KSZ9021RL/RN. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support. Revision 1.2
|
|
|
- Jessie Gallagher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
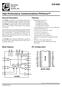
1 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 1.2 General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver for transmission and reception of data over standard CAT-5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. The KSZ9021RL provides the Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) for direct connection to RGMII MACs in Gigabit Ethernet Processors and Switches for data transfer at 10/100/1000Mbps speed. The KSZ9021RL reduces board cost and simplifies board layout by using on-chip termination resistors for the four differential pairs and by integrating a LDO controller to drive a low cost MOSFET to supply the 1.2V core. The KSZ9021RL provides diagnostic features to facilitate system bring-up and debugging in production testing and in product deployment. Parametric NAND tree support enables fault detection between KSZ9021 I/Os and board. Micrel LinkMD TDR-based cable diagnostics permit identification of faulty copper cabling. Remote and local loopback functions provide verification of analog and digital data paths. The KSZ9021RL is available in a 64-pin, lead-free E-LQFP package, and is offered as the KSZ9021RN in the smaller 48-pin QFN package (See Ordering Information). Features Single-chip 10/100/1000Mbps IEEE compliant Ethernet Transceiver RGMII interface compliant to RGMII Version 1.3 RGMII I/Os with 3.3V/2.5V tolerant and programmable timings to adjust and correct delays on both Tx and Rx paths Auto-negotiation to automatically select the highest link up speed (10/100/100Mbps) and duplex (half/full) On-chip termination resistors for the differential pairs On-chip LDO controller to support single 3.3V supply operation requires only external FET to generate 1.2V for the core Jumbo frame support up to 16KB 125MHz Reference Clock Output Programmable LED outputs for link, activity and speed Baseline Wander Correction LinkMD TDR-based cable diagnostics for identification of faulty copper cabling Parametric NAND Tree support for fault detection between chip I/Os and board. Loopback modes for diagnostics Functional Diagram RGMII 10/100/1000 Mbps RGMII Ethernet MAC MDC / MDIO Management On-chip Termination Resistors Magnetics RJ-45 Connector Media Types: 10Base-T 100Base-TX 1000Base-T LDO Controller VIN 3.3VA VOUT 1.2V (for core voltages) LinkMD is a registered trademark of Micrel, Inc. Micrel Inc Fortune Drive San Jose, CA USA tel +1 (408) fax + 1 (408) February 13, 2014 Revision 1.2
2 More Features Automatic MDI/MDI-X crossover for detection and correction of pair swap at all speeds of operation Automatic detection and correction of pair swap, pair skew and pair polarity MDC/MDIO Management Interface for PHY register configuration Interrupt pin option Power down and power saving modes Operating Voltages Core: 1.2V (external FET or regulator) I/O: 3.3V or 2.5V Transceiver: 3.3V Available packages 64-pin E-LQFP (10mm x 10mm): KSZ9021RL 48-pin QFN (7mm x 7mm): KSZ9021RN Applications Laser/Network printer Network attached storage (NAS) Network server Gigabit LAN on motherboard (GLOM) Broadband gateway Gigabit SOHO/SMB router IPTV IP Set-top box Game console Triple-play (data, voice, video) media center Media converter Ordering Information Part Number Temp. Range Package Lead Finish Description KSZ9021RL 0 C to +70 C 64-Pin E-LQFP Pb-Free RGMII, Commercial Temperature, 64-E-LQFP KSZ9021RLI (1) 40 C to +85 C 64-Pin E-LQFP Pb-Free RGMII, Industrial Temperature, 64-E-LQFP KSZ9021RN 0 C to +70 C 48-Pin QFN Pb-Free RGMII, Commercial Temperature, 48-QFN KSZ9021RNI (1) 40 C to +85 C 48-Pin QFN Pb-Free RGMII, Industrial Temperature, 48-QFN Note: 1. Contact factory for availability. February 13, Revision 1.2
3 Revision History Revision Date Summary of Changes 1.0 1/16/09 Data sheet created /13/09 Updated current consumption in Electrical Characteristics section. Corrected data sheet omission of register 1 bit 8 for 1000Base-T Extended Status information. Added the following register bits to provide further power saving during software power down: Tristate all digital I/Os (reg ), LDO disable (reg ), Low frequency oscillator mode (reg ). Added KSZ9021RN device and updated entire data sheet accordingly. Added 48-Pin QFN package information /13/14 Added RGMII Pad Skew Registers section. Corrected pad skew steps in Registers 260 (104h) and 261 (105h). Datasheet values are incorrect. There is no change to the silicon. Added Register 262 (106h) for RGMII TX Data Pad Skew. Updated boilerplate. February 13, Revision 1.2
4 Contents Pin Configuration KSZ9021RL... 8 Pin Description KSZ9021RL... 9 Strapping Options KSZ9021RL Pin Configuration KSZ9021RN Pin Description KSZ9021RN Strapping Options KSZ9021RN Functional Overview Functional Description: 10Base-T/100Base-TX Transceiver Base-TX Transmit Base-TX Receive Scrambler/De-scrambler (100Base-TX only) Base-T Transmit Base-T Receive Functional Description: 1000Base-T Transceiver Analog Echo Cancellation Circuit Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Timing Recovery Circuit Adaptive Equalizer Trellis Encoder and Decoder Functional Description: 10/100/1000 Transceiver Features Auto MDI/MDI-X Pair- Swap, Alignment, and Polarity Check Wave Shaping, Slew Rate Control and Partial Response PLL Clock Synthesizer Auto-Negotiation RGMII Interface RGMII Signal Definition RGMII Signal Diagram RGMII Pad Skew Registers RGMII In-band Status MII Management (MIIM) Interface Interrupt (INT_N) LED Mode Single LED Mode Tri-color Dual LED Mode NAND Tree Support Power Management Power Saving Mode Software Power Down Mode Chip Power Down Mode Register Map February 13, Revision 1.2
5 Register Description IEEE Defined Registers Vendor Specific Registers Extended Registers Absolute Maximum Ratings Operating Ratings Electrical Characteristics Timing Diagrams RGMII Timing Auto-Negotiation Timing MDC/MDIO Timing Reset Timing Reset Circuit Reference Circuits LED Strap-in Pins Reference Clock Connection and Selection Magnetics Specification Package Information February 13, Revision 1.2
6 List of Figures Figure 1. Block Diagram Figure Base-T Block Diagram Single Channel Figure 3. Auto-Negotiation Flow Chart Figure 4. RGMII Interface Figure 5. RGMII v1.3 Specification (Figure 2 Multiplexing and Timing Diagram) Figure 6. Auto-Negotiation Fast Link Pulse (FLP) Timing Figure 7. MDC/MDIO Timing Figure 8. Reset Timing Figure 9. Recommended Reset Circuit Figure 10. Recommended Reset Circuit for Interfacing with CPU/FPGA Reset Output Figure 11. Reference Circuits for LED Strapping Pins Figure MHz Crystal/Oscillator Reference Clock Connection February 13, Revision 1.2
7 List of Tables Table 1. MDI/MDI-X Pin Mapping Table 2. Auto-Negotiation Timers Table 3. RGMII Signal Definition Table 4. RGMII Pad Skew Registers Table 5. Absolute Delay for 4-Bit Pad Skew Setting Table 6. RGMII In-Band Status Table 7. MII Management Frame Format for Table 8. Single LED Mode Pin Definition Table 9. Tri-color Dual LED Mode Pin Definition Table 10. NAND Tree Test Pin Order for KSZ9021RL Table 11. NAND Tree Test Pin Order for KSZ9021RN Table 12. RGMII v1.3 Specification (Timing Specifics from Table 2) Table 13. Auto-Negotiation Fast Link Pulse (FLP) Timing Parameters Table 14. MDC/MDIO Timing Parameters Table 15. Reset Timing Parameters Table 16. Reference Crystal/Clock Selection Criteria Table 17. Magnetics Selection Criteria Table 18. Qualified Single Port 10/100/1000 Magnetics February 13, Revision 1.2
8 Pin Configuration KSZ9021RL TXRXP_A 2 TXRXM_A 3 AGNDH 4 AVDDL 5 AVDDL 6 AVDDH 7 TXRXP_B 8 TXRXM_B 9 AGNDH 10 TXRXP_C 11 TXRXM_C 12 AVDDL 13 AVDDL 14 TXRXP_D 15 TXRXM_D 16 AVDDH VSS AVDDH AGNDH_BG VSS ISET LED2 / PHYAD1 AVDDH DVDDH XI LED1 / PHYAD0 XO DVDDL AVDDL_PLL Exposed Pad on bottom of chip VSS LDO_O TXD0 RESET_N TXD1 CLK125_NDO / LED_MODE TXD2 DVDDL TXD3 VSS VSS DVDDL DVDDL INT_N DVDDH COL TX_ER MDIO GTX_CLK MDC CRS RX_CLK / PHYAD2 RX_ER DVDDH RX_DV / CLK125_EN RXD0 / MODE0 RXD1 / MODE1 DVDDL VSS RXD2 / MODE2 DVDDH RXD3 / MODE3 DVDDL VSS TX_EN Pin E-LQFP (Top View) February 13, Revision 1.2
9 Pin Description KSZ9021RL Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 1 TXRXP_A I/O Media Dependent Interface[0], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_A corresponds to BI_DA+ for MDI configuration and BI_DB+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_A is the positive transmit signal (TX+) for MDI configuration and the positive receive signal (RX+) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 2 TXRXM_A I/O Media Dependent Interface[0], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: 3 AGNDH Gnd Analog ground TXRXM_A corresponds to BI_DA- for MDI configuration and BI_DB- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 4 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD 5 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD 6 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD TXRXM_A is the negative transmit signal (TX-) for MDI configuration and the negative receive signal (RX-) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 7 TXRXP_B I/O Media Dependent Interface[1], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_B corresponds to BI_DB+ for MDI configuration and BI_DA+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_B is the positive receive signal (RX+) for MDI configuration and the positive transmit signal (TX+) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 8 TXRXM_B I/O Media Dependent Interface[1], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: 9 AGNDH Gnd Analog ground TXRXM_B corresponds to BI_DB- for MDI configuration and BI_DA- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXM_B is the negative receive signal (RX-) for MDI configuration and the negative transmit signal (TX-) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10 TXRXP_C I/O Media Dependent Interface[2], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_C corresponds to BI_DC+ for MDI configuration and BI_DD+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_C is not used. 11 TXRXM_C I/O Media Dependent Interface[2], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_C corresponds to BI_DC- for MDI configuration and BI_DD- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 12 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD TXRXM_C is not used. February 13, Revision 1.2
10 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 13 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD 14 TXRXP_D I/O Media Dependent Interface[3], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_D corresponds to BI_DD+ for MDI configuration and BI_DC+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_D is not used. 15 TXRXM_D I/O Media Dependent Interface[3], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_D corresponds to BI_DD- for MDI configuration and BI_DC- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 16 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD 17 VSS Gnd Digital ground 18 VSS Gnd Digital ground 19 LED2 / PHYAD1 TXRXM_D is not used. I/O LED Output: Programmable LED2 Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[1] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. The LED2 pin is programmed by the LED_MODE strapping option (pin 55), and is defined as follows. Single LED Mode Link Pin State LED Definition Link off H OFF Link on (any speed) L ON Tri-color Dual LED Mode Link / Activity Pin State LED Definition LED2 LED1 LED2 LED1 Link off H H OFF OFF 1000 Link / No Activity L H ON OFF 1000 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle H Blinking OFF 100 Link / No Activity H L OFF ON 100 Link / Activity (RX, TX) H Toggle OFF Blinking 10 Link / No Activity L L ON ON 10 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Toggle Blinking Blinking For Tri-color Dual LED Mode, LED2 works in conjunction with LED1 (pin 21) to indicate 10 Mbps Link and Activity. 20 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD February 13, Revision 1.2
