EYE: THE PHOTORECEPTOR SYSTEM. Prof. Dr. Huda Al Khateeb
|
|
|
- Vincent Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 EYE: THE PHOTORECEPTOR SYSTEM Prof. Dr. Huda Al Khateeb
3 Lecture 1 The eye ball
4 Objectives By the end of this lecture the student should: 1. List the layers and chambers of the eye ball 2. Describe the sclera 3. Name and describe the layers of the cornea 4. Define parts of uvea 5. Discuss the choroid, ciliary body and iris 6. Outline the lens and its parts
5 EYE eye The is a complex and highly developed photosensitive organ that analyses light reflected from objects, providing the sense of sight..
6 EYE The eye is composed of 1. eye ball-(about 22 mm in adults) 2. its protective structures What are they?
7 EYE The protective structures of the eye ball are: 1. The bony orbit 2. The adipose tissue between eye ball and orbit 3. the eyelids 4. the conjunctiva 5. the lacrimal apparatus HOW THEY PROTECT THE EYE BALL???????
8 EYE Eye ball consist of three layers 1. Outer layer (Sclera and cornea) 2. Middle layer (Uvea) 3. Inner layer (Retina)
9 Chambers Inside the eye ball there is three chambers 1. Anterior chamber- contains aqueous humor 2. Posterior chamber- contains aqueous humor 3. Vitreous cavity- contains vitreous humor
10 Lens The lens is placed in front of vitreous cavity and posterior to posterior chamber
11 Sclera It is a white, fibrous, external layer of the eyeball that protects the more delicate internal structures and provides sites for muscle insertion It makes the white posterior five-sixths of the external layer of the outer layer of the eye ball
12 Sclera The sclera is relatively avascular, and consists of dense connective tissue containing flat type I collagen bundles Tendons of the extra-ocular muscles that move the eyes insert into anterior areas of the sclera Posteriorly the sclera joins with the epineurium covering the optic nerve
13 Cornea The cornea is avascular, transparent and the most anterior part of the eye ball. It lacks blood and lymphatic vessels It is very sensitive because it is rich in nerve endings.
14 Cornea The cornea consists of five layers Corneal epithelium Bowman s membrane Corneal stroma (90 %)- (substantia propria) Descemet s membrane Corneal endothelium single layer
15 Cornea Corneal epithelium is stratified squamous non keratinized. The surface cells (apical layer) have microvilli that retain a film of tears that keeps the anterior surface of cornea wet
16 Cornea The basement membrane of this epithelium is very thick (8 12 µm) and contributes to the stability and strength of the cornea, helping to protect against infection of the underlying stroma
17 Cornea The corneal stroma is transparent It represents 90% of the corneal thickness Composed of type I and V collagen fibers that are regularly arranged. Fibers and layers are separated by extracellular matrix rich in prteoglycans containing chondrotin and keratin sulfate
18 MEDICAL APPLICATION The curvature of the cornea can be changed surgically to improve visual abnormalities involving the ability to focus. In the common ophthalmological procedure (LASIK surgery), where the stroma reshaped by laser. The relatively rapid regenerative response reestablishes normal corneal physiology.
19 Cornea Descement membrane is a very thik basement membrane. It is produced by the corneal endothelium and contains type VII collagen
20 Cornea The corneal endothelium lines the posterior surface of the cornea and faces the anterior chamber of the eye. It consists of single layer of squamous epithelial cells.
21 Cornea The cornea can be transplanted without the risk of rejection..why?? The cornea is very sensitive.why?? The corneal anterior surface is always wet WHY?? Corneal epithelium has a remarkable wound healing capacity...why???
22 Limbus Encircling the cornea is the Corneo-scleral junction, or Limbus, a transitional area where the transparent stroma merges with the opaque sclera. This region has micro-vasculature which, along with aqueous humor in the anterior chamber, provides metabolites for the corneal cells by diffusion Discuss the modes of nutrition of cornea?????
