SIMULATIONS WITH THE BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified February 2006
|
|
|
- Martina McCormick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIMULATIONS WITH THE BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 26 Page 1 of 24
2 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Boost converter using ORCAD to better familiarize the student with some of its operating characteristics. This lab will explore some of the following aspects of the boost converter: Discontinuous Conduction Mode Inductor sizing Differential voltage across the inductor Time it takes for the converter to reach steady state Output Ripple voltage and selection of the capacitor. Ripple current through the capacitor Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) of the output capacitor. Effects of changing and removing load resistance Effects of the ON resistance of the switch Efficiency Effects of changing frequency NOTE: The simulations that follow are intended to be completed with ORCAD Capture CIS. It is assumed that the student has a fundamental understanding of the operation of ORCAD. ORCAD provides tutorials for users that are not experienced with its functions. PROCEDURE: Build the schematic shown in Figure 1. V1 is a DC voltage source (VDC) from the source library. It needs to be set for 24 volts. L1 is an ideal inductor from the Analog Library. Set for 1µH. R1 is an ideal resistor from the Analog Library. Set for 1kΩ. D1 is an ideal diode (Dbreak) and can be found in the Breakout library. C1 is an ideal capacitor from the Analog library. Change the value to 1µ F. Page 2 of 24
3 S2 is a voltage controlled switch and can be found in the Analog library. Change RON from 1Ω to 1mΩ. V2 is a pulsed voltage source and is intended to act as the output of a pulse width modulator. V2 needs the following parameters set: DC=, AC = 1, V1=, V2= 1, TR=1ns, TF=1ns, PW = 2µ, PER = 4µ. This results in a switching frequency of 25 khz. R2 Set to 1 kω. The purpose of R1 is to prevent any floating nodes. Two voltage markers need to be placed as shown in the schematic of figure 1. Figure 1 Boost schematic ORCAD. Once the above schematic is built simulations can be ran. First, the type of simulation will need to be specified. Most of these simulations are Transient simulations. The Transient simulation can be set by selecting PSpice on the menu then New Simulation Profile. The Run Time will need to be set to 1µsec. Page 3 of 24
4 Figure 2 Transient Analysis setup. Running the simulation will result in the following output. Figure 3 Page 4 of 24
5 Remove the voltage markers, and use a current marker to measure the inductor L1 current. Place the marker in series next to L1. Figure 4 QUESTION 1: What is the peak operating current, and what is the operating mode of the converter? Verify mathematically the mode and the peak current. 2L 2 Hint: K =, Kcrit D(1 D) RTs =, Vin = L Ipk DTs Figure 5 Page 5 of 24
6 QUESTION 2: What is the output voltage of the converter at steady state? Verify your results mathematically. Hint: 1+ Vout = Vin 4 D1 1+ K 2 2 Figure 6 Page 6 of 24
7 Now change L1 from 1µH to 1mH and rerun the simulation. Remember you can vary the Final Time in Transient Analysis. Keep the Print Step at. (Hint: Start this analysis with a Final Time = 1msec) QUESTION 3: What is the peak operating current now? What is the operating mode of the converter (remember that you can observe this by zooming in)? Also, verify the mode mathematically. Figure 7 Page 7 of 24
8 QUESTION 4: How long does it take for the converter to reach steady state? What is the peak inductor current during steady state? Verify peak current result mathematically. Hint: Vin = L Ipk DTs Figure 8 QUESTION 5: Calculate the size of the inductor required to put this converter in CCM. Hint: R Ts D(1 D) L 2 2 Page 8 of 24
9 Remove the current marker and add a differential voltage marker across L1. Change the Run to time to 18u and Start saving data after 15u. Figure 9 QUESTION 6: What can be said about the differential voltage measurement across L1? Figure 1 Page 9 of 24
10 Now change the Final Time to 25µ and remove any No Print Delay from the Transient Analysis setup. Remove the differential voltage markers across L1 and add a voltage marker to the top of C1. From this simulation we can see the output voltage stair step up to its final value. Figure 11 QUESTION 7: How long does it take for the output voltage to reach its peak? Figure 12 Page 1 of 24
11 QUESTION 8: How long does it take for the output voltage to reach its final value? What is the output voltage? Prove your simulation results mathematically (Vout). Hint: 1+ Vout = Vin 4 D1 1+ K 2 2 Figure 13 Now run the simulation for 1 µsec at a time greater than 2 µsec. QUESTION 9: What is the peak-to-peak ripple voltage? Figure 14 Page 11 of 24
12 QUESTION 1: With everything else left as is, what is the minimum output capacitance be to limit the output voltage ripple to 2 volts peak to peak? Figure 15 Now, place a current marker on one of the pins of the capacitor. Run the simulation for 2 µsec at a time greater than 1 msec. QUESTION 11: What can be said about the current through the capacitor? Figure 16 Page 12 of 24
13 QUESTION 12: If the ESR of the capacitor is modeled by a 1Ω resistor in series with the capacitor. What happens to the output voltage ripple and the capacitor current? Figure 17 Figure 18 Page 13 of 24
14 Figure 19 Page 14 of 24
15 Change the load resistance from 1kΩ to 1Ω with C=1µFand L=1mH. QUESTION 13: What happens to the inductor ripple current, capacitor ripple voltage, and capacitor current with respect to the original values? Figure 2 Figure 21 Page 15 of 24
16 QUESTIONS 14: What operating mode is the converter in now? QUESTION 15: What happens if the load resistance is removed? Figure 22 Figure 23 Replace the load resistance. QUESTION 16: What observations can be made from increasing the on resistance of the switch? Page 16 of 24
17 Figure 24 Figure 25 *Remember that your on resistance value of the switch will provide you a complete different output value from your classmates. QUESTION 17: What can be said about the efficiency of the converter? (Comment on the different configurations of the circuit used throughout this lab.) η = Pout Pin η = ( Vo Vg)*(1 D) Page 17 of 24
