Exercise 5 EnSite NavX OneMap. Objectives
|
|
|
- Patience Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise 5 EnSite NavX OneMap Objectives Following completion of this exercise the user will have acquired knowledge of the following: Contact Mapping Reference/Roving Source Detection Algorithms Sensitivity Low-V ID Map Displays Standard LAT Reentrant Map Propagation Map Interior Projection Exterior Projection Interpolation 3D Points, 3D Labels, Surface Points Auto Color HR/CL Indicator OneMap The text contained in these boxes is from the EnSite Velocity Instructions for Use. Please reference this document for more information.
2 1. Login to the system: a. Username: training b. Password: esi Select Past Studies. EnSite Velocity NavX OneMap Exercise 3. Select NavX Case 01 from 05/04/2009 and open the study. 4. In the catheter setup subtask change the color of the CS catheter to aqua. 5. In the model surface list, select [Edit Model] and delete all surfaces in the list. 6. Hide the DIF model using the Map Settings drop-down menu. 7. Switch to dual view and set the translucency to 50 for both viewports. Set one to RAO and the other to LAO. 8. Turn the page and read the Chapter from the EnSite Velocity IFU on Contact Mapping. (If you completed Exercise #4 Mapping move to step 9)
3 Types of Contact Maps Figure 1. The contact mapping screen. The mapping tool organizes data collected during conventional electrophysiology procedures and displays the data in three-dimensional maps. During mapping, the clinician samples various heart locations (points) in a stable rhythm using EnGuide-located conventional catheters. The 3D location of each sampled location (point) is saved along with voltage and activation data, which can be displayed on the nearest surface as color. A single set of collected data can be used to display several types of maps. Cardiac Triggered Maps Cardiac triggered maps use a surface electrocardiogram or an intra-cardiac electrogram as the reference to which collected points are measured. There are four types of cardiac triggered maps: Local Activation Time (LAT) isochronal maps display color-coded activation times for each collected location (or nearest surface). The local activation time is the difference in milliseconds between detected activation on the roving waveform and the reference waveform. Colors range from white (early) to purple (late). Peak-to-Peak (P-P) voltage maps display color-coded voltage values for each collected location (or nearest surface). The P-P voltage is the difference in millivolts between the peak positive and peak negative components of the detected activation complex on the roving waveform. Colors range from grey (low voltage) to purple (high voltage). Peak Negative (P-Neg) voltage maps display color-coded voltage values for each collected location (or nearest surface). The P-Neg voltage is the difference in millivolts between baseline and the peak negative component of the detected activation complex on the roving waveform. Colors range from grey (low voltage) to purple (high voltage). CFE Mean maps provide a fractionation index based on the cycle length between multiple, discrete, local activations in an electrogram. Collected points with a lower value are mapped toward the white end of the color spectrum. Note: At least one LAT point must be mapped and saved in order for Peak-to-Peak and Peak-Negative, and CFE Mean options to become available. Prior to this action, these options are greyed out. Non-Cardiac Triggered Maps Non-cardiac triggered maps collect points at one second intervals. CFE Mean maps provide a fractionation index based on the cycle length between multiple, discrete, local activations in an electrogram. Collected points with a lower value are mapped toward the white end of the color spectrum. CFE Standard Deviation maps provide a fractionation index based on the cycle length between multiple, discrete, local activations in an electrogram. The CFE standard deviation calculates the standard deviation between activations. Collected points with a lower value are mapped toward the white end of the color spectrum.
4 Signals Collection Reference Signal Source Cardiac triggered maps require a reference signal. The reference signal is provided by a surface electrocardiogram or an intra-cardiac electrogram. The electrodes that provide the reference signal must remain in a stable position throughout the mapping procedure. The reference signal is set once before beginning a mapping procedure, and is used for timing of the roving signals. Non-cardiac triggered maps do not use any part of the cardiac signal as a reference. Instead, the waveform window refreshes once each second. Roving Signal Source Both cardiac triggered and non-cardiac triggered maps require a roving signal. The roving signal is used for sampling local activation times and voltages from various locations in the heart. The roving signal source can be any intracardiac electrode; it can be changed during a procedure, and data can be sampled from one or from multiple electrodes. Detection Algorithm Both reference signals and roving signals require a detection algorithm. Detection algorithms locate the best point on the waveform signal to use to identify activation. The detection algorithm selected for a given map should be the one that provides the most consistent and accurate detection. -dvdt Sharpest negative slope +dv/dt Sharpest positive slope abs dvdt Sharpest slope, regardless of positive or negative Max Peak positive Min Peak negative abs Peak Largest peak (difference from baseline) regardless of positive or negative QS First deflection from baseline Figure 2. Collection tab. Note: Cardiac triggered CFE maps use the same detection algorithm as LAT, P-P, and P-Neg. Non-cardiac CFE maps use the one second window refresh signal as a trigger. The detection algorithm is not selectable. Note: Detection on the roving waveform will take place within the Roving Activation Interval ( Roving Activation Interval (RAI) on page 163). P-P Sensitivity (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) The minimum peak-to-peak voltage required for the detection algorithm to operate. Incoming signal complexes must be larger in amplitude than the P-P Sensitivity in order to be considered activations by the system. While changing the P-P Sensitivity, red amplitude lines will appear on the related signal in the acquisition panel to indicate the current setting. Additional Signals Additional ECG or intracardiac signals may be selected to facilitate confirmation of rhythm stability. These signals are only for reference and are not involved in detection. Figure 3. Signals control panel.
5 Considerations Non-Cardiac Triggered CFE Maps Multiple detections are possible in a single sample. Tick marks in CFE maps are not individually adjustable. In CFE maps, some detection settings can be adjusted retrospectively and affect all points in the current map, including P-P Sensitivity, Width, Refractory, the RAI, and Segment Length. P-P Sensitivity is set independently for CFE maps and other map types. The Width slider controls the minimum complex width to consider for activation. The Refractory slider controls the minimum amount of time between detections. The Segment Length slider controls the number of seconds per sample. Reentrant Maps LAT maps present the mapping of reentrant arrhythmias and are displayed in a manner similar to activation maps. The color displayed within the map is linked to the cardiac cycle length (CL). The CL of a Reentrant LAT map is determined by the spacing between the curtains. Adjustment of the CL can be made by clicking and dragging the edge of the curtains to the desired location. The CL will not take effect until the Reentrant checkbox is turned on. Note: Adjusting the CL and then collecting points may invalidate the map. Propagation Maps These maps display areas of activation times that fall within a specific time interval. The interval, represented by a white band on a purple background, can be moved forward through one heart cycle either automatically or by user control. A button beneath the Propagation checkbox controls automatic motion of the activation interval with [Play] and [Freeze] options. These options are available in Review mode only. [Play] loops over the user-selected cycle length. Propagation maps may be played in Realtime or RealReview but recordings can only be exported in Offline Review. When Propagation is enabled, the colors of the map change to purple and white only. The leading edge of the white stripe is brighter than the trailing edge of the stripe to indicate the direction of travel activation. Using the side color bar, the stripe can be widened (increasing the interval in milliseconds [ms]), by clicking and dragging above the white stripe. This action can also be accomplished by clicking to the right of the stripe in the color bar at the top of the window.
6 Cardiac Triggered Mapping Settings Mapping Control Panel Cardiac Triggered Reference This checkbox determines which map types are available for use. Current Map These checkboxes control the type of data displayed on the map that has focus. When the checkbox is changed, the scale, values, and colors on the color bar will change in the map display. The numeric display type for the waveforms under the Points tab will also change to the current map type. The following display types are available: LAT Local Activation Time isochrone Peak-to-Peak Peak-to-Peak voltage Peak-Negative Peak-negative voltage CFE Mean Complex Fractionated Electrogram Mean activation between complexes CFE Std. Dev. Complex Fractionated Electrogram Standard Deviation between complexes. (Available only if Cardiac Triggered Reference is unchecked). Low-V ID (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Identifies low-voltage zones in LAT or CFE maps (see Figure 4). If a collected point s P-P value is lower than the specified Low-V ID value, then that point will display a grey area instead of the color-coded scale for the current map type. Grey points do not interpolate with color points. The Low-V ID control and the Color Low value of a P-P map are linked, and adjusting one will adjust the other to the same value. Figure 4. An LAT isochrone with Low-V ID Figure 5. Cardiac Triggered Mapping control panel Map Display (LAT maps only) The type of LAT map: Standard LAT, Reentrant Map, or Propagation Map. Map Appearance Includes slider controls that modify various features of the map. Interior Projection (Applies to both maps when Split Screen mode is active.) This slider controls the maximum distance that an interior 3D Point (represented as a triangle) can project to a location on the surface (represented by a square). For multiple-surface models, points will project to the nearest surface. Exterior Projection (Applies to both maps when Split Screen mode is active.) This slider controls the maximum distance that an exterior 3D Point (represented as a triangle) can project to a location on the surface (represented by a square). For multiple-surface models, points will project to the nearest surface. Interpolation (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) This slider controls the minimum distance between surface points necessary for the system to interpolate color. For multiple surface models, points will interpolate between surfaces in the same group.
