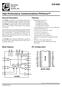
10/100BASE-TX/FX Mini-Φ ΤΜ Transceiver. Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram. 10Base-T PCS. 100Base-X PCS. Digital Adaptive Equalizer.
|
|
|
- Dustin Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BCM521/BCM522 1/1BASE-TX/FX Mini-Φ ΤΜ Transceiver GENERAL DESCRPTON The BCM521/522 is a single-chip 1/1BASE-TX/FX transceiver targeted at Fast Ethernet switches and CardBus Network nterface devices. The BCM521 operates at 3.3 volts while the BCM522 operates at 5 volts. These devices contain a full-duplex 1BASE-T/1BASE-TX/1BASE- FX Fast Ethernet transceiver which performs all of the physical layer interface functions for 1BASE-T Ethernet on CAT 3, 4, and 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable and 1BASE-TX Fast Ethernet on CAT 5 UTP cable. 1BASE-FX is supported through the use of external fiberoptic transmit and receive devices. The BCM521/522 is a highly integrated solution combining a digital adaptive equalizer, ADC, phase lock loop, line driver, encoder, decoder and all the required support circuitry into a single monolithic CMOS chip. t complies fully with the EEE 82.3u specification, including the Media ndependent nterface (M) and Auto- Negotiation subsections, providing compatibility with all industry standard Fast Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) and repeater devices. FEATURES 1BASE-T/1BASE-TX/FX EEE 82.3u compliant Single-chip physical interface - M to Magnetics 3.3 Volt (BCM521) or 5 Volt (BCM522) Operation ntelligent Power Management with cable signal detect Media ndependent nterface (M) Fully-integrated digital adaptive equalizer 125 MHz clock generator and timing recovery On-chip multi-mode transmit waveshaping ntegrated digital baseline wander correction Full-duplex support EEE 82.3u-compliant Auto-Negotiation M management interface up to 12.5 Mbps LED status pins Loopback mode for diagnostics nternal Oscillator utilizes 25 MHz Crystal High Speed Token Ring frame length support Compatible with 3.3 Volt and 5 Volt /O 64-Pin TQFP for low-profile applications 8-Pin MQFP for standard applications APPLCATONS The effective use of digital technology in the BCM521/ 522 design results in robust performance over a broad range of operating scenarios. Problems inherent to mixedsignal implementations, such as analog offset and on-chip noise, are eliminated by employing field proven digital adaptive equalization and digital clock recovery techniques. Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram PCMCA and CardBus Adapter Cards PC Rev 2.2 Adapter Cards Dual-Speed Switches Printers and Print Servers Transceiver Pods (M MAU) Computer Motherboards Dual Speed Repeaters Token Ring adapters, switches, and hubs TD± RD± SD± XTAL XTALO RDAC S/H CRS/Link Detection Clock Generator Bias Generator Multimode Xmt DAC Baseline Wander Correction ADC Energy Detect Digital Adaptive Equalizer Clock Recovery Auto-Negotiation M Registers 1Base-T PCS 1Base-X PCS LED Drivers M Mgmt Control TXD[3:] TXEN TXER TXC COL/RXEN RXC CRS RXDV RXER RXD[3:] LNKLED# SPDLED# RCVLED# XMTLED# FDXLED# (BCM522 KPF only) MODES MDC MDO ENERGY_DET 521/2-DS3-R Alton Parkway P.O. Box 5713 rvine, California Phone: Fax: March 2, 1999
2 16215 Alton Parkway P.O. Box 5713 rvine, California by All rights reserved PrintedintheU.S.A.
3 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 REVSON HSTORY REVSON # DATE CHANGE DESCRPTON SP2. September 3, 1998 Preliminary Release SP3. March 2, 1999 Final Release: 1. Page 12 1Base-T Serial Mode now includes details of associated signals (Table 4 was added). 2. Force1/1 ndication explanation updated on page 28 and Table 32, 1Base-X Receive Timings updated. 4. Table 41, Recommended operating conditions updated. 5. Table 43, Electrical characteristics updated. 6. Changed from Preliminary to Final (the qualifier Preliminary is removed). Document 521/2-DS3-R Page iii
4 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 Page iv Document 521/2-DS3-R
5 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 Table of Contents Cover Page General Description Features Applications Revision History... iii Section 1: Functional Description... 1 Overview...1 Encoder/Decoder...1 Link Monitor...1 Carrier Sense...2 Collision Detection...2 Auto-Negotiation...2 Digital Adaptive Equalizer...2 ADC...2 Digital Clock Recovery/Generator...2 Baseline Wander Correction...3 Multimode Transmit DAC...3 Stream Cipher...3 Far-End Fault...3 M Management...3 Section 2: Hardware Signal Definition Table... 6 Section 3: Pinout Diagrams... 1 Section 4: Operational Description Reset...11 Mode Latching...11 Clock nput...11 solate Mode...11 Loopback Mode...11 Full-Duplex Mode...12 Repeater Mode BASE-FX Mode BASE-T Mode BASE-T Serial Mode...13 Special LED Modes...13 nterrupt Mode...13 Power Saving Modes...14 Energy Detection...14 Document 521/2-DS3-R Page v
6 521/2-DS3-R BCM522 March 2, 1999 Table of Contents Section 5: Register Summary Media ndependent nterface (M) Management nterface: Register Programming...15 M Register Map Summary...15 M Control Register...18 M Status Register...19 PHY dentifier Registers...2 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register...21 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner (LP) Ability Register...22 Auto-Negotiation Expansion Register...23 Auto-Negotiation Next Page Register BASE-X Auxiliary Control Register BASE-X Auxiliary Status Register BASE-X Receive Error Counter BASE-X False Carrier Sense Counter BASE-X Disconnect Counter...26 Ptest Register...26 Auxiliary Control/Status Register...27 Auxiliary Status Summary Register...28 nterrupt Register...29 Auxiliary Mode 2 Register...3 1BASE-T Auxiliary Error and General Status Register...31 Auxiliary Mode Register...32 Auxiliary Multiple PHY Register...32 Broadcom Test Register...33 Section 6: Timing and AC Characteristics Section 7: Electrical Characteristics Section 8: Application Examples Section 9: Mechanical nformation Section 1: Ordering nformation Page vi BCM521-SP3.
7 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 List of Figures Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram...Cover Page Figure 2: Pin Diagrams...1 Figure 3: Clock and Reset Timing...34 Figure 4: Transmit Start of Packet Timing (1BASE-TX)...35 Figure 5: Transmit End of Packet Timing (1BASE-TX)...36 Figure 6: Receive Start of Packet Timing (1BASE-TX)...37 Figure 7: Receive End of Packet Timing (1BASE-TX)...38 Figure 8: Receive Packet Premature End (1BASE-TX)...38 Figure 9: Link Failure or Stream Cipher Error During Receive Packet...39 Figure 1: False Carrier Sense Timing (1BASE-TX)...39 Figure 11: 1BASE-T Transmit Start of Packet Timing...4 Figure 12: Management nterface Timing...42 Figure 13: Management nterface Timing (with Preamble Suppression On)...42 Figure 14: Power Connections...45 Figure 15: Pins Sampled at Reset...45 Figure 16: 64-Pin TQFP 1mm Pkg (BCM521 KPT)...46 Figure 17: 64-Pin TQFP 14mm Pkg (BCM522 KET)...47 Figure 18: 8-Pin MQFP 14mm Pkg (BCM522 KPF)...48 Document 521/2-DS3-R Page vii
8 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 List of Tables Table 1: 4B5B Encoding...4 Table 2: Receive Error Encoding...5 Table 3: Pin Descriptions...6 Table 5: Power Modes...14 Table 6: M Management Frame Format...15 Table 7: M Register Map Summary...16 Table 8: M Control Register (Address b, d, h)...18 Table 9: M Status Register (Address 1B, 1d, 1h)...19 Table 1: PHY ndentifier Registers (Addresses 1 and 11b, 2 and 3b, 2 and 3h)... 2 Table 11: Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (Address 1b, 4d, and 4h)...21 Table 12: Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (Address 11b, 5d, 5h)...22 Table 13: Auto-Negotiation Expansion Register (Address 11b, 6d, 6h)...23 Table 14: Next Page Transmit Register (Address 111b, 7d, 7h)...23 Table 15: 1BASE-X Auxiliary Control Register (Address 1b, 16d, 1h)...24 Table 16: 1BASE-X Auxiliary Status Register (Address 11b, 17d, 11h)...25 Table 17: 1BASE-X Receive Error Counter (Address 11b, 18d, 12h)...26 Table 18: 1BASE-X False Carrier Sense Counter (Address 111b, 19d, 13h)...26 Table 19: 1BASE-X Disconnect Counter (Address 11b, 2d, 14h)...26 Table 2: PTEST Register (Address 1111b, 23d, 17h)...26 Table 21: Auxiliary Control/Status Register (Address 11b, 24d, 18h)...27 Table 22: Auxiliary Status Summary Register (Address 111b, 25d, 19h)...28 Table 23: nterrupt Register (Address 111b, 26d, 1Ah)...29 Table 24: Auxiliary Mode 2 (Address 1111b, 27d, 1Bh)...3 Table 25: 1BASE-T Auxiliary Error and General Status Register (Address 111b, 28d, 1Ch) Table 26: Auxiliary Mode Register (Address 1111b, 29d, 1Dh)...32 Table 27: Auxiliary Multiple PHY Register (Address 1111b, 3d, 1Eh)...32 Table 28: Broadcom Test (Address 11111b, 31d, 1Fh)...33 Table 29: Clock Timing...34 Table 3: Reset Timing...34 Table 31: 1BASE-X Transmit Timing...35 Table 32: 1BASE-X Receive Timing...36 Table 33: 1BASE-T Transmit Timing...4 Table 34: 1BASE-T Receive Timing...41 Table 35: 1BASE-T Collision Timing...41 Table 36: Loopback Timing...41 Table 37: Auto-Negotiation Timing...41 Table 38: LED Timing...41 Table 39: Management Data nterface Timing...42 Table 4: Absolute Maximum Ratings...43 Table 41: Recommended Operating Conditions for BCM521/BCM Table 42: Package Thermal Characteristics...43 Table 43: Electrical Characteristics...44 Page viii Document 521/2-DS3-R
