HIGH FREQUENCY CHAOS IN DIODE RESONATOR AND ITS CONTROLS
|
|
|
- Angelina Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIGH FREQUENCY CHAOS IN DIODE RESONATOR AND ITS CONTROLS Md. Moinul Islam 1, Deepak Pandit 2, A De 3 and Srijit Bhattacharya 1,* Department of Physics, Barasat Government College,Kolkata , WB, India. 1 Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, 1/AF Bidhannagar, Kolkata , WB, India 2 Department of Physics, Raniganj Girls College, Raniganj, Burdwan , W. B., India. 3 srijit.bha@gmail.com 1,* Abstract: The chaotic dynamics of different diodes (1N4007, 1N4148, green light emitting diode and zener diode) in R-L- D circuit (R=1k Ohm, L=100mH) is studied at higher frequencies (1.6kHz-20kHz) and constant input voltage (3Vp-p). A novel but simple technique is shown to measure diode reverse recovery time based on its chaotic dynamics. The experimental outputs of R-L-D circuit are found in agreement with the PSPICE model simulation, except in 1N4148. The chaos involved is confirmed by the bifurcation plot and Lyapunov exponents. This technique could facilitate the fabrication of fast and ultrafast diodes. Finally, two simple but elegant experimental methods are demonstrated to control chaos in R-L-D circuit. Keywords: Chaos, R-L-D, reverse recovery time, frequency, PSPICE, control of chaos, Lyapunov exponent I INTRODUCTION Non-linearity and chaos are ubiquitous in science and technology. Applied sciences e.g secure communication, cryptography, applied biology like brain dynamics, cardiac rhythm etc [1, 2] have been aided tremendously by nonlinear science. Ardent research works have been focused on nonlinear resonating oscillator circuits comprising of p-n junction diode (D), resistor (R) and inductor (L) to understand the general behaviour of chaos [3, 4, 5]. Chaos is highly important in both low and high frequency (f) domains [6,7]. Hence the chaotic behaviour of R-L-D circuits, depending on the memory effect due to the reverse recovery time ( RR ) of p-n junction diode, is required to be wellunderstood for better performance of electronic circuits at different input frequency regions. In the past, generally, the chaotic behaviour of the varactor diode has been studied by varying the amplitude of the input sinusoidal signal [3, 4, 8]. However, RR is not a function of input voltage alone. De Moraes and Anlage [3] suggested that, RR (for diodes 1N4007, 1N5400, 1N5475 and NTE610), should be a function of input driving frequency, DC offset, duty cycle and circuit resistance. This paper, for the first time, investigates the f- dependency of RR of diodes. Here, to confirm the chaotic nature, the experimental bifurcation diagram has been plotted. Besides, Lyapunov exponent ( ) has also been estimated in this work. In the present work, a novel technique is introduced to measure RR of a diode utilizing the chaotic properties of R-L-D circuit. In this method the parameters of diodes 1N4007 and 1N4148, 6.8V breakdown zener diode BZX85C6V8, and green light emitting diode i.e LED are investigated varying the driving frequencies. Two simple methods are also initiated to control the chaos involved in R- L-D circuit. Although chaos control in R-L-D is essential for superior performance, practical chaos control is very rarely studied in such circuit. II MATERIALS AND METHODS The experimental circuit, shown in Fig. 1, consists of a resistor R=1k, inductor L= 100mH and a p-n junction diode driven by a sinusoidal waveform. The sinusoidal voltage is obtained from a 100Hz-1MHz function generator with 50 transmission line output. The output voltage across L (V L ) is checked using the online oscilloscope facility of ExpEyes kit developed by IUAC, India. The kit is computer interfaced and powered by USB port of the computer ( A four channel oscilloscope is enabled in 1
2 the interface with maximum sampling rate of 250kHz. The response of the circuit is also simulated by Orcad PSPICE simulator student version ( arrow, is approximately 16 µs and the number of bifurcation peak is 1 within it. Figure 1 The R-L-D circuit diagram. III EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS 3.1- Frequency driven chaos A R-L-D circuit behaving as series R-L-C circuit resonates at a frequency of f 0 =26.5 khz. The frequencydriven dynamics is studied near this resonating frequency. V L shows only one peak with no bifurcation above f=15.0 khz. Thereafter period-2 bifurcation can be seen. At input frequencies 8.0 khz onwards, the output moves into period-4. Higher bifurcations arise on lowering the frequency further. The detail is given in Table 1. In Fig.2, the panels A, F and E are the