REL 300 (MDAR) Numerical Transmission Line Protection
|
|
|
- Irene Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Descriptive Bulletin Relay Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Page 1 Effective: Supersedes D.B. Dated December 1995 Mailed to: E, D, C/40-100C, B Multi-Zoned Distance Device Number: 21, 21N, 21NP, 21P, 02, 67/67N, 50/51N REL 300 (MDAR) Numerical Transmission Line Protection BASIC SYSTEM Standard Functions 100% Numerical Processing Three Zone Distance Relay. Zone 3 Reversible (21, 21N, 21S). Independent Timers for Phase and Ground (Zone 1, Zone 2 and Zone 3) (02) Four Impedance Units Per Zone (1 Phaseto- Phase Unit and 3 Phase-to-Ground Units) Inverse Time, Directional/Non-Directional (Selectable) Overcurrent Ground Characteristic (67N/51N) Overcurrent Supervision of Ground Distance Units (50 FD) High Set Overcurrent Phase and Ground Trip Units (50 HS, 50N HS) Power Swing Block (68) Close into Fault Detection and Tripping Unequal Pole Closing Load Pickup Logic Selectable Load Loss Accelerated Trip Zone 1 Non-Pilot Extension Scheme Loss of Potential Supervision Block Distance Tripping Only and/or Alarm Block All Tripping and/or Alarm FEATURES Loss of Current Monitoring Fault Locator Function Unique Faulted Phase Selector for Logic Control and Targeting Self Check Function Monitoring of Voltage, Current and Power Factor Angle (Metering) Unique Current Change Fault Detector Man-Machine Interface Includes: 2-Four Character Vacuum Fluorescent Displays (With Screen Saver Blanking Feature) 6-Pushbuttons For Data Entry/Retrieval 6-LEDs For Targeting and Relay Status Sealable Settings, Entry Pushbutton RS-232C Communications Interface 19-inch Rack Mounting - 4 Rack Units High or FT-42 Case 1 Ampere or 5 Ampere Current Transformer Operation 50/60 Hz Drawout Construction Optional Functions Pilot System - includes additional zone of phase and ground distance (21P, 21NP) plus the following logic functions: Logic for Block, Unblock, POTT, PUTT Three Terminal Line Capability Transient Block Capability Carrier Signal Continuation Weak Feed Capability Ft-14 Test Switches Single Pole Trip Logic and Trip Outputs Standard RS-232C Interface can be replaced with an INtegrated COMmunications (IN- COM ) Product Operated Network Interface (PONI) when networking is desired. Networking requires a Basic Interface to Remote Terminal (BIRT) or an INCOM -based Multi Access Controller (IMAC) to act as a network controller. Standard RS-232C Interface can be replaced with RS-232C Interfaces With IRIG-B Time Synchronization Port Software for Oscillographic Data Analysis (16 Events) 8 Programmable Output Contacts (Available With 3 Pole Trip Version Only) Magneto-Optic Current Transducer (MOCT) Input Interface APPLICATION MDAR is a numerical transmission line protection system with three or four zones of distance protection, optional pilot zone logic, metering, a fault locator and self diagnostics. All measurements and logic use microprocessor technology. MDAR is recommended for protection of transmission lines where to 1 1 / 2-2 cycle relaying time is acceptable. MDAR can be applied as a pilot or non-pilot system and includes Zone 1 extension and loss-of-load accelerated trip logic. It can be used on 2 and 3 terminal lines including weak feed terminals. For lines where power swings can occur, MDAR includes out-of-step blocking functions. One set of blinders functions to restrict three-phase distance elements from operating on heavily loaded long lines. The phase-to-phase elements are unaffected by power swings. In certain situations, systems operations may be enhanced by single pole tripping thus allowing load flow over the unfaulted phases. MDAR provides optional single pole tripping hardware and logic. When the single pole trip option is not selected extra programmable output contacts may be added for indication and/or tripping functions. There are internal logic signals to choose from. MDAR records up to 16 fault records and provides indication and fault location. An RS-232/PONI provides remote communications for accessing data and remote setting changes. Option: oscillographic data function provides 1 cycle of prefault and 7 cycles of fault data for up to 16 faults.
2 Page 2 These added data features facilitate system protection operation analysis. The self checking functions improve relaying reliability and availability while reducing maintenance requirements. Draw-out construction and optional FT test switches improve testing and maintenance functions. DESIGN The MDAR design is compact, flexible and easy to use. Its numerical design provides complete system protection and self supervision. The microprocessor checks itself, the peripheral circuitry, A/D converter calibration, RAM, NOVRAM and EPROM memories and the power supply. In addition it monitors the ac inputs and provides indication for LOP (Loss of Potential) and LOI (Loss of Current). The self-checking feature improves reliability by reducing or eliminating periodic maintenance requirements. MDAR combines precise measurements and years of experience. The MDAR Operator Interface Panel offers both ease-of-use and powerful capability. There are two four-digit alphanumeric displays that show up to 62 separate settings, plus seven indicating LEDs. It is easy to access stored data and easy to input new data. In addition, MDAR provides fault designations and fault location information. The metering display shows three-phase voltage, current, load angle, and signal monitoring. Fully digital design gives MDAR a level of flexibility uniquely capable of meeting the most complex transmission line protection requirements. The flexibility begins with three zones of phase and ground distance protection. Zones 1 and 2 are forward set, Zone 3 is optionally reversible. There is an independent pilot zone. MDAR has a built in fault locator which indicates the distance to the fault in either miles or kilometers and in ohms. It stores fault records for up to 16 faults. Each record contains information on which MDAR units operated, fault location, prefault voltage, current and angle and fault values of voltage, current and angles. The MDAR has eight modes of operation: Non pilot zone distance Zone 1 extension Blocking Permissive underreach transfer trip Permissive overreach transfer trip Permissive overreach transfer trip with weak feed Unblocking Unblocking with weak feed The backup time overcurrent ground protection can be directional or non-directional. Its characteristic curve, pickup value and time dial setting can be selected from the front panel. MDAR has been designed to offer maximum benefits with minimum disruption to existing installations. Application is universal. MDAR accepts 1A or 5A current transformers, 50 or 60 Hertz. For pilot teleprotection systems, MDAR provides a universal channel interface. It features: Isolated contact inputs and outputs Transient block/unblock circuitry Three terminal line capability Carrier signal continuation and weak feed capability. The dc-dc converter power supply offers exceptionally high reliability. It features a loss-of-power indicator and alarm. It provides complete protection from overvoltage and overcurrent. Power supply test points are conveniently located on the front panel. The power supply is available in three ranges: 48/60 Vdc 110/125 Vdc 220/250 Vdc MDAR offers high-speed tripping. The minimum trip time is milliseconds. Typical trip time is 22 milliseconds. The MDAR features an optically isolated RS- 232C communications port as standard. The MDAR can be easily networked with other protection and control devices in the substation by simply replacing the RS-232C interface with an optional ABB INCOM interface. This allows networking of up to 2500 devices in a substation. Operating Principles The R-X Diagram, (Figure 1) illustrates the MDAR impedance characteristics. Zone 1 phase and ground settings are chosen to provide substantial coverage of the protected line without overreaching the next bus. A setting of 75 to 85% of the line impedance is typical. Faults occurring within the reach of the Zone 1 measurement cause direct tripping. The user can select to add a two cycle time delay to Zone 1 trip. Zone 2 settings are chosen to assure that faults occurring on the next bus are recognized. Settings are generally chosen (independent of the Zone 1 settings), to be 120 to 150% of the line impedance. Any fault occurring on the protected line will be recognized by this Zone 2 measurement (within the fault resistance and current limitations of the relaying system). Zone 2 tripping occurs with separate phase and ground delay timers (T2P and T2G.) There is an optional, independent pilot zone which functions with the user selected pilot logic. It is typically set to 120 to 150% of the protected line impedance. It provides high speed tripping subject to the pilot system logic and channel. RU RT RT RU J X Figure 1 The Zone 3 measurement is directional, and may be chosen to respond to forward or reverse faults. The reverse sensing option is chosen for the pilot blocking system where the reverse fault carrier start function or transient block logic is required. It is set to overreach the pilot zone or opposite terminal. It is also used in conjunction with weakfeed logic. Direct tripping can be blocked or achieved via Time Delay (T3P or T3G). The forward sensing option produces time delayed backup to other devices sensing forward faults. Zone 3 is set to coordinate with adjacent terminal Zone 2 relays. Blinder measurements (RT and RU) are available for out-of-step sensing. The inner blinder also restricts the trip zone of each of the 3-phase fault measuring units for load restriction. Line measurement techniques applied to each zone include: Single-Phase-to-Ground fault detection Three-Phase fault detection Phase-to-Phase fault detection Transmission Line Characteristic Phase-to-Phase-to-Ground fault detection A unique characteristic of the MDAR system is its phase selection principle. It determines the sum of positive and negative sequence currents for each phase by a novel method which excludes the influence of pre-fault load current. From this information, the fault type can be clearly identified and a much better approximation can be obtained of the actual distance to a fault. Also by a new method requiring agreement between two measurements, the tendency toward leading-phase overreach for phase-tophase faults is eliminated. Z3 Pilot Zone Z2 Z1 Z3 Reversible R dtp
