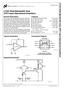
Description OA3 OA2. Figure 1. Block Diagram (pin numbers are for DIP only) Table 1. Ordering Information
|
|
|
- Winifred Cross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THAT Corporation THAT Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor THAT 4301, 4301A FEATURES HighPerformance Voltage Controlled Amplifier HighPerformance RMSLevel Detector Three GeneralPurpose Opamps Wide Dynamic Range: >115 db Low THD: <0.03% Low Cost DIP & SurfaceMount Packages APPLICATIONS Compressors Limiters Gates Expanders DeEssers Duckers Noise Reduction Systems WideRange Level Meters Description THAT 4301 Dynamics Processor, dubbed THAT Analog Engine, combines in a single IC all the active circuitry needed to construct a wide range of dynamics processors. The 4301 includes a highperformance, exponentiallycontrolled VCA, a logresponding RMSlevel sensor and three general purpose opamps. The VCA provides two opposingpolarity, voltagesensitive control ports. Dynamic range exceeds 115 db, and THD is typically 0.003% at 0 db gain. In the 4301A, the VCA is selected for low THD at extremely high levels. The RMS detector provides accurate rmstodc conversion over an 80 db dynamic range for signals with crest factors up to 10. One opamp is dedicated as a currenttovoltage converter for the VCA, while the other two may be used for the signal path or control voltage processing. The combination of exponential VCA gain control and logarithmic detector response decibellinear response simplifies the mathematics of designing the control paths of dynamics processors. This makes it easy to design audio compressors, limiters, gates, expanders, deessers, duckers, noise reduction systems and the like. The high level of integration ensures excellent temperature tracking between the VCA and the detector, while minimizing the external parts count Model 20 pin DIP Pkg 30 pin DMP (SO) Pkg OA1 IT VCC THAT4301 RMS CT EC GND VCA SYM VEE EC OA3 OA RoHS Compliant 4301A RoHS Compliant 4301P20I 4301M30I 4301AP20I M A 4301AP20 Figure 1. Block Diagram (pin numbers are for DIP only) Table 1. Ordering Information Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web: Document Rev. 07
2 Page 2 Document Rev 07 SPECIFICATIONS 1,2 Absolute Maximum Ratings (T A = 25 C) Positive Supply Voltage (V CC ) 18 V Power Dissipation (P D )(T A = 75 C) 700 mw Negative Supply Voltage (V EE ) 18 V Operating Temperature Range (T OP ) 0 to 70 C Supply Current (I CC ) 20 ma Storage Temperature Range (T ST ) 40 to 125 C Overall Electrical Characteristics Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units Positive Supply Voltage V CC 7 15 V Negative Supply Voltage V EE 7 15 V Positive Supply Current I CC ma Negative Supply Current I EE ma Thermal Resistance JC SOPackage 140 C/W VCA Electrical Characteristics A Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units Input Bias Current I B(VCA) No Signal pa Input Offset Voltage V OFF(VCA In) No Signal mv Input Signal Current I (VCA) or I (VCA) Arms Gain at 0V Control G 0 E C =E C = 0.000V db GainControl Constant T A = 25 C (T CHIP 55 C) 60 db < gain < 40dB E C /Gain (db) E C & SYM mv/db E C /Gain (db) E C mv/db GainControl TempCo E C / T CHIP Ref T CHIP = 27 C %/ C GainControl Linearity 60 to 40 db gain % Off Isolation E C =SYM=375mV, E C =375mV db Output Offset Voltage Change V OFF() R out = 20k 0 db gain mv 15 db gain mv 30 db gain mv Gain Cell Idling Current I IDLE A Output Noise e n() 20 Hz20 khz R out = 20k 0 db gain dbv 15 db gain dbv Total Harmonic Distortion THD V = 0 dbv, 1 khz 0 db gain % 1. All specifications subject to change without notice. 2. Unless otherwise noted, T A =25 C, V CC = 15V, V EE = 15V; VCA SYM adjusted for min 0 db gain. 3. Test circuit is the VCA section only from Figure 2. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
3 THAT 4301 Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor Page 3 SPECIFICATIONS 1,2 (Cont d.) VCA Electrical Characteristics 3 (Cont d.) A Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units Total Harmonic Distortion (cont d.) THD V = 10 dbv, 1 khz 0 db gain % 15 db gain % V = 10 dbv, 1 khz 15 db gain % V = 19.5 dbv, 1 khz 0 db gain % Symmetry Control Voltage V SYM minimum THD mv RMS Detector Electrical Characteristics 4 Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units Input Bias Current I B (RMS) No Signal pa Input Offset Voltage V OFF(RMS In) No Signal 4 15 mv Input Signal Current I (RMS) A Input Current for 0 V Output I in0 I T = 7.5A A Output Scale Factor E O / 20log(I in /I in0 ) 31.6nA< I < 1mA T A = 25 C (T CHIP 55 C) mv/db Scale Factor Match (RMS to VCA) 20 db < VCA Gain < 20 db 1A<I in (DET) <100A Output Linearity f = 1kHz 1A<I in < 100A 0.1 db 100nA < I in < 316A 0.5 db 31.6nA < I in < 1mA 1.5 db Rectifier Balance f = 100 Hz, =.001 s 1A< I in < 100A % Crest Factor 1ms pulse repetition rate 0.2 db error db error db error 10 Maximum Frequency for 2 db Additional Error I in 10A 100 khz I in 3A 45 khz I in 300nA 7 khz Timing Current Set Range I T A Voltage at I T Pin I T = 7.5A mv Timing Current Accuracy I CT /I T I T = 7.5A Filtering Time Constant T CHIP =55C Output Temp. Coefficient E o / T CHIP Re: T CHIP =27C 0.33 %/ C Output Current I 300mV < V < 300mV A CT IT s 4. Except as noted, test circuit is the RMSDetector section only from Figure 2. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
4 Page 4 Document Rev 07 Specifications 1,2 (Cont d) Opamp Electrical Characteristics 5 OA1 OA2 OA3 Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units Input Offset Voltage V OS mv Input Bias Current I B na Input Offset Current I OS N/A na Input Voltage Range I VR N/A V Common Mode Rej. Ratio CMRR R S <10k N/A Power Supply Rej. Ratio PSRR VS=7V to 15V Gain Bandwidth Product GBW (@50kHz) MHz Open Loop Gain A VO R L =10k R L =2k N/A N/A 120 Output Voltage Swing V L =5k V V L =2k N/A N/A 13 V Short Circuit Output Current ma Slew Rate SR V/s Total Harmonic Distortion THD 1kHz, A V =1, R L =10k % 1kHz, A V = 1, R L =2k N/A N/A % Input Noise Voltage Density e n f O =1kHz nv Hz Input Noise Current Density i n f O =1kHz pa Hz 5. Test circuit for opamps is a unitygain follower configuration, with load resistor R L as specified. R5 15V SIGNAL C1 47uF R1 20K0 1% 15V R3 50K VCA SYM R4 300K C2 47pF R2 C7 100n 15V 51 20K0 1% SYM OA1 VCA OA3 EC EC SIGNAL C3 47uF C8 100n R6 10K0 1% 15V VCC VEE THAT4301 It RMS Ct GND OA2 C6 22uF R7 2M00 1% C4 10uF RMS Ec 15V Figure 2. VCA and RMS detector test circuit Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
5 THAT 4301 Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor Page 5 Pin Name DIP Pin SO Pin RMS In 1 3 I T (I Time ) 2 4 No Connection 3 5 RMS Out 4 6 C T (C Time ) 5 7 OA2 In 6 9 OA2 Out 7 10 OA2 In 8 11 GND 9 12 VEE VCC OA3 Out VCA Out SYM E C Pin Name DIP Pin SO Pin E C VCA In OA1 Out OA1 In OA1 In No Connection 1 No Connection 2 No Connection 8 No Connection 14 No Connection 15 No Connection 16 No Connection 17 No Connection 21 No Connection 29 No Connection 30 Table 2. Pin Connections E 1 F G B A 015 C D P J M K N L I O H ITEM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P MILLIMETERS CHES 24.8 Max Max 24.2 / / / / / / / / / / Typ Typ Typ Typ / / Max Max Min Min. 2.8 Min Min Figure 3. Plastic dual inline package outline Figure 4. Plastic surfacemount package outline Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
6 Page 6 Document Rev 07 Representative Data Figure 5. VCA Gain vs. Control Voltage (Ec) at 25 C Figure 6. VCA 1kHz THDNoise vs. Input, 15 db Gain Figure 7. VCA 1kHz THDNoise vs. Input, 15 db Gain Figure 8. VCA 1kHz THDNoise vs. Input, 0 db Gain Figure 9. VCA THD vs. Frequency, 0 db Gain, 1Vrms Input Figure 10. RMS Output vs. Input Level, 1 khz & 10 khz Figure 11. Departure from Ideal Detector Law vs. Level Figure 12. Detector Output vs. Frequency at Various Levels Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
