MAKING COLOR CHOICES FOR WEB SITES
|
|
|
- Iris Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAKING COLOR CHOICES FOR WEB SITES Bibliography: The following information was gathered through Web and book research. It was then edited into the current color guide (Making Color Choices for Web sites).
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS COLOR... 3 ABSORPTION AND REFLECTION... 4 YOUR EYE'S PERCEPTION... 4 COLOR MODELS AND MANAGEMENT... 4 Additive Color... 5 Subtractive Color... 5 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF COLOR... 7 Physiological Reactions... 8 The Symbolism of Color... 9 CHOOSING EFFECTIVE COLOR SCHEMES... 9 CONSIDERING COLOR BLINDNESS APPENDIX A... 12
3 Color One of the nagging questions on every (good) Web designer's mind today is, "What color choices should I make when putting together my Web site. There are the conservativeminded who stick to black text on a white background; this is a solid concept for delivering no-frills information in a usable manner. Remember the term usable when reading through the rest of this document; usability is key and everything else is secondary, but usability doesn't always equal minimalism. The more artistic-minded Web designers and many existing and potential clients looking to make their Web sites unique and memorable tend toward more robust color choices and layout. In complex Web sites that use varying levels of intricate programming (animation, Javascript, Java, Perl, etc.) that need to draw attention on a page full of color and still maintain the usability of finite elements, there must be distinguishing color choices. What color is, how it is created, and how we as humans view it is a centuries-old debate that can, to this day, break down into a vehement religious argument. Socrates postulated that fire originating from the eye combined with an object's intrinsic whiteness to produce color. Isaac Newton explored the true relationship between color and light in the 17 th century, demonstrating that color did not reside in objects themselves but was rather a product of light, and that white light could be reconstructed by combining all of the individual wavelengths in the visible light spectrum. These wavelengths corresponded to seven individual colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. The visible light spectrum isolated by Newton in his experiments makes up a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that ranges from low frequency, long wavelength regions (such as radio waves) to high frequency, short wavelength regions (such as X- rays). In between infrared and ultraviolet waves resides the visible light spectrum that includes the range of waves from 700nm (red) to 400nm (violet). While Newton proved that these individual wavelengths produced white light when combined, in actuality only three visible wavelengths are necessary to reconstitute white light: red, green, and blue. The modern scientific study of color harmony and the evocative properties of color yield information that influences the work of fine artists, designers, and advertising executives. This guide to color theory sheds light on some of the more enigmatic aspects of the effective use of color on the Web, and it illustrates techniques that you can use to reveal color harmonies and harness the power of color symbols on Web sites. How humans perceive color depends on the interplay of three elements: The nature of light. The reflective properties of an object. The ways that our retina and visual cortex process light waves. Regardless of what medium we work in (paint, print, or the Web) our ability to effectively use color depends on these processes.
4 Absorption and Reflection When light waves strike an object in nature, the object can transmit, absorb, or reflect various individual light waves. Depending on the nature of the object and its atomic structure, it might reflect green light while absorbing the other wavelengths. The retina and visual cortex process this reflected light to produce our perception of color. When artists and designers reproduce color on canvas or paper, they mimic this process by using pigments that absorb certain light waves while reflecting others. For instance, to produce green, we use pigments that absorb red and blue wavelengths. This process forms the basis of the color models used in both painting and print media. Your Eye's Perception Our ability to process light waves, whether reflected off of an object or emitted from a light source, depends on the retina of the human eye and the visual cortex of the brain. The retina contains three receptors, or cones, that respond to certain light wave frequencies. Red cones respond to low frequency waves, green cones respond to middle frequency waves, and blue cones respond to high frequency waves. These cones are not binary but rather act as channels that transmit levels of stimulation to the visual cortex, which processes the sum of these signals to produce the perceived color. In order to produce the desired color, artists and designers must either add or subtract light waves, so that only certain light waves are reflected to the receptors. Whether you add or subtract light depends on the medium in which you are working. Color Models and Management When designers deal with color, they usually rely on one of two color models: the additive color model, in which individual color waves combine to form white light, or the subtractive color model, in which pigments are used to subtract light waves. Both the traditional artist's palette and the CMYK systems are subtractive color models. On the Web, where we deal with light projection rather than light reflecting off of objects, we use an additive color model called RGB.