23 Canal of Schlemm It is a circular canal that lie in the corneo-scleral junction (limbus). It drains the aquoes humor from the anterior chamber through the meshwork trabeculae into the veins that drain the eye ball
24
25 Middle layer: UVEA Vascular Layer It consists of three parts, from posterior to anterior: 1. the choroid 2. the ciliary body 3. the iris
26 The choroid It is a highly vascular layer in the posterior two-thirds of the eye, with loose connective tissue rich in collagen and elastic fibers, fibroblasts, melanocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, mast cells, and plasma cells. The abundant melanocytes give the layer its characteristic black color. they block light from entering the eye except through the pupil
27 The ciliary body It is an anterior expansion of the choroid. It is a thickened ring of tissue lying just inside the anterior portion of the sclera. In transverse section the ciliary body is roughly a triangle, with its long base contacting the sclera, another side in contact with the vitreous body, and the third facing the posterior chamber.
28 The ciliary body It is composed of Ciliary muscle (smooth muscle) that is surrounded by a stroma of loose connective tissue, rich in microvasculature, elastic fibers, and melanocytes,
29 The ciliary body The ciliary muscle contraction (in response to parasympathetic nerves) decreases the internal diameter of the ciliary body ring, reducing tension on the fibers that run from this body to the lens. This allows the lens to become more rounded and better focus light from nearby objects onto the retina. The ciliary muscles are therefore important in visual accommodation
30 The ciliary body The surfaces of the ciliary body that face the vitreous body, posterior chamber, and lens has the ciliary processes (a series of about 75 radial ridges)
31 The ciliary body The surface epithelial cells is connected to the lens capsule by zonular fibers (suspensory ligament of the lens.)
32 The ciliary body Both ciliary body and processes are covered by a double layer of low columnar epithelium, the Ciliary epithelium. The epithelial cells directly covering the ciliary stroma are rich in melanin (Pigmented Layer). The surface layer of cells lacks melanin (Secretory Layer) (Non-pigmented layer)- secrets the aquous humor to the posterior chamber.
33 The ciliary body Secreted into the posterior chamber, aqueous humor flows between the lens and the iris to reach the anterior chamber through the pupil. The aqueous then flows into the channels of the trabecular meshwork at the corneo-scleral junction then to the Canal of Schlemm then drained to scleral venous sinus.
34 MEDICAL APPLICATION Aqueous humor is produced continuously. If its drainage is impeded, typically by obstruction of the trabecular meshwork or scleral venous sinus, intraocular pressure can increase, causing the condition called glaucoma. Untreated glaucoma can cause pressing of the vitreous body against the retina, affecting visual function.
35 Iris It is the most anterior extension of the uvea (middle layer) that partially covers the lens, leaving a round opening in the center called the pupil.
36 Pupil Pupil
37 Iris: Flowers
38 Iris: Goddess of Rainbow
39 The anterior surface of the iris is covered by irregular, discontinuous layer of fibroblasts and melanocytes, densely packed and with interdigitating processes.
40 Iris The stroma is composed of loose connective tissue with microvasculature, dilator and constrictor pupillae muscles. The dilator and sphincter muscles of the iris have sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation, respectively, for enlarging and constricting the pupil. The posterior surface of the iris is composed of twolayered epithelium (both are pigmented epithelium).
41
42 Iris color Melanocytes of the iris stroma provide the color of the eyes. In individuals with very few lightly pigmented cells in the stroma = blue color is iris surface. As the number of melanocytes and amount of collagen increases in the stroma, the iris color changes through various shades of green, gray, and brown.
43 Iris Individuals with albinism have almost no pigment and the pink color of their irises is due to the reflection of incident light from the blood vessels of the stroma.
44 Lens The lens is a transparent biconvex structure immediately behind the iris, used to focus light on the retina. The lens is a unique avascular tissue. It is highly elastic, a feature that is lost with age as lens tissue hardens. The lens has three principal components (capsule, anterior epithelium and lens fibers).