11 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 21 LED1 / PHYAD0 I/O LED Output: Programmable LED1 Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[0] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. The LED1 pin is programmed by the LED_MODE strapping option (pin 55), and is defined as follows. Single LED Mode Activity Pin State LED Definition No Activity H OFF Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Blinking Tri-color Dual LED Mode Link / Activity Pin State LED Definition LED2 LED1 LED2 LED1 Link off H H OFF OFF 1000 Link / No Activity L H ON OFF 1000 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle H Blinking OFF 100 Link / No Activity H L OFF ON 100 Link / Activity (RX, TX) H Toggle OFF Blinking 10 Link / No Activity L L ON ON 10 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Toggle Blinking Blinking For Tri-color Dual LED Mode, LED1 works in conjunction with LED2 (pin 19) to indicate 10 Mbps Link and Activity. 22 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 23 VSS Gnd Digital ground 24 TXD0 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD0 (Transmit Data 0) 25 TXD1 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD1 (Transmit Data 1) 26 TXD2 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD2 (Transmit Data 2) 27 TXD3 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD3 (Transmit Data 3) 28 VSS Gnd Digital ground 29 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 30 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD 31 TX_ER I RGMII Mode: This pin is not used and should be left as a no connect. 32 GTX_CLK I RGMII Mode: RGMII TXC (Transmit Reference Clock) 33 TX_EN I RGMII Mode: RGMII TX_CTL (Transmit Control) 34 VSS Gnd Digital ground 35 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD February 13, Revision 1.2
12 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 36 RXD3 / MODE3 I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD3 (Receive Data 3) Output / Config Mode: 37 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD 38 RXD2 / MODE2 The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE3 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD2 (Receive Data 2) Output / Config Mode: 39 VSS Gnd Digital ground 40 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 41 RXD1 / MODE1 42 RXD0 / MODE0 43 RX_DV / CLK125_EN The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE2 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD1 (Receive Data 1) Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE1 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD0 (Receive Data 0) Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE0 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RX_CTL (Receive Control) Output / Config Mode: 44 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD Latched as CLK125_NDO Output Enable during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. 45 RX_ER O RGMII Mode: This pin is not used and should be left as a no connect. 46 RX_CLK / PHYAD2 I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RXC (Receive Reference Clock) Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[2] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. 47 CRS O RGMII Mode: This pin is not used and should be left as a no connect. 48 MDC Ipu Management Data Clock This pin is the input reference clock for MDIO (pin 49). 49 MDIO Ipu/O Management Data /Output This pin is synchronous to MDC (pin 48) and requires an external pull-up resistor to 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD in a range from 1.0kΩ to 4.7kΩ. 50 COL O RGMII Mode: This pin is not used and should be left as a no connect. 51 INT_N O Interrupt Output This pin provides a programmable interrupt output and requires an external pull-up resistor to 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD in a range from 1.0kΩ to 4.7kΩ when active low. Register 1Bh is the Interrupt Control/Status Register for programming the interrupt conditions and reading the interrupt status. Register 1Fh bit 14 sets the interrupt output to active low (default) or active high. 52 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 53 VSS Gnd Digital ground 54 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 55 CLK125_NDO / I/O 125MHz Clock Output This pin provides a 125MHz reference clock output option for use by the MAC. / LED_MODE Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as LED_MODE during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. February 13, Revision 1.2
13 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 56 RESET_N Ipu Chip Reset (active low) Hardware pin configurations are strapped-in at the de-assertion (rising edge) of RESET_N. See Strapping Options section for more details. 57 LDO_O O On-chip 1.2V LDO Controller Output This pin drives the input gate of a P-channel MOSFET to generate 1.2V for the chip s core voltages. If 1.2V is provided by the system and this pin is not used, it can be left floating. 58 AVDDL_PLL P 1.2V analog V DD for PLL 59 XO O 25MHz Crystal feedback This pin is a no connect if oscillator or external clock source is used. 60 XI I Crystal / Oscillator / External Clock 25MHz ±50ppm tolerance 61 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD 62 ISET I/O Set transmit output level Connect a 4.99KΩ 1% resistor to ground on this pin. 63 AGNDH_BG Gnd Analog ground 64 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD E-PAD E-PAD Gnd Exposed Pad on bottom of chip Connect E-PAD to ground. Note: 1. P = Power supply. Gnd = Ground. I =. O = Output. I/O = Bi-directional. Ipu = with internal pull-up. Ipu/O = with internal pull-up / Output. February 13, Revision 1.2
14 Strapping Options KSZ9021RL Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function PHYAD2 PHYAD1 PHYAD0 MODE3 MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O The PHY Address, PHYAD[2:0], is latched at power-up/reset and is configurable to any value from 1 to 7. Each PHY address bit is configured as follows: Pull-up = 1 Pull-down = 0 PHY Address bits [4:3] are always set to 00. The MODE[3:0] strap-in pins are latched at power-up/reset and are defined as follows: MODE[3:0] Mode 0000 Reserved not used 0001 Reserved not used 0010 Reserved not used 0011 Reserved not used 0100 NAND Tree Mode 0101 Reserved not used 0110 Reserved not used 0111 Chip Power Down Mode 1000 Reserved not used 1001 Reserved not used 1010 Reserved not used 1011 Reserved not used 1100 RGMII Mode advertise 1000Base-T full-duplex only 1101 RGMII Mode advertise 1000Base-T full and half-duplex only 1110 RGMII Mode advertise all capabilities (10/100/1000 speed half/full duplex),except 1000Base-T half-duplex 1111 RGMII Mode advertise all capabilities (10/100/1000 speed half/full duplex) 43 CLK125_EN I/O CLK125_EN is latched at power-up/reset and is defined as follows: Pull-up = Enable 125MHz Clock Output Pull-down = Disable 125MHz Clock Output Pin 55 (CLK125_NDO) provides the 125MHz reference clock output option for use by the MAC. 55 LED_MODE I/O LED_MODE is latched at power-up/reset and is defined as follows: Pull-up = Single LED Mode Pull-down = Tri-color Dual LED Mode Note: 1. I/O = Bi-directional. Pin strap-ins are latched during power-up or reset. In some systems, the MAC receive input pins may be driven during power-up or reset, and consequently cause the PHY strap-in pins on the RGMII signals to be latched to the incorrect configuration. In this case, it is recommended to add external pull-ups/pull-downs on the PHY strap-in pins to ensure the PHY is configured to the correct pin strap-in mode. February 13, Revision 1.2
15 Pin Configuration KSZ9021RN AVDDH 1 36 TXRXP_A 2 35 TXRXM_A 3 34 AVDDL 4 33 TXRXP_B 5 32 TXRXM_B TXRXP_C 6 7 Paddle Ground (on bottom of chip) TXRXM_C 8 AVDDL 9 TXRXP_D 10 TXRXM_D 11 AVDDH VSS_PS DVDDL LED2 / PHYAD1 DVDDH LED1 / PHYAD0 TXD0 TXD1 TXD2 TXD3 GTX_CLK ISET AVDDH XI XO AVDDL_PLL LDO_O RESET_N CLK125_NDO / LED_MODE DVDDH DVDDL INT_N MDIO MDC RX_CLK / PHYAD2 DVDDH RX_DV / CLK125_EN RXD0 / MODE0 RXD1 / MODE1 DVDDL 29 VSS 28 RXD2 / MODE2 27 RXD3 / MODE3 26 DVDDL 25 TX_EN DVDDL DVDDL 48-Pin QFN (Top View) February 13, Revision 1.2
16 Pin Description KSZ9021RN Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 1 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD 2 TXRXP_A I/O Media Dependent Interface[0], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_A corresponds to BI_DA+ for MDI configuration and BI_DB+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_A is the positive transmit signal (TX+) for MDI configuration and the positive receive signal (RX+) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 3 TXRXM_A I/O Media Dependent Interface[0], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_A corresponds to BI_DA- for MDI configuration and BI_DB- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 4 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD TXRXM_A is the negative transmit signal (TX-) for MDI configuration and the negative receive signal (RX-) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 5 TXRXP_B I/O Media Dependent Interface[1], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_B corresponds to BI_DB+ for MDI configuration and BI_DA+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_B is the positive receive signal (RX+) for MDI configuration and the positive transmit signal (TX+) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 6 TXRXM_B I/O Media Dependent Interface[1], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_B corresponds to BI_DB- for MDI configuration and BI_DA- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXM_B is the negative receive signal (RX-) for MDI configuration and the negative transmit signal (TX-) for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 7 TXRXP_C I/O Media Dependent Interface[2], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_C corresponds to BI_DC+ for MDI configuration and BI_DD+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_C is not used. 8 TXRXM_C I/O Media Dependent Interface[2], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_C corresponds to BI_DC- for MDI configuration and BI_DD- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 9 AVDDL P 1.2V analog V DD TXRXM_C is not used. February 13, Revision 1.2
17 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 10 TXRXP_D I/O Media Dependent Interface[3], positive signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXP_D corresponds to BI_DD+ for MDI configuration and BI_DC+ for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: TXRXP_D is not used. 11 TXRXM_D I/O Media Dependent Interface[3], negative signal of differential pair 1000Base-T Mode: TXRXM_D corresponds to BI_DD- for MDI configuration and BI_DC- for MDI-X configuration, respectively. 10Base-T/100Base-TX Mode: 12 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD 13 VSS_PS Gnd Digital ground 14 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 15 LED2 / PHYAD1 TXRXM_D is not used. I/O LED Output: Programmable LED2 Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[1] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. The LED2 pin is programmed by the LED_MODE strapping option (pin 41), and is defined as follows. Single LED Mode Link Pin State LED Definition Link off H OFF Link on (any speed) L ON Tri-color Dual LED Mode Link/Activity Pin State LED Definition LED2 LED1 LED2 LED1 Link off H H OFF OFF 1000 Link / No Activity L H ON OFF 1000 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle H Blinking OFF 100 Link / No Activity H L OFF ON 100 Link / Activity (RX, TX) H Toggle OFF Blinking 10 Link / No Activity L L ON ON 10 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Toggle Blinking Blinking For Tri-color Dual LED Mode, LED2 works in conjunction with LED1 (pin 17) to indicate 10 Mbps Link and Activity. 16 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD February 13, Revision 1.2
18 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 17 LED1 / PHYAD0 I/O LED Output: Programmable LED1 Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[0] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. The LED1 pin is programmed by the LED_MODE strapping option (pin 41), and is defined as follows. Single LED Mode Activity Pin State LED Definition No Activity H OFF Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Blinking Tri-color Dual LED Mode Link/Activity Pin State LED Definition LED2 LED1 LED2 LED1 Link off H H OFF OFF 1000 Link / No Activity L H ON OFF 1000 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle H Blinking OFF 100 Link / No Activity H L OFF ON 100 Link / Activity (RX, TX) H Toggle OFF Blinking 10 Link / No Activity L L ON ON 10 Link / Activity (RX, TX) Toggle Toggle Blinking Blinking For Tri-color Dual LED Mode, LED1 works in conjunction with LED2 (pin 15) to indicate 10 Mbps Link and Activity. 18 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 19 TXD0 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD0 (Transmit Data 0) 20 TXD1 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD1 (Transmit Data 1) 21 TXD2 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD2 (Transmit Data 2) 22 TXD3 I RGMII Mode: RGMII TD3 (Transmit Data 3) 23 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 24 GTX_CLK I RGMII Mode: RGMII TXC (Transmit Reference Clock) 25 TX_EN I RGMII Mode: RGMII TX_CTL (Transmit Control) 26 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 27 RXD3 / I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD3 (Receive Data 3) Output / MODE3 Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE3 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. 28 RXD2 / I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD2 (Receive Data 2) Output / MODE2 Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE2 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. 29 VSS Gnd Digital ground 30 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 31 RXD1 / I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD1 (Receive Data 1) Output / MODE1 Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE1 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. February 13, Revision 1.2
