De Angela Duff Fall HOMEWORK EXERCISES Wk 7 DUE NEXT WEEK ASSIGNED SHOW & TELLS: Mark Rothko (Daniella)
|
|
|
- Edith Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VCS Visual Communication Studio De Angela Duff Fall 2007 HOMEWORK EXERCISES Wk 7 DUE NEXT WEEK ASSIGNED SHOW & TELLS: Mark Rothko (Daniella) READ: BOOK: Understanding Comics by Scott McCloud (on reserve at the UArts Library) Chapter 8: A Word About Color BOOK: Introduction to Two-Dimensional Design: Understanding Form and Function by John Bowers (on reserve at the UArts Library) Chapter 4, Color: Types, Interactions, and Roles DO: 1 COLOR WHEEL Buy a color wheel at Utrecht OR Create a color wheel IN ILLUSTRATOR See color wheel example on website Draw on top of imported image with Illustrator s drawing tools 8 x 8 square picture plane (not stroked) Your color wheel should show the following: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary colors Your color wheel should result in the twelve tone scale: yellow / yellow orange / orange / red orange / red / red violet / violet / blue violet / blue / blue green / green / yellow green Bring in Digital file for Class Crit Print in Color for Your End of Semester Binder Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 1 of 10
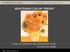
2 2 Nine Color Studies in Illustrator Bring in 9 Digital Files with.ai extension for Class Crit Print in Color for Your End of Semester Binder Select 1 of your compositions from week 5 ( Compositions using Relational Elements) o 8 x 8 stroked, square picture plane on 8 1/2 x 11 paper Use this same composition for each of the 9 color studies 1 Achromatic colors (grayscale) 2 Analogous colors 3 Warm Colors 4 5 Cool Colors Neutral Colors 6 The contrast of hue 7 The contrast of value (or light and dark or monochromatic) 8 The contrast of warm and cool 9 The contrast of complements Analogous colors Analogous colors are any three colors which are side by side on a 12 part color wheel, such as yellow-green, yellow, and yellow-orange. They are closely related because they have a color in common. For example, blue, blue-green, and green all contain blue. Red, orange, and yellow are analogous because red and yellow make orange. This is one of the most simple, yet elegant schemes to use. Look around you, and you will see that Mother Nature paints the best examples of analogous schemes. The warm, rich colors of firelight, the cool colors of twilight, the sea greens and blues of the ocean, the jewel-toned tail of a peacock, the stripes of a tabby cat...the soft fuzz of a peach. Nature illustrates this scheme far better than any example I could provide here, leave your computer, take a walk, and really look at the colors around you. Warm colors Warm colors are made mostly of red, orange and yellow. This family of colors is called warm because they remind you of warm things like the sun or fire. Warm colors can even make you feel warmer because they can slightly increase your circulation and body temperature! Artists use warm, cool and neutral colors to create moods, show contrast and create depth in artworks. Vincent van Gogh used warm colors in this painting of Sunflowers. Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 2 of 10
3 Cool colors Cool colors are made mostly of green, blue and violet (purple). This family of colors is called cool because they remind you of cool things like a cool forest or a cold lake. Cool colors can even make you feel cooler because they can slightly decrease your circulation and body temperature! Claude Monet's Water Lilies (see website) uses cool colors to suggest a quiet pond. Neutral colors The last family of colors are neutral: black, white, gray, and brown Neutral colors or earth tones are not seen on most color wheels. Black, gray, whites are neutral. Browns, beiges and tans are sometimes neutral too. Neutral colors can be made by mixing: black and white complementary colors all three primaries together (plus some black or white) Mood is the feeling created by an artwork. In the painting, Paris Street: Rainy Day, French artist Gustave Caillebotte (see website) creates a gloomy mood by showing the neutral gray and brown colors of a rainy day. Artists use warm, cool and neutral colors to create moods, show contrast and create depth in artworks. The contrast of hue (also known as contrast of saturation) Contrast of hue is illustrated by undiluted colors in their most intense luminosity. Just as black-white represents the extreme of light-dark contrast, so yellow/red/blue is the extreme instance of contrast of hue. The intensity of contrast of hue diminishes as the hues employed are removed from the three primaries. Thus orange, green, and vilolet are weaker in character than yellow, red, and blue; and the effect of tertiary colors is still less distinct. When the single colors are separated by black or white lines, their individual characters emerge more sharply. Their interaction and mutual influences are suppressed to some extent. The contrast of value (or light and dark) also known as contrast of monochromatic Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 3 of 10
4 The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of light and dark values. One color? How can I possibly use only one color? Why, by using some of its tints, shades, and tones, of course; with the addition of a basic neutral or neutrals, (black/white/grey); and varying the values in order to add contrast and interest. The contrast of warm and cool The contrast is formed by the juxtaposition of hues considered 'warm' or 'cool.' This is often the easiest contrast to achieve perceived three dimensional depth due to advancing & receding characteristics of most warm colors in relation to cool colors. The contrast of complements Complementary colors are directly across from each other on the color wheel. Complementary pairs all contain one primary and one secondary color. So, together each complementary pair has all three primary colors! That means complementary pairs contrast because they share no common colors. They are complete opposites! Complementary colors complement each other! You may have heard "opposites attract." In the same way, complementary pairs look good together. They complement each other! However, sometimes complementary colors can seem to vibrate when placed side by side. When mixed together, complements make a neutral gray. You can make a color less bright and intense by blending in a small amount of its complement. Split Complementary Key color combined with the two colors that are next to its complement. COLOR THEORY COLOR is a phenomenon of perception not an objective component or characteristic of a substance. Color is an aspect of vision; it is a psychophysical response consisting of the physical reaction of the eye and the automatic interpretive response of the brain to wavelength characteristics of light above a certain brightness level (at lower levels the eye senses brightness differences but is unable to make color discriminations). ( 1 ) (see spectrum.gif on website) That light is the source of color was first demonstrated in 1666 by Isaac Newton, who passed a beam of sunlight through a glass prism, producing the rainbow of hues of the visible spectrum. This phenomenon had often been observed before, but it had always been related to latent color that was said to exist in the glass of the prism. Newton, however, took this simple experiment a step further. He passed his miniature rainbow through a second prism that reconstituted the original white beam of light, His conclusion was revolutionary: color is Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 4 of 10
5 in the light, not in the glass, and the light people see as white is a mixture of all the colors of the visible spectrum. The colors of the visible light spectrum are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. White light consists of all of the colors mixed together. The color of an object depends on how it absorbs and/or reflects light. If an object absorbs all of the light wavelengths, it will appear black. If it reflects all of them, it will appear white. If an object absorbs all wavelengths except red, for example, it will look red. The reason rainbows appear colored is because the light is broken down into its constituent parts by passing through the water droplets in the air. (The perception of color in a rainbow is proportional to the viewer's perspective, you move, it moves.) The theory of color has gone through some changes over time, and it is now an accepted fact that color is truly in the eye of the beholder. "This is due to the fact that, as sensed by man, color is a sensation and not a substance." Different people can also see color differently. We all agree the sky is blue, but a piece of reflective art may look slightly blue to one person while another sees it as slightly cyan. If you don't know the difference between the look of blue as opposed to cyan then communicating your preferences to a technician can be problematic. Subtle color variances are best seen under correct viewing conditions (not by a window, etc.) and can take some time to learn to even see them. Color is an enormous topic. We are constantly processing visual information based on color references. In understanding color theory it s helpful to break it down into three parts: IMPRESSION / visually, EXPRESSION / emotionally, and CONSTRUCTION / symbolically. This initial class on color deals with the more objective principles. Since 1676, when Issac Newton analyzed sunlight through a glass prism and the color it produced, many color theories have been put in place. It should be mentioned that color theory is just that, theory. For centuries people came to understand and use color based on their inherent perceptions and emotional responses. Theory helps us to understand their practices and our own perceptions. Artists have invented many different media that imitate the colors of light. Painters, for example, use powdered pigments to reproduce the colors of the rainbow. Color is yet another elements of art and design, like point, line, and shape. Color wheels (see colorwheel.jpg on website) Color wheels show how visible colors are related. Primary, secondary, and intermediate (or tertiary) colors are organized on a circular chart. Color wheels help artists remember how to mix and think about pigments. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors in 1666 (see website). Since then scientists and artists have studied and designed numerous variations of this concept. Differences of opinion about the Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 5 of 10
6 validity of one format over another continue to provoke debate. In reality, any color circle or color wheel which presents a logically arranged sequence of pure hues has merit. Color wheels are based on color theory, which is based on the physics of light. Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 6 of 10
7 There are two common types of color: additive color and subtractive color. Additive color refers to the mixing of colors of light. Example 1 (see website) shows how the light from red, green and blue flashlights would appear if shone on a dark wall. The three primaries in light are red, blue, and green. When all of the colors of the spectrum are combined, they add up to white light. Subtractive color refers to the mixing of colors of pigment, such as paint or the ink in your computer's printer. This type of color is what is used in the art and design world. When learning basic color theory, students typically use familiar colors like red, yellow, and blue. Printers' primaries yellow, cyan, and magenta are typically used by professional designers and printing presses. Example 2 (see website) illustrates subtractive color by showing how primary colors mix on a piece of white paper. Primary colors (see primarywheel.gif on website) The primary colors are: red, blue, and yellow. In traditional color theory, these are the 3 pigment (see definition below) colors that can not be mixed or formed by any combination of other colors. All other colors are derived from these 3. Artists create secondary and intermediate colors by mixing primary pigments. Pigments Pigments give color to paint. In the past, pigments were powders made by grinding up minerals, plants and animal parts. The most expensive pigments used to be gold, vermilion (a red pigment made from sulfur and mercury) and ultramarine (a blue pigment made from a stone called lapis lazuli). Modern pigments are made from chemicals which come in brighter colors, resist fading, and are less expensive. Pigments are mixed with a "binding agent" such as egg, oil, animal fat, water or synthetic resin to make a paintable liquid that dries. Secondary colors (see secondary2.gif on website) A secondary color is made by mixing two primary colors: blue + yellow = green red + blue = purple red + yellow = orange The secondary colors are: green, orange, and violet (purple). Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 7 of 10