7 THAT 4301 Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor Page 7 Theory of Operation THAT 4301 Dynamics Processor combines THAT Corporation s proven VoltageControlled Amplifier (VCA) and RMSLevel Detector designs with three generalpurpose opamps to produce an Analog Engine useful in a variety of dynamics processor applications. For details of the theory of operation of the VCA and RMSDetector building blocks, the interested reader is referred to THAT Corporation s data sheets on the 2150 Series VCAs and the 2252 RMSLevel Detector. Theory of the interconnection of exponentiallycontrolled VCAs and logresponding level detectors is covered in THAT Corporation s application note AN101, The Mathematics of LogBased Dynamic Processors. The VCA in Brief THAT 4301 VCA is based on THAT Corporation s highly successful complementary logantilog gain cell topology, as used in THAT 2150Series IC VCAs, and the modular 202 Series VCAs. THAT 4301 is integrated using a fully complementary, BiFET process. The combination of FETs with highquality, complementary bipolar transistors (NPNs and PNPs) allows additional flexibility in the design of the VCA over previous efforts. Input signals are currents to the VCA pin. This pin is a virtual ground, so in normal operation an input voltage is converted to input current via an appropriately sized resistor (R 1 in Figure 2, Page 4). Because dc offsets present at the input pin and any dc offset in preceeding stages will be modulated by gain changes (thereby becoming audible as thumps), the input pin is normally accoupled (C 1 in Figure 2). The VCA output signal is also a current, inverted with respect to the input current. In normal operation, the output current is converted to a voltage via inverter OA 3, where the ratio of the conversion is determined by the feedback resistor (R 2, Figure 2) connected between OA 3 s output and its inverting input. The signal path through the VCA and OA 3 is noninverting. The gain of the VCA is controlled by the voltage applied to E C,E C, and SYM. Gain (in decibels) is proportional to E C E C, provided E C and SYM are at essentially the same voltage (see below). The constant of proportionality is 6.5 mv/db for the voltage at E C, and 6.5 mv/db for the voltage at E C and SYM. As mentioned, for proper operation, the same voltage must be applied to E C and SYM, except for a small (2.5 mv) dc bias applied between these pins. This bias voltage adjusts for internal mismatches in the VCA gain cell which would otherwise cause small differences between the gain of positive and negative halfcycles of the signal. The voltage is usually applied via an external trim potentiometer (R 5 in Figure 2), which is adjusted for minimum signal distortion at unity (0 db) gain. The VCA may be controlled via E C, as shown in Figure 2, or via the combination of E C and SYM. This connection is illustrated in Figure 13. Note that this figure shows only that portion of the circuitry needed to drive the positive VCA control port; circuitry associated with OA 1,OA 2 and the RMS detector has been omitted. While the 4301 s VCA circuitry is very similar to that of the THAT 2150 Series VCAs, there are several important differences, as follows: 1) Supply current for the VCA is fixed internally. Approximately 2mA is available for the Positive Control In Signal In C1 47uF It R1 20K0 1% THAT4301 Ct sum of input and output signal currents. (This is also the case in a 2150 Series VCA when biased as recommended.) 2) The signal current output of the VCA is internally connected to the inverting input of an onchip opamp. In order to provide external feedback around this opamp, this node is brought out to a pin. 3) The controlvoltage constant is approximately 6.5 mv/db, due primarily to the higher internal operating temperature of the 4301 compared to that of the 2150 Series. 4) The input stage of the 4301 VCA uses integrated Pchannel FETs rather than a biascurrent corrected bipolar differential amplifier. Input bias currents have therefore been reduced. The RMS Detector in Brief R K R5 R4 300K C2 47pF R2 20K0 1% The 4301 s detector computes rms level by rectifying input current signals, converting the rectified current to a logarithmic voltage, and applying that voltage to a logdomain filter. The output signal is a dc voltage proportional to the decibellevel of the rms value of the input signal current. Some ac component (at twice the input frequency) remains superimposed on the dc out SYM OA1 VCA OA3 EC EC VCC VEE RMS GND VCA SYM OA2 Signal Out Figure 13. Driving the VCA via the Positive Control Port Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
8 Page 8 Document Rev 07 put. The ac signal is attenuated by a logdomain filter, which constitutes a singlepole rolloff with cutoff determined by an external capacitor and a programmable dc current. As in the VCA, input signals are currents to the RMS pin. This input is a virtual ground, so a resistor (R 6 in Figure 2) is normally used to convert input voltages to the desired current. The level detector is capable of accurately resolving signals well below 10 mv (with a 10 k input resistor). However, if the detector is to accurately track such lowlevel signals, ac coupling is normally required. The logdomain filter cutoff frequency is usually placed well below the frequency range of interest. For an audioband detector, a typical value would be 5 Hz, or a 32 ms time constant (). The filter s time constant is determined by an external capacitor attached to the C T pin, and an internal current source (I CT ) connected to C T. The current source is programmed via the I T pin: current in I T is mirrored to I CT with a gain of approximately 1.1. The resulting time constant is approximately equal to C T /I T. Note that, as a result of the mathematics of RMS detection, the attack and release time constants are fixed in their relationship to each other. The dc output of the detector is scaled with the same constant of proportionality as the VCA gain control: 6.5 mv/db. The detector s 0 db reference (I in0, the input current which causes 0 V output), is determined by I T as follows: I in0 = 9.6A I T The detector output stage is capable of sinking or sourcing 100 A. Differences between the 4301 s RMSLevel Detector circuitry and that of the THAT 2252 RMS Detector are as follows: 1) The rectifier in the 4301 RMS Detector is internally balanced by design, and cannot be balanced via an external control. The 4301 will typically balance positive and negative halves of the input signal within 1.5%, but in extreme cases the mismatch may reach 15%. However, a 15% mismatch will not significantly increase rippleinduced distortion in dynamics processors over that caused by signal ripple alone. 2) The time constant of the 4301 s RMS detector is determined by the combination of an external capacitor (connected to the C T pin) and an internal, programmable current source. The current source is equal to 1.1 I T. Normally, a resistor is not connected directly to the C T pin on the ) The 0 db reference point, or level match, isnot adjustable via an external current source. However, as in the 2252, the level match is affected by the timing current, which, in this case, is drawn from the I T pin and mirrored internally to C T. 4) The input stage of the 4301 RMS detector uses integrated Pchannel FETs rather than a biascurrent corrected bipolar differential amplifier. Input bias currents are therefore negligible, improving performance at low signal levels. The Opamps in Brief The three opamps in the 4301 are intended for general purpose applications. All are 5 MHz opamps with slew rates of approximately 2V/s. All use bipolar PNP input stages. However, the design of each is optimized for its expected use. Therefore, to get the most out of the 4301, it is useful to know the major differences among these opamps. OA 3, being internally connected to the output of the VCA, is intended for currenttovoltage conversion. Its input noise performance, at 75. nv Hz, complements that of the VCA, adding negligible noise at unity gain. Its output section is capable of driving a 2 k load to within 2V of the power supply rails, making it possible to use this opamp directly as the output stage in singleended designs. OA 1 is the quietest opamp of the three. Its input noise voltage, at 65. nv Hz, makes it the opamp of choice for input stages. Note that its output drive capability is limited (in order to reduce the chip s power dissipation) to approximately 3 ma. It is comfortable driving loads of 5 k or more to within 1V of the power supply rails. OA 2 is intended primarily as a controlvoltage processor. Its input noise parallels that of OA 3, and its output drive capability parallels that of OA 1. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