9 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 SECTON 1: FUNCTONAL DESCRPTON OVERVEW The BCM521/522 is a single-chip Fast Ethernet transceiver. t performs all of the physical layer interface functions for 1BASE-TX full- or half-duplex Ethernet on CAT 5 twisted pair cable and 1BASE-T full- or half-duplex Ethernet on CAT 3, 4 or 5 cable. t may also be configured for 1BASE-FX full- or half-duplex transmission over fiber-optic cabling when paired with an external fiber-optic line driver and receiver. The chip performs 4B5B, MLT3, NRZ, and Manchester encoding and decoding, clock and data recovery, stream cipher scrambling/descrambling, digital adaptive equalization, line transmission, carrier sense and link integrity monitor, Auto- Negotiation and Media ndependent nterface (M) management functions. The BCM521/522 may be connected to a MAC, switch controller or repeater controller through the M on one side, and connects directly to the network media on the other side (through isolation transformers for unshielded twisted pair (UTP) modes or fiber-optic transmitter/receiver components for FX modes). n repeater mode, the M port may be bussed with other BCM521/522 devices. The BCM521/522 is fully compliant with the EEE 82.3 and 82.3u standards. ENCODER/DECODER n 1BASE-TX and 1BASE-FX modes, the BCM521/522 transmits and receives a continuous data stream on twisted pair or fiber-optic cable. When the M transmit enable is asserted, nibble-wide (4-bit) data from the transmit data pins is encoded into 5-bit code-groups and inserted into the transmit data stream. The 4B5B encoding is shown in Table 1. The transmit packet is encapsulated by replacing the first two nibbles of preamble with a start of stream delimiter (J/K codes) and appending an end of stream delimiter (T/R codes) to the end of the packet. When the M transmit error input is asserted during a packet, the transmit error code group (H) is sent in place of the corresponding data code group. The transmitter will repeatedly send the idle code group between packets. n TX mode, the encoded data stream is scrambled by a stream cipher block and then serialized and encoded into MLT3 signal levels. A multi-mode transmit DAC is used to drive the MLT3 data onto the twisted pair cable. n FX mode, the scrambling function is bypassed and the data is NRZ encoded. The multimode transmit DAC drives differential positive ECL (PECL) levels to an external fiber-optic transmitter. Following baseline wander correction, adaptive equalization, and clock recovery in TX mode, the receive data stream is converted from MLT3 to serial NRZ data. The NRZ data is descrambled by the stream cipher block and then deserialized and aligned into 5-bit code groups. n FX mode, the receive data stream differential PECL levels are sampled from the fiber-optic receiver. Baseline wander correction, adaptive equalization, and stream cipher descrambling functions are bypassed and NRZ decoding is used instead of MLT3. The 5-bit code groups are decoded into 4-bit data nibbles, as shown in Table 1. The start of stream delimiter is replaced with preamble nibbles and the end of stream delimiter and idle codes are replaced with all zeros. The decoded data is driven onto the M receive data pins. When an invalid code group is detected in the data stream, the BCM521/522 will assert the M RXER signal. The chip will also assert RXER for several other error conditions which improperly terminate the data stream. While RXER is asserted, the receive data pins will be driven with a 4-bit code indicating the type of error detected. The error codes are listed in Table 2. n 1BASE-T mode, Manchester encoding and decoding is performed on the data stream. The multimode transmit DAC performs pre-equalization for 1 meters of CAT 3 cable. LNK MONTOR n 1BASE-TX mode, receive signal energy is detected by monitoring the receive pair for transitions in the signal level. Signal levels are qualified using squelch detect circuits. When no signal or certain invalid signals are detected on the receive pair, the link monitor will enter and remain in the Link Fail state where only idle codes will be transmitted. When a valid signal is detected on the receive pair for a minimum period of time, the link monitor will enter the Link Pass state and the transmit and receive functions will be enabled. n 1BASE-FX mode, the external fiber-optic receiver performs the signal energy detection function and communicates this information directly to the BCM521/522 through the differential SD± pins. n 1BASE-T mode, a link-pulse detection circuit constantly monitors the RD± pins for the presence of valid link pulses. Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 1
10 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 CARRER SENSE n 1BASE-X modes, carrier sense is asserted asynchronously on the CRS pin as soon as activity is detected in the receive data stream. RXDV is asserted as soon as a valid Start-of-Stream Delimiter (SSD) is detected. Carrier sense and RXDV are deasserted synchronously upon detection of a valid end of stream delimiter or two consecutive idle code groups in the receive data stream. f carrier sense is asserted and a valid SSD is not detected immediately, then RXER will be asserted in place of RXDV. A value of 111 will be driven on the receive data pins to indicate false carrier sense. n 1BASE-T mode, carrier sense is asserted asynchronously on the CRS pin when valid preamble activity is detected on the RD+/ input pins. n half-duplex DTE mode, the BCM521/522 will also assert carrier sense while transmit enable is asserted and the link monitor is in the Pass state. n full-duplex mode, CRS is only asserted for receive activity. COLLSON DETECTON n half-duplex mode, collision detect is asserted on the COL pin whenever carrier sense is asserted and transmission is in progress. Collision detect is never asserted in full-duplex mode or repeater mode. AUTO-NEGOTATON The BCM521/522 contains the ability to negotiate its mode of operation over the twisted pair link using the Auto-Negotiation mechanism defined in the EEE 82.3u specification. Auto-Negotiation may be enabled or disabled by hardware or software control. When the Auto-Negotiation function is enabled, the BCM521/522 will automatically choose its mode of operation by advertising its abilities and comparing them with those received from its link partner. The BCM521/522 can be configured to advertise 1BASE-TX full-duplex and/or half-duplex and 1BASE-T full and/or half-duplex. The transceiver will negotiate with its link partner, and choose the highest level of operation available for its own link. Auto-Negotiation is not operational during 1BASE-FX operation and will not advertise full-duplex abilities when the device is configured in repeater mode. DGTAL ADAPTVE EQUALZER The digital adaptive equalizer removes ntersymbol nterference (S) created by the transmission channel media. The equalizer accepts sampled unequalized data from the ADC on each channel and produces equalized data. The BCM521/ 522 achieves an optimum signal to noise ratio by using a combination of feed forward equalization and decision feedback equalization. This powerful technique achieves a 1BASE-TX BER of less than 1 x 1-12 fortransmissionupto1meters on CAT 5 twisted pair cable, even in harsh noise environments. The digital adaptive equalizers in the BCM521/522 achieve performance close to theoretical limits. The all-digital nature of the design makes the performance very tolerant to on-chip noise. The filter coefficients are self adapting to any quality of cable or cable length. Due to transmit pre-equalization in 1BASE-T mode and complete lack of S in 1BASE-FX mode, the adaptive equalizer is bypassed in these two modes of operation. ADC The receive channel has a 6-bit 125 MHz analog to digital converter (ADC). The ADC samples the incoming data on the receive channel and produces a 6-bit output. The output of the ADC is fed to the digital adaptive equalizer. Advanced analog circuit techniques achieve low offset, high power supply noise rejection, fast settling time, and low bit error rate. DGTAL CLOCK RECOVERY/GENERATOR The all-digital clock recovery and generator block creates all internal transmit and receive clocks. The transmit clock is locked to the 25 MHz clock input while the receive clock is locked to the incoming data stream. Clock recovery circuits optimized to MLT3, NRZ, and Manchester encoding schemes are included for use with each of the three different operating modes. The input data stream is sampled by the recovered clock and fed synchronously to the digital adaptive equalizer. Page 2 Document 521/2-DS3-R
11 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 BASELNE WANDER CORRECTON A 1BASE-TX data stream is not always DC balanced. Because the receive signal must pass through a transformer, the DC offset of the differential receive input can wander. This effect, known as baseline wander, can greatly reduce the noise immunity of the receiver. The BCM521/522 automatically compensates for baseline wander by removing the DC offset from the input signal, and thereby significantly reduces the chance of a receive symbol error. The baseline wander correction circuit is not required, and therefore bypassed, in 1BASE-T and 1BASE-FX operating modes. MULTMODE TRANSMT DAC The multimode transmit digital to analog converter (DAC) transmits MLT3-coded symbols in 1BASE-TX mode, NRZcoded symbols in 1BASE-FX mode, and Manchester-coded symbols in 1BASE-T mode. t allows programmable edgerate control in TX mode which decreases unwanted high frequency signal components thus reducing EM. High-frequency pre-emphasis is performed in 1BASE-T mode; no filtering is performed in 1BASE-FX mode. The transmit DAC utilizes a current drive output which is well balanced and produces very low-noise transmit signals. PECL voltage levels are produced with resistive terminations in 1BASE-FX mode. STREAM CPHER n 1BASE-TX mode, the transmit data stream is scrambled in order to reduce radiated emissions on the twisted pair cable. The data is scrambled by exclusive or ing the NRZ signal with the output of an 11-bit wide linear feedback shift register (LFSR), which produces a 247-bit non-repeating sequence. The scrambler reduces peak emissions by randomly spreading the signal energy over the transmit frequency range, and eliminating peaks at certain frequencies. The receiver descrambles the incoming data stream by exclusive or ing it with the same sequence generated at the transmitter. The descrambler detects the state of the transmit LFSR by looking for a sequence representing consecutive idle codes. The descrambler will lock to the scrambler state after detecting a sufficient number of consecutive idle code-groups. The receiver will not attempt to decode the data stream unless the descrambler is locked. Once locked, the descrambler will continuously monitor the data stream to make sure that it has not lost synchronization. The receive data stream is expected to contain inter-packet idle periods. f the descrambler does not detect enough idle codes within 724µs, it will become unlocked, and the receive decoder will be disabled. The descrambler will always be forced into the unlocked state when a link failure condition is detected. A special node called High Speed Token Ring can be enabled. t will increase the scrambler timeout from 724 µs to 5816 µs, thus allowing frames as large as the Token Ring maximum length to be received without error. Stream cipher scrambling/descrambling is not used in 1BASE-FX and 1BASE-T modes. FAR-END FAULT Auto-Negotiation provides a Remote Fault capability for detection of asymmetric link failures. Since Auto-Negotiation is not available for 1BASE-FX, the BCM521/522 implements the EEE 82.3 standard Far-End Fault mechanism for the indication and detection of remote error conditions. When the Far-End Fault mechanism is enabled, a transceiver will transmit the Far-End Fault ndication whenever a receive channel failure is detected (signal detect is deasserted). The transceiver will also continuously monitor the receive channel when a valid signal is present (signal detect asserted). When its link partner is indicating a remote error, the transceiver will force its link monitor into the link fail state and set the Remote Fault bit in the M status register. The Far-End Fault mechanism is enabled by default in 1BASE-FX mode and disabled in 1BASE-TX and 1BASE-T modes, and may be controlled by software after reset. M MANAGEMENT The BCM521/522 contains a complete set of M management registers accessible by using the management clock line (MDC) and the bidirectional serial data line (MDO). Many transceivers can be bussed together on a single MDO/MDC wire pair by giving each a unique PHY address, defined by configuring the five external PHY address input pins. Every time an M read or write operation is executed, the BCM521/522 compares the operation s PHY address with its own PHY address definition. The operation is executed only when the addresses match. For further details, see Section 5: Register Summary on page 15. Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 3