45 Lens Lens Capsule The lens is covered by a thick, homogeneous capsule rich in proteoglycans and type IV collagen. The lens capsule protects the underlying cells and provides the place of attachment for zonular fibers
46 Lens Lens Epithelium Subcapsular lens epithelium consists of a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells and is present only on the anterior surface of the lens. The basal ends of the epithelial cells attach to the lens capsule and their apical surfaces have interdigitations that bind the epithelium to the internal lens fibers..
47 Lens Lens fibers At the posterior edge of this epithelium, near the equator of the lens, the cells divide to provide new cells that differentiate as lens fibers. This process allows for growth of the lens and continues at a slow, decreasing rate near the equator of the lens throughout adult life
48 Lens Lens Fibers Lens fibers are highly elongated and appear as thin, flattened structures. Differentiating lens fibers eventually lose their nuclei and other organelles, fill the cytoplasm with a group of proteins called crystallins, and become very long.
49 Lens The lens is held in place by a radially oriented group of fibers, the elastic ciliary zonule, which inserts on both the lens capsule and on the ciliary body. This system is important in the process known as accommodation, which permits focusing on near and far objects by changing the curvature of the lens..
50 Lens When the eye is at rest or gazing at distant objects, the lens is kept stretched by the zonule in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis. To focus on a near object, the ciliary muscles contract. This relieves some of the tension exerted by the zonule on the lens, allowing the latter to round up and become thicker, keeping the object in focus
51 MEDICAL APPLICATION Advancing age reduces the elasticity of the lens, making accommodation for near objects difficult. This is a normal process (presbyopia, Gr. eyes of elders), which can be corrected by wearing glasses with convex lenses (reading glasses).
52 MEDICAL APPLICATIOn In old individuals, denaturation of crystallins commonly begins to occur in lens fibers, making them less transparent. When areas of the lens become opaque or cloudy and vision is impaired, the condition is termed cataract. Other causes of cataract include exposure to ultraviolet light or other radiation, trauma, and as secondary effects in diseases such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
53 Vitreous Body The vitreous body occupies the vitreous chamber behind the lens. It is composed of transparent connective tissue containing mostly (99%) water (vitreous humor)
54 summary Eye ball consist of three layers and three chambers Cornea has five layers Uvea composed of choroid, ciliary body and iris Lens
55 Quiz A 56-year-old woman complains of decreased vision in her left eye of 4 years duration. White discoloration of her left pupil is noted on physical examination (shown in the image). The white appearance of the pupil in this patient represents a pathological change affecting: 1. Conjunctiva 2. Cornea 3. Iris 4. Lens 5. Vitreous body
56
1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa
 1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa Fig 1: A Cross section of the human eye. Let us imagine we are traveling with a ray of light into the eye. The first structure we will encounter is
1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa Fig 1: A Cross section of the human eye. Let us imagine we are traveling with a ray of light into the eye. The first structure we will encounter is
The Eye. Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division
 The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein
 By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
4Basic anatomy and physiology
 Hene_Ch09.qxd 8/30/04 6:51 AM Page 348 348 4Basic anatomy and physiology The eye is a highly specialized organ with an average axial length of 24 mm and a volume of 6.5 ml. Except for its anterior aspect,
Hene_Ch09.qxd 8/30/04 6:51 AM Page 348 348 4Basic anatomy and physiology The eye is a highly specialized organ with an average axial length of 24 mm and a volume of 6.5 ml. Except for its anterior aspect,
Coarse hairs that overlie the supraorbital margins Functions include: Shading the eye Preventing perspiration from reaching the eye
 SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
Eye. Eye Major structural layer of the wall of the eye is a thick layer of dense C.T.; that layer has two parts:
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
November 14, 2017 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes 2- lacrimal apparatus:
 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
ABO Certification Training. Part I: Anatomy and Physiology
 ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
EYE. The eye is an extension of the brain
 I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
Special Senses- THE EYE. Pages
 Special Senses- THE EYE Pages 548-569 Accessory Structures Eyebrows Eyelids Conjunctiva Lacrimal Apparatus Extrinsic Eye Muscles EYEBROWS Deflect debris to side of face Facial recognition Nonverbal communication
Special Senses- THE EYE Pages 548-569 Accessory Structures Eyebrows Eyelids Conjunctiva Lacrimal Apparatus Extrinsic Eye Muscles EYEBROWS Deflect debris to side of face Facial recognition Nonverbal communication
The Eye. (We ll leave the Lord Sauron jokes to you.)