19 Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function 32 RXD0 / MODE0 33 RX_DV / CLK125_EN I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RD0 (Receive Data 0) Output / Config Mode: The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as MODE0 during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RX_CTL (Receive Control) Output / Config Mode: 34 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD 35 RX_CLK / PHYAD2 Latched as CLK125_NDO Output Enable during power-up/ reset. See Strapping Options section for details. I/O RGMII Mode: RGMII RXC (Receive Reference Clock) Output / Config Mode: 36 MDC Ipu Management Data Clock The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as PHYAD[2] during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. This pin is the input reference clock for MDIO (pin 37). 37 MDIO Ipu/O Management Data /Output 38 INT_N O Interrupt Output 39 DVDDL P 1.2V digital V DD 40 DVDDH P 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD 41 CLK125_NDO / LED_MODE I/O This pin is synchronous to MDC (pin 36) and requires an external pull-up resistor to 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD in a range from 1.0kΩ to 4.7kΩ. This pin provides a programmable interrupt output and requires an external pull-up resistor to 3.3V/2.5V digital V DD in a range from 1.0kΩ to 4.7kΩ when active low. Register 1Bh is the Interrupt Control/Status Register for programming the interrupt conditions and reading the interrupt status. Register 1Fh bit 14 sets the interrupt output to active low (default) or active high. 125MHz Clock Output This pin provides a 125MHz reference clock output option for use by the MAC. / Config Mode: 42 RESET_N Ipu Chip Reset (active low) 43 LDO_O O On-chip 1.2V LDO Controller Output 44 AVDDL_PLL P 1.2V analog V DD for PLL 45 XO O 25MHz Crystal feedback The pull-up/pull-down value is latched as LED_MODE during power-up/reset. See Strapping Options section for details. Hardware pin configurations are strapped-in at the de-assertion (rising edge) of RESET_N. See Strapping Options section for more details. This pin drives the input gate of a P-channel MOSFET to generate 1.2V for the chip s core voltages. If 1.2V is provided by the system and this pin is not used, it can be left floating. This pin is a no connect if oscillator or external clock source is used. 46 XI I Crystal / Oscillator / External Clock 25MHz ±50ppm tolerance 47 AVDDH P 3.3V analog V DD 48 ISET I/O Set transmit output level Connect a 4.99kΩ 1% resistor to ground on this pin. PADDLE P_GND Gnd Exposed Paddle on bottom of chip Connect P_GND to ground. February 13, Revision 1.2
20 Note: 1. P = Power supply. Gnd = Ground. I =. O = Output. I/O = Bi-directional. Ipu = with internal pull-up. Ipu/O = with internal pull-up / Output. February 13, Revision 1.2
21 Strapping Options KSZ9021RN Pin Number Pin Name Type (1) Pin Function PHYAD2 PHYAD1 PHYAD0 MODE3 MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O I/O The PHY Address, PHYAD[2:0], is latched at power-up/reset and is configurable to any value from 1 to 7. Each PHY address bit is configured as follows: Pull-up = 1 Pull-down = 0 PHY Address bits [4:3] are always set to 00. The MODE[3:0] strap-in pins are latched at power-up/reset and are defined as follows: MODE[3:0] Mode 0000 Reserved not used 0001 Reserved not used 0010 Reserved not used 0011 Reserved not used 0100 NAND Tree Mode 0101 Reserved not used 0110 Reserved not used 0111 Chip Power Down Mode 1000 Reserved not used 1001 Reserved not used 1010 Reserved not used 1011 Reserved not used 1100 RGMII Mode advertise 1000Base-T full-duplex only 1101 RGMII Mode advertise 1000Base-T full and half-duplex only 1110 RGMII Mode advertise all capabilities (10/100/1000 speed half/full duplex), except 1000Base-T half-duplex 1111 RGMII Mode advertise all capabilities (10/100/1000 speed half/full duplex) 33 CLK125_EN I/O CLK125_EN is latched at power-up/reset and is defined as follows: Pull-up = Enable 125MHz Clock Output Pull-down = Disable 125MHz Clock Output Pin 41 (CLK125_NDO) provides the 125MHz reference clock output option for use by the MAC. 41 LED_MODE I/O LED_MODE is latched at power-up/reset and is defined as follows: Pull-up = Single LED Mode Pull-down = Tri-color Dual LED Mode Note: 1. I/O = Bi-directional. Pin strap-ins are latched during power-up or reset. In some systems, the MAC receive input pins may be driven during power-up or reset, and consequently cause the PHY strap-in pins on the RGMII signals to be latched to the incorrect configuration. In this case, it is recommended to add external pull-ups/pull-downs on the PHY strap-in pins to ensure the PHY is configured to the correct pin strap-in mode. February 13, Revision 1.2
22 Functional Overview The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver solution for transmission and reception of data over a standard CAT-5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. Its on-chip proprietary 1000Base-T transceiver and Manchester/MLT-3 signaling-based 10Base-T/100Base-TX transceivers are all IEEE compliant. The reduces board cost and simplifies board layout by using on-chip termination resistors for the four differential pairs and by integrating a LDO controller to drive a low cost MOSFET to supply the 1.2V core. On the copper media interface, the can automatically detect and correct for differential pair misplacements and polarity reversals, and correct propagation delays and re-sync timing between the four differential pairs, as specified in the IEEE standard for 1000Base-T operation. The provides the RGMII interface for a direct and seamless connection to RGMII MACs in Gigabit Ethernet Processors and Switches for data transfer at 10/100/1000Mbps speed. The following figure shows a high-level block diagram of the. PMA TX10/100/1000 Clock Reset Configurations PMA RX1000 MEDIA INTERFACE PCS1000 PMA RX100 PCS100 RGMII Interface PMA RX10 PCS10 AUTO NEGOTIATION LED DRIVERS Figure 1. Block Diagram February 13, Revision 1.2
23 Functional Description: 10Base-T/100Base-TX Transceiver 100Base-TX Transmit The 100Base-TX transmit function performs parallel to serial conversion, 4B/5B coding, scrambling, NRZ-to-NRZI conversion, and MLT-3 encoding and transmission. The circuitry starts with a parallel-to-serial conversion, which converts the RGMII data from the MAC into a 125MHz serial bit stream. The data and control stream is then converted into 4B/5B coding, followed by a scrambler. The serialized data is further converted from NRZ-to-NRZI format, and then transmitted in MLT-3 current output. The output current is set by an external 4.99kΩ 1% resistor for the 1:1 transformer ratio. The output signal has a typical rise/fall time of 4ns and complies with the ANSI TP-PMD standard regarding amplitude balance, overshoot, and timing jitter. The wave-shaped 10Base-T output is also incorporated into the 100Base-TX transmitter. 100Base-TX Receive The 100BASE-TX receiver function performs adaptive equalization, DC restoration, MLT-3-to-NRZI conversion, data and clock recovery, NRZI-to-NRZ conversion, de-scrambling, 4B/5B decoding, and serial-to-parallel conversion. The receiving side starts with the equalization filter to compensate for inter-symbol interference (ISI) over the twisted pair cable. Since the amplitude loss and phase distortion is a function of the cable length, the equalizer must adjust its characteristics to optimize performance. In this design, the variable equalizer makes an initial estimation based on comparisons of incoming signal strength against some known cable characteristics, and then tunes itself for optimization. This is an ongoing process and self-adjusts against environmental changes such as temperature variations. Next, the equalized signal goes through a DC restoration and data conversion block. The DC restoration circuit is used to compensate for the effect of baseline wander and to improve the dynamic range. The differential data conversion circuit converts the MLT-3 format back to NRZI. The slicing threshold is also adaptive. The clock recovery circuit extracts the 125MHz clock from the edges of the NRZI signal. This recovered clock is then used to convert the NRZI signal into the NRZ format. This signal is sent through the de-scrambler followed by the 4B/5B decoder. Finally, the NRZ serial data is converted to the RGMII format and provided as the input data to the MAC. Scrambler/De-scrambler (100Base-TX only) The purpose of the scrambler is to spread the power spectrum of the signal to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and baseline wander. Transmitted data is scrambled through the use of an 11-bit wide linear feedback shift register (LFSR). The scrambler generates a 2047-bit non-repetitive sequence, and the receiver then de-scrambles the incoming data stream using the same sequence as at the transmitter. 10Base-T Transmit The output 10Base-T driver is incorporated into the 100Base-TX driver to allow transmission with the same magnetic. They are internally wave-shaped and pre-emphasized into typical outputs of 2.5V amplitude. The harmonic contents are at least 31 db below the fundamental when driven by an all-ones Manchester-encoded signal. 10Base-T Receive On the receive side, input buffer and level detecting squelch circuits are employed. A differential input receiver circuit and a phase-locked loop (PLL) perform the decoding function. The Manchester-encoded data stream is separated into clock signal and NRZ data. A squelch circuit rejects signals with levels less than 300 mv or with short pulse widths in order to prevent noises at the receive inputs from falsely triggering the decoder. When the input exceeds the squelch limit, the PLL locks onto the incoming signal and the decodes a data frame. The receiver clock is maintained active during idle periods in between receiving data frames. February 13, Revision 1.2
24 Functional Description: 1000Base-T Transceiver The 1000Base-T transceiver is based on a mixed-signal/digital signal processing (DSP) architecture, which includes the analog front-end, digital channel equalizers, trellis encoders/decoders, echo cancellers, cross-talk cancellers, precision clock recovery scheme, and power efficient line drivers. The following figure shows a high-level block diagram of a single channel of the 1000Base-T transceiver for one of the four differential pairs. XTAL TX Signal Clk Generation Transmit Block OTHER CHANNELS Side-Stream Scrambler & Symbol Encoder PCS State Machines LED Driver Analog Hybrid Baseline Wander Compensation Echo Canceller NEXT Canceller NEXT Canceller NEXT Canceller Pair Swap & Align Unit Descrambler + Decoder RX Signal AGC RX- ADC + FFE SLICER Clock & Phase Recovery DFE Auto-Negotiation MII Registers MII Management Control PMA State Machines Figure Base-T Block Diagram Single Channel Analog Echo Cancellation Circuit In 1000Base-T mode, the analog echo cancellation circuit helps to reduce the near-end echo. This analog hybrid circuit relieves the burden of the ADC and the adaptive equalizer. This circuit is disabled in 10Base-T/100Base-TX mode. Automatic Gain Control (AGC) In 1000Base-T mode, the automatic gain control (AGC) circuit provides initial gain adjustment to boost up the signal level. This pre-conditioning circuit is used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the receive signal. Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) In 1000Base-T mode, the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) digitizes the incoming signal. ADC performance is essential to the overall performance of the transceiver. This circuit is disabled in 10Base-T/100Base-TX mode. February 13, Revision 1.2
