backward, left and right Power factor Tilt Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) Reference (no tilt) 3 forward 3 backward 3 left 3 right Check that each error shift limit. 20
21 5.7 Severe voltage variations (6.3.8) If several U nom values are stated, the test shall be repeated for each U nom value. Test procedure 1 U nom (V): Power factor Voltage variation Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (U nom ) 0.8 U nom 0.85 U nom 1.15 U nom Test procedure 2 Does the meter have distinct shut-down / turn-on voltages? (Yes/No) Shut-down voltage (V): Turn-on voltage (V): If yes, two additional mandatory test points (shutdown low and shutdown high) shall be included. Shutdown low shall be within a 2 V range below the shut-down voltage. Shutdown high shall be within a 2 V range above the turn-on voltage. U nom (V): Power factor Voltage variation Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (U nom ) 0.7 U nom +10 to U nom 0.5 U nom 0.4 U nom 0.3 U nom 0.2 U nom 0.1 U nom 0 U nom shutdown low shutdown high Check that each error shift limit. 21
22 5.8 One or two phases interrupted (6.3.9) This test is only for poly-phase meters with three measuring elements One or two phases are removed while keeping the load current constant. Power factor Load Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (no phases removed) Phase L1 removed Phase L2 removed Phase L3 removed Phases L1, L2 removed Phases L1, L3 removed Phases L2, L3 removed Check that each error shift limit. 5.9 Sub-harmonics in the AC current circuit (6.3.10) The sub-harmonic waveform is formed from a sinusoidal signal with twice the amplitude of the reference signal, which is switched on and off every second period (as shown in Figure 3 b)). Power factor Current signal Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (sinusoidal, f nom ) Sub-harmonic waveform Check that each error shift limit. 22
23 5.10 Harmonics in the AC current circuit (6.3.11) The harmonic waveform is formed from a sinusoidal signal with twice the amplitude of the reference signal, which is set to zero during the first and third quarters of the period. Power factor Current signal Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (sinusoidal, f nom ) Harmonic waveform Check that each error shift limit Reversed phase sequence (any two phases interchanged) (6.3.12) This test only applies to three-phase meters. Power factor Phase sequence Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (L1, L2, L3) L1, L3, L2 L2, L1, L3 L3, L2, L1 Check that each error shift limit. 23
24 5.12 Continuous (DC) magnetic induction of external origin (6.3.13) Permanent magnet with a surface area of at least 2000 mm 2 Field along axis of magnet s core at 30 mm from surface: 200 mt ± 30 mt 6 points per meter surface. Report greatest error shift for each surface Specify or illustrate the surfaces designated as front, back, top, bottom, left and right. Power factor Meter surface tested Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) 10 Reference (no magnetic induction) Front Back Top Bottom Left Right Check that each error shift limit. 24
25 5.13 Magnetic field (AC, power frequency) of external origin (6.3.14) Continuous field, 400 A/m, f = f nom Field at three orthogonal directions Report greatest error shift for each test point and direction under the most unfavorable condition of phase Specify or illustrate the three orthogonal directions relative to the meter designated as x, y & z: Power factor Magnetic field axis direction Phase Error (%) 10 Reference (no magnetic induction) x-axis y-axis z-axis I max Reference (no magnetic induction) x-axis y-axis z-axis Check that each error shift limit. Error shift (%) Limit (%) 25
26 5.14 Radiated, radio frequency (RF), electromagnetic fields ( ) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to radiated radiofrequency fields. Test condition 1 with current Frequency range: 80 to 6000 MHz Field strength: 10 V/m Modulation: 80 % AM, 1 khz sine wave The meter shall be separately tested at the manufacturer s specified clock frequencies Any other sensitive frequencies shall also be analysed separately Report greatest error shift for each test condition Power Frequency value / Polariz- Facing Antenna / facility factor range (MHz) ation meter 10 Vertical Front Back Right Left Top Bottom Horizontal Front Back Right Left Top Bottom [extend for each antenna/facility] Check that each error shift limit. [extend for clock frequencies and any other sensitive frequencies] Error shift (%) Limit (%) 26
27 5.15 Imm to conducted disturbances, induced by radiofrequency fields ( ) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to conducted disturbances induced by RF fields. Frequency range: 0.15 to 80 MHz Field strength: 10 V (e.m.f.) Modulation: 80 % AM, 1 khz sine wave Test all power ports and I/O ports Report greatest error shift for each test condition Power factor 10 Power or I/O port Error shift (%) Limit (%) Check that each error shift limit DC in the AC current circuit (6.3.16) Electromechanical and transformer operated meters shall be assumed to be immune to DC in the AC current circuit. Power factor Current test wave Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) I max /2 2 Sinusoidal (intrinsic error) I max / 2 Half-wave rectified Check that each error shift limit. 27
28 5.17 High-order harmonics (6.3.17) Asynchronous test signals, swept from f = 15 f nom to 40 f nom Sweep from low frequency to high frequency, and then back down One reading shall be taken per harmonic frequency (report maximum error within the frequency range) Report greatest error and error shift for each sweep Voltage circuit test Asynchronous test signal: 0.02 U nom Power factor Signal on voltage circuit Sinusoidal (intrinsic error) Test signal superimposed Sweep direction low to high high to low Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit (%) Current circuit test Asynchronous test signal: 0.1 Power factor Signal on current circuit Sweep Error (%) Sinusoidal (intrinsic error) Test signal superimposed low to high high to low Check that each error shift limit. Error shift (%) Limit (%) 28
29 6 Test for disturbances 6.1 Critical change value (6.4.1 a); ) The critical change value is used as a criterion for significant fault in many disturbance tests. Number of measuring elements, m: Nominal voltage, U nom : V Maximum current, I max : A Critical change value ( m U nom I max 10 6 ): kwh 6.2 Magnetic field (AC, power frequency) of external origin (6.4.2) Magnetic field strength short duration (3 s): 1000 A/m, f = f nom Voltage circuits energized with U nom No current in the current circuits Field at three orthogonal directions Specify the three orthogonal directions relative to the meter designated as x, y & z: a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Magnetic field axis direction x-axis y-axis z-axis Register Change in Equivalent energy of the test output Critical change value b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 29
30 6.3 Electrostatic discharge (6.4.3) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to electrostatic discharges. Contact discharge is the preferred test method. Air discharges shall be used where contact discharge cannot be applied Voltage circuits energized with U nom Current and auxiliary circuits open, with no current a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Application Discharge mode Test voltage (kv) Polarity Direct Contact 8 Positive Negative Air 15 Positive Negative Indirect, Horizontal coupling plane Indirect, Vertical coupling plane Contact 8 Positive Negative Contact 8 Positive Negative Number of discharges ( 10) Change in Equivalent energy Register of the test output Critical change value b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 30
31 6.4 Fast transients (6.4.4) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to fast transients. The test voltage shall be applied in common mode (line-to-earth) to: a) the voltage circuits; b) the current circuits, if separated from the voltage circuits in normal operation; c) the auxiliary circuits, if separated from the voltage circuits in normal operation and with a reference voltage over 40 V. a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 Power Test voltage Circuit / Auxiliary circuit factor (kv) 10 Voltage 4 Current [Auxiliary circuits] 2 Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 31
32 6.5 Voltage dips and interruptions (6.4.5) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to voltage dips and interruptions. Voltage circuits energized with U nom Without current in the current circuit a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Dip / Interruption Test Amplitude relative to U nom Duration (cycles) Repetitions Dip Test a 30 % Test b 60 % 1 10 Test c 60 % [25/30] [1] 10 Interruption - 0 % [250/300] [2] 10 Change in Equivalent Register energy of the test output Note [1]: Duration (cycles) for Voltage dip test c depends on the reference frequency 25 for 50 Hz, 30 for 60 Hz. Note [2]: Duration (cycles) for Voltage interruption test depends on the reference frequency 250 for 50 Hz, 300 for 60 Hz. b) & c) Operational checks Power factor d) Check base mpe b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe Critical change value 32