 The Eye (We ll leave the Lord Sauron jokes to you.) When you look in the mirror, you only see a very small part of your eyes. In reality, they are incredibly complex organs with a pretty big job: enabling
The Eye (We ll leave the Lord Sauron jokes to you.) When you look in the mirror, you only see a very small part of your eyes. In reality, they are incredibly complex organs with a pretty big job: enabling
Handout G: The Eye and How We See
 Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure
![[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure [Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure](/thumbs/95/124174711.jpg) [Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography Before Sam Clemens became Mark Twain, he had been, among other things, a riverboat pilot, a placer miner, and a newspaper reporter, occupations in which success
[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography Before Sam Clemens became Mark Twain, he had been, among other things, a riverboat pilot, a placer miner, and a newspaper reporter, occupations in which success
THE EYE. People of Asian descent have an EPICANTHIC FOLD in the upper eyelid; no functional difference.
 THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
Chapter 6 Human Vision
 Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Sheep Eye Dissection
 Sheep Eye Dissection Question: How do the various parts of the eye function together to make an image appear on the retina? Materials and Equipment: Preserved sheep eye Scissors Dissection tray Tweezers
Sheep Eye Dissection Question: How do the various parts of the eye function together to make an image appear on the retina? Materials and Equipment: Preserved sheep eye Scissors Dissection tray Tweezers
Objectives. 3. Visual acuity. Layers of the. eye ball. 1. Conjunctiva : is. three quarters. posteriorly and
 OCULAR PHYSIOLOGY (I) Dr.Ahmed Al Shaibani Lab.2 Oct.2013 Objectives 1. Review of ocular anatomy (Ex. after image) 2. Visual pathway & field (Ex. Crossed & uncrossed diplopia, mechanical stimulation of
OCULAR PHYSIOLOGY (I) Dr.Ahmed Al Shaibani Lab.2 Oct.2013 Objectives 1. Review of ocular anatomy (Ex. after image) 2. Visual pathway & field (Ex. Crossed & uncrossed diplopia, mechanical stimulation of
Special Senses: The Eye
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Chapter Human Vision
 Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
HSC Biology. Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION. By Sahar (99.1 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2014 Mark 92.00 Pages 11 Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION By Sahar (99.1 ATAR) Your notes author, Sahar. Sahar achieved an ATAR of 99.1 in 2014 while attending Carlingford
HSC Biology Year 2014 Mark 92.00 Pages 11 Published Feb 9, 2017 HSC BIOLOGY OPTION: COMMUNICATION By Sahar (99.1 ATAR) Your notes author, Sahar. Sahar achieved an ATAR of 99.1 in 2014 while attending Carlingford
25 Things To Know. Vision
 25 Things To Know Vision Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Light Frequency Amplitude Light Frequency How often it comes Wave length Peak to peak
25 Things To Know Vision Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Light Frequency Amplitude Light Frequency How often it comes Wave length Peak to peak
Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony
 Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony sockets in the skull. It is held in place by six muscles which are joined to the outside of
Sense Organs (Eye) The eye is the sense organ of sight. The eye is shaped like a ball and is located in bony sockets in the skull. It is held in place by six muscles which are joined to the outside of
Biology 70 Slides for Lecture 1 Fall 2007
 Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
Health Science 1110 Module 9 Sensations LAB 9. View the Film on Cornea Transplant and answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet.