25 Timing Recovery Circuit In 1000Base-T mode, the mixed-signal clock recovery circuit, together with the digital phase locked loop, is used to recover and track the incoming timing information from the received data. The digital phase locked loop has very low longterm jitter to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio of the receive signal. The 1000Base-T slave PHY is required to transmit the exact receive clock frequency recovered from the received data back to the 1000Base-T master PHY. Otherwise, the master and slave will not be synchronized after long transmission. Additionally, this helps to facilitate echo cancellation and NEXT removal. Adaptive Equalizer In 1000Base-T mode, the adaptive equalizer provides the following functions: Detection for partial response signaling Removal of NEXT and ECHO noise Channel equalization Signal quality is degraded by residual echo that is not removed by the analog hybrid and echo due to impedance mismatch. The employs a digital echo canceller to further reduce echo components on the receive signal. In 1000Base-T mode, the data transmission and reception occurs simultaneously on all four pairs of wires (four channels). This results in high frequency cross-talk coming from adjacent wires. The employs three NEXT cancellers on each receive channel to minimize the cross-talk induced by the other three channels. In 10Base-T/100Base-TX mode, the adaptive equalizer needs only to remove the inter-symbol interference and recover the channel loss from the incoming data. Trellis Encoder and Decoder In 1000Base-T mode, the transmitted 8-bit data is scrambled into 9-bit symbols and further encoded into 4D-PAM5 symbols. The initial scrambler seed is determined by the specific PHY address to reduce EMI when more than one is used on the same board. On the receiving side, the idle stream is examined first. The scrambler seed, pair skew, pair order and polarity have to be resolved through the logic. The incoming 4D-PAM5 data is then converted into 9-bit symbols and then de-scrambled into 8-bit data. Functional Description: 10/100/1000 Transceiver Features Auto MDI/MDI-X The Automatic MDI/MDI-X feature eliminates the need to determine whether to use a straight cable or a crossover cable between the and its link partner. This auto-sense function detects the MDI/MDI-X pair mapping from the link partner, and then assigns the MDI/MDI-X pair mapping of the accordingly. The following table shows the 10/100/1000 pin-out assignments for MDI/MDI-X pin mapping. Pin (RJ-45 pair) MDI MDI-X 1000Base-T 100Base-TX 10Base-T 1000Base-T 100Base-TX 10Base-T TXRXP/M_A (1,2) A+/- TX+/- TX+/- B+/- RX+/- RX+/- TXRXP/M_B (3,6) B+/- RX+/- RX+/- A+/- TX+/- TX+/- TXRXP/M_C (4,5) C+/- Not used Not used D+/- Not used Not used TXRXP/M_D (7,8) D+/- Not used Not used C+/- Not used Not used Table 1. MDI/MDI-X Pin Mapping Auto MDI/MDI-X is enabled by default. It is disabled by writing a one to register 28 (1Ch) bit 6. MDI and MDI-X mode is set by register 28 (1Ch) bit 7 if auto MDI/MDI-X is disabled. An isolation transformer with symmetrical transmit and receive data paths is recommended to support auto MDI/MDI-X. February 13, Revision 1.2
26 Pair- Swap, Alignment, and Polarity Check In 1000Base-T mode, the Detects incorrect channel order and automatically restore the pair order for the A, B, C, D pairs (four channels) Supports 50 ±10ns difference in propagation delay between pairs of channels in accordance with the IEEE standard, and automatically corrects the data skew so the corrected 4-pairs of data symbols are synchronized Incorrect pair polarities of the differential signals are automatically corrected for all speeds. Wave Shaping, Slew Rate Control and Partial Response In communication systems, signal transmission encoding methods are used to provide the noise-shaping feature and to minimize distortion and error in the transmission channel. For 1000Base-T, a special partial response signaling method is used to provide the band-limiting feature for the transmission path. For 100Base-TX, a simple slew rate control method is used to minimize EMI. For 10Base-T, pre-emphasis is used to extend the signal quality through the cable. PLL Clock Synthesizer The generates 125MHz, 25MHz and 10MHz clocks for system timing. Internal clocks are generated from the external 25MHz crystal or reference clock. Auto-Negotiation The conforms to the auto-negotiation protocol, defined in Clause 28 of the IEEE Specification. Auto-negotiation allows UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) link partners to select the highest common mode of operation. During auto-negotiation, link partners advertise capabilities across the UTP link to each other, and then compare their own capabilities with those they received from their link partners. The highest speed and duplex setting that is common to the two link partners is selected as the mode of operation. The following list shows the speed and duplex operation mode from highest to lowest. Priority 1: 1000Base-T, full-duplex Priority 2: 1000Base-T, half-duplex Priority 3: 100Base-TX, full-duplex Priority 4: 100Base-TX, half-duplex Priority 5: 10Base-T, full-duplex Priority 6: 10Base-T, half-duplex If auto-negotiation is not supported or the link partner is forced to bypass auto-negotiation for 10Base-T and 100Base-TX modes, then the sets its operating mode by observing the input signal at its receiver. This is known as parallel detection, and allows the to establish a link by listening for a fixed signal protocol in the absence of auto-negotiation advertisement protocol. The auto-negotiation link up process is shown in the following flow chart. February 13, Revision 1.2
27 Figure 3. Auto-Negotiation Flow Chart For 1000Base-T mode, auto-negotiation is required and always used to establish link. During 1000Base-T autonegotiation, Master and Slave configuration is first resolved between link partners, and then link is established with the highest common capabilities between link partners. Auto-negotiation is enabled by default at power-up or after hardware reset. Afterwards, auto-negotiation can be enabled or disabled through register 0 bit 12. If auto-negotiation is disabled, then the speed is set by register 0 bits 6 and 13, and the duplex is set by register 0 bit 8. If the speed is changed on the fly, then the link goes down and either auto-negotiation or parallel detection will initiate until a common speed between and its link partner is re-established for link. If link is already established, and there is no change of speed on the fly, then the changes will not take effect unless either auto-negotiation is restarted through register 0 bit 9, or a link down to link up transition occurs (i.e., disconnecting and reconnecting the cable). After auto-negotiation is completed, the link status is updated in register 1 and the link partner capabilities are updated in registers 5, 6, and 10. The auto-negotiation finite state machines employ interval timers to manage the auto-negotiation process. The duration of these timers under normal operating conditions are summarized in the following table. February 13, Revision 1.2
28 Auto-Negotiation Interval Timers Time Duration Transmit Burst interval 16ms Transmit Pulse interval 68µs FLP detect minimum time 17.2µs FLP detect maximum time 185µs Receive minimum Burst interval 6.8ms Receive maximum Burst interval 112ms Data detect minimum interval 35.4µs Data detect maximum interval 95µs NLP test minimum interval 4.5ms NLP test maximum interval 30ms Link Loss time 52ms Break Link time 1480ms Parallel Detection wait time 830ms Link Enable wait time 1000ms Table 2. Auto-Negotiation Timers RGMII Interface The Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) is compliant with the RGMII Version 1.3 Specification. It provides a common interface between RGMII PHYs and MACs, and has the following key characteristics: Pin count is reduced from 24 pins for the IEEE Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII) to 12 pins for RGMII. All speeds (10Mbps, 100Mbps, and 1000Mbps) are supported at both half and full duplex. Data transmission and reception are independent and belong to separate signal groups. Transmit data and receive data are each 4-bit wide, a nibble. In RGMII operation, the RGMII pins function as follow: The MAC sources the transmit reference clock, TXC, at 125MHz for 1000Mbps, 25MHz for 100Mbps and 2.5MHz for 10Mbps. The PHY recovers and sources the receive reference clock, RXC, at 125MHz for 1000Mbps, 25MHz for 100Mbps and 2.5MHz for 10Mbps. For 1000Base-T, the transmit data, TXD[3:0], is presented on both edges of TXC, and the received data, RXD[3:0], is clocked out on both edges of the recovered 125 MHz clock, RXC. For 10Base-T/100Base-TX, the MAC will hold TX_CTL low until both PHY and MAC operate at the same speed. During the speed transition, the receive clock will be stretched on either positive or negative pulse to ensure that no clock glitch is presented to the MAC at any time. TX_ER and RX_ER are combined with TX_EN and RX_DV, respectively, to form TX_CTL and RX_CTL. These two RGMII control signals are valid at the falling clock edge. After power-up or reset, the is configured to RGMII mode if the MODE[3:0] strap-in pins are set to one of the RGMII mode capability options. See Strapping Options section for available options. The has the option to output a low jitter 125MHz reference clock on the CLK125_NDO pin. This clock provides a lower cost reference clock alternative for RGMII MACs that require a 125MHz crystal or oscillator. The 125MHz clock output is enabled after power-up or reset if the CLK125_EN strap-in pin is pulled high. February 13, Revision 1.2
29 RGMII Signal Definition The following table describes the RGMII signals. Refer to the RGMII Version 1.3 Specification for more detailed information. RGMII Signal Name (per spec) RGMII Signal Name (per ) Pin Type (with respect to PHY) Pin Type (with respect to MAC) Description TXC GTX_CLK Output Transmit Reference Clock (125MHz for 1000Mbps, 25MHz for 100Mbps, 2.5MHz for 10Mbps) TX_CTL TX_EN Output Transmit Control TXD[3:0] TXD[3:0] Output Transmit Data [3:0] RXC RX_CLK Output Receive Reference Clock (125MHz for 1000Mbps, 25MHz for 100Mbps, 2.5MHz for 10Mbps) RX_CTL RX_DV Output Receive Control RXD[3:0] RXD[3:0] Output Receive Data [3:0] Table 3. RGMII Signal Definition RGMII Signal Diagram The RGMII pin connections to the MAC are shown in the following figure. RGMII Ethernet MAC GTX_CLK TXC TX_EN TX_CTL TXD[3:0] TXD[3:0] RX_CLK RXC RX_DV RX_CTL RXD[3:0] RXD[3:0] Figure 4. RGMII Interface February 13, Revision 1.2
30 RGMII Pad Skew Registers Pad skew registers are available for all RGMII pins (clocks, control signals, and data bits) to provide programming options to adjust or correct the timing relationship for each RGMII pin. Because RGMII is a source-synchronous bus interface, the timing relationship needs to be maintained only within the RGMII pin s respective timing group. RGMII transmit timing group pins: GTX_CLK, TX_EN, TXD[3:0] RGMII receive timing group pins: RX_CLK, RX_DV, RXD[3:0] The following three registers located at Extended Registers 260 (104h), 261 (105h), and 262 (106h) are provided for pad skew programming. Address Name Description Mode Default Register 260 (104h) RGMII Clock and Control Pad Skew :12 rxc_pad_skew RGMII RXC PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :8 rxdv_pad_skew RGMII RX_CTL PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :4 txc_pad_skew RGMII TXC PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :0 txen_pad_skew RGMII TX_CTL PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW 0111 Register 261 (105h) RGMII RX Data Pad Skew :12 rxd3_pad_skew RGMII RXD3 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :8 rxd2_pad_skew RGMII RXD2 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :4 rxd1_pad_skew RGMII RXD1 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :0 rxd0_pad_skew RGMII RXD0 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW 0111 Register 262 (106h) RGMII TX Data Pad Skew :12 txd3_pad_skew RGMII TXD3 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :8 txd2_pad_skew RGMII TXD2 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :4 txd1_pad_skew RGMII TXD1 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW :0 txd0_pad_skew RGMII TXD0 PAD Skew Control (0.12ns/step) RW 0111 Table 4. RGMII Pad Skew Registers The RGMII clocks, control signals, and data bits have 4-bit skew settings. Each register bit is approximately a 0.12ns step change. A single-bit decrement decreases the delay by approximately 0.12ns, while a single-bit increment increases the delay by approximately 0.12ns. The following table lists the approximate absolute delay for each pad skew (value) setting. February 13, Revision 1.2
KSZ9021RL/RN. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver for transmission
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support General Description The KSZ9021RL is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver for transmission