7 3D Points (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Enables/disables the display of collected points as triangular markers. The triangular markers are placed on the positive electrode of the roving signal channel (Figure 6). 3D Labels (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Allows data to be numerically displayed adjacent to the triangular 3D points. 3D Points must be enabled in order to show 3D labels (Figure 6). Surface Points (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Enables/disables the display of small square points on the surface. These squares represent the point on the surface closest to a collected 3D point (Figure 6). Auto Color (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Controls whether the system automatically controls the pointers on the color bar during mapping. If Auto Color is enabled, the pointers will adjust to the minimum and maximum data values for all points in the current map. Auto Color applies separately for each display type. Auto Color will be disabled if any color is manually adjusted. Show HR/CL (Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode.) Enables/disables the display of the heart rate (in beats per minute [bpm]) reference cycle length (in mm), and the measurement of the current roving point in the lower right corner of the map display. The reference rate and cycle length are computed from detections on the reference catheter. Figure 6. A collected point displayed as A: surface point; B: 3D point; C: 3D label.
8 Non-Cardiac Triggered Mapping Settings Notice that in the Mapping Settings control panel (see Figure 7) the available settings have changed slightly from those shown in Figure 141 on page 160 of the EnSite Velocity IFU. The Map Display controls have been replaced with the following slider controls: The Width slider (CFE maps only) determines the minimum complex width to consider for activation. Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode. The Refractory slider (CFE maps only) determines the minimum amount of time between detections. Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode. The Segment Length slider (CFE maps only) determines the duration of the selected segment length. Applies to the map that has focus when in Split Screen mode. Figure 7. Non Cardiac Triggered Mapping control panel.
9 Collecting Points Figure 8.The waveform display for contact maps. A. Time scale The time scale (in milliseconds) appears at the top edge of the waveform display. The detected timing reference appears at 0 msec. Right-click on the Time Scale to display a menu to set the sweep speed, font size, and waveform thickness. B. Color bar (LAT maps only) When collecting or displaying LAT isochronal data, the color bar appears above the waveform display. The function of the color bar duplicates the color bar in the map display. Dragging the pointers on the color bar will adjust the range. C. Roving Activation Interval (RAI) The Roving Activation Interval is a timing parameter that is used in the detection of roving catheter activation. The RAI is defined by the black area between the curtains. The curtains appear as shaded areas on either side of the RAI. Roving catheter activation will not be reliably detected unless the beat falls within the black-background portion of the waveform display. To adjust the RAI, click and drag the edge of the shaded background. The current RAI value appears in the lower right of the waveform display. For non-cardiac CFE maps, the RAI is equivalent to the segment length, and appears as a left curtain only. For cardiac triggered CFE maps, the RAI is set independently for CFE maps and other contact map types. D. RAI Curtain Click and drag the curtain to adjust the RAI. E. Reference Activation Caliper (Green) Reference catheter activation as defined by the selected reference detection algorithm. The reference caliper will always appear at 0 msec on the time scale. Note: If the current rhythm does not meet the reference detection settings, this caliper will be magenta. Points may still be collected and adjusted. F. Roving Activation Caliper (Yellow) Roving catheter activation as defined by the selected roving detection algorithm, within the Roving Activation Interval. When adjusting this caliper, the associated location in the map display will move to reflect the roving position at the time of the caliper measurement. Note: If the current rhythm does not meet the roving detection settings, this caliper will be magenta. Points may still be collected and adjusted. If a time is adjusted and there are error conditions in the signal and the reference caliper is not purple, the caliper will turn yellow. Note: For CFE maps, multiple tick marks may appear on the roving waveform. Activation tick marks for CFE maps are not adjustable. G. Voltage High Caliper Roving catheter high voltage. This voltage caliper is set to the highest voltage within 100 msec of detected roving activation, within the RAI. This caliper is used in determining peak-to-peak (P-P) voltage.
10 H. Voltage Low Caliper Roving catheter low voltage. This voltage caliper is set to the lowest voltage within 100 msec of detected roving activation, within the RAI. This caliper is used in determining peak-to-peak (P-P) voltage and peak-negative voltage. I. Time Interval The RAI time interval. J. [Freeze]/[Save] When data is being collected (gated to detection of the timing reference), the [Freeze] button may be used to stop the display and review data. After pressing [Freeze], the label on the button will change to [Save]. Pressing [Save] will save the current point to the map and the point display. The following data is saved with each collected beat: electrode position, current waveforms (reference, roving, signal1, signal2, signal3), buffered waveforms and related roving electrode locations, timing, and voltage. Performance may begin to slow after 1000 points. When mapping is used in Review mode, [Freeze] will also freeze the waveform display and [Save] will cause the waveform display to play. Hot key: <F11> duplicates the function of the [Freeze] and [Save] buttons. K. [Cancel]/[Resume]. When the waveform display is frozen, [Cancel] will remove the currently displayed beat and resume gated data collection without adding information to the map. [Resume] will resume gated data collection. Hot key: <F12> duplicates the function of the [Cancel] button. L. Collected point buffer. As data is collected, each detected beat is temporarily saved in a buffer. When the waveform display is frozen, buffered data can be accessed using the buffer controls below the waveform display (Figure 145 on page 163 of the EnSite Velocity IFU). The beat that was present at the time that [Freeze] was selected is represented by [0]. Previous beats may be accessed by selecting the buttons for [1], [-2], etc. The arrow keys at the sides of the buffer controls may also be used to access previous beats. When reviewing beats in the buffer, the associated location in the map display will change to reflect the roving location at each selected beat. Hot key: The left and right arrow buttons in the beat buffer are duplicated by the left and right arrow keys on the keyboard. M. Points list This is a list of the points that have been collected for the map. Waveform Shadows Shadows behind the waveform indicate morphology of previous beats. Grey Grey shadows appear for reference signals occurring after the first point is saved in a map. The morphology of these shadows begins with the first point on the map. The shadow s amplitude matches the current amplitude for the related waveform. Shadows are used to confirm rhythm stability. Note: Changing the reference signal of the waveform will remove the shadow. Dark red A dark red shadow appears behind the current waveform for the roving catheter. This waveform indicates the morphology of the previous beat for this catheter. This shadow is used to confirm beat-to-beat stability. Note: If data does not exist for the previous beat (earliest beat in the buffer, etc.), then the dark red shadow will not appear. Amplitude The amplitude for ganged waveforms may be adjusted by middle-clicking the waveform and dragging up or down. To adjust the amplitude of an individual waveform, Shift + middle-click on the waveform. Sweep Speed To adjust the sweep speed for waveforms, right-click in the waveform area and then select the sweep speed from the pop-up menu.
11 Points Display Click on the Points tab to display the collected points. The display is a combined waveform segment, synchronized in time, of every roving catheter waveform incorporated into the map. Each waveform includes a tick mark indicating the activation point and a numeric metric that is determined by the current map type. Selecting a waveform in the Points display shows the original data for that heartbeat in the waveform display including all saved waveforms, timing calipers, voltage calipers, and all buffered data. The beat of interest and voltage caliper settings may be adjusted. All changes are saved automatically. The point in the map display that is related to the highlighted waveform will flash red. A. Sort The waveforms can be sorted by order of collection, current map type, and cycle length. B. Time scale The time scale, in milliseconds (msec), appears at the top edge of the waveform display. The timing reference of all waveforms is synchronized to 0 msec. The Sweep Speed may be adjusted by right-clicking in the black background and selecting Sweep Speed. The available options are 40, 50, 100, 200, and 400 mm/sec. C. Waveform number The waveform number indicates the order of collection. When multiple points are acquired simultaneously, all of the related points will have the same waveform number. D. Electrode Polarity Shows the polarity of the electrodes on the catheter. E. Hide point checkbox When checked, this checkbox indicates that this point on the map may show. Clear the check mark to hide this point. F. Dashed line A dashed waveform line indicates that a point is not used to color the map. The following types of points are drawn as dashed: hidden points, duplicate points, points outside the projection distances, and points with no locations. G. Solid line A solid line indicates a point that is used in the map. H. Blue background A blue background indicates the selected waveform. The data for the waveform is shown in the waveform display. If the corresponding point is used in the map, the 3D point, its projection on the map surface, and its text, flash red. I. Timing caliper Indicates the roving activation time. J. Map point measurement Displays the Timing (in ms) or Voltage (in mv) of the map point. K. Number of points This is the number of points that have been collected. The list may have to be scrolled to see all of the waveforms. L. Delete To delete a waveform from the Points display and its corresponding point from the map, select the waveform and click [Delete]. Figure 9. The Points display. M. Delete last Removes the point(s) last saved. Amplitude Waveform amplitude may be adjusted by middle-clicking the waveform and dragging up or down. For the Points display, amplitudes are ganged for all waveforms. Panning The Points display will default to centering on the timing reference. The display can be panned by <Shift> + middle-clicking in the background and dragging left or right. Waveform indicators The type of line used in the waveform indicates the effect of the waveform on the map. Solid, bold with blue background The waveform is selected. The original data for this waveform is currently displayed in the waveform display. If displayed in the map display, the 3D point, 3D text, and surface point for this waveform flash red. Solid The waveform is used in the 3D points and surface isochrone. Dashed The point is a duplicate or is degraded.