8 Intermediate (or Tertiary) colors (see tertiary_triange_wheel.gif on website) Intermediate colors are made by mixing a secondary and a primary color together. The intermediate colors are: yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green and yellow-green Triadic Colors Three colors that are evenly and equally spaced from each other forming an equilateral triangle within the color wheel. Tetrad A double complementary contrast as illustrated by a square or a rectangle The question: Now that we have 12 colors...where do the rest of the colors come from? The answer: Variations in value, tint, shade, tone, and saturation. Chromatic Our common notion of color refers to the chromatic colors, which relate to the spectrum as can be observed in a rainbow. Each chromatic color can be described in three ways: hue, value, and saturation or intensity or chroma Achromatic Neutral colors (black, white, and grays) are not part of these chromatic colors and can be referred to as achromatic colors. (see munsell.html on website) Hue (color with no black, white or gray added) Hue is the attribute that permits colors to be classified as red, yellow, blue, etc. The description of hue can be more precise by identifying the color s actual inclination from one hue to the next. For example, a particular red may be more accurately called orange-red. Value Value is the lightness or darkness of a color. You can get different values of a color by mixing in white or black to create shades, tints, and tones. Shades (Color + Black) Shades are dark values of a color. One usually makes shades by mixing a color with different amounts of black. Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 8 of 10
9 Tints (Color + White) Tints are light values of a color. One usually makes tints by mixing a color with different amounts of white. Tone (Color + Grey or Color + varying degrees of its complementary color) Tints are light values of a color. One usually makes tints by mixing a color with different amounts of white. Saturation (or Intensity or Chroma) The brightness or dullness of a color; the intensity or purity of a color. Saturated colors are the most brilliant, most vivid colors that can be obtained. Desaturated colors are dull; they contain a large proportion of gray. Many people find choosing colors that "go together" an intimidating and confusing process. Certainly it can be when confronted with all the colors of creation! The first step, then, is to keep it simple. Color Harmony Harmony can be defined as a pleasing arrangement of parts, whether it be music, poetry, color, or even an ice cream sundae. In visual experiences, harmony is something that is pleasing to the eye. It engages the viewer and it creates an inner sense of order, a balance in the visual experience. When something is not harmonious, it's either boring or chaotic. At one extreme is a visual experience that is so bland that the viewer is not engaged. The human brain will reject understimulating information. At the other extreme is a visual experience that is so overdone, so chaotic that the viewer can't stand to look at it. The human brain rejects what it can not organize, what it can not understand. The visual task requires that we present a logical structure. Color harmony delivers visual interest and a sense of order. In summary, extreme unity leads to under-stimulation, extreme complexity leads to over-stimulation. Harmony is a dynamic equilibrium. When people speak of color harmony, they are evaluating the joint effect of two or more colors. Experience and experiments with subjective color combinations show that individuals differ in their judgements of harmony and discord. There are many theories for harmony, but we can make the general statement that all analogous colors, complementary pairs, all triads whose colors form equilateral or isosceles triangles in the twelve-member color circle, and all tetrads forming squares or rectangles are harmonious. Seven kinds of color contrast Johannes Itten was one of the first people to define and identify strategies for successful color combinations. Through his research he devised seven methodologies for coordinating colors utilizing the hue's contrasting properties. Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 9 of 10
10 We speak of contrast when distinct differences can be perceived between two compared effects. When such differences attain their maximum degree, we speak of diametrical or polar contrasts. Thus, large-small, white-black, cold-warm, in their extremes, are polar contrasts. Our sense organs can function only by means of comparisons. The eye accepts a line as long when a shorter line is presented for comparison. The same line is taken as short when the line compared with it is longer. Color effects are similarly intensified or weakened by contrast. The seven kinds of color contrast are the following: Contrast of Hue Light-Dark Contrast Cold-Warm Contrast Complementary Contrast Simultaneous Contrast Contrast of Saturation Contrast of Extension References: The Art of Color by Johannes Itten and Principles of Color Design by Wucius Wong Interaction of Color by Josef Albers Color (4th Edition) by Paul J. Zelansk Visual Communication Studio Fall 2007 pg. 10 of 10
UBT128X Colour theory
 UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
Color Theory. Additive Color
 Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes.
 Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Color Theory and Mixing
 MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS
 LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle.
 The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
COLOR THEORY. The Color Wheel
 COLOR THEORY COLOR THEORY Color theory encompasses a multitude of definitions, concepts and design applications. All the information would fill several encyclopedias. As an introduction, here are a few
COLOR THEORY COLOR THEORY Color theory encompasses a multitude of definitions, concepts and design applications. All the information would fill several encyclopedias. As an introduction, here are a few
The Color Wheel. The color wheel shows relationships between the colors.
 Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
Color Wheel The Color Wheel The color wheel shows relationships between the colors. Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another. The Color Wheel Let s learn about
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
NEWTONIAN COLOR THEORY
 THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
Properties of Color. Value: Tint: Shade: Tone: Intensity:
 Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING
 TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING PHASE 2 Module 3 Imitative and Decorative Arts UNIT: 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Learning Outcomes... 2 1.0 Pigmental, primary, secondary & tertiary colours...
TRADE OF PAINTING & DECORATING PHASE 2 Module 3 Imitative and Decorative Arts UNIT: 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Learning Outcomes... 2 1.0 Pigmental, primary, secondary & tertiary colours...
Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red.
 Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT
 COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right
 COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
COLOUR With colours you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a statement. You can use colour to energise, or to cool down. By selecting the right colour scheme, you can create an ambiance of elegance,
Art & Design visual elements
 Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR
 Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
Answer the questions below.
 Color Theory Answer the questions below. The two images to the right were created by the same artist. How is the color in these two paintings different? How does the color tone of these paintings effect
Color Theory Answer the questions below. The two images to the right were created by the same artist. How is the color in these two paintings different? How does the color tone of these paintings effect
Horace A picture is worth a thousand words. Napoleon Bonaparte A work of art is the unique result of a unique
 A man paints with his brains and not with his hands. Michelangelo A painting that is well composed is half finished. A picture is a poem without words. Pierre Bonnard Horace A picture is worth a thousand
A man paints with his brains and not with his hands. Michelangelo A painting that is well composed is half finished. A picture is a poem without words. Pierre Bonnard Horace A picture is worth a thousand
COLOR CO C L O O L R O
 COLOR COLOR Y O G R B V informal definitions HUE a particular gradation of color. It is another word for color. PRIMARY & secondary RED BLUE PURPLE GREEN YELLOW ORANGE Primary: Red, Yellow, Blue. All Colors
COLOR COLOR Y O G R B V informal definitions HUE a particular gradation of color. It is another word for color. PRIMARY & secondary RED BLUE PURPLE GREEN YELLOW ORANGE Primary: Red, Yellow, Blue. All Colors
Color is derived from Reflected Light.
 How We See Color Color is derived from Reflected Light. White light from the sun is actually a combination of all colors. When light passes through a prism, a wedge-shaped glass, the beam of light bends
How We See Color Color is derived from Reflected Light. White light from the sun is actually a combination of all colors. When light passes through a prism, a wedge-shaped glass, the beam of light bends
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with
 DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
Color is a property of light.
 Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site
 The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
The art of colour Date: Venerdì, febbraio 15 @ 12:17:49 CET Topic: Educational Lighting Site Primary colours Newton's disc Complementary colours Secondary colours Tertiary colours Warm and cold colours
The Color Wheel. The color wheel is a chart of colors of the visible spectrum that is used to show how colors relate to each other.