33 6.6 Radiated, radio frequency (RF), electromagnetic fields (6.4.6) Meters, such as electromechanical meters, which have been constructed using only passive elements shall be assumed to be immune to radiated radiofrequency fields. Test Condition 2 without current Voltage circuits energized with U nom, auxiliary circuits energized with reference voltage Without current in the current circuits and with the current circuits open-circuited Otherwise conditions as specified for the influence test with current in 5.14 above a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Antenna [extend for each antenna] b) & c) Operational checks Power factor d) Check base mpe Frequency value / range (MHz) [extend for clock frequencies and any other sensitive frequencies] Polarization Vertical Horizontal Facing meter Front Back Right Left Top Bottom Front Back Right Left Top Bottom Change in Equivalent energy Register of the test output b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe Critical change value 33
34 6.7 Surges on AC mains power lines (6.4.7) This test is not applicable for meters such as electromechanical meters which shall be assumed to be immune to surges. Without any current in the current circuits and the current terminals open Number of tests: 5 positive and 5 negative Repetition rate: maximum 1 per minute a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Change in Amplitude (kv) Application Angle Polarity Equivalent energy of Register the test output Voltage circuits 2 Line to line 60 Positive Negative 240 Positive Negative 4 Line to earth (1) 60 Positive Negative 240 Positive Negative Auxiliary circuits with a reference voltage over 40V (Repeat table below for each auxiliary circuit) Specify auxiliary circuit: 1 Line to line 60 Positive Negative 240 Positive Negative 2 Line to earth (1) 60 Positive Negative 240 Positive Negative (1) For cases where the earth of the meter is separate to neutral. Critical change value b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 34
35 6.8 Damped oscillatory waves imm test (6.4.8) This test is only for meters intended to be operated with voltage transformers. Test duration: 60 s (15 cycles with 2 s on, 2 s off, for each frequency) a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Test current Power factor Mode Test voltage (kv) Test frequency (khz) Repetition rate (Hz) Voltage Circuits 20 Common Intrinsic error (%) inductive Differential inductive Auxiliary circuits with a reference voltage over 40V (Repeat table below for each auxiliary circuit) Specify auxiliary circuit: 20 Common inductive Differential inductive b) & c) Operational checks Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 35
36 6.9 Short-time overcurrent (6.4.9) For direct connected meters: 30 I max +0 %, 10 % for one half cycle at rated frequency For meters connected through current transformers: a current equivalent to 20 I max + 0%, 10 %, for 0.5 s a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Phase Intrinsic error (%) 10 L1 L2 L3 Application of overcurrent Power Short-time Phase factor overcurrent 10 L1 L2 L3 Duration Damage caused? After return to normal temperature Error Limit of error Error (%) shift (%) shift (%) b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 36
37 6.10 Impulse voltage (6.4.10) For each test, the impulse voltage is applied 10 times for each polarity. Minimum of 30 s between impulses Specify each circuit tested a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Test Impulse voltage (V) Polarity Positive Circuits tested Flashover, disruptive discharge or puncture? Change in Equivalent Register energy of the test output Critical change value For circuits and between circuits Negative Circuits relative to earth Positive Negative b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that during the test, there is no flashover, disruptive discharge or puncture Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 37
38 6.11 Earth fault (6.4.11) This test only applies to three-phase four-wire transformer-operated meters connected to distribution networks which are equipped with earth fault neutralizers or in which the star point is isolated. Simulated earth fault condition in one of the three lines All voltages increased to 1.1 U nom Duration: 4 hours a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 Earth-fault condition Power Duration Voltage (V) factor (hours) U nom 4 b) & c) Operational checks Damage caused? After return to normal temperature Error shift Limit of error Error (%) (%) shift (%) Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that after the test, the meter shows no damage Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 38
39 6.12 Operation of auxiliary devices (6.4.12) Error continuously monitored while auxiliary devices are operated a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) I max Power factor Auxiliary device Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) I max I max b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 39
40 6.13 Vibrations ( ) Meter mounted as in normal operation Vibrations applied, in turn, in three mutually perpendicular axes a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 After vibrations applied Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 40
41 6.14 Shock ( ) Meter not operational during tests a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 After shocks applied Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 41
42 6.15 Protection against solar radiation (6.4.14) For outdoor meters only. Meter condition: non-operational during test Partially mask a section of the meter for later comparison Meter exposed to artificial radiation according to clause Visual inspection requirements after exposure Clause Check for effects on Remarks (3.5) Markings on the meter Legibility and permanency of markings ( ) Protection of metrological properties (3.7.1) Readability of result ( ; Table 5) No alteration in appearance b) & c) Operational checks Seals Transparent surfaces on indicating device Indicating device Appearance Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each visual inspection requirement is satisfied Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 42
43 6.16 Protection against ingress of dust (6.4.15) Visual inspection requirements after dust test Visually inspect interior of meter Check if the talcum powder or other dust used in the test has accumulated in a quantity or location such that it could interfere with the correct operation of the equipment or impair safety. Check that no dust has deposited where it could lead to tracking along the creepage distances. Remarks b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each visual inspection requirement is satisfied Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 43
44 6.17 Extreme temperatures - Dry heat ( ) Meter condition: non-operational a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 Dry heat test Test temperature (one step higher than upper specified temperature) ( C) Duration (hours) 2 After dry heat test Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 44
45 6.18 Extreme temperatures - Cold ( ) Meter condition: non-operational a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 Cold test Test temperature (one step lower than lower specified temperature) ( C) Duration (hours) 2 After cold test Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 45
46 6.19 Damp heat, steady-state (non-condensing), for humidity class H1 ( ) For humidity class H1 only. Voltage and auxiliary circuits energized with reference voltage Without any current in the current circuits Damp Heat, steady-state test Temperature 30 C Humidity 85 % Duration 2 days a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift and see critical change value in 6.1) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 Register Change in Equivalent energy of the test output Critical change value Immediately after the test, check error shift according to Table 5 Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks 24 hours after the test Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe 24 hours after the test Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Checks for damage or corrosion 24 hours after test Requirement Check for evidence of any mechanical damage or corrosion which may affect the functional properties of the meter Remarks Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check that error shift limit of error shift immediately after the test Check all operational checks pass 24 hours after the test Check that error base mpe 24 hours after the test Check that the requirements for damage or corrosion are satisfied 46
47 6.20 Damp heat, cyclic (condensing), for humidity class H2 and H3 ( ) For humidity class H2 or H3 only. Voltage and auxiliary circuits energized with reference voltage Without any current in the current circuits Damp heat, cyclic test Specified humidity class Lower temperature ( C) 25 C Upper temperature ( C) Duration 2 cycles a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift and see critical change value in 6.1) Power factor Initial error (%) 10 Register Change in Equivalent energy of the test output Critical change value Immediately after the test, check error shift according to Table 5 Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 b) & c) Operational checks 24 hours after the test Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe 24 hours after the test Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Checks for damage or corrosion 24 hours after test Requirement Check for evidence of any mechanical damage or corrosion which may affect the functional properties of the meter Remarks Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check that error shift limit of error shift immediately after the test Check all operational checks pass 24 hours after the test Check that error base mpe 24 hours after the test Check that the requirements for damage or corrosion are satisfied 47