12 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 Table 1: 4B5B Encoding NAME 4B CODE 5B CODE MEANNG 1111 Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data 9 A Data A B Data B C Data C D Data D E Data E F Data F * dle J 11* 11 Start-of-Stream Delimiter, Part 1 K 11* 11 Start-of-Stream Delimiter, Part 2 T * 111 End-of-Stream Delimiter, Part 1 R * 111 End-of-Stream Delimiter, Part 2 H 1 1 Transmit Error (used to force signalling errors) V 111 nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code V nvalid Code * Treated as invalid code (mapped to 111) when received in data field. Page 4 Document 521/2-DS3-R
13 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 Table 2: Receive Error Encoding ERROR TYPE RXD[3:] Stream cipher error - descrambler lost lock 1 Link failure 11 Premature end of stream 11 nvalid code 111 Transmit error 1 False carrier sense 111 Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 5
14 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 SECTON 2: HARDWARE SGNAL DEFNTON TABLE Table 3 provides the pin descriptions for the BCM521 and BCM KPT 522 KET 522 KPF MEDA CONNECTONS 26, 25 26, 25 31, 3 31, 3 31, 3 36, 35 CLOCK 6, 5 6, 5 8, 7 M NTERFACE Table 3: Pin Descriptions PN LABEL TYPE DESCRPTON RD+ RD TD+ TD XTAL, XTALO TXC O 6, 59, 58, 57 6, 59, 58, 57 74, 73, 72, 71 O,O Receive Pair. Differential data from the media is received on the RD± signal pair. Transmit Pair. Differential data is transmitted to the media on the TD± signal pair. 25 MHz Crystal Oscillator nput, Output. A 25 MHz parallel-resonant crystal may be connected between these pins to stabilize the internal oscillator. Connect a 27 pf capacitor from each pin to GND. Alternatively, a stable 25 MHz clock may be applied to the XTAL pin. n this case, leave XTALO unconnected. No capacitors are required. Transmit Clock. 25 MHz output in 1BASE-X mode and 2.5 MHz in 1BASE-T M mode. 1 MHz output in 1BASE-T serial mode. This clock is a continuously driven output, generated from the XTAL input. TXD[3:] PD these pins synchronous with TXC. TXD[3] is the most significant bit. Transmit Data nput. Nibble-wide transmit data stream is input on Only bit is used in 1BASE-T serial mode TXEN Transmit Enable. Active high. ndicates that the data nibble on PD TXD[3:] is valid TXER Transmit Error. An active high input is asserted when a transmit error PD condition is requested by the repeater controller RXC O 43, 44, 47, 48 43, 44, 47, 48 53, 54, 57, 58 RXD[3:] RXDV O RXER O O Receive Clock. 25 MHz output in 1BASE-X M mode and 2.5 MHz output in 1BASE-T mode. 1 MHz output in 1BASE-T serial mode. This clock is recovered from the incoming data on the cable inputs. RXC is a continuously running output clock resynchronized at the start of each incoming packet. This synchronization may result in an elongated period during one cycle while RXDV is low. Receive Data Outputs. Nibble-wide receive data stream is driven out on these pins synchronous with RXC. RXD[3] is the most significant bit. Only bit is used in 1BASE-T serial mode. Receive Data Valid. Active high. ndicates that a receive frame is in progress, and that the data stream present on the RXD output pins is valid. Receive Error Detected. Active high. ndicates that an error is occurring during a receive frame. [MSB:LSB]; # = active-low signal, = input, O = output, /O = bidirectional, PU = input w/ internal pull-up, O OD = open-drain output, O 3S = three-state output, B = Bias, PWR = power supply, GND = ground Page 6 Document 521/2-DS3-R
15 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM KPT CRS O Carrier Sense. Active high. ndicates traffic on link. n 1BASE-X modes, CRS is asserted when a non-idle condition is detected in the receive data stream and deasserted when idle or a valid end of stream delimiter is detected. n 1BASE-T mode, CRS is asserted when a valid preamble is detected and deasserted when end-of-file or an idle condition is detected. CRS is also asserted during transmission of packets except in repeater or full-duplex modes. CRS is an asynchronous output signal COL/RXEN /O PD Collision Detect. n half-duplex modes, active high output indicates that a collision has occurred. n full-duplex mode, COL remains low. COL is an asynchronous output signal. Receive Enable. n repeater mode, RXEN becomes an active high input allowing the repeater controller to enable the M receive bus MDO /O PU and write to the M registers. The data value on the MDO pin is valid Management Data /O. This serial input/output bit is used to read from and latched on the rising edge of MDC MDC PD allow M management functions. Clock frequencies up to 12.5 MHz are Management Data Clock. The MDC clock input must be provided to supported RESET# Reset. Active Low. Resets the BCM521/522. Also used to enable PU Power Off and Low Power modes. MODE 14, 13, 12, 11, KET 14, 13, 12, 11, KPF 16, 15, 14, 13, 12 PHYAD [4:] PD PHY Address Selects. These inputs set the M management PHY address FDX PD logically OR ed with register, bit 8 to select full-duplex (1) or half-duplex () operation. This selection is only performed in DTE mode Full-Duplex Mode. When Auto-Negotiation is disabled, the FDX pin is as full-duplex operation is not allowed in repeater mode F1/SD+ Table 3: Pin Descriptions (Continued) PN LABEL TYPE DESCRPTON 1BASE-FX Signal Detect/Force 1BASE-X Control. When 1BASE-FX is selected, SD+ and SD indicate signal quality status on the fiber optic link. When the signal quality is good, the SD+ pin will be high relative to the SD pin. When 1BASE-FX mode is not selected, the F1 function is enabled. When F1 is high and ANEN is low, the transceiver will be forced to 1BASE-TX operation. When F1 is low and ANEN is low, the transceiver is forced to 1BASE-T operation. When ANEN is high, F1 has no effect on operation ANEN/SD 1BASE-FX Signal Detect/Auto-Negotiation Enable. When 1BASE-FX is selected, the SD function is enabled. See SD+ description above. When 1BASE-FX is not selected, the ANEN function is enabled. ANEN is active high. When pulled high, Auto- Negotiation will begin immediately after reset. When low, Auto- Negotiation is disabled by default. After reset, the Auto-Negotiation function is under software control TESTEN Test Mode Enable. Active high. May float or be grounded for normal PD operation. [MSB:LSB]; # = active-low signal, = input, O = output, /O = bidirectional, PU = input w/ internal pull-up, O OD = open-drain output, O 3S = three-state output, B = Bias, PWR = power supply, GND = ground Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 7
16 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, KPT LOWPWR PD into Low Power operation with the chip deactivated except for the energy detect block and the crystal oscillator. When asserted with Low Power Mode Enable. Active high input places the BCM521/522 RESET# pulled low, the entire chip is deactivated (Power Off mode) ENERGY_DET O BAS RDAC B LEDS LNKLED# /O PU SPDLED# /O PU POWER 522 KET 522 KPF XMTLED# NTR# FDXLED# RCVLED# ACTLED# 2 FDXLED# O Table 3: Pin Descriptions (Continued) PN LABEL TYPE DESCRPTON O OD O OD Energy Detection. Active high output indicates the presence of a signal on RD+/ receive analog wire pair. Operational in all modes except Power Off. DAC Bias Resistor. Adjusts the current level of the transmit DAC. A resistor of 1.27 kω ±1% must be connected between the RDAC pin and GND. Link ntegrity LED. The Link ntegrity LED indicates the link status of the PHY. LNKLED# is driven low when the link to the PHY is good. During RESET, the output driver is tri-stated and the input value is used to latch the fiber mode. f the pin is low, 1BASE-FX mode is selected. f the pin is high or floating, 1BASE-T or 1BASE-TX mode is selected. When FX mode is enabled, the polarity of LNKLED# is inverted. 1BASE-X LED. The 1 Base-X LED is driven low when operating in 1BASE-X modes and high when operating in 1BASE-T modes. During RESET, the output driver is tri-stated and the input value is used to latch the repeater mode. f the pin is pulled low, the chip will enter repeater mode. f the pin is high or floating, DTE mode is selected. When repeater mode is enabled, the polarity of SPDLED# is inverted. Transmit Activity LED. Active low output. The transmit activity LED is driven low for approximately 8ms each time there is transmit activity while in the link pass state. When the interrupt mode is enabled, pin becomes NTR#. When FDXLED mode is enabled, pin becomes FDXLED#. Receive Activity LED. Active low output. The receive activity LED is driven low for approximately 8ms each time there is receive activity while in the link pass state. n either interrupt or FDXLED mode, pin becomes ACTLED#, indicating both receive and transmit activity. Full Duplex LED. BCM522KPF 8-Pin Package Only. The Full Duplex LED is driven low when operating in full duplex mode and driven high in half duplex mode. This output always relates the duplex status, regardless of what type of output appears on the XMTLED# pin. 8 VDD PWR nput VDD, BCM V or 5V. f any of the inputs are driven to 5.V, this pin must be connected to a 5.V supply. f none of the inputs are driven above 3.3V, this pin must be connected to the 3.3V supply. 8 1 VDD PWR nput VDD, BCM522. This pin must be connected to the 5.V supply. [MSB:LSB]; # = active-low signal, = input, O = output, /O = bidirectional, PU = input w/ internal pull-up, O OD = open-drain output, O 3S = three-state output, B = Bias, PWR = power supply, GND = ground Page 8 Document 521/2-DS3-R