9 THAT 4301 Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor Page 9 Applications The circuit of Figure 14, Page 9, shows a typical application for THAT This simple compressor/limiter design features adjustable hardknee threshold, compression ratio, and static gain 1. The applications discussion in this data sheet will center on this circuit for the purpose of illustrating important design issues. However, it is posslble to configure many other types of dynamics processors with THAT Hopefully, the following discussion will imply some of these possibilities. Signal Path As mentioned in the section on theory, the VCA input pin is a virtual ground with negative feedback provided internally. An input resistor (R 1, 20k) is required to convert the ac input voltage to a current within the linear range of the (Peak VCA input currents should be kept under 1 ma for best distortion performance.) The coupling capacitor (C 1,47f) is strongly recommended to block dc current from preceding stages (and from offset voltage at the input of the VCA). Any dc current into the VCA will be modulated by varying gain in the VCA, showing up in the output as thumps. Note that C 1, in conjunction with R 1, will set the low frequency limit of the circuit. The VCA output is connected to OA 3, configured as an inverting currenttovoltage converter. OA 3 s feedback components (R 2, 20 k, and C 2, 47 pf) determine the constant of currenttovoltage conversion. The simplest way to deal with this is to recognize that when the VCA is set for unity (0 db) gain, the input to output voltage gain is simply R 2 /R 1, just as in the case of a single inverting stage. If, for some reason, more than 0 db gain is required when the VCA is set to COMPRESSION R13 10K CW C7 C8 CCW C3 47uF 4k99 1% n 100n R14 1K43 1% C1 47uF THRESHOLD CCW R11 R12 10K 383K 1% R10 CW 2M00 1% R8 15 R6 10K0 1% C6 22uF R9 unity, then the resistors may be skewed to provide it. Note that the feedback capacitor (C 2 )is required for stability. The VCA output has approximately 45 pf of capacitance to ground, which must be neutralized via the 47 pf feedback capacitor across R 2. The VCA gain is controlled via the E C terminal, whereby gain will be proportional to the negative of the voltage at E C. The E C terminal is grounded, and the SYM terminal is returned nearly to ground via a small resistor (R 3,51). The VCA SYM trim (R 5,50k) allows a small voltage to be applied to the SYM terminal via R 4 (300 k). This voltage adjusts for small mismatches within the VCA gain cell, thereby reducing evenorder distortion products. To adjust the trim, apply to the input a middlelevel, middlefrequency signal (1 khz at 1 V is a good 10K0 1% C9 R1 20K0 1% VCC VEE 22p CR1 OA1 R7 2M00 1% IT 15 CR2 THAT4301 RMS C4 10uF CT EC 15 VCA SYM R K R3 51 VCA GND SYM EC R15 10K0 1% R4 300K Figure 14. Typical Compressor/Limiter Application Circuit 20K0 1% C2 OA3 R2 OA2 R16 4k99 1% C5 100N R17 590K 1% 47pF 15 GA 15 CW R18 10K CCW 1. More information on this compressor design, along with suggestions for converting it to softknee operation, is given in AN100, Basic Compressor Limiter Design. The designs in AN100 are based on THAT Corporation s 2150Series VCAs and 2252 RMS Detector, but are readily adaptable to the 4301 with only minor modifications. In fact, the circuit presented here is functionally identical to the hardknee circuit published in AN100. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
10 Page 10 Document Rev 07 choice with this circuit) and observe THD at the signal output. Set the trim for minimum THD. RMSLevel Detector The RMS detector s input is similar to that of the VCA. An input resistor (R 6,10k) converts the ac input voltage to a current within the linear range of the (Peak detector input currents should be kept under 1 ma for best linearity.) The coupling capacitor (C 3,47f) is recommended to block dc current from preceeding stages (and from offset voltage at the input of the detector). Any dc current into the detector will limit the lowlevel resolution of the detector, and will upset the rectifier balance at low levels. Note that, as with the VCA input circuitry, C 3 in conjunction with R 6 will set the lower frequency limit of the detector. The time response of the RMS detector is determined by the capacitor attached to C T (C 4,10f) and the size of the current in pin I T (determined by R 7, 2M and the negative power supply, 15V). Since the voltage at I T is approximately 0 V, the circuit of Figure 14 produces 7.5 A ini T. The current in I T is mirrored with a gain of 1.1 to the C T pin, where it is available to discharge the timing capacitor (C 4 ). The combination produces a log filter with time constant equal to approximately C T /I T (~35 ms in the circuit shown). The waveform at C T will follow the logged (decibel) value of the input signal envelope, plus a dc offset of about 1.3 V (2 V BE ). This allows a polarized capacitor to be used for the timing capacitor, usually an electrolytic. The capacitor used should be a lowleakage type in order not to add significantly to the timing current. The output stage of the RMS detector serves to buffer the voltage at C T and remove the 1.3 V dc offset, resulting in an output centered around 0 V for input signals of about 85 mv. The output voltage increases 6.5 mv for every 1 db increase in input signal level. This relationship holds over more than a 60 db range in input currents. Control Path A compressor/limiter is intended to reduce its gain as signals rise above a threshold. The output of the RMS detector represents the input signal level over a wide range of levels, but compression only occurs when the level is above the threshold. OA 1 is configured as a variable threshold detector to block envelope information for lowlevel signals, passing only information for signals above threshold. OA 1 is an inverting stage with gain of 2 above threshold and 0 below threshold. Neglecting the action of the THRESHOLD control (R 12 ) and its associated resistors (R 11 and R 10 ), positive signals from the RMS detector output drive the output of OA 1 negative. This forward biases CR 2, closing the feedback loop such that the junction of R 9 and CR 2 (the output of the threshold detector) sits at (R 9 /R 8 ) RMS. For the circuit of Figure 14, this is 2 RMS. Negative signals from the RMS detector drive the output of OA 1 positive, reverse biasing CR 2 and forward biasing CR 1. In this case, the junction of R 9 and CR 2 rests at 0 V, and no signal level informaion is passed to the threshold detector s output. In order to vary the threshold, R 12, the THRESH OLD control, is provided. Via R 11 (383 k), R 12 adds up to 39.2 A of current to OA 1 s summing junction, requiring the same amount of oppositepolarity current from the RMS detector output to counterbalance it. At 4.99 k, the voltage across R 8 required to produce a counterbalancing current is 195 mv, which represents a 30 db change in RMS detector input level. Since the RMS detector s 0 db reference level is 85 mv, the center of the THRESHOLD pot s range would be 85 mv, were it not for R 10 (2 M), which provides an offset. R 10 adds an extra 7.5 A tooa 1 s summing junction, which would be counterbalanced by 37.4 mv at the detector output. This corresponds to 5.8 db, offsetting the THRESHOLD center by this much to 165 mv, or approximately 16 dbv. The output of the threshold detector represents the signal level above the determined threshold, at a constant of about 13 mv/db (from [R 9 /R 8 ] 6.5 mv/db). This signal is passed on to the COMPRESSION control (R 13 ), which variably attenuates the signal passed on to OA 2. Note that the gain of OA 2, from the wiper of the COMPRESSION control to OA 2 s output, is R 16 /R 15 (0.5), precisely the inverse of the gain of OA 1. Therefore, the COMPRESSION control lets the user vary the abovethreshold gain between the RMS detector output and the output of OA 1 from zero to a maximum of unity. The gain control constant of the VCA, 6.5 mv/db, is exactly equal to the output scaling constant of the RMS detector. Therefore, at maximum COMPRES SION, above threshold, every db increase in input signal level causes a 6.5 mv increase in the output of OA 2, which in turn causes a1dbdecrease in the VCA gain. With this setting, the output will not increase despite large increases in input level above threshold. This is infinite compression. For intermediate settings of COMPRESSION, a1dbincrease in input signal level will cause less than a1dbdecrease in gain, thereby varying the compression ratio. The resistor R 14 is included to alter the taper of the COMPRESSION pot to better suit common use. If a linear taper pot is used for R 13, the compression ratio will be 1:2 at the middle of the rotation. However, 1:2 compression in an abovethreshold compressor is not very strong processing, so 1:4 is often preferred at the midpoint. R 14 warps the taper of R 13 so that 1:4 compression occurs at approximately the midpoint of R 13 s rotation. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