48 6.21 Water test ( ) For humidity class H3 only. The meter shall be in functional mode, with no current Water test Flow rate (per nozzle): 0.07 L/min Angle of inclination: 0 and 180 Duration 10 minutes a) Check for significant fault (see critical change value in 6.1) Register Change in Equivalent energy of the test output Critical change value Accuracy immediately after the test Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive b) & c) Operational checks 24 hours after the test Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe 24 hours after the test Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Checks for damage or corrosion 24 hours after test Requirement Check for evidence of any mechanical damage or corrosion which may affect the functional properties of the meter Remarks Check that each change in register critical change value Check that each change in equivalent energy of the test output critical change value Check that error base mpe immediately after the test Check all operational checks pass 24 hours after the test Check that error base mpe 24 hours after the test Check that the requirements for damage or corrosion are satisfied 48
49 6.22 Durability (6.4.17) Specify durability standard applied: Specify details of durability test: a) Check for significant fault (limit of error shift) Power factor Intrinsic error (%) 10 I max After durability Power factor Error (%) Error shift (%) Limit of error shift (%) 10 I max b) & c) Operational checks Power factor b) Operational check c) Check correct operation of Does meter register energy? Pulse outputs? Tariff change inputs? d) Check base mpe Power factor Error (%) Base mpe (%) inductive Check that each error shift limit of error shift Check all operational checks pass Check that error base mpe 49
OIML R 46-1/-2 RECOMMENDATION. Edition 2012 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION
 INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 46-1/-2 Edition 2012 (E) Active electrical energy meters. Part 1: Metrological and technical requirements Part 2: Metrological controls and performance tests Compteurs
INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 46-1/-2 Edition 2012 (E) Active electrical energy meters. Part 1: Metrological and technical requirements Part 2: Metrological controls and performance tests Compteurs
OIML R 130 RECOMMENDATION. Edition 2001 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION. Octave-band and one-third-octave-band filters
 INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 130 Edition 2001 (E) Octave-band and one-third-octave-band filters Filtres à bande d octave et de tiers d octave OIML R 130 Edition 2001 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE
INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 130 Edition 2001 (E) Octave-band and one-third-octave-band filters Filtres à bande d octave et de tiers d octave OIML R 130 Edition 2001 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 103 RECOMMENDATION
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 103 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1992 (E) Measuring instrumentation for human response to vibration (with reference to International Standards 8041 and 5347 of the International Organization
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 103 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1992 (E) Measuring instrumentation for human response to vibration (with reference to International Standards 8041 and 5347 of the International Organization
OIML E 5 EXPERT REPORT. 6th Edition 2015 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION
 EXPERT REPORT OIML E 5 6th Edition 2015 (E) Overview of the present status of the standards referred to in OIML D 11:2013 General requirements for measuring instruments Environmental conditions Revue du
EXPERT REPORT OIML E 5 6th Edition 2015 (E) Overview of the present status of the standards referred to in OIML D 11:2013 General requirements for measuring instruments Environmental conditions Revue du
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale
 Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Sound level meters Sonomètres OIML R 58 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword... 3 1 Scope... 4 2 Construction and maximum permissible
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Sound level meters Sonomètres OIML R 58 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword... 3 1 Scope... 4 2 Construction and maximum permissible
Metal stamps for verification officers
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 42 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1981 (E) Metal stamps for verification officers Poinçons de métal pour agents de vérification OIML R 42 Edition 1981 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE MÉTROLOGIE
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 42 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1981 (E) Metal stamps for verification officers Poinçons de métal pour agents de vérification OIML R 42 Edition 1981 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE MÉTROLOGIE
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale
 Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Integrating-averaging sound level meters Sonomètres intégrateurs-moyenneurs OIML R 88 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword...
Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION Integrating-averaging sound level meters Sonomètres intégrateurs-moyenneurs OIML R 88 Edition 1998 (E) CONTENTS Foreword...
Material measures of length for general use
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 35 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1985 (E) Material measures of length for general use Material measures of length for general use OIML R 35 Edition 1985 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 35 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1985 (E) Material measures of length for general use Material measures of length for general use OIML R 35 Edition 1985 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE
THE WEIGHTS AND MEASURES (ELECTRICITY METERS) RULES, ARRANGEMENT OF RULES
 THE WEIGHTS AND MEASURES (ELECTRICITY METERS) RULES, 2015. ARRANGEMENT OF RULES PART I PRELIMINARY Rule 1. Title. 2. Interpretation. PART II UNITS OF MEASUREMENT AND STANDARDS. 3. Units of electrical energy.
THE WEIGHTS AND MEASURES (ELECTRICITY METERS) RULES, 2015. ARRANGEMENT OF RULES PART I PRELIMINARY Rule 1. Title. 2. Interpretation. PART II UNITS OF MEASUREMENT AND STANDARDS. 3. Units of electrical energy.
OIML R 75-2 RECOMMENDATION. Edition 2002 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION
 INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 75-2 Edition 2002 (E) Heat meters Part 2: Type approval tests and initial verification tests Compteurs d énergie thermique Partie 2: Essais d approbation de type et
INTERNATIONAL RECOMMENDATION OIML R 75-2 Edition 2002 (E) Heat meters Part 2: Type approval tests and initial verification tests Compteurs d énergie thermique Partie 2: Essais d approbation de type et
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 45 RECOMMENDATION. Casks and barrels ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION. Edition 1980 (E)
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 45 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1980 (E) Casks and barrels Tonneaux et futailles OIML R 45 Edition 1980 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE MÉTROLOGIE LÉGALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 45 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1980 (E) Casks and barrels Tonneaux et futailles OIML R 45 Edition 1980 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE MÉTROLOGIE LÉGALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF
Westergren tubes for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 78 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1989 (E) Westergren tubes for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate Pipettes Westergren pour la mesure de la vitesse de sédimentation des hématies
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 78 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1989 (E) Westergren tubes for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate Pipettes Westergren pour la mesure de la vitesse de sédimentation des hématies
Australian Standard. Electricity metering equipment (AC) Particular requirements. Part 22: Static meters for active energy (classes 0.2 S and 0.
 AS 62053.22 2005 IEC 62053-22, Ed.1.0 (2003) AS 62053.22 2005 Australian Standard Electricity metering equipment (AC) Particular requirements Part 22: Static meters for active energy (classes 0.2 S and
AS 62053.22 2005 IEC 62053-22, Ed.1.0 (2003) AS 62053.22 2005 Australian Standard Electricity metering equipment (AC) Particular requirements Part 22: Static meters for active energy (classes 0.2 S and
OIML D 11 DOCUMENT. Edition 2013 (E) ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION
 INTERNATIONAL DOCUMENT OIML D 11 Edition 2013 (E) General requirements for measuring instruments - Environmental conditions Exigences générales pour les instruments de mesure - Conditions environnementales
INTERNATIONAL DOCUMENT OIML D 11 Edition 2013 (E) General requirements for measuring instruments - Environmental conditions Exigences générales pour les instruments de mesure - Conditions environnementales
Standards and Specially Focused on Electricity Metering Standards by B.M.Vyas
 Standards and Specially Focused on Electricity Metering Standards by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module 1.
Standards and Specially Focused on Electricity Metering Standards by B.M.Vyas A specifically designed programme for Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) Afghanistan 1 Areas Covered Under this Module 1.
