6.02 Fall 2010 Lecture #16. Reminders FD sharing Fourier Series and Pictures Mod and Demod New issue, sine mod -> cosine demod Channel Delay
|
|
|
- Ross Hoover
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.02 Fall 2010 Lecture #16 Reminders FD sharing Fourier Series and Pictures Mod and Demod New issue, sine mod -> cosine demod Channel Delay
2 x 1 [n] Frequency Domain Sharing Big Picture Mod DeMod y 1 [n] x 2 [n]... Mod + X Channel Y DeMod y 2 [n]... x P [n] Mod DeMod y P [n] Questions What is Modulation (Mod in figure)? What do typical X s look like? What should the Demodulator be? What is the relation between x i [n] and y i [n] What happens if there is channel delay (NEW)
3 Modulation by Cosine Multiplication x 1 [n]... cos 1 n x[n] = P P i=1 x i[n] cos i n x P [n] cos P n
4 What does a modulated X look like? Can Fourier Series Help us understand Modulation?
5 Periodic Assumption (with period N) One Period Periodic with Period N (N even) means Only certain frequency complex exponentials x[n] can be represented with a Fourier series
6 Discrete-Time Fourier Series OR
7 Key DTFS Modulation Identity
8 Key DTFS Modulation Identity ~ / M Q.lJ.. ",.::h9/l P:re: 't '"e. i\ C'7 Et 1< Q [ "!<;J. '1.. < /(In x[n] COS Om [n] = L X[k]e J " k.s k~-k 1... n.~.,,,,, s : 1 f. ('l ').?"-i _. ej.. /. '...'.' ';'n4n+ -«:» 'tnn, J Y\Jt c,...r..-"-) p;' L-11 k - Z11. J! -::,-:~~ N tj +e.. ~ ilk =: N" Q(V1 - NM Ffe~telE 1 K 1 K 2 L X[k]ejcnk+n.n)n + 2 L X[klej(nk-r~'rr1,)Tl, k:::::::.-k k=...-l< 1<[(\J 5l nl4t [{\J -= r L "Z(bJ e.-l.(lt<- () i t:~q.., f\f'.j.e,-j s:t",il' R \ K::.-R z, / - ~ ~~"'LCK]~--\~K+.Q~)(\ -t ~ b~j~&.q K-JS k:::...,]s 6.02 Spring 2010 Lecture 14, Slide #3
9 Frequency Axes Alternatives Fourier Coefficient versus Radial Frequency Careless about end case Fourier Coefficient versus Coefficient Index Fourier Coefficient versus Sampling Frequency
10 DTFS of x (versus 4Mhz sampling frequency)
11 DTFS of modulation using 400khz and 800khz cosine multiplication
12 Mod with 400khz and 800khz cosines Demod with a 400khz cosine
13 Demodulation using cosine multiplication and a Low-pass Filter (Ideal Channel) Low Pass Filter
14 Mod by multiplication with nearby cosines (400khz, 520khz)
15 Demod of nearby cosine case (at 400khz)
16 Modulation/Demodulation using cosine multiplication and I/O LPF s Low Pass Filter Low Pass Filter x 1 [n] x 1 [n] Low Pass Filter. cos 1 n.. Ideal Channel cos. 1 n.. Low Pass Filter x P [n] x P [n] cos P n cos P n
17 LPF d before cosine multiplication case LPF then Modulation by Cosine Multiplication After Demodulation by Cosine Multiplication
18 Mod by LPF then Sine Multiplication, Demod by Cosine Multiplication then LPF Low Pass Filter Low Pass Filter x 1 [n] x 1 [n] Low Pass Filter... Ideal Channel cos. 1 n.. Low Pass Filter x P [n] x P [n] cos P n
19 DTFS of Mod by sine multiplication
20 DTFS of Demod by cos multiplication, From Mod by sin multiplication
21 Mod by Cos Multiplication with Channel Delay Low Pass Filter Low Pass Filter x 1 [n] x 1 [n] Low Pass Filter. cos 1 n.. D-sample Delay Channel...??? Low Pass Filter x P [n] x P [n] cos P n??? With what shall I demodulation it dear Liza, dear Liza?