3 Page 3 Single-Phase-to-Ground fault detection is accomplished by three quadrature polarized, I O compensated phase units (ØA, ØB, ØC). Equations 1 and 2 are for operate and reference quantities respectively. The unit will produce output when the operate quantity leads the reference quantity. Z OL Z 1L V XG I X Z I O Z CG 1L Vector( V Q ) where V XG I X Z 1L, Z 0L = V AG, V BG, V CG = I A, I B, I C (Eq. 1) (Eq. 2) = positive and zero sequence line impedance I 0 + 1/3 (I A +I B +I C ) Z CG V Q = Zone reach setting in secondary ohms. = Quadrature phase voltages, I.e., V CB, V AC, and V BA for ØA, ØB, ØC units, respectively. Three-phase fault detection is accomplished by the logic operation of one of the three ground units, plus the 3ØF output signal from the faulted phase selector unit. However, for a three-phase fault condition, the computation of the distance units will be: V XG I X Z CP and ( V Q ) (Eq. 3) (Eq. 4) where V XG I X Z CP V Q = V AG, V BG, or V CG = I A, I B, or I C = Zone reach setting (PLTP, Z1P, Z2P, and Z3P) in secondary ohms for multi-phase faults. = Quadrature phase voltages, i.e., V CB, V AC, and V BA for ØA, ØB and ØC units, respectively. The phase-to-phase unit responds to all phaseto-phase faults, and some single-phase-toground faults. Equations (5) and (6) are for operate and reference quantity, respectively. They will produce an output when the operate quantity leads the reference quantity. ( V AB I AB Z CP ) ( V CB I CB Z CP ) (Eq. 5) (Eq. 6) MDAR provides high impedance ground fault detection when pilot logic is selected. A sensitive directional ground overcurrent unit supplements the pilot ground distance detection logic. It can be delayed or blocked to allow normal pilot ground operation to avoid any overtripping tendency. Load-loss tripping entails high speed, essentially simultaneous clearing at both terminals of a transmission line for all fault types, except threephase, without the need of a pilot channel. Any fault location on the protected circuit will be within the reach of the Zone 1 logic at one or both terminals. This causes direct tripping of the local breaker without the need of any information from the remote terminal. The remote terminal recognizes the loss of load-current in the unfaulted phase(s), as evidence of tripping of the remote breaker. This, combined with Zone 2 distance or directional overcurrent ground fault recognition at that terminal, allows immediate tripping to take place at that terminal. Zone 1 extension logic can be selected. In this scheme, Zone 1 assumes the Zone 2 overreach setting. Upon tripping, the reach is pulled back to a normal Zone 1 reach for 5 seconds. Use of this scheme requires the use of a high speed reclosing relay. HARDWARE The block diagram shows the overall arrangement of hardware in MDAR. Line voltages and currents from vt s and ct s are connected to isolating transformers, surge suppression, and antialiasing filters. The ac inputs are connected through a multiplexer to the analog conversion subsystem. An A/D converter places instantaneous samples of these ac signals in the microprocessor memory. Status or contact inputs are also scanned. All relaying measurements and logic are performed by software executed in the microprocessor. The programs also handle operator interface and self-checking functions. The programs perform tripping or other control outputs through a series of contacts as shown in block diagram. The relay also includes an integral man-machine interface and a RS-232C serial port for remote communications. X Z C CENTER = 1 Z S -- 2 Z C Z 0L I L 2k 1 + Z k L I F X R Z C = Setting Impedance Z S = Source Impedance k 1 = Pos. Seq. Current Distr. Factor OFFSET = k 0 = Zero Seq. Current Distr. Factor Z S Z 0L = Pos. Seq. Line Impedance Z 0L I L Z 1L = Zero Seq. Line Impedance 2k 1 + Z k L I F I L = Prefault Load Current I F = Fault Current 9654A13 Figure 2: Single Phase-to-Ground Characteristics Figure 3: 9654A14
4 Page 4 DESCRIPTION OF SOFTWARE The diagram in Figure 6 shows a simplified flowchart for the relaying algorithms in MDAR. All algorithms are executed in a loop, as shown, which the processor repeats eight times per power cycle. Most relaying operations are performed at all times. An important detail not shown in the flow diagram is that many of the checks are broken into small parcels, so that the whole complement of tasks is performed over a one-cycle period eight passes through the loop. Some of the checks are done more than once each cycle. The instantaneous sample values are converted to voltage and current phasor values using a Fourier notch-filter algorithm. An additional dcoffset correction algorithm reduces overreach errors from decaying exponential transients. During nonfault operation, the program follows the Background Mode branch near the bottom. The processor uses its excess time to perform hardware self checking, service the man-machine interface, and check for a disturbance in voltage or current indicating a possible fault. If a disturbance is detected, the program switches to the fault mode for several power cycles. While operating in the fault mode, Zone 1 phase and ground measurements, pilot logic and channel control functions are executed. Fault mode operation restricts non-essential functions such as hardware self checking and servicing of the man-machine interface. 9654A15 Figure 4. Mho Characteristics for Phase-to-Phase and Two Phase-to-Ground Faults (No Load Flow)
5 Page 5 Figure 5. Simplified Block Diagram of MDAR Relay
6 Page 6 POWER ON initialization SELF-CHECKS MODE = FAULT SAMPLE V and I COMPUTE FOURIER & SUM-OF-SQUARES FAULT SETUP MODE = FAULT YES DISTURBANCE dv or di? NO MODE? BACKGROUND FAULT OPERATOR INTERFACE SELF-CHECK RELAYING CALCULATIONS: Phase Selection Direction Zone 2 Zone 3 Out-of-Step Inst. Overcurrent Ground Backup LOGIC Loss of Potential Loss of Current Contact Inputs Single-Pole-Trip Trip Logic Reclosing RELAYING CALCULATIONS Phase Selection Direction Zone 1 Pilot Zone 2 Zone 3 Out-of-Step Inst. Overcurrent Ground Backup LOGIC Loss of Potential Loss of Current Contact Inputs Pilot Logic Channel Control Single-Pole-trip Trip Logic Reclosing NO Zone 1 or Pilot Fault & V & I Stable? Yes MODE = Background No Data Bank Control Data Communications Target Data Collection Figure 6. MDAR Relay Program Functions
7 Page 7 Communications ABB introduced the first intelligent family of relay communication products: WRELCOM. WREL- COM was born out of the necessity of substation devices to exchange data effectively and quickly. Through a standard phone circuit, data from modern communication-based relays and older electromechanical or solid-state relays can be obtained over the same network. INCOM (INtegrated COMmunications) defines the protocol and medium used to communicate through the network among various INCOM - based products. The network of up to 2500 protective relays and associated devices is continually scanned by the network master device. Network communications between protective devices is guided through the network master device which is a Basic Interface to Remote Terminal (BIRT) or an INCOM -based Multi Access Controller (IMAC), which stores and organizes pertinent data, generating reports for each event. Access to this information permits intelligent decisions, such as the need to dispatch crews after a fault or relay failure. The WRELCOM Remote Communications Program (RCP)has been written to facilitate communications with INCOM -based protective relays and other network devices. It will run on any MS- DOS based system. Pull-down menus and Pop-up screens are incorporated providing a user friendly man-machine interface. RCP is required to communicate with any INCOM protocol relay.see I.L for complete details about RCP. Functions Include: Relay Acknowledgment Relay Self-Checking Status Remote Settings (can be downloaded from stored files) Fault Record Summary 16 fault Records Metering (Voltage, Current, Phase angle, Watt Flow, Varflow, Power Factor and status of Monitoring functions) Intermediate Targets Reset Targets/LEDs Optional Oscillographic Data Retrieval, Listing, Plotting OSCILLOGRAPHY MDAR provides oscillographic data storage capabilities for recording system fault currents and voltages with 2 ms resolution. The information is captured with every general