Test Specification for Type Approval
 A2 (1991) (Rev.1 1993) (Rev.2 1997) (Rev. 2.1 July 1999) (Rev.3 May 2001) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.4 May 2004) (Rev.5 Dec 2006) (Rev.6 Oct 2014) Test Specification for Type Approval.1 General This Test
A2 (1991) (Rev.1 1993) (Rev.2 1997) (Rev. 2.1 July 1999) (Rev.3 May 2001) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.4 May 2004) (Rev.5 Dec 2006) (Rev.6 Oct 2014) Test Specification for Type Approval.1 General This Test
Overcurrent Protection / 7SJ45
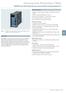 Overcurrent Protection / SJ SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by CTs Fig. / Description SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by current transformers
Overcurrent Protection / SJ SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by CTs Fig. / Description SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by current transformers
Checklist for electromechanical and electronic active energy meters in accordance with the MID Directive (2004/22/EC)
 Checklist for electromechanical and electronic active energy meters in accordance with the MID Directive (2004/22/EC) Applicant: Instrument type: 1. General requirements NOTE: Definitions are based on
Checklist for electromechanical and electronic active energy meters in accordance with the MID Directive (2004/22/EC) Applicant: Instrument type: 1. General requirements NOTE: Definitions are based on
SIPROTEC easy 7SJ46 Numerical Overcurrent Protection Relay
 Overcurrent Protection / 7SJ46 SIPROTEC easy 7SJ46 Numerical Overcurrent Protection Relay Function overview Fig. /11 Description The SIPROTEC easy 7SJ46 is a numerical overcurrent protection relay which
Overcurrent Protection / 7SJ46 SIPROTEC easy 7SJ46 Numerical Overcurrent Protection Relay Function overview Fig. /11 Description The SIPROTEC easy 7SJ46 is a numerical overcurrent protection relay which
ALPHA 20 MULTIFUNCTION METER (ALPHA SERIES)
 Alpha Series www.sifamtinsley.co.uk Multifunction Meters Transducers & Isolators Temperature Controllers Converters & Recorders Digital Panel Meters Current Transformers Analogue Panel Meters Shunts ALPHA
Alpha Series www.sifamtinsley.co.uk Multifunction Meters Transducers & Isolators Temperature Controllers Converters & Recorders Digital Panel Meters Current Transformers Analogue Panel Meters Shunts ALPHA
Power Sensors Ltd. PQube 3 AC Analyzer IEC Class 0,2 S Accuracy Compliance Report
 PSL Standards Lab 980 Atlantic Avenue Alameda, CA 94501 USA TEL ++1-510-522-4400 FAX ++1-510-522-4455 www.standards.com Sensors Ltd. PQube 3 AC Analyzer IEC Class 0,2 S Accuracy Compliance Report IEC 62053-22
PSL Standards Lab 980 Atlantic Avenue Alameda, CA 94501 USA TEL ++1-510-522-4400 FAX ++1-510-522-4455 www.standards.com Sensors Ltd. PQube 3 AC Analyzer IEC Class 0,2 S Accuracy Compliance Report IEC 62053-22
2620 Modular Measurement and Control System
 European Union (EU) Council Directive 89/336/EEC Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Test Report 2620 Modular Measurement and Control System Sensoray March 31, 2006 April 4, 2006 Tests Conducted by: ElectroMagnetic
European Union (EU) Council Directive 89/336/EEC Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Test Report 2620 Modular Measurement and Control System Sensoray March 31, 2006 April 4, 2006 Tests Conducted by: ElectroMagnetic
Protein Measuring Instruments for Cereal Grain and Oil Seeds
 OIML TC17 / SC 8 / N 4 May 2006 Supersedes document: N 3 INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF LEGAL METROLOGY First Committee Draft of a Recommendation on Protein Measuring Instruments for Cereal Grain and Oil
OIML TC17 / SC 8 / N 4 May 2006 Supersedes document: N 3 INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF LEGAL METROLOGY First Committee Draft of a Recommendation on Protein Measuring Instruments for Cereal Grain and Oil
NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function.
 REGULATION AUTOMATIC SYNCHRONIZER for GENERATOR NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
REGULATION AUTOMATIC SYNCHRONIZER for GENERATOR NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
NPRG860 NPRG870 REGULATION. Automatic Synchronizer for Generator
 REGULATION Automatic Synchronizer for Generator NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
REGULATION Automatic Synchronizer for Generator NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
Australian Standard. Electricity metering equipment (ac) Particular requirements. Part 23: Static meters for reactive energy (classes 2 and 3)
 AS 62053.23 2006 IEC 62053-23, Ed.1.0 (2003) AS 62053.23 2006 Australian Standard Electricity metering equipment (ac) Particular requirements Part 23: Static meters for reactive energy (classes 2 and 3)
AS 62053.23 2006 IEC 62053-23, Ed.1.0 (2003) AS 62053.23 2006 Australian Standard Electricity metering equipment (ac) Particular requirements Part 23: Static meters for reactive energy (classes 2 and 3)
DRAFT TANZANIA STANDARD (Draft for comments only) Part 8: Electricity metering minimum accuracy and environmental requirements
 EDC1 (5240) P3 DRAFT TANZANIA STANDARD (Draft for comments only) Mini-Grid Systems Part 8: Electricity metering minimum accuracy and environmental requirements TANZANIA BUREAU OF STANDARDS TBS 2017 First
EDC1 (5240) P3 DRAFT TANZANIA STANDARD (Draft for comments only) Mini-Grid Systems Part 8: Electricity metering minimum accuracy and environmental requirements TANZANIA BUREAU OF STANDARDS TBS 2017 First
RE22R2MMU Multifunction Timer Relay - 24VDC/ V AC - 2 C/O
 Product data sheet Characteristics RE22R2MMU Multifunction Timer Relay - 24VDC/24..240 V AC - 2 C/O Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Device short name Nominal output
Product data sheet Characteristics RE22R2MMU Multifunction Timer Relay - 24VDC/24..240 V AC - 2 C/O Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Device short name Nominal output
Application Alpha 20 Measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase 4 Wire and 3 phase 3 Wire Network & replaces the multiple analog panel meters
 Technical Data Sheet Alpha 20 Alpha 20 is a compact multifunction instrument which Measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase 4 Wire and 3 phase 3 Wire Network & replaces the multiple analog panel
Technical Data Sheet Alpha 20 Alpha 20 is a compact multifunction instrument which Measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase 4 Wire and 3 phase 3 Wire Network & replaces the multiple analog panel
EMC TEST REPORT For MPP SOLAR INC Inverter/ Charger Model Number : PIP 4048HS
 EMC-E20130903E EMC TEST REPORT For MPP SOLAR INC Inverter/ Charger Model Number : PIP 4048HS Prepared for : MPP SOLAR INC Address : 4F, NO. 50-1, SECTION 1, HSIN-SHENG S. RD. TAIPEI, TAIWAN Prepared by
EMC-E20130903E EMC TEST REPORT For MPP SOLAR INC Inverter/ Charger Model Number : PIP 4048HS Prepared for : MPP SOLAR INC Address : 4F, NO. 50-1, SECTION 1, HSIN-SHENG S. RD. TAIPEI, TAIWAN Prepared by
Data Sheet. RISH Master Record %THD
 Data Sheet %THD Application : measures important electrical parameters & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current, Voltage, frequency, active energy
Data Sheet %THD Application : measures important electrical parameters & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current, Voltage, frequency, active energy
Device Under Test: ALTEA VS- 24-I VS-24-I. 0 24/09/12 First issue A. Peretto L. Peretto 1 24/06/16 All text review E. Scala L. Peretto J. L.