11 THAT 4301 Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor Page 11 The GA control (R 18 ) is used to provide static gain or attenuation in the signal path. This control adds up to R 130 mv offset to the output of OA 2 (from V 16 to V R 17 R16 R ), which is approximately 20 db change in gain of 17 the VCA. C 5 is used to attenuate the noise of OA 2,OA 1 and the resistors R 8 through R 16 used in the control path. All these active and passive components produce noise which is passed on to the control port of the VCA, causing modulation of the signal. By itself, the 4301 VCA produces very little noise modulation, and its performance can be significantly degraded by the use of noisy components in the control voltage path. Overall Result The resulting compressor circuit provides hardknee compression above threshold with three essential useradjustable controls. The threshold of compression may be varied over a 30 db range from about 46 dbv to 14 dbv. The compression ratio may be varied from 1:1 (no compression) to :1. And, static gain may be added up to 20 db. Audio performance is excellent, with THD running below 0.05% at middle frequencies even with 10 db of compression, and an input dynamic range of over 115 db. Perhaps most important, this example design only scratches the surface of the large body of applications circuits which may be constructed with THAT The combination of an accurate, widedynamicrange, logresponding level detector with a highquality, exponentiallyresponding VCA produces a versatile and powerful analog engine. The opamps provided in the 4301 enable the designer to configure these building blocks with few external components to construct gates, expanders, deessers, noise reduction systems and the like. For further information, samples and pricing, please contact us at the address below. Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web:
12 Page 12 Document Rev 07 Notes Tel: 1 (508) ; Fax: 1 (508) ; Web: Copyright 2012, THAT Corporation
THAT4301 FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Description. THAT Analog Engine IC Dynamics Processor VCA + 15 RMS
 THAT Analog Engine THAT4301 FEATURES HighPerformance Blackmer Voltage Controlled Amplifier HighPerformance RMSLevel Detector Three GeneralPurpose Opamps Wide Dynamic Range: >115 db Low THD:
THAT Analog Engine THAT4301 FEATURES HighPerformance Blackmer Voltage Controlled Amplifier HighPerformance RMSLevel Detector Three GeneralPurpose Opamps Wide Dynamic Range: >115 db Low THD:
Basic Compressor/Limiter Design with the THAT4305
 THAT Corporation Design Brief 203 Abstract Basic Compressor/Limiter Design THAT Corporation s Analog Engines are ideal basic building blocks for compressor/limiter designs. This design brief describes
THAT Corporation Design Brief 203 Abstract Basic Compressor/Limiter Design THAT Corporation s Analog Engines are ideal basic building blocks for compressor/limiter designs. This design brief describes
Description. Vbe MULTI- PLIER
 THAT Corporation IC Voltage-Controlled Amplifiers 1 6 BIAS CURRENT COMPENSATION FEATURES Wide Dynamic Range: >116 db Wide Gain Range: >130 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion: (0.008% @ 0 db
THAT Corporation IC Voltage-Controlled Amplifiers 1 6 BIAS CURRENT COMPENSATION FEATURES Wide Dynamic Range: >116 db Wide Gain Range: >130 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion: (0.008% @ 0 db
Self-Contained Audio Preamplifier SSM2019
 a FEATURES Excellent Noise Performance:. nv/ Hz or.5 db Noise Figure Ultra-low THD:
a FEATURES Excellent Noise Performance:. nv/ Hz or.5 db Noise Figure Ultra-low THD:
Description. minimal support circuitry. Fabricated in a controlled amplifiers (VCAs) are high-performance
 THAT Corporation IC Voltage-Controlled Amplifiers 1 6 BIAS CURRENT COMPENSATION FEATURES Wide Dynamic Range: >116 db Wide Gain Range: >130 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion: (0.008% @ 0 db
THAT Corporation IC Voltage-Controlled Amplifiers 1 6 BIAS CURRENT COMPENSATION FEATURES Wide Dynamic Range: >116 db Wide Gain Range: >130 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion: (0.008% @ 0 db
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from V to V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load Drive
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from V to V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load Drive
OBSOLETE. Low Cost Quad Voltage Controlled Amplifier SSM2164 REV. 0
 a FEATURES Four High Performance VCAs in a Single Package.2% THD No External Trimming 12 db Gain Range.7 db Gain Matching (Unity Gain) Class A or AB Operation APPLICATIONS Remote, Automatic, or Computer
a FEATURES Four High Performance VCAs in a Single Package.2% THD No External Trimming 12 db Gain Range.7 db Gain Matching (Unity Gain) Class A or AB Operation APPLICATIONS Remote, Automatic, or Computer
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
Programmable analog compandor
 DESCRIPTION The NE572 is a dual-channel, high-performance gain control circuit in which either channel may be used for dynamic range compression or expansion. Each channel has a full-wave rectifier to
DESCRIPTION The NE572 is a dual-channel, high-performance gain control circuit in which either channel may be used for dynamic range compression or expansion. Each channel has a full-wave rectifier to
Input Limiter for ADCs
 Input Limiter for ADCs The circuits within this application note feature THAT8x to provide the essential function of voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) and THAT 5 as an rms-level detector (RMS). Since
Input Limiter for ADCs The circuits within this application note feature THAT8x to provide the essential function of voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) and THAT 5 as an rms-level detector (RMS). Since
Description. Output Stage. 5k (10k) - + 5k (10k)
 THAT Corporation Low Noise, High Performance Audio Preamplifier IC FEATURES Low Noise: 1 nv/hz input noise (60dB gain) 34 nv/hz input noise (0dB gain) (1512) Low THD+N (full audio bandwidth): 0.001% 40dB
THAT Corporation Low Noise, High Performance Audio Preamplifier IC FEATURES Low Noise: 1 nv/hz input noise (60dB gain) 34 nv/hz input noise (0dB gain) (1512) Low THD+N (full audio bandwidth): 0.001% 40dB
Matched Monolithic Quad Transistor MAT04
 a FEATURES Low Offset Voltage: 200 V max High Current Gain: 400 min Excellent Current Gain Match: 2% max Low Noise Voltage at 100 Hz, 1 ma: 2.5 nv/ Hz max Excellent Log Conformance: rbe = 0.6 max Matching
a FEATURES Low Offset Voltage: 200 V max High Current Gain: 400 min Excellent Current Gain Match: 2% max Low Noise Voltage at 100 Hz, 1 ma: 2.5 nv/ Hz max Excellent Log Conformance: rbe = 0.6 max Matching
OBSOLETE. Self-Contained Audio Preamplifier SSM2017 REV. B
 a FEATURES Excellent Noise Performance: 950 pv/ Hz or 1.5 db Noise Figure Ultralow THD: < 0.01% @ G = 100 Over the Full Audio Band Wide Bandwidth: 1 MHz @ G = 100 High Slew Rate: 17 V/ s typ Unity Gain
a FEATURES Excellent Noise Performance: 950 pv/ Hz or 1.5 db Noise Figure Ultralow THD: < 0.01% @ G = 100 Over the Full Audio Band Wide Bandwidth: 1 MHz @ G = 100 High Slew Rate: 17 V/ s typ Unity Gain
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. SA571 Compandor. Product specification 1997 Aug 14 IC17 Data Handbook
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1997 Aug 14 IC17 Data Handbook DESCRIPTION The is a versatile low cost dual gain control circuit in which either channel may be used as a dynamic range compressor or expandor. Each
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1997 Aug 14 IC17 Data Handbook DESCRIPTION The is a versatile low cost dual gain control circuit in which either channel may be used as a dynamic range compressor or expandor. Each
Quad Current Controlled Amplifier SSM2024
 a Quad Current Controlled Amplifier FEATURES Four VCAs in One Package Ground Referenced Current Control Inputs 82 db S/N at 0.3% THD Full Class A Operation 40 db Control Feedthrough (Untrimmed) Easy Signal
a Quad Current Controlled Amplifier FEATURES Four VCAs in One Package Ground Referenced Current Control Inputs 82 db S/N at 0.3% THD Full Class A Operation 40 db Control Feedthrough (Untrimmed) Easy Signal
V CC OUT MAX9945 IN+ V EE
 19-4398; Rev 1; 12/ 38V, Low-Noise, MOS-Input, General Description The operational amplifier features an excellent combination of low operating power and low input voltage noise. In addition, MOS inputs
19-4398; Rev 1; 12/ 38V, Low-Noise, MOS-Input, General Description The operational amplifier features an excellent combination of low operating power and low input voltage noise. In addition, MOS inputs