5 Additive Color In the natural world, the light waves that reach our retina are reflected off of objects, but there are other ways to produce color. Stage lights, for example, produce color by projecting white light through colored filters. Computer monitors also use projected light, but in that case the light is produced when electron guns are fired against a phosphor screen. These guns fire electrons in three colors: red, green, and blue. Using only these three colors, monitors can produce a full spectrum. This is known as the RGB color system. Within the RGB system, designers can also produce a color spectrum by amalgamating these three primary colors. Combining two of the primary colors generates three secondary colors: cyan, magenta, and yellow. As previously noted, adding all three primary colors together produces white light. Thus, an RGB value of 255,255,255 produces white, as seen in the center of the previous graphic. The complete absence of the three primary colors (RGB: 0,0,0) produces black. Subtractive Color The inverse of the RGB model is the CMYK model, in which light waves are subtracted to produce the desired color. Since the color of an object is derived from reflected light waves, this system uses three primary colors that each absorbs red, green, or blue light. For instance, if you subtract red light, the remaining green and blue waves produce cyan. The pigment used to subtract red light and reflect green and blue appears cyan. Similarly, print designers use magenta to absorb a percentage of green light and yellow to absorb a percentage of blue light At this point, it should be apparent that the primary colors of the CYMK model are the secondary colors of the RGB model, and vice versa. Moreover, if red, green, and blue light combine to produce white light, it stands to reason that cyan, yellow, and magenta pigments should combine to create black, since they should absorb all of the light waves. However, due to the limitations of the pigments and the printing system, the full combination of cyan, yellow, and magenta doesn't quite absorb all light. In practice, it's necessary to add black (the K in the CMYK model) to the system.
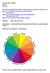
6 COLOR HARMONY One of the most challenging aspects of visual design is developing effective color harmonies that strike a balance between monotony and overstimulation. One place to begin exploring balanced and engaging color relationships is a color wheel--a representation of the hues available in a color model. Each color model contains three primary colors from which all other colors are derived. In traditional color theory, the three primary colors are blue, red, and yellow. In the RGB color model, the primary colors are red, green, and blue. Any two primary colors combine to produce a secondary color. Tertiary colors are derived from either a combination of a primary and a secondary color or from a combination of two secondary colors. We use color wheels to present all of these colors in a logically arranged sequence. As you can see from the illustrations below, an RGB color wheel (right) differs significantly from the traditional artist's color wheel (left): Color wheels expose relationships between colors that can be used to achieve both balance and contrast. The wheels include a number of full-intensity (saturated) hues as well as a variety of tints, tones, and shades, which are less saturated versions of the hue that include more white, gray, or black, respectively. While combinations of pure hues create dynamic color harmonies, you can design more subtle and subdued harmonies by using less saturated colors that are closer in value--that is, colors with similar degrees of lightness or darkness. Some common color harmonies include: Monochromatic: A monochromatic color set, as it sounds, uses a single hue but with varying tints and shades. Used correctly, this scheme can give a Web site a nice, clean look. Analogous: Colors that are side-by-side or very near each other on a color wheel. A grouping of three is shown to the left, but choosing four contiguous colors along the color wheel can also work well. Complementary: Colors appearing across from one another on a color wheel. These color combinations offer the maximum amount of contrast but can be overstimulating if used extensively. These are called complementary colors because, when used together, they seem to make each other brighter and more vivid
7 Split-complementary: One hue plus the two colors on either side of its complement. Split-complement harmony provides less contrast than straight complements. Triad: Three colors that are equidistant on a color wheel. This is the simplest approach to choosing colors. Simply imagine (or use) an equilateral triangle floating above a color wheel. Each color at the vertices is a usable color. In total, there are four possible triads that can be derived from the color wheel. See the color wheel in Appendix A. You can print it out (using a color printer of course) and begin drawing equilateral triangle points or vertices on the wheel. Repeat for each of the 4 possible triads. Now we're ready to start mixing things up a bit, what with the triads and the complementary colors and all. For example, you could combine two complementary pairs together, called a double complement. Something like yellow and purple, blue and orange. Another iteration of glorious color would be an alternate complement, where you combine a triad with the complement to one of the triadic hues. Green, reddish-purple, red, and orange for instance. You can also have a split complement that uses three colors, a hue and the two adjacent to its complement. Finally, in the combination category, you can have a tetrad, an example of which is shown next, where you combine four colors that are directly across from each other. Here you would be using a primary, a secondary, and two tertiary colors. Tetrad: Two pairs of complementary colors. When exploring color harmonies, it's often useful to begin with pure hues, then experiment with various tints, tones, and shades. You can then test the visual effect of a particular color combination by using a wireframe diagram. Remember that the importance of contrast doesn't end with designing for impact; it can also help or hinder readability. The Significance of Color While examining the scientific nature of color and the aesthetic considerations of color harmony, we've seen that perception plays a large part in the effective use of color. Beyond the mechanics of perception and the recognition of balanced color palettes lies the intangible, visceral reaction that humans have to color. Colors evoke strong physiological and emotional responses both positive and negative. When you develop your color palette, make sure that the colors you select elicit the appropriate response.