18 QUESTION 18: What can be observed by increasing the switching frequency to 1KHz? Hints: With everything else left as it is, change your PW and PER on PULSED voltage to 5u and 1u. Also change your Run to time in the simulation profile to 1 finaltime := 25 Switchfrequency. Figure 26 Page 18 of 24
19 Vg := 24 V L := H C := F R := Ω Duty cycle Switchfrequency := Hz 1 T := Switchfrequency PW := Duty cycle PW T = D f D := Switchfrequency PW D =.5 The output voltage Vo Vg 1 1 D 1 Vg 1 + D 1 Vo := 1 + Vg D Vo = 48 Inductor current Vin L il D T 1 il:= L Vg D T il = 48 Vo Io := R Io =.48 Page 19 of 24
20 IL := Io 1 D IL =.96 ILmin:= IL il ILmin = ILmax:= IL + il 2 ILmax= t := D T D T ( 1 D) T ( 1 D) T ( 1 D) T T T VL:= Vg Vg Vg Vg Vo Vg Vo Vg Vo Vg Vo Vg t1 := D T D T T IL1:= ILmin ILmax ILmax ILmin 4 Inductor voltage 4 inductor current inductor Voltage V VL 2 2 inductor current A IL1 2 2 ILmax is := id := t duty cycle ILmin ILmax ILmin t1 duty cycle ic := Io Io ILmax Io ILmax Io Page 2 of 24
21 capacitor current (A) ic Capacitor current t1 duty cycle Icmax:= ILmax Io Icmax = switch current diode current Vs. duty cycle 4 current A is 2 2 diode current (A) id t1 duty cycle Is := D IL Is = t1 ID duty := ( 1 cycle D) IL ID =.48 2 L K := K = R T Kcrit := D ( 1 D) 2 Kcrit =.125 D1 :=.1, DC gain for K>Kcrit V Vg 1 ( 1 D) M( D1) := 1 ( 1 D1) M1( t) := t 2 K Page 21 of 24
22 1 DC gain V/Vg M( D1) D1 Duty cycle 1 Vo := C Io D T Vo = for K<Kcrit DC gain vs. duty cycle 6 DC gain M1( D1) D1 duty cycle Page 22 of 24
23 Input and output Power Po := Io Vo Po = 2.34 W Ig := IL Pg := Ig Vg Pg = 2.34 W Efficiency η Pout pin Vo η := Vg ( 1 D) η = 1 DCM/CCM boundary Case 1: When inductor, switching frequency and other circuit parameters are constant, but R is varied ilmin:= ilmax:= il il il1:= 2 Io1 := ( 1 D) il1 il1 = 24 Io1 = 12 Vo R := R = 4 Io1 inductor current Vs. duty cycle 6 IL1:= ilmin ilmax ilmax ilmin inductor current IL t1 duty cycle Case 2: when R, switching frequency and other circuit parameters are constant, but L is varied ilmin:= ilmax:= 2 IL ilmax=.192 il:= ilmax Page 23 of 24
24 1 Lmin := il Vg D T Lmin = il2:= ilmin ilmax ilmax ilmin.2 il t1 R T D ( 1 D) 2 L1:= 2 L1 = Page 24 of 24
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified February 2006
 SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
SIMULATION WITH THE BOOST TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified in Fall 2011
 SIMULATION WITH THE BOOST TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Boost Converter (NL5 Simulation) Laboratory 2 Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this
SIMULATION WITH THE BOOST TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Boost Converter (NL5 Simulation) Laboratory 2 Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this
PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Created by Colorado State University student
 PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Created by Colorado State University student Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the resonant
PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Created by Colorado State University student Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the resonant
SIMULATION WITH THE CUK TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified in Fall 2011
 SIMULATION WITH THE CUK TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Cuk Converter (NL5 Simulation) Laboratory Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is
SIMULATION WITH THE CUK TOPOLOGY ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Cuk Converter (NL5 Simulation) Laboratory Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is
SIMULATION OF A SERIES RESONANT CIRCUIT ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified in Fall 2011
 SIMULATION OF A SERIES RESONANT CIRCUIT ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Series Resonant Circuit (NL5 Simulation) Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this
SIMULATION OF A SERIES RESONANT CIRCUIT ECE562: Power Electronics I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Fall 2011 ECE 562 Series Resonant Circuit (NL5 Simulation) Page 1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this
SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified in Spring 2006
 SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Spring 2006 Page 1 of 27 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and CAPTURE
SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Spring 2006 Page 1 of 27 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and CAPTURE
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE
 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
Principle Of Step-up Chopper
 Principle Of Step-up Chopper L + D + V Chopper C L O A D V O 1 Step-up chopper is used to obtain a load voltage higher than the input voltage V. The values of L and C are chosen depending upon the requirement
Principle Of Step-up Chopper L + D + V Chopper C L O A D V O 1 Step-up chopper is used to obtain a load voltage higher than the input voltage V. The values of L and C are chosen depending upon the requirement
Engineering 3821 Fall Pspice TUTORIAL 1. Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill
 Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter
![ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter](/thumbs/72/67440195.jpg) ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies Homework Assignment #4 Due date October 31, 2014, beginning of the lecture Part 1 [100 pts] Redo Term Test 1 (attached) Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber
ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies Homework Assignment #4 Due date October 31, 2014, beginning of the lecture Part 1 [100 pts] Redo Term Test 1 (attached) Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber
Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits
 Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior
Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior
LAB1 WEBENCH SIMULATION EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
 LAB1 WEBENCH SIMULATION EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to explore National Semiconductors WEBENCH, which is an online design and prototyping tool.