 Health Science 1110 Module 9 Sensations LAB 9 View the Film on Cornea Transplant and answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. Webpage Activities o Open Internet Explorer o Go to the Health Sciences
Health Science 1110 Module 9 Sensations LAB 9 View the Film on Cornea Transplant and answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. Webpage Activities o Open Internet Explorer o Go to the Health Sciences
Materials Cow eye, dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, and gloves
 Cow Eye Dissection Guide Introduction How do we see? The eye processes the light through photoreceptors located in the eye that send signals to the brain and tells us what we are seeing. There are two
Cow Eye Dissection Guide Introduction How do we see? The eye processes the light through photoreceptors located in the eye that send signals to the brain and tells us what we are seeing. There are two
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Lecture 2 Slit lamp Biomicroscope
 Lecture 2 Slit lamp Biomicroscope 1 Slit lamp is an instrument which allows magnified inspection of interior aspect of patient s eyes Features Illumination system Magnification via binocular microscope
Lecture 2 Slit lamp Biomicroscope 1 Slit lamp is an instrument which allows magnified inspection of interior aspect of patient s eyes Features Illumination system Magnification via binocular microscope
Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert
 University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test.
 Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test. When light travels from a fast material like air into a slow material like glass, Snell s Law always works. Material from here on out though is
Material after quiz and still on everyone s Unit 11 test. When light travels from a fast material like air into a slow material like glass, Snell s Law always works. Material from here on out though is
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Introduction. Chapter Aim of the Thesis
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Aim of the Thesis The main aim of this investigation was to develop a new instrument for measurement of light reflected from the retina in a living human eye. At the start of
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Aim of the Thesis The main aim of this investigation was to develop a new instrument for measurement of light reflected from the retina in a living human eye. At the start of
In the following diagram the parts of the eye are visualized and labeled for you.
 Investigation 3.12B: The Eye In the preceding case study marker of the problem of greatest concern to you lay in finding the pupils fixed in a dilated position. But what is the pupil and what makes it
Investigation 3.12B: The Eye In the preceding case study marker of the problem of greatest concern to you lay in finding the pupils fixed in a dilated position. But what is the pupil and what makes it
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University, Brno. Biophysics of visual perception
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University, Brno 1 Lecture outline Basic properties of light Anatomy of eye Optical properties of eye Retina biological
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University, Brno 1 Lecture outline Basic properties of light Anatomy of eye Optical properties of eye Retina biological
Special Senses. Important Concepts. Anatomy of the Eye. Anatomy of the Eye. Biol 219 Lecture 17 Vision Fall The Eye and Vision
 Special Senses The Eye and Vision Important Concepts Describe the structures of the eye and the role of each structure in vision. Trace the pathway for vis ion from the retina to the visual cortex. Explain
Special Senses The Eye and Vision Important Concepts Describe the structures of the eye and the role of each structure in vision. Trace the pathway for vis ion from the retina to the visual cortex. Explain
Ch.2 Optical Properties of Biological Tissues
 Ch.2 Optical Properties of Biological Tissues 2.1 Optical Properties of Biological Tissues 2.1.1 Skin 2.1.2 Eye 2.1.3 Muscle 2.1.4 Fat 2.1.5 Brain 2.1.6 Tumor tissues 2.2 Laser Safety 1 2000/5/17 2.1 Optical
Ch.2 Optical Properties of Biological Tissues 2.1 Optical Properties of Biological Tissues 2.1.1 Skin 2.1.2 Eye 2.1.3 Muscle 2.1.4 Fat 2.1.5 Brain 2.1.6 Tumor tissues 2.2 Laser Safety 1 2000/5/17 2.1 Optical
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
 CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World
 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
BLOSSOMS_- What s_in_an_eye?