V CC OUT MAX9945 IN+ V EE
 19-4398; Rev ; 2/9 38V, Low-Noise, MOS-Input, General Description The operational amplifier features an excellent combination of low operating power and low input voltage noise. In addition, MOS inputs
19-4398; Rev ; 2/9 38V, Low-Noise, MOS-Input, General Description The operational amplifier features an excellent combination of low operating power and low input voltage noise. In addition, MOS inputs
Low Cost, Balanced Line Receiver ICs
 Low Cost, Balanced Line Receiver ICs THAT 0,, FEATURES Good CMRR: typ. 0 db at 0Hz Low cost, self-contained Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >8. MHz High slew rate: typ. V/μs Low distortion:
Low Cost, Balanced Line Receiver ICs THAT 0,, FEATURES Good CMRR: typ. 0 db at 0Hz Low cost, self-contained Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >8. MHz High slew rate: typ. V/μs Low distortion:
High Current, High Power OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Current, High Power OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: A WIDE POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: ±V to ±5V USER-SET CURRENT LIMIT SLEW RATE: V/µs FET INPUT: I B = pa max CLASS A/B OUTPUT STAGE
High Current, High Power OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: A WIDE POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: ±V to ±5V USER-SET CURRENT LIMIT SLEW RATE: V/µs FET INPUT: I B = pa max CLASS A/B OUTPUT STAGE
Low Cost Dual Balanced Line Receiver ICs
 Low Cost Dual Balanced Line Receiver ICs THAT 190, 19, 19 FEATURES Good CMRR: typ. 0 db at 0Hz Low cost, self-contained, dual Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >7. MHz High slew rate: typ.
Low Cost Dual Balanced Line Receiver ICs THAT 190, 19, 19 FEATURES Good CMRR: typ. 0 db at 0Hz Low cost, self-contained, dual Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >7. MHz High slew rate: typ.
THAT 2162 FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Description. Dual Pre-trimmed Blackmer Voltage Controlled Amplifier
 Dual Pre-trimmed Blackmer Voltage Controlled Amplifier THAT 6 FEATURES Two Independent Channels Wide Dynamic Range: >8 db Wide Gain Range: >3 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion:.5% typ. Wide
Dual Pre-trimmed Blackmer Voltage Controlled Amplifier THAT 6 FEATURES Two Independent Channels Wide Dynamic Range: >8 db Wide Gain Range: >3 db Exponential (db) Gain Control Low Distortion:.5% typ. Wide
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD822
 Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp FEATURES True Single-Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single-Supply Capability from 3 V to 36
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp FEATURES True Single-Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single-Supply Capability from 3 V to 36
Precision Micropower Single Supply Operational Amplifier OP777
 a FEATURES Low Offset Voltage: 1 V Max Low Input Bias Current: 1 na Max Single-Supply Operation: 2.7 V to 3 V Dual-Supply Operation: 1.35 V to 15 V Low Supply Current: 27 A/Amp Unity Gain Stable No Phase
a FEATURES Low Offset Voltage: 1 V Max Low Input Bias Current: 1 na Max Single-Supply Operation: 2.7 V to 3 V Dual-Supply Operation: 1.35 V to 15 V Low Supply Current: 27 A/Amp Unity Gain Stable No Phase
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM4562 Dual High Performance, High Fidelity Audio Operational Amplifier
 Dual High Performance, High Fidelity Audio Operational Amplifier General Description The is part of the ultra-low distortion, low noise, high slew rate operational amplifier series optimized and fully
Dual High Performance, High Fidelity Audio Operational Amplifier General Description The is part of the ultra-low distortion, low noise, high slew rate operational amplifier series optimized and fully
Improving Loudspeaker Signal Handling Capability
 Design Note 04 (formerly Application Note 104) Improving Loudspeaker Signal Handling Capability The circuits within this application note feature THAT4301 Analog Engine to provide the essential elements
Design Note 04 (formerly Application Note 104) Improving Loudspeaker Signal Handling Capability The circuits within this application note feature THAT4301 Analog Engine to provide the essential elements
LM321 Low Power Single Op Amp
 Low Power Single Op Amp General Description The LM321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With a high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed 0.4V/µs slew rate, the quiescent current is
Low Power Single Op Amp General Description The LM321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With a high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed 0.4V/µs slew rate, the quiescent current is
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
Quad Picoampere Input Current Bipolar Op Amp AD704
 a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V Max Offset Voltage V/ C Max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa Max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C Typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p Typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A Max Supply
a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V Max Offset Voltage V/ C Max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa Max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C Typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p Typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A Max Supply
High Speed BUFFER AMPLIFIER
 High Speed BUFFER AMPLIFIER FEATURES WIDE BANDWIDTH: MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: 1mA LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: 1.mV REPLACES HA-33 IMPROVED PERFORMANCE/PRICE: LH33, LTC11, HS APPLICATIONS OP
High Speed BUFFER AMPLIFIER FEATURES WIDE BANDWIDTH: MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: 1mA LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: 1.mV REPLACES HA-33 IMPROVED PERFORMANCE/PRICE: LH33, LTC11, HS APPLICATIONS OP
UTC572M LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT YOUWANG ELECTRONICS CO.LTD PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG COMPANDOR DESCRIPTION ORDERING INFORMATION FEATURES APPLICATIOS
 PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG COMPANDOR DESCRIPTION The UTC572/M is a dual-channel, high-performance gain control circuit in which either channel may be used for dynamic range compression or expansion. Each channel
PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG COMPANDOR DESCRIPTION The UTC572/M is a dual-channel, high-performance gain control circuit in which either channel may be used for dynamic range compression or expansion. Each channel
THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 102
 THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 0 Digital Gain Control With Analog VCAs Abstract In many cases, a fully analog signal path provides the least compromise to sonic integrity, and ultimately delivers the
THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 0 Digital Gain Control With Analog VCAs Abstract In many cases, a fully analog signal path provides the least compromise to sonic integrity, and ultimately delivers the
Department Analog Secrets Your Subject Mother Never Told You
 Engineering Department Analog Secrets Your Subject Mother Never Told You Name Address Les Tyler, Gary Hebert, Ros Bortoni, Bob Moses 123 rd AES Convention New York, October 2007 2 Seminar Outline New ICs
Engineering Department Analog Secrets Your Subject Mother Never Told You Name Address Les Tyler, Gary Hebert, Ros Bortoni, Bob Moses 123 rd AES Convention New York, October 2007 2 Seminar Outline New ICs
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
AN174 Applications for compandors SA570/571 SA571
 RF COMMUNICATIONS PRODUCTS Applications for compandors SA570/571 SA571 1997 Aug 20 Philips Semiconductors APPLICATIONS The following circuits will illustrate some of the wide variety of applications for
RF COMMUNICATIONS PRODUCTS Applications for compandors SA570/571 SA571 1997 Aug 20 Philips Semiconductors APPLICATIONS The following circuits will illustrate some of the wide variety of applications for
6 db Differential Line Receiver
 a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 9 db typ Hz: 9 db typ khz: 8 db typ Ultralow THD:.% typ @ khz Fast Slew Rate: V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 7 MHz typ (G = /) Two Gain Levels Available: G = / or Low