start and/or trip, but is only saved based on the data storing option selected. This option permits saving events for: trips only, Zone 2 initiate or trip, Zone 2 or 3 initiate or trip, or general start or trip. This allows a variable degree of system area coverage with MDAR s oscillography. Also, when the MDAR general start mode is activated longer than 7 cycles and subsequently trips, a second event second event record will be saved. The basic oscillographic functions and capabilities are shown below. Graphical Oscillographic Data display is accomplished by using the optional OSCillographic And Recording (OSCAR) software. OSCAR gives the user a method for displaying the fault information graphically, a form which is more conducive to analysis than the tabular form. OSCAR also gives the user many ways to incorporate the graphics information in hardcopy reports. See I.L for complete details about OSCAR 16 Events 8 samples per cycle 1 cycle pre-trigger 7 cycles post-trigger 9 analog traces (2 ms resolution) 24 digital traces (2 ms resolution) Trigger options Trip Z2 or trip Z2, Z3 or trip General start REFERENCE DOCUMENTS: DOCUMENT NUMBER: MDAR COLOR BROCHURE B-385 MDAR RELAY SYSTEM INSTRUCTION LEAFLETS I.L RCP INSTRUCTION LEAFLET I.L OSCAR INSTRUCTION LEAFLET I.L ACCESSORIES: FT-14 TEST PLUG Right Hand Plug Left Hand Plug TEST FIXTURES AND EXTENDER BOARD Inner Chassis Test Fixture 5 A Inner Chassis Test Fixture 1 A Extender Board Assembly SOFTWARE Remote Communications Program (RCP) OSCillographic And Recording (OSCAR) COMMUNICATIONS CABLE KIT STYLE NUMBER: S# 1355D32G01 S#1355D32G02 S# 2409F39G01 S# 2409F39G02 S# 1609C55G01 S# SWRCP01 S# SWOSC01 S# 1504B78G01
8 Page 8 Technical Specifications (Pilot and Non-Pilot) General Operating Speed 12 milliseconds Minimum 22 milliseconds Typical AC Voltage Input V 60 Hz 120 V rms V LN 70 V rms V Hz 110 V rms V LN 63.5 V rms AC Current Input In 1 or 5 A Maximum Permissible ac Voltage Continuous 1.5 x Nominal 10 Seconds 2.5 x Nominal Maximum Permissible ac Current Continuous 3 x In 1 Second 100 x In Minimum Operating Current Rated Frequency DC Battery Voltages 0.1 x In 50 or 60 Hz Nominal Operating Range 48/60 Vdc Vdc 110/125 Vdc Vdc 220/250 Vdc Vdc Burdens dc Battery Voltage Current External Connections 7 Watts Normal 30 Watts Tripping 0.02 VA/Phase at 70 Vac 0.15 VA/Phase at 5 A Terminal blocks located on the rear of the chassis suitable for #14 square torque lugs Wiring to FT-14 switches suitable for #12 wire lugs Dimensions & Weight (4RU) 7.0 high (177.8mm) Standard 19 rack 19.0 wide (482.6mm) 14 deep (356mm) Including terminal blocks 35 pounds (16 kg net) Contact Data Two Breaker Trip Contacts* Two Breaker Failure Initiate Contacts** Two Reclose Initiate Contacts** One General Start Contact (Indicates Power System Disturbance)** One System Failure Alarm Contact** Two Trip Alarm Contacts** Eight Programmable Output Contacts (Optional): Four NO Trip Rated With FT-Switch Isolation* Four NO/NC (Jumper Selectable) Contacts** Six Single Pole Trip Contacts (Optional)* *Trip Contacts Make and carry 30 A for 1 second, 10 A continuous capability. Break 50 watts resistive or 25 watts with L/R seconds **Non-Trip Contacts 1 A Continuous 0.1 A Resistive Interrupt Capability Supports 1000 Vac across open contacts Ambient Temperature Range For Operation -20 C to +60 C For Storage -40 C to +80 C Insulation Test Voltage 2.8k Vdc, 1 minute (ANSI C37.90) (IEC-255-6) Impulse Voltage Withstand 5k V Peak, 1.2x50 ms 0.5 Joule, (IEC-255-5) Surge Withstand Voltage 2.5k V, 1 MHz (ANSI C , IEC-255-6) Fast Transient Voltage 4k V, 5x50 ms (IEC 801-4); 5k V, 10x150 ms (ANSI C ) EMI Volts/Meter Withstand 25 MHz-1GHz, 10V/m Withstand (ANSI C ) Standards: ANSI C37.90 IEC IEC-255-6A BS IEC Measurements Number of Zones 3 zones are standard; optional pilot adds additional zone; 3rd zone reversible Equivalent Measurement Units Three variable mho phase-to-ground and one variable mho phase-to-phase impedance unit per zone. One three phase unit consisting of any one variable mho phase-to-ground unit operation plus a three phase fault output from the Faulted Phase Selector Three phase and one ground directional high set overcurrent units. Three phase non-directional overcurrent units for load loss trip and close-into-fault trip. Three phase non-directional medium set overcurrent units for phase distance supervision. One ground medium set non-directional overcurrent unit for ground distance supervision. One ground overcurrent unit for loss of current monitoring. One inverse time overcurrent ground unit with selectable directional or non-directional capability. One forward set instantaneous directional overcurrent ground unit. (Pilot logic high-resistance ground fault protection.) Three undervoltage units for weakfeed and loss of potential supervision. Three voltage change ( V) fault detectors. Four current change ( I) fault detectors. One instantaneous overcurrent unit low set. One reverse set instantaneous directional overcurrent ground unit (pilot carrier start, weakfeed, transient block). Optional Single-Pole-Trip Logic and Outputs a) Single Pole Trip/Single Pole Reclose Initiate on first fault b) 3 Pole Trip/Reclose Block if reclosing on a permanent fault c) 3 Pole Trip/Reclose Block if second fault occurs during single phasing d) 3 Pole Trip on a selectable time delay limit if the system fails to reclose Setting Ranges CT ratio: :1 VT ratio: :1 Phase & Ground Distance Z1, Z2, Z3, Pilot Option ohms in 0.01 ohm steps for 5 A ct ohms in 0.05 ohm steps for 1 A ct Zone Timers: Independent timers for phase and ground. Zone 1 Selectable on 2 cycles in Ver. 2.xx Zone to 2.9 seconds in 0.01 second steps Zone to 9.99 seconds in 0.01 second steps Ohms per unit distance in 0.001/DTYP (Km or Mi) Inverse Time Overcurrent Ground Pickup in 0.5 A increments for 5 A ct Pickup in 0.1 A increments for 1 A ct Choice of 10 time curves Set for directional or non-directional operation High set instantaneous overcurrent trip units - phase and ground in 0.5 A steps for 5 A ct in 0.1A steps for 1 A ct Mediumset and Lowset instantaneous overcurrent trip units -phase and ground in 0.5 A steps for 5 A ct in 0.1A steps for 1 A ct Load Loss Current Units (I AL, I BL, I CL ) in 0.5 A steps for 5 A ct in 0.1 A steps for 1 A ct Out-of-Step Block OSB Override Timer milliseconds in 16 millisecond steps OSB Inner Blinder ohms in 0.1 ohm steps OSB Inner Blinder ohms in 0.1 ohm steps Positive/Zero Sequence Impedance Characteristic Angles 40 to 90 in 1.0 degree steps Zero Sequence Compensation (ZOL/Z1) in 0.1 steps Single Phasing Limit Timer milliseconds in 50 millisecond steps Time and Date Year, month, weekday, date, hour, minute Blocking System Channel Coordination Timer 0-32 ms in 2 ms steps Additional Settings Pilot System Logic Selection 3 Zone Non-Pilot Zone 1 Extension POTT Weakfeed Enable Unblock Block Yes or No Close Into Fault Trip Stub Bus, Close Into Fault With Time Delay, Close into Fault or No Load Loss Trip Yes or No Loss Of Potential Block Distance Trip Only, All Trips or No
9 Page 9 MDAR Outline Drawing
10 Page 10 REL 300 CATALOG NUMBERING SYSTEM REL 300 NUMERICAL MD 3 B 1 S P F R G RELAY SYSTEM (50/60 HZ) TRIP Three Pole Trip 3 Single Pole Trip 1 Three Pole Trip w/programmable Contacts * 8 CURRENT INPUT 1A 5A A B BATTERY SUPPLY VOLTAGE 48/60 Vdc 4 110/125 Vdc 1 220/250 Vdc 2 POWER SWING BLOCK Power Swing Block PILOT SYSTEM/CHANNEL INTERFACE Pilot System-Channel Interface Non-Pilot System, No Channel Interface TEST SWITCHES FT-14 Switches No FT-14 Switches COMMUNICATION DEVICE RS-232C RS-232C (with IRIG - B port) INCOM S P N F N R B C SOFTWARE OPTION (Oscillographic Data Storage STD)** Version 2.0X Version 2.1X Version 2.2X G A B ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division 4300 Coral Ridge Drive Coral Springs, FL v ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division 7036 Snowdrift Road, Suite 2 Allentown, PA
REL301/302 Firmware Version 1.23 (08/19/03) Addendum to Instruction book V1.20, F
 REL301/302 Firmware Version 1.23 (08/19/03) Addendum to Instruction book V1.20, 40-386.1F Revisions These revisions are to be added (inserted) to the REL301/302 Version 1.20 Instruction Book Revision History
REL301/302 Firmware Version 1.23 (08/19/03) Addendum to Instruction book V1.20, 40-386.1F Revisions These revisions are to be added (inserted) to the REL301/302 Version 1.20 Instruction Book Revision History
Type REL 350 High-Speed Segregated Phase Comparison Line Protection System
 A Automation Inc Descriptive ulletin Substation and Automation Division 41-461M Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA September 2000 Device Number: 78 For Phase and Ground Fault Protection of Transmission Lines
A Automation Inc Descriptive ulletin Substation and Automation Division 41-461M Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA September 2000 Device Number: 78 For Phase and Ground Fault Protection of Transmission Lines
Numerical Distance Protection REL-300 (MDAR) Relaying System Version 2.02
 ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.1B Effective: May, 1992 Supersedes IL 40-385.1A dated January, 1992 Numerical
ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.1B Effective: May, 1992 Supersedes IL 40-385.1A dated January, 1992 Numerical
! CAUTION I.L
 ! CAUTION It is recommended that the user of REL 301/302 equipment become acquainted with the information in this instruction leaflet before energizing the system. Failure to do so may result in injury