22 ( J -." I, }') I \ I, \ I, 1'l t, ~ I.../'. Modv of X [f\-'(). -e..- x C~-
23 I -- \ I -- -, (~ -,A ~ ~vrv\1f\c. X Cf\l is ~ ~ 1\ J LM \~c.rj 'Qr J L.. JL.- ~(~\ X Cf\\.~ II )~ 1.. jll. f) 7\ / '7 (...\J ~..,\(..., _,... Ii"- " t\. 7 i /~ h ~( ;~MjDr~ ~y, /'\ "- Ir( \ ) ("JS..HJI --~ r~ ----~-- ---L - Pt= --'..,---.-.i->: ~..,.---,...f'" "" /' <" J.1'. / i A \ / J~T? 0- ~ "'-~c.....-~ J -., rr-: ~ ;, - J. /\...;- \.r r- I,,' -!'Ul-Vj J \... - J i. ' '\.; ~' ~... I 7\ J.-", j J I 7 />::,. I. - ~\.- I I -~I~ ~ I C- 05.1[.j) - 2-.eli'. (1 A ~ 11\ fi V\ ~ 'I f 'X [~ - 0 "'".. USA.., \1 r.. v _ --..., ~ Ls-, I
24 Example: Consider modulation and demodulation using sine and cosine multiplication. The signal, x[n], is multiplied by a cosine, then transmitted through a channel with a D-sample delay, then multiplie d by a sine and a cosine. For this example, we will assume periodicity, with a N=1000 sample period. Then, the only frequencies that are periodic with period 1000 are multiples of As a specific case, let x[n] be given by and be modulated by. Note that if the channel has a five-sample delay, then
25 The plots on the following slides show the impact of a fivesample channel delay on modulation and demodulation for four different modulation frequencies (but always a fivesample delay). The different modulation frequencies will change the phase shift introduced by the delay, and generate different outputs from sine and cosine demodulation. In particular, the modulation frequencies considered are 25, 50, 75 and 100 times.
26 Plots of x[n] versus n, Real and Imaginary parts of X[k] versus Note: 0.3 for coefficient 0 and ½*0.3 for coefficients -5, -4,-3 and 3, 4, 5
27 Modulation using multiplication by Cos25 Omega_1 n Note: ½*0.3 for coefficient 25 and -25, 1/4*0.3 for coefficients -30, -29,-28, 22,-21, -20 and 30, 29, 28, 22, 21, 20
28 Plots of x after modulation without and with 5 sample delay (note periodicity!)
29 Modulation with Cos25 Omega_1 n multiplication followed by 5 sample delay Note impact of pi/4 phase shift (peaks are 0.3*½ *sqrt(2)/2 for real and imaginary part).
30 Demod by Cos25 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
31 Demod by Sin 25 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
32 Modulation by Cos50 Omega_1 n multiplication Note: ½*0.3 for coefficient 50 and -50, 1/4*0.3 for coefficients -55, -54, -53, -47,-46, -45 and 55, 54, 53,47,46, 45
33 Modulation by Cos50 Omega_1 n multiplication followed by 5 sample delay Note impact of pi/2 phase shift (peaks are 0.3*½ but are now in the imaginary part).
34 Demod by Cos50 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
35 Demod by Sin 50 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
36 Modulation by Cos75 Omega_1 n multiplication Note: ½*0.3 for coefficient 75 and -75 and 1/4*0.3 for coefficients -80, -79,-78, -72,-71,-70, 80, 79, 78, 72,71, 70
37 Modulation by Cos 75 Omega_1 n multiplication followed by 5 sample delay Note impact of approximately 3pi/4 phase shift (peaks are 0.3*½*sqrt(2)/2 for real and imaginary part, and opposite in sign from 25 Omega_1 case.
38 Demod by Cos75 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
39 Demod by Sin 75 Omega_1 multiplication after delay
40 Modulation by Cos100 Omega_1 n multiplication Note: ½*0.3 for coefficient 100 and -100, and 1/4*0.3 for coefficients -105, -104, -103, -97, -96, -95, 105, 104, 103, 97, 96, 95
41 Mod by Cos 100 Omega_1 n multiplication followed by 5 sample delay Note impact of pi phase shift (peaks are 0.3* ½ and real, but flipped in sign).