17 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM KPT 18, 22, 27, 28 21, 24, 29, 32 18, 22, 27, 28 21, 24, 29, 32 23, 27, 32, 33 26, 29, 34, 37 AVDD PWR Analog VDD. AGND GND Analog GND. 3 5 REGDVDD PWR Voltage Regulator nput. BCM522 Only. 19, 2 24, 25 REGAVDD PWR Voltage Regulator nput. BCM522 Only. 2, 55 2, 55 4, 69 DVDD PWR Digital Core VDD. 54, 63 54, 63 68, 77 DGND GND Digital Core GND. 1, 4, 46 7, 4, 45, KET 1, 4, 46 7, 4, 45, KPF 3, 6, 56 9, 5, 55, 78 Table 3: Pin Descriptions (Continued) PN LABEL TYPE DESCRPTON OVDD PWR Digital Periphery (Output Buffer) VDD. OGND GND Digital Periphery (Output Buffer) GND. [MSB:LSB]; # = active-low signal, = input, O = output, /O = bidirectional, PU = input w/ internal pull-up, O OD = open-drain output, O 3S = three-state output, B = Bias, PWR = power supply, GND = ground Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 9
18 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 SECTON 3: PNOUT DAGRAMS Figure 2 provides the pin diagrams for the BCM521 and BCM522. Figure 2: Pin Diagrams NC NC AGND AVDD RDAC AGND RD - RD + AVDD AVDD AGND TD - TD + AGND OGND DGND CRS COL/RXEN TXD3 TXD2 TXD1 TXD TXEN DVDD DGND TXC TXER RXER RXC RXDV OVDD DVDD NC OVDD XTALO XTAL OGND VDD RESET# PHYAD PHYAD1 PHYAD2 PHYAD3 PHYAD4 TESTEN LOWPWR BCM521 KPT RXD RXD1 OVDD OGND RXD2 RXD3 MDC MDO OGND FDX ANEN/SD - F1/SD + SPDLED# LNKLED# XMTLED#/NTR#/FDXLED# RCVLED#/ACTLED# ENERGY_DET AVDD (Top View) BCM522 KET 64 PNS (Top View) OGND NC NC AVDD REGAVDD REGAVDD AGND AVDD RDAC AGND RD - RD + AVDD AVDD AGND TD - TD + AGND NC NC NC NC NC OGND DGND CRS COL/RXEN TXD3 TXD2 TXD1 TXD TXEN DVDD DGND TXC TXER RXER RXC RXDV NC NC NC NC OVDD DVDD REGDVDD OVDD XTALO XTAL OGND VDD RESET# PHYAD PHYAD1 PHYAD2 PHYAD3 PHYAD4 TESTEN LOWPWR ENERGY_DET FDXLED# BCM522 KPF NC NC RXD RXD1 OVDD OGND RXD2 RXD3 MDC MDO OGND FDX ANEN/SD - F1/SD + SPDLED# LNKLED# XMTLED#/NTR#/FDXLED# RCVLED#/ACTLED# NC NC ENERGY_DET AVDD REGAVDD REGAVDD AGND AVDD RDAC AGND RD - RD + AVDD AVDD AGND TD - TD + AGND DGND CRS COL/RXEN TXD3 TXD2 TXD1 TXD TXEN DVDD DGND TXC TXER RXER RXC RXDV OVDD DVDD REGDVDD OVDD XTALO XTAL OGND VDD RESET# PHYAD PHYAD1 PHYAD2 PHYAD3 PHYAD4 TESTEN LOWPWR RXD RXD1 OVDD OGND RXD2 RXD3 MDC MDO OGND FDX ANEW/SD - F1/SD + SPDLED# LNKLED# XMTLED#/NTR#/FDXLED# RCVLED#/ACTLED# Pins (Top View) Page 1 Document 521/2-DS3-R
19 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 SECTON 4: OPERATONAL DESCRPTON RESET There are two ways to reset the BCM521/522. A hardware reset pin has been provided that resets all internal nodes in the chip to a known state. The reset pulse must be asserted for at least 4 ns. Hardware reset should always be applied to the BCM521/522 after power-up. The BCM521/522 also has a software reset capability. To perform software reset, a 1 must be written to bit 15 of the M Control Register. This bit is self-clearing, meaning that a second write operation is not necessary to end the reset. There is no effect if a is written to the M Control Register reset bit. MODE LATCHNG n order to reduce chip pin count, two pins have been given dual functionality. The LNKLED# and SPDLED# pins, normally LED drivers, are used as inputs during hardware RESET to sample requests for fiber mode and repeater mode operation. After RESET, the pins revert to outputs. The LNKLED# pin will interpret a during hardware RESET to be a request for fiber mode of operation and a 1 to be a request for copper UTP operation. Similarly, a 1 on the SPDLED# pin during hardware RESET will be interpreted as a request for DTE mode and a a request for repeater mode. The connection of the LED to the chip must be modified as shown in Figure 15, on page 45, to provide the signal input, yet retain the LED indication function. f it is desired to have either pin sample a 1 during RESET, the LED would be connected fromthepintovddasinfigure15a.tosamplea during RESET, the LED would be connected from the pin to ground as in Figure 15B. After the chip samples the input, it will latch the value and generate the proper polarity signal to drive the LED. For example, if either LED pin is sampled as during RESET, the subsequent output signal becomes inverted, active high. This potential inversion of signal polarity may need to be accounted for if loads other than the LEDs are driven from these terminals. f no connection is made to the LNKLED# or SPDLED# pins, internal pull-ups cause the chip to sample a logical 1 at reset and give the default operation of copper UTP mode and DTE. CLOCK NPUT The BCM521/522 clock input can be driven two ways: internal crystal oscillator or external oscillator. To take advantage of the internal oscillator, attach a 25 MHz crystal between the XTAL and XTALO pins. Connect 27 pf capacitors from each pin to ground. Alternatively, a 5% duty cycle 25MHz clock may be directly applied to the XTAL pin. n this case, the XTALO output must be left unconnected. No capacitors are used. SOLATE MODE When the BCM521/522 is put into isolate mode, all M inputs (TXD[3:], TXEN, and TXER) are ignored, and all M outputs (TXC, COL, CRS, RXC, RXDV, RXER, and RXD[3:]) are set to high impedance. Only the M management pins (MDC, MDO) operate normally. Upon resetting the chip, the isolate mode is off. Writing a 1 to bit 1 of the M Control Register puts the transceiver into isolate mode. Writing a tothesamebitremovesitfromisolatemode. LOOPBACK MODE Loopback mode allows in-circuit testing of the BCM521/522 chip. All packets sent in through the TXD pins are loopedback internally to the RXD pins, and are not sent out to the cable. The loopback mode is enabled by writing a 1 to bit 14 of the M Control Register. n order to resume normal operation, bit 14 of the M Control Register must be. ncoming packets on the cable are ignored in loopback mode. Because of this, the COL pin will normally not be activated during loopback mode. n order to test that the COL pin is actually working, the BCM521/522 may be placed into collision test mode. This mode is enabled by writing a 1 to bit 7 of the M Control Register. Asserting TXEN will cause the COL output to go high, and deasserting TXEN will cause the COL output to go low. Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 11
20 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 While in loopback mode, several function bypass modes are also available that can provide a number of different combinations of feedback paths during loopback testing. These bypass modes include: bypass scrambler, bypass MLT3 encoder and bypass 4B5B encoder. All bypass modes can be accessed by writing bits of the Auxiliary Control Register (1h). mportant Note: Due to the nature of the Block RXDV mode (bit 9 of M Register 1Bh), which is enabled by default, 1BASE-T loopback will not function properly. t is necessary to first disable the Block RXDV mode by writing FD to the Aux Mode 2 Register (1Bh). FULL-DUPLEX MODE The BCM521/522 supports full-duplex operation. While in full-duplex mode, a transceiver may simultaneously transmit and receive packets on the cable. The COL signal is never activated while in full-duplex mode. The CRS output is asserted only during receive packets, not transmit packets. By default, the BCM521/522 powers up in half-duplex mode. When Auto-Negotiation is disabled, full-duplex operation can be enabled either by FDX pin control or by an M register bit (Register, bit 8). When Auto-Negotiation is enabled in DTE mode, full-duplex capability is advertised by default, but can be overridden by a write to the Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (4h). n repeater mode, full-duplex capability can never be advertised. One of the LED outputs can be modified to signal full-duplex vs. half-duplex operation. This capability is enabled by setting M Register 1Ah, bit 15. n this mode, XMTLED# becomes FDXLED#, where a 1 output indicates half-duplex and a output indicates full-duplex. This value is the inverse of M register 18h, bit. When the FDXLED mode is activated, the RCVLED# becomes ACTLED#. The BCM522 KPF also contains a dedicated FDXLED# pin that is always active regardless of the type of output appearing on the XMTLED# pin. REPEATER MODE The BCM521/522 supports a repeater mode for 1Mbps operation only. Activation of this mode requires a pulldown resistor on the SPDLED# output. The pin is tri-stated during hardware reset and the value is sampled on the trailing edge of RESET#. While in the repeater mode, the BCM521/522 allows only 1BASE-TX or 1BASE-FX operation. Several signals change their functionality in repeater mode. The COL output becomes a RXEN input, allowing the repeater controller to enable the M receive bus. The CRS output is asserted only during receive packets, not transmit packets. No full-duplex operation is allowed. 1BASE-FX MODE For 1BASE-FX mode, the BCM521/522 transceiver interfaces with an external 1BASE-FX fiber-optic driver and receiver instead of the magnetics module used with twisted-pair cable. The differential transmit and receive data pairs operate at PECL voltage levels instead of those required for twisted-pair transmission. The data stream is encoded using two-level NRZ instead of three-level MLT3. Since scrambling is not used in 1BASE-FX operation, the stream cipher function is bypassed. To activate the 1BASE-FX mode, a pull down resistor must be placed on the LNKLED# output. During hardware reset, the output driver is tri-stated and the value is sampled on the trailing edge of RESET#. The external fiber-optic receiver will detect signal status and pass it into the BCM521/522 through the SD± pins. The SD± pins are functional only after the 1BASE-FX mode is selected. 1BASE-T MODE The same magnetics module used in 1BASE-TX mode can be used to interface to the twisted-pair cable when operating in 1BASE-T mode. The data will be two-level Manchester encoded instead of three-level MLT3 and no scrambling/ descrambling or 4B5B coding is performed. Data and clock rates are decreased by a factor of 1, with the M interface signals operating at 2.5 MHz. Page 12 Document 521/2-DS3-R