a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 9 db typ Hz: 9 db typ khz: 8 db typ Ultralow THD:.% typ @ khz Fast Slew Rate: V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 7 MHz typ (G = /) Two Gain Levels Available: G = / or Low
Precision, High-Bandwidth Op Amp
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX9622 General Description The MAX9622 op amp features rail-to-rail output and MHz GBW at just 1mA supply current. At power-up, this device autocalibrates its input offset voltage
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX9622 General Description The MAX9622 op amp features rail-to-rail output and MHz GBW at just 1mA supply current. At power-up, this device autocalibrates its input offset voltage
Low Cost, General Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825
 a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
High Common-Mode Rejection. Differential Line Receiver SSM2141 REV. B FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM FEATURES. High Common-Mode Rejection
 a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 100 db typ 60 Hz: 100 db typ 20 khz: 70 db typ 40 khz: 62 db typ Low Distortion: 0.001% typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz typ Low Cost Complements
a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 100 db typ 60 Hz: 100 db typ 20 khz: 70 db typ 40 khz: 62 db typ Low Distortion: 0.001% typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz typ Low Cost Complements
LF147 - LF247 LF347 WIDE BANDWIDTH QUAD J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 LF147 - LF247 LF347 WIDE BANDWIDTH QUAD J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LOW POWER CONSUMPTION WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT
LF147 - LF247 LF347 WIDE BANDWIDTH QUAD J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LOW POWER CONSUMPTION WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power, FET Input Op Amp AD820
 Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power, FET Input Op Amp AD82 FEATURES True single-supply operation Output swings rail-to-rail Input voltage range extends below ground Single-supply capability from 5 V
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power, FET Input Op Amp AD82 FEATURES True single-supply operation Output swings rail-to-rail Input voltage range extends below ground Single-supply capability from 5 V
Description OA3 RMS OUT. Figure 1. THAT4320 equivalent block diagram (QSOP-28 pin assignments shown)
 Pre-trimmed Low-voltage Low-power THAT FEATURES Pre-trimmed VCA & RMS detector Wide supply voltage range:.v~16v Low supply current: 3.7mA typ. (V) Four opamps One low-noise opamp (
Pre-trimmed Low-voltage Low-power THAT FEATURES Pre-trimmed VCA & RMS detector Wide supply voltage range:.v~16v Low supply current: 3.7mA typ. (V) Four opamps One low-noise opamp (
nanopower Op Amp in a Tiny 6-Bump WLP
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX4464 General Description The MAX4464 is an ultra-small (6-bump WLP) op amp that draws only 75nA of supply current. It operates from a single +.8V to +5.5V supply and features
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX4464 General Description The MAX4464 is an ultra-small (6-bump WLP) op amp that draws only 75nA of supply current. It operates from a single +.8V to +5.5V supply and features
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD82 FEATURES True single-supply operation Output swings rail-to-rail Input voltage range extends below ground Single-supply capability from 5 V
Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD82 FEATURES True single-supply operation Output swings rail-to-rail Input voltage range extends below ground Single-supply capability from 5 V
DUAL ULTRA MICROPOWER RAIL-TO-RAIL CMOS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD276A/ALD276B ALD276 DUAL ULTRA MICROPOWER RAILTORAIL CMOS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD276 is a dual monolithic CMOS micropower high slewrate operational
ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD276A/ALD276B ALD276 DUAL ULTRA MICROPOWER RAILTORAIL CMOS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD276 is a dual monolithic CMOS micropower high slewrate operational
QUAD 5V RAIL-TO-RAIL PRECISION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD472A/ALD472B ALD472 QUAD 5V RAILTORAIL PRECISION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD472 is a quad monolithic precision CMOS railtorail operational amplifier
ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD472A/ALD472B ALD472 QUAD 5V RAILTORAIL PRECISION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD472 is a quad monolithic precision CMOS railtorail operational amplifier
Micropower, Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Precision Instrumentation Amplifiers MAX4194 MAX4197
 General Description The is a variable-gain precision instrumentation amplifier that combines Rail-to-Rail single-supply operation, outstanding precision specifications, and a high gain bandwidth. This
General Description The is a variable-gain precision instrumentation amplifier that combines Rail-to-Rail single-supply operation, outstanding precision specifications, and a high gain bandwidth. This
Balanced Line Receiver ICs
 THAT 0,, FEATURES High CMRR: typ. 90 db at 0Hz Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >8. MHz High slew rate: typ. V/μs Low distortion: typ. 0.000% THD Low noise: typ. -0 dbu Low current: typ.
THAT 0,, FEATURES High CMRR: typ. 90 db at 0Hz Excellent audio performance Wide bandwidth: typ. >8. MHz High slew rate: typ. V/μs Low distortion: typ. 0.000% THD Low noise: typ. -0 dbu Low current: typ.
Dual FET-Input, Low Distortion OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 www.burr-brown.com/databook/.html Dual FET-Input, Low Distortion OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW DISTORTION:.3% at khz LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz HIGH SLEW RATE: 25V/µs WIDE GAIN-BANDWIDTH: MHz UNITY-GAIN STABLE
www.burr-brown.com/databook/.html Dual FET-Input, Low Distortion OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW DISTORTION:.3% at khz LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz HIGH SLEW RATE: 25V/µs WIDE GAIN-BANDWIDTH: MHz UNITY-GAIN STABLE
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD LM321
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD LM321 LOW POWER SINGLE OP AMP DESCRIPTION The UTC LM321 s quiescent current is only 430µA (5V). The UTC LM321 brings performance and economy to low power systems, With a
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD LM321 LOW POWER SINGLE OP AMP DESCRIPTION The UTC LM321 s quiescent current is only 430µA (5V). The UTC LM321 brings performance and economy to low power systems, With a
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF444 quad low power operational amplifier provides many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM148 while
LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF444 quad low power operational amplifier provides many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM148 while
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Precision, High-Bandwidth Op Amp
 19-227; Rev ; 9/1 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Precision, High-Bandwidth Op Amp General Description The op amp features rail-to-rail output and MHz GBW at just 1mA supply current. At power-up, this device
19-227; Rev ; 9/1 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Precision, High-Bandwidth Op Amp General Description The op amp features rail-to-rail output and MHz GBW at just 1mA supply current. At power-up, this device
NE/SA5234 Matched quad high-performance low-voltage operational amplifier
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Supersedes data of 2001 Aug 03 File under Integrated Circuits, IC11 Handbook 2002 Feb 22 DESCRIPTION The is a matched, low voltage, high performance quad operational amplifier. Among
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Supersedes data of 2001 Aug 03 File under Integrated Circuits, IC11 Handbook 2002 Feb 22 DESCRIPTION The is a matched, low voltage, high performance quad operational amplifier. Among
LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed input
Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed input
Quad Picoampere Input Current Bipolar Op Amp AD704
 a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V Max Offset Voltage V/ C Max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa Max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C Typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p Typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A Max Supply