LAB1 WEBENCH SIMULATION EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to explore National Semiconductors WEBENCH, which is an online design and prototyping tool.
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, 2 nd Order Circuits
 LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
Two Stage Interleaved Boost Converter Design and Simulation in CCM and DCM
 Two Stage Interleaved Boost Converter Design and Simulation in CCM and DCM Ajit T N PG Student (MTech, Power Electronics) Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Reva Institute of Technology
Two Stage Interleaved Boost Converter Design and Simulation in CCM and DCM Ajit T N PG Student (MTech, Power Electronics) Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Reva Institute of Technology
Cal Poly SuPER System Photovoltaic Array Universal DC-DC Step Down Converter
 Cal Poly SuPER System Photovoltaic Array Universal DC-DC Step Down Converter A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial Fulfillment of the
Cal Poly SuPER System Photovoltaic Array Universal DC-DC Step Down Converter A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial Fulfillment of the
Chapter 2 Buck PWM DC DC Converter
 Chapter 2 Buck PWM DC DC Converter H. Wang, Power Management and High-speed I/O in CMOS Systems 1/25 Buck Circuit and Its equivalent circuits CCM: continuous conduction mode DCM: discontinuous conduction
Chapter 2 Buck PWM DC DC Converter H. Wang, Power Management and High-speed I/O in CMOS Systems 1/25 Buck Circuit and Its equivalent circuits CCM: continuous conduction mode DCM: discontinuous conduction
DESCRIPTION FEATURES APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATION. 500KHz, 18V, 2A Synchronous Step-Down Converter
 DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated, high-efficiency 2A synchronous rectified step-down converter. The operates at high efficiency over a wide output current load range. This device offers two operation
DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated, high-efficiency 2A synchronous rectified step-down converter. The operates at high efficiency over a wide output current load range. This device offers two operation
AC : PSCAD SIMULATION IN A POWER ELECTRONICS APPLICATION COURSE
 AC 2007-2855: PSCAD SIMULATION IN A POWER ELECTRONICS APPLICATION COURSE Liping Guo, University of Northern Iowa Liping Guo received the B. E. degree in Automatic Control from Beijing Institute of Technology,
AC 2007-2855: PSCAD SIMULATION IN A POWER ELECTRONICS APPLICATION COURSE Liping Guo, University of Northern Iowa Liping Guo received the B. E. degree in Automatic Control from Beijing Institute of Technology,
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 2186 TRIMESTER 1 (218/219) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice *Note: You will be given an assessment sheet during the lab session to be completed
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 2186 TRIMESTER 1 (218/219) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice *Note: You will be given an assessment sheet during the lab session to be completed
Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program.
 PSpice Analysis Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program. PSpice can be downloaded from the following
PSpice Analysis Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program. PSpice can be downloaded from the following
Sample Exam Solution
 Session 44; 1/6 Sample Exam Solution Problem 1: You are given a single phase diode rectifier, as shown below. Do the following: L d I s v (t) s L s C d V d Load : 310V Xs : 0.4ohm at 400 Hz Vspk : 360V
Session 44; 1/6 Sample Exam Solution Problem 1: You are given a single phase diode rectifier, as shown below. Do the following: L d I s v (t) s L s C d V d Load : 310V Xs : 0.4ohm at 400 Hz Vspk : 360V
A8133 HIGH EFFICIENCY, HIGH POWER WHITE LED DRIVER 1MHz FREQUENCY, INTERNAL 2A MOSFET SWITCH
 DESCRIPTION The is a boost DC-DC converter that delivers a regulated output current. The switches at a 1.0MHz constant frequency, allowing for the use of small value external inductor and ceramic capacitors.
DESCRIPTION The is a boost DC-DC converter that delivers a regulated output current. The switches at a 1.0MHz constant frequency, allowing for the use of small value external inductor and ceramic capacitors.