21 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 1BASE-T SERAL MODE The BCM521/522 supports 1BASE-T serial mode, also know as the 7-wire interface. n this mode, 1BASE-T transmit and receive packets appear at the M in serial fashion, at a rate of 1 MHz. Receive packet data is output on RXD () synchronously with RXC. Transmit packet data must be input on TXD () synchronously with TXC. Both clocks toggle at 1 MHz. The 1BASE-T serial mode is enabled by writing a 1 to bit 1 of the Auxiliary Multiple-PHY register (1Eh). Note that this mode is not available in 1BASE-X modes. The following table shows the M pins used in this mode and their direction of operation. 521 KPT 522 KET 522 KPF Table 4: 1BASE-T Serial Mode (7-Wire) Signals PN LABEL TYPE DESCRPTON TXD () Serial Transmit Data TXC O Tranmit Data Clock (1 MHz) TXEN Transmit Enable RXD () O Serial Receive Data RXC O Receive Data Clock (1 MHz) CRS O Carrier Sense COL/RXEN O Collision Detect SPECAL LED MODES Traffic Meter Mode. The blink rate of XMTLED# and RCVLED# is decreased dramatically to better show the volume of traffic. Lower traffic levels will make the corresponding LED appear dimmer than higher traffic levels. This mode is activated by writing a 1 to bit 6 of the Aux Mode 2 register (1Bh). Two Link LED Mode. n this mode, the functions of SPDLED# and LNKLED# are changed. SPDLED# becomes an indicator of 1BASE-T link while LNKLED# becomes an indicator of 1BASE-X link. The Two Link LED mode is enabled by writing a 1 to bit 2 of the Aux Mode 2 Register (1Bh). Note that the polarities of these two outputs are influenced by whether FX mode or RPTR mode are enabled. See the definitions of SPDLED# and LNKLED# pins. Force LEDs On. The XMTLED# and RCVLED# outputs can be forced on ( value) by writing a 1 to bit 5 of the Aux Mode 2 register(1bh). Disable LEDs. The XMTLED# and RCVLED# outputs can be forced off ( 1 value) by writing a 1 to bit 4 of the Aux Mode register (1Dh). Similarly, the LNKLED# output can be forced off (value depends on FX mode, see definition of LNKLED# pin) by writing a 1 to bit 3 of the Aux Mode register (1Dh). NTERRUPT MODE The BCM521/522 can be programmed to provide an interrupt output. Three conditions can cause an interrupt to be generated: changes in the duplex mode, changes in the speed of operation or changes in the link status. The interrupt feature is disabled by default. When the interrupt capability is enabled by setting M register 1Ah, bit 14, the XMTLED# pin becomes the NTR# pin and the RCVLED# pin becomes an activity pin named ACTLED#. The NTR# pin is open-drain and may be wire-ored with NTR# pins of other chips on a board. The status of each interrupt source is reflected in register 1Ah, bits 1, 2 and 3. f any type of interrupt occurs, the nterrupt Status bit, register 1Ah, bit, will be set. Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 13
22 BCM521 BCM522 March 2, 1999 The nterrupt Register (1Ah) also contains several bits to control different facets of the interrupt function. f the interrupt enable bit is set to, no status bits will be set and no interrupts will be generated. f the interrupt enable bit is set to 1, the following conditions apply: 1. f mask status bits (bits 9,1,11) are set to and the interrupt mask (bit 8) is set to, status bits and interrupts will be available. 2. f mask status bits (bits 9,1,11) are set to and the interrupt mask (bit 8) is set to 1, statusbitswillbesetbutno interrupts generated. 3. f any mask status bit is set to 1 and the interrupt mask is set to, that status bit will not be set and no interrupt of that type will be generated. 4. f any mask status bit is set to 1 and the interrupt mask is set to 1, that status bit will not be set and no interrupt of any kind will be generated. POWER SAVNG MODES Two power saving modes are implemented in the BCM521/522, which target PCMCA and CardBus applications. The first, called Power Off, disables all circuitry on the chip and consumes the least amount of power. n this mode, register contents are not preserved. Thus, a hard reset should be issued at least 2 milliseconds after exiting this mode. The Power Off mode is enabled by setting LOWPWR to 1 and RESET# to. The second power saving mode is Low Power. n this modes, all chip circuitry is disabled except for the crystal oscillator and the special Energy Detection function. This mode is useful for determining whether the transceiver is connected to a link partner. The Energy Detection block outputs its result on the ENERGYDET pin which can be used by external logic to control when the transceiver is placed in Full Power or Low Power modes. Register contents are preserved while the chip is in Low Power mode, so a hard reset is not necessary after resuming Full Power. The Low Power Mode is enabled by setting LOWPWR to 1 and RESET# to 1. Table 5: Power Modes MODE OSCLLATOR AND ENERGY DETECTON LOWPWR RESET# Full Power Active X Low Power Active 1 1 Power Off Disabled 1 ENERGY DETECTON An on-chip Energy Detection circuit has the capability of determining when a link partner is connected to the end of the transmission media. The circuit monitors the receive inputs for any type of energy, including 1BASE-T, 1BASE-TX or 1BASE-FX packets, and 1BASE-T or Auto-Negotiation link pulses. When energy is detected on the receive inputs for longer than 1.3 milliseconds, the ENERGYDET output is asserted. f all traces of energy disappear for longer the 1.3 seconds, it is assumed that the link partner has disconnected, and the ENERGYDET output is deasserted. The Energy Detection circuit is operational in both Full Power and Low Power modes. n addition, there is a special mode called Automatic Low Power which is enabled by writing a 1 to bit 3 of the Aux Mode 2 register (1Bh). n this mode, a loss of energy on the receive inputs automatically causes the chip to enter the Low Power mode. Similarly, the next time energy is detected, the chip will resume Full Power mode. Page 14 Document 521/2-DS3-R
23 March 2, 1999 BCM521 BCM522 SECTON 5: REGSTER SUMMARY MEDA NDEPENDENT NTERFACE (M) MANAGEMENT NTERFACE: REGSTER PROGRAMMNG The BCM521/522 fully complies with the EEE 82.3u Media ndependent nterface (M) specification. The M management interface registers are serially written-to and read-from using the MDO and MDC pins. A single clock waveform must be provided to the BCM521/522 at a rate of MHz through the MDC pin. The serial data is communicated on the MDO pin. Every MDO bit must have the same period as the MDC clock. The MDO bits are latched on the rising edge of the MDC clock. See Table 6 for the fields in every M instruction s read or write packet frame. Table 6: M Management Frame Format OPERATON PRE ST OP PHYAD REGAD TA DATA DLE DRECTON READ AAAAA RRRRR ZZ Z Z...Z D...D Preamble (PRE). Thirty two consecutive 1 bits must be sent through the MDO pin to the BCM521/522 to signal the beginning of an M instruction. Fewer than 32 1 bits will cause the remainder of the instruction to be ignored, unless the Preamble Suppression mode is enabled (register 1, bit 6). StartofFrame(ST).A 1 pattern indicates that the start of the instruction follows. Operation Code (OP). A READ instruction is indicated by 1, while a WRTE instruction is indicated by 1. PHY Address (PHYAD). A 5-bit PHY address follows next, with the MSB transmitted first. The PHY address allows a single MDO bus to access multiple transceivers. The BCM521/522 supports the full 32-PHY address space. Register Address (REGAD). A 5-bit Register Address follows, with the MSB transmitted first. The register map of the BCM521/522, containing register addresses and bit definitions, are provided on the following pages. Turnaround (TA). The next two bit times are used to avoid contention on the MDO pin when a Read operation is performed. For a Write operation, 1 must be sent to the chip during these two bit times. For a Read operation, the MDO pin must be placed into High-mpedance during these two bit times. The chip will drive the MDO pin to during the second bit time. Data. The last 16 bits of the frame are the actual data bits. For a Write operation, these bits are sent to the BCM521/522. For a Read operation, these bits are driven by the BCM521/522. n either case, the MSB is transmitted first. When writing to the BCM521/522, the data field bits must be stable 1 ns before the rising-edge of MDC, and must be held valid for 1 ns after the rising edge of MDC. When reading from the BCM521/522, the data field bits are valid after the rising edge of MDC until the next rising-edge of MDC. dle. A high impedance state of the MDO line. All drivers are disabled and the PHYs pull-up resistor pulls the line high. Following are two examples of M write and read instructions: n order to put a chip with PHY address 1 into Loopback mode, the following M write instruction must be issued: n order to determine if a PHY is in the link pass state, the following M read instruction must be issued: ZZ ZZZZ ZZZZ ZZZZ ZZZZ For the M read operation, the BCM521/522 will drive the MDO line during the TA and Data fields (the last 17 bit times). Z Z Driven to BCM521/522 Driven by BCM521/522 WRTE AAAAA RRRRR 1 D... D Z Driven to BCM521/522 M REGSTER MAP SUMMARY Table 7 contains the M register summary for the BCM521/522. The register addresses are specified in hex form, and the name of register bits have been abbreviated. When writing to the reserved bits, always write a value, and when reading from these bits, ignore the output value. Never write any value to an undefined register address. The reset value of the registers are shown in the NT column. Document 521/2-DS3-R Page 15
KSZ8021RNL / KSZ8031RNL
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support General Description The KSZ8031RNL is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data over standard
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support General Description The KSZ8031RNL is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data over standard
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.3 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.3 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Data Sheet Rev. 1.0 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Data Sheet Rev. 1.0 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception
KSZ8061RNB/KSZ8061RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX Physical Layer Transceiver Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8061RNB/RND is a single-chip 10Base-T/ 100Base-TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception
10Base-T/100Base-TX Physical Layer Transceiver Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8061RNB/RND is a single-chip 10Base-T/ 100Base-TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai. Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES DATASHEET. Highlights.
 LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY) Comprehensive flexpwr Technology
LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY) Comprehensive flexpwr Technology
Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver
 Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver Features 10/100Mbps TX Full-duplex or half-duplex Supports Auto MDI/MDIX function Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u Supports IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver Features 10/100Mbps TX Full-duplex or half-duplex Supports Auto MDI/MDIX function Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u Supports IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
Am79C989. Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 Am79C989 Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Four independent 10BASE-T transceivers compliant with the IEEE 802.3 standard Four digital Manchester Encode/Decode (MENDEC)
Am79C989 Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Four independent 10BASE-T transceivers compliant with the IEEE 802.3 standard Four digital Manchester Encode/Decode (MENDEC)
Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver
 Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver The () directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It provides a Media Independent Interface (MII) for easy attachment to
Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver The () directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It provides a Media Independent Interface (MII) for easy attachment to
KSZ9021RL/RN. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver for transmission
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver for transmission
LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology
 LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
KSZ9031MNX. Features. General Description. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support. Data Sheet Rev. 0.13
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support Data Sheet Rev. 0.13 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support Data Sheet Rev. 0.13 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr )
 PRELIMINARY Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Repeater functions comply with IEEE 802.3 Repeater Unit specifications Four integral 10BASE-T transceivers
PRELIMINARY Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Repeater functions comply with IEEE 802.3 Repeater Unit specifications Four integral 10BASE-T transceivers
KSZ9021RL/RN. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support. Revision 1.2
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 1.2 General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 1.2 General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver
 Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver Datasheet The Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver (called hereafter the LXT971A Transceiver) directly supports both 100BASE-TX and
Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver Datasheet The Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver (called hereafter the LXT971A Transceiver) directly supports both 100BASE-TX and
3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver
 Intel LXT971A 3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver Datasheet The LXT971A is an IEEE compliant Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver that directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It
Intel LXT971A 3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver Datasheet The LXT971A is an IEEE compliant Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver that directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It
Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting
 Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting PIERGIORGIO BERUTO ANTONIO ORZELLI TF Short Reach PCS, PMA and PLCA baseline proposal November 7 th, 2017 Supporters Gergely Huszak (Kone) Kirsten Matheus (BMW)
Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting PIERGIORGIO BERUTO ANTONIO ORZELLI TF Short Reach PCS, PMA and PLCA baseline proposal November 7 th, 2017 Supporters Gergely Huszak (Kone) Kirsten Matheus (BMW)
EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006
 EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006 Six projects have been identified. It will be our goal to have approximately an equal number of teams working on each project. You may work individually or in groups of
EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006 Six projects have been identified. It will be our goal to have approximately an equal number of teams working on each project. You may work individually or in groups of
KSZ8001L/S. 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04
 L/S 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04 General Description The is a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX Physical Layer Transceiver, operating the core at 1.8 volts
L/S 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04 General Description The is a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX Physical Layer Transceiver, operating the core at 1.8 volts
KSZ9031RNX. Features. General Description. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support. Data Sheet Rev 0.
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Data Sheet Rev 0.11 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Data Sheet Rev 0.11 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Features. NRZ/NRZI MLT3 Encoder. Clock Recovery. Auto Negotiation. Power Down or Saving LED X1. Driver PLL X2
 KS8737 3.3V 10/100BaseTX/FX MII Physical Layer Transceiver Rev 3.11 General Description Operating at 3.3 Volts to meet low voltage and low power requirement, the KS8737 is a 10/100BaseTX/FX Physical Layer
KS8737 3.3V 10/100BaseTX/FX MII Physical Layer Transceiver Rev 3.11 General Description Operating at 3.3 Volts to meet low voltage and low power requirement, the KS8737 is a 10/100BaseTX/FX Physical Layer
Maximum data rate: 50 MBaud Data rate range: ±15% Lock-in time: 1 bit
 MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH MII INTERFACE
 DATASHEET ICS1894-34 Description The ICS1894-34 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
DATASHEET ICS1894-34 Description The ICS1894-34 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations
 100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations 1 0 INTRODUCTION This application note provides the information necessary to design an unmanaged 12-port 100BASE-TX repeater based on National Semiconductor
100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations 1 0 INTRODUCTION This application note provides the information necessary to design an unmanaged 12-port 100BASE-TX repeater based on National Semiconductor
ICS1885. High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM. Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. General Description. Pin Configuration.
 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS1885 High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM General Description The ICS1885 is designed to provide high performance clock recovery and generation for either 25.92
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS1885 High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM General Description The ICS1885 is designed to provide high performance clock recovery and generation for either 25.92
KSZ9031RNX. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0 General Description The is a completely integrated triple-speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet physicallayer transceiver for transmission
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0 General Description The is a completely integrated triple-speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet physicallayer transceiver for transmission
LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology
 LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
CrystalLAN 100BASE-X and 10BASE-T Transceiver
 Features! Single-Chip IEEE 802.3 Physical Interface IC for 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX and 10BASE-T! Adaptive Equalizer provides Extended Length Operation (>160 m) with Superior Noise Immunity and NEXT Margin!
Features! Single-Chip IEEE 802.3 Physical Interface IC for 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX and 10BASE-T! Adaptive Equalizer provides Extended Length Operation (>160 m) with Superior Noise Immunity and NEXT Margin!
ML BASE-TX Physical Layer with MII
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML6692 implements the complete physical layer of the Fast Ethernet 100BASE-TX standard. The ML6692 interfaces to the controller through the standard-compliant Media Independent
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML6692 implements the complete physical layer of the Fast Ethernet 100BASE-TX standard. The ML6692 interfaces to the controller through the standard-compliant Media Independent
RTL8201. Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver
 RTL8201 Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver 1. Features Realtek s RTL8201 is a Fast Ethernet Phyceiver with MII interface to MAC chip. It provides the following features: Support MII interface
RTL8201 Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver 1. Features Realtek s RTL8201 is a Fast Ethernet Phyceiver with MII interface to MAC chip. It provides the following features: Support MII interface
78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver
 78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver Simplifying System Integration TM DESCRIPTION The 78Q2123 and 78Q2133, MicroPHY TM, are the smallest 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet transceivers in
78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver Simplifying System Integration TM DESCRIPTION The 78Q2123 and 78Q2133, MicroPHY TM, are the smallest 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet transceivers in
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH RMII INTERFACE
 DATASHEET ICS1894-33 Description The ICS1894-33 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
DATASHEET ICS1894-33 Description The ICS1894-33 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Low-power coaxial Ethernet transceiver
 DESCRIPTION The is a low power BiCMOS coaxial transceiver interface (CTI) for Ethernet (10base5) and Thin Ethernet (10base) local area networks. The CTI is connected between the coaxial cable and the Data
DESCRIPTION The is a low power BiCMOS coaxial transceiver interface (CTI) for Ethernet (10base5) and Thin Ethernet (10base) local area networks. The CTI is connected between the coaxial cable and the Data
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH RMII INTERFACE. Not recommended for new designs
 DATASHEET ICS1894-40 Description Features The ICS1894-40 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection
DATASHEET ICS1894-40 Description Features The ICS1894-40 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection
Serial Input/Output. Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 Serial Input/Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Serial communication Concepts Standards USART in AVR Lecture overview 2 Why Serial I/O? Problems with Parallel I/O: Needs a wire for
Serial Input/Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Serial communication Concepts Standards USART in AVR Lecture overview 2 Why Serial I/O? Problems with Parallel I/O: Needs a wire for
SD2057 Low Power HART TM Modem
 Low Power HART TM Modem Features Meets HART physical layer requirements Bell 202 shift frequencies of 1200Hz and 2200Hz Integrated receive filter, minimal external components required Buffered HART output
Low Power HART TM Modem Features Meets HART physical layer requirements Bell 202 shift frequencies of 1200Hz and 2200Hz Integrated receive filter, minimal external components required Buffered HART output
Application Note 5044
 HBCU-5710R 1000BASE-T Small Form Pluggable Low Voltage (3.3V) Electrical Transceiver over Category 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Characterization Report Application Note 5044 Summary The Physical Medium
HBCU-5710R 1000BASE-T Small Form Pluggable Low Voltage (3.3V) Electrical Transceiver over Category 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Characterization Report Application Note 5044 Summary The Physical Medium
AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY
 AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview This application note discusses how to migrate from an existing design using the SMSC LAN83C183 PHY
AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview This application note discusses how to migrate from an existing design using the SMSC LAN83C183 PHY
Computer-Based Project in VLSI Design Co 3/7
 Computer-Based Project in VLSI Design Co 3/7 As outlined in an earlier section, the target design represents a Manchester encoder/decoder. It comprises the following elements: A ring oscillator module,
Computer-Based Project in VLSI Design Co 3/7 As outlined in an earlier section, the target design represents a Manchester encoder/decoder. It comprises the following elements: A ring oscillator module,
4 x 10 bit Free Run A/D 4 x Hi Comparator 4 x Low Comparator IRQ on Compare MX839. C-BUS Interface & Control Logic
 DATA BULLETIN MX839 Digitally Controlled Analog I/O Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features x 4 input intelligent 10 bit A/D monitoring subsystem 4 High and 4 Low Comparators External IRQ Generator
DATA BULLETIN MX839 Digitally Controlled Analog I/O Processor PRELIMINARY INFORMATION Features x 4 input intelligent 10 bit A/D monitoring subsystem 4 High and 4 Low Comparators External IRQ Generator
ERTEC 200. PHY Description. Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller
 ERTEC 200 Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller PHY Description Copyright Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Page 1 ERTEC 200 PHY Edition (11/2007) Disclaimer of Liability We have checked the contents
ERTEC 200 Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller PHY Description Copyright Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Page 1 ERTEC 200 PHY Edition (11/2007) Disclaimer of Liability We have checked the contents
10/100Base. 100Base-FX Switching Converter. User s Manual
 10/100Base to 100Base-FX Switching Converter User s Manual COPYRIGHT All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
10/100Base to 100Base-FX Switching Converter User s Manual COPYRIGHT All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
Applications. Operating Modes. Description. Part Number Description Package. Many to one. One to one Broadcast One to many
 RXQ2 - XXX GFSK MULTICHANNEL RADIO TRANSCEIVER Intelligent modem Transceiver Data Rates to 100 kbps Selectable Narrowband Channels Crystal controlled design Supply Voltage 3.3V Serial Data Interface with
RXQ2 - XXX GFSK MULTICHANNEL RADIO TRANSCEIVER Intelligent modem Transceiver Data Rates to 100 kbps Selectable Narrowband Channels Crystal controlled design Supply Voltage 3.3V Serial Data Interface with
Ethernet Coax Transceiver Interface
 1CY7B8392 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3 10BASE5 and 10BASE2 Pin compatible with the popular 8392 Internal squelch circuit to eliminate input noise Hybrid mode collision detect for extended distance
1CY7B8392 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3 10BASE5 and 10BASE2 Pin compatible with the popular 8392 Internal squelch circuit to eliminate input noise Hybrid mode collision detect for extended distance
SD2085 Low Power HART TM Modem
 Low Power HART TM Modem Feature Single chip, half duplex 1200 bps FSK modem Meets HART physical layer requirements Bell 202 shift frequencies of 1200Hz and 2200Hz Buffered HART output for drive capability
Low Power HART TM Modem Feature Single chip, half duplex 1200 bps FSK modem Meets HART physical layer requirements Bell 202 shift frequencies of 1200Hz and 2200Hz Buffered HART output for drive capability
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with track/hold function ADC0820
 8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
SC16C550B. 1. General description. 2. Features. 5 V, 3.3 V and 2.5 V UART with 16-byte FIFOs
 Rev. 05 1 October 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART) used for serial data communications. Its principal function
Rev. 05 1 October 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART) used for serial data communications. Its principal function
Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers
 Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers The Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E are 8-port Fast Ethernet PHY Transceivers supporting IEEE 802.3 physical layer
Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers The Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E are 8-port Fast Ethernet PHY Transceivers supporting IEEE 802.3 physical layer
DATASHEET IDT77V7101 GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER
 GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER DATASHEET Features IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet compatible 1.25 Gbps full duplex transmission and reception in a single IC Optical interface through fiber module 10-bit
GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER DATASHEET Features IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet compatible 1.25 Gbps full duplex transmission and reception in a single IC Optical interface through fiber module 10-bit
6-Bit A/D converter (parallel outputs)
 DESCRIPTION The is a low cost, complete successive-approximation analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, fabricated using Bipolar/I L technology. With an external reference voltage, the will accept input voltages
DESCRIPTION The is a low cost, complete successive-approximation analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, fabricated using Bipolar/I L technology. With an external reference voltage, the will accept input voltages
Programmable Dual RS-232/RS-485 Transceiver
 SP331 Programmable Dual RS-3/ Transceiver Only Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or Selection Four RS-3 Transceivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Two RS-3 Transceivers and One Transceiver
SP331 Programmable Dual RS-3/ Transceiver Only Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or Selection Four RS-3 Transceivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Two RS-3 Transceivers and One Transceiver
LM12L Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration
 LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
ROM/UDF CPU I/O I/O I/O RAM
 DATA BUSSES INTRODUCTION The avionics systems on aircraft frequently contain general purpose computer components which perform certain processing functions, then relay this information to other systems.