experimental oscilloscope outputs at f=15, 8.0 and 3.8 khz, while panels B, C and D are corresponding PSPICE simulated outputs. The experimental output is found to be in complete agreement with PSPICE simulation. To confirm the chaotic dynamics involved, we estimated the experimental bifurcation diagram and Lyapunov exponent. The experimental bifurcation diagram, keeping the driving frequency as a parameter, is shown in Fig.3. The period multiplication can be seen clearly at f=15, 8 and 3.8 khz Technique for measuring RR A unique technique for measuring RR of the diode is adopted in this work. Reversing a forward biased diode very abruptly, takes finite amount of time RR to release the stored charge. Therefore, due to those unrecovered charges from the negative half up to the next positive half cycle of the output voltage (V L ) the state fluctuates (positive to negative) so many times depending on the driving frequency and RR. Dividing the time duration within which the diode repeatedly changes state by the number of bifurcations (shown as peaks) appearing in the said duration, RR is estimated. In the panels A and B of Fig.2, the process of measuring RR is depicted very clearly. In the panel A, the time interval, shown by an Figure 2 Panels A, F and E: Oscilloscope output V L at f=15, 8 and 3.8kHz, respectively, for diode 1N4007. Panels B, C and D: Corresponding PSPICE simulations. The panels A, F and E indicate the time interval for measuring RR using an arrow. So, RR is 16µs/1 peak=16 µs. Similar value of RR is also obtained from the PSPICE simulation in panel B. In the panel F for period 4 bifurcation, the time interval 56µs is divided by the number of peaks. Therefore, RR =56µs/3 peaks=19µs (approx) and similar value is also obtained from PSPICE simulation (panel C). For period-8 bifurcation, shown in panel E we get, RR = 132 µs/7 peaks=19 µs (approx). Using PSPICE simulation the calculation of RR is extended up to f= 200 khz. The simulated data of RR is fitted against driving frequencies and found to be dependent on f (-0.29±0.14) (fitted line is shown as dashed line in the fig. 4). The correlation coefficient (r 2 ) of the fit is found to be 0.91.The experimental data is also plotted in the same figure. Frequency-driven chaotic dynamics of zener diode BZX85C6V8 and 1N4148, and green light emitting diode (LED) is also investigated in the same way and the values of RR are given in table 1. To understand the degree of chaos, the Lyapunov exponent ( ) is also calculated from time series data and mentioned in table
3 Figure 3 : The bifurcation diagram for diode 1N Control of Chaos Often chaos is undesirable in many practical cases. So the idea of control of chaos is highly important. In the R- L-D circuit mentioned in this paper, we have controlled chaos using two different methods. In the first method, as shown in [9], a dc voltage source (V 2 ) is connected additionally with the R-L-D circuit. The dc input voltage is taken as 1.53V for 1N4007 and the peak to peak value of the sinusoidal input voltage (V 1 ) is taken as 3V. The circuit diagram is given in the top panel of Fig.5. The output voltage (Fig.5 bottom panels) shows suppression of chaos for V 2 =1.53V. Chaos suppression is not possible below that voltage. In the second method, a sinusoidal voltage source (V 2 ) is connected in addition to the one (V 1 ) that is already applied in the R-L-D circuit. Fig.6 top panel shows the corresponding circuit and bottom panels A and B give the simulated and experimental outputs, respectively. The output voltage V L is now chaos free, although this time it looks like a half-wave rectifier output. IV DISCUSSIONS In this paper, using the frequency driven chaotic dynamics of R-L-D circuit, different diodes have been tested and the dependence of their reverse recovery time on input driving frequency of sinusoidal waves have been measured, both experimentally and theoretically. It could be reaffirmed that, very rarely, such an investigation was done the past. In our work a new technique has been introduced to measure the reverse recovery time of a diode using the chaotic framework. Using the RR, the values of junction capacitance C J0 is also determined following the equations given in [10] and corroborated with the measurement done by a HIOKI LCR meter IM The input ac voltage is taken as only 15mV, dc voltage remaining zero. The zero bias capacitance (C J0 ) is found to be 19pF for the diode 1N4007. Besides diffusion capacitance (C d ) is also calculated as per [10] and given in table 1. Figure 4: Input frequency variation of RR in diode 1N4007. Solid line is PSPICE data, dashed line is functional