 The Color Wheel The color wheel is a chart of colors of the visible spectrum that is used to show how colors relate to each other. Color is Emotion Color is not given to us in order that we should imitate
The Color Wheel The color wheel is a chart of colors of the visible spectrum that is used to show how colors relate to each other. Color is Emotion Color is not given to us in order that we should imitate
SSIS CAGLIARI AA Lingue Inglese- Prof. Cuccu, Linguaggi Settoriali e Multimedialità. CLIL Module. English-Visual Arts. Reading a Painting
 SSIS CAGLIARI AA 2005-2006 Lingue Inglese- Prof. Cuccu, Linguaggi Settoriali e Multimedialità CLIL Module English-Visual Arts Reading a Painting Unit 3 Unit 4 De-constructing a Painting Colour Matters
SSIS CAGLIARI AA 2005-2006 Lingue Inglese- Prof. Cuccu, Linguaggi Settoriali e Multimedialità CLIL Module English-Visual Arts Reading a Painting Unit 3 Unit 4 De-constructing a Painting Colour Matters
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes
 Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
This chapter will cover the following topics: Colour terminology. The colour spectrum. The colour wheel. Organisation of colour.
 What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric!
 for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II
 GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Value. Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page.
 Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Design and Colour. Jacquie Wilson
 Design and Colour Jacquie Wilson The colours of the spectrum violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red Colour range for questionnaire violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red black, white Colour
Design and Colour Jacquie Wilson The colours of the spectrum violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red Colour range for questionnaire violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red black, white Colour
Notes on colour mixing
 INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements
 Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition. Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout.
 The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
Designing Flower Beds with Colors
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Hue Value Intensity tint shade Tones
 COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
COLOR Color Color is the element of art that is derived from reflective light. You see color because light waves are reflected from objects to your eyes. White light from the sun is actually a combination
H10: Description of Colour
 page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
Elements Of Art Study Guide
 Elements Of Art Study Guide General Elements of Art- tools artists use to create artwork; Line, shape, color, texture, value, space, form Composition- the arrangement of elements of art to create a balanced
Elements Of Art Study Guide General Elements of Art- tools artists use to create artwork; Line, shape, color, texture, value, space, form Composition- the arrangement of elements of art to create a balanced
CUT the wheel vertically IN HALF: WARM (right) AND COOL COLORS (left)
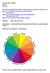 COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON.
 COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON. COLOR CONCEPTS & SYSTEMS 1. Additive mixing 2. Subtractive mixing 3. Munsell color system 4. Pantone System 5. Artist s circle 6. Traditional color schemes
COLOR PLANNING FOR INTERIORS JOSHIMA V.M., UON. COLOR CONCEPTS & SYSTEMS 1. Additive mixing 2. Subtractive mixing 3. Munsell color system 4. Pantone System 5. Artist s circle 6. Traditional color schemes
Art Vocabulary Assessment
 Art Vocabulary Assessment Name: Date: Abstract Artwork in which the subject matter is stated in a brief, simplified manner; little or no attempt is made to represent images realistically, and objects are
Art Vocabulary Assessment Name: Date: Abstract Artwork in which the subject matter is stated in a brief, simplified manner; little or no attempt is made to represent images realistically, and objects are
CColor Theory in Design
 CColor Theory in Design The Color Wheel The Color Wheel A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors
CColor Theory in Design The Color Wheel The Color Wheel A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors
Elements of Art. Define: Line. Shape. Value. Texture. Color. Form. Space
 Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
What influences colour and what does colour influence?
 1 What influences colour and what does colour influence? COLOUR has associations of feelings eg.red: Anger, Passion, power, love etc Green: Freshness, re-birth, life, growth Blue: Tranquility, sadness,
1 What influences colour and what does colour influence? COLOUR has associations of feelings eg.red: Anger, Passion, power, love etc Green: Freshness, re-birth, life, growth Blue: Tranquility, sadness,
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR
 THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
Color Wheel. Warm Colors. Cool Colors
 Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Studies for Kids
 Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Color Schemes.
 Color Schemes http://www.hgtv.com/video/warm-orangelivingdining-room-video/index.html COLOR (Schemes)HARMONIES A color (scheme) harmony is a pleasing combination of colors based on their respective positions
Color Schemes http://www.hgtv.com/video/warm-orangelivingdining-room-video/index.html COLOR (Schemes)HARMONIES A color (scheme) harmony is a pleasing combination of colors based on their respective positions
Deposit Central School District Curriculum Map
 GRADE LEVEL: 5-6 What are the most effective ways to use the elements of art and principals of design in art? In what ways can I incorporate the elements of art and principles of design together in art?