ACT111A. 4.8V to 30V Input, 1.5A LED Driver with Dimming Control GENERAL DESCRIPTION FEATURES APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
 4.8V to 30V Input, 1.5A LED Driver with Dimming Control FEATURES Up to 92% Efficiency Wide 4.8V to 30V Input Voltage Range 100mV Low Feedback Voltage 1.5A High Output Capacity PWM Dimming 10kHz Maximum
4.8V to 30V Input, 1.5A LED Driver with Dimming Control FEATURES Up to 92% Efficiency Wide 4.8V to 30V Input Voltage Range 100mV Low Feedback Voltage 1.5A High Output Capacity PWM Dimming 10kHz Maximum
Low Cost 8W Off-line LED Driver using RT8487
 Application Note AN019 Jun 2014 Low Cost 8W Off-line LED Driver using RT8487 Abstract RT8487 is a boundary mode constant current controller with internal high side driver, which can be used in buck and
Application Note AN019 Jun 2014 Low Cost 8W Off-line LED Driver using RT8487 Abstract RT8487 is a boundary mode constant current controller with internal high side driver, which can be used in buck and
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling
 Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
Advances in Averaged Switch Modeling Robert W. Erickson Power Electronics Group University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado USA 80309-0425 rwe@boulder.colorado.edu http://ece-www.colorado.edu/~pwrelect 1
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme
 Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
Power Factor Pre-regulator Using Constant Tolerance Band Control Scheme Akanksha Mishra, Anamika Upadhyay Akanksha Mishra is a lecturer ABIT, Cuttack, India (Email: misakanksha@gmail.com) Anamika Upadhyay
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 286 TRIMESTER (26/27) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice Experiment : Circuit analysis using ORCAD Pspice PRECAUTIONARY STEPS:. Read this experiment
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 286 TRIMESTER (26/27) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice Experiment : Circuit analysis using ORCAD Pspice PRECAUTIONARY STEPS:. Read this experiment
Experiment DC-DC converter
 POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
Introduction to SPICE. Simulator of Electronic devices
 Introduction to SPICE Simulator of Electronic devices Main steps: Download Instalation Open OrCAD capture CIS Lite Create a circuit. Place parts. Design a Simulation Profile Run PSpice F11 View simulation
Introduction to SPICE Simulator of Electronic devices Main steps: Download Instalation Open OrCAD capture CIS Lite Create a circuit. Place parts. Design a Simulation Profile Run PSpice F11 View simulation
3A, 36V, Step-Down Converter
 3A, 36, Step-Down Converter FP6150 General Description The FP6150 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 3A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with
3A, 36, Step-Down Converter FP6150 General Description The FP6150 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 3A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with
TFT-LCD DC/DC Converter with Integrated Backlight LED Driver
 TFT-LCD DC/DC Converter with Integrated Backlight LED Driver Description The is a step-up current mode PWM DC/DC converter (Ch-1) built in an internal 1.6A, 0.25Ω power N-channel MOSFET and integrated
TFT-LCD DC/DC Converter with Integrated Backlight LED Driver Description The is a step-up current mode PWM DC/DC converter (Ch-1) built in an internal 1.6A, 0.25Ω power N-channel MOSFET and integrated
Voltage Gain Enhancement Using Ky Converter
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 27-34 www.iosrjournals.org Voltage Gain Enhancement Using Ky Converter Meera R Nair 1, Ms. Priya
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 27-34 www.iosrjournals.org Voltage Gain Enhancement Using Ky Converter Meera R Nair 1, Ms. Priya
ANP012. Contents. Application Note AP2004 Buck Controller
 Contents 1. AP004 Specifications 1.1 Features 1. General Description 1. Pin Assignments 1.4 Pin Descriptions 1.5 Block Diagram 1.6 Absolute Maximum Ratings. Hardware.1 Introduction. Typical Application.
Contents 1. AP004 Specifications 1.1 Features 1. General Description 1. Pin Assignments 1.4 Pin Descriptions 1.5 Block Diagram 1.6 Absolute Maximum Ratings. Hardware.1 Introduction. Typical Application.
D1 GS SS12 AIC AIC AIC AIC VOUT GND. One Cell Step-Up DC/DC Converter
 1-Cell, 3-Pin, Step-Up DC/DC Converter FEATURES A Guaranteed Start-Up from less than 0.9 V. High Efficiency. Low Quiescent Current. Less Number of External Components needed. Low Ripple and Low Noise.
1-Cell, 3-Pin, Step-Up DC/DC Converter FEATURES A Guaranteed Start-Up from less than 0.9 V. High Efficiency. Low Quiescent Current. Less Number of External Components needed. Low Ripple and Low Noise.