 BLOSSOMS_- What s_in_an_eye? Hello and welcome. My name is Ishara Mills-Henry, and I am the director of a program called Science of the Eye: Bringing Vision into the Classroom. This program is based in
BLOSSOMS_- What s_in_an_eye? Hello and welcome. My name is Ishara Mills-Henry, and I am the director of a program called Science of the Eye: Bringing Vision into the Classroom. This program is based in
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Introduction. Strand F Unit 3: Optics. Learning Objectives. Introduction. At the end of this unit you should be able to;
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
VISUAL SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY. Discipline of Physiology and Neuroscience, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania
 VISUAL SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY Discipline of Physiology and Neuroscience, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Outer layer of the eye Cornea - No bood vessels - Most powerful
VISUAL SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY Discipline of Physiology and Neuroscience, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Outer layer of the eye Cornea - No bood vessels - Most powerful
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lenses. Images. Difference between Real and Virtual Images
 Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
COW S EYE. dissection. Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions. Safety first!
 COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
-eyelashes are richly innervated and triggers reflex blinking
 The Eye and Vision -vision is the dominant sense -70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes -half of the cerebral cortex is involved in some aspect of visual processing -accessory structures
The Eye and Vision -vision is the dominant sense -70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes -half of the cerebral cortex is involved in some aspect of visual processing -accessory structures
Subjective refraction OPTICS OF HUMAN EYE & REFRACTIVE ERRORS
 Subjective refraction OPTICS OF HUMAN EYE & REFRACTIVE ERRORS Dr. Ali Abusharha Optics of human eye Eye as a camera Components Schematic eye and reduced eyes Axes and visual angles Optical aberrations
Subjective refraction OPTICS OF HUMAN EYE & REFRACTIVE ERRORS Dr. Ali Abusharha Optics of human eye Eye as a camera Components Schematic eye and reduced eyes Axes and visual angles Optical aberrations
used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. State the precautions necessary when X ray machines and CT scanners are used.
 Page 1 State the properties of X rays. Describe how X rays can be used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. State the precautions necessary when X ray machines and CT scanners are used. What is meant
Page 1 State the properties of X rays. Describe how X rays can be used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. State the precautions necessary when X ray machines and CT scanners are used. What is meant
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Ocular Jeopardy. The major refractive portion of the eye 5/12/2015. Presented by Jill J Luebbert, CPOT, ABOC. Watch This Refractive optios
 Ocular Jeopardy Presented by Jill J Luebbert, CPOT, ABOC In the beginning anterior Way back Visual Pathway Say What? terminolog y Watch This Refractive optios Posterior Segment 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20
Ocular Jeopardy Presented by Jill J Luebbert, CPOT, ABOC In the beginning anterior Way back Visual Pathway Say What? terminolog y Watch This Refractive optios Posterior Segment 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves
 Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves 2. Medium 3. Mechanical waves 4. Longitudinal waves 5. Transverse waves 6. Frequency 7. Reflection
Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves 2. Medium 3. Mechanical waves 4. Longitudinal waves 5. Transverse waves 6. Frequency 7. Reflection
A. The Eye A1. Eye in detail
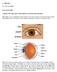 A. The Eye A1. Eye in detail EYE ANATOMY A guide to the many parts of the human eye and how they function. The ability to see is dependent on the actions of several structures in and around the eyeball.
A. The Eye A1. Eye in detail EYE ANATOMY A guide to the many parts of the human eye and how they function. The ability to see is dependent on the actions of several structures in and around the eyeball.