KSZ9031RNX. Features. General Description. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support. Data Sheet Rev 0.
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Data Sheet Rev 0.11 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Data Sheet Rev 0.11 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
KSZ9031RNX. General Description. Features. Functional Diagram. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0 General Description The is a completely integrated triple-speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet physicallayer transceiver for transmission
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with RGMII Support Revision 2.0 General Description The is a completely integrated triple-speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet physicallayer transceiver for transmission
KSZ9031MNX. Features. General Description. Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support. Data Sheet Rev. 0.13
 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support Data Sheet Rev. 0.13 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver with GMII / MII Support Data Sheet Rev. 0.13 General Description The is a completely integrated triple speed (10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T) Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
KSZ8021RNL / KSZ8031RNL
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support General Description The KSZ8031RNL is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data over standard
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support General Description The KSZ8031RNL is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data over standard
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Data Sheet Rev. 1.0 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Data Sheet Rev. 1.0 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
KSZ8081RNA/KSZ8081RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.3 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
10Base-T/100Base-TX PHY with RMII Support Revision 1.3 General Description The KSZ8081RNA is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base- TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and reception of data
KSZ8061RNB/KSZ8061RND
 10Base-T/100Base-TX Physical Layer Transceiver Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8061RNB/RND is a single-chip 10Base-T/ 100Base-TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception
10Base-T/100Base-TX Physical Layer Transceiver Revision 1.1 General Description The KSZ8061RNB/RND is a single-chip 10Base-T/ 100Base-TX Ethernet physical layer transceiver for transmission and reception
Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver
 Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver The () directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It provides a Media Independent Interface (MII) for easy attachment to
Cortina Systems LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver The () directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It provides a Media Independent Interface (MII) for easy attachment to
KSZ8001L/S. 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04
 L/S 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04 General Description The is a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX Physical Layer Transceiver, operating the core at 1.8 volts
L/S 1.8V, 3.3V 10/100BASE-T/TX/FX Physical Layer Transceiver Data Sheet Rev. 1.04 General Description The is a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX Physical Layer Transceiver, operating the core at 1.8 volts
LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai. Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES DATASHEET. Highlights.
 LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY) Comprehensive flexpwr Technology
LAN8720A/LAN8720Ai Small Footprint RMII 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver (PHY) Comprehensive flexpwr Technology
Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting
 Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting PIERGIORGIO BERUTO ANTONIO ORZELLI TF Short Reach PCS, PMA and PLCA baseline proposal November 7 th, 2017 Supporters Gergely Huszak (Kone) Kirsten Matheus (BMW)
Canova Tech The Art of Silicon Sculpting PIERGIORGIO BERUTO ANTONIO ORZELLI TF Short Reach PCS, PMA and PLCA baseline proposal November 7 th, 2017 Supporters Gergely Huszak (Kone) Kirsten Matheus (BMW)
Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514
 Cover Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Doc. No. MV-S107146-U0, Rev. B February 23, 2018 Marvell. Moving Forward Faster Document
Cover Alaska 88E1510/88E1518/ 88E1512/88E1514 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Doc. No. MV-S107146-U0, Rev. B February 23, 2018 Marvell. Moving Forward Faster Document
Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver
 Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver Datasheet The Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver (called hereafter the LXT971A Transceiver) directly supports both 100BASE-TX and
Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver Datasheet The Intel LXT971A Single-Port 10/100 Mbps PHY Transceiver (called hereafter the LXT971A Transceiver) directly supports both 100BASE-TX and
Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver
 Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver Features 10/100Mbps TX Full-duplex or half-duplex Supports Auto MDI/MDIX function Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u Supports IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
Single port 10/100 Fast Ethernet Transceiver Features 10/100Mbps TX Full-duplex or half-duplex Supports Auto MDI/MDIX function Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u Supports IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver
 Intel LXT971A 3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver Datasheet The LXT971A is an IEEE compliant Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver that directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It
Intel LXT971A 3.3V Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver Datasheet The LXT971A is an IEEE compliant Fast Ethernet PHY Transceiver that directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. It
LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology
 LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
LAN8741A/LAN8741Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
Application Note 5044
 HBCU-5710R 1000BASE-T Small Form Pluggable Low Voltage (3.3V) Electrical Transceiver over Category 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Characterization Report Application Note 5044 Summary The Physical Medium
HBCU-5710R 1000BASE-T Small Form Pluggable Low Voltage (3.3V) Electrical Transceiver over Category 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Characterization Report Application Note 5044 Summary The Physical Medium
Am79C989. Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 Am79C989 Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Four independent 10BASE-T transceivers compliant with the IEEE 802.3 standard Four digital Manchester Encode/Decode (MENDEC)
Am79C989 Quad Ethernet Switching Transceiver (QuEST ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Four independent 10BASE-T transceivers compliant with the IEEE 802.3 standard Four digital Manchester Encode/Decode (MENDEC)
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH MII INTERFACE
 DATASHEET ICS1894-34 Description The ICS1894-34 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
DATASHEET ICS1894-34 Description The ICS1894-34 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver
 78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver Simplifying System Integration TM DESCRIPTION The 78Q2123 and 78Q2133, MicroPHY TM, are the smallest 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet transceivers in
78Q2123/78Q2133 MicroPHY 10/100BASE-TX Transceiver Simplifying System Integration TM DESCRIPTION The 78Q2123 and 78Q2133, MicroPHY TM, are the smallest 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet transceivers in
Features. NRZ/NRZI MLT3 Encoder. Clock Recovery. Auto Negotiation. Power Down or Saving LED X1. Driver PLL X2
 KS8737 3.3V 10/100BaseTX/FX MII Physical Layer Transceiver Rev 3.11 General Description Operating at 3.3 Volts to meet low voltage and low power requirement, the KS8737 is a 10/100BaseTX/FX Physical Layer
KS8737 3.3V 10/100BaseTX/FX MII Physical Layer Transceiver Rev 3.11 General Description Operating at 3.3 Volts to meet low voltage and low power requirement, the KS8737 is a 10/100BaseTX/FX Physical Layer
Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) 4/1/2002 Version 2.0. Reduced Pin-count Interface For Gigabit Ethernet Physical Layer Devices
 Page 1 of 9 Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) 4/1/2002 Version 2.0 Reduced Pin-count Interface For Gigabit Ethernet Physical Layer Devices Page 2 of 9 Revision Level Date Revision Description
Page 1 of 9 Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) 4/1/2002 Version 2.0 Reduced Pin-count Interface For Gigabit Ethernet Physical Layer Devices Page 2 of 9 Revision Level Date Revision Description
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH RMII INTERFACE. Not recommended for new designs
 DATASHEET ICS1894-40 Description Features The ICS1894-40 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection
DATASHEET ICS1894-40 Description Features The ICS1894-40 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection
Adaptive Cable Equalizer for IEEE 1394b
 EQCO400T Features Adaptive Cable Equalizer for IEEE 1394b Functional Description Multi-Rate Adaptive Equalization Supports IEEE 1394b - S400, S200 and S100 data rates Seamless connection with compliant
EQCO400T Features Adaptive Cable Equalizer for IEEE 1394b Functional Description Multi-Rate Adaptive Equalization Supports IEEE 1394b - S400, S200 and S100 data rates Seamless connection with compliant
EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006
 EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006 Six projects have been identified. It will be our goal to have approximately an equal number of teams working on each project. You may work individually or in groups of
EE 434 Final Projects Fall 2006 Six projects have been identified. It will be our goal to have approximately an equal number of teams working on each project. You may work individually or in groups of
LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology
 LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
LAN8740A/LAN8740Ai Small Footprint MII/RMII 10/100 Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver with HP Auto-MDIX and flexpwr Technology PDUCT FEATURES Highlights Single-Chip Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
DATASHEET IDT77V7101 GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER
 GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER DATASHEET Features IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet compatible 1.25 Gbps full duplex transmission and reception in a single IC Optical interface through fiber module 10-bit
GIGABIT ETHERNET SERDES TRANSCEIVER DATASHEET Features IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet compatible 1.25 Gbps full duplex transmission and reception in a single IC Optical interface through fiber module 10-bit
FCOPPER-SFP BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver
 100BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver March 27, 2012 Product Overview The electrical Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver module is specifically designed for converting 100BASE-FX NRZI port interface
100BASE-TX Copper SFP Transceiver March 27, 2012 Product Overview The electrical Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver module is specifically designed for converting 100BASE-FX NRZI port interface
Single Port, Low-Power, 10/100/1000BASE-T PHY with GMII/MII, RGMII, TBI, RTBI MAC Interfaces. 128-pin LQFP (14mm x 20mm) 100-ball LBGA (11mm x 11mm)
 VSC821 Single Port, Low-Power, 1/1/1BASE-T PHY with GMII/MII, RGMII, TBI, RTBI MAC Interfaces 1 General Description Enabling widespread, low-cost, Gigabit-to-the-Desktop deployment, Vitesse s low-power,
VSC821 Single Port, Low-Power, 1/1/1BASE-T PHY with GMII/MII, RGMII, TBI, RTBI MAC Interfaces 1 General Description Enabling widespread, low-cost, Gigabit-to-the-Desktop deployment, Vitesse s low-power,
PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance
 PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance 1.0 Introduction The use of a reference clock that is less stable than those directly driven from an oscillator may be required for some applications.