GRADE LEVEL: 5-6 What are the most effective ways to use the elements of art and principals of design in art? In what ways can I incorporate the elements of art and principles of design together in art?
Introduction. The Spectral Basis for Color
 Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction to Color Theory
 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
OBJECT OF THE GAME The goal of Pastiche is to score the most points, which are earned by completing commission cards through collecting the necessary
 A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths.
 Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
GAME SETUP. Game Setup Diagram
 A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
A world of beautiful colors comes alive as players complete commissions that picture some of the finest European and American art works from the past six centuries. The word pastiche is used in the fields
Spears Art Studio High School and Adult Beginners Painting with Oil and/oracrylic. Can You Answer? Brushy Creek
 Spears Art Studio High School and Adult Beginners Painting with Oil and/oracrylic Can You Answer? Brushy Creek Brushy Creek reference photo and painting D. S. Spears oil on canvas image size: 40"x30" Spears
Spears Art Studio High School and Adult Beginners Painting with Oil and/oracrylic Can You Answer? Brushy Creek Brushy Creek reference photo and painting D. S. Spears oil on canvas image size: 40"x30" Spears
Art 177 :: Creative Photography. Color & Color Theory
 Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
check it out online at
 check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
Elements and Principles
 Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Elements and Principles of Art The building blocks and how we use them Your recipe for creating art! Lets learn the ingredients! ART INGREDIENTS! Elements of Art: The basic building blocks/ foundation
Hot or Cold? Warm Colors: Yellow, Orange, Red (excitement) Cool Colors: Green, Blue, Violet (calmness)
 Art Basics The Color Wheel Primary Colors: a group of colors from which all other colors can be obtained by mixing. Ex: Yellow, Red, and Blue Secondary Colors: a color resulting from the mixing of two
Art Basics The Color Wheel Primary Colors: a group of colors from which all other colors can be obtained by mixing. Ex: Yellow, Red, and Blue Secondary Colors: a color resulting from the mixing of two
ARTS D Design. Project 1: Art Elements. Reading Guide: form. elements of art. line. shape. value. texture. color. principles of organization
 ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
Color 911 HOW TO WORK WITH (AND ENHANCE) YOUR YARN COLLECTION. Lisa Check Fiber Farmer and Indie Dyer Flying Goat Farm
 Color 911 HOW TO WORK WITH (AND ENHANCE) YOUR YARN COLLECTION Lisa Check Fiber Farmer and Indie Dyer Flying Goat Farm HELP!! I buy the same yarn at every fiber festival Purple (insert color here) is my
Color 911 HOW TO WORK WITH (AND ENHANCE) YOUR YARN COLLECTION Lisa Check Fiber Farmer and Indie Dyer Flying Goat Farm HELP!! I buy the same yarn at every fiber festival Purple (insert color here) is my
THE MEANING OF COLOR VISUAL COMMUNICATION III 3D DESIGN PRINCIPLES
 COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
COLOR THE MEANING OF COLOR Color in design is very subjective. What evokes one reaction in one person may evoke a very different reaction in someone else. Sometimes this is due to personal preference,
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS
 LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS- Lecture 4 LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS 1. COLOR 2. FORM AND COLOR 1. COLOR COLORS Color Interaction Color never appears
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS- Lecture 4 LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS 1. COLOR 2. FORM AND COLOR 1. COLOR COLORS Color Interaction Color never appears
chrysanthos Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved.
 chrysanthos C O L O R C O M P A N Y L T D Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved. 1 contents Outline 3 Lesson 1 5 Lesson 2 9 Lesson 3 17 2 outline The Color Wheel project
chrysanthos C O L O R C O M P A N Y L T D Version 2.2 by Chrysanthos Color Company Limited China. All rights reserved. 1 contents Outline 3 Lesson 1 5 Lesson 2 9 Lesson 3 17 2 outline The Color Wheel project
The Color Wheel NEXT. An Introduction to the Color Wheel and Color Theory. By Pam & Tim O Loughlin Art Specialists Oshkosh Area School District
 The Color Wheel An Introduction to the Color Wheel and Color Theory Weblinks By Pam & Tim O Loughlin Art Specialists Oshkosh Area School District Resource List NEXT The Color Wheel The color wheel shows
The Color Wheel An Introduction to the Color Wheel and Color Theory Weblinks By Pam & Tim O Loughlin Art Specialists Oshkosh Area School District Resource List NEXT The Color Wheel The color wheel shows
The Visual Elements Part II. Lecture 3B
 The Visual Elements Part II Lecture 3B Lecture Overview: The 5 Main Visual Elements 1. Line /Shape 2 Space 3. Texture/Pattern 4. Time / Motion 5. Light / Color The language of art is the visual elements.