12 Delete Hidden Points To delete points that were hidden using the Show checkbox, right-click in the waveform display or Points display and select Delete Hidden Points. Delete Unused Points To delete all points that are not displayed due to the current projection settings, right-click in the waveform display or Points display and select Delete Unused Points. Scroll bar Use this control to scroll through all activation points. Hot key: When the Points display is open, the up and down arrow keys select the previous or next point, respectively. When the Points display is open, [Delete] will remove the current beat in the waveform display. Interpreting Color Color interpretation of contact maps is similar to color interpretation of isopotential maps (refer to Interpreting Isopotential Maps on page 144 of the EnSite Velocity System IFU).
13 OneMap OneMap is used to simultaneously create a model and a map. By default, OneMap is disabled. To use OneMap, select the [OneMap] button at the top of the Mapping control panel. If no model surfaces have been created (most likely scenario), a default surface will be created. If model surfaces have already been created, the currently selected surface is chosen by default. To create a new map, click on the drop-down menu in the top right of the control panel. Click on [New Map]. Enter a name for the new map and click [OK]. Refer to Creating a Map on page 169. There are three tabs located above the catheter selections (Settings, Points, and Model). The Model tab is only available when [One Map] is selected. Except for Show/Hide Field Scaling, the Model tab displays the entire menu that is available under the Model task. This permits the user to easily edit the model without the need to return to the Model task. There is no need to click on the [Finish Model] button. When exiting OneMap, the model finishes automatically. Note: When [OneMap] is enabled, model surfaces may appear to be modified because intersecting surfaces are no longer being calculated. Figure 10. OneMap - Model control panel.
14 Setting up a New Map 1. Select the Mapping task from the tool bar. The Mapping screen will appear. 2. Select New Map from the drop-down menu, in the upper right of the Mapping control panel. 3. Name the map, and click [OK]. 4. Select the reference timing signal. In the Collection control panel (lower left corner) Reference section: a. Select a timing reference source from the drop-down menu. b. Select a detection algorithm from the Detection drop-down men. c. Adjust the Sensitivity to a level just outside of baseline noise. After the timing reference and detection algorithms have been selected, waveforms will begin to refresh in the waveform display, gated to detected activation on the timing reference. 5. Adjust the Roving Activation Interval by clicking and dragging the edge of the shaded boundary. Generally, the Roving Activation Interval should be set to encompass one activation sequence on the roving catheter. 6. Select an initial roving catheter signal. The roving catheter can be any intracardiac electrogram. In the Collection control panel Roving section: a. Select a roving source from the drop-down menu. The roving signal can be changed during mapping, allowing any intracardiac electrode to be used as part of the mapping process. b. Select a detection algorithm from the Detection drop-down men. c. Adjust the Sensitivity to a level just outside of baseline noise. Sensitivity is set independently for CFE and other map types. 7. (OneMap only) Select the source for collecting model points from the From drop-down menu: select Active EnGuide to use the Active EnGuide to collect points, or Active Electrode to use the active electrode to collect points. Collecting Points 1. With the patient in the clinical rhythm, place the roving catheter to collect data. When a beat of interest appears in the RAI, select [Freeze]. Note: (OneMap only) Selecting [Freeze] will automatically enable [Collect Points] when model type is set to OneModel. 2. In the frozen mapping window, review the morphology of the beat and placement of the caliper lines. If necessary, select an optimal beat from the collected point buffer and/or adjust calipers. 3. Select [Save] to save the point; otherwise, select [Cancel]. The waveform display will return to acquisition mode.
15 To Map from a Segment Figure 10. Map from Segment (example). 1. Click the Split Screen Mode button in the upper right corner of the Mapping screen. 2. Select the appropriate segment from the drop-down list at the bottom of the right display. 3. If necessary, use the Waveform control panel in the right display to set the roving catheter and electrode. 4. Reference J through M under Collecting Points on page 163. (Refer to Figure 145 on page 163 of the EnSite Velocity IFU). Note: Points can be added to either the left or right display and will be applied to both displays.
16 Managing Maps New Map New Map may be selected from the drop-down menu in the upper right corner of the Mapping control panel. Select New Map; the Map Name window comes up with a prompt to name the map. Type a name in the Name field and click [OK]. Copy Open Map - Copy Open Map may be selected from the drop-down menu in the upper right corner of the Mapping control panel. Select Copy Open Map; the Map Name window comes up with a prompt to name the map. Type a name in the Name field and click [OK]. Note: Renaming and deleting maps is not available in Mapping. To rename or delete a map, go to the Notebook in RealReview. Mapping Controls The following Mapping controls can be accessed by clicking on the eye ball icon in the upper right of the map workspace. Label Text On. Turns Label text on and off. Label Show Through. Projects the labels through surfaces that may be obscuring them. Show EnSite Model. Turns the entire model on and off during mapping. Map Transparency On. Turn the map Transparency on and off. Note: Do not turn on Transparency unless a map is currently displayed. Fixed Proximity Indicator. Turning this checkbox on sets the diameter of the Proximity Indicator to a maximum of 10mm, regardless of the current lesion size. Edge Enhancement. When turned on, provides a rendering of the model where the body is translucent but the edge remains distinctly defined.. Figure 11. Map Displays
17 9. Using the Model Task, in the waveform display, right click and adjust the sweep speed to 200 mm/sec. 10. Read the section below on how to create calipers. How to Create a Caliper In RealReview or Offline Review, while playing a segment of interest, select the [ll] pause button beneath the waveforms. Then select the [ ] caliper button and select the beat of interest in the waveform display. Using Calipers Calipers are used to measure timing between signal features in the waveform display during review mode. The caliper is a set of two vertical lines with a horizontal line between them. The time between the vertical lines is displayed above the horizontal line in milliseconds. The frequency is displayed beneath the waveform if it is greater than 1hz. Ten calipers are available. To move vertical caliper lines, click on the lines to move that side of the caliper. To move the entire caliper without changing the distance between the vertical lines, middle-click the caliper and drag left or right. To move a horizontal caliper line, left-click and drag the horizontal line up or down. To add a caliper, click the [Caliper] button, next to the [Show/Hide Wave Controls] button. To remove a caliper, left-click and drag the horizontal line past the top or the bottom of the waveform display. Calipers move with the waveform display. When a vertical line or caliper moves outside of the display area, a small arrow appears at the edge of the screen. This arrow may be middle-clicked to select the vertical caliper line then dragged to bring the caliper back into the waveform display. The relative caliper position also appears in the segment overview. 11. Pause the segment playback. Use the calipers by selecting the [ ] button in the lower left corner to measure the cycle length of the tachycardia on one of the CS catheter electrograms (Figure 12). a. Record the tachycardia cycle length (TCL) here ms 12. Move to the Mapping task to setup a Local Activation Time (LAT) map. 13. Set the sweep speed of the waveform display to 200 or 400 mm/s 14. Adjust the curtains of the Roving Activation Interval (RAI) to be no longer than the tachycardia cycle length (<100%). The measurement of each curtain from the zero reference is displayed in the bottom of the window. Set the total interval to be around 90% of the measured tachycardia cycle length. This ensures only one complex will be in the curtains at a time (see Figure 13 on next page). a. Example: RAI = 0.9 TCL, ms = 270 ms = (RAI) Figure 12. Calipers measuring cycle length of the rhythm. b. Your measured (TCL) = 0.9 = = (RAI) c. Your calculated (RAI) = / 2 = this is the number you will use for setting each side of your RAI (+/-) in front of your reference signal.
18 15. Set your RAI using the numbers from the previous page. Use the right hand number from step c and set your RAI window by clicking on the small triangle at the bottom of the waveform display and dragging the RAI curtain until its value displayed in white text in the middle of the RAI equals the number you wrote down on the previous page (Figure 13). 16. Setup the collection criteria for the Reference (Figure 14): a. Source: The reference source should be an electrode that remains in a stable position throughout the mapping procedure. This is set once at the beginning and cannot be changed. For this case, select CS-5-6. b. Detection: Choose the method that provides the most consistent and accurate detection. For this case, select Max. Figure 13. RAI adjusted to 90% of the TCL (arrows). The numbers at the bottom of the RAI indicate how wide (in ms) the RAI window is. c. Sensitivity: Adjust the slider to eliminate any baseline noise. Any signal between the red lines will not be used for time or voltage data. (0.500 for this case) Figure 14. Reference source, detection and sensitivity settings (left) red lines showing sensitivity on reference source electrogram when adjusted (right). Play the segment and ensure that the Reference signal and green caliper tracks consistently at zero. Note: You may use the HR/CL window to visualize the cycle length detected from your reference signal. 17. Setup the collection criteria for the Roving (Figure 15): a. Source: The roving source is the catheter used to move around the chamber to collect points. It can be any catheter, can be changed during the procedure, and can be one or multiple electrodes. For this case select, Spir- D-2. For more experienced users, select Spir-ALL and choose to Show All Roving Waves b. Detection: Choose dv/dt as a roving detection algorithm. Figure 15. Roving source, detection and sensitivity settings. c. Sensitivity: Adjust the roving sensitivity to eliminate any baseline noise. Use filters if needed. (0.200 for this case) 18. Uncheck the waveform shadows to hide the dark red shadow behind the current roving waveform. This is used to confirm beat-to-beat stability and is helpful when mapping PVC s by creating a snapshot of the morphology of the first beat saved for each map. 19. Use the Signals tab to add the following ECG signals to the waveform display; II and V 1. This is helpful to ensure the appropriate signal is saved (i.e. atrial signal and not ventricular). Also add the proximal and distal CS electrograms. To add, highlight signal in Available Signals column and click on the button. Figure 16. Signals Tab.