 /9 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS VOLTAGE LOW-POWER TRANSFORMER VS- Rev. Date Revision Description Prepared by Checked by Approved by 0 24/09/2 First issue A. Peretto L. Peretto 24/06/6 All text review E. Scala
/9 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS VOLTAGE LOW-POWER TRANSFORMER VS- Rev. Date Revision Description Prepared by Checked by Approved by 0 24/09/2 First issue A. Peretto L. Peretto 24/06/6 All text review E. Scala
RS Pro ENGLISH. Datasheet
 Datasheet Article No: 136-5385 Digital AC Ammeter, 48x96, 1Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5387 Digital AC Ammeter, 96x96, 1Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5388 Digital
Datasheet Article No: 136-5385 Digital AC Ammeter, 48x96, 1Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5387 Digital AC Ammeter, 96x96, 1Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5388 Digital
Harmonizing the ANSI-C12.1(2008) EMC Tests. Harmonizing the ANSI-C12.1(2008) EMC Tests
 Harmonizing the ANSI-C12.1(2008) EMC Tests Subcommittee 1 (Emissions) Subcommittee 5 (Immunity) Joint Task Force on C12.1 June 17, 2013 1 The Accredited Standards Committee C63 presents Harmonizing the
Harmonizing the ANSI-C12.1(2008) EMC Tests Subcommittee 1 (Emissions) Subcommittee 5 (Immunity) Joint Task Force on C12.1 June 17, 2013 1 The Accredited Standards Committee C63 presents Harmonizing the
RS Pro ENGLISH. Datasheet
 Datasheet ENGLISH Article No: 136-5390 Digital AC Ammeter, 48x96, 3Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5391 Digital AC Ammeter, 96x96, 3Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5393
Datasheet ENGLISH Article No: 136-5390 Digital AC Ammeter, 48x96, 3Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5391 Digital AC Ammeter, 96x96, 3Phase, 1 or 5 Amps AC, Supply 40-300V ac/dc 136-5393
High-set undervoltage stage with definitetime. or inverse definite minimum time (IDMT) characteristic. Low-set undervoltage stage with definitetime
 Issued: 5.06.999 Status: 5.06.999 Version: B/09..00 Data subject to change without notice Features Overvoltage and undervoltage protection Single- or three-phase operation High-set overvoltage stage with
Issued: 5.06.999 Status: 5.06.999 Version: B/09..00 Data subject to change without notice Features Overvoltage and undervoltage protection Single- or three-phase operation High-set overvoltage stage with
RE17RAMU on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h V AC - 1 OC
 Characteristics on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Complementary Contacts material Control type [Us] rated supply voltage Voltage range Main Range of product Product or component
Characteristics on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Complementary Contacts material Control type [Us] rated supply voltage Voltage range Main Range of product Product or component
SPECIFICATION FOR OVERCURRENT RELAYS
 SPECIFICATION FOR OVERCURRENT RELAYS 1/9 1. Procedure A manufacturer willing to classify an overcurrent relay according to this specification should provide: A complete file providing a clear, unambiguous
SPECIFICATION FOR OVERCURRENT RELAYS 1/9 1. Procedure A manufacturer willing to classify an overcurrent relay according to this specification should provide: A complete file providing a clear, unambiguous
CP-E range Benefits and advantages
 Benefits and advantages Characteristics Output voltages 5 V, 12 V, 2 V, 8 V DC Adjustable output voltages Benefits Signalling output/contact Output currents 0.625 A / 0.75 A / 1.25 A / 2.5 A / A / 5 A
Benefits and advantages Characteristics Output voltages 5 V, 12 V, 2 V, 8 V DC Adjustable output voltages Benefits Signalling output/contact Output currents 0.625 A / 0.75 A / 1.25 A / 2.5 A / A / 5 A
RISH EM 3490 DS Dual Source Energy Meter (With All Display Parameters) RISH EM 3490 DS. Application : Product Features:
 (With All Display Parameters) Application : RISH EM 3490 DS measures important electrical parameters of Utility (in normal mode) & Generators (in Power back up) in three phase and single phase Network
(With All Display Parameters) Application : RISH EM 3490 DS measures important electrical parameters of Utility (in normal mode) & Generators (in Power back up) in three phase and single phase Network
TEST SUMMARY. Prüfbericht - Nr.: Test Report No.: Seite 2 von 25. Page 2 of 25
 15072259 001 Seite 2 von 25 Page 2 of 25 TEST SUMMARY 4.1.1 HARMONICS ON AC MAINS 4.1.2 VOLTAGE FLUCTUATIONS ON AC MAINS 4.1.3 MAINS TERMINAL CONTINUOUS DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE 4.1.4 DISCONTINUOUS INTERFERENCE
15072259 001 Seite 2 von 25 Page 2 of 25 TEST SUMMARY 4.1.1 HARMONICS ON AC MAINS 4.1.2 VOLTAGE FLUCTUATIONS ON AC MAINS 4.1.3 MAINS TERMINAL CONTINUOUS DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE 4.1.4 DISCONTINUOUS INTERFERENCE
EN 55022: 2010+AC:2011 Clause 6.1 Pass. Harmonic Current EN :2006+A1:2009+A2:2009 Class A N/A
 Reference No.: WT12106773-N-S-E Page 2 of 33 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 150KHz to 30MHz Radiation Emission, 30MHz to 1000MHz EMISSION Test Standard Class / Severity Result
Reference No.: WT12106773-N-S-E Page 2 of 33 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 150KHz to 30MHz Radiation Emission, 30MHz to 1000MHz EMISSION Test Standard Class / Severity Result
TEST SUMMARY. Prüfbericht - Nr.: Test Report No.: Seite 2 von 27. Page 2 of 27
 15072768 001 Seite 2 von 27 Page 2 of 27 TEST SUMMARY 4.1.1 HARMONICS ON AC MAINS 4.1.2 VOLTAGE CHANGES, VOLTAGE FLUCTUATIONS AND FLICKER ON AC MAINS 4.1.3 MAINS TERMINAL CONTINUOUS DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE
15072768 001 Seite 2 von 27 Page 2 of 27 TEST SUMMARY 4.1.1 HARMONICS ON AC MAINS 4.1.2 VOLTAGE CHANGES, VOLTAGE FLUCTUATIONS AND FLICKER ON AC MAINS 4.1.3 MAINS TERMINAL CONTINUOUS DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE
EU-TYPE EXAMINATION CERTIFICATE
 Semel Oy taximeter system M2 Issued to Semel Oy Valimotie 21, 00380 HELSINKI, FINLAND 0402-MID-502305 Semel Oy taximeter system M2 is fulfilling module B (Annex II) of directive 2014/32/EU on measuring
Semel Oy taximeter system M2 Issued to Semel Oy Valimotie 21, 00380 HELSINKI, FINLAND 0402-MID-502305 Semel Oy taximeter system M2 is fulfilling module B (Annex II) of directive 2014/32/EU on measuring
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 89 RECOMMENDATION
 INTERNATIONAL OIML R 89 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1990 (E) Electroencephalographs - Metrological characteristics - Methods and equipment for verification Electroencéphalographes - Caractéristiques métrologiques
INTERNATIONAL OIML R 89 RECOMMENDATION Edition 1990 (E) Electroencephalographs - Metrological characteristics - Methods and equipment for verification Electroencéphalographes - Caractéristiques métrologiques
VIM Series. 90 & 60 W, Efficient, CV Class 2 LED Drivers ORDERING INFORMATION
 060W-12 100W-24 Nominal Input Voltage 90 &, Efficient, CV Class 2 Max. Output Power Nominal Output Voltage Max. Output Current 120 & 277 Vac 12, 24 Vdc 5, 3.75 A Efficiency up to 90% typical Max. Case
060W-12 100W-24 Nominal Input Voltage 90 &, Efficient, CV Class 2 Max. Output Power Nominal Output Voltage Max. Output Current 120 & 277 Vac 12, 24 Vdc 5, 3.75 A Efficiency up to 90% typical Max. Case
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION SERIES K: PROTECTION AGAINST INTERFERENCE
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T K.42 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (05/98) SERIES K: PROTECTION AGAINST INTERFERENCE Preparation of emission and immunity requirements for
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T K.42 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (05/98) SERIES K: PROTECTION AGAINST INTERFERENCE Preparation of emission and immunity requirements for
Harmonic Current emission EN :2014 Class A Pass. Voltage Fluctuation and Flicker EN :2013 Clause 5 Pass
 Reference No.: WTS15F0323845E Page 2 of 33 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 148.5kHz to 30MHz Disturbance Power, 30MHz to 300MHz Discontinuous Disturbance (Click) Radiated Emission,
Reference No.: WTS15F0323845E Page 2 of 33 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 148.5kHz to 30MHz Disturbance Power, 30MHz to 300MHz Discontinuous Disturbance (Click) Radiated Emission,
Digital Multifunction Instrument - Rish Master 3440
 Application Rish Master 3440 measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase and single phase etwork & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current,
Application Rish Master 3440 measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase and single phase etwork & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current,
Electronic timer CT-MVS.23 Multifunctional with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts
 Data sheet Electronic timer CT-MVS.23 Multifunctional with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-MVS.23 is a multifunctional electronic timer from the CT-S range. It provides 11 timing functions and 10 time ranges.