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter
 2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
A Fast, Self-stabilizing, Boost DC-DC Converter - Sliding-mode Vs Hysteretic Controls
 A Fast, Self-stabilizing, Boost DC-DC Converter - Sliding-mode Vs Hysteretic Controls Neeraj Keskar Advisor: Prof. Gabriel A. Rincón-Mora Analog and Power IC Design Lab School of Electrical and Computer
A Fast, Self-stabilizing, Boost DC-DC Converter - Sliding-mode Vs Hysteretic Controls Neeraj Keskar Advisor: Prof. Gabriel A. Rincón-Mora Analog and Power IC Design Lab School of Electrical and Computer
AA SERIES (1 x 1 Package) Up to 10 Watt DC-DC Converter
 FEATURES Industry standard footprint (1 inch X 1 inch) Regulated Outputs, Fixed Switching Frequency Up to 87 % Efficiency Low No Load Power Consumption Designed for use without tantalum capacitors -40
FEATURES Industry standard footprint (1 inch X 1 inch) Regulated Outputs, Fixed Switching Frequency Up to 87 % Efficiency Low No Load Power Consumption Designed for use without tantalum capacitors -40
UC Berkeley, EECS Department
 UC Berkeley, EECS Department B. Boser EECS 4 Lab LAB5: Boost Voltage Supply UID: Boost Converters We have tried to use resistors (voltage dividers) to transform voltages but found that these solutions
UC Berkeley, EECS Department B. Boser EECS 4 Lab LAB5: Boost Voltage Supply UID: Boost Converters We have tried to use resistors (voltage dividers) to transform voltages but found that these solutions
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter
 Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Designing and Implementing of 72V/150V Closed loop Boost Converter for Electoral Vehicle
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 77 4106, P-ISSN 347 5161 017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Designing
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 77 4106, P-ISSN 347 5161 017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Designing
FP kHz 7A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter
 500kHz 7A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter General Description The FP6277 is a current mode boost DC-DC converter with PWM/PSM control. Its PWM circuitry with built-in 30mΩ high side switch
500kHz 7A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter General Description The FP6277 is a current mode boost DC-DC converter with PWM/PSM control. Its PWM circuitry with built-in 30mΩ high side switch
MPM V-5.5V, 4A, Power Module, Synchronous Step-Down Converter with Integrated Inductor
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MPM3840 2.8V-5.5V, 4A, Power Module, Synchronous Step-Down Converter with Integrated Inductor DESCRIPTION The MPM3840 is a DC/DC module that includes a monolithic, step-down,
The Future of Analog IC Technology MPM3840 2.8V-5.5V, 4A, Power Module, Synchronous Step-Down Converter with Integrated Inductor DESCRIPTION The MPM3840 is a DC/DC module that includes a monolithic, step-down,
340KHz, 2A, Asynchronous Step-Down Regulator
 340KHz, 2A, Asynchronous Step-Down Regulator FP6115 General Description The FP6115 is a buck switching regulator for wide operating voltage application fields. The FP6115 includes a high current P-MOSFET,
340KHz, 2A, Asynchronous Step-Down Regulator FP6115 General Description The FP6115 is a buck switching regulator for wide operating voltage application fields. The FP6115 includes a high current P-MOSFET,
EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits I. Introduction In transient analyses, we determine voltages and currents as functions of time. Typically, the time dependence is demonstrated
EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits I. Introduction In transient analyses, we determine voltages and currents as functions of time. Typically, the time dependence is demonstrated
Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink
 Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink Extensive introductory tutorials for MATLAB and Simulink, including Control Systems Toolbox and Simulink Control Design
Introduction to Modeling of Switched Mode Power Converters Using MATLAB and Simulink Extensive introductory tutorials for MATLAB and Simulink, including Control Systems Toolbox and Simulink Control Design
A7221A DC-DC CONVERTER/BUCK (STEP-DOWN) 600KHz, 16V, 2A SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
 DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated, high efficiency 2A synchronous rectified step-down converter. The operates at high efficiency over a wide output current load range. This device offers two operation
DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated, high efficiency 2A synchronous rectified step-down converter. The operates at high efficiency over a wide output current load range. This device offers two operation
EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II. Issa Batarseh. January 13, 2015
 EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II Issa Batarseh January 13, 2015 Agenda About the course Syllabus Review Course Topics Review of Power Electronics I Questions Introduction (cont d) Introduction (cont d) 5
EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II Issa Batarseh January 13, 2015 Agenda About the course Syllabus Review Course Topics Review of Power Electronics I Questions Introduction (cont d) Introduction (cont d) 5
Power Management for Computer Systems. Prof. C Wang
 ECE 5990 Power Management for Computer Systems Prof. C Wang Fall 2010 Course Outline Fundamental of Power Electronics cs for Computer Systems, Handheld Devices, Laptops, etc More emphasis in DC DC converter
ECE 5990 Power Management for Computer Systems Prof. C Wang Fall 2010 Course Outline Fundamental of Power Electronics cs for Computer Systems, Handheld Devices, Laptops, etc More emphasis in DC DC converter
LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial. TA: 黃玉龍
 OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial TA: 黃玉龍 r9994320@ntu.edu.tw Outline 2 Introduction Preparation Schematic Simulation Conclusion Introduction 3 OrCAD PSpice is developed by Cadence Analog circuit simulation tool
OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial TA: 黃玉龍 r9994320@ntu.edu.tw Outline 2 Introduction Preparation Schematic Simulation Conclusion Introduction 3 OrCAD PSpice is developed by Cadence Analog circuit simulation tool
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE
 MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
CHAPTER 3 APPLICATION OF THE CIRCUIT MODEL FOR PHOTOVOLTAIC ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM
 63 CHAPTER 3 APPLICATION OF THE CIRCUIT MODEL FOR PHOTOVOLTAIC ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM 3.1 INTRODUCTION The power output of the PV module varies with the irradiation and the temperature and the output
63 CHAPTER 3 APPLICATION OF THE CIRCUIT MODEL FOR PHOTOVOLTAIC ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM 3.1 INTRODUCTION The power output of the PV module varies with the irradiation and the temperature and the output
Xcircuit and Spice. February 26, 2007
 Xcircuit and Spice February 26, 2007 This week we are going to start with a new tool, namely Spice. Spice is a circuit simulator. The variant of spice we will use here is called Spice-Opus, and is a combined
Xcircuit and Spice February 26, 2007 This week we are going to start with a new tool, namely Spice. Spice is a circuit simulator. The variant of spice we will use here is called Spice-Opus, and is a combined
Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens and from the pull down menus you can start your design. Figure 2.