! CAUTION It is recommended that the user of REL 301/302 equipment become acquainted with the information in this instruction leaflet before energizing the system. Failure to do so may result in injury
Numerical Distance Protection REL-300 (MDAR) Relaying System Version 2.50
 ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.2 Effective: March, 1992 Preliminary Numerical Distance Protection REL-300 (MDAR)
ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.2 Effective: March, 1992 Preliminary Numerical Distance Protection REL-300 (MDAR)
Transmission Line Protection Objective. General knowledge and familiarity with transmission protection schemes
 Transmission Line Protection Objective General knowledge and familiarity with transmission protection schemes Transmission Line Protection Topics Primary/backup protection Coordination Communication-based
Transmission Line Protection Objective General knowledge and familiarity with transmission protection schemes Transmission Line Protection Topics Primary/backup protection Coordination Communication-based
Digital Line Protection System
 Digital Line Protection System! Microprocessor Based Protection, Control and Monitoring System! Waveform Sampling! Proven Protection! Economical! Ease of Retrofit 1 DLP-D D Enhancements ASCII SUBSET Three
Digital Line Protection System! Microprocessor Based Protection, Control and Monitoring System! Waveform Sampling! Proven Protection! Economical! Ease of Retrofit 1 DLP-D D Enhancements ASCII SUBSET Three
Numerical Distance Protection REL-300 (MDAR) Relaying System Version 2.62
 ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.5 Effective: January, 1996 Supersedes IL 40-385.5 dated November, 1995 Numerical
ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 40-385.5 Effective: January, 1996 Supersedes IL 40-385.5 dated November, 1995 Numerical
BE1-67N GROUND DIRECTIONAL OVERCURRENT RELAY FEATURES ADDITIONAL INFORMATION. FUNCTIONS AND FEATURES Pages 2-4. APPLICATIONS Page 2
 BE1-67N GROUND DIRECTIONAL OVERCURRENT RELAY The BE1-67N Ground Directional Overcurrent Relay provides ground fault protection for transmission and distribution lines by sensing the direction and magnitude
BE1-67N GROUND DIRECTIONAL OVERCURRENT RELAY The BE1-67N Ground Directional Overcurrent Relay provides ground fault protection for transmission and distribution lines by sensing the direction and magnitude
Transmission Protection Overview
 Transmission Protection Overview 2017 Hands-On Relay School Daniel Henriod Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Pullman, WA Transmission Line Protection Objective General knowledge and familiarity with
Transmission Protection Overview 2017 Hands-On Relay School Daniel Henriod Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Pullman, WA Transmission Line Protection Objective General knowledge and familiarity with
PROTECTION SIGNALLING
 PROTECTION SIGNALLING 1 Directional Comparison Distance Protection Schemes The importance of transmission system integrity necessitates high-speed fault clearing times and highspeed auto reclosing to avoid
PROTECTION SIGNALLING 1 Directional Comparison Distance Protection Schemes The importance of transmission system integrity necessitates high-speed fault clearing times and highspeed auto reclosing to avoid
Sequence Networks p. 26 Sequence Network Connections and Voltages p. 27 Network Connections for Fault and General Unbalances p. 28 Sequence Network
 Preface p. iii Introduction and General Philosophies p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Classification of Relays p. 1 Analog/Digital/Numerical p. 2 Protective Relaying Systems and Their Design p. 2 Design Criteria
Preface p. iii Introduction and General Philosophies p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Classification of Relays p. 1 Analog/Digital/Numerical p. 2 Protective Relaying Systems and Their Design p. 2 Design Criteria
www. ElectricalPartManuals. com Transformer Differential Relay MD32T Transformer Differential Relay
 Transformer Differential Relay The MD3T Transformer Differential Relay is a member of Cooper Power Systems Edison line of microprocessor based protective relays. The MD3T relay offers the following functions:
Transformer Differential Relay The MD3T Transformer Differential Relay is a member of Cooper Power Systems Edison line of microprocessor based protective relays. The MD3T relay offers the following functions:
SEL-311C TRANSMISSION PROTECTION SYSTEM
 SEL-3C TRANSMISSION PROTECTION SYSTEM ADVANCED TRANSMISSION LINE PROTECTION, AUTOMATION, AND CONTROL Bus ANSI NUMBERS/ACRONYMS AND FUNCTIONS 52 3 3 2 P G 8 O U 27 68 50BF 67 P G Q 50 P G Q 59 P G Q 5 P
SEL-3C TRANSMISSION PROTECTION SYSTEM ADVANCED TRANSMISSION LINE PROTECTION, AUTOMATION, AND CONTROL Bus ANSI NUMBERS/ACRONYMS AND FUNCTIONS 52 3 3 2 P G 8 O U 27 68 50BF 67 P G Q 50 P G Q 59 P G Q 5 P
Power systems Protection course
 Al-Balqa Applied University Power systems Protection course Department of Electrical Energy Engineering 1 Part 5 Relays 2 3 Relay Is a device which receive a signal from the power system thought CT and
Al-Balqa Applied University Power systems Protection course Department of Electrical Energy Engineering 1 Part 5 Relays 2 3 Relay Is a device which receive a signal from the power system thought CT and
Protective Relays Digitrip 3000
 New Information Technical Data Effective: May 1999 Page 1 Applications Provides reliable 3-phase and ground overcurrent protection for all voltage levels. Primary feeder circuit protection Primary transformer
New Information Technical Data Effective: May 1999 Page 1 Applications Provides reliable 3-phase and ground overcurrent protection for all voltage levels. Primary feeder circuit protection Primary transformer
This webinar brought to you by the Relion product family Advanced protection and control IEDs from ABB
 This webinar brought to you by the Relion product family Advanced protection and control IEDs from ABB Relion. Thinking beyond the box. Designed to seamlessly consolidate functions, Relion relays are smarter,
This webinar brought to you by the Relion product family Advanced protection and control IEDs from ABB Relion. Thinking beyond the box. Designed to seamlessly consolidate functions, Relion relays are smarter,
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Note: Bold italic type refers to entries in the Table of Contents, refers to a Standard Title and Reference number and # refers to a specific standard within the buff book 91, 40, 48* 100, 8, 22*,
Index Note: Bold italic type refers to entries in the Table of Contents, refers to a Standard Title and Reference number and # refers to a specific standard within the buff book 91, 40, 48* 100, 8, 22*,
Generator Protection M 3420
 PROTECTION Generator Protection M 3420 Integrated Protection System for Generators of All Sizes Unit shown with optional M 3920 Target Module and M 3931 HMI (Human-Machine Interface) Module Microprocessor-based
PROTECTION Generator Protection M 3420 Integrated Protection System for Generators of All Sizes Unit shown with optional M 3920 Target Module and M 3931 HMI (Human-Machine Interface) Module Microprocessor-based
www. ElectricalPartManuals. com Generator Differential Relay MD32G Rotating Machine Differential Relay
 Generator Differential Relay The MD3G Rotating Machine Differential Relay is a member of Cooper Power Systems Edison line of microprocessor based protective relays. The MD3G relay offers the following
Generator Differential Relay The MD3G Rotating Machine Differential Relay is a member of Cooper Power Systems Edison line of microprocessor based protective relays. The MD3G relay offers the following
Multimeter 500CVD21 RTU500 series
 Remote Terminal Units - Data sheet Multimeter 500CVD21 RTU500 series CT/VT interface with 4 voltage and 24 current inputs for direct monitoring of 3/4 wire 0 300 V AC (line to earth), 0...500 V AC (phase
Remote Terminal Units - Data sheet Multimeter 500CVD21 RTU500 series CT/VT interface with 4 voltage and 24 current inputs for direct monitoring of 3/4 wire 0 300 V AC (line to earth), 0...500 V AC (phase
Transmission Lines and Feeders Protection Pilot wire differential relays (Device 87L) Distance protection
 Transmission Lines and Feeders Protection Pilot wire differential relays (Device 87L) Distance protection 133 1. Pilot wire differential relays (Device 87L) The pilot wire differential relay is a high-speed
Transmission Lines and Feeders Protection Pilot wire differential relays (Device 87L) Distance protection 133 1. Pilot wire differential relays (Device 87L) The pilot wire differential relay is a high-speed
Distance Element Performance Under Conditions of CT Saturation
 Distance Element Performance Under Conditions of CT Saturation Joe Mooney Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Published in the proceedings of the th Annual Georgia Tech Fault and Disturbance Analysis
Distance Element Performance Under Conditions of CT Saturation Joe Mooney Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Published in the proceedings of the th Annual Georgia Tech Fault and Disturbance Analysis
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
 GEK-00682D INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The MDP Digital Time Overcurrent Relay is a digital, microprocessor based, nondirectional overcurrent relay that protects against phase-to-phase