PHYTER 100 Base-TX Reference Clock Jitter Tolerance 1.0 Introduction The use of a reference clock that is less stable than those directly driven from an oscillator may be required for some applications.
ICS Description. Features DATASHEET 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX INTEGRATED PHYCEIVER WITH RMII INTERFACE
 DATASHEET ICS1894-33 Description The ICS1894-33 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
DATASHEET ICS1894-33 Description The ICS1894-33 is a low-power, physical-layer device (PHY) that supports the ISO/IEC 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Carrier-Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
2.5G/5G/10G ETHERNET Testing Service
 2.5G/5G/10G ETHERNET Testing Service Clause 126 2.5G/5GBASE-T PMA Test Plan Version 1.3 Technical Document Last Updated: February 4, 2019 2.5, 5 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet Testing Service 21 Madbury Road,
2.5G/5G/10G ETHERNET Testing Service Clause 126 2.5G/5GBASE-T PMA Test Plan Version 1.3 Technical Document Last Updated: February 4, 2019 2.5, 5 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet Testing Service 21 Madbury Road,
CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 Specifications Rev. D00A
 CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 Specifications Rev. D00A Preliminary DATA SHEET CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 10GBASE-CX4 X2 Transceiver CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 Overview CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 10GBd X2 Electrical transceivers are designed
CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 Specifications Rev. D00A Preliminary DATA SHEET CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 10GBASE-CX4 X2 Transceiver CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 Overview CFORTH-X2-10GB-CX4 10GBd X2 Electrical transceivers are designed
ML BASE-TX Physical Layer with MII
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML6692 implements the complete physical layer of the Fast Ethernet 100BASE-TX standard. The ML6692 interfaces to the controller through the standard-compliant Media Independent
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ML6692 implements the complete physical layer of the Fast Ethernet 100BASE-TX standard. The ML6692 interfaces to the controller through the standard-compliant Media Independent
SFP- GE- RJ45- AO. 1.25Gbps SFP Copper Transceiver
 SFP- GE- RJ45- AO ZTE 1000BASE- TX SFP COPPER 100M REACH RJ- 45 SFP- GE- RJ45- AO 1.25Gbps SFP Copper Transceiver Features Up to 1.25Gb/s bi- directional data links Hot- pluggable SFP footprint Extended
SFP- GE- RJ45- AO ZTE 1000BASE- TX SFP COPPER 100M REACH RJ- 45 SFP- GE- RJ45- AO 1.25Gbps SFP Copper Transceiver Features Up to 1.25Gb/s bi- directional data links Hot- pluggable SFP footprint Extended
GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM
 GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM Clause 126 2.5G/5GBASE-T PMA Test Suite Version 1.2 Technical Document Last Updated: March 15, 2017 2.5, 5 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet Testing Service 21 Madbury Road, Suite 100
GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM Clause 126 2.5G/5GBASE-T PMA Test Suite Version 1.2 Technical Document Last Updated: March 15, 2017 2.5, 5 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet Testing Service 21 Madbury Road, Suite 100
University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory Fast Ethernet Consortium
 University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory Fast Ethernet Consortium As of February 25, 2004 the Fast Ethernet Consortium Clause 25 Physical Medium Dependent Conformance Test Suite version
University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory Fast Ethernet Consortium As of February 25, 2004 the Fast Ethernet Consortium Clause 25 Physical Medium Dependent Conformance Test Suite version
ERTEC 200. PHY Description. Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller
 ERTEC 200 Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller PHY Description Copyright Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Page 1 ERTEC 200 PHY Edition (11/2007) Disclaimer of Liability We have checked the contents
ERTEC 200 Enhanced Real-Time Ethernet Controller PHY Description Copyright Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. Page 1 ERTEC 200 PHY Edition (11/2007) Disclaimer of Liability We have checked the contents
1000BASE-T Copper SFP Transceiver
 1000BASE-T Copper SFP Transceiver Features: Operating data rate up to 1.25 Gbps Compact RJ-45 connector assembly Single 3.3V power supply and Low power dissipation Hot Pluggable 1000 BASE-T operation in
1000BASE-T Copper SFP Transceiver Features: Operating data rate up to 1.25 Gbps Compact RJ-45 connector assembly Single 3.3V power supply and Low power dissipation Hot Pluggable 1000 BASE-T operation in
Maximum data rate: 50 MBaud Data rate range: ±15% Lock-in time: 1 bit
 MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
MONOLITHIC MANCHESTER ENCODER/DECODER (SERIES 3D7503) FEATURES 3D7503 data 3 delay devices, inc. PACKAGES All-silicon, low-power CMOS technology CIN 1 14 Encoder and decoder function independently Encoder
SFP Cooper 1000Base-T 100M SL-SFP-3T-XX
 SFP Cooper 1000Base-T 100M SL-SFP-3T-XX Overview Sourcelight SL-SFP-3T-XX Copper Small Form Pluggable (SFP) transceiver is high performance, cost effective module compliant with the Gigabit Ethernet and
SFP Cooper 1000Base-T 100M SL-SFP-3T-XX Overview Sourcelight SL-SFP-3T-XX Copper Small Form Pluggable (SFP) transceiver is high performance, cost effective module compliant with the Gigabit Ethernet and
10GECTHE 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM
 10GECTHE 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM 10GBASE-T Clause 55 PMA Electrical Test Suite Version 1.0 Technical Document Last Updated: September 6, 2006, 3:00 PM 10 Gigabit Ethernet Consortium 121 Technology
10GECTHE 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET CONSORTIUM 10GBASE-T Clause 55 PMA Electrical Test Suite Version 1.0 Technical Document Last Updated: September 6, 2006, 3:00 PM 10 Gigabit Ethernet Consortium 121 Technology
RTL8201. Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver
 RTL8201 Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver 1. Features Realtek s RTL8201 is a Fast Ethernet Phyceiver with MII interface to MAC chip. It provides the following features: Support MII interface
RTL8201 Single port 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet Phyceiver 1. Features Realtek s RTL8201 is a Fast Ethernet Phyceiver with MII interface to MAC chip. It provides the following features: Support MII interface
AUTOMOTIVE ETHERNET CONSORTIUM
 AUTOMOTIVE ETHERNET CONSORTIUM Clause 96 100BASE-T1 Physical Medium Attachment Test Suite Version 1.0 Technical Document Last Updated: March 9, 2016 Automotive Ethernet Consortium 21 Madbury Rd, Suite
AUTOMOTIVE ETHERNET CONSORTIUM Clause 96 100BASE-T1 Physical Medium Attachment Test Suite Version 1.0 Technical Document Last Updated: March 9, 2016 Automotive Ethernet Consortium 21 Madbury Rd, Suite
ICS1885. High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM. Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. General Description. Pin Configuration.