 Running Cadence Once the Cadence environment has been setup you can start working with Cadence. You can run cadence from your directory by typing Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens
Running Cadence Once the Cadence environment has been setup you can start working with Cadence. You can run cadence from your directory by typing Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens
3A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter
 3A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 3A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
3A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 3A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
HT7938A High Current and Performance White LED Driver
 High Current and Performance White LED Driver Feature Efficiency up to 90% at V IN =4.0V, 5S2P, I LED =20mA 1.2MHz fixed switching frequency Low standby current: 0.1mA (typ.) at V EN =0V Matches LED current
High Current and Performance White LED Driver Feature Efficiency up to 90% at V IN =4.0V, 5S2P, I LED =20mA 1.2MHz fixed switching frequency Low standby current: 0.1mA (typ.) at V EN =0V Matches LED current
ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE
 Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Power Electronics in PV Systems
 Introduction to Power Electronics in PV Systems EEN 2060 References: EEN4797/5797 Intro to Power Electronics ece.colorado.edu/~ecen5797 Textbook: R.W.Erickson, D.Maksimovic, Fundamentals of Power Electronics,
Introduction to Power Electronics in PV Systems EEN 2060 References: EEN4797/5797 Intro to Power Electronics ece.colorado.edu/~ecen5797 Textbook: R.W.Erickson, D.Maksimovic, Fundamentals of Power Electronics,
A New Averaged Switch Model Including Conduction Losses for PWM Converters Operating in Discontinuous Inductor Current Mode
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 19, no. 2, August 2006, 219-230 A New Averaged Switch Model Including Conduction Losses for PWM Converters Operating in Discontinuous Inductor Current
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 19, no. 2, August 2006, 219-230 A New Averaged Switch Model Including Conduction Losses for PWM Converters Operating in Discontinuous Inductor Current
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFET AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATIONS AND INPUT/OUTPUT IMPEDANCE OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFET AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATIONS AND INPUT/OUTPUT IMPEDANCE OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment
MP A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP24943 3A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP24943 is a monolithic, step-down, switch-mode converter. It supplies
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP24943 3A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP24943 is a monolithic, step-down, switch-mode converter. It supplies
Purpose. Table of Contents. Purpose...1. Introduction...2. General Product Information...2. Key Performance Summary Table...3
 Purpose The RT8008 is a high-efficiency 1.5MHz current mode synchronous step-down regulator that can deliver up to 600mA output current from an input voltage range of 2.5V to 5.5V. This document explains
Purpose The RT8008 is a high-efficiency 1.5MHz current mode synchronous step-down regulator that can deliver up to 600mA output current from an input voltage range of 2.5V to 5.5V. This document explains
Problem 1: Voltage Limiting 1.1. Simulate the following simple resistor-diode circuit (shown on the left in Figure 1):
 EEE 33 Electronics I (Summer 218) PSPICE: Diode Applications Diode Limiters, Rectifiers and Voltage Regulation (Due Tuesday, June 26, 218) Homework 2 Problem 1: Voltage Limiting 1.1. Simulate the following
EEE 33 Electronics I (Summer 218) PSPICE: Diode Applications Diode Limiters, Rectifiers and Voltage Regulation (Due Tuesday, June 26, 218) Homework 2 Problem 1: Voltage Limiting 1.1. Simulate the following
TSTE25 Power Electronics. Lecture 6 Tomas Jonsson ISY/EKS
 TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 6 Tomas Jonsson ISY/EKS 2016-11-15 2 Outline DC power supplies DC-DC Converter Step-down (buck) Step-up (boost) Other converter topologies (overview) Exercises 7-1, 7-2,
TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 6 Tomas Jonsson ISY/EKS 2016-11-15 2 Outline DC power supplies DC-DC Converter Step-down (buck) Step-up (boost) Other converter topologies (overview) Exercises 7-1, 7-2,
Lab Session 4 Hardware
 Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I
 Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of diodes. We used a 1N914 diode in two previous experiments, but now we
Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of diodes. We used a 1N914 diode in two previous experiments, but now we
Vout Adjust V OUT LOAD GND
 PT6705 Series 13 Amp 5V/3.3V Input Adjustable Integrated Switching Regulator New Space-Saving Package 3.3V/5V input (12V Bias) Adjustable Output Voltage 90% Efficiency Differential Remote Sense 17-pin
PT6705 Series 13 Amp 5V/3.3V Input Adjustable Integrated Switching Regulator New Space-Saving Package 3.3V/5V input (12V Bias) Adjustable Output Voltage 90% Efficiency Differential Remote Sense 17-pin
DIO6305 High-Efficiency 1.2MHz, 1.1A Synchronous Step-Up Converter
 High-Efficiency 1.2MHz, 1.1A Synchronous Step-Up Converter Rev 1.2 Features High-Efficiency Synchronous-Mode 2.7-5.25V input voltage range Device Quiescent Current: 30µA (TYP) Less than 1µA Shutdown Current
High-Efficiency 1.2MHz, 1.1A Synchronous Step-Up Converter Rev 1.2 Features High-Efficiency Synchronous-Mode 2.7-5.25V input voltage range Device Quiescent Current: 30µA (TYP) Less than 1µA Shutdown Current
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
SE014S110 Power Module; dc-dc Converter: 48 Vdc Input, 110 Vdc Output, 14 W
 Data Sheet SE014S110 Power Module; dc-dc Converter: Features The SE014S110 Power Module uses advanced, surface-mount technology and delivers high-quality, compact, dc-dc conversion at an economical price.