fit and filled circles are from experiment. Figure 5: top panel: The circuit diagram for chaos control under method 1 as described in manuscript. Bottom panels: The demise of chaos for V 2 =1.53 V. The chaos free output V L is shown in bottom panels C and D (experimental and simulated outputs, respectively). The PSPICE simulation of f-driven chaos in diode 1N4148 disagreed with the experimental data. This could be due to the high speed switching ability of the diode. The positive values of indicates chaotic dynamics involved in the circuit. The knowledge on the non-linearity introduced by RR is essential to use diodes in high density electronic circuits. Off late, avid research work is going on to prepare fast and ultrafast diodes using different kinds of material like 3
4 p-p-i-n-n + GaAs. In this context any simple method to measure RR will be an added advantage [11]. IV CONCLUSIONS R-L-D circuits are essential to understand chaos. In this work, the driving frequency dependent chaos in R-L-D circuit has been investigated and the bifurcation diagram along with Lyapunov exponent ( ) has been presented at different frequencies to confirm chaotic nature. A new technique has been described here to find the reverse recovery time RR of different diodes by both experiment and PSPICE simulations. Using this technique, RR of a diode can be measured very easily and accurately without constructing any complicated circuits. This would benefit the fabrication of fast and ultrafast diode immensely. The frequency driven dynamics of diode has rarely been studied in the past. Besides, the ways to suppress strong chaotic motion in R-L-D circuit have also been accounted for in this work. Figure 6: top panel is the circuit diagram for chaos control as per method 2 described in manuscript. Bottom panels A and B are PSPICE and experimental outputs, respectively. Table 1: Chaotic Dynamics and Different Parameters of Diods Diode Freq(f) khz Period REFERENCES [1] Kocarev L.J., Halle, K.S., Eckert K., Parlitz, U. and Chua L.O., Experimental demonstration of secure communications via chaotic synchronization. International Journal of Bifurcations and Chaos, vol.2, pp [2] Garfinkel A., Spano M.L., Ditto W.L. and Weiss J.N., Controlling cardiac chaos, Science, vol. 257, pp [3] de Moraes R. M. and Anlage S. N., Unified model and reverse recovery nonlinearities of the driven diode resonator, Physical Review E. vol.68, pp , [4] Hanias M. P., Giannaris G., Spyridakis A. and Rigasvan A., Time series analysis in chaotic diode resonator. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. vol.27(2),pp , [5]Caroll T. and Pecora L.M., Parameter ranges for the onset of period doubling in the diode resonator, Physical Review E.vol.66, pp , [6]Bose B.K., Modern power electronics and ac drives, Prentice Hall PTR [7] Demergis V., Glasser A., Miller M., Antonsen Jr. T.M., Ott E. and Anlage S.M., Delayed feedback and chaos on the driven diode-terminated transmission line, Arxiv:nlin/ , [8]Hanias M.P., Avgerinos, Z. and Tombras G.S., Period doubling, Feigenbaum constant and time series prediction in an experimental chaotic RLD circuit, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, vol. 40, pp , [9] Rajasekar S., Murali, K. and Lakshmanan M., Control of Chaos by Nonfeedback Methods in a Simple Electronic Cd pf RR µs 1N BZX C6V N Green LED
5 Circuit System and the FitzHugh-Nagumo Equation, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, vol. 8(9), pp. 1545, [10] Millman J. and Halkias C.C., Integrated Electronics: Analog and Digital Circuits, McGraw-Hill, New York [11]Koel A., Rang T., Voitovich V. and Toompuu J., Numerical simulations for reverse recovery process investigations of LPE GaAs power diodes, 13th Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference (BEC2012) Tallinn, Estonia, October 3-5,
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems
 EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
Rich Variety of Bifurcation and Chaos in a Simple Non-Source Free Electronic Circuit with a Diode
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 6, Number 1 (2010), pp. 63 69 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Rich Variety of Bifurcation and
International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 6, Number 1 (2010), pp. 63 69 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Rich Variety of Bifurcation and
Experiment Topic : FM Modulator
 7-1 Experiment Topic : FM Modulator 7.1: Curriculum Objectives 1. To understand the characteristics of varactor diodes. 2. To understand the operation theory of voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). 3.