8 Physiological Reactions Although there has not been a great deal of conclusive evidence linking colors to specific responses, research suggests that certain colors do evoke physical responses. Red, for instance, is a very stimulating color and has been shown to produce increased heart and respiratory rates. Thus, red works as an excellent attention grabber and accent but could easily overstimulate when used as a background color. Similarly, yellow also demands attention, but since it is highly reflective, it creates eye fatigue and aggravation. On the other hand, the color blue has a relaxing effect on the nervous system, and some studies have shown that it increases productivity when used as a background color. However, don't use blue in your color scheme if your product is food-related, as blue is a natural appetite suppressant.
9 The Symbolism of Color The symbolic meaning associated with colors sometimes has precedent in nature. For instance, the color of the sky or the sun creates certain fairly universal associations. However, the underlying meaning that we derive from most colors is based on culturalspecific elements--politics, religion, mythology, and other shared social structures--that may shift over time and across geographical boundaries. Be careful when designing and marketing sites specifically for audiences outside of your cultural reference, since a color that has a positive connotation in one culture may have a negative connotation in another. In addition, most colors have both positive and negative associations. You can emphasize certain meanings over others by using variations of value and saturation, or by using colors that combine two hues. Common Color Connotations in Western Culture: Red: passion, romance, fire, violence, aggression. Red means stop or signals warning or forbidden actions in many cultures. Purple: creativity, mystery, royalty, mysticism, rarity. Purple is associated with death in some cultures. Blue: loyalty, security, conservatism, tranquility, coldness, sadness. Green: nature, fertility, growth, envy. In North American cultures, green means go, is associated with environmental awareness, and is often linked to fiscal matters. Yellow: brightness, illumination, illness, cowardice. Black: power, sophistication, contemporary style, death, morbidity, evil. White: purity, innocence, cleanliness, truth, peace, coldness, sterility. White is also the color of death in Chinese culture Choosing Effective Color Schemes Choosing the right colors for your Web site is a complex and often daunting task; many companies hire independent, special consultants just to devise color schemes that support and enhance an overall brand. However, if you have a sense of color harmony and understand the responses that certain colors can evoke, you can be your own color consultant and develop highly effective color combinations. Before you begin mixing and matching colors, you must first have a firm understanding of your site's message and goals. Once you understand what message you want to communicate, remember that perfecting a color palette is an iterative process, and above all, a creative one. Don't be afraid to experiment with surprising color combinations, but be sure to adequately test the results before unveiling your product to the public. Color Tips and Guidelines 1. Understand your site's message and brand. Choose colors that reinforce your message. For instance, if designing a site for a financial institution hoping to convey stability, choose cool, muted colors such as blue, gray, and green. In this case, using warm, vibrant hues would undermine the site's brand.