Data Sheet SE014S110 Power Module; dc-dc Converter: Features The SE014S110 Power Module uses advanced, surface-mount technology and delivers high-quality, compact, dc-dc conversion at an economical price.
Notes. 1. Midterm 1 Thursday February 24 in class.
 Notes 1. Midterm 1 Thursday February 24 in class. Covers through text Sec. 4.3, topics of HW 4. GSIs will review material in discussion sections prior to the exam. No books at the exam, no cell phones,
Notes 1. Midterm 1 Thursday February 24 in class. Covers through text Sec. 4.3, topics of HW 4. GSIs will review material in discussion sections prior to the exam. No books at the exam, no cell phones,
FP6276B 500kHz 6A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter
 500kHz 6A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter General Description The is a current mode boost DC-DC converter with PWM/PSM control. Its PWM circuitry with built-in 40mΩ high side switch and
500kHz 6A High Efficiency Synchronous PWM Boost Converter General Description The is a current mode boost DC-DC converter with PWM/PSM control. Its PWM circuitry with built-in 40mΩ high side switch and
PWM Controlled, Step-up DC/DC Converter in Tiny Package
 PWM Controlled, Step-up DC/DC Converter in Tiny Package Description The is a high efficiency PWM DC/DC step -up converter with internally compensated current mode controller. The output voltage is set
PWM Controlled, Step-up DC/DC Converter in Tiny Package Description The is a high efficiency PWM DC/DC step -up converter with internally compensated current mode controller. The output voltage is set
AS SERIES (2.00 x 1.6 Package) Up to 20 Watt DC-DC Converter
 PRODUCT OVERVIEW The AS series offer up to 20 watts of output power in standard 2.00 x 1.60 x 0.45 inches packages. This series features high efficiency and 1500 Volts of DC isolation. The AS series provides
PRODUCT OVERVIEW The AS series offer up to 20 watts of output power in standard 2.00 x 1.60 x 0.45 inches packages. This series features high efficiency and 1500 Volts of DC isolation. The AS series provides
Low-Noise 4.5A Step-Up Current Mode PWM Converter
 Low-Noise 4.5A Step-Up Current Mode PWM Converter FP6298 General Description The FP6298 is a current mode boost DC-DC converter. It is PWM circuitry with built-in 0.08Ω power MOSFET make this regulator
Low-Noise 4.5A Step-Up Current Mode PWM Converter FP6298 General Description The FP6298 is a current mode boost DC-DC converter. It is PWM circuitry with built-in 0.08Ω power MOSFET make this regulator
4 Experiment 3: DC to DC Converters
 4 Experiment 3: DC to DC Converters 4.1 Purpose and Goals In this experiment the student will study DC-DC converters and their applications. It will introduce the use of PWM ( Pulse Width Modulation )
4 Experiment 3: DC to DC Converters 4.1 Purpose and Goals In this experiment the student will study DC-DC converters and their applications. It will introduce the use of PWM ( Pulse Width Modulation )
NB634 High Effeciency 5A, 24V, 500kHz Synchronous Step-down Converter
 The Future of Analog IC Technology NB634 High Effeciency 5A, 24, 500kHz Synchronous Step-down Converter DESCRIPTION The NB634 is a high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter with
The Future of Analog IC Technology NB634 High Effeciency 5A, 24, 500kHz Synchronous Step-down Converter DESCRIPTION The NB634 is a high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter with
A Brief Handout for Introduction to
 A Brief Handout for Introduction to Electric cal Engineering Course This handout is a compilation of PSPICE, A Brief Primer, Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, University of Pennsylvania
A Brief Handout for Introduction to Electric cal Engineering Course This handout is a compilation of PSPICE, A Brief Primer, Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, University of Pennsylvania
1.5MHz, 3A Synchronous Step-Down Regulator
 1.5MHz, 3A Synchronous Step-Down Regulator FP6165 General Description The FP6165 is a high efficiency current mode synchronous buck PWM DC-DC regulator. The internal generated 0.6V precision feedback reference
1.5MHz, 3A Synchronous Step-Down Regulator FP6165 General Description The FP6165 is a high efficiency current mode synchronous buck PWM DC-DC regulator. The internal generated 0.6V precision feedback reference
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 6.3.5. Boost-derived isolated converters A wide variety of boost-derived isolated dc-dc converters
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 6.3.5. Boost-derived isolated converters A wide variety of boost-derived isolated dc-dc converters
Purpose. Table of Contents. Purpose Introduction General Product Information Key Performance Summary Table... 3
 Purpose The RT8295A is a high-efficiency current mode synchronous step-down regulator that can deliver up to 2A output current from a wide input voltage range of 4.5V to 23V. This document explains the
Purpose The RT8295A is a high-efficiency current mode synchronous step-down regulator that can deliver up to 2A output current from a wide input voltage range of 4.5V to 23V. This document explains the
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab. Prelab Part I: RC Circuit
 EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
Week 9: Series RC Circuit. Experiment 14
 Week 9: Series RC Circuit Experiment 14 Circuit to be constructed It is good practice to short the unused pin on the trimpot when using it as a variable resistor Velleman function generator Shunt resistor
Week 9: Series RC Circuit Experiment 14 Circuit to be constructed It is good practice to short the unused pin on the trimpot when using it as a variable resistor Velleman function generator Shunt resistor