7-1 Experiment Topic : FM Modulator 7.1: Curriculum Objectives 1. To understand the characteristics of varactor diodes. 2. To understand the operation theory of voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). 3.
Multiple Time Scale Chaos in a Schmitt Trigger Circuit
 Multiple Time Scale Chaos in a Schmitt Trigger Circuit Thomas L Carroll Code 636, US Naval Research Lab Abstract-- It is known that stray rf signals can produce nonlinear effects that disrupt the operation
Multiple Time Scale Chaos in a Schmitt Trigger Circuit Thomas L Carroll Code 636, US Naval Research Lab Abstract-- It is known that stray rf signals can produce nonlinear effects that disrupt the operation
Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit
 Typeset using jjap.cls Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit J.-M. Friedt 1, D. Gillet 2, M. Planat 2 1 : IMEC, MCP/BIO, Kapeldreef 75, 3001 Leuven, Belgium
Typeset using jjap.cls Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit J.-M. Friedt 1, D. Gillet 2, M. Planat 2 1 : IMEC, MCP/BIO, Kapeldreef 75, 3001 Leuven, Belgium
ETEK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
 Trainer Model: ETEK DCS-6000-07 FSK Modulator ETEK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. E-mail: etek21@ms59.hinet.net mlher@etek21.com.tw http: // www.etek21.com.tw Digital Communication Systems (ETEK DCS-6000) 13-1:
Trainer Model: ETEK DCS-6000-07 FSK Modulator ETEK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. E-mail: etek21@ms59.hinet.net mlher@etek21.com.tw http: // www.etek21.com.tw Digital Communication Systems (ETEK DCS-6000) 13-1:
1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier. (2 points)
 Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
Exam 1 Name: Score /60 Question 1 Short Takes 1 point each unless noted otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as. Estimate the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier.
B.Sc. Syllabus for Electronics under CBCS. Semester-I
 Semester-I Title: Electronic Circuit Analysis Course Code: UELTC101 Credits: 4 Total Marks: 100 Internal Examination: 20 marks End Semester Examination: 80 marks Duration: 3 hours Validity of Syllabus:
Semester-I Title: Electronic Circuit Analysis Course Code: UELTC101 Credits: 4 Total Marks: 100 Internal Examination: 20 marks End Semester Examination: 80 marks Duration: 3 hours Validity of Syllabus:
Studies of Upset and Nonlinear Effects in Circuits and Systems
 IREAP Studies of Upset and Nonlinear Effects in Circuits and Systems John Rodgers, Todd Firestone, Victor Granatstein, Thomas Antonsen, Ed Ott, Steve Anlage*, Renato Mariz de Moraes*, Vassili Demergis*,
IREAP Studies of Upset and Nonlinear Effects in Circuits and Systems John Rodgers, Todd Firestone, Victor Granatstein, Thomas Antonsen, Ed Ott, Steve Anlage*, Renato Mariz de Moraes*, Vassili Demergis*,
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall Diodes and Diode Applications
 EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall 2007 Diodes and Diode Applications Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to develop familiarity with diodes and diode applications. The relationship between the actual
EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall 2007 Diodes and Diode Applications Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to develop familiarity with diodes and diode applications. The relationship between the actual
Communicating using filtered synchronized chaotic signals. T. L. Carroll
 Communicating using filtered synchronized chaotic signals. T. L. Carroll Abstract- The principles of synchronization of chaotic systems are extended to the case where the drive signal is filtered. A feedback
Communicating using filtered synchronized chaotic signals. T. L. Carroll Abstract- The principles of synchronization of chaotic systems are extended to the case where the drive signal is filtered. A feedback
ITT Technical Institute. ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections
 ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections 2.8-2.10 Chapter 2 Section 2.8 Special-Purpose Diodes The preceding discussions of diodes has focused on applications that exploit the fact that
ITT Technical Institute ET215 Devices I Chapter 2 Sections 2.8-2.10 Chapter 2 Section 2.8 Special-Purpose Diodes The preceding discussions of diodes has focused on applications that exploit the fact that
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
COURSE SCHEDULE SECTION. A (Room No: TP 301) B (Room No: TP 302) Hours Timings Hours Timings. Name of the staff Sec Office Office Hours Mail ID
 SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : IT0201 Course Title : Electron Devices and Circuits
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : IT0201 Course Title : Electron Devices and Circuits
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 7 (1999) 1393 1424 c World Scientific Publishing Company EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 7 (1999) 1393 1424 c World Scientific Publishing Company EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Core Technology Group Application Note 1 AN-1
 Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback
 Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback S. Tang, L. Illing, J. M. Liu, H. D. I. barbanel and M. B. Kennel Department of Electrical Engineering,
Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback S. Tang, L. Illing, J. M. Liu, H. D. I. barbanel and M. B. Kennel Department of Electrical Engineering,
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab3 LABORATORY 3. Diode. Guide
 LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification
 Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
Demonstration of Chaos
 revised 4/27/01 Demonstration of Chaos Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract A simple resonant inductor-resistor-diode series circuit can be used to
revised 4/27/01 Demonstration of Chaos Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract A simple resonant inductor-resistor-diode series circuit can be used to
Design & Simulation of Rectifier through Multisim
 Design & Simulation of Rectifier through Multisim Udit Mamodiya, Deepak Purohit, Goverdhan Singh Poornima College of Engineering,jaipur Abstract- The manuscript contained simulation of common physics experiment,
Design & Simulation of Rectifier through Multisim Udit Mamodiya, Deepak Purohit, Goverdhan Singh Poornima College of Engineering,jaipur Abstract- The manuscript contained simulation of common physics experiment,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (EDC) LABORATORY MANUAL
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (EDC) LABORATORY MANUAL (B.E. THIRD SEMESTER - BEENE302P / BEECE302P/ BEETE302P) Prepared by Prof. S. Irfan Ali HOD PROF. M. NASIRUDDIN DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (EDC) LABORATORY MANUAL (B.E. THIRD SEMESTER - BEENE302P / BEECE302P/ BEETE302P) Prepared by Prof. S. Irfan Ali HOD PROF. M. NASIRUDDIN DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
A 7ns, 6mA, Single-Supply Comparator Fabricated on Linear s 6GHz Complementary Bipolar Process
 A 7ns, 6mA, Single-Supply Comparator Fabricated on Linear s 6GHz Complementary Bipolar Process Introduction The is an ultrafast (7ns), low power (6mA), single-supply comparator designed to operate on either
A 7ns, 6mA, Single-Supply Comparator Fabricated on Linear s 6GHz Complementary Bipolar Process Introduction The is an ultrafast (7ns), low power (6mA), single-supply comparator designed to operate on either
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS
 TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS Aim: Testing of diode clipping circuits. Apparatus required: Diode (1N4007/BY127), Resistor, DC regulated power supply, signal generator and CRO. Theory: The circuit
TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS Aim: Testing of diode clipping circuits. Apparatus required: Diode (1N4007/BY127), Resistor, DC regulated power supply, signal generator and CRO. Theory: The circuit
Assume availability of the following components to DESIGN and DRAW the circuits of the op. amp. applications listed below:
 ========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro,
 Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes Edward H. Hellen a) and Matthew J. Lanctot b) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Greensboro,
Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes Edward H. Hellen a) and Matthew J. Lanctot b) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Greensboro,
Design of Dynamic Frequency Divider using Negative Differential Resistance Circuit
 Design of Dynamic Frequency Divider using Negative Differential Resistance Circuit Kwang-Jow Gan 1*, Kuan-Yu Chun 2, Wen-Kuan Yeh 3, Yaw-Hwang Chen 2, and Wein-So Wang 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Design of Dynamic Frequency Divider using Negative Differential Resistance Circuit Kwang-Jow Gan 1*, Kuan-Yu Chun 2, Wen-Kuan Yeh 3, Yaw-Hwang Chen 2, and Wein-So Wang 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Complex Dynamic Phenomena in Power Converters: Bifurcation Analysis and Chaotic Behavior
 Complex Dynamic Phenomena in Power Converters: Bifurcation Analysis and Chaotic Behavior DONATO CAFAGNA, GIUSEPPE GRASSI Dipartimento Ingegneria Innovazione Università di Lecce via Monteroni, 700 Lecce
Complex Dynamic Phenomena in Power Converters: Bifurcation Analysis and Chaotic Behavior DONATO CAFAGNA, GIUSEPPE GRASSI Dipartimento Ingegneria Innovazione Università di Lecce via Monteroni, 700 Lecce
Analog Electronic Circuits
 Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, JANUARY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, OL. 21, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 73 Maximum Power Tracking of Piezoelectric Transformer H Converters Under Load ariations Shmuel (Sam) Ben-Yaakov, Member, IEEE, and Simon
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, OL. 21, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 73 Maximum Power Tracking of Piezoelectric Transformer H Converters Under Load ariations Shmuel (Sam) Ben-Yaakov, Member, IEEE, and Simon
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi
 JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi FETs are popular among experimenters, but they are not as universally understood as the
JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi FETs are popular among experimenters, but they are not as universally understood as the
Scheme & Syllabus. B.Sc. Electronics. Honours Course. I st & II nd Semester. w.e.f. July Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore (M.P.