GEK-00682D INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The MDP Digital Time Overcurrent Relay is a digital, microprocessor based, nondirectional overcurrent relay that protects against phase-to-phase
T/3000 T/3000. Substation Maintenance and Commissioning Test Equipment
 T/3000 Substation Maintenance and Commissioning Test Equipment MULTI FUNCTION SYSTEM FOR TESTING SUBSTATION EQUIPMENT SUCH AS: CURRENT, VOLTAGE AND POWER TRANSFORMERS, ALL TYPE OF PROTECTION RELAYS, ENERGY
T/3000 Substation Maintenance and Commissioning Test Equipment MULTI FUNCTION SYSTEM FOR TESTING SUBSTATION EQUIPMENT SUCH AS: CURRENT, VOLTAGE AND POWER TRANSFORMERS, ALL TYPE OF PROTECTION RELAYS, ENERGY
PD300. Transformer, generator and motor protection Data sheet
 PD300 Transformer, generator and motor protection Data sheet DSE_PD300_eng_AO No part of this publication may be reproduced by whatever means without the prior written permission of Ingeteam T&D. One of
PD300 Transformer, generator and motor protection Data sheet DSE_PD300_eng_AO No part of this publication may be reproduced by whatever means without the prior written permission of Ingeteam T&D. One of
ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA
 ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 41-348.1H Effective: November 1997 Supersedes I.L. I.L. 41-348.1G, Dated January 1985
ABB Automation, Inc. Substation Automation & Protection Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA Instruction Leaflet 41-348.1H Effective: November 1997 Supersedes I.L. I.L. 41-348.1G, Dated January 1985
NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June 9, Phil Tatro Jon Gardell
 Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination GSU Phase Overcurrent (51T), GSU Ground Overcurrent (51TG), and Breaker Failure (50BF) Protection NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series
Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination GSU Phase Overcurrent (51T), GSU Ground Overcurrent (51TG), and Breaker Failure (50BF) Protection NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series
DRTS 66 The new generation of advanced test equipments for Relays, Energy meters, Transducers and Power quality meters
 The new generation of advanced test equipments for Relays, Energy meters, Transducers and Power quality meters Testing all relay technologies: electromechanical, solid state, numerical and IEC61850 Manual
The new generation of advanced test equipments for Relays, Energy meters, Transducers and Power quality meters Testing all relay technologies: electromechanical, solid state, numerical and IEC61850 Manual
BUS2000 Busbar Differential Protection System
 BUS2000 Busbar Differential Protection System Differential overcurrent system with percentage restraint protection 1 Typical Busbar Arrangements Single Busbar Double Busbar with Coupler Breaker and a Half
BUS2000 Busbar Differential Protection System Differential overcurrent system with percentage restraint protection 1 Typical Busbar Arrangements Single Busbar Double Busbar with Coupler Breaker and a Half
Stabilized Differential Relay SPAD 346. Product Guide
 Issued: July 1998 Status: Updated Version: D/21.03.2006 Data subject to change without notice Features Integrated three-phase differential relay, three-phase overcurrent relay and multiconfigurable earth-fault
Issued: July 1998 Status: Updated Version: D/21.03.2006 Data subject to change without notice Features Integrated three-phase differential relay, three-phase overcurrent relay and multiconfigurable earth-fault
Using a Multiple Analog Input Distance Relay as a DFR
 Using a Multiple Analog Input Distance Relay as a DFR Dennis Denison Senior Transmission Specialist Entergy Rich Hunt, M.S., P.E. Senior Field Application Engineer NxtPhase T&D Corporation Presented at
Using a Multiple Analog Input Distance Relay as a DFR Dennis Denison Senior Transmission Specialist Entergy Rich Hunt, M.S., P.E. Senior Field Application Engineer NxtPhase T&D Corporation Presented at
www. ElectricalPartManuals. com Basler Electric P. 0. BOX 269 HIGHLAND, ILLINOIS 62249, U.S.A. PHONE FAX
 The BE1-47N Voltage Phase Sequence Relay provides protection for rotating equipment from the damaging effects of excessive negative sequence voltage resulting from phase failure, phase unbalance and reversed
The BE1-47N Voltage Phase Sequence Relay provides protection for rotating equipment from the damaging effects of excessive negative sequence voltage resulting from phase failure, phase unbalance and reversed
Generator Protection M 3425
 PROTECTION Generator Protection M 3425 Integrated Protection System for Generators of All Sizes Unit shown with optional M 3925 Target Module and M 3931 HMI (Human Machine Interface) Module Provides all
PROTECTION Generator Protection M 3425 Integrated Protection System for Generators of All Sizes Unit shown with optional M 3925 Target Module and M 3931 HMI (Human Machine Interface) Module Provides all
NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June 16, Phil Tatro Jon Gardell
 Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Phase Distance (21) and Voltage-Controlled or Voltage-Restrained Overcurrent Protection (51V) NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June
Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Phase Distance (21) and Voltage-Controlled or Voltage-Restrained Overcurrent Protection (51V) NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June
APPLICATION: The heart of the system is a DSR 100 Digital Static Regulator used in conjunction with standard SCR based rectifier bridges.
 APPLICATION: Basler Electric offers a New Line of digitally controlled brush (static) or brushless excitation systems designed for use with existing Hydro, Gas as well as Diesel driven generators requiring
APPLICATION: Basler Electric offers a New Line of digitally controlled brush (static) or brushless excitation systems designed for use with existing Hydro, Gas as well as Diesel driven generators requiring
Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions
 1 Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions Joe Mooney, P.E. and Satish Samineni, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Abstract Modern distance relays use various filtering
1 Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions Joe Mooney, P.E. and Satish Samineni, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Abstract Modern distance relays use various filtering
Type KLF Generator Field Protection-Loss of Field Relay
 Supersedes DB 41-745B pages 1-4, dated June, 1989 Mailed to: E, D, C/41-700A ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA For Use With Delta Connected Potential Transformers
Supersedes DB 41-745B pages 1-4, dated June, 1989 Mailed to: E, D, C/41-700A ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA For Use With Delta Connected Potential Transformers
SEL-311A Protection and Automation System
 SEL-311A Protection and Automation System Powerful Solutions for Transmission Line Protection Major Features and Benefits The SEL-311A Protection and Automation System is a basic, three-pole trip/reclose
SEL-311A Protection and Automation System Powerful Solutions for Transmission Line Protection Major Features and Benefits The SEL-311A Protection and Automation System is a basic, three-pole trip/reclose
Utility Communications Teleprotection Equipment TPT-200
 Utility Communications Teleprotection Equipment TPT-200 5C Communications Inc. All rights reserved Teleprotection is designed to transfer protection commands coming, in most cases, from distance protection
Utility Communications Teleprotection Equipment TPT-200 5C Communications Inc. All rights reserved Teleprotection is designed to transfer protection commands coming, in most cases, from distance protection
EE Lecture 14 Wed Feb 8, 2017
 EE 5223 - Lecture 14 Wed Feb 8, 2017 Ongoing List of Topics: URL: http://www.ece.mtu.edu/faculty/bamork/ee5223/index.htm Labs - EE5224 Lab 3 - begins on Tues Feb 14th Term Project - details posted. Limit
EE 5223 - Lecture 14 Wed Feb 8, 2017 Ongoing List of Topics: URL: http://www.ece.mtu.edu/faculty/bamork/ee5223/index.htm Labs - EE5224 Lab 3 - begins on Tues Feb 14th Term Project - details posted. Limit
Line protection REL 100
 Page 1 Issued June 1999 Changed since July 1998 Data subject to change without notice (SE970130) Features Simultaneous phase-phase and phaseearth loop impedance measurement, with individual numerical measuring
Page 1 Issued June 1999 Changed since July 1998 Data subject to change without notice (SE970130) Features Simultaneous phase-phase and phaseearth loop impedance measurement, with individual numerical measuring
DRTS-6. DRTS-6 has been designed to test: DRTS-6. Advanced Protection Relay Test Set and Measurement System
 DRTS-6 Advanced Protection Relay Test Set and Measurement System MULTI-TASKING EQUIPMENT DESIGNED FOR TESTING PROTECTION RELAYS, ENERGY METERS, TRANSDUCERS POWERFUL AND LIGHTWEIGHT HIGH ACCURACY: BETTER
DRTS-6 Advanced Protection Relay Test Set and Measurement System MULTI-TASKING EQUIPMENT DESIGNED FOR TESTING PROTECTION RELAYS, ENERGY METERS, TRANSDUCERS POWERFUL AND LIGHTWEIGHT HIGH ACCURACY: BETTER
RETROFITTING. Motor Protection Relay. Two mountings are available, Flush Rear Connection (EDPAR) or Projecting Rear Connection (SDPAR).