19 20. Using the Map Control Panel, set the Interior and Exterior Projection and Interpolation to Using the Map Control panel turn uncheck 3D points and check Auto Color. 22. Set Low-V ID to Figure 17. Map Control Panel Settings for Projection, Interpolation, Points/Labels and Appearance. 23. Click on OneMap to enable the model tab on the Map Control Panel. 24. Click the to add a model surface, call in RA. 25. Collect model points 26. Change the type to OneModel 27. Left mouse click on the timing tick mark and drag to the beginning of segment 09: RA Geometry. Note: For users new to mapping, adjust the waveform speed from 1:1 to 1:2 or slower. 28. Click 29. When a beat of interest appears in the RAI, select [Freeze]. 30. Review the morphology of the frozen beat. a. Are the calipers marking the signal appropriately? Examine both timing and voltage (Figure 18). Figure 18. Collected beat showing that timing (red arrow) and voltage (yellow arrows) have been appropriately marked.
20 b. Is it the appropriate signal? [A vs. V] No QRS QRS Figure 19. Collected beats comparing A vs. V signals. No QRS in RAI window (left). QRS shown on top of a fused atrial electrogram (right). The collected beat on the (left) will be saved. The collected beat on the (right) will not be saved to the map. c. If the beat is suboptimal, choose a point from the collected point buffer by clicking on the beat number or using the left and right arrow keys on the keyboard. Once a new beat is selected click [Resume]. 31. When satisfied with the frozen beat, select [Save], otherwise select [Cancel]. Hotkey: F11: Freeze/Save Mapping Point, F12: Discard Mapping Point 32. Continue to freeze and save points as the catheter moves around the chamber to create the timing map. Play through the segment multiple times if needed. Note: If it appears there is no electrogram on your ROV catheter take a look at your map to see where the catheter is in the chamber. (IVC or SVC?) Is it in close proximity to the model surface? (Figure 20). If not, increase the gain on your ROV electrograms. Middle-mouse click on the electrogram and push the mouse up. Figure 20. SPIR catheter in the IVC.
21 33. Advanced users: Set the roving source to Spir-All and check the box for Show All Roving Waves. Now each time you freeze you will have to verify the timing of five contact bipolar elecrograms instead of just one. (Figure 21). 34. After changing the roving source to All, check the box next to Show All Roving Waves to show all of the electrograms used for collection. Figure 21. Roving source electrode selection (above). Drop down menu allows for selection of ALL electrodes on Source for collection. All roving waveforms shown in RAI window (right). 35. When you feel the chamber is adequately sampled, Click Figure 22. OneMap before finishing model. 36. Click and remove any model points if necessary. Then click. 37. Turn on Auto Color in the Mapping Control Panel. This will automatically adjust the color spectrum to the earliest collected point colored white and the latest collected point colored purple. Does the color spectrum fill the RAI? (Figure 23). Figure 23. Auto Color ON, color spectrum distributed across the RAI window. 38. Move to the Points tab in the Mapping Control Panel. Use the Sort drop-down menu to sort by LAT. The earliest point collected will be shown at the top of the list. 39. Prior to making any edits, preserve the original map data set by selecting Copy Open Map from the dropdown menu in the upper right corner of the Mapping Control Panel. Name it Map Copy. Figure 24. Collected points can be sorted by LAT.
22 40. In the Points tab, right-click and Delete Unused Points. Unused points fall outside of the currently selected interior and exterior projection criteria. Figure 25. Points with a dotted line appearance fall outside the set projection values and are not displayed on the map. In this map only 1035 points are being used out of 2815 points total. 41. Click on the earliest point. The point will now be displayed in the waveform display window. If the point was collected using ALL roving electrograms the electrogram for the selected point in the list will have a blue halo on the right and left sides of the electrogram highlighted in the list (Figure 25). Figure 26. Selected point in list (left) and the electrogram shown in the waveform display (right). The selected point has a blue halo on the left and right sides of the electrogram in the waveform display. The highlighted point is not appropriately marked for timing (tick mark is on far left side of RAI). a. Are the calipers marking the signal appropriately? Review timing and voltage. b. Where is the point located? Rotate the model to find the point; it will flash red on the model. c. Adjust the point or delete as needed. d. Review a few more points with early activation times. 42. Rotate the map and locate a point with a late activation time. This will be in a purple color area. Click on the point. The point will be displayed in the waveform display window. Review the point as was done with the early points. Review a few more late points and adjust or delete as needed. Note: If you see an area of white/red in the middle of a large area of blue/purple or vice-versa, check the points in that area for correct activation timing.
23 Figure 27. Inappropriately triggered signals(left) can be identified by being surrounded by late points (if early) or vice-versa, late points surrounded by many early points. New beat selected from the buffer (right) corrects the display of the map data. 43. Scroll through all the collected points in the points and edit or delete as necessary. Click on any points on the model that display color that may not make sense and review those points for timing and voltage. 44. Adjust the interpolation slider to the maximum value of 30. Watch the effect in the color display on the map. Interpolation is the radial distance of color that projects around a map point. This should be used with caution as a full map of color does not equal a full set of map data. 45. Switch the Map Display Type to a Reentrant Map. Note the change in the map display. The reentrant map emphasizes the area where early meets late. Figure 28. Standard LAT (left), Reentrant (right).
24 46. Switch to a Propagation Map and press [Play] to view the animation of the map. Change the playback speed of the propagation map to 100. Figure 29. Propagation map controls. Animations may only be saved in review mode. 47. Bonus: Navigate to the Therapy Task and turn on the lesion markers. Is this where you expected the ablation target would be? Figure 30. Propagation Map Unless otherwise noted, indicates that the name is a trademark of, or licensed to, St. Jude Medical or one of its subsidiaries. ST. JUDE MEDICAL and the nine-squares symbol are trademarks and services marks of St. Jude Medical, Inc. and its related companies St. Jude Medical, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Electrophysiology Navigant v2.11. Left Atrial Mapping for Supra-Ventricular Tachycardia. TRG-0098 Rev A Effective Date: 11/019/07
 Electrophysiology Navigant v2.11 Left Atrial Mapping for Supra-Ventricular Tachycardia TRG-0098 Rev A Effective Date: 11/019/07 Getting Started The Opening Screen displays the application procedure selection
Electrophysiology Navigant v2.11 Left Atrial Mapping for Supra-Ventricular Tachycardia TRG-0098 Rev A Effective Date: 11/019/07 Getting Started The Opening Screen displays the application procedure selection
Chapter 6: TVA MR and Cardiac Function
 Chapter 6 Cardiac MR Introduction Chapter 6: TVA MR and Cardiac Function The Time-Volume Analysis (TVA) optional module calculates time-dependent behavior of volumes in multi-phase studies from MR. An
Chapter 6 Cardiac MR Introduction Chapter 6: TVA MR and Cardiac Function The Time-Volume Analysis (TVA) optional module calculates time-dependent behavior of volumes in multi-phase studies from MR. An
ArbStudio Triggers. Using Both Input & Output Trigger With ArbStudio APPLICATION BRIEF LAB912
 ArbStudio Triggers Using Both Input & Output Trigger With ArbStudio APPLICATION BRIEF LAB912 January 26, 2012 Summary ArbStudio has provision for outputting triggers synchronous with the output waveforms
ArbStudio Triggers Using Both Input & Output Trigger With ArbStudio APPLICATION BRIEF LAB912 January 26, 2012 Summary ArbStudio has provision for outputting triggers synchronous with the output waveforms
Page 1/10 Digilent Analog Discovery (DAD) Tutorial 6-Aug-15. Figure 2: DAD pin configuration
 Page 1/10 Digilent Analog Discovery (DAD) Tutorial 6-Aug-15 INTRODUCTION The Diligent Analog Discovery (DAD) allows you to design and test both analog and digital circuits. It can produce, measure and
Page 1/10 Digilent Analog Discovery (DAD) Tutorial 6-Aug-15 INTRODUCTION The Diligent Analog Discovery (DAD) allows you to design and test both analog and digital circuits. It can produce, measure and
Progeny Imaging Veterinary
 Progeny Imaging Veterinary User Guide V1.14 and higher 00-02-1605 Rev. K1 ECN: ECO052875 Revision Date: 5/17/2017 Contents 1. About This Manual... 6 How to Use this Guide... 6 Text Conventions... 6 Getting
Progeny Imaging Veterinary User Guide V1.14 and higher 00-02-1605 Rev. K1 ECN: ECO052875 Revision Date: 5/17/2017 Contents 1. About This Manual... 6 How to Use this Guide... 6 Text Conventions... 6 Getting
FlashChart. Symbols and Chart Settings. Main menu navigation. Data compression and time period of the chart. Chart types.
 FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add indicators and draw on
FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add indicators and draw on
VTube-LASER Quick Start Guide
 VTube-LASER Quick Start Guide This guide shows how to import a STEP file and then MEASURE and qualify demo tube 4 using the standard UNISCAN method of measuring. The steps in this workflow are from version
VTube-LASER Quick Start Guide This guide shows how to import a STEP file and then MEASURE and qualify demo tube 4 using the standard UNISCAN method of measuring. The steps in this workflow are from version
House Design Tutorial
 House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have created a
House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have created a
Introduction to NeuroScript MovAlyzeR Handwriting Movement Software (Draft 14 August 2015)
 Introduction to NeuroScript MovAlyzeR Page 1 of 20 Introduction to NeuroScript MovAlyzeR Handwriting Movement Software (Draft 14 August 2015) Our mission: Facilitate discoveries and applications with handwriting
Introduction to NeuroScript MovAlyzeR Page 1 of 20 Introduction to NeuroScript MovAlyzeR Handwriting Movement Software (Draft 14 August 2015) Our mission: Facilitate discoveries and applications with handwriting
Digital Photography 1
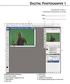 Digital Photography 1 Photoshop Lesson 1 Photoshop Workspace & Layers Name Date Default Photoshop workspace A. Document window B. Dock of panels collapsed to icons C. Panel title bar D. Menu bar E. Options
Digital Photography 1 Photoshop Lesson 1 Photoshop Workspace & Layers Name Date Default Photoshop workspace A. Document window B. Dock of panels collapsed to icons C. Panel title bar D. Menu bar E. Options
Imaging Features Available in HTML5. it just makes sense
 Imaging Features Available in HTML5 it just makes sense August, 2018 Imaging Features Available in HTML5 As part of the 5.2 SP1 release, the Images functionality is now available in HTML5 and provides
Imaging Features Available in HTML5 it just makes sense August, 2018 Imaging Features Available in HTML5 As part of the 5.2 SP1 release, the Images functionality is now available in HTML5 and provides
Progeny Imaging. User Guide V x and Higher. Part Number: ECN: P1808 REV. F
 Progeny Imaging User Guide V. 1.6.0.x and Higher Part Number: 00-02-1598 ECN: P1808 REV. F Contents 1 About This Manual... 5 How to Use this Guide... 5 Text Conventions... 5 Getting Assistance... 6 2 Overview...
Progeny Imaging User Guide V. 1.6.0.x and Higher Part Number: 00-02-1598 ECN: P1808 REV. F Contents 1 About This Manual... 5 How to Use this Guide... 5 Text Conventions... 5 Getting Assistance... 6 2 Overview...
Importing and processing gel images
 BioNumerics Tutorial: Importing and processing gel images 1 Aim Comprehensive tools for the processing of electrophoresis fingerprints, both from slab gels and capillary sequencers are incorporated into
BioNumerics Tutorial: Importing and processing gel images 1 Aim Comprehensive tools for the processing of electrophoresis fingerprints, both from slab gels and capillary sequencers are incorporated into
Adobe Studio on Adobe Photoshop CS2 Enhance scientific and medical images. 2 Hide the original layer.
 1 Adobe Studio on Adobe Photoshop CS2 Light, shadow and detail interact in wild and mysterious ways in microscopic photography, posing special challenges for the researcher and educator. With Adobe Photoshop
1 Adobe Studio on Adobe Photoshop CS2 Light, shadow and detail interact in wild and mysterious ways in microscopic photography, posing special challenges for the researcher and educator. With Adobe Photoshop
Photoshop CS2. Step by Step Instructions Using Layers. Adobe. About Layers:
 About Layers: Layers allow you to work on one element of an image without disturbing the others. Think of layers as sheets of acetate stacked one on top of the other. You can see through transparent areas
About Layers: Layers allow you to work on one element of an image without disturbing the others. Think of layers as sheets of acetate stacked one on top of the other. You can see through transparent areas
Silhouette Connect Layout... 4 The Preview Window... 5 Undo/Redo... 5 Navigational Zoom Tools... 5 Cut Options... 6
 user s manual Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Sending Designs to Silhouette Connect... 3 Sending a Design to Silhouette Connect from Adobe Illustrator... 3 Sending a Design to Silhouette Connect from
user s manual Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Sending Designs to Silhouette Connect... 3 Sending a Design to Silhouette Connect from Adobe Illustrator... 3 Sending a Design to Silhouette Connect from
House Design Tutorial
 Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When we are finished, we will have created
Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When we are finished, we will have created
TeleTrader FlashChart
 TeleTrader FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With TeleTrader FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add
TeleTrader FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With TeleTrader FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add
ECG Simulation. Rob MacLeod, Brian Birchler, Cris Lapierre, Jess Tate, and Josh Silvernagel. March 6, 2014
 ECG Simulation Rob MacLeod, Brian Birchler, Cris Lapierre, Jess Tate, and Josh Silvernagel March 6, 2014 Contents 1 Purpose and Background 1 1.1 Purpose........................................... 1 1.2
ECG Simulation Rob MacLeod, Brian Birchler, Cris Lapierre, Jess Tate, and Josh Silvernagel March 6, 2014 Contents 1 Purpose and Background 1 1.1 Purpose........................................... 1 1.2
Using Adobe Photoshop
 Using Adobe Photoshop 4 Colour is important in most art forms. For example, a painter needs to know how to select and mix colours to produce the right tones in a picture. A Photographer needs to understand
Using Adobe Photoshop 4 Colour is important in most art forms. For example, a painter needs to know how to select and mix colours to produce the right tones in a picture. A Photographer needs to understand
LabVIEW Day 2: Other loops, Other graphs
 LabVIEW Day 2: Other loops, Other graphs Vern Lindberg From now on, I will not include the Programming to indicate paths to icons for the block diagram. I assume you will be getting comfortable with the
LabVIEW Day 2: Other loops, Other graphs Vern Lindberg From now on, I will not include the Programming to indicate paths to icons for the block diagram. I assume you will be getting comfortable with the
REVIT - RENDERING & DRAWINGS
 TUTORIAL L-15: REVIT - RENDERING & DRAWINGS This Tutorial explains how to complete renderings and drawings of the bridge project within the School of Architecture model built during previous tutorials.
TUTORIAL L-15: REVIT - RENDERING & DRAWINGS This Tutorial explains how to complete renderings and drawings of the bridge project within the School of Architecture model built during previous tutorials.