42 Demod by Cos100 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
43 Demod by Sin 100 Omega_1 n multiplication after delay
w h(t) 6.02 Spring 2010 Lecture #14 DIGITAL C,OMMUNICATIOfi SblSTE:I'1S L, ---1~ Modulation Review Delay Issue JJl J r
 / w h(t) JJl J r L, ---1~ rf (free. domain) a M ~ "II, i\.il II j,!i ~.: ' II II N\ 1\!A (!! i.1 i ;,I \,) \~1 I 1'\ ii 1.1 I ~l '['Ii If I 1/" \!,~i \.!\:\4 "I.~ lfjl Y i! 1 I( \! \ J - 1'1 (!,fi:1 I',."!.ao~J-
/ w h(t) JJl J r L, ---1~ rf (free. domain) a M ~ "II, i\.il II j,!i ~.: ' II II N\ 1\!A (!! i.1 i ;,I \,) \~1 I 1'\ ii 1.1 I ~l '['Ii If I 1/" \!,~i \.!\:\4 "I.~ lfjl Y i! 1 I( \! \ J - 1'1 (!,fi:1 I',."!.ao~J-
6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation
 1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N]
![Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N] Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N]](/thumbs/88/116022205.jpg) Frequency Division Multiplexing 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture #4 complex exponentials discrete-time Fourier series spectral coefficients band-limited signals To engineer the sharing of a channel through frequency
Frequency Division Multiplexing 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture #4 complex exponentials discrete-time Fourier series spectral coefficients band-limited signals To engineer the sharing of a channel through frequency
Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series
 MIT 6.02 DRAFT Lecture Notes Fall 200 (Last update: November 9, 200) Comments, questions or bug reports? Please contact 6.02-staff@mit.edu LECTURE 4 Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series In earlier
MIT 6.02 DRAFT Lecture Notes Fall 200 (Last update: November 9, 200) Comments, questions or bug reports? Please contact 6.02-staff@mit.edu LECTURE 4 Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series In earlier
Midterm 1. Total. Name of Student on Your Left: Name of Student on Your Right: EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems
 EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: N time samples
 EE445M/EE38L.6 Lecture. Lecture objectives are to: The Discrete Fourier Transform Windowing Use DFT to design a FIR digital filter Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: time samples {a n = {a,a,a 2,,a
EE445M/EE38L.6 Lecture. Lecture objectives are to: The Discrete Fourier Transform Windowing Use DFT to design a FIR digital filter Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: time samples {a n = {a,a,a 2,,a
Fourier and Wavelets
 Fourier and Wavelets Why do we need a Transform? Fourier Transform and the short term Fourier (STFT) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The continues Wavelet Transform Discrete Wavelet Transform Wavelets
Fourier and Wavelets Why do we need a Transform? Fourier Transform and the short term Fourier (STFT) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The continues Wavelet Transform Discrete Wavelet Transform Wavelets
Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Imagine we would like to know the precise, instantaneous,
Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Imagine we would like to know the precise, instantaneous,
Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE4900/EE6420: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE4900/EE6420: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
Frequency Domain Representation of Signals
 Frequency Domain Representation of Signals The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a sampled time domain waveform x n x 0, x 1,..., x 1 is a set of Fourier Coefficients whose samples are 1 n0 X k X0, X
Frequency Domain Representation of Signals The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a sampled time domain waveform x n x 0, x 1,..., x 1 is a set of Fourier Coefficients whose samples are 1 n0 X k X0, X
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, Introduction to EECS 2
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing
 Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12
 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12 Bounded-input, bounded-output stability Frequency response 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 12, Slide #1 Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) Stability What ensures that the infinite sum
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12 Bounded-input, bounded-output stability Frequency response 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 12, Slide #1 Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) Stability What ensures that the infinite sum
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 10 Feb 14 th, 2019 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and S. Narasimhan Time and Frequency example : g(t) = sin(2π f t) + (1/3)sin(2π (3f) t)
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 10 Feb 14 th, 2019 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and S. Narasimhan Time and Frequency example : g(t) = sin(2π f t) + (1/3)sin(2π (3f) t)
EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class
 EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class Description In this project, MATLAB and Simulink are used to construct a system experiment. The experiment
EEL 4350 Principles of Communication Project 2 Due Tuesday, February 10 at the Beginning of Class Description In this project, MATLAB and Simulink are used to construct a system experiment. The experiment
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters
 Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM
 Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
ECE 301, final exam of the session of Prof. Chih-Chun Wang Saturday 10:20am 12:20pm, December 20, 2008, STEW 130,
 ECE 301, final exam of the session of Prof. Chih-Chun Wang Saturday 10:20am 12:20pm, December 20, 2008, STEW 130, 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided
ECE 301, final exam of the session of Prof. Chih-Chun Wang Saturday 10:20am 12:20pm, December 20, 2008, STEW 130, 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided
Module 9 AUDIO CODING. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 9 AUDIO CODING Lesson 30 Polyphase filter implementation Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to : 1. Show how a bank of bandpass filters can be realized
Module 9 AUDIO CODING Lesson 30 Polyphase filter implementation Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to : 1. Show how a bank of bandpass filters can be realized
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain
 Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain Author: Gareth Forbes Created: 3/11/9 Revised: 7/1/1 Revision: 1 The general idea A phase modulated signal is a type of signal which
Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain Author: Gareth Forbes Created: 3/11/9 Revised: 7/1/1 Revision: 1 The general idea A phase modulated signal is a type of signal which
Physics 115 Lecture 13. Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018
 Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2
 Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing
 DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
Revision of Lecture 2
 Revision of Lecture 2 Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Design of Tx/Rx filters (pulse shaping): to achieve zero ISI and to maximise received signal to noise ratio Combined Tx/Rx filters: Nyquist system
Revision of Lecture 2 Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Design of Tx/Rx filters (pulse shaping): to achieve zero ISI and to maximise received signal to noise ratio Combined Tx/Rx filters: Nyquist system
DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN
 DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 03 Spectrum of a Square Wave 2 Results of Some Filters 3 Notation 4 x[n]
DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 03 Spectrum of a Square Wave 2 Results of Some Filters 3 Notation 4 x[n]
The aim is to understand the power spectrum for non-white noise and non-coherent oscillations.
 In the present lecture I will first discuss issues related to non-white noise sources and noncoherent oscillations (oscillations that are not described as a simple harmonic oscillator). The aim is to understand
In the present lecture I will first discuss issues related to non-white noise sources and noncoherent oscillations (oscillations that are not described as a simple harmonic oscillator). The aim is to understand
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 9 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Analog to Digital Conversion Most real life signals are analog signals These
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 9 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Analog to Digital Conversion Most real life signals are analog signals These
6.003: Signals and Systems. Sampling
 6.003: Signals and Systems Sampling April 27, 200 Mid-term Examination #3 om orrow: W ednesday, A pril 2 8, 7 : 3 0-9 : 3 0 pm. No recitations tomorrow. Coverage: Lectures 20 Recitations 20 Homeworks Homework
6.003: Signals and Systems Sampling April 27, 200 Mid-term Examination #3 om orrow: W ednesday, A pril 2 8, 7 : 3 0-9 : 3 0 pm. No recitations tomorrow. Coverage: Lectures 20 Recitations 20 Homeworks Homework
ECE 6560 Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 9
 Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 9 Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin estern Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 193. Michigan Ave. Kalamazoo
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 9 Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin estern Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 193. Michigan Ave. Kalamazoo
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 638/4393 Lecture 9 Sept 26 th, 217 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu, S. Narasimhan HISTOGRAM SHAPING We now describe methods for histogram
Digital Image Processing COSC 638/4393 Lecture 9 Sept 26 th, 217 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu, S. Narasimhan HISTOGRAM SHAPING We now describe methods for histogram
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Instruction Manual for Concept Simulators. Signals and Systems. M. J. Roberts
 Instruction Manual for Concept Simulators that accompany the book Signals and Systems by M. J. Roberts March 2004 - All Rights Reserved Table of Contents I. Loading and Running the Simulators II. Continuous-Time
Instruction Manual for Concept Simulators that accompany the book Signals and Systems by M. J. Roberts March 2004 - All Rights Reserved Table of Contents I. Loading and Running the Simulators II. Continuous-Time
Fourier transforms and series
 Fourier transforms and series A Fourier transform converts a function of time into a function of frequency f is frequency in hertz t is time in seconds t = 1 and f = 1 f t ω = πf i is ( 1) e ia = cos(a)
Fourier transforms and series A Fourier transform converts a function of time into a function of frequency f is frequency in hertz t is time in seconds t = 1 and f = 1 f t ω = πf i is ( 1) e ia = cos(a)
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Signal Processing. Introduction
 Signal Processing 0 Introduction One of the premiere uses of MATLAB is in the analysis of signal processing and control systems. In this chapter we consider signal processing. The final chapter of the
Signal Processing 0 Introduction One of the premiere uses of MATLAB is in the analysis of signal processing and control systems. In this chapter we consider signal processing. The final chapter of the
CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems
 CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems Wireless Foundation: Modulation and Demodulation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 208A Watson Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs434/
CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems Wireless Foundation: Modulation and Demodulation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 208A Watson Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs434/
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Digital Image Processing
 In the Name of Allah Digital Image Processing Introduction to Wavelets Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform.