INTRODUCING OPTICS CONCEPTS TO STUDENTS THROUGH THE OX EYE EXPERIMENT
 INTRODUCING OPTICS CONCEPTS TO STUDENTS THROUGH THE OX EYE EXPERIMENT Marcela L. Redígolo redigolo@univap.br Leandro P. Alves leandro@univap.br Egberto Munin munin@univap.br IP&D Univap Av. Shishima Hifumi,
INTRODUCING OPTICS CONCEPTS TO STUDENTS THROUGH THE OX EYE EXPERIMENT Marcela L. Redígolo redigolo@univap.br Leandro P. Alves leandro@univap.br Egberto Munin munin@univap.br IP&D Univap Av. Shishima Hifumi,
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Physics of the Eye *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
Lenses. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
nearly to that of the sclerotic. Instead of the normal radius
 THE REFRACTON N BUPHTHALMA THE REFRACTON N BUPHTHALMA BY J. HERBERT PARSONS, LONDON. T is a well-known fact that, in spite of the great enlargement of the eyeball in buphthalmia, the eye is not nearly
THE REFRACTON N BUPHTHALMA THE REFRACTON N BUPHTHALMA BY J. HERBERT PARSONS, LONDON. T is a well-known fact that, in spite of the great enlargement of the eyeball in buphthalmia, the eye is not nearly
Instruments Commonly Used For Examination of the Eye
 Instruments Commonly Used For Examination of the Eye There are many instruments that the eye doctor might use to evaluate the eye and the vision system. This report presents some of the more commonly used
Instruments Commonly Used For Examination of the Eye There are many instruments that the eye doctor might use to evaluate the eye and the vision system. This report presents some of the more commonly used
Please feel to contact Sonomed for any suggestions, comments or request about this bulletin.
 Sonomed Quarterly Bulletin Volume One, January 2008 Dear Sonomed Colleagues: Sonomed is proud to announce the VuMAX II Ultrasound Biomicroscope is experiencing huge success in the global ophthalmic markets.
Sonomed Quarterly Bulletin Volume One, January 2008 Dear Sonomed Colleagues: Sonomed is proud to announce the VuMAX II Ultrasound Biomicroscope is experiencing huge success in the global ophthalmic markets.
OpenStax-CNX module: m Vision Correction * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42484 1 Vision Correction * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Identify and discuss common vision
OpenStax-CNX module: m42484 1 Vision Correction * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Identify and discuss common vision
4. Cut away the fat and muscle.
 1. Safety first! You ll be using a scalpel or a razor to cut the cow s eye. Be careful. A scalpel or razor can cut you as easily as it cuts the cow s eye. Whenever you handle raw meat (whether it s a cow
1. Safety first! You ll be using a scalpel or a razor to cut the cow s eye. Be careful. A scalpel or razor can cut you as easily as it cuts the cow s eye. Whenever you handle raw meat (whether it s a cow
sclera pupil What happens to light that enters the eye?
 Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
OCULAR MEDIA* PHOTOGRAPHIC RECORDING OF OPACITIES OF THE. development by the control of diabetes, the supply of a deficient hormone
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 85. PHOTOGRAPHIC RECORDING OF OPACITIES OF THE OCULAR MEDIA* BY E. F. FINCHAM Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London THE value of photography for recording pathological
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 85. PHOTOGRAPHIC RECORDING OF OPACITIES OF THE OCULAR MEDIA* BY E. F. FINCHAM Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London THE value of photography for recording pathological
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Types of lenses. Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging.