MP A, 24V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2371 1.8A, 24V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The MP2371 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2371 1.8A, 24V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The MP2371 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves
ELEC 387 Power electronics Study of flyback stepdown converter and comparison with buck converter
 ELEC 87 Power electronics Study of flyback stepdown converter and comparison with buck converter Edmond Gheury Jonathan Goldwasser th May Abstract i D This paper will focus on the study of a flyback stepdown
ELEC 87 Power electronics Study of flyback stepdown converter and comparison with buck converter Edmond Gheury Jonathan Goldwasser th May Abstract i D This paper will focus on the study of a flyback stepdown
Lab 1 Power electronics
 5--24 (5) Lab Power electronics Contents Introduction... Initial setup... 2 Starting the software... 2 Notes on the schematics... 2 Simulating the design... 2 Existing simulation variables... 3 Extra measurement
5--24 (5) Lab Power electronics Contents Introduction... Initial setup... 2 Starting the software... 2 Notes on the schematics... 2 Simulating the design... 2 Existing simulation variables... 3 Extra measurement
Assuming continuous conduction, the circuit has two topologies switch closed, and switch open. These are shown in Figures 2a and 2b. L i C.
 EE46, Power Electronics, DC-DC Buck Converter Version Sept. 9, 011 Overview DC-DC converters provide efficient conversion of DC voltage from one level to another. Specifically, the term buck converter
EE46, Power Electronics, DC-DC Buck Converter Version Sept. 9, 011 Overview DC-DC converters provide efficient conversion of DC voltage from one level to another. Specifically, the term buck converter
Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver
 Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver General Description The is boost topology switching regulator for LED driver. It provides built-in gate driver pin for driving external N-MOSFET. The
Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver General Description The is boost topology switching regulator for LED driver. It provides built-in gate driver pin for driving external N-MOSFET. The
Experiment 2: Simulation of DC Resistive Circuits
 Experiment 2: Simulation of DC Resistive Circuits Objectives: Simulate DC Resistive circuits using Orcad PSpice Software. Verify experimental and theoretically calculated results for a given resistive
Experiment 2: Simulation of DC Resistive Circuits Objectives: Simulate DC Resistive circuits using Orcad PSpice Software. Verify experimental and theoretically calculated results for a given resistive
Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design procedure and concern
 Active Clamp Forward Converters Design Using UCC2897 Hong Huang August 2007 1 Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design
Active Clamp Forward Converters Design Using UCC2897 Hong Huang August 2007 1 Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design
Impact of inductor current ringing in DCM on output voltage of DC-DC buck power converters
 ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 66(2), pp. 313-323 (2017) DOI 10.1515/aee-2017-0023 Impact of inductor current ringing in DCM on output voltage of DC-DC buck power converters MARCIN WALCZAK Department
ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 66(2), pp. 313-323 (2017) DOI 10.1515/aee-2017-0023 Impact of inductor current ringing in DCM on output voltage of DC-DC buck power converters MARCIN WALCZAK Department
Linear Peak Current Mode Controlled Non-inverting Buck-Boost Power-Factor-Correction Converter
 Linear Peak Current Mode Controlled Non-inverting Buck-Boost Power-Factor-Correction Converter Mr.S.Naganjaneyulu M-Tech Student Scholar Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, VRS&YRN College
Linear Peak Current Mode Controlled Non-inverting Buck-Boost Power-Factor-Correction Converter Mr.S.Naganjaneyulu M-Tech Student Scholar Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, VRS&YRN College
1.2Vdc 1N4002. Anode V+
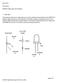 ECE 2274 Pre-Lab for MOSFET Night Light and Voltmeter 1. Night Light The purpose of this part of experiment is to use the switching characteristics of the MOSFET to design a Night Light using a LED, MOSFET,
ECE 2274 Pre-Lab for MOSFET Night Light and Voltmeter 1. Night Light The purpose of this part of experiment is to use the switching characteristics of the MOSFET to design a Night Light using a LED, MOSFET,
MP8619 8A, 25V, 600kHz Synchronous Step-down Converter
 The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP8619 is a high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter with built in internal power MOSFETs. It offers a very compact solution
The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP8619 is a high frequency synchronous rectified step-down switch mode converter with built in internal power MOSFETs. It offers a very compact solution
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter
 2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter FP6182 General Description The FP6182 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter FP6182 General Description The FP6182 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range
Testing and Stabilizing Feedback Loops in Today s Power Supplies
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT
 EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