DATA BUSSES INTRODUCTION The avionics systems on aircraft frequently contain general purpose computer components which perform certain processing functions, then relay this information to other systems.
Tel: Fax:
 B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
B Tel: 78.39.4700 Fax: 78.46.33 SPECIFICATIONS (T A = +5 C, V+ = +5 V, V = V or 5 V, all voltages measured with respect to digital common, unless otherwise noted) AD57J AD57K AD57S Model Min Typ Max Min
RS-232 Electrical Specifications and a Typical Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
ML BASE-T Transceiver
 November 1998 ML4658 10BASE-T Transceiver GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML4658 10BASE-T Transceiver is a single-chip cable line driver/receiver that provides all of the functionality required to implement both
November 1998 ML4658 10BASE-T Transceiver GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML4658 10BASE-T Transceiver is a single-chip cable line driver/receiver that provides all of the functionality required to implement both
DS1075 EconOscillator/Divider
 EconOscillator/Divider www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (30 KHz - 100 MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1-513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
EconOscillator/Divider www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (30 KHz - 100 MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1-513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
REALTEK SINGLE CHIP SINGLE PORT 10/100M FAST ETHERNET PHYCEIVER RTL8201BL
 REALTEK SINGLE CHIP SINGLE PORT 10/100M FAST ETHERNET PHYCEIVER RTL8201BL 1. Features... 2 2. General Description... 2 3. Block Diagram... 3 4. Pin Assignments... 4 5. Pin Description... 5 5.1 100 Mbps
REALTEK SINGLE CHIP SINGLE PORT 10/100M FAST ETHERNET PHYCEIVER RTL8201BL 1. Features... 2 2. General Description... 2 3. Block Diagram... 3 4. Pin Assignments... 4 5. Pin Description... 5 5.1 100 Mbps
DS1075. EconOscillator/Divider PRELIMINARY FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT FREQUENCY OPTIONS
 PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
+Denotes lead-free package. *EP = Exposed paddle. V CC GND AGND AV CC GND I 2 C INTERFACE. -35dB TO +25dB GAIN AUDIO SOURCE AUDIO AMPLIFIER DS4420
 Rev ; 9/6 I 2 C Programmable-Gain Amplifier General Description The is a fully differential, programmable-gain amplifier for audio applications. It features a -35dB to +25dB gain range controlled by an
Rev ; 9/6 I 2 C Programmable-Gain Amplifier General Description The is a fully differential, programmable-gain amplifier for audio applications. It features a -35dB to +25dB gain range controlled by an
DS Wire Digital Potentiometer
 Preliminary 1-Wire Digital Potentiometer www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Single element 256-position linear taper potentiometer Supports potentiometer terminal working voltages up to 11V Potentiometer terminal
Preliminary 1-Wire Digital Potentiometer www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Single element 256-position linear taper potentiometer Supports potentiometer terminal working voltages up to 11V Potentiometer terminal
4. SONET Mode. Introduction
 4. SONET Mode SGX52004-1.2 Introduction One of the most common serial backplanes in the communications or telecom area is the SONET/SDH interface. For SONET/SDH applications the synchronous transport signal
4. SONET Mode SGX52004-1.2 Introduction One of the most common serial backplanes in the communications or telecom area is the SONET/SDH interface. For SONET/SDH applications the synchronous transport signal
+2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel 8-Bit DAC with Rail-to-Rail Voltage Outputs
 19-1560; Rev 1; 7/05 +2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel General Description The parallel-input, voltage-output, triple 8-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V
19-1560; Rev 1; 7/05 +2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel General Description The parallel-input, voltage-output, triple 8-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V
High-Frequency Programmable PECL Clock Generator
 High-Frequency Programmable PECL Clock Generator 1CY2213 Features Jitter peak-peak (TYPICAL) = 35 ps LVPECL output Default Select option Serially-configurable multiply ratios Output edge-rate control 16-pin
High-Frequency Programmable PECL Clock Generator 1CY2213 Features Jitter peak-peak (TYPICAL) = 35 ps LVPECL output Default Select option Serially-configurable multiply ratios Output edge-rate control 16-pin
DACPORT Low Cost, Complete P-Compatible 8-Bit DAC AD557*
 a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit DAC Voltage Output 0 V to 2.56 V Internal Precision Band-Gap Reference Single-Supply Operation: 5 V ( 10%) Full Microprocessor Interface Fast: 1 s Voltage Settling to 1/2 LSB
a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit DAC Voltage Output 0 V to 2.56 V Internal Precision Band-Gap Reference Single-Supply Operation: 5 V ( 10%) Full Microprocessor Interface Fast: 1 s Voltage Settling to 1/2 LSB
EVDP610 IXDP610 Digital PWM Controller IC Evaluation Board
 IXDP610 Digital PWM Controller IC Evaluation Board General Description The IXDP610 Digital Pulse Width Modulator (DPWM) is a programmable CMOS LSI device, which accepts digital pulse width data from a
IXDP610 Digital PWM Controller IC Evaluation Board General Description The IXDP610 Digital Pulse Width Modulator (DPWM) is a programmable CMOS LSI device, which accepts digital pulse width data from a
SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER
 SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER Intelligent RF Modem Module RF Data Rates to 19200bps Up to 300 metres Range Programmable to 433, 868, or 915MHz Selectable Narrowband RF Channels Crystal Controlled RF Design
SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER Intelligent RF Modem Module RF Data Rates to 19200bps Up to 300 metres Range Programmable to 433, 868, or 915MHz Selectable Narrowband RF Channels Crystal Controlled RF Design
Programmable RS-232/RS-485 Transceiver
 SP334 Programmable RS-3/ Transceiver V Single Supply Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or Selection Three RS-3 Drivers and Five Receivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Full Differential
SP334 Programmable RS-3/ Transceiver V Single Supply Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or Selection Three RS-3 Drivers and Five Receivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Full Differential
Programmable RS-232/RS-485 Transceiver
 SP334 Programmable RS-3/ Transceiver V Only Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or RS- 48 Selection Three RS-3 Drivers and Five Receivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Full Differential
SP334 Programmable RS-3/ Transceiver V Only Operation Software Programmable RS-3 or RS- 48 Selection Three RS-3 Drivers and Five Receivers in RS-3 Mode Two Full-Duplex Transceivers in Mode Full Differential
DM Mbps Twisted Pair/Fiber Ethernet Media Converter Chip
 General Description The is a physical-layer, single-chip, low power transceiver for media converter application. On the media side, it provides a direct interface either to Unshielded Twisted Pair Category
General Description The is a physical-layer, single-chip, low power transceiver for media converter application. On the media side, it provides a direct interface either to Unshielded Twisted Pair Category
Quad 12-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface)
 Quad 1-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface) FEATURES COMPLETE QUAD DAC INCLUDES INTERNAL REFERENCES AND OUTPUT AMPLIFIERS GUARANTEED SPECIFICATIONS OVER TEMPERATURE GUARANTEED MONOTONIC OVER
Quad 1-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface) FEATURES COMPLETE QUAD DAC INCLUDES INTERNAL REFERENCES AND OUTPUT AMPLIFIERS GUARANTEED SPECIFICATIONS OVER TEMPERATURE GUARANTEED MONOTONIC OVER
Powerline Communication Analog Front-End Transceiver
 General Description The MAX2980 powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) integrated circuit (IC) is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high performance and low cost. This highly integrated
General Description The MAX2980 powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) integrated circuit (IC) is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high performance and low cost. This highly integrated
REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE. A Release B Added QuickCheck Pinout Table
 REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE A Release 6-24-03 B Added QuickCheck Pinout Table 8-28-03 C Added Required External Pull-ups, nldev Clarification, New Logo 5-24-04 D Clarified Crystal Circuit Requirements
REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE A Release 6-24-03 B Added QuickCheck Pinout Table 8-28-03 C Added Required External Pull-ups, nldev Clarification, New Logo 5-24-04 D Clarified Crystal Circuit Requirements
TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017
 TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017 1. RS485 basic knowledge... 2 1.1. RS485 BUS basic Characteristics... 2 1.2. RS485 Transmission Distance... 2 1.3. RS485 bus connection and termination
TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017 1. RS485 basic knowledge... 2 1.1. RS485 BUS basic Characteristics... 2 1.2. RS485 Transmission Distance... 2 1.3. RS485 bus connection and termination
PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance
 PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance 1.0 Introduction The use of a reference clock that is less stable than those directly driven from an oscillator may be required for some applications.
PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance 1.0 Introduction The use of a reference clock that is less stable than those directly driven from an oscillator may be required for some applications.