Data sheet Electronic timer CT-MVS.23 Multifunctional with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-MVS.23 is a multifunctional electronic timer from the CT-S range. It provides 11 timing functions and 10 time ranges.
VGM Series. 100 & 60 W, Efficient, CV Class 2 LED Drivers for Signage Applications ORDERING INFORMATION
 Nominal Input Voltage Max. Output Power Nominal Output Voltage Max. Output Current 120/277 Vac 12, 24, Vdc 5, 3.92 A Efficiency up to 90% typical Max. Case Temperature 100 C (measured at the hot spot)
Nominal Input Voltage Max. Output Power Nominal Output Voltage Max. Output Current 120/277 Vac 12, 24, Vdc 5, 3.92 A Efficiency up to 90% typical Max. Case Temperature 100 C (measured at the hot spot)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 60071-2 Third edition 1996-12 Insulation co-ordination Part 2: Application guide This English-language version is derived from the original bilingual publication by leaving out
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 60071-2 Third edition 1996-12 Insulation co-ordination Part 2: Application guide This English-language version is derived from the original bilingual publication by leaving out
Power supply CP-T 48/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply
 Data sheet Power supply CP-T 48/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
Data sheet Power supply CP-T 48/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
EN 55015: 2013 Clause Pass. EN 55015: 2013 Clause Pass. EN 55015: 2013 Clause Pass
 Reference No.: WTD15S0730643E Page 2 of 42 1 Test Summary Test Item Conducted Disturbance at Mains Terminal, 9kHz to 30MHz Radiation electromagnetic disturbance, 9kHz to 30MHz Radiation Emission, 30MHz
Reference No.: WTD15S0730643E Page 2 of 42 1 Test Summary Test Item Conducted Disturbance at Mains Terminal, 9kHz to 30MHz Radiation electromagnetic disturbance, 9kHz to 30MHz Radiation Emission, 30MHz
By order of ZHONGSHAN LIANGYI LIGHTING CO., LTD. at Zhongshan, China
 4317137.50 EMC Test report for LED Fixed luminaires Models LED12036-1R, LED12036-2TU, LED120363R, LED12036-4TU2, LED12036-6TR, LED12036-1R CHR, LED12036-2TU CHR, LED12036-3R CHR, LED12036-4TU2 CHR, LED12036-6TR
4317137.50 EMC Test report for LED Fixed luminaires Models LED12036-1R, LED12036-2TU, LED120363R, LED12036-4TU2, LED12036-6TR, LED12036-1R CHR, LED12036-2TU CHR, LED12036-3R CHR, LED12036-4TU2 CHR, LED12036-6TR
Jewell DPM EINE BEST IN CLASS
 Application: Silent Features: The digital panel meter has been designed Fast & Easy installation on panel with the for industrial applications, which help of external swivel screws. frequently require
Application: Silent Features: The digital panel meter has been designed Fast & Easy installation on panel with the for industrial applications, which help of external swivel screws. frequently require
RE17RMMW time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h V AC/DC - 1 OC
 Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay
Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay
RE17RMMW time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h V AC/DC - 1 OC
 Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay
Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay
CP-T range Benefits and advantages
 Benefits and advantages Characteristics Rated output voltages V, V DC Output voltage adjustable via front-face rotary potentiometer OUTPUT Adjust Rated output currents 5 A, 10 A, A, A Rated output powers
Benefits and advantages Characteristics Rated output voltages V, V DC Output voltage adjustable via front-face rotary potentiometer OUTPUT Adjust Rated output currents 5 A, 10 A, A, A Rated output powers
Discontinuous Disturbance (Click) EN :2006+A1:2009+A2:2011 Clause N/A** Radiated Emission, 30MHz to 1000MHz
 Reference No.: WTN13F0706038E Page 2 of 40 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 148.5kHz to 30MHz Disturbance Power, 30MHz to 300MHz EMISSION Test Standard Class / Severity Result
Reference No.: WTN13F0706038E Page 2 of 40 1 Test Summary Test Item Mains Terminal Disturbance Voltage, 148.5kHz to 30MHz Disturbance Power, 30MHz to 300MHz EMISSION Test Standard Class / Severity Result
Measuring Instruments Directive 2014/32/EU Thermal Energy Meters Corresponding Tables OIML R 75:2002
 CT-004, 2018 Issue 2, October 2018 Old reference: WELMEC 8.14 Issue 1, 2006 Measuring Instruments Thermal Energy Meters Corresponding Tables OIML R 75:2002 For information: This Guide is available to the
CT-004, 2018 Issue 2, October 2018 Old reference: WELMEC 8.14 Issue 1, 2006 Measuring Instruments Thermal Energy Meters Corresponding Tables OIML R 75:2002 For information: This Guide is available to the
WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology
 WELMEC 8.14 Issue 1 WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22/EC Heat Meters Corresponding Tables OIML R 75-1 and R 75-2 2002 MID-004 November 2006 1 WELMEC
WELMEC 8.14 Issue 1 WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22/EC Heat Meters Corresponding Tables OIML R 75-1 and R 75-2 2002 MID-004 November 2006 1 WELMEC
EMC Test Report. Report Number: M030826
 Page 1 of 36 EMC Technologies Pty Ltd ABN 82 057 105 549 57 Assembly Drive Tullamarine Victoria Australia 3043 Ph: + 613 9335 3333 Fax: + 613 9338 9260 email: melb@emctech.com.au EMC Test Report Report
Page 1 of 36 EMC Technologies Pty Ltd ABN 82 057 105 549 57 Assembly Drive Tullamarine Victoria Australia 3043 Ph: + 613 9335 3333 Fax: + 613 9338 9260 email: melb@emctech.com.au EMC Test Report Report
RISH PQM. Power Quality Monitor. Preliminary Datasheet subject to change without notice. Individual Harmonics measurement upto 56th Harmonics
 Power Quality Monitor Individual Harmonics measurement upto 56th Harmonics True representation of Voltage & Current waveforms. Phasor Representation of All 3 phases for system analysis Real Time Clock
Power Quality Monitor Individual Harmonics measurement upto 56th Harmonics True representation of Voltage & Current waveforms. Phasor Representation of All 3 phases for system analysis Real Time Clock
AMIK 200 / 201 Technical Data Sheet
 AMIK 200 / 201 Technical Data Sheet AMIK Special Features MODBUS (RS-485) Communication available only on Amik 201 On site Programmable CT/PT Ratios User selectable CT Secondary 1A/5A User selectable PT
AMIK 200 / 201 Technical Data Sheet AMIK Special Features MODBUS (RS-485) Communication available only on Amik 201 On site Programmable CT/PT Ratios User selectable CT Secondary 1A/5A User selectable PT
Notes: Note1: Efficiency is tested at nominal input and full load at +25 C ambient. Output Voltage 400VAC 320VAC 360VAC 400VAC 400VAC
 Features DIN-Rail 2 and 3-phase operation Input voltage range: 320 575VAC Output trim range: 22.5 29.5VDC High electrical strength; high reliability Permanent overload and short-circuit protection Parallel
Features DIN-Rail 2 and 3-phase operation Input voltage range: 320 575VAC Output trim range: 22.5 29.5VDC High electrical strength; high reliability Permanent overload and short-circuit protection Parallel
RISH Delta Energy / Demand (Multifunction instrument) Data Sheet
 ISH Delta Energy / Demand (Multifunction instrument) Data Sheet www.rishabh.co.in Page 1 of 6 Version: D 14 / 03 / 2012 Application: ISH Delta Energy measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase
ISH Delta Energy / Demand (Multifunction instrument) Data Sheet www.rishabh.co.in Page 1 of 6 Version: D 14 / 03 / 2012 Application: ISH Delta Energy measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase
A Comparison Between MIL-STD and Commercial EMC Requirements Part 2. By Vincent W. Greb President, EMC Integrity, Inc.