a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V Max Offset Voltage V/ C Max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa Max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C Typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p Typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A Max Supply
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Micropower Precision CMOS Operational Amplifier AD8500
 Micropower Precision CMOS Operational Amplifier AD85 FEATURES Supply current: μa maximum Offset voltage: mv maximum Single-supply or dual-supply operation Rail-to-rail input and output No phase reversal
Micropower Precision CMOS Operational Amplifier AD85 FEATURES Supply current: μa maximum Offset voltage: mv maximum Single-supply or dual-supply operation Rail-to-rail input and output No phase reversal
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
TL072 TL072A - TL072B
 A - B LOW NOISE J-FET DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT LOW NOISE e n = 15nV/ Hz (typ) OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT PROTECTION
A - B LOW NOISE J-FET DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT LOW NOISE e n = 15nV/ Hz (typ) OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT PROTECTION
Quad Audio Switch REV. B BLOCK DIAGRAM OF ONE SWITCH CHANNEL
 a FEATURES CIickless Bilateral Audio Switching Four SPST Switches in a -Pin Package Ultralow THD+N:.8% @ khz ( V rms, R L = k ) Low Charge Injection: 3 pc typ High OFF Isolation: db typ (R L = k @ khz)
a FEATURES CIickless Bilateral Audio Switching Four SPST Switches in a -Pin Package Ultralow THD+N:.8% @ khz ( V rms, R L = k ) Low Charge Injection: 3 pc typ High OFF Isolation: db typ (R L = k @ khz)
Dual Precision, Low Cost, High Speed BiFET Op Amp AD712-EP
 Dual Precision, Low Cost, High Speed BiFET Op Amp FEATURES Supports defense and aerospace applications (AQEC standard) Military temperature range ( 55 C to +125 C) Controlled manufacturing baseline One
Dual Precision, Low Cost, High Speed BiFET Op Amp FEATURES Supports defense and aerospace applications (AQEC standard) Military temperature range ( 55 C to +125 C) Controlled manufacturing baseline One
LM2904AH. Low-power, dual operational amplifier. Related products. Description. Features. See LM2904WH for enhanced ESD performances
 LM2904AH Low-power, dual operational amplifier Datasheet - production data Related products See LM2904WH for enhanced ESD performances Features Frequency compensation implemented internally Large DC voltage
LM2904AH Low-power, dual operational amplifier Datasheet - production data Related products See LM2904WH for enhanced ESD performances Features Frequency compensation implemented internally Large DC voltage
High Common-Mode Voltage Difference Amplifier AD629
 a FEATURES Improved Replacement for: INAP and INAKU V Common-Mode Voltage Range Input Protection to: V Common Mode V Differential Wide Power Supply Range (. V to V) V Output Swing on V Supply ma Max Power
a FEATURES Improved Replacement for: INAP and INAKU V Common-Mode Voltage Range Input Protection to: V Common Mode V Differential Wide Power Supply Range (. V to V) V Output Swing on V Supply ma Max Power
Nanopower Op Amp in Ultra-Tiny WLP and SOT23 Packages
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX47 General Description The MAX47 is a single operational amplifier that provides a maximized ratio of gain bandwidth (GBW) to supply current and is ideal for battery-powered
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX47 General Description The MAX47 is a single operational amplifier that provides a maximized ratio of gain bandwidth (GBW) to supply current and is ideal for battery-powered
Quad Picoampere Input Current Bipolar Op Amp AD704
 a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V max Offset Voltage V/ C max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A max Supply
a FEATURES High DC Precision 75 V max Offset Voltage V/ C max Offset Voltage Drift 5 pa max Input Bias Current.2 pa/ C typical I B Drift Low Noise.5 V p-p typical Noise,. Hz to Hz Low Power 6 A max Supply
Precision, Low Power, Micropower Dual Operational Amplifier OP290
 Precision, Low Power, Micropower Dual Operational Amplifier OP9 FEATURES Single-/dual-supply operation:. V to 3 V, ±.8 V to ±8 V True single-supply operation; input and output voltage Input/output ranges
Precision, Low Power, Micropower Dual Operational Amplifier OP9 FEATURES Single-/dual-supply operation:. V to 3 V, ±.8 V to ±8 V True single-supply operation; input and output voltage Input/output ranges
LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF444 quad low power operational amplifier provides many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM148 while
LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF444 quad low power operational amplifier provides many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM148 while
CA3140, CA3140A. 4.5MHz, BiMOS Operational Amplifier with MOSFET Input/Bipolar Output. Description. Features. Applications. Ordering Information
 November 99 SEMICONDUCTOR CA, CAA.MHz, BiMOS Operational Amplifier with MOSFET Input/Bipolar Output Features MOSFET Input Stage - Very High Input Impedance (Z IN ) -.TΩ (Typ) - Very Low Input Current (I
November 99 SEMICONDUCTOR CA, CAA.MHz, BiMOS Operational Amplifier with MOSFET Input/Bipolar Output Features MOSFET Input Stage - Very High Input Impedance (Z IN ) -.TΩ (Typ) - Very Low Input Current (I
Rail-to-Rail, 200kHz Op Amp with Shutdown in a Tiny, 6-Bump WLP
 19-579; Rev ; 12/1 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Rail-to-Rail, 2kHz Op Amp General Description The op amp features a maximized ratio of gain bandwidth (GBW) to supply current and is ideal for battery-powered
19-579; Rev ; 12/1 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Rail-to-Rail, 2kHz Op Amp General Description The op amp features a maximized ratio of gain bandwidth (GBW) to supply current and is ideal for battery-powered
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LM6142 and LM MHz Rail-to-Rail Input-Output Operational Amplifiers
 LM6142 and LM6144 17 MHz Rail-to-Rail Input-Output Operational Amplifiers General Description Using patent pending new circuit topologies, the LM6142/44 provides new levels of performance in applications
LM6142 and LM6144 17 MHz Rail-to-Rail Input-Output Operational Amplifiers General Description Using patent pending new circuit topologies, the LM6142/44 provides new levels of performance in applications
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
3 Circuit Theory. 3.2 Balanced Gain Stage (BGS) Input to the amplifier is balanced. The shield is isolated
 Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
Precision OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 OPA77 查询 OPA77 供应商 OPA77 OPA77 Precision OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW DRIFT:.µV/ C HIGH OPEN-LOOP GAIN: db min LOW QUIESCENT CURRENT:.mA typ REPLACES INDUSTRY-STANDARD
OPA77 查询 OPA77 供应商 OPA77 OPA77 Precision OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW DRIFT:.µV/ C HIGH OPEN-LOOP GAIN: db min LOW QUIESCENT CURRENT:.mA typ REPLACES INDUSTRY-STANDARD
ADA485-/ADA485- TABLE OF CONTENTS Features... Applications... Pin Configurations... General Description... Revision History... Specifications... 3 Spe
 NC NC NC NC 5 6 7 8 6 NC 4 PD 3 PD FEATURES Ultralow power-down current: 5 na/amplifier maximum Low quiescent current:.4 ma/amplifier High speed 75 MHz, 3 db bandwidth V/μs slew rate 85 ns settling time
NC NC NC NC 5 6 7 8 6 NC 4 PD 3 PD FEATURES Ultralow power-down current: 5 na/amplifier maximum Low quiescent current:.4 ma/amplifier High speed 75 MHz, 3 db bandwidth V/μs slew rate 85 ns settling time
LM6162/LM6262/LM6362 High Speed Operational Amplifier
 LM6162/LM6262/LM6362 High Speed Operational Amplifier General Description The LM6362 family of high-speed amplifiers exhibits an excellent speed-power product, delivering 300 V/µs and 100 MHz gain-bandwidth
LM6162/LM6262/LM6362 High Speed Operational Amplifier General Description The LM6362 family of high-speed amplifiers exhibits an excellent speed-power product, delivering 300 V/µs and 100 MHz gain-bandwidth
Precision, Low Power, Micropower Dual Operational Amplifier OP290
 a FEATURES Single-/Dual-Supply Operation, 1. V to 3 V,. V to 1 V True Single-Supply Operation; Input and Output Voltage Ranges Include Ground Low Supply Current (Per Amplifier), A Max High Output Drive,