 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS1885 High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM General Description The ICS1885 is designed to provide high performance clock recovery and generation for either 25.92
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS1885 High-Performance Communications PHYceiver TM General Description The ICS1885 is designed to provide high performance clock recovery and generation for either 25.92
CDR in Mercury Devices
 CDR in Mercury Devices February 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 130 Introduction Preliminary Information High-speed serial data transmission allows designers to transmit highbandwidth data using differential,
CDR in Mercury Devices February 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 130 Introduction Preliminary Information High-speed serial data transmission allows designers to transmit highbandwidth data using differential,
Ethernet Coax Transceiver Interface
 1CY7B8392 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3 10BASE5 and 10BASE2 Pin compatible with the popular 8392 Internal squelch circuit to eliminate input noise Hybrid mode collision detect for extended distance
1CY7B8392 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3 10BASE5 and 10BASE2 Pin compatible with the popular 8392 Internal squelch circuit to eliminate input noise Hybrid mode collision detect for extended distance
2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices
 2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices November 2011 AV-54002-1.1 AV-54002-1.1 This chapter contains basic technical details pertaining to specific features in the Arria V device transceivers. This
2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices November 2011 AV-54002-1.1 AV-54002-1.1 This chapter contains basic technical details pertaining to specific features in the Arria V device transceivers. This
Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr )
 PRELIMINARY Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Repeater functions comply with IEEE 802.3 Repeater Unit specifications Four integral 10BASE-T transceivers
PRELIMINARY Am79C984A enhanced Integrated Multiport Repeater (eimr ) DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Repeater functions comply with IEEE 802.3 Repeater Unit specifications Four integral 10BASE-T transceivers
RS-232 Electrical Specifications and a Typical Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
Features. Applications. Markets
 3.2Gbps Precision, LVDS 2:1 MUX with Internal Termination and Fail Safe Input General Description The is a 2.5V, high-speed, fully differential LVDS 2:1 MUX capable of processing clocks up to 2.5GHz and
3.2Gbps Precision, LVDS 2:1 MUX with Internal Termination and Fail Safe Input General Description The is a 2.5V, high-speed, fully differential LVDS 2:1 MUX capable of processing clocks up to 2.5GHz and
NBASE-T Copper Transceiver Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP+), 3.3V 100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10Gbps Ethernet. Features
 Features 10Gbps Links up to 35 m using Cat 6a/7 Cable 100M/1G/2.5G/5Gbps Links up to 100 m using Cat5e Cable Low Power Consumption 2.2W Max, 35m @ 10Gbps, 75 C 1.88W Max, 100m @ 2.5G and 5Gbps, 75 C 1.88W
Features 10Gbps Links up to 35 m using Cat 6a/7 Cable 100M/1G/2.5G/5Gbps Links up to 100 m using Cat5e Cable Low Power Consumption 2.2W Max, 35m @ 10Gbps, 75 C 1.88W Max, 100m @ 2.5G and 5Gbps, 75 C 1.88W
Alaska 88E1545/ 88E1543/88E1548
 Cover Alaska 88E1545/ 88E1543/88E1548 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Datasheet - Unrestricted Doc. No. MV-S106839-U0, Rev. B May 5, 2017, Advance Marvell. Moving Forward
Cover Alaska 88E1545/ 88E1543/88E1548 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Energy Efficient Ethernet Transceiver Datasheet - Unrestricted Doc. No. MV-S106839-U0, Rev. B May 5, 2017, Advance Marvell. Moving Forward
3 Definitions, symbols, abbreviations, and conventions
 T10/02-358r2 1 Scope 2 Normative references 3 Definitions, symbols, abbreviations, and conventions 4 General 4.1 General overview 4.2 Cables, connectors, signals, transceivers 4.3 Physical architecture
T10/02-358r2 1 Scope 2 Normative references 3 Definitions, symbols, abbreviations, and conventions 4 General 4.1 General overview 4.2 Cables, connectors, signals, transceivers 4.3 Physical architecture
±50V Isolated, 3.0V to 5.5V, 250kbps, 2 Tx/2 Rx, RS-232 Transceiver MAX3250
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX325 General Description The MAX325 is a 3.V to 5.5V powered, ±5V isolated EIA/TIA-232 and V.28/V.24 communications interface with high data-rate capabilities. The MAX325 is
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX325 General Description The MAX325 is a 3.V to 5.5V powered, ±5V isolated EIA/TIA-232 and V.28/V.24 communications interface with high data-rate capabilities. The MAX325 is
ICS CLOCK SYNTHESIZER FOR PORTABLE SYSTEMS. Description. Features. Block Diagram PRELIMINARY DATASHEET
 PRELIMINARY DATASHEET ICS1493-17 Description The ICS1493-17 is a low-power, low-jitter clock synthesizer designed to replace multiple crystals and oscillators in portable audio/video systems. The device
PRELIMINARY DATASHEET ICS1493-17 Description The ICS1493-17 is a low-power, low-jitter clock synthesizer designed to replace multiple crystals and oscillators in portable audio/video systems. The device
XRT7295AE E3 (34.368Mbps) Integrated line Receiver
 E3 (34.368Mbps) Integrated line Receiver FEATURES APPLICATIONS March 2003 Fully Integrated Receive Interface for E3 Signals Integrated Equalization (Optional) and Timing Recovery Loss-of-Signal and Loss-of-Lock
E3 (34.368Mbps) Integrated line Receiver FEATURES APPLICATIONS March 2003 Fully Integrated Receive Interface for E3 Signals Integrated Equalization (Optional) and Timing Recovery Loss-of-Signal and Loss-of-Lock
2. Arria GX Transceiver Protocol Support and Additional Features
 2. Arria GX Transceiver Protocol Support and Additional Features AGX52002-2.0 Introduction Arria GX transceivers have a dedicated physical coding sublayer (PCS) and physical media attachment (PMA) circuitry
2. Arria GX Transceiver Protocol Support and Additional Features AGX52002-2.0 Introduction Arria GX transceivers have a dedicated physical coding sublayer (PCS) and physical media attachment (PMA) circuitry
100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations
 100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations 1 0 INTRODUCTION This application note provides the information necessary to design an unmanaged 12-port 100BASE-TX repeater based on National Semiconductor
100BASE-TX Unmanaged Repeater Design Recommendations 1 0 INTRODUCTION This application note provides the information necessary to design an unmanaged 12-port 100BASE-TX repeater based on National Semiconductor
x-mgc Part Number: FCU-022M101
 x-mgc Part Number: FCU-022M101 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3ak (10GBASE-CX4) X2 MSA Rev 1.0b Compatible module Industry standard electrical connector, microgigacn TM (I/O interface) XAUI Four channel
x-mgc Part Number: FCU-022M101 Features Compliant with IEEE802.3ak (10GBASE-CX4) X2 MSA Rev 1.0b Compatible module Industry standard electrical connector, microgigacn TM (I/O interface) XAUI Four channel
AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY
 AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview This application note discusses how to migrate from an existing design using the SMSC LAN83C183 PHY
AN 13.9 Migrating from the LAN83C183 10/100 PHY to the LAN83C185 10/100 PHY 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview This application note discusses how to migrate from an existing design using the SMSC LAN83C183 PHY
Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers
 Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers The Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E are 8-port Fast Ethernet PHY Transceivers supporting IEEE 802.3 physical layer
Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E Advanced 8-Port 10/ 100 Mbps PHY Transceivers The Cortina Systems LXT9785 and LXT9785E are 8-port Fast Ethernet PHY Transceivers supporting IEEE 802.3 physical layer
TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017
 TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017 1. RS485 basic knowledge... 2 1.1. RS485 BUS basic Characteristics... 2 1.2. RS485 Transmission Distance... 2 1.3. RS485 bus connection and termination
TD_485 Transceiver Modules Application Guide 2017 1. RS485 basic knowledge... 2 1.1. RS485 BUS basic Characteristics... 2 1.2. RS485 Transmission Distance... 2 1.3. RS485 bus connection and termination
10/100BASE-TX/FX Mini-Φ ΤΜ Transceiver. Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram. 10Base-T PCS. 100Base-X PCS. Digital Adaptive Equalizer.
 BCM521/BCM522 1/1BASE-TX/FX Mini-Φ ΤΜ Transceiver GENERAL DESCRPTON The BCM521/522 is a single-chip 1/1BASE-TX/FX transceiver targeted at Fast Ethernet switches and CardBus Network nterface devices. The
BCM521/BCM522 1/1BASE-TX/FX Mini-Φ ΤΜ Transceiver GENERAL DESCRPTON The BCM521/522 is a single-chip 1/1BASE-TX/FX transceiver targeted at Fast Ethernet switches and CardBus Network nterface devices. The
10GBASE-T Transmitter Key Specifications
 10GBASE-T Transmitter Key Specifications Sandeep Gupta, Jose Tellado Teranetics, Santa Clara, CA sgupta@teranetics.com 5/19/2004 1 1000BASE-T Transmitter spec. overview Differential voltage at MDI output
10GBASE-T Transmitter Key Specifications Sandeep Gupta, Jose Tellado Teranetics, Santa Clara, CA sgupta@teranetics.com 5/19/2004 1 1000BASE-T Transmitter spec. overview Differential voltage at MDI output
Features. Applications. Markets
 Precision LVPECL Runt Pulse Eliminator 2:1 MUX with 1:2 Fanout and Internal Termination General Description The is a low jitter PECL, 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX) optimized for redundant source
Precision LVPECL Runt Pulse Eliminator 2:1 MUX with 1:2 Fanout and Internal Termination General Description The is a low jitter PECL, 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX) optimized for redundant source
Features. Applications. Markets
 Precision LVPECL Runt Pulse Eliminator 2:1 Multiplexer General Description The is a low jitter PECL, 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX) optimized for redundant source switchover applications. Unlike
Precision LVPECL Runt Pulse Eliminator 2:1 Multiplexer General Description The is a low jitter PECL, 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX) optimized for redundant source switchover applications. Unlike
IC Plus IP1001 Verification Report Ver:1.3. Date: Jul, 29, 2006 Index Test Result Summery MII Register and LoopBack Test
 Index Test Summery...2 1 MII Register and LoopBack Test...3 1.1 MII Register Read / Write...3 1.2 External Loopback...3 2 Compatibility Test under Various Cable Length...4 2.1 Environment Setup...4 2.2
Index Test Summery...2 1 MII Register and LoopBack Test...3 1.1 MII Register Read / Write...3 1.2 External Loopback...3 2 Compatibility Test under Various Cable Length...4 2.1 Environment Setup...4 2.2
DS1267B Dual Digital Potentiometer
 Dual Digital Potentiometer FEATURES Two digitally controlled, 256-position potentiometers Serial port provides means for setting and reading both potentiometers Resistors can be connected in series to
Dual Digital Potentiometer FEATURES Two digitally controlled, 256-position potentiometers Serial port provides means for setting and reading both potentiometers Resistors can be connected in series to
5Gbps Serial Link Transmitter with Pre-emphasis
 Gbps Serial Link Transmitter with Pre-emphasis Chih-Hsien Lin, Chung-Hong Wang and Shyh-Jye Jou Department of Electrical Engineering,National Central University,Chung-Li, Taiwan R.O.C. Abstract- High-speed
Gbps Serial Link Transmitter with Pre-emphasis Chih-Hsien Lin, Chung-Hong Wang and Shyh-Jye Jou Department of Electrical Engineering,National Central University,Chung-Li, Taiwan R.O.C. Abstract- High-speed
Keysight Technologies An Overview of the Electrical Validation of 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T Devices
 Keysight Technologies An Overview of the Electrical Validation of 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T Devices Application Note The number of devices that come with a built-in network interface card has
Keysight Technologies An Overview of the Electrical Validation of 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T Devices Application Note The number of devices that come with a built-in network interface card has
SY89838U. General Description. Features. Applications. Markets. Precision 1:8 LVDS Clock Fanout Buffer with 2:1 Runt Pulse Eliminator Input MUX