 Scheme & Syllabus of B.Sc. Electronics Honours Course I st & II nd Semester w.e.f. July 2011 Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore (M.P.), 452001 SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2011-2014 PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc. ELECTRONICS
Scheme & Syllabus of B.Sc. Electronics Honours Course I st & II nd Semester w.e.f. July 2011 Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore (M.P.), 452001 SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2011-2014 PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc. ELECTRONICS
Reduction of Voltage Stresses in Buck-Boost-Type Power Factor Correctors Operating in Boundary Conduction Mode
 Reduction of oltage Stresses in Buck-Boost-Type Power Factor Correctors Operating in Boundary Conduction Mode ars Petersen Institute of Electric Power Engineering Technical University of Denmark Building
Reduction of oltage Stresses in Buck-Boost-Type Power Factor Correctors Operating in Boundary Conduction Mode ars Petersen Institute of Electric Power Engineering Technical University of Denmark Building
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
EE EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION
 EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose voltage and current are related by a differential equation. For a capacitor, the
EE 2101 - EXPERIMENT 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP INTRODUCTION A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose voltage and current are related by a differential equation. For a capacitor, the
Sheet 2 Diodes. ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering. Problem (1) Draw the
 Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 43-49 DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control Preeta John 1 Electronics Department,
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 43-49 DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control Preeta John 1 Electronics Department,
Design and study of frequency response of band pass and band reject filters using operational amplifiers
 International Journal of Advanced Educational Research ISSN: 2455-6157 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.12 www.educationjournal.org Volume 2; Issue 6; November 2017; Page No. 22-26 Design and study of frequency response
International Journal of Advanced Educational Research ISSN: 2455-6157 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.12 www.educationjournal.org Volume 2; Issue 6; November 2017; Page No. 22-26 Design and study of frequency response
After performing this experiment, you should be able to:
 Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
Glossary of VCO terms
 Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
Detailed measurements of Ide transformer devices
 Detailed measurements of Ide transformer devices Horst Eckardt 1, Bernhard Foltz 2, Karlheinz Mayer 3 A.I.A.S. and UPITEC (www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com, www.upitec.org) July 16, 2017 Abstract The
Detailed measurements of Ide transformer devices Horst Eckardt 1, Bernhard Foltz 2, Karlheinz Mayer 3 A.I.A.S. and UPITEC (www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com, www.upitec.org) July 16, 2017 Abstract The
Homework Assignment True or false. For both the inverting and noninverting op-amp configurations, V OS results in
 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each. Homework Assignment 02 1. An op-amp has input bias current I B = 1 μa. Make an estimate for the input offset current I OS. Answer. I OS is normally an order of
Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each. Homework Assignment 02 1. An op-amp has input bias current I B = 1 μa. Make an estimate for the input offset current I OS. Answer. I OS is normally an order of
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011
 VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
Simulation Comparison of Resonant Reset Forward Converter with Auxiliary Winding Reset Forward Converter
 Simulation Comparison of Resonant Reset Forward Converter with Auxiliary Winding Reset Forward Converter Santosh B L 1, Dr.P.Selvan M.E. 2 1 M.E.(PED),ESCE Perundurai, (India) 2 Ph.D,Dept. of EEE, ESCE,
Simulation Comparison of Resonant Reset Forward Converter with Auxiliary Winding Reset Forward Converter Santosh B L 1, Dr.P.Selvan M.E. 2 1 M.E.(PED),ESCE Perundurai, (India) 2 Ph.D,Dept. of EEE, ESCE,
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
ENGR4300 Test 3A Fall 2002
 1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
Experiment 5: CMOS FET Chopper Stabilized Amplifier 9/27/06
 Experiment 5: CMOS FET Chopper Stabilized Amplifier 9/27/06 This experiment is designed to introduce you to () the characteristics of complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) field effect transistors
Experiment 5: CMOS FET Chopper Stabilized Amplifier 9/27/06 This experiment is designed to introduce you to () the characteristics of complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) field effect transistors
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
Radio Frequency Electronics
 Radio Frequency Electronics Active Components I Harry Nyquist Born in 1889 in Sweden Received B.S. and M.S. from U. North Dakota Received Ph.D. from Yale Worked and Bell Laboratories for all of his career