Navigant Software New Features in v2.11
 Navigant Software New Features in v2.11 TRG-000 Rev A Effective Date: 00/00/00 Navigant v2.11 New Features Highlight of new features: NaviLine Automated linear navigation Automapping of Pulmonary Veins
Navigant Software New Features in v2.11 TRG-000 Rev A Effective Date: 00/00/00 Navigant v2.11 New Features Highlight of new features: NaviLine Automated linear navigation Automapping of Pulmonary Veins
Planmeca Romexis. quick guide. Viewer EN _2
 Planmeca Romexis Viewer quick guide EN 10029550_2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 START-UP OF PLANMECA ROMEXIS VIEWER...1 1.1 Selecting the interface language... 1 1.2 Selecting images...1 1.3 Starting the Planmeca
Planmeca Romexis Viewer quick guide EN 10029550_2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 START-UP OF PLANMECA ROMEXIS VIEWER...1 1.1 Selecting the interface language... 1 1.2 Selecting images...1 1.3 Starting the Planmeca
Organizing artwork on layers
 3 Layer Basics Both Adobe Photoshop and Adobe ImageReady let you isolate different parts of an image on layers. Each layer can then be edited as discrete artwork, allowing unlimited flexibility in composing
3 Layer Basics Both Adobe Photoshop and Adobe ImageReady let you isolate different parts of an image on layers. Each layer can then be edited as discrete artwork, allowing unlimited flexibility in composing
User Guide V10 SP1 Addendum
 Alibre Design User Guide V10 SP1 Addendum Copyrights Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement or
Alibre Design User Guide V10 SP1 Addendum Copyrights Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement or
AutoCAD Tutorial First Level. 2D Fundamentals. Randy H. Shih SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial
 Starting a New Project ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial 1. Double-click the Archicad Icon from the desktop 2. Click on the Grey Warning/Information box when it appears on the screen. 3. Click on the Create
Starting a New Project ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial 1. Double-click the Archicad Icon from the desktop 2. Click on the Grey Warning/Information box when it appears on the screen. 3. Click on the Create
House Design Tutorial
 House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have created a
House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have created a
Learning Guide. ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. # Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6. Fax:
 Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
06/17/02 Page 1 of 12
 Understanding the Graphical User Interface When you start AutoCAD, the AutoCAD window opens. The window is your design work space. It contains elements that you use to create your designs and to receive
Understanding the Graphical User Interface When you start AutoCAD, the AutoCAD window opens. The window is your design work space. It contains elements that you use to create your designs and to receive
A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building
 11/28/2005-3:00 pm - 4:30 pm Room:Americas Seminar [Lab] (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building Amy Fietkau - Autodesk and John Jansen;
11/28/2005-3:00 pm - 4:30 pm Room:Americas Seminar [Lab] (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida A Quick Spin on Autodesk Revit Building Amy Fietkau - Autodesk and John Jansen;
Using the Desktop Recorder
 Mediasite Using the Desktop Recorder Instructional Media publication: 09-Students 9/8/06 Introduction The new Desktop Recorder from Mediasite allows HCC users to record content on their computer desktop
Mediasite Using the Desktop Recorder Instructional Media publication: 09-Students 9/8/06 Introduction The new Desktop Recorder from Mediasite allows HCC users to record content on their computer desktop
User Manual for HoloStudio M4 2.5 with HoloMonitor M4. Phase Holographic Imaging
 User Manual for HoloStudio M4 2.5 with HoloMonitor M4 Phase Holographic Imaging 1 2 HoloStudio M4 2.5 Software instruction manual 2013 Phase Holographic Imaging AB 3 Contact us: Phase Holographic Imaging
User Manual for HoloStudio M4 2.5 with HoloMonitor M4 Phase Holographic Imaging 1 2 HoloStudio M4 2.5 Software instruction manual 2013 Phase Holographic Imaging AB 3 Contact us: Phase Holographic Imaging
Apple Photos Quick Start Guide
 Apple Photos Quick Start Guide Photos is Apple s replacement for iphoto. It is a photograph organizational tool that allows users to view and make basic changes to photos, create slideshows, albums, photo
Apple Photos Quick Start Guide Photos is Apple s replacement for iphoto. It is a photograph organizational tool that allows users to view and make basic changes to photos, create slideshows, albums, photo
Click here to give us your feedback. New FamilySearch Reference Manual
 Click here to give us your feedback. New FamilySearch Reference Manual January 25, 2011 2009 by Intellectual Reserve, Inc. All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America English approval:
Click here to give us your feedback. New FamilySearch Reference Manual January 25, 2011 2009 by Intellectual Reserve, Inc. All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America English approval:
Digital Photo Guide. Version 8
 Digital Photo Guide Version 8 Simsol Photo Guide 1 Simsol s Digital Photo Guide Contents Simsol s Digital Photo Guide Contents 1 Setting Up Your Camera to Take a Good Photo 2 Importing Digital Photos into
Digital Photo Guide Version 8 Simsol Photo Guide 1 Simsol s Digital Photo Guide Contents Simsol s Digital Photo Guide Contents 1 Setting Up Your Camera to Take a Good Photo 2 Importing Digital Photos into
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS REV1
 UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual
 Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual Cricut Explore design-and-cut system From inspiration to creation in just a few taps! Cricut Design Space App for ipad 1. ipad Setup A. Setting up the app B.
Cricut Design Space App for ipad User Manual Cricut Explore design-and-cut system From inspiration to creation in just a few taps! Cricut Design Space App for ipad 1. ipad Setup A. Setting up the app B.
AutoCAD LT Drawing Formats
 AutoCAD LT Section 5 AutoCAD LT Drawing Formats This section covers: 1. Layers 2. Colors 3. Linetypes 4. Units 5. Text Styles 6. Dimension Styles 7. Point Styles AutoCAD LT Introduction AutoCAD LT Drawing
AutoCAD LT Section 5 AutoCAD LT Drawing Formats This section covers: 1. Layers 2. Colors 3. Linetypes 4. Units 5. Text Styles 6. Dimension Styles 7. Point Styles AutoCAD LT Introduction AutoCAD LT Drawing
HP 16533A 1-GSa/s and HP 16534A 2-GSa/s Digitizing Oscilloscope
 User s Reference Publication Number 16534-97009 February 1999 For Safety Information, Warranties, and Regulatory Information, see the pages behind the Index Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 1991 1999
User s Reference Publication Number 16534-97009 February 1999 For Safety Information, Warranties, and Regulatory Information, see the pages behind the Index Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 1991 1999
Galix WinTer. Holter Analyzer
 Galix WinTer Holter Analyzer User s Manual 2555 Collins Avenue, Suite C-5, Miami Beach, FL 33140, U.S.A. Tel.: (305) 534-5905 Fax: (305) 534-8222 INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 CORRECT ELECTRODE PLACEMENT...4
Galix WinTer Holter Analyzer User s Manual 2555 Collins Avenue, Suite C-5, Miami Beach, FL 33140, U.S.A. Tel.: (305) 534-5905 Fax: (305) 534-8222 INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 CORRECT ELECTRODE PLACEMENT...4
6. Cloud Database retrieval of ECG reports by Mobile Phone, Tablet, or Notebook.
 CardioScan 77a, with Build Date 20141117 v.78a This Section A is for Holter customers who are updating their CardioScan Software. 1. Additional ECG Analysis capabilities. 2. New Editing Process. 3. Respiration
CardioScan 77a, with Build Date 20141117 v.78a This Section A is for Holter customers who are updating their CardioScan Software. 1. Additional ECG Analysis capabilities. 2. New Editing Process. 3. Respiration
Toothbrush Holder. A drawing of the sheet metal part will also be created.
 Prerequisite Knowledge Previous knowledge of the following commands is required to complete this lesson; Sketch (Line, Centerline, Circle, Add Relations, Smart Dimension,), Extrude Boss/Base, and Edit
Prerequisite Knowledge Previous knowledge of the following commands is required to complete this lesson; Sketch (Line, Centerline, Circle, Add Relations, Smart Dimension,), Extrude Boss/Base, and Edit
AreaSketch Pro Overview for ClickForms Users
 AreaSketch Pro Overview for ClickForms Users Designed for Real Property Specialist Designed specifically for field professionals required to draw an accurate sketch and calculate the area and perimeter
AreaSketch Pro Overview for ClickForms Users Designed for Real Property Specialist Designed specifically for field professionals required to draw an accurate sketch and calculate the area and perimeter
Advance Dimensioning and Base Feature Options
 Chapter 4 Advance Dimensioning and Base Feature Options Learning Objectives After completing this chapter you will be able to: Dimension the sketch using the autodimension sketch tool. Dimension the sketch
Chapter 4 Advance Dimensioning and Base Feature Options Learning Objectives After completing this chapter you will be able to: Dimension the sketch using the autodimension sketch tool. Dimension the sketch
Example Application C H A P T E R 4. Contents
 C H A P T E R 4 Example Application This chapter provides an example application of how to perform steady flow water surface profile calculations with HEC-RAS. The user is taken through a step-by-step
C H A P T E R 4 Example Application This chapter provides an example application of how to perform steady flow water surface profile calculations with HEC-RAS. The user is taken through a step-by-step
Key Terms. Where is it Located Start > All Programs > Adobe Design Premium CS5> Adobe Photoshop CS5. Description
 Adobe Adobe Creative Suite (CS) is collection of video editing, graphic design, and web developing applications made by Adobe Systems. It includes Photoshop, InDesign, and Acrobat among other programs.
Adobe Adobe Creative Suite (CS) is collection of video editing, graphic design, and web developing applications made by Adobe Systems. It includes Photoshop, InDesign, and Acrobat among other programs.