 A Comparison Between MIL-STD and Commercial EMC Requirements Part 2 By Vincent W. Greb President, EMC Integrity, Inc. OVERVIEW Compare and contrast military (i.e., MIL-STD) and commercial EMC immunity
A Comparison Between MIL-STD and Commercial EMC Requirements Part 2 By Vincent W. Greb President, EMC Integrity, Inc. OVERVIEW Compare and contrast military (i.e., MIL-STD) and commercial EMC immunity
Relion 605 series Self-Powered Feeder Protection REJ603 Product Guide
 Relion 605 series Relion 605 series Self-Powered Feeder Protection Product Guide Contents 1 Description...3 2 Protection functions...3 3 Application...4 4 Self-supervision...4 5 Inputs and outputs...4
Relion 605 series Relion 605 series Self-Powered Feeder Protection Product Guide Contents 1 Description...3 2 Protection functions...3 3 Application...4 4 Self-supervision...4 5 Inputs and outputs...4
Power supply CP-T 48/5.0 Primary switch mode power supply
 Data sheet Power supply CP-T 48/5.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
Data sheet Power supply CP-T 48/5.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
Power supply CP-T 24/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply
 Data sheet Power supply CP-T 24/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
Data sheet Power supply CP-T 24/20.0 Primary switch mode power supply The CP-T range of three-phase power supply units is the youngest member of ABB s power supply family. In terms of design and functionality,
RE17RAMU on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h V AC - 1 OC
 Characteristics on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay range Nominal
Characteristics on-delay timing relay - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Main Range of product Product or component type Discrete output type Width Device short name Time delay type Time delay range Nominal
Primary switch mode power supplies Product group picture
 Primary switch mode power supplies Product group picture /1 ABB Catalog Electronic Products and Relays 2015 2CDC 110 004 C0210 Primary switch mode power supplies Table of contents Primary switch mode power
Primary switch mode power supplies Product group picture /1 ABB Catalog Electronic Products and Relays 2015 2CDC 110 004 C0210 Primary switch mode power supplies Table of contents Primary switch mode power
Electronic timer CT-SDS.22
 CDC 0 F0t07 Features Rated control supply voltage 8 V DC, 0 V AC Single function timer with star delta change over One device includes 7 time ranges (0.0 s 0 min) n/o contacts LEDs for status indication
CDC 0 F0t07 Features Rated control supply voltage 8 V DC, 0 V AC Single function timer with star delta change over One device includes 7 time ranges (0.0 s 0 min) n/o contacts LEDs for status indication
WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology
 WELMEC 8.18-2 Issue 1 WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology Guide for Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22/EC Capacity Serving Measures Corresponding Tables 2007 MID-008 II December 2008 WELMEC
WELMEC 8.18-2 Issue 1 WELMEC European cooperation in legal metrology Guide for Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22/EC Capacity Serving Measures Corresponding Tables 2007 MID-008 II December 2008 WELMEC
TEST REPORT... 1 CONTENT...
 CONTENT TEST REPORT... 1 CONTENT... 2 1 TEST RESULTS SUMMARY... 3 2 EMC RESULTS CONCLUSION... 4 3 LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS... 6 4 EMI TEST... 7 4.1 CONTINUOUS CONDUCTED DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE TEST... 7 4.2
CONTENT TEST REPORT... 1 CONTENT... 2 1 TEST RESULTS SUMMARY... 3 2 EMC RESULTS CONCLUSION... 4 3 LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS... 6 4 EMI TEST... 7 4.1 CONTINUOUS CONDUCTED DISTURBANCE VOLTAGE TEST... 7 4.2
RE17RMMW time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h V AC/DC - 1 OC
 Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Product availability : Stock - Normally stocked in distribution facility Price* : 75.00 USD Main Range of product Product
Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 12..240 V AC/DC - 1 OC Product availability : Stock - Normally stocked in distribution facility Price* : 75.00 USD Main Range of product Product
Electronic timer CT-AHS.22 OFF-delayed with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts
 Data sheet Electronic timer CT-AHS.22 OFF-delayed with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-AHS.22 is an electronic timer from the CT-S range with OFF-delay and 10 time ranges. All electronic timers from the CT-S
Data sheet Electronic timer CT-AHS.22 OFF-delayed with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-AHS.22 is an electronic timer from the CT-S range with OFF-delay and 10 time ranges. All electronic timers from the CT-S
RISH Master Digital Multifunction Instrument with onsite pluggable output options. Application : Product Features:
 Application : RISH Master 3430 measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase and single phase Network & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current,
Application : RISH Master 3430 measures important electrical parameters in 3 phase and single phase Network & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. It measures electrical parameters like AC current,
ALPHA 50 MULTIFUNCTION METER (ALPHA SERIES)
 Alpha Series www.sifamtinsley.co.uk Multifunction Meters Transducers & Isolators Temperature Controllers Converters & Recorders Digital Panel Meters Current Transformers Analogue Panel Meters Shunts ALPHA
Alpha Series www.sifamtinsley.co.uk Multifunction Meters Transducers & Isolators Temperature Controllers Converters & Recorders Digital Panel Meters Current Transformers Analogue Panel Meters Shunts ALPHA
Electronic timer CT-TGD.12 Pulse generator with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact
 Data sheet Electronic timer CT-TGD.12 Pulse generator with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact The CT-TGD.12 is an electronic time relay with the function pulse generator. It is from the CT-D range. With their MDRC profile
Data sheet Electronic timer CT-TGD.12 Pulse generator with 1 c/o (SPDT) contact The CT-TGD.12 is an electronic time relay with the function pulse generator. It is from the CT-D range. With their MDRC profile
CP-T range Product group picture
 Product group picture /1 ABB Catalog Electronic Products and Relays 1/1 2CDC 110 00 C09 Table of contents CP-T range Product group picture /1 Table of contents /2 Benefits and advantages / Ordering details
Product group picture /1 ABB Catalog Electronic Products and Relays 1/1 2CDC 110 00 C09 Table of contents CP-T range Product group picture /1 Table of contents /2 Benefits and advantages / Ordering details
Scale Manufacturers Association (SMA) Recommendation on. Electrical Disturbance
 Scale Manufacturers Association (SMA) Recommendation on Electrical Disturbance (SMA RED-0499) Provisional First Edition Approved by SMA Pending Final Comment April 24, 1999 Copyright: SMA, April, 1999
Scale Manufacturers Association (SMA) Recommendation on Electrical Disturbance (SMA RED-0499) Provisional First Edition Approved by SMA Pending Final Comment April 24, 1999 Copyright: SMA, April, 1999
RISH EM 3490 SS Kilowatt Hour Energy Meter With Rs485 RISH EM 3490 SS. Application : Product Features: Indication: Pulse Indication:
 Application : RISH Master 3490 SS is a 96mm x 96mm panel mounted kilowatt hour meter it measures active energy with class 1.0 accuracy having auto-resetting 8 digit seven segment LED counter. The unit
Application : RISH Master 3490 SS is a 96mm x 96mm panel mounted kilowatt hour meter it measures active energy with class 1.0 accuracy having auto-resetting 8 digit seven segment LED counter. The unit