10 2. Understand your audience. Cultural differences can lead to unexpected responses to color. Additionally, demographic segments and age groups respond to colors differently. Younger audiences generally respond to more saturated hues that are less effective with older segments. 3. Use a small number of colors in your palette. Four or five colors, in addition to white and black, should be sufficient. Too many colors create discord and distract the user. 4. Use contrast for readability. Colors similar in value do not provide enough contrast and hinder legibility. Black text on white backgrounds provides the highest degree of contrast. 5. Use grayscale to test contrast. When dealing with hues other than black, white, and gray, it's sometimes difficult to determine the relative value of each color. To ensure that your color palette provides enough contrast, create a wireframe mockup and convert it to grayscale. 6. Be aware of timeliness when choosing colors. Color trends can quickly saturate the marketplace, and consumers rapidly become numb to fashionable hues. On the other hand, you can use popular color palettes from decades past to evoke feelings of nostalgia. 7. Consider functional colors when choosing a palette. Don't forget to establish functional colors for elements that communicate contextual information, such as headings and links. 8. Prepare for color differences on the Web. Every Web developer knows that even Web-safe colors appear differently across platforms. Be sure to correct for gamma differences and test your color palette on multiple platforms. Considering Color Blindness Well, now that we've gone through an exhaustive and somewhat daunting lesson in color choices, I'm going to drop a real bomb on you. What about color-blindness? I know, I know; you're sitting there with your head in your hands saying, "oh, forget it, I'm going back to my job as a nuclear physicist." Before you do that though, let's try to approach this issue of color blindness and see if we can't make some headway. There are two basic kinds of color deficiency: anomalous trichromasy and dichromasy, as well as several categories within those two forms. A dichromatic person tends to have a more severe shifting or weakness, where an anomalously trichromatic person could have a wide range of color blindness. The differences between various forms of color blindness can be subtle and hard to diagnose. An anomalously trichromatic person has either the red curve shifted toward the green range, or the green range shifted toward the red. These people are less sensitive to the color range that has shifted. An anomalously trichromatic person might see the green text as lime green, which would be quite hard to read. If the effect is subtle, an anomalously trichromatic person can see all the colors. It's just harder to tell them apart.
11 When a dichromatic person sees something green, both the red and green cones are activated, in addition to the shifting. Because red and green make yellow, green objects appear yellow. So if a site contains green text on a yellow background, both the text and the background appear yellow, making the text invisible. A dichromatic person with green cones shifted toward the red will also see the green as more yellow. This unpredictability makes simulating color blindness more difficult, and no doubt contributes to the difficulty in diagnosing the exact form of a person's color blindness. Not only can most color-blind people see black and white accurately, but they also see all shades of yellow and blue. Most color-blind people can even see dimmer shades of yellow like gold and olive, for example. Another trick is to keep colors bright. Bright colors are the easiest to tell apart. This is especially useful for those with a color weakness. They can see all the colors, but it's hard to tell them apart. By placing colors against an appropriate background, you can make even less-safe colors visible. You can use red against white, green against black, turquoise against black, and magenta against black, although magenta does tend to appear lighter than it does for people who are not color blind. Also remember that even when using these colors against these backgrounds, something other than color should be used as an additional cue. Considering that most color blind people have red-green color blindness, using red and green together is obviously a bad choice. Actually, red is most easily confused with a darker forest or racing green. With magenta and teal, appearances crisscross the spectrum from turquoise to pink and from orange to green. The grays in between get confused as well. Another problem is the use of various shades of one color. Shades of turquoise all appear quite light, for example. This is why it's best to keep your colors bright and distinct. Take into account that studies of color blind users of the Web revealed that a viewing problem is prevalent even among popular sites, and people are bothered by poor viewing ability even if the problem exists only on part of a page or site. A Web site does exist for testing Web pages against the factor of color-blindness. The URL for the Web site is: Vischeck is a way of showing you what things look like to someone who is color blind. You can use it on a single image or on a Web page. You can also download programs to let you run it on your own computer. In conclusion, I think you will see that there are no easy answers, but hopefully this guide provides some starting points and metrics for making your color choices.
12 Appendix A The usage of the following color wheel is detailed in the Color Harmony section of this guide to color.
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II
 GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT
 COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle.