ISCapture User Guide. advanced CCD imaging. Opticstar
 advanced CCD imaging Opticstar I We always check the accuracy of the information in our promotional material. However, due to the continuous process of product development and improvement it is possible
advanced CCD imaging Opticstar I We always check the accuracy of the information in our promotional material. However, due to the continuous process of product development and improvement it is possible
SolidWorks Part I - Basic Tools SDC. Includes. Parts, Assemblies and Drawings. Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI
 SolidWorks 2015 Part I - Basic Tools Includes CSWA Preparation Material Parts, Assemblies and Drawings Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered
SolidWorks 2015 Part I - Basic Tools Includes CSWA Preparation Material Parts, Assemblies and Drawings Paul Tran CSWE, CSWI SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered
SCHEDULE USER GUIDE. Version Noventri Suite Schedule User Guide SF100E REV 08
 SCHEDULE USER GUIDE Version 2.0 1 Noventri Suite Schedule User Guide SF100E-0162-02 REV 08 Table of Contents 1. SCHEDULE... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Start SCHEDULE... 3 1.3 Select Project... 4 1.4 Select
SCHEDULE USER GUIDE Version 2.0 1 Noventri Suite Schedule User Guide SF100E-0162-02 REV 08 Table of Contents 1. SCHEDULE... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Start SCHEDULE... 3 1.3 Select Project... 4 1.4 Select
PlanSwift 3D Viewer Plugin User Guide
 PlanSwift 3D Viewer Plugin User Guide UPDATED ON 7/13/2018 PlanSwift Authored by: Dave Hansen 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Purchasing and Installation... 4 Purchasing Plugins... 4 Installation and
PlanSwift 3D Viewer Plugin User Guide UPDATED ON 7/13/2018 PlanSwift Authored by: Dave Hansen 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Purchasing and Installation... 4 Purchasing Plugins... 4 Installation and
Introduction to 3D Printing. Activity 1: Design a keychain using computer-aided design software
 Introduction to 3D Printing Activity 1: Design a keychain using computer-aided design software 1 In this activity we ll design a keychain name tag and learn the fundamentals of computer-aided design, the
Introduction to 3D Printing Activity 1: Design a keychain using computer-aided design software 1 In this activity we ll design a keychain name tag and learn the fundamentals of computer-aided design, the
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started
 MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1
 Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1 Part Tutorial Exercise 5: Loft-Tube-1 [Complete] In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first, then part options. Then, in sketch
Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1 Part Tutorial Exercise 5: Loft-Tube-1 [Complete] In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first, then part options. Then, in sketch
1 Sketching. Introduction
 1 Sketching Introduction Sketching is arguably one of the more difficult techniques to master in NX, but it is well-worth the effort. A single sketch can capture a tremendous amount of design intent, and
1 Sketching Introduction Sketching is arguably one of the more difficult techniques to master in NX, but it is well-worth the effort. A single sketch can capture a tremendous amount of design intent, and
Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim
 Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim Section 1. Oscilloscope Introduction Equipment and Components Safety glasses Logic probe ETS-7000 Digital-Analog Training System Fluke 45 Digital Multimeter
Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim Section 1. Oscilloscope Introduction Equipment and Components Safety glasses Logic probe ETS-7000 Digital-Analog Training System Fluke 45 Digital Multimeter
AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial. Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS. Schroff Development Corporation
 AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction
AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
House Design Tutorial
 Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have
Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have
Image Viewing. with ImageScope
 Image Viewing with ImageScope ImageScope Components Use ImageScope to View These File Types: ScanScope Virtual Slides.SVS files created when the ScanScope scanner scans glass microscope slides. JPEG files
Image Viewing with ImageScope ImageScope Components Use ImageScope to View These File Types: ScanScope Virtual Slides.SVS files created when the ScanScope scanner scans glass microscope slides. JPEG files
House Design Tutorial
 Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have
Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When you are finished, you will have
Create styles that control the display of Civil 3D objects. Copy styles from one drawing to another drawing.
 NOTES Module 03 Settings and Styles In this module, you learn about the various settings and styles that are used in AutoCAD Civil 3D. A strong understanding of these basics leads to more efficient use
NOTES Module 03 Settings and Styles In this module, you learn about the various settings and styles that are used in AutoCAD Civil 3D. A strong understanding of these basics leads to more efficient use
EinScan-SE. Desktop 3D Scanner. User Manual
 EinScan-SE Desktop 3D Scanner User Manual Catalog 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.1. 1.2. 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.1. 1.2. Device List and Specification... 2 Device List... 3 Specification Parameter...
EinScan-SE Desktop 3D Scanner User Manual Catalog 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.1. 1.2. 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.1. 1.2. Device List and Specification... 2 Device List... 3 Specification Parameter...
4 Working With Scan Modes
 4 Working With Scan Modes Scan Modes Overview All of the information in this chapter pertains to live imaging. Many of the controls and functions change when you freeze the scan. For information on using
4 Working With Scan Modes Scan Modes Overview All of the information in this chapter pertains to live imaging. Many of the controls and functions change when you freeze the scan. For information on using
Getting Started with. Vectorworks Architect
 Getting Started with Vectorworks Architect Table of Contents Introduction...2 Section 1: Program Installation and Setup...6 Installing the Vectorworks Architect Program...6 Exercise 1: Launching the Program
Getting Started with Vectorworks Architect Table of Contents Introduction...2 Section 1: Program Installation and Setup...6 Installing the Vectorworks Architect Program...6 Exercise 1: Launching the Program
PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution
 PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution We measure it all! General information Copyright All rights reserved. Apart from the legally laid down exceptions, no part of this publication may be reproduced,
PRODIM CT 3.0 MANUAL the complete solution We measure it all! General information Copyright All rights reserved. Apart from the legally laid down exceptions, no part of this publication may be reproduced,
EnSite Precision Cardiac Mapping System ACCURACY OF THE ENSITE NAVX NAVIGATION AND VISUALIZATION TECHNOLOGY, SENSOR ENABLED
 EnSite Precision Cardiac Mapping System ACCURACY OF THE ENSITE NAVX NAVIGATION AND VISUALIZATION TECHNOLOGY, SENSOR ENABLED all trodes IN using a or using rep) that gritty l the gel he skin. ith soap
EnSite Precision Cardiac Mapping System ACCURACY OF THE ENSITE NAVX NAVIGATION AND VISUALIZATION TECHNOLOGY, SENSOR ENABLED all trodes IN using a or using rep) that gritty l the gel he skin. ith soap
Roof Tutorial Wall Specification
 Roof Tutorial The majority of Roof Tutorial describes some common roof styles that can be created using settings in the Wall Specification dialog and can be completed independent of the other tutorials.
Roof Tutorial The majority of Roof Tutorial describes some common roof styles that can be created using settings in the Wall Specification dialog and can be completed independent of the other tutorials.
54645D. Mixed Signal Oscilloscope
 54645D Mixed Signal Oscilloscope Page 1 of 42 Instructions for the use of the 54645D Mixed Signal Oscilloscope This pamphlet is intended to give you (the student) an overview on the use of the 54645D Mixed
54645D Mixed Signal Oscilloscope Page 1 of 42 Instructions for the use of the 54645D Mixed Signal Oscilloscope This pamphlet is intended to give you (the student) an overview on the use of the 54645D Mixed
Batch Counting of Foci
 Batch Counting of Foci Getting results from Z stacks of images. 1. First it is necessary to determine suitable CHARM parameters to be used for batch counting. First drag a stack of images taken with the
Batch Counting of Foci Getting results from Z stacks of images. 1. First it is necessary to determine suitable CHARM parameters to be used for batch counting. First drag a stack of images taken with the
PASS Sample Size Software. These options specify the characteristics of the lines, labels, and tick marks along the X and Y axes.
 Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at:
 Dusk Getting Started Installing the Software We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at: https://www.atik-cameras.com/downloads/ Locate and
Dusk Getting Started Installing the Software We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at: https://www.atik-cameras.com/downloads/ Locate and
Color and More. Color basics
 Color and More In this lesson, you'll evaluate an image in terms of its overall tonal range (lightness, darkness, and contrast), its overall balance of color, and its overall appearance for areas that
Color and More In this lesson, you'll evaluate an image in terms of its overall tonal range (lightness, darkness, and contrast), its overall balance of color, and its overall appearance for areas that
Android User manual. Intel Education Lab Camera by Intellisense CONTENTS
 Intel Education Lab Camera by Intellisense Android User manual CONTENTS Introduction General Information Common Features Time Lapse Kinematics Motion Cam Microscope Universal Logger Pathfinder Graph Challenge
Intel Education Lab Camera by Intellisense Android User manual CONTENTS Introduction General Information Common Features Time Lapse Kinematics Motion Cam Microscope Universal Logger Pathfinder Graph Challenge
Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop
 Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop This hand-out will take you through the steps to render a perspective line drawing using Adobe Photoshop. The first important element in this process
Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop This hand-out will take you through the steps to render a perspective line drawing using Adobe Photoshop. The first important element in this process
Sash Clamp. Sash Clamp SW 2015 Design & Communication Graphics Page 1.
 Sash Clamp 1 Introduction: The Sash clamp consists of nine parts. In creating the clamp we will be looking at the improvements made by SolidWorks in linear patterns, adding threads and in assembling the
Sash Clamp 1 Introduction: The Sash clamp consists of nine parts. In creating the clamp we will be looking at the improvements made by SolidWorks in linear patterns, adding threads and in assembling the
Tas Engineering Training Workbook 1
 Tas Engineering Training Workbook 1 Tas 3D Modeller Tas Manager Your Tas Manager contains two main folders: a Tas folder and a Tas Data folder. See the directory-tree on the left-hand side above. If you
Tas Engineering Training Workbook 1 Tas 3D Modeller Tas Manager Your Tas Manager contains two main folders: a Tas folder and a Tas Data folder. See the directory-tree on the left-hand side above. If you
Motion Blur with Mental Ray
 Motion Blur with Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to take a look at the settings and what they do for us in using Motion Blur with the Mental Ray renderer that comes with 3D Studio. For this little
Motion Blur with Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to take a look at the settings and what they do for us in using Motion Blur with the Mental Ray renderer that comes with 3D Studio. For this little
Introduction to: Microsoft Photo Story 3. for Windows. Brevard County, Florida
 Introduction to: Microsoft Photo Story 3 for Windows Brevard County, Florida 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Downloading Photo Story 3... 4 Adding Pictures to Your PC... 7 Launching Photo Story 3...