Notes: Note1: Efficiency is tested at nominal input and full load at +25 C ambient. Output Voltage 400VAC 400VAC
 Features DIN-Rail Description 2 and 3-phase operation Input voltage range: 320 575VAC Output trim range: 22.5 29.5VDC High electrical strength; high reliability Permanent overload and short-circuit protection
Features DIN-Rail Description 2 and 3-phase operation Input voltage range: 320 575VAC Output trim range: 22.5 29.5VDC High electrical strength; high reliability Permanent overload and short-circuit protection
EMC standards. Presented by: Karim Loukil & Kaïs Siala
 Training Course on Conformity and Interoperability on Type Approval testing for Mobile Terminals, Homologation Procedures and Market Surveillance, Tunis-Tunisia, from 20 to 24 April 2015 EMC standards
Training Course on Conformity and Interoperability on Type Approval testing for Mobile Terminals, Homologation Procedures and Market Surveillance, Tunis-Tunisia, from 20 to 24 April 2015 EMC standards
STRATO 70W LED P DESCRIPTION KEY FEATURES APPLICATIONS AND BENEFITS MODEL CODING AND OUTPUT RATINGS TRC ELECTRONICS, INC
 STRATO 70W LED P S DESCRIPTION STRATO switch mode driver technology is designed to generate one constant voltage output from a wide range AC input. The size and performance of these products make them
STRATO 70W LED P S DESCRIPTION STRATO switch mode driver technology is designed to generate one constant voltage output from a wide range AC input. The size and performance of these products make them
Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFS
 Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFS The CM-PFS is a three-phase monitoring relay that is used to monitor three phase mains for incorrect phase sequence and phase failure. All devices are available
Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFS The CM-PFS is a three-phase monitoring relay that is used to monitor three phase mains for incorrect phase sequence and phase failure. All devices are available
RE17RMMU time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h V AC - 1 OC
 Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Product availability : Stock - Normally stocked in distribution facility Price* : 62.00 USD Main Range of product Product
Characteristics time delay relay 10 functions - 1 s..100 h - 24..240 V AC - 1 OC Product availability : Stock - Normally stocked in distribution facility Price* : 62.00 USD Main Range of product Product
Electronic timer CT-WBS.22 Impulse generating and flashing with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts
 Data sheet Electronic timer CT-WBS.22 Impulse generating and flashing with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-WBS.22 is a multifunctional electronic timer from the CT-S range. It provides 10 timing functions
Data sheet Electronic timer CT-WBS.22 Impulse generating and flashing with 2 c/o (SPDT) contacts The CT-WBS.22 is a multifunctional electronic timer from the CT-S range. It provides 10 timing functions
ENCORE 300 SERIES INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 ENCORE 300 SERIES INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Copyright 2002-2006 PRI Ltd. 9600-3004-2 Issue C Information contained within this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent
ENCORE 300 SERIES INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Copyright 2002-2006 PRI Ltd. 9600-3004-2 Issue C Information contained within this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent
Technical Data Sheet
 Technical Data Sheet parameters in 3 phase 4 Wire and 3 phase 3 Wire Network & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. Special Features Pulse/Limit Switch output (optional) Number of interruption Application
Technical Data Sheet parameters in 3 phase 4 Wire and 3 phase 3 Wire Network & replaces the multiple analog panel meters. Special Features Pulse/Limit Switch output (optional) Number of interruption Application
Power supply CP-E 24/2.5
 2CDC 271 015 F0t06 a OUTPUT L+, L : terminals output b DC OK: terminal signalling output c INPUT L, N, PE: terminals input d OUTPUT OK: green LED output voltage OK e OUTPUT Adjust: potentiometer adjustment
2CDC 271 015 F0t06 a OUTPUT L+, L : terminals output b DC OK: terminal signalling output c INPUT L, N, PE: terminals input d OUTPUT OK: green LED output voltage OK e OUTPUT Adjust: potentiometer adjustment
EMC REPORT. ShenZhen KY Technology Co.,Ltd. No.369, BaoTian 1st RD, TieGang Industrial Park, Xixiang Town, Baoan District, ShenZhen, PRC.
 Report No.: UNI2016121702ER-01 Page 1 / 30 ShenZhen KY Technology Co.,Ltd EMC REPORT Prepared For: ShenZhen KY Technology Co.,Ltd Product Name: Smart bracelet No.369, BaoTian 1st RD, TieGang Industrial
Report No.: UNI2016121702ER-01 Page 1 / 30 ShenZhen KY Technology Co.,Ltd EMC REPORT Prepared For: ShenZhen KY Technology Co.,Ltd Product Name: Smart bracelet No.369, BaoTian 1st RD, TieGang Industrial
High precision measurement system for current and voltage IHC-A/B-RM01/03
 Measurement Offset-free and low-noise 16 bit data acquisition system ISA-ASIC Internal sample rate 3,500 Hz Communication Standard RS232- or RS485 interface Advantages Direct measurement on the bus bar
Measurement Offset-free and low-noise 16 bit data acquisition system ISA-ASIC Internal sample rate 3,500 Hz Communication Standard RS232- or RS485 interface Advantages Direct measurement on the bus bar
I. DRAFT G E N E R A L M E A S U R E
 Czech Metrology Institute Okružní 31, 638 00 Brno 1. ------IND- 2018 0338 CZ- EN- ------ 20180803 --- --- PROJET Executive summary for the EC (not part of this legislation) Spectrometric assemblies for
Czech Metrology Institute Okružní 31, 638 00 Brno 1. ------IND- 2018 0338 CZ- EN- ------ 20180803 --- --- PROJET Executive summary for the EC (not part of this legislation) Spectrometric assemblies for
Prepared by Mick Maytum
 IEC Technical Committee 109: Standards on insulation co-ordination for low-voltage equipment Warning Prepared by Mick Maytum mjmaytum@gmail.com The document content is of a general nature only and is not
IEC Technical Committee 109: Standards on insulation co-ordination for low-voltage equipment Warning Prepared by Mick Maytum mjmaytum@gmail.com The document content is of a general nature only and is not
Power supply CP-E 24/20.0
 2CDC 271 027 F0008 a OUTPUT L+, L+, L, L-: terminals output b INPUT L, N, PE: terminals input c 13-14: terminals - signalling contact d OUTPUT OK: green LED output voltage OK e OUTPUT LOW: red LED output
2CDC 271 027 F0008 a OUTPUT L+, L+, L, L-: terminals output b INPUT L, N, PE: terminals input c 13-14: terminals - signalling contact d OUTPUT OK: green LED output voltage OK e OUTPUT LOW: red LED output
Overview of EMC Regulations and Testing. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
 Overview of EMC Regulations and Testing Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is EMC Electro-Magnetic Compatibility ( 電磁相容 ) EMC EMI (Interference) Conducted
Overview of EMC Regulations and Testing Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is EMC Electro-Magnetic Compatibility ( 電磁相容 ) EMC EMI (Interference) Conducted
MT372 Three-phase electronic meter with built-in modem or RS485 communication interface
 Energy Measurement and Management MT372 Three-phase electronic meter with built-in modem or RS485 communication interface Technical Description Version 1, 09.06. 2005 Content: MT372 Three-phase electronic
Energy Measurement and Management MT372 Three-phase electronic meter with built-in modem or RS485 communication interface Technical Description Version 1, 09.06. 2005 Content: MT372 Three-phase electronic