a FEATURES Single-/Dual-Supply Operation, 1. V to 3 V,. V to 1 V True Single-Supply Operation; Input and Output Voltage Ranges Include Ground Low Supply Current (Per Amplifier), A Max High Output Drive,
Quad 150 MHz Rail-to-Rail Amplifier AD8044
 a FEATURES Single AD84 and Dual AD842 Also Available Fully Specified at + V, +5 V, and 5 V Supplies Output Swings to Within 25 mv of Either Rail Input Voltage Range Extends 2 mv Below Ground No Phase Reversal
a FEATURES Single AD84 and Dual AD842 Also Available Fully Specified at + V, +5 V, and 5 V Supplies Output Swings to Within 25 mv of Either Rail Input Voltage Range Extends 2 mv Below Ground No Phase Reversal
High Speed FET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA High Speed FET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS FEATURES FET INPUT: I B = 5pA max WIDE BANDWIDTH: MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz (khz) LOW DISTORTION:.% HIGH
OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA OPA High Speed FET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS FEATURES FET INPUT: I B = 5pA max WIDE BANDWIDTH: MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz (khz) LOW DISTORTION:.% HIGH
Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amp AD8599
 Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amp FEATURES Low noise: 1 nv/ Hz at 1 khz Low distortion: 5 db THD @ khz
Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amp FEATURES Low noise: 1 nv/ Hz at 1 khz Low distortion: 5 db THD @ khz
LM837 Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier
 LM837 Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier General Description The LM837 is a quad operational amplifier designed for low noise, high speed and wide bandwidth performance. It has a new type of output stage
LM837 Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier General Description The LM837 is a quad operational amplifier designed for low noise, high speed and wide bandwidth performance. It has a new type of output stage
LF153 LF253 - LF353 WIDE BANDWIDTH DUAL J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 LF153 LF253 - LF353 WIDE BANDWIDTH DUAL J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LOW POWER CONSUMPTION WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT
LF153 LF253 - LF353 WIDE BANDWIDTH DUAL J-FET OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LOW POWER CONSUMPTION WIDE COMMON-MODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
150 μv Maximum Offset Voltage Op Amp OP07D
 5 μv Maximum Offset Voltage Op Amp OP7D FEATURES Low offset voltage: 5 µv max Input offset drift:.5 µv/ C max Low noise:.25 μv p-p High gain CMRR and PSRR: 5 db min Low supply current:. ma Wide supply
5 μv Maximum Offset Voltage Op Amp OP7D FEATURES Low offset voltage: 5 µv max Input offset drift:.5 µv/ C max Low noise:.25 μv p-p High gain CMRR and PSRR: 5 db min Low supply current:. ma Wide supply
HA-2600, HA Features. 12MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers. Applications. Pinouts. Ordering Information
 HA26, HA26 September 998 File Number 292.3 2MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers HA26/26 are internally compensated bipolar operational amplifiers that feature very high input impedance (MΩ,
HA26, HA26 September 998 File Number 292.3 2MHz, High Input Impedance Operational Amplifiers HA26/26 are internally compensated bipolar operational amplifiers that feature very high input impedance (MΩ,
Very Low Distortion, Precision Difference Amplifier AD8274
 Very Low Distortion, Precision Difference Amplifier AD8274 FEATURES Very low distortion.2% THD + N (2 khz).% THD + N ( khz) Drives Ω loads Excellent gain accuracy.3% maximum gain error 2 ppm/ C maximum
Very Low Distortion, Precision Difference Amplifier AD8274 FEATURES Very low distortion.2% THD + N (2 khz).% THD + N ( khz) Drives Ω loads Excellent gain accuracy.3% maximum gain error 2 ppm/ C maximum
LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed
LF412 Low Offset, Low Drift Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, JFET input operational amplifiers with very low input offset voltage and guaranteed
LF453 Wide-Bandwidth Dual JFET-Input Operational Amplifiers
 LF453 Wide-Bandwidth Dual JFET-Input Operational Amplifiers General Description The LF453 is a low-cost high-speed dual JFET-input operational amplifier with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
LF453 Wide-Bandwidth Dual JFET-Input Operational Amplifiers General Description The LF453 is a low-cost high-speed dual JFET-input operational amplifier with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
Not Recommended for New Designs
 Not Recommended for New Designs The MAX9 was manufactured for Maxim by an outside wafer foundry using a process that is no longer available. It is not recommended for new designs. A Maxim replacement or
Not Recommended for New Designs The MAX9 was manufactured for Maxim by an outside wafer foundry using a process that is no longer available. It is not recommended for new designs. A Maxim replacement or
Single and Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amps AD8597/AD8599 PIN CONFIGURATIONS FEATURES APPLICATIONS
 Single and Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amps FEATURES Low noise:. nv/ Hz at khz Low distortion: db THD @ khz Input noise,. Hz to Hz:
Single and Dual, Ultralow Distortion, Ultralow Noise Op Amps FEATURES Low noise:. nv/ Hz at khz Low distortion: db THD @ khz Input noise,. Hz to Hz:
High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
 High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER FEATURES FET INPUT: I B = 2pA max HIGH SPEED: T S = 4µs (G =,.%) LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT: µv/ C max HIGH COMMON-MODE REJECTION:
High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER FEATURES FET INPUT: I B = 2pA max HIGH SPEED: T S = 4µs (G =,.%) LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT: µv/ C max HIGH COMMON-MODE REJECTION:
EE LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS & APPLICATIONS
 UNITII CHARACTERISTICS OF OPAMP 1. What is an opamp? List its functions. The opamp is a multi terminal device, which internally is quite complex. It is a direct coupled high gain amplifier consisting of
UNITII CHARACTERISTICS OF OPAMP 1. What is an opamp? List its functions. The opamp is a multi terminal device, which internally is quite complex. It is a direct coupled high gain amplifier consisting of
AD864/AD8642/AD8643 TABLE OF CONTENTS Specifications... 3 Electrical Characteristics... 3 Absolute Maximum Ratings... 5 ESD Caution... 5 Typical Perfo
 FEATURES Low supply current: 25 µa max Very low input bias current: pa max Low offset voltage: 75 µv max Single-supply operation: 5 V to 26 V Dual-supply operation: ±2.5 V to ±3 V Rail-to-rail output Unity-gain
FEATURES Low supply current: 25 µa max Very low input bias current: pa max Low offset voltage: 75 µv max Single-supply operation: 5 V to 26 V Dual-supply operation: ±2.5 V to ±3 V Rail-to-rail output Unity-gain
LF451 Wide-Bandwidth JFET-Input Operational Amplifier
 LF451 Wide-Bandwidth JFET-Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF451 is a low-cost high-speed JFET-input operational amplifier with an internally trimmed input offset voltage (BI- FET IITM
LF451 Wide-Bandwidth JFET-Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF451 is a low-cost high-speed JFET-input operational amplifier with an internally trimmed input offset voltage (BI- FET IITM
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz max High Gain: 100 min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz max High Gain: 100 min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% max Excellent Logarithmic
LP2902/LP324 Micropower Quad Operational Amplifier
 LP2902/LP324 Micropower Quad Operational Amplifier General Description The LP324 series consists of four independent, high gain internally compensated micropower operational amplifiers. These amplifiers
LP2902/LP324 Micropower Quad Operational Amplifier General Description The LP324 series consists of four independent, high gain internally compensated micropower operational amplifiers. These amplifiers
OBSOLETE. High Performance, BiFET Operational Amplifiers AD542/AD544/AD547 REV. B
 a FEATURES Ultralow Drift: 1 V/ C (AD547L) Low Offset Voltage: 0.25 mv (AD547L) Low Input Bias Currents: 25 pa max Low Quiescent Current: 1.5 ma Low Noise: 2 V p-p High Open Loop Gain: 110 db High Slew
a FEATURES Ultralow Drift: 1 V/ C (AD547L) Low Offset Voltage: 0.25 mv (AD547L) Low Input Bias Currents: 25 pa max Low Quiescent Current: 1.5 ma Low Noise: 2 V p-p High Open Loop Gain: 110 db High Slew