 RETROFITTING Motor Protection Relay NPM800R (R2 case) and NPM800RE (R3 case) are dedicated to the refurbishment of 7000 series (R2 and R3 cases) of CEE relays providing the protection of medium voltage
RETROFITTING Motor Protection Relay NPM800R (R2 case) and NPM800RE (R3 case) are dedicated to the refurbishment of 7000 series (R2 and R3 cases) of CEE relays providing the protection of medium voltage
Fault indicator. Application. SPEF 3A2 C 1MRS MBG Issued: April 1999 Status: Updated Version: B/ Data subject to change without notice
 Issued: April 1999 Status: Updated Version: B/08.11.200 Data subject to change without notice Features Versatile, multifunction line fault indicator for distribution networks Overcurrent, earth-fault and
Issued: April 1999 Status: Updated Version: B/08.11.200 Data subject to change without notice Features Versatile, multifunction line fault indicator for distribution networks Overcurrent, earth-fault and
MLP MICROPROCESSOR BASED DISTANCE PROTECTION
 GEK-98846A MLP GE Power Management MLP MICROPROCESSOR BASED DISTANCE PROTECTION We bring good things to life TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. DESCRIPTION... 3 2. APPLICATION... 6 3. CHARACTERISTICS... 7 3.1 GENERAL
GEK-98846A MLP GE Power Management MLP MICROPROCESSOR BASED DISTANCE PROTECTION We bring good things to life TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. DESCRIPTION... 3 2. APPLICATION... 6 3. CHARACTERISTICS... 7 3.1 GENERAL
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR TIME OVERCURRENT RELAY BE1-51
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR TIME OVERCURRENT RELAY BE1-51 Publication: 9137200997 Revision: E 07/10 INTRODUCTION This instruction manual provides information about the operation and installation of the BE1-51
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR TIME OVERCURRENT RELAY BE1-51 Publication: 9137200997 Revision: E 07/10 INTRODUCTION This instruction manual provides information about the operation and installation of the BE1-51
SOLUTIONS FOR AN EVOLVING WORLD RFL Programmable FSK Powerline carrier system
 SOLUTIONS FOR AN EVOLVING WORLD RFL 9780 Programmable FSK Powerline carrier system Your world is changing and so are we. At RFL, we know your needs change much faster than your infrastructure. Our comprehensive
SOLUTIONS FOR AN EVOLVING WORLD RFL 9780 Programmable FSK Powerline carrier system Your world is changing and so are we. At RFL, we know your needs change much faster than your infrastructure. Our comprehensive
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832)
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) The toolbox for substation 3-phase testing Three currents and four voltages Stand-alone functionality Rugged and reliable
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) The toolbox for substation 3-phase testing Three currents and four voltages Stand-alone functionality Rugged and reliable
Addendum to Instructions for Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Digitrip 3000 Protective Relays
 Dual-Source Power Supply Addendum to I.B. 17555 Addendum to Instructions for Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Digitrip 3000 Protective Relays Table of Contents Page 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 General
Dual-Source Power Supply Addendum to I.B. 17555 Addendum to Instructions for Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Digitrip 3000 Protective Relays Table of Contents Page 1.0 Introduction...1 2.0 General
Application for A Sub-harmonic Protection Relay. ERLPhase Power Technologies
 Application for A Sub-harmonic Protection Relay ERLPhase Power Technologies 1 Outline Introduction System Event at Xcel Energy Event Analysis Microprocessor based relay hardware architecture Sub harmonic
Application for A Sub-harmonic Protection Relay ERLPhase Power Technologies 1 Outline Introduction System Event at Xcel Energy Event Analysis Microprocessor based relay hardware architecture Sub harmonic
N. TEST TEST DESCRIPTION
 Multi function system for testing substation equipment such as: current, voltage and power transformers, all type of protection relays, energy meters and transducers Primary injection testing capabilities
Multi function system for testing substation equipment such as: current, voltage and power transformers, all type of protection relays, energy meters and transducers Primary injection testing capabilities
I.L A 1-2 (5/95)
 1. 2. MRC-T FEATURES 1.2.1 Standard Features Multiple-Shot Reclosing 1-4 Instantaneous or time delay reclosures Reclosure dead time (settable for each reclose) 0.01-250 seconds Selectable reclosing initiate
1. 2. MRC-T FEATURES 1.2.1 Standard Features Multiple-Shot Reclosing 1-4 Instantaneous or time delay reclosures Reclosure dead time (settable for each reclose) 0.01-250 seconds Selectable reclosing initiate
Static Breaker Back-up Relay Type SBC Relay SBC231B
 GEK 106210 Supplement GEK-100637 GE Power Management Static Breaker Back-up Relay Type SBC Relay SBC231B INSTRUCTIONS These instructions, GEK-106210 together with GEK-100637, constitute the complete instructions
GEK 106210 Supplement GEK-100637 GE Power Management Static Breaker Back-up Relay Type SBC Relay SBC231B INSTRUCTIONS These instructions, GEK-106210 together with GEK-100637, constitute the complete instructions
NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function.
 REGULATION AUTOMATIC SYNCHRONIZER for GENERATOR NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
REGULATION AUTOMATIC SYNCHRONIZER for GENERATOR NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
BE1-87G VARIABLE PERCENTAGE DIFFERENTIAL RELAY
 BE1-87G VARIABLE PERCENTAGE DIFFERENTIAL RELAY The BE1-87G is a single or three-phase solid-state variable percentage differential relay designed to provide selective, high-speed, differential protection
BE1-87G VARIABLE PERCENTAGE DIFFERENTIAL RELAY The BE1-87G is a single or three-phase solid-state variable percentage differential relay designed to provide selective, high-speed, differential protection
POWER SYSTEM PRINCIPLES APPLIED IN PROTECTION PRACTICE. Professor Akhtar Kalam Victoria University
 POWER SYSTEM PRINCIPLES APPLIED IN PROTECTION PRACTICE Professor Akhtar Kalam Victoria University The Problem Calculate & sketch the ZPS, NPS & PPS impedance networks. Calculate feeder faults. Calculate
POWER SYSTEM PRINCIPLES APPLIED IN PROTECTION PRACTICE Professor Akhtar Kalam Victoria University The Problem Calculate & sketch the ZPS, NPS & PPS impedance networks. Calculate feeder faults. Calculate
AF91 Adjustable Frequency Drives Series B
 Effective: January, 00 Page New Information AF9 Adjustable Model AF9 Description Model AF9 Adjustable Frequency AC Drives are designed to provide adjustable speed control of -phase motors. These microprocessor-based
Effective: January, 00 Page New Information AF9 Adjustable Model AF9 Description Model AF9 Adjustable Frequency AC Drives are designed to provide adjustable speed control of -phase motors. These microprocessor-based
USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK
 USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK P Horton, S Swain patricia.horton@ge.com, simon.swain@ge.com UK INTRODUCTION Superimposed techniques
USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK P Horton, S Swain patricia.horton@ge.com, simon.swain@ge.com UK INTRODUCTION Superimposed techniques
Setting Generic Distance Relay UTP-100#WPSC1. in the. Computer-Aided Protection Engineering System (CAPE)
 Setting Generic Distance Relay UTP-100#WPSC1 in the Computer-Aided Protection Engineering System (CAPE) Prepared for CAPE Users' Group August 6, 1998 Revised August 24, 1998 Electrocon International, Inc.
Setting Generic Distance Relay UTP-100#WPSC1 in the Computer-Aided Protection Engineering System (CAPE) Prepared for CAPE Users' Group August 6, 1998 Revised August 24, 1998 Electrocon International, Inc.