Radio Frequency Electronics Active Components I Harry Nyquist Born in 1889 in Sweden Received B.S. and M.S. from U. North Dakota Received Ph.D. from Yale Worked and Bell Laboratories for all of his career
Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption
 Course: PHY42 Instructor: Dr. Ken Kiers Date: 0/2/202 Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption Talbot Knighton Abstract This paper looks at a method for using chaotic circuits to encrypt analog signals. Two
Course: PHY42 Instructor: Dr. Ken Kiers Date: 0/2/202 Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption Talbot Knighton Abstract This paper looks at a method for using chaotic circuits to encrypt analog signals. Two
POWERED electronic equipment with high-frequency inverters
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 115 A Novel Single-Stage Power-Factor-Correction Circuit With High-Frequency Resonant Energy Tank for DC-Link
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 115 A Novel Single-Stage Power-Factor-Correction Circuit With High-Frequency Resonant Energy Tank for DC-Link
LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS
 LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the
LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the
Lab 6: Building a Function Generator
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM 6. INTRODUCTION The DC-DC Cuk converter is used as an interface between the PV array and the load,
CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM 6. INTRODUCTION The DC-DC Cuk converter is used as an interface between the PV array and the load,
CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO).
 1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
1. 1 To study CRO. CRO AIM:- To study the use of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO). Apparatus: - C.R.O, Connecting probe (BNC cable). Theory:An CRO is easily the most useful instrument available for testing
Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction
 Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction Sindhu.K.S 1, B. Devi Vighneshwari 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, The Oxford College of Engineering, Bangalore-560068,
Current Rebuilding Concept Applied to Boost CCM for PF Correction Sindhu.K.S 1, B. Devi Vighneshwari 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, The Oxford College of Engineering, Bangalore-560068,
Osmania University B.Sc Electronics - Syllabus (under CBCS w.e.f ) I ST and II nd Year
 Osmania University B.Sc Electronics - Syllabus (under CBCS w.e.f 2016-2017) I ST and II nd Year UNIT - I B.Sc. ELECTRONICS SYLLABUS B.Sc. I YEAR Semester - I DSC- Paper I : Circuit Analysis Total number
Osmania University B.Sc Electronics - Syllabus (under CBCS w.e.f 2016-2017) I ST and II nd Year UNIT - I B.Sc. ELECTRONICS SYLLABUS B.Sc. I YEAR Semester - I DSC- Paper I : Circuit Analysis Total number
Synchronization Limits of Chaotic Circuits
 Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science Volume 68 Article 9 2014 C. M. Church University of Central Arkansas, churchcm13@gmail.com Stephen R. Addison University of Central Arkansas Follow this and additional
Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science Volume 68 Article 9 2014 C. M. Church University of Central Arkansas, churchcm13@gmail.com Stephen R. Addison University of Central Arkansas Follow this and additional
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Coil in the AC circuit
 Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:041 Electronic Circuits Chapter 1 & 2 A. Kruger Diode Review, Page-1 Semiconductors licon () atoms have 4 electrons in valence band and form strong covalent bonds with surrounding atoms. Section 1.1.2
55:041 Electronic Circuits Chapter 1 & 2 A. Kruger Diode Review, Page-1 Semiconductors licon () atoms have 4 electrons in valence band and form strong covalent bonds with surrounding atoms. Section 1.1.2
EE 230 Lab Lab 9. Prior to Lab
 MOS transistor characteristics This week we look at some MOS transistor characteristics and circuits. Most of the measurements will be done with our usual lab equipment, but we will also use the parameter
MOS transistor characteristics This week we look at some MOS transistor characteristics and circuits. Most of the measurements will be done with our usual lab equipment, but we will also use the parameter
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS. B.Sc. Part - I
 TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab*
 JLAB-ACT--9 Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab* Tom Powers Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility Newport
JLAB-ACT--9 Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab* Tom Powers Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility Newport
LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT
 1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
Univ. Maryland Boise State Univ
 MURI 01: Effects of High Power Microwaves and Chaos in 21 st Century Analog & Digital Electronics* (www.ireap.umd.edu/muri-2001)) Overview of Research Progress Univ. Maryland V.L. Granatstein, S.M. Anlage,
MURI 01: Effects of High Power Microwaves and Chaos in 21 st Century Analog & Digital Electronics* (www.ireap.umd.edu/muri-2001)) Overview of Research Progress Univ. Maryland V.L. Granatstein, S.M. Anlage,
2) The larger the ripple voltage, the better the filter. 2) 3) Clamping circuits use capacitors and diodes to add a dc level to a waveform.