Introduction to: Microsoft Photo Story 3 for Windows Brevard County, Florida 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Downloading Photo Story 3... 4 Adding Pictures to Your PC... 7 Launching Photo Story 3...
BSketchList 3D. BSoftware for the Design and Planning of Cabinetry and Furniture RTD AA. SketchList Inc.
 1 BSketchList 3D 1 BSoftware for the Design and Planning of Cabinetry and Furniture 2 RTD10000651AA 2 Overview of SketchList 3D SketchList 3D is a software program that aids woodworkers in the design and
1 BSketchList 3D 1 BSoftware for the Design and Planning of Cabinetry and Furniture 2 RTD10000651AA 2 Overview of SketchList 3D SketchList 3D is a software program that aids woodworkers in the design and
Go Daddy Online Photo Filer
 Getting Started and User Guide Discover an easier way to share, print and manage your photos online! Online Photo Filer gives you an online photo album site for sharing photos, as well as easy-to-use editing
Getting Started and User Guide Discover an easier way to share, print and manage your photos online! Online Photo Filer gives you an online photo album site for sharing photos, as well as easy-to-use editing
BIO 365L Neurobiology Laboratory. Training Exercise 1: Introduction to the Computer Software: DataPro
 BIO 365L Neurobiology Laboratory Training Exercise 1: Introduction to the Computer Software: DataPro 1. Don t Panic. When you run DataPro, you will see a large number of windows, buttons, and boxes. In
BIO 365L Neurobiology Laboratory Training Exercise 1: Introduction to the Computer Software: DataPro 1. Don t Panic. When you run DataPro, you will see a large number of windows, buttons, and boxes. In
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. UCORE ELECTRONICS
 UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
Floorplanner Editor Manual
 Editor Manual Floorplanner Editor Manual 1 Overview 2 Canvas a 2D view b View Settings 3 3D view a Orbital and walkthrough mode b How to navigate c Adding cameras d Scenery image e Create a render 4 Sidebar
Editor Manual Floorplanner Editor Manual 1 Overview 2 Canvas a 2D view b View Settings 3 3D view a Orbital and walkthrough mode b How to navigate c Adding cameras d Scenery image e Create a render 4 Sidebar
Understanding OpenGL
 This document provides an overview of the OpenGL implementation in Boris Red. About OpenGL OpenGL is a cross-platform standard for 3D acceleration. GL stands for graphics library. Open refers to the ongoing,
This document provides an overview of the OpenGL implementation in Boris Red. About OpenGL OpenGL is a cross-platform standard for 3D acceleration. GL stands for graphics library. Open refers to the ongoing,
Creo Extrude Tutorial 2: Cutting and Adding Material
 Creo Extrude Tutorial 2: Cutting and Adding Material 1. Open Creo Parametric 2. File > Open > extrudeturial (From Creo Extrude Tutorial 1) 3. Cutting Material a. Click Extrude Icon > Select the following
Creo Extrude Tutorial 2: Cutting and Adding Material 1. Open Creo Parametric 2. File > Open > extrudeturial (From Creo Extrude Tutorial 1) 3. Cutting Material a. Click Extrude Icon > Select the following
Operating Rausch ScanCam within POSM.
 Operating Rausch ScanCam within POSM. POSM (Pipeline Observation System Management) // posmsoftware.com // info@posmsoftware.com // 859-274-0041 RAUSCH USA // www.rauschusa.com // reusa@rauschusa.com //
Operating Rausch ScanCam within POSM. POSM (Pipeline Observation System Management) // posmsoftware.com // info@posmsoftware.com // 859-274-0041 RAUSCH USA // www.rauschusa.com // reusa@rauschusa.com //
Getting Started with. Vectorworks Architect
 Getting Started with Vectorworks Architect Table of Contents Introduction...2 Section 1: Program Installation and Setup...6 Installing the Vectorworks Architect Program...6 Exercise 1: Launching the Program
Getting Started with Vectorworks Architect Table of Contents Introduction...2 Section 1: Program Installation and Setup...6 Installing the Vectorworks Architect Program...6 Exercise 1: Launching the Program
USER MANUAL VOLANS PUBLIC DISPLAY FOR JOHN WAYNE AIRPORT
 VOLANS PUBLIC DISPLAY FOR JOHN WAYNE AIRPORT BridgeNet International Contents 1 Welcome... 2 1.1 Accessibility... 2 1.2 Navigation... 2 1.3 Map Display... 4 2 Menu Bar... 5 2.1 Show Flights... 5 2.2 Adjust
VOLANS PUBLIC DISPLAY FOR JOHN WAYNE AIRPORT BridgeNet International Contents 1 Welcome... 2 1.1 Accessibility... 2 1.2 Navigation... 2 1.3 Map Display... 4 2 Menu Bar... 5 2.1 Show Flights... 5 2.2 Adjust
CONTENT INTRODUCTION BASIC CONCEPTS Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing DRAWING STROKES...
 USER MANUAL CONTENT INTRODUCTION... 3 1 BASIC CONCEPTS... 3 2 QUICK START... 7 2.1 Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing... 7 3 DRAWING STROKES... 15 3.1 Creating a group of strokes...
USER MANUAL CONTENT INTRODUCTION... 3 1 BASIC CONCEPTS... 3 2 QUICK START... 7 2.1 Creating an element of a black-and white line drawing... 7 3 DRAWING STROKES... 15 3.1 Creating a group of strokes...
Geometry Controls and Report
 Geometry Controls and Report 2014 InnovMetric Software Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in part or in whole in any way without permission from InnovMetric Software is strictly prohibited except for
Geometry Controls and Report 2014 InnovMetric Software Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in part or in whole in any way without permission from InnovMetric Software is strictly prohibited except for
Support Tutorial. Project Settings. Adding Bolts. Select: File New. Select: Analysis Project Settings. Select: Support Add Bolt
 Support Tutorial 4-1 Support Tutorial Bolts may be added to a RocPlane model to evaluate the effect of support on wedge stability. Bolt orientation can be optimized, or the bolt capacity for a required
Support Tutorial 4-1 Support Tutorial Bolts may be added to a RocPlane model to evaluate the effect of support on wedge stability. Bolt orientation can be optimized, or the bolt capacity for a required
Revit Structure 2012 Basics:
 SUPPLEMENTAL FILES ON CD Revit Structure 2012 Basics: Framing and Documentation Elise Moss autodesk authorized publisher SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Structural
SUPPLEMENTAL FILES ON CD Revit Structure 2012 Basics: Framing and Documentation Elise Moss autodesk authorized publisher SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Structural
Sense. 3D scanning application for Intel RealSense 3D Cameras. Capture your world in 3D. User Guide. Original Instructions
 Sense 3D scanning application for Intel RealSense 3D Cameras Capture your world in 3D User Guide Original Instructions TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION.... 3 COPYRIGHT.... 3 2 SENSE SOFTWARE SETUP....
Sense 3D scanning application for Intel RealSense 3D Cameras Capture your world in 3D User Guide Original Instructions TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION.... 3 COPYRIGHT.... 3 2 SENSE SOFTWARE SETUP....
SigCalRP User s Guide
 SigCalRP User s Guide . . Version 4.2 Copyright 1997 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose
SigCalRP User s Guide . . Version 4.2 Copyright 1997 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose
IMPULSE 6000D/7000DP DEFIBRILLATOR/TRANSCUTANEOUS PACER ANALYZER. 25 reasons to differentiate Impulse 6000D/7000DP from all others
 IMPULSE 6000D/7000DP DEFIBRILLATOR/TRANSCUTANEOUS PACER ANALYZER INTRODUCTION 25 reasons to differentiate Impulse 6000D/7000DP from all others Function 1. Compatible with full range of defibrillation technologies
IMPULSE 6000D/7000DP DEFIBRILLATOR/TRANSCUTANEOUS PACER ANALYZER INTRODUCTION 25 reasons to differentiate Impulse 6000D/7000DP from all others Function 1. Compatible with full range of defibrillation technologies
AutoCAD 2020 Fundamentals
 Autodesk AutoCAD 2020 Fundamentals ELISE MOSS Autodesk Certified Instructor SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Autodesk AutoCAD 2020 Fundamentals ELISE MOSS Autodesk Certified Instructor SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
About the DSR Dropout, Surge, Ripple Simulator and AC/DC Voltage Source
 About the DSR 100-15 Dropout, Surge, Ripple Simulator and AC/DC Voltage Source Congratulations on your purchase of a DSR 100-15 AE Techron dropout, surge, ripple simulator and AC/DC voltage source. The
About the DSR 100-15 Dropout, Surge, Ripple Simulator and AC/DC Voltage Source Congratulations on your purchase of a DSR 100-15 AE Techron dropout, surge, ripple simulator and AC/DC voltage source. The