Protection Basics Presented by John S. Levine, P.E. Levine Lectronics and Lectric, Inc GE Consumer & Industrial Multilin
 Protection Basics Presented by John S. Levine, P.E. Levine Lectronics and Lectric, Inc. 770 565-1556 John@L-3.com 1 Protection Fundamentals By John Levine 2 Introductions Tools Outline Enervista Launchpad
Protection Basics Presented by John S. Levine, P.E. Levine Lectronics and Lectric, Inc. 770 565-1556 John@L-3.com 1 Protection Fundamentals By John Levine 2 Introductions Tools Outline Enervista Launchpad
High-set undervoltage stage with definitetime. or inverse definite minimum time (IDMT) characteristic. Low-set undervoltage stage with definitetime
 Issued: 5.06.999 Status: 5.06.999 Version: B/09..00 Data subject to change without notice Features Overvoltage and undervoltage protection Single- or three-phase operation High-set overvoltage stage with
Issued: 5.06.999 Status: 5.06.999 Version: B/09..00 Data subject to change without notice Features Overvoltage and undervoltage protection Single- or three-phase operation High-set overvoltage stage with
System Protection and Control Subcommittee
 Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Reverse Power (32), Negative Sequence Current (46), Inadvertent Energizing (50/27), Stator Ground Fault (59GN/27TH), Generator Differential (87G),
Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Reverse Power (32), Negative Sequence Current (46), Inadvertent Energizing (50/27), Stator Ground Fault (59GN/27TH), Generator Differential (87G),
Model 3102D 0-2 kv H.V. Power Supply
 Features Compact single width NIM package Regulated up to ±2000 V dc. 1 ma output Noise and ripple 3 mv peak to peak Overload and short circuit protected Overload, inhibit and polarity status indicators
Features Compact single width NIM package Regulated up to ±2000 V dc. 1 ma output Noise and ripple 3 mv peak to peak Overload and short circuit protected Overload, inhibit and polarity status indicators
Reducing the Effects of Short Circuit Faults on Sensitive Loads in Distribution Systems
 Reducing the Effects of Short Circuit Faults on Sensitive Loads in Distribution Systems Alexander Apostolov AREVA T&D Automation I. INTRODUCTION The electric utilities industry is going through significant
Reducing the Effects of Short Circuit Faults on Sensitive Loads in Distribution Systems Alexander Apostolov AREVA T&D Automation I. INTRODUCTION The electric utilities industry is going through significant
Replacement solution
 Replacement solution for the ABB DPU2000R protection and control relay Specification File, Revision, Date (Pages) Replacement Relay Specification_ABB DPU2000R_0.doc, Revision 0, August 2, 2013 (37) Table
Replacement solution for the ABB DPU2000R protection and control relay Specification File, Revision, Date (Pages) Replacement Relay Specification_ABB DPU2000R_0.doc, Revision 0, August 2, 2013 (37) Table
Protective Relaying for DER
 Protective Relaying for DER Rogerio Scharlach Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Basking Ridge, NJ Overview IEEE 1547 general requirements to be met at point of common coupling (PCC) Distributed
Protective Relaying for DER Rogerio Scharlach Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Basking Ridge, NJ Overview IEEE 1547 general requirements to be met at point of common coupling (PCC) Distributed
SECTION LOW VOLTAGE ACTIVE HARMONIC FILTER SYSTEM NEMA 1 ENCLOSED
 SECTION 16280 LOW VOLTAGE ACTIVE HARMONIC FILTER SYSTEM NEMA 1 ENCLOSED PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY This specification defines the requirements for active harmonic filter systems in order to meet IEEE-519-2014
SECTION 16280 LOW VOLTAGE ACTIVE HARMONIC FILTER SYSTEM NEMA 1 ENCLOSED PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY This specification defines the requirements for active harmonic filter systems in order to meet IEEE-519-2014
SPAD 346 C Stabilized differential relay
 SPAD 346 C Stabilized differential relay Stabilized Differential Relay Type SPAD 346 C Features Integrated three-phase differential relay, three-phase overcurrent relay and multiconfigurable earth-fault
SPAD 346 C Stabilized differential relay Stabilized Differential Relay Type SPAD 346 C Features Integrated three-phase differential relay, three-phase overcurrent relay and multiconfigurable earth-fault
NO WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND ARE IMPLIED ON THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT.
 MODBUS/BECO2200-M3425A Communication Data Base for M-3425A Integrated Protection System Device I.D. = 150 Specifications presented herein are thought to be accurate at the time of publication but are subject
MODBUS/BECO2200-M3425A Communication Data Base for M-3425A Integrated Protection System Device I.D. = 150 Specifications presented herein are thought to be accurate at the time of publication but are subject
Model 931A Power System Analyzer. Model 930A Three Phase Power Analyzer. Model 929A Three Phase Power Meter. with. Digital Signal Analysis
 Model 931A Power System Analyzer Model 930A Three Phase Power Analyzer Model 929A Three Phase Power Meter with Digital Signal Analysis Model 931A shown with included accessories Arbiter Systems, Inc. Models
Model 931A Power System Analyzer Model 930A Three Phase Power Analyzer Model 929A Three Phase Power Meter with Digital Signal Analysis Model 931A shown with included accessories Arbiter Systems, Inc. Models
NPRG860 NPRG870 REGULATION. Automatic Synchronizer for Generator
 REGULATION Automatic Synchronizer for Generator NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
REGULATION Automatic Synchronizer for Generator NPRG860 & NPRG870 perform synchronization and paralleling of generators with electrical network. NPRG860 features a speed adjustment function. NPRG870 adds
1 INTRODUCTION ORDER CODE / INFORMATION
 INTRODUCTION ORDER CODE / INFORMATION 269/269Plus * * * * * * 269/269Plus SV D/O.4 ORDER CODE / INFORMATION Motor management relay Standard version Drawout version Phase CT Ground CT (required for D/O
INTRODUCTION ORDER CODE / INFORMATION 269/269Plus * * * * * * 269/269Plus SV D/O.4 ORDER CODE / INFORMATION Motor management relay Standard version Drawout version Phase CT Ground CT (required for D/O
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. AQ F3x0 Feeder protection IED
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL AQ F3x0 Feeder protection IED Instruction manual AQ F3x0 Feeder protection IED 2 (173) Revision 1.00 Date November 2010 Changes - The first revision. Revision 1.01 Date January 2011
INSTRUCTION MANUAL AQ F3x0 Feeder protection IED Instruction manual AQ F3x0 Feeder protection IED 2 (173) Revision 1.00 Date November 2010 Changes - The first revision. Revision 1.01 Date January 2011
TOSHIBA International Corp
 TOSHIBA International Corp GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS THREE PHASE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SYSTEM TOSHIBA 4200FA 30 kva CT Internal Battery UPS GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS 1 (30 kva CT) 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 System This specification
TOSHIBA International Corp GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS THREE PHASE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SYSTEM TOSHIBA 4200FA 30 kva CT Internal Battery UPS GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS 1 (30 kva CT) 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 System This specification
Types CDG 11 and CDG 16 Inverse Time Overcurrent and Earth Fault Relay
 Types CDG 11 and CDG 16 Inverse Time Overcurrent and Earth Fault Relay Types CDG 11 and CDG 16 Inverse Time Overcurrent and Earth Fault Relay Relay withdrawn from case Application The type CDG 11 relay
Types CDG 11 and CDG 16 Inverse Time Overcurrent and Earth Fault Relay Types CDG 11 and CDG 16 Inverse Time Overcurrent and Earth Fault Relay Relay withdrawn from case Application The type CDG 11 relay
BE1-32R, BE1-32 O/U DIRECTIONAL POWER RELAY
 BE1-32R, BE1-32 O/U DIRECTIONAL POWER RELAY The BE1-32R Directional Overpower Relay and the BE1-32 O/U Directional Over/Underpower Relay are solid-state devices which provide versatility and control in
BE1-32R, BE1-32 O/U DIRECTIONAL POWER RELAY The BE1-32R Directional Overpower Relay and the BE1-32 O/U Directional Over/Underpower Relay are solid-state devices which provide versatility and control in
ASHIDA Numerical OC/EF Protection Relay
 ASHIDA Numerical OC/EF Protection Relay Features: 4 Element (3 Phase + EF) over current IDMT with instant trip. Back - lit LCD display for settings. Display of fault current. / Load current. Selection
ASHIDA Numerical OC/EF Protection Relay Features: 4 Element (3 Phase + EF) over current IDMT with instant trip. Back - lit LCD display for settings. Display of fault current. / Load current. Selection
Distance Protection: Why Have We Started With a Circle, Does It Matter, and What Else Is Out There? What Is a Distance Protection Element?