 Types of lenses Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging. Any lens that is thicker at its center than at its edges is a converging lens with positive f; and any lens that
Types of lenses Shown below are various types of lenses, both converging and diverging. Any lens that is thicker at its center than at its edges is a converging lens with positive f; and any lens that
OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS
 OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS BIONIKO designs innovative surgical models, task trainers and teaching tools for the ophthalmic industry. Our surgical models present the user with dexterity and coordination
OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS BIONIKO designs innovative surgical models, task trainers and teaching tools for the ophthalmic industry. Our surgical models present the user with dexterity and coordination
General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) - Lecture Notes. General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes
 General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes Lecture 036: Application of Lenses - the Human Eye SteveSekula, 1 December 2010 (created 30 November 2010) Goals of this lecture no tags conclude the discussion
General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes Lecture 036: Application of Lenses - the Human Eye SteveSekula, 1 December 2010 (created 30 November 2010) Goals of this lecture no tags conclude the discussion
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS
 OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS BIONIKO designs innovative surgical models, task trainers and teaching tools for the ophthalmic industry. Our surgical models present the user with dexterity and coordination
OPHTHALMIC SURGICAL MODELS BIONIKO designs innovative surgical models, task trainers and teaching tools for the ophthalmic industry. Our surgical models present the user with dexterity and coordination
OPTI-201/202 Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Copyright 2018 John E. Greivenkamp. Section 16. The Eye
 16-1 Section 16 The Eye The Eye Ciliary Muscle Iris Pupil Optical Axis Visual Axis 16-2 Cornea Right Eye Horizontal Section Zonules Crystalline Lens Vitreous Sclera Retina Macula And Fovea Optic Nerve
16-1 Section 16 The Eye The Eye Ciliary Muscle Iris Pupil Optical Axis Visual Axis 16-2 Cornea Right Eye Horizontal Section Zonules Crystalline Lens Vitreous Sclera Retina Macula And Fovea Optic Nerve
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Eyeball Model Lab Date Block
 Science 8 Name Eyeball Model Lab Date Block Problem: Identify the twelve key parts of the eye and describe their function. Materials: dissecting scissors ping pong ball transparent plastic ordinary scissors
Science 8 Name Eyeball Model Lab Date Block Problem: Identify the twelve key parts of the eye and describe their function. Materials: dissecting scissors ping pong ball transparent plastic ordinary scissors
Section 22. The Eye The Eye. Ciliary Muscle. Sclera. Zonules. Macula And Fovea. Iris. Retina. Pupil. Optical Axis.
 Section 22 The Eye 22-1 The Eye Optical Axis Visual Axis Pupil Iris Cornea Right Eye Horizontal Section Ciliary Muscle Zonules Crystalline Lens Vitreous Sclera Retina Macula And Fovea Optic Nerve 22-2
Section 22 The Eye 22-1 The Eye Optical Axis Visual Axis Pupil Iris Cornea Right Eye Horizontal Section Ciliary Muscle Zonules Crystalline Lens Vitreous Sclera Retina Macula And Fovea Optic Nerve 22-2
Cow Eye Dissection. Online dissection, for kids abstaining:
 Cow Eye Dissection Introductory Discussion: Tell the students that we will be learning about what eyes are made of and how they work by dissecting a cow eye. Talk about where the eye comes from, and how
Cow Eye Dissection Introductory Discussion: Tell the students that we will be learning about what eyes are made of and how they work by dissecting a cow eye. Talk about where the eye comes from, and how
11 Human Eye & colourful world IMPORTANT NOTES ANIL TUTORIALS
 11 Human Eye & colourful world IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Parts of the Human Eye : (i) Sclerotic is the outermost white fibrous covering of the eye. (ii) Cornea is the transparent front bulging portion of the
11 Human Eye & colourful world IMPORTANT NOTES 1. Parts of the Human Eye : (i) Sclerotic is the outermost white fibrous covering of the eye. (ii) Cornea is the transparent front bulging portion of the
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
A&P 1 Eye & Vision Lab Vision Concepts
 A&P 1 Eye & Vision Lab Vision Concepts In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of vision. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order of the videos. You should be able to read this
A&P 1 Eye & Vision Lab Vision Concepts In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of vision. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order of the videos. You should be able to read this
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10
 HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10 Human Eye Eye is one of the most sensitive sense organs in the human body. Our eye enables us to see this beautiful world. It consists of a lens,
HUMAN EYE AND COLOURFUL WORLD Notes Physics - Grade 10 Human Eye Eye is one of the most sensitive sense organs in the human body. Our eye enables us to see this beautiful world. It consists of a lens,
The angle of the anterior chamber needs to be assessed
 Thomas George MS Common Tests Simplified Gonioscopy The angle of the anterior chamber needs to be assessed in all glaucomas. It usually holds the secrets to pathogenesis in that particular case. It may
Thomas George MS Common Tests Simplified Gonioscopy The angle of the anterior chamber needs to be assessed in all glaucomas. It usually holds the secrets to pathogenesis in that particular case. It may
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