 Precision 1:8 LVDS Clock Fanout Buffer with 2:1 Runt Pulse Eliminator Input MUX General Description The is a low jitter, low skew, high-speed 1:8 fanout buffer with a unique, 2:1 differential input multiplexer
Precision 1:8 LVDS Clock Fanout Buffer with 2:1 Runt Pulse Eliminator Input MUX General Description The is a low jitter, low skew, high-speed 1:8 fanout buffer with a unique, 2:1 differential input multiplexer
PROGRAMMABLE FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER (25MHz to 400MHz)
 PROGRAMMABLE FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER (25MHz to 400MHz) FEATURES Improved jitter performance over SY89429 25MHz to 400MHz differential PECL outputs ±25ps peak-to-peak output jitter Minimal frequency over-shoot
PROGRAMMABLE FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER (25MHz to 400MHz) FEATURES Improved jitter performance over SY89429 25MHz to 400MHz differential PECL outputs ±25ps peak-to-peak output jitter Minimal frequency over-shoot
Low-power coaxial Ethernet transceiver
 DESCRIPTION The is a low power BiCMOS coaxial transceiver interface (CTI) for Ethernet (10base5) and Thin Ethernet (10base) local area networks. The CTI is connected between the coaxial cable and the Data
DESCRIPTION The is a low power BiCMOS coaxial transceiver interface (CTI) for Ethernet (10base5) and Thin Ethernet (10base) local area networks. The CTI is connected between the coaxial cable and the Data
COM-1505 INTEGRATED PSK MODEM
 COM-1505 INTEGRATED PSK MODEM Overview The COM-1505 is a complete digital PSK modem, including PSK modulation, demodulation, convolutional error correction, V35 scrambling, HDLC framing, TCP-IP network
COM-1505 INTEGRATED PSK MODEM Overview The COM-1505 is a complete digital PSK modem, including PSK modulation, demodulation, convolutional error correction, V35 scrambling, HDLC framing, TCP-IP network
1000BASE-T SFP Copper Transceiver Hot Pluggable, Cat-5 UTP Cable, 100m
 Mini-GBIC Module INEO-MD-MSFP-TE 1000BASE-T SFP Copper Transceiver Hot Pluggable, Cat-5 UTP Cable, 100m tactio TM s INEO-MD-MSFP-TE 1000BASE-T copper SFP transceiver is high performance, cost effective
Mini-GBIC Module INEO-MD-MSFP-TE 1000BASE-T SFP Copper Transceiver Hot Pluggable, Cat-5 UTP Cable, 100m tactio TM s INEO-MD-MSFP-TE 1000BASE-T copper SFP transceiver is high performance, cost effective
1000BASE-T Copper Transceiver Small Form Pluggable (SFP), 3.3V 1.25Gbps Gigabit Ethernet. Features
 Features Hot-pluggable SFP Footprint Fully Metallic Enclosure for Low EMI Low Power Dissipation Compact RJ-45 Connector Assembly Detailed Product Information in EEPROM +3.3V Single Power Supply Access
Features Hot-pluggable SFP Footprint Fully Metallic Enclosure for Low EMI Low Power Dissipation Compact RJ-45 Connector Assembly Detailed Product Information in EEPROM +3.3V Single Power Supply Access
ANLAN203. KSZ84xx GPIO Pin Output Functionality. Introduction. Overview of GPIO and TOU
 ANLAN203 KSZ84xx GPIO Pin Output Functionality Introduction Devices in Micrel s ETHERSYNCH family have several GPIO pins that are linked to the internal IEEE 1588 precision time protocol (PTP) clock. These
ANLAN203 KSZ84xx GPIO Pin Output Functionality Introduction Devices in Micrel s ETHERSYNCH family have several GPIO pins that are linked to the internal IEEE 1588 precision time protocol (PTP) clock. These
Features. Applications. Markets FTTH/FTTP
 2.5Gbps GPON/BPON ONU SERDES General Description The is a single chip transceiver for data rates up to 2.5Gbps. On the receive side, it includes a complete clock recovery and data retiming circuit with
2.5Gbps GPON/BPON ONU SERDES General Description The is a single chip transceiver for data rates up to 2.5Gbps. On the receive side, it includes a complete clock recovery and data retiming circuit with
AN-1397 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Using the 50 Mbps RS-485 Transceiver in EnDat Motor Control Encoder Applications
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Using the 50 Mbps RS-485 Transceiver in EnDat Motor Control Encoder Applications
Using High-Speed Transceiver Blocks in Stratix GX Devices
 Using High-Speed Transceiver Blocks in Stratix GX Devices November 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 237 Introduction Applications involving backplane and chip-to-chip architectures have become increasingly
Using High-Speed Transceiver Blocks in Stratix GX Devices November 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 237 Introduction Applications involving backplane and chip-to-chip architectures have become increasingly
SY89847U. General Description. Functional Block Diagram. Applications. Markets
 1.5GHz Precision, LVDS 1:5 Fanout with 2:1 MUX and Fail Safe Input with Internal Termination General Description The is a 2.5V, 1:5 LVDS fanout buffer with a 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX). A
1.5GHz Precision, LVDS 1:5 Fanout with 2:1 MUX and Fail Safe Input with Internal Termination General Description The is a 2.5V, 1:5 LVDS fanout buffer with a 2:1 differential input multiplexer (MUX). A
CrystalLAN 100BASE-X and 10BASE-T Transceiver
 Features! Single-Chip IEEE 802.3 Physical Interface IC for 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX and 10BASE-T! Adaptive Equalizer provides Extended Length Operation (>160 m) with Superior Noise Immunity and NEXT Margin!
Features! Single-Chip IEEE 802.3 Physical Interface IC for 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX and 10BASE-T! Adaptive Equalizer provides Extended Length Operation (>160 m) with Superior Noise Immunity and NEXT Margin!
Integrated Powerline Communication Analog Front-End Transceiver and Line Driver
 19-4736; Rev 0; 7/09 Integrated Powerline Communication Analog General Description The powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) and line-driver IC is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high
19-4736; Rev 0; 7/09 Integrated Powerline Communication Analog General Description The powerline communication analog frontend (AFE) and line-driver IC is a state-of-the-art CMOS device that delivers high
SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester
 SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester Data Sheet SV2C Personalized SerDes Tester Data Sheet Revision: 1.0 2015-03-19 Revision Revision History Date 1.0 Document release. March 19, 2015 The information in
SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester Data Sheet SV2C Personalized SerDes Tester Data Sheet Revision: 1.0 2015-03-19 Revision Revision History Date 1.0 Document release. March 19, 2015 The information in
ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES
 ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES 10BASE-T Embedded MAU Test Suite Version 5.4 Technical Document Last Updated: June 21, 2012 Ethernet Testing Services 121 Technology Dr., Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 University of
ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES 10BASE-T Embedded MAU Test Suite Version 5.4 Technical Document Last Updated: June 21, 2012 Ethernet Testing Services 121 Technology Dr., Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 University of
ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES
 ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES 10BASE-Te Embedded MAU Test Suite Version 1.1 Technical Document Last Updated: June 21, 2012 Ethernet Testing Services 121 Technology Dr., Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 University
ETHERNET TESTING SERVICES 10BASE-Te Embedded MAU Test Suite Version 1.1 Technical Document Last Updated: June 21, 2012 Ethernet Testing Services 121 Technology Dr., Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 University
The SOL-20 Computer s Cassette interface.
 The SOL-20 Computer s Cassette interface. ( H. Holden. Dec. 2018 ) Introduction: The Cassette interface designed by Processor Technology (PT) for their SOL-20 was made to be compatible with the Kansas
The SOL-20 Computer s Cassette interface. ( H. Holden. Dec. 2018 ) Introduction: The Cassette interface designed by Processor Technology (PT) for their SOL-20 was made to be compatible with the Kansas
Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication
 Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication Abstract: Double-edged pulse width modulation (DPWM) is less sensitive to frequency-dependent losses in electrical
Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication Abstract: Double-edged pulse width modulation (DPWM) is less sensitive to frequency-dependent losses in electrical
SY89540U. General Description. Features. Typical Performance. Applications. Precision Low Jitter 4x4 LVDS Crosspoint Switch with Internal Termination
 Precision Low Jitter 4x4 LVDS Crosspoint Switch with Internal Termination General Description The is a low-jitter, low skew, high-speed 4x4 crosspoint switch optimized for precision telecom and enterprise
Precision Low Jitter 4x4 LVDS Crosspoint Switch with Internal Termination General Description The is a low-jitter, low skew, high-speed 4x4 crosspoint switch optimized for precision telecom and enterprise
DS1075. EconOscillator/Divider PRELIMINARY FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT FREQUENCY OPTIONS
 PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
SP339E RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 TRANSCEIVER WITH INTERNAL TERMINATION
 RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 TRANSCEIVER WITH INTERNAL TERMINATION DECEMBER 2011 REV. 1.0.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SP339 is an advanced multiprotocol transceiver supporting RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422 serial standards
RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 TRANSCEIVER WITH INTERNAL TERMINATION DECEMBER 2011 REV. 1.0.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SP339 is an advanced multiprotocol transceiver supporting RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422 serial standards
SFP+ Copper 10GBase-T SL-SFP-10G-T
 SFP+ Copper 10GBase-T SL-SFP-10G-T Overview SFP+ 10G copper transceiver module is a high performance integrated duplex data link for bi-directional communication over copper cable. It is specifically designed
SFP+ Copper 10GBase-T SL-SFP-10G-T Overview SFP+ 10G copper transceiver module is a high performance integrated duplex data link for bi-directional communication over copper cable. It is specifically designed
Integrated 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver
 Integrated // Gigait Ethernet Transceiver IP LF Features IEEE 82.3 compliant BASE-T, BASE-TX, and BASE-T Support auto-negotiation Support timing programmale MII/ GMII/ RGMII (delay clock, and driving current
Integrated // Gigait Ethernet Transceiver IP LF Features IEEE 82.3 compliant BASE-T, BASE-TX, and BASE-T Support auto-negotiation Support timing programmale MII/ GMII/ RGMII (delay clock, and driving current
PHY Layout APPLICATION REPORT: SLLA020. Ron Raybarman Burke S. Henehan 1394 Applications Group
 PHY Layout APPLICATION REPORT: SLLA020 Ron Raybarman Burke S. Henehan 1394 Applications Group Mixed Signal and Logic Products Bus Solutions November 1997 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves
PHY Layout APPLICATION REPORT: SLLA020 Ron Raybarman Burke S. Henehan 1394 Applications Group Mixed Signal and Logic Products Bus Solutions November 1997 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves
Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters
 9-292; Rev ; 7/04 Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters General Description The are dual-rate (.0625Gbps and 2.25Gbps) fibre channel repeaters. They are optimized for use in fibre channel arbitrated loop applications
9-292; Rev ; 7/04 Dual-Rate Fibre Channel Repeaters General Description The are dual-rate (.0625Gbps and 2.25Gbps) fibre channel repeaters. They are optimized for use in fibre channel arbitrated loop applications
ICS309 SERIAL PROGRAMMABLE TRIPLE PLL SS VERSACLOCK SYNTH. Description. Features. Block Diagram DATASHEET
 DATASHEET ICS309 Description The ICS309 is a versatile serially-programmable, triple PLL with spread spectrum clock source. The ICS309 can generate any frequency from 250kHz to 200 MHz, and up to 6 different
DATASHEET ICS309 Description The ICS309 is a versatile serially-programmable, triple PLL with spread spectrum clock source. The ICS309 can generate any frequency from 250kHz to 200 MHz, and up to 6 different
10/100Base. 100Base-FX Switching Converter. User s Manual
 10/100Base to 100Base-FX Switching Converter User s Manual COPYRIGHT All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
10/100Base to 100Base-FX Switching Converter User s Manual COPYRIGHT All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