In the Name of Allah Digital Image Processing Introduction to Wavelets Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform.
Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain
 Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain Author: Gareth Forbes Created: 3/11/9 Revision: The general idea A phase modulated signal is a type of signal which contains information
Phase demodulation using the Hilbert transform in the frequency domain Author: Gareth Forbes Created: 3/11/9 Revision: The general idea A phase modulated signal is a type of signal which contains information
EECS 452 Practice Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 2014
 EECS 452 Practice Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 2014 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points Section
EECS 452 Practice Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 2014 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points Section
CHAPTER 9. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals
 Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
I-Q transmission. Lecture 17
 I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
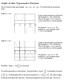 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections , pp Angle Modulation No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c Instantaneous Frequency 2 dt dt No Modulation
 page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class)
 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2015/1 HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class) Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do
ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2015/1 HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class) Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do
Chapter 5 OFDM. Office Hours: BKD Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30
 Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 2 OFDM: Overview Let S 1, S 2,, S N be the information symbol. The discrete baseband OFDM modulated symbol can be expressed
Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 2 OFDM: Overview Let S 1, S 2,, S N be the information symbol. The discrete baseband OFDM modulated symbol can be expressed
Graphs of sin x and cos x
 Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Sinusoids. Lecture #2 Chapter 2. BME 310 Biomedical Computing - J.Schesser
 Sinusoids Lecture # Chapter BME 30 Biomedical Computing - 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gain an Appreciation of the Various Types of Signals and Systems To Analyze The Various Types of Systems To
Sinusoids Lecture # Chapter BME 30 Biomedical Computing - 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gain an Appreciation of the Various Types of Signals and Systems To Analyze The Various Types of Systems To
Laboratory Assignment 4. Fourier Sound Synthesis
 Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
NAME: EE301 Signals and Systems Exam 3. NAME In-Class Exam Thursday, Apr. 20, Cover Sheet
 NAME: EE31 Signals and Systems Exam 3 NAME n-class Exam Thursday, Apr. 2, 217 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet Calculators
NAME: EE31 Signals and Systems Exam 3 NAME n-class Exam Thursday, Apr. 2, 217 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet Calculators
Topic 6. The Digital Fourier Transform. (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith)
 Topic 6 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0-1 -0.8-0.6-0.4-0.2 0 0.2 0.4
Topic 6 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0-1 -0.8-0.6-0.4-0.2 0 0.2 0.4
Principles of Communications ECS 332
 Principles of Communications ECS 332 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 5. Angle Modulation Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Wednesday 4:3-5:3 Friday 4:3-5:3 Example
Principles of Communications ECS 332 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 5. Angle Modulation Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Wednesday 4:3-5:3 Friday 4:3-5:3 Example
The Periodogram. Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
 The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides
 MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II)
 EE3054 Signals and Systems Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II Yao Wang Polytechnic University Most of the slides included are extracted from lecture presentations prepared by McClellan and
EE3054 Signals and Systems Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II Yao Wang Polytechnic University Most of the slides included are extracted from lecture presentations prepared by McClellan and
Fourier Transform. Any signal can be expressed as a linear combination of a bunch of sine gratings of different frequency Amplitude Phase
 Fourier Transform Fourier Transform Any signal can be expressed as a linear combination of a bunch of sine gratings of different frequency Amplitude Phase 2 1 3 3 3 1 sin 3 3 1 3 sin 3 1 sin 5 5 1 3 sin
Fourier Transform Fourier Transform Any signal can be expressed as a linear combination of a bunch of sine gratings of different frequency Amplitude Phase 2 1 3 3 3 1 sin 3 3 1 3 sin 3 1 sin 5 5 1 3 sin
Lecture 17 z-transforms 2
 Lecture 17 z-transforms 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/3 1 Factoring z-polynomials We can also factor z-transform polynomials to break down a large system into