The Visual Elements Part II Lecture 3B Lecture Overview: The 5 Main Visual Elements 1. Line /Shape 2 Space 3. Texture/Pattern 4. Time / Motion 5. Light / Color The language of art is the visual elements.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Drawing terms Shading terms Design elements Explanation and assignments.
 Drawing terms Shading terms Design elements Explanation and assignments. 1 Art terminology Portrait View Format what you are doing art on. Medium What you are using to create the art. Ex. Use watercolor
Drawing terms Shading terms Design elements Explanation and assignments. 1 Art terminology Portrait View Format what you are doing art on. Medium What you are using to create the art. Ex. Use watercolor
outline: a line that surrounds and defines the edge of a shape; does not apply line variation and shows little depth.
 Elements of Art The elements of art should be considered as the basic building blocks in a piece of art. Line, texture, value, space, color, shape and form/volume are the seven elements of design from
Elements of Art The elements of art should be considered as the basic building blocks in a piece of art. Line, texture, value, space, color, shape and form/volume are the seven elements of design from
Line Line Characteristic of Line are: Width Length Direction Focus Feeling Types of Line: Outlines Contour Lines Gesture Lines Sketch Lines
 Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
Line. The path created by a point moving through space. i n. Horizontal Line. Thin Line. Thick Line
 Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
Line The path created by a point moving through space. V er Horizontal Line Diagonal Line Zig-Zag Line Wavy Line t i c a l L i n e Spiral Line Thin Line Thick Line Line can help create the illusion of
Elements of Art. Line Shape Form Space Value Color Texture
 Elements of Art Line Shape Form Space Value Color Texture Line Line is the path of a moving point through space. Mark on a surface usually created by a pencil, pen, crayon, marker or paintbrush. Thick
Elements of Art Line Shape Form Space Value Color Texture Line Line is the path of a moving point through space. Mark on a surface usually created by a pencil, pen, crayon, marker or paintbrush. Thick
Primary Hue Color Wheels
 Primary Hue Color Wheels You can make your own basic six color wheels using different combinations of your primary colors, and then mixing the secondaries from your choices. This will give you a quick
Primary Hue Color Wheels You can make your own basic six color wheels using different combinations of your primary colors, and then mixing the secondaries from your choices. This will give you a quick
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018
 Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018 Definition: What is a Line? Definition: Line is the most basic design tool. A line has length, width, tone, and texture. It may divide space, define a form, describe contour,
Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018 Definition: What is a Line? Definition: Line is the most basic design tool. A line has length, width, tone, and texture. It may divide space, define a form, describe contour,
Chapter Objectives. Color Management. Color Management. Chapter Objectives 1/27/12. Beyond Design
 1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
outline: a line that surrounds and defines the edge of a shape; does not apply line variation and shows little depth.