 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
Electronic Instrumentation. Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link
 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link Agenda Brief Review: Diodes Zener Diodes Project 4: Optical Communication Link Why optics? Understanding
Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 8: Diodes (continued) Project 4: Optical Communications Link Agenda Brief Review: Diodes Zener Diodes Project 4: Optical Communication Link Why optics? Understanding
Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits
 1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
Keywords: rf, rfic, wireless, cellular, cdma, if, oscillator, rfics, IF frequencies, VCO, rf ic
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 272 Keywords: rf, rfic, wireless, cellular, cdma, if, oscillator, rfics, IF frequencies, VCO, rf ic APPLICATION
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 272 Keywords: rf, rfic, wireless, cellular, cdma, if, oscillator, rfics, IF frequencies, VCO, rf ic APPLICATION
ECEN Network Analysis Section 3. Laboratory Manual
 ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C.
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 5A The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C. Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Validate the Schottky diode equation. Calculate the dc and dynamic (ac) resistance
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 5A The preferred Exercise is shown in Exercises 5B or 5C. Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Validate the Schottky diode equation. Calculate the dc and dynamic (ac) resistance
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A. Name. Section. Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points)
 ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
Sine-wave oscillator
 Sine-wave oscillator In Fig. 1, an op-'amp can be made to oscillate by feeding a portion of the output back to the input via a frequency-selective network, and controlling the overall voltage gain. For
Sine-wave oscillator In Fig. 1, an op-'amp can be made to oscillate by feeding a portion of the output back to the input via a frequency-selective network, and controlling the overall voltage gain. For
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
1) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz
 ) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
New Results in Chaotic Time-Reversed Electromagnetics: High Frequency One-Recording-Channel Time-Reversal Mirror
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena Warsaw, Poland, May 25-27, 2007 New Results in Chaotic Time-Reversed Electromagnetics:
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Quantum Chaos and Localisation Phenomena Warsaw, Poland, May 25-27, 2007 New Results in Chaotic Time-Reversed Electromagnetics:
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
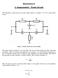 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Design and Hardware Implementation of L-Type Resonant Step Down DC-DC Converter using Zero Current Switching Technique
 Design and Hardware Implementation of L-Type Resonant Step Down DC-DC Converter using Zero Current Switching Technique Mouliswara Rao. R Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, AITAM, Tekkali, Andhra Pradesh,
Design and Hardware Implementation of L-Type Resonant Step Down DC-DC Converter using Zero Current Switching Technique Mouliswara Rao. R Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, AITAM, Tekkali, Andhra Pradesh,
Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits
 Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits By: Mark Porubsky Milwaukee Area Technical College Electronic Technology Electronic Communications Milwaukee, WI Purpose: The various parts of this lab unit will
Amplitude Modulation Methods and Circuits By: Mark Porubsky Milwaukee Area Technical College Electronic Technology Electronic Communications Milwaukee, WI Purpose: The various parts of this lab unit will
EE-2302 Passive Filters and Frequency Response
 EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages.
 Figure 3-1 Simple radio receiver block diagram. Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages. Jeffrey
Figure 3-1 Simple radio receiver block diagram. Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages. Jeffrey
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting AC to DC
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