 Distance Protection: Why Have We Started With a Circle, Does It Matter, and What Else Is Out There? Edmund O. Schweitzer, III and Bogdan Kasztenny Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Copyright SEL 2017
Distance Protection: Why Have We Started With a Circle, Does It Matter, and What Else Is Out There? Edmund O. Schweitzer, III and Bogdan Kasztenny Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Copyright SEL 2017
Overcurrent Protection / 7SJ45
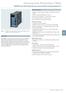 Overcurrent Protection / SJ SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by CTs Fig. / Description SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by current transformers
Overcurrent Protection / SJ SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by CTs Fig. / Description SIPROTEC easy SJ numerical overcurrent protection relay powered by current transformers
DIAC Type 66K. DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAY Instruction Manual. GE Power Management
 g GE Power Management DIAC Type K DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAY Instruction Manual DIAC K Revision: SPDV0.A0 Manual P/N: GEK-0C Copyright 000 GE Power Management GE Power Management Anderson Avenue, Markham,
g GE Power Management DIAC Type K DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAY Instruction Manual DIAC K Revision: SPDV0.A0 Manual P/N: GEK-0C Copyright 000 GE Power Management GE Power Management Anderson Avenue, Markham,
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
 ELECTRONIC PTE RANGE Protective relay test sets with direct on-board control and computer-based test automation THE ELECTRONIC PTE TEST EQUIPMENT RANGE The electronic PTE test equipment range has been
ELECTRONIC PTE RANGE Protective relay test sets with direct on-board control and computer-based test automation THE ELECTRONIC PTE TEST EQUIPMENT RANGE The electronic PTE test equipment range has been
Distribution/Substation Transformer
 Distribution/Substation Transformer Type VFI, Vacuum Fault Interrupter Transformer Option Functional Specification Guide Functional specification for 15 kv, 25 kv, or 35 kv vacuum fault interrupter distribution/substation
Distribution/Substation Transformer Type VFI, Vacuum Fault Interrupter Transformer Option Functional Specification Guide Functional specification for 15 kv, 25 kv, or 35 kv vacuum fault interrupter distribution/substation
PRODUCT/TEST MANUAL 2V162K12 VOLTAGE REGULATOR RELAY
 Sheet 1 of 15 TEST DATE: CUSTOMER: SERIAL NO: OLTC ACKNOWLEDGE SETUP AUTOMATIC or FEEDBACK CONTROL PRODUCT/TEST MANUAL 2V162K12 VOLTAGE REGULATOR RELAY Issue Date Level A 06/01/1997 Initial issue. Summary
Sheet 1 of 15 TEST DATE: CUSTOMER: SERIAL NO: OLTC ACKNOWLEDGE SETUP AUTOMATIC or FEEDBACK CONTROL PRODUCT/TEST MANUAL 2V162K12 VOLTAGE REGULATOR RELAY Issue Date Level A 06/01/1997 Initial issue. Summary
Communication Aided Tripping. Common Methods, Schemes and Considerations
 Communication Aided Tripping Common Methods, Schemes and Considerations Presented by: Matt Horvath, P.E. March 13, 2017 Content Summary Background Purpose Methods and Mediums Schemes Considerations Application:
Communication Aided Tripping Common Methods, Schemes and Considerations Presented by: Matt Horvath, P.E. March 13, 2017 Content Summary Background Purpose Methods and Mediums Schemes Considerations Application:
Generator Protection GENERATOR CONTROL AND PROTECTION
 Generator Protection Generator Protection Introduction Device Numbers Symmetrical Components Fault Current Behavior Generator Grounding Stator Phase Fault (87G) Field Ground Fault (64F) Stator Ground Fault
Generator Protection Generator Protection Introduction Device Numbers Symmetrical Components Fault Current Behavior Generator Grounding Stator Phase Fault (87G) Field Ground Fault (64F) Stator Ground Fault
POWER DELEGATOR SERIES 7200A POWER DISTRIBUTION UNIT WITH POWER CONDITIONING GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
 POWER DELEGATOR SERIES 7200A POWER DISTRIBUTION UNIT WITH POWER CONDITIONING GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.0 SCOPE The following specification describes the features, design, and application of the Series 7200A
POWER DELEGATOR SERIES 7200A POWER DISTRIBUTION UNIT WITH POWER CONDITIONING GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 1.0 SCOPE The following specification describes the features, design, and application of the Series 7200A
DIFFERENTIAL CURRENT GENERATOR «POCDIF» (AC/DC - 32A - 50V - 12 ranges)
 PERFORMANCES 12 ranges of AC current from 16 ma to 128 A peak AC permanent current up to 26 ARMS Nine ranges of DC permanent current from 16 ma to 12 A DC current ± 6mA or ± 10 ma stackable to AC current
PERFORMANCES 12 ranges of AC current from 16 ma to 128 A peak AC permanent current up to 26 ARMS Nine ranges of DC permanent current from 16 ma to 12 A DC current ± 6mA or ± 10 ma stackable to AC current
Arbiter Systems, Inc Vendels Circle, Suite 121 Paso Robles, CA USA
 Model 931A Power System Analyzer Model 930A Three Phase Power Analyzer Model 929A Three Phase Power Meter with Digital Signal Analysis Model 931A shown with included accessories Arbiter Systems, Inc. Models
Model 931A Power System Analyzer Model 930A Three Phase Power Analyzer Model 929A Three Phase Power Meter with Digital Signal Analysis Model 931A shown with included accessories Arbiter Systems, Inc. Models
MVCT. Megger VT & CT Analyzer. MVCT Megger VT & CT Analyzer
 MVCT Ability to test both VT and CT Easy to use one-button automated test plans Industry leading test duration using patented simultaneous tap measurements Smallest and lightest unit on the market CT Kneepoints
MVCT Ability to test both VT and CT Easy to use one-button automated test plans Industry leading test duration using patented simultaneous tap measurements Smallest and lightest unit on the market CT Kneepoints
Data. Dr Murari Mohan Saha ABB AB. KTH/EH2740 Lecture 3. Data Acquisition Block. Logic. Measurement. S/H and A/D Converter. signal conditioner
 Digital Protective Relay Dr Murari Mohan Saha ABB AB KTH/EH2740 Lecture 3 Introduction to Modern Power System Protection A digital protective relay is an industrial microprocessor system operating in real
Digital Protective Relay Dr Murari Mohan Saha ABB AB KTH/EH2740 Lecture 3 Introduction to Modern Power System Protection A digital protective relay is an industrial microprocessor system operating in real
Modular range of digital protection relays
 S e p a m s e r i e s 2 0, 4 0, 8 0 Modular range of digital protection relays Fast Dependable Simple Fast response Maximum dependability Your electrical equipment is under control. With Sepam protection
S e p a m s e r i e s 2 0, 4 0, 8 0 Modular range of digital protection relays Fast Dependable Simple Fast response Maximum dependability Your electrical equipment is under control. With Sepam protection
Advanced Test Equipment Rentals ATEC (2832) CP RC. Resonance circuit for GIS testing
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) CP RC Resonance circuit for GIS testing A new approach to testing gas-insulated switchgear Testing gas-insulated switchgear
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) CP RC Resonance circuit for GIS testing A new approach to testing gas-insulated switchgear Testing gas-insulated switchgear
Transformer differential protection
 Transformer differential protection Page 1 Issued June 1999 Changed since July 1998 Data subject to change without notice (SE970883) Features Three phase differential protection with two, three, five or
Transformer differential protection Page 1 Issued June 1999 Changed since July 1998 Data subject to change without notice (SE970883) Features Three phase differential protection with two, three, five or
ALP-UDR Universal Detection Relay user-defined protection, automation, and monitoring
 ALP-UDR Universal Detection Relay user-defined protection, automation, and monitoring The first Real-Time Protection and Automation platform that can be adapted to a wide variety of applications. While
ALP-UDR Universal Detection Relay user-defined protection, automation, and monitoring The first Real-Time Protection and Automation platform that can be adapted to a wide variety of applications. While
SEL-251 Distribution Relay
 SEL-251 Distribution Relay Phase Overcurrent Relay with Voltage Control Negative-Sequence Overcurrent Relay * Ground Overcurrent Relay Multiple Shot Reclosing Relay Selectable Setting Groups Circuit Breaker
SEL-251 Distribution Relay Phase Overcurrent Relay with Voltage Control Negative-Sequence Overcurrent Relay * Ground Overcurrent Relay Multiple Shot Reclosing Relay Selectable Setting Groups Circuit Breaker
SVERKER 900 Relay and Substation Test System
 SVERKER 900 The toolbox for substation 3-phase testing Three currents and four voltages Stand-alone functionality Rugged and reliable for field use Generation of 900 V and 105 A in single phase mode Secondary
SVERKER 900 The toolbox for substation 3-phase testing Three currents and four voltages Stand-alone functionality Rugged and reliable for field use Generation of 900 V and 105 A in single phase mode Secondary
Transformer and generator time-overexcitation relay and protection assemblies RXLK 2H and RALK
 Transformer and generator time-overexcitation relay and protection assemblies RXLK 2H and RALK (RXLK_2H.tif) RALK.psd Features Micro-processor based time-overexcitation relay with continuous settings for
Transformer and generator time-overexcitation relay and protection assemblies RXLK 2H and RALK (RXLK_2H.tif) RALK.psd Features Micro-processor based time-overexcitation relay with continuous settings for
T 1000 PLUS. Secondary Injection Relay Test Set. Designed for testing relays and transducers
 Secondary Injection Relay Test Set Designed for testing relays and transducers Microprocessor controlled With phase angle shifter Frequency generator Test results and settings are saved into local memory
Secondary Injection Relay Test Set Designed for testing relays and transducers Microprocessor controlled With phase angle shifter Frequency generator Test results and settings are saved into local memory
presentation contents application advantages
 presentation contents page presentation protection functional and connection schemes other connection schemes connection characteristics 9 installation 0 commissioning ordering information Sepam 00 is
presentation contents page presentation protection functional and connection schemes other connection schemes connection characteristics 9 installation 0 commissioning ordering information Sepam 00 is