 Elements of Art (The elements of art should be considered as the basic building blocks in a piece of art. Line, texture, value, space, color, shape and form/volume are the seven elements of design from
Elements of Art (The elements of art should be considered as the basic building blocks in a piece of art. Line, texture, value, space, color, shape and form/volume are the seven elements of design from
elements of design worksheet
 elements of design worksheet Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed
elements of design worksheet Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory
 Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7. Elements and Principles of Design
 Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7 Elements and Principles of Design Standards Students will recognize the use of the principles and elements of design. Standard 1: Reassess elements of design. Standard 2:
Fashion Merchandising: Strand 7 Elements and Principles of Design Standards Students will recognize the use of the principles and elements of design. Standard 1: Reassess elements of design. Standard 2:
Surrealism Art Test Study Guide
 Surrealism Art Test Study Guide THEORY OF COLOUR Primary Colours Red Yellow Blue Tip to Remember: Roses are Red, Violets are Blue, what makes them grow? Yellow Secondary Colours Red + Yellow = Orange Blue
Surrealism Art Test Study Guide THEORY OF COLOUR Primary Colours Red Yellow Blue Tip to Remember: Roses are Red, Violets are Blue, what makes them grow? Yellow Secondary Colours Red + Yellow = Orange Blue
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of the spectrum of color. It consists of warm and cool hues (Hue is the word used to describe a pure
 Mini Color Review The Color Wheel is a visual representation of the spectrum of color. It consists of twelve warm and cool hues (Hue is the word used to describe a pure color) and visually describes the
Mini Color Review The Color Wheel is a visual representation of the spectrum of color. It consists of twelve warm and cool hues (Hue is the word used to describe a pure color) and visually describes the
Sketchbook Assignments Due Monday, November 15, 2010
 Sketchbook Assignments Due Monday, November 15, 2010 1. CONTINUOUS LINE DRAWING - From observation, create a continuous line drawing of an object or person as you look at it. The line in the continuous
Sketchbook Assignments Due Monday, November 15, 2010 1. CONTINUOUS LINE DRAWING - From observation, create a continuous line drawing of an object or person as you look at it. The line in the continuous
Advanced Art Test Study Guide
 Advanced Art Test Study Guide THEORY OF COLOUR Primary Colours Red Yellow Blue Tip to Remember: Roses are Red, Violets are Blue, what makes them grow? Yellow Secondary Colours Red + Yellow = Orange Blue
Advanced Art Test Study Guide THEORY OF COLOUR Primary Colours Red Yellow Blue Tip to Remember: Roses are Red, Violets are Blue, what makes them grow? Yellow Secondary Colours Red + Yellow = Orange Blue
Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART
 Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART TEXTURE IS: the surface quality of a work of art. VISUAL texture that is created to look like something it is not SIMULATED the visual effect of texture without actually
Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART TEXTURE IS: the surface quality of a work of art. VISUAL texture that is created to look like something it is not SIMULATED the visual effect of texture without actually
Colour Theory Explained
 Colour Theory Explained And Why all artists need to understand it. The beginnings of how we now understand colour Sir Isaac Newton discovered the spectrum in the 1660 s The colour (similar to how we see
Colour Theory Explained And Why all artists need to understand it. The beginnings of how we now understand colour Sir Isaac Newton discovered the spectrum in the 1660 s The colour (similar to how we see
Elements of Art Principles of Organization
 Elements of Art Principles of Organization Robert Spahr Associate Professor Department of Cinema & Photography rspahr@siu.edu http://www.robertspahr.com Pieter Claesz. (Dutch, about 1597 1660), Still
Elements of Art Principles of Organization Robert Spahr Associate Professor Department of Cinema & Photography rspahr@siu.edu http://www.robertspahr.com Pieter Claesz. (Dutch, about 1597 1660), Still
Color Theory: Defining Brown
 Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography. April 24, 2006
 Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Geography 360 Principles of Cartography April 24, 2006 Outlines 1. Principles of color Color as physical phenomenon Color as physiological phenomenon 2. How is color specified? (color model) Hardware-oriented
Elements and Principles of Design
 Elements and Principles of Design All visual art can be described with the vocabulary of the basic elements and principles of design. The elements of design can be conceived as the building blocks of art,
Elements and Principles of Design All visual art can be described with the vocabulary of the basic elements and principles of design. The elements of design can be conceived as the building blocks of art,
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
Principles of Design
 Principles of Design Balance A. Stability of an arrangement 1. Arrangement appears secure and stable 2. Balance must be both visual and actual Balance a. visual balance refers to the way an arrangement
Principles of Design Balance A. Stability of an arrangement 1. Arrangement appears secure and stable 2. Balance must be both visual and actual Balance a. visual balance refers to the way an arrangement
Elements of Art. Robert Spahr Associate Professor Department of Cinema & Photography
 Elements of Art Robert Spahr Associate Professor Department of Cinema & Photography rspahr@siu.edu http://www.robertspahr.com Pieter Claesz. (Dutch, about 1597 1660), Still Life with Stoneware Jug, Wine
Elements of Art Robert Spahr Associate Professor Department of Cinema & Photography rspahr@siu.edu http://www.robertspahr.com Pieter Claesz. (Dutch, about 1597 1660), Still Life with Stoneware Jug, Wine
Wright Field Scale Modelers. Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong.
 Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2.
 Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO
 MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 07 COLORS IN IMAGES & VIDEO IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR LIGHT AND SPECTRA Visible light is an electromagnetic wave in the 400nm 700 nm range. The eye is basically similar
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART
 Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color
 Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
Understand brightness, intensity, eye characteristics, and gamma correction, halftone technology, Understand general usage of color 1 ACHROMATIC LIGHT (Grayscale) Quantity of light physics sense of energy