RayStar Microelectronics Technology Inc. Ver: 1.4
 Features Description Product Datasheet Using external 32.768kHz quartz crystal Supports I 2 C-Bus's high speed mode (400 khz) The serial real-time clock is a low-power clock/calendar with a programmable
Features Description Product Datasheet Using external 32.768kHz quartz crystal Supports I 2 C-Bus's high speed mode (400 khz) The serial real-time clock is a low-power clock/calendar with a programmable
FCOPPER-SFP BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver
 100BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver March 27, 2012 Product Overview The electrical Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver module is specifically designed for converting 100BASE-FX NRZI port interface
100BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver March 27, 2012 Product Overview The electrical Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver module is specifically designed for converting 100BASE-FX NRZI port interface
FDDI on Copper with AMD PHY Components
 Advanced Micro Devices FDDI on Copper with AMD PHY Components by Eugen Gershon Publication # Rev. Amendment Issue Date 15923 A /0 6/91 1991 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. by Eugen Gershon INTRODUCTION This
Advanced Micro Devices FDDI on Copper with AMD PHY Components by Eugen Gershon Publication # Rev. Amendment Issue Date 15923 A /0 6/91 1991 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. by Eugen Gershon INTRODUCTION This
DISCONTINUED. Modulation Type Number of RF Channels 15
 RFM Products are now Murata products. 2.4 GHz Spread Spectrum Transceiver Module Small Size, Light Weight, Built-In Antenna Sleep Current less than 3 µa FCC, Canadian IC and ETSI Certified for Unlicensed
RFM Products are now Murata products. 2.4 GHz Spread Spectrum Transceiver Module Small Size, Light Weight, Built-In Antenna Sleep Current less than 3 µa FCC, Canadian IC and ETSI Certified for Unlicensed
Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514
 Cover Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Doc. No. MV-S107146-U0, Rev. B February 23, 2018 Marvell. Moving Forward Faster Document
Cover Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Doc. No. MV-S107146-U0, Rev. B February 23, 2018 Marvell. Moving Forward Faster Document
NJ88C Frequency Synthesiser with non-resettable counters
 NJ88C Frequency Synthesiser with non-resettable counters DS8 -. The NJ88C is a synthesiser circuit fabricated on the GPS CMOS process and is capable of achieving high sideband attenuation and low noise
NJ88C Frequency Synthesiser with non-resettable counters DS8 -. The NJ88C is a synthesiser circuit fabricated on the GPS CMOS process and is capable of achieving high sideband attenuation and low noise
DS2186. Transmit Line Interface FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT
 Transmit Line Interface FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks PIN ASSIGNMENT TAIS 1 20 LCLK On chip transmit LBO (line build out) and line drivers eliminate
Transmit Line Interface FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks PIN ASSIGNMENT TAIS 1 20 LCLK On chip transmit LBO (line build out) and line drivers eliminate
Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators
 Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators 1. What is the definition of "Switching Control Frequency"? The switching control frequency is the frequency of the control signals.
Frequently Asked Questions DAT & ZX76 Series Digital Step Attenuators 1. What is the definition of "Switching Control Frequency"? The switching control frequency is the frequency of the control signals.
10-Bit µp-compatible D/A converter
 DESCRIPTION The is a microprocessor-compatible monolithic 10-bit digital-to-analog converter subsystem. This device offers 10-bit resolution and ±0.1% accuracy and monotonicity guaranteed over full operating
DESCRIPTION The is a microprocessor-compatible monolithic 10-bit digital-to-analog converter subsystem. This device offers 10-bit resolution and ±0.1% accuracy and monotonicity guaranteed over full operating
CMX867 Low Power V.22 Modem
 CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Low Power V.22 Modem D/867/5 March 2004 Provisional Issue Features V.22, Bell 212A 1200/1200 or 600/600 bps DPSK V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75, 1200 bps FSK
CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Low Power V.22 Modem D/867/5 March 2004 Provisional Issue Features V.22, Bell 212A 1200/1200 or 600/600 bps DPSK V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75, 1200 bps FSK
AD557 SPECIFICATIONS. T A = 25 C, V CC = 5 V unless otherwise noted) REV. B
 SPECIFICATIONS Model Min Typ Max Unit RESOLUTION 8 Bits RELATIVE ACCURACY 0 C to 70 C ± 1/2 1 LSB Ranges 0 to 2.56 V Current Source 5 ma Sink Internal Passive Pull-Down to Ground 2 SETTLING TIME 3 0.8
SPECIFICATIONS Model Min Typ Max Unit RESOLUTION 8 Bits RELATIVE ACCURACY 0 C to 70 C ± 1/2 1 LSB Ranges 0 to 2.56 V Current Source 5 ma Sink Internal Passive Pull-Down to Ground 2 SETTLING TIME 3 0.8
10-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail Voltage-Output Serial DAC in SOT23
 19-195; Rev 1; 1/4 1-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail General Description The is a small footprint, low-power, 1-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +.7V to +5.5V supply. The
19-195; Rev 1; 1/4 1-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail General Description The is a small footprint, low-power, 1-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +.7V to +5.5V supply. The
AN-1397 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Using the 50 Mbps RS-485 Transceiver in EnDat Motor Control Encoder Applications
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Using the 50 Mbps RS-485 Transceiver in EnDat Motor Control Encoder Applications
Integrated Powerline Communication Analog Front-End Transceiver and Line Driver
 19-4736; Rev 0; 7/09 Integrated Powerline Communication Analog General Description The powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) and line-driver IC is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high
19-4736; Rev 0; 7/09 Integrated Powerline Communication Analog General Description The powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) and line-driver IC is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high
Low-Power, 12-Bit, Rail to Rail Voltage-Output Serial DAC in SOT23
 General Description The MAX5712 is a small footprint, low-power, 12-bit digitalto-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V supply. The MAX5712 on-chip precision output amplifier
General Description The MAX5712 is a small footprint, low-power, 12-bit digitalto-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V supply. The MAX5712 on-chip precision output amplifier
CMX868A Low Power V.22 bis Modem
 CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Low Power V.22 bis Modem D/868A/3 May 2008 Features V.22 bis 2400/2400 bps QAM V.22, Bell 212A 1200/1200 or 600/600 bps DPSK V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75,
CML Microcircuits COMMUNICATION SEMICONDUCTORS Low Power V.22 bis Modem D/868A/3 May 2008 Features V.22 bis 2400/2400 bps QAM V.22, Bell 212A 1200/1200 or 600/600 bps DPSK V.23 1200/75, 1200/1200, 75,
78A207 MFR1 Receiver DATA SHEET DESCRIPTION FEATURES OCTOBER 2005
 DESCRIPTION The 78A207 is a single-chip, Multi-Frequency (MF) receiver that can detect all 15 tone-pairs, including ST and KP framing tones. This receiver is intended for use in equal access applications
DESCRIPTION The 78A207 is a single-chip, Multi-Frequency (MF) receiver that can detect all 15 tone-pairs, including ST and KP framing tones. This receiver is intended for use in equal access applications
Module -18 Flip flops
 1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
FOSTCDR. Industrial Serial to Multimode Fiber Optic Converter PRODUCT INFORMATION B&B ELECTRONICS. Specifications Serial Technology
 FOSTCDR pn 8684R1 FOSTCDR-0812ds page 1/5 Industrial Serial to Multimode Fiber Optic Converter Data Rates up to 115.2 kbps 2.5 Mile (4 km) Range 10 to 30 VDC Input Voltage Wide Operating Temperature 2000V
FOSTCDR pn 8684R1 FOSTCDR-0812ds page 1/5 Industrial Serial to Multimode Fiber Optic Converter Data Rates up to 115.2 kbps 2.5 Mile (4 km) Range 10 to 30 VDC Input Voltage Wide Operating Temperature 2000V
8-Bit A/D Converter AD673 REV. A FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
 a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
Kongsberg Mesotech Ltd.
 Kongsberg Mesotech Ltd. Doc. No. : 974-00007904 Title : Digital Telemetry Notes elease : Version 1.4 Date : 2010-04-30 1. PUPOSE This document briefly describes the digital telemetry standards, formats
Kongsberg Mesotech Ltd. Doc. No. : 974-00007904 Title : Digital Telemetry Notes elease : Version 1.4 Date : 2010-04-30 1. PUPOSE This document briefly describes the digital telemetry standards, formats
RV-8564 Application Manual. Application Manual. Real-Time Clock Module with I 2 C-Bus Interface. October /62 Rev. 2.1
 Application Manual Application Manual Real-Time Clock Module with I 2 C-Bus Interface October 2017 1/62 Rev. 2.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW... 5 1.1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 5 1.2. APPLICATIONS... 5
Application Manual Application Manual Real-Time Clock Module with I 2 C-Bus Interface October 2017 1/62 Rev. 2.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. OVERVIEW... 5 1.1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 5 1.2. APPLICATIONS... 5
IsoLoop Isolated QSOP CAN Transceiver Evaluation Board
 IsoLoop Isolated QSOP CAN Transceiver Evaluation Board Board No.: IL41050-1-01 About This Evaluation Board This Evaluation Board provides a complete isolated CAN node using the world s smallest isolated
IsoLoop Isolated QSOP CAN Transceiver Evaluation Board Board No.: IL41050-1-01 About This Evaluation Board This Evaluation Board provides a complete isolated CAN node using the world s smallest isolated
Low Jitter, Low Emission Timing Solutions For High Speed Digital Systems. A Design Methodology
 Low Jitter, Low Emission Timing Solutions For High Speed Digital Systems A Design Methodology The Challenges of High Speed Digital Clock Design In high speed applications, the faster the signal moves through
Low Jitter, Low Emission Timing Solutions For High Speed Digital Systems A Design Methodology The Challenges of High Speed Digital Clock Design In high speed applications, the faster the signal moves through
NBASE-T Copper Transceiver Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP+), 3.3V 100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10Gbps Ethernet. Features
 Features 10Gbps Links up to 35 m using Cat 6a/7 Cable 100M/1G/2.5G/5Gbps Links up to 100 m using Cat5e Cable Low Power Consumption 2.2W Max, 35m @ 10Gbps, 75 C 1.88W Max, 100m @ 2.5G and 5Gbps, 75 C 1.88W
Features 10Gbps Links up to 35 m using Cat 6a/7 Cable 100M/1G/2.5G/5Gbps Links up to 100 m using Cat5e Cable Low Power Consumption 2.2W Max, 35m @ 10Gbps, 75 C 1.88W Max, 100m @ 2.5G and 5Gbps, 75 C 1.88W