 The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
Color Theory. Additive Color
 Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
SISTA 230. Color Theory
 SISTA 230 Color Theory CSS Colors CSS color:red; CSS background-color:blue; 17 valid color keywords CSS Color Keywords aqua black blue fuchsia gray green lime maroon navy olive orange purple red silver
SISTA 230 Color Theory CSS Colors CSS color:red; CSS background-color:blue; 17 valid color keywords CSS Color Keywords aqua black blue fuchsia gray green lime maroon navy olive orange purple red silver
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes
 Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Properties of Color. Value: Tint: Shade: Tone: Intensity:
 Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
CUT the wheel vertically IN HALF: WARM (right) AND COOL COLORS (left)
 COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
THE MEANING OF COLOR VISUAL COMMUNICATION III 3D DESIGN PRINCIPLES
 COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
check it out online at
 check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
CColor Theory in Design
 CColor Theory in Design The Color Wheel The Color Wheel A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors
CColor Theory in Design The Color Wheel The Color Wheel A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS
 LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography. April 24, 2006
 Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right
 COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
Colors in Images & Video
 LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
LECTURE 8 Colors in Images & Video CS 5513 Multimedia Systems Spring 2009 Imran Ihsan Principal Design Consultant OPUSVII www.opuseven.com Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciences 1. Light and Spectra
COLOR Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2016
 COLOR Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2016 Edward Tufte s Color Tufteisms Graphical excellence is the well-designed presentation of interesting data a matter of substance, of statistics, and of
COLOR Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2016 Edward Tufte s Color Tufteisms Graphical excellence is the well-designed presentation of interesting data a matter of substance, of statistics, and of
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory
 Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
In order to manage and correct color photos, you need to understand a few
 In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
In This Chapter 1 Understanding Color Getting the essentials of managing color Speaking the language of color Mixing three hues into millions of colors Choosing the right color mode for your image Switching
LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO
 MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
COLOR THEORY. The Color Wheel
 COLOR THEORY COLOR THEORY Color theory encompasses a multitude of definitions, concepts and design applications. All the information would fill several encyclopedias. As an introduction, here are a few
COLOR THEORY COLOR THEORY Color theory encompasses a multitude of definitions, concepts and design applications. All the information would fill several encyclopedias. As an introduction, here are a few
Art 177 :: Creative Photography. Color & Color Theory
 Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
Color Theory Basics. What is color theory? Classic color schemes supported by Color Wheel Pro:
 Color Theory Basics What is color theory? Color Theory is a set of principles used to create harmonious color combinations. Color relationships can be visually represented with a color wheel the color
Color Theory Basics What is color theory? Color Theory is a set of principles used to create harmonious color combinations. Color relationships can be visually represented with a color wheel the color
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg
 Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
Color Theory and Mixing
 MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements
 Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition. Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout.
 The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red.
 Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Introduction. The Spectral Basis for Color
 Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Objective Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics.
 Objective 102.01 Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. PART 1: ELEMENTS OF DESIGN o Color o Line o Shape o Texture o Watch this video on Fundamentals of Design. 2 COLOR o Helps identify
Objective 102.01 Explain design concepts used to create digital graphics. PART 1: ELEMENTS OF DESIGN o Color o Line o Shape o Texture o Watch this video on Fundamentals of Design. 2 COLOR o Helps identify
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
COLOR! You will need to take notes!
 COLOR! You will need to take notes! What is Color? How do we see it? As illustrated in the diagram below, light goes from the source (the sun) to the object (the apple), and finally to the detector (the
COLOR! You will need to take notes! What is Color? How do we see it? As illustrated in the diagram below, light goes from the source (the sun) to the object (the apple), and finally to the detector (the
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Line. The path created by a point moving through space. i n. Horizontal Line. Thin Line. Thick Line
 Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
ONE K CREATIVE. tools for social impact storytelling: color
 tools for social impact storytelling: color THe basics of color application EACH COLOR EVOKES A DIFFERENT EMOTION IN HUMANS; MAKE SURE YOU ARE AWARE OF THE EMOTIONAL RESPONSES TO COLOR, AS WELL AS WHEN
tools for social impact storytelling: color THe basics of color application EACH COLOR EVOKES A DIFFERENT EMOTION IN HUMANS; MAKE SURE YOU ARE AWARE OF THE EMOTIONAL RESPONSES TO COLOR, AS WELL AS WHEN
UBT128X Colour theory
 UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
EnvSci 360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci 360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 6 Mapping with Color Why Use Color? It is one of the available visual variables you can mix with other graphic elements to improve communication Color
EnvSci 360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 6 Mapping with Color Why Use Color? It is one of the available visual variables you can mix with other graphic elements to improve communication Color
Art & Design visual elements
 Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
Hue Do You Think Hue Are?
 Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths.
 Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
the messenger of experience! form! and color! product design!
 the messenger of experience! form! and color! 2.744 product design! the messenger of experience! color! 2.744 product design! but first! a mini quiz!! list 4 steps/levels in a systematic form-giving process!
the messenger of experience! form! and color! 2.744 product design! the messenger of experience! color! 2.744 product design! but first! a mini quiz!! list 4 steps/levels in a systematic form-giving process!
color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric!
 for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
Light and Colour. Light as part of the EM spectrum. Light as part of the EM spectrum
 Light and Colour Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light as part of the EM spectrum Visible light can be seen as part
Light and Colour Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light as part of the EM spectrum Visible light can be seen as part
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site
 The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING
 TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING PHASE 2 Module 3 Imitative and Decorative Arts UNIT: 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Learning Outcomes... 2 1.0 Pigmental, primary, secondary & tertiary colours...
TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING PHASE 2 Module 3 Imitative and Decorative Arts UNIT: 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Learning Outcomes... 2 1.0 Pigmental, primary, secondary & tertiary colours...
Notes on colour mixing
 INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color
 Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Introduction to Color Theory
 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
This chapter will cover the following topics: Colour terminology. The colour spectrum. The colour wheel. Organisation of colour.
 What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes.
 Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with
 DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON.
 COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON. COLOR CONCEPTS & SYSTEMS 1. Additive mixing 2. Subtractive mixing 3. Munsell color system 4. Pantone System 5. Artist s circle 6. Traditional color schemes
COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON. COLOR CONCEPTS & SYSTEMS 1. Additive mixing 2. Subtractive mixing 3. Munsell color system 4. Pantone System 5. Artist s circle 6. Traditional color schemes
Introduction to Color Theory
 Introduction to Color Theory This overview will give you an essential primer on the definition of color, from its origins to current day definitions. It provides a deeper understanding of the printing
Introduction to Color Theory This overview will give you an essential primer on the definition of color, from its origins to current day definitions. It provides a deeper understanding of the printing
Color theory Quick guide for graphic artists
 Quick guide for graphic artists We can talk about color using two kinds of terminology: Color generation systems. Color harmony system. Graphic artists and photographers certainly have to understand color
Quick guide for graphic artists We can talk about color using two kinds of terminology: Color generation systems. Color harmony system. Graphic artists and photographers certainly have to understand color
Hue Value Intensity tint shade Tones
 COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
Color Studies for Kids
 Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
NEWTONIAN COLOR THEORY
 THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
The Color Wheel. The color wheel shows relationships between the colors.
 Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester
 Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester Lecture 8: Color Image Processing 04.11.2017 Dr. Mohammed Abdel-Megeed Salem Media
Image Processing for Mechatronics Engineering For senior undergraduate students Academic Year 2017/2018, Winter Semester Lecture 8: Color Image Processing 04.11.2017 Dr. Mohammed Abdel-Megeed Salem Media
Elements of Art. Define: Line. Shape. Value. Texture. Color. Form. Space
 Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Color is a property of light.
 Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2.
 Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
Color in Landscaping. By C. Kohn Agricultural Sciences Waterford WI
 Color in Landscaping By C. Kohn Agricultural Sciences Waterford WI Color Color is the difference in the visual appearance of objects due to how they reflect light into a person s eyes. Different objects
Color in Landscaping By C. Kohn Agricultural Sciences Waterford WI Color Color is the difference in the visual appearance of objects due to how they reflect light into a person s eyes. Different objects
ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR
 Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
chrysanthos Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved.
 chrysanthos C O L O R C O M P A N Y L T D Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved. 1 contents Outline 3 Lesson 1 5 Lesson 2 9 Lesson 3 17 2 outline The Color Wheel project
chrysanthos C O L O R C O M P A N Y L T D Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved. 1 contents Outline 3 Lesson 1 5 Lesson 2 9 Lesson 3 17 2 outline The Color Wheel project
Designing Flower Beds with Colors
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Chapter 4. Incorporating Color Techniques
 Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
Value. Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page.
 Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Colour. Cunliffe & Elliott, Chapter 8 Chapman & Chapman, Digital Multimedia, Chapter 5. Autumn 2016 University of Stirling
 CSCU9N5: Multimedia and HCI 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Cunliffe & Elliott,
CSCU9N5: Multimedia and HCI 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Cunliffe & Elliott,
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393. Lecture 20 Oct 25 th, 2018 Pranav Mantini
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 20 Oct 25 th, 2018 Pranav Mantini What is color? Color is a psychological property of our visual experiences when we look at objects and lights, not a physical
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 20 Oct 25 th, 2018 Pranav Mantini What is color? Color is a psychological property of our visual experiences when we look at objects and lights, not a physical
Colour. Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!) Colour Lecture!
 Colour Lecture! ITNP80: Multimedia 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Richardson,
Colour Lecture! ITNP80: Multimedia 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Richardson,
Additive. Subtractive
 Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
Physics 106 Additive Subtractive Subtractive Mixing Rules: Mixing Cyan + Magenta, one gets Blue Mixing Cyan + Yellow, one gets Green Mixing Magenta + Yellow, one gets Red Mixing any two of the Blue, Red,
White light can be split into constituent wavelengths (or colors) using a prism or a grating.
 Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
Colors and the perception of colors Visible light is only a small member of the family of electromagnetic (EM) waves. The wavelengths of EM waves that we can observe using many different devices span from
TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY SCHOOL
 Page 1 of 7 TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY IN SCHOOL Teachers in public schools are still teaching the wrong color theory to children. Here is a list of reasons why this is done, why it is wrong for teachers
Page 1 of 7 TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY IN SCHOOL Teachers in public schools are still teaching the wrong color theory to children. Here is a list of reasons why this is done, why it is wrong for teachers
Colour. Why/How do we perceive colours? Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!
 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
What influences colour and what does colour influence?
 1 What influences colour and what does colour influence? COLOUR has associations of feelings eg.red: Anger, Passion, power, love etc Green: Freshness, re-birth, life, growth Blue: Tranquility, sadness,
1 What influences colour and what does colour influence? COLOUR has associations of feelings eg.red: Anger, Passion, power, love etc Green: Freshness, re-birth, life, growth Blue: Tranquility, sadness,
Psy 280 Fall 2000: Color Vision (Part 1) Oct 23, Announcements
 Announcements 1. This week's topic will be COLOR VISION. DEPTH PERCEPTION will be covered next week. 2. All slides (and my notes for each slide) will be posted on the class web page at the end of the week.
Announcements 1. This week's topic will be COLOR VISION. DEPTH PERCEPTION will be covered next week. 2. All slides (and my notes for each slide) will be posted on the class web page at the end of the week.
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Test 1: Example #2. Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, Note: * indicates the correct answer.
 Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
OBJECT OF THE GAME The goal of Pastiche is to score the most points, which are earned by completing commission cards through collecting the necessary
 A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
Color Reproduction. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 Color Reproduction Take a digital camera and click a picture of a scene. This is the color reproduction of the original scene. The success of a color reproduction lies in how close the reproduced
Chapter 6 Color Reproduction Take a digital camera and click a picture of a scene. This is the color reproduction of the original scene. The success of a color reproduction lies in how close the reproduced
GAME SETUP. Game Setup Diagram
 A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
a color companion for designers of any skill level
 a color companion for designers of any skill level A Shanty Studios Publication 2017 CONTENTS Introduction....4 Color....6 Models...8 Light....10 Temperature....12 Gamuts....14 Red....16 Orange....18 Yellow....20
a color companion for designers of any skill level A Shanty Studios Publication 2017 CONTENTS Introduction....4 Color....6 Models...8 Light....10 Temperature....12 Gamuts....14 Red....16 Orange....18 Yellow....20
Image and video processing (EBU723U) Colour Images. Dr. Yi-Zhe Song
 Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
Image and video processing () Colour Images Dr. Yi-Zhe Song yizhe.song@qmul.ac.uk Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images Today s agenda Colour spaces Colour images PGM/PPM images History
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
Multimedia Systems and Technologies
 Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
Horace A picture is worth a thousand words. Napoleon Bonaparte A work of art is the unique result of a unique
 A man paints with his brains and not with his hands. Michelangelo A painting that is well composed is half finished. A picture is a poem without words. Pierre Bonnard Horace A picture is worth a thousand
A man paints with his brains and not with his hands. Michelangelo A painting that is well composed is half finished. A picture is a poem without words. Pierre Bonnard Horace A picture is worth a thousand
Chapter Objectives. Color Management. Color Management. Chapter Objectives 1/27/12. Beyond Design
 1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
ARTS D Design. Project 1: Art Elements. Reading Guide: form. elements of art. line. shape. value. texture. color. principles of organization
 ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
Basics of Colors in Graphics Denbigh Starkey
 Basics of Colors in Graphics Denbigh Starkey 1. Visible Spectrum 2 2. Additive vs. subtractive color systems, RGB vs. CMY. 3 3. RGB and CMY Color Cubes 4 4. CMYK (Cyan-Magenta-Yellow-Black 6 5. Converting
Basics of Colors in Graphics Denbigh Starkey 1. Visible Spectrum 2 2. Additive vs. subtractive color systems, RGB vs. CMY. 3 3. RGB and CMY Color Cubes 4 4. CMYK (Cyan-Magenta-Yellow-Black 6 5. Converting
Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7. Elements and Principles of Design
 Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7 Elements and Principles of Design Standards Students will recognize the use of the principles and elements of design. Standard 1: Reassess elements of design. Standard 2:
Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7 Elements and Principles of Design Standards Students will recognize the use of the principles and elements of design. Standard 1: Reassess elements of design. Standard 2:
De Angela Duff Fall HOMEWORK EXERCISES Wk 7 DUE NEXT WEEK ASSIGNED SHOW & TELLS: Mark Rothko (Daniella)
 VCS Visual Communication Studio De Angela Duff Fall 2007 HOMEWORK EXERCISES Wk 7 DUE NEXT WEEK ASSIGNED SHOW & TELLS: Mark Rothko (Daniella) READ: BOOK: Understanding Comics by Scott McCloud (on reserve
VCS Visual Communication Studio De Angela Duff Fall 2007 HOMEWORK EXERCISES Wk 7 DUE NEXT WEEK ASSIGNED SHOW & TELLS: Mark Rothko (Daniella) READ: BOOK: Understanding Comics by Scott McCloud (on reserve
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Elements of Art and Fashion
 Elements of Art and Fashion Ø Line Ø Shape Ø Value Ø Texture Ø Color Ø Volume/Form Ø Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements.
Elements of Art and Fashion Ø Line Ø Shape Ø Value Ø Texture Ø Color Ø Volume/Form Ø Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements.
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Color Wheel. Warm Colors. Cool Colors
 Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Schemes.
 Color Schemes http://www.hgtv.com/video/warm-orangelivingdining-room-video/index.html COLOR (Schemes)HARMONIES A color (scheme) harmony is a pleasing combination of colors based on their respective positions
Color Schemes http://www.hgtv.com/video/warm-orangelivingdining-room-video/index.html COLOR (Schemes)HARMONIES A color (scheme) harmony is a pleasing combination of colors based on their respective positions
Color. Chapter 6. (colour) Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition
 Color (colour) Chapter 6 Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition What is color? Color is how our eyes perceive different forms of energy. Energy moves in the form of waves. What is a wave? Think of a fat guy (Dr.
Color (colour) Chapter 6 Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition What is color? Color is how our eyes perceive different forms of energy. Energy moves in the form of waves. What is a wave? Think of a fat guy (Dr.