Lecture 17 z-transforms 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/3 1 Factoring z-polynomials We can also factor z-transform polynomials to break down a large system into
Topic 2. Signal Processing Review. (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music)
 Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation
 Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang 09/11/2012 Outline Admin and recap Amplitude demodulation Digital modulation 2 Admin Assignment 1 posted 3 Recap: Modulation Objective o Frequency
Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang 09/11/2012 Outline Admin and recap Amplitude demodulation Digital modulation 2 Admin Assignment 1 posted 3 Recap: Modulation Objective o Frequency
ELT Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Fall Mandatory homework exercises
 ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Fall 2014 1 Mandatory homework exercises - Individual solutions to be returned to Markku Renfors by email or in paper format. - Solutions are expected
ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Fall 2014 1 Mandatory homework exercises - Individual solutions to be returned to Markku Renfors by email or in paper format. - Solutions are expected
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
Biomedical Signals. Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar
 Biomedical Signals Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar Noise Removal: Time Domain Techniques 1. Synchronized Averaging (covered in lecture 1) 2. Moving Average Filters (today s topic) 3. Derivative
Biomedical Signals Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar Noise Removal: Time Domain Techniques 1. Synchronized Averaging (covered in lecture 1) 2. Moving Average Filters (today s topic) 3. Derivative
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals. Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer.
 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Recap: Modulation. Admin. Recap: Demod of AM. Page 1. Recap: Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Admin and recap Amplitude demodulation Digital modulation Y. Richard Yang 9// Admin Assignment posted Recap: Modulation Objective o Frequency assignment
Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Admin and recap Amplitude demodulation Digital modulation Y. Richard Yang 9// Admin Assignment posted Recap: Modulation Objective o Frequency assignment
Linear Time-Invariant Systems
 Linear Time-Invariant Systems Modules: Wideband True RMS Meter, Audio Oscillator, Utilities, Digital Utilities, Twin Pulse Generator, Tuneable LPF, 100-kHz Channel Filters, Phase Shifter, Quadrature Phase
Linear Time-Invariant Systems Modules: Wideband True RMS Meter, Audio Oscillator, Utilities, Digital Utilities, Twin Pulse Generator, Tuneable LPF, 100-kHz Channel Filters, Phase Shifter, Quadrature Phase
Basic Signals and Systems
 Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Fall Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class
 Fall 2018 2019 Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class Theory Problems 1. 15 pts) [Sinusoids] Define xt) as xt) = 2sin
Fall 2018 2019 Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class Theory Problems 1. 15 pts) [Sinusoids] Define xt) as xt) = 2sin
LABORATORY - FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS
 LABORATORY - FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS INTRODUCTION The objective of this lab is to explore many issues involved in sampling and reconstructing signals, including analysis of the frequency
LABORATORY - FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS INTRODUCTION The objective of this lab is to explore many issues involved in sampling and reconstructing signals, including analysis of the frequency
Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE4900/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE4900/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 3 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 2 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM
 Spring 2018 What to Turn In: ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM Dr. Havlicek Submit your solution for this assignment electronically on Canvas by uploading a file to ECE-2713-001 > Assignments
Spring 2018 What to Turn In: ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM Dr. Havlicek Submit your solution for this assignment electronically on Canvas by uploading a file to ECE-2713-001 > Assignments
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 16 Angle Modulation (Contd.) We will continue our discussion on Angle
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 16 Angle Modulation (Contd.) We will continue our discussion on Angle
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring Semester, Introduction to EECS 2
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring Semester, 2007 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Lab #3: Modulation and Filtering Goal:... 2 Instructions:...
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring Semester, 2007 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Lab #3: Modulation and Filtering Goal:... 2 Instructions:...
ECEGR Lab #8: Introduction to Simulink
 Page 1 ECEGR 317 - Lab #8: Introduction to Simulink Objective: By: Joe McMichael This lab is an introduction to Simulink. The student will become familiar with the Help menu, go through a short example,
Page 1 ECEGR 317 - Lab #8: Introduction to Simulink Objective: By: Joe McMichael This lab is an introduction to Simulink. The student will become familiar with the Help menu, go through a short example,
Design of Bandpass Delta-Sigma Modulators: Avoiding Common Mistakes
 Design of Bandpass Delta-Sigma Modulators: Avoiding Common Mistakes R. Jacob Baker and Vishal Saxena Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr., ET 201
Design of Bandpass Delta-Sigma Modulators: Avoiding Common Mistakes R. Jacob Baker and Vishal Saxena Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boise State University 1910 University Dr., ET 201
= 36 M symbols/second
 Tutorial (3) Solution Problem 1: Suppose a CATV system uses coaxial cable to carry 100 channels, each of 6 MHz bandwidth. Suppose that QAM modulation is used. What is the symbol rate/channel if a four-point
Tutorial (3) Solution Problem 1: Suppose a CATV system uses coaxial cable to carry 100 channels, each of 6 MHz bandwidth. Suppose that QAM modulation is used. What is the symbol rate/channel if a four-point
Digital Video and Audio Processing. Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises
 Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Introduction to Signals and Systems Lecture #9 - Frequency Response. Guillaume Drion Academic year
 Introduction to Signals and Systems Lecture #9 - Frequency Response Guillaume Drion Academic year 2017-2018 1 Transmission of complex exponentials through LTI systems Continuous case: LTI system where
Introduction to Signals and Systems Lecture #9 - Frequency Response Guillaume Drion Academic year 2017-2018 1 Transmission of complex exponentials through LTI systems Continuous case: LTI system where
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
Costas Loop. Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier
 Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation
 Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation Contents Slide 1 Single-Sideband Modulation Slide 2 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering Slide 3 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering (cont.) Slide
Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation Contents Slide 1 Single-Sideband Modulation Slide 2 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering Slide 3 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering (cont.) Slide
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 2277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 0 Fax ++49 30 / 753 0 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz Tutorial
PROBLEM SET 6. Note: This version is preliminary in that it does not yet have instructions for uploading the MATLAB problems.
 PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation
 ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
Analysis and Simulation of UHF RFID System
 ICSP006 Proceedings Analysis and Simulation of UHF RFID System Jin Li, Cheng Tao Modern Telecommunication Institute, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 00044, P. R. China Email: lijin3@63.com Abstract
ICSP006 Proceedings Analysis and Simulation of UHF RFID System Jin Li, Cheng Tao Modern Telecommunication Institute, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 00044, P. R. China Email: lijin3@63.com Abstract
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
EE123 Digital Signal Processing
 EE123 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 5A Time-Frequency Tiling Subtleties in filtering/processing with DFT x[n] H(e j! ) y[n] System is implemented by overlap-and-save Filtering using DFT H[k] π 2π Subtleties
EE123 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 5A Time-Frequency Tiling Subtleties in filtering/processing with DFT x[n] H(e j! ) y[n] System is implemented by overlap-and-save Filtering using DFT H[k] π 2π Subtleties
A New Approach to Current Differential Protection for Transmission Lines
 A New Approach to Current Differential Protection for Transmission Lines CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL MODEL Normal Condition: I 1 + I 2 = I C - the line charging current Fault Condition: I 1 + I 2 = I C Can be
A New Approach to Current Differential Protection for Transmission Lines CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL MODEL Normal Condition: I 1 + I 2 = I C - the line charging current Fault Condition: I 1 + I 2 = I C Can be
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing. Cartoon View 1 A Wave of Energy
 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
Digital Communication System
 Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at certain rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth requirement
Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at certain rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth requirement
Design of Frequency Demodulator Using Goertzel Algorithm
 Design of Frequency Demodulator Using Goertzel Algorithm Rahul Shetty, Pavanalaxmi Abstract Far distance Communication between millions without a modulation is worthless, and Frequency modulation has many
Design of Frequency Demodulator Using Goertzel Algorithm Rahul Shetty, Pavanalaxmi Abstract Far distance Communication between millions without a modulation is worthless, and Frequency modulation has many
