Physics 30 Lesson 9 Optics Thin Lenses
|
|
|
- Baldric Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reer t Pearsn pages 677 t 68. Physics 30 Lessn 9 Optics Thin Lenses The stuy lenses is very similar t that curve mirrrs. Hwever, while mirrrs invlve relectin, lenses invlve reractin. In act, r lenses there are tw reractins ne when the light ray enters the lens an ne when the light ray exits the lens. Reractin Reractin 2 Using the law reractin can yu explain reractin an reractin 2? Cnvex lens Nte that r a cnvex lens like the ne epicte abve the light ray is bent twar the principle axis twice, while r a cncave lens the light ray is bent away rm the principle axis. Using the law reractin can yu explain the reractins r a iverging lens? Cncave lens Cnvex lenses are cnverging lenses, an cncave lenses are iverging lenses. R.L. & A.K. 9 2//203
2 The equatins use r calculating the psitin an image rm a lens are ientical t the equatins r mirrrs. where cal length real (+), virtual ( ) istance rm lens t the bject i i istance rm the lens t the image hi i M real (+), virtual ( ) h h height bject h i height image real ( ), virtual (+) M magniicatin real, inverte ( ), virtual, upright (+) While the equatins r curve mirrrs an thin lenses are the same, it is imprtant t nte that real images rm in rnt a mirrr an real images rm behin a lens. This is ue t the act that mirrrs relect light back while lenses reract light thrugh t the ther sie the lens. I. Images Create by Lenses (Ray Diagrams) Ray travels rm the bject parallel t the principal axis. In passing thrugh the lens, the ray is reracte t the real cal pint n the ther sie the lens. Ray travels rm the bject parallel t the principal axis. In passing thrugh the lens, the ray is reracte away rm the virtual cal pint the lens. Ray 2 travels thrugh the virtual cal pint an is then reracte by the lens t emerge parallel t the principal axis. Ray 2 travels rm the bject twar the real cal pint. It then emerges parallel t the principal axis. Ray 3 travels thrugh the centre the thin lens straight thrugh. Ray 3 travels thrugh the centre the thin lens straight thrugh. R.L. & A.K //203
3 The iagrams belw illustrate the basic ray iagrams r bjects at ierent psitins relative t the lens. image rme rm a iverging lens R.L. & A.K //203
4 Example Utilising the rays r lenses, cmplete the ray iagram r the lens belw an escribe the image. slutin image is inverte, real an iminishe Image Frmatin Cnverging Lens R.L. & A.K //203
5 Image Frmatin Diverging Lens II. Calculatins Using the Lens Equatins Example 2 A 4.0 cm tall bject is place 50 cm away rm a cnvex lens that has a cal length 20 cm. Describe the image rme. h = 4.0 cm = 50 cm = +20 cm cnvex, cnverging lens 20 cm i i 50 cm i = cm hi i h ih hi The (+) i means that the image is real an inverte. The image is 2.67 cm tall, i.e. iminishe cm(4.0 cm) 50 cm = 2.67 cm R.L. & A.K //203
6 Example 3 A 5.0 cm tall bject is place 60 cm away rm a iverging lens that has a cal length 40 cm. Describe the image rme. h = 5.0 cm = 60 cm = 40 cm iverging lens i i 40 cm 60 cm i = 24 cm hi i h ih hi The ( ) i means that the image is virtual, erect an iminishe. 24 cm(5.0 cm) = + 2 cm 60 cm Example 4 An experiment is ne where an ptical evice, either a mirrr r a lens, is use. When the bject is place 20 cm rm the ptical evice, an erect image the bject is un n the ppsite sie the ptical evice. The image is ne-quarter the size the bject. What kin ptical evice is it an what is its cal length? The image is erect (i.e. virtual), smaller (i.e. i is less than ) an it is n the ppsite sie rm the bject (i.e. virtual an n ther sie happens r mirrrs nly). The nly way this can happen is with a cnvex (iverging) mirrr. i 4 20 cm 4 i is ( ) r an erect image = 5.0 cm i = cm 20 cm = 6.67 cm 0.5 R.L. & A.K //203
7 III. Practice Prblems a. (real, inverte, smaller) b. (real, inverte, same size) c. (real, inverte, larger). (n image rms) e. (virtual, erect, larger) R.L. & A.K //203
8 . (virtual, erect, smaller) IV. Han-in Assignment. Cmplete the iagrams belw by rawing in the light rays as they emerge rm the lenses. Label each the lenses belw as either cnvex r cncave. Label each the lenses belw as either cnverging r iverging. 2. Using the rules r light rays sketch ray iagrams r the llwing cases. State whether the image is: Real r virtual, erect r inverte, an larger r smaller than the bject. a. b. R.L. & A.K //203
9 c.. e.. 3. An bject 8.0 cm high is place 80 cm in rnt a cnverging lens cal length 25 cm. Determine the image psitin an its height. (36 cm, 3.6 cm) 4. A lamp 0 cm high is place 60 cm in rnt a iverging lens cal length 20 cm. Calculate the image psitin an the height the image. ( 5 cm, 2.5 cm) 5. A typical single lens relex (SLR) camera has a cnverging lens with a cal length 50.0 mm. What is the psitin an size the image a 25 cm canle lcate.0 m rm the lens? (5.3 cm,.3 cm) R.L. & A.K //203
10 6. A cnverging lens with a cal length 20 cm is use t create an image the sun n a paper screen. Hw ar rm the lens must the paper be place t pruce a clear image? (20 cm) 7. The cal length a slie prjectr's cnverging lens is 0.0 cm. (a) I a 35 mm slie is psitine 0.2 cm rm the lens, hw ar away must the screen be place t create a clear image? (5.0 m) (b) I the height a g n the slie ilm is 2.5 mm, hw tall will the g's image n the screen be? ( 62.5 cm) (c) I the screen is then remve t a pint 5 m rm the lens, by hw much will the separatin between ilm an lens have t change rm part (a)? (0.3 cm) *8. A cnvex lens has a cal length + 20 cm an a magniicatin 4. Hw ar apart are the bject an the image? (45 cm) 9. A prjectr is require t make a real image, 0.50 m tall, a 5.0 cm bject place n a slie. Within the prjectr, the bject is t be place 0.0 cm rm the lens. What must be the cal length the lens? (9. cm) 0. An bject 5.0 cm high is place at the 20 cm mark n a metre stick ptical bench. A cnverging lens with a cal length 20 cm is munte at the 50 cm mark. What are the psitin an size the image relative t the metre stick? (0 cm, 0 cm). A camera lens has a cal length 6.0 cm an is lcate 7.0 cm rm the ilm. Hw ar rm the lens is the bject psitine i a clear image has been pruce n the ilm? (42 cm) R.L. & A.K //203
11 Activity Cnvex lens Purpse: T etermine the cal length a uble cnvex lens. Apparatus: Set up yur wn apparatus base n the iagram belw. Be sure t return all materials t their apprpriate places ater yu have cmplete the lab. light surce lens meter sticks stan Thery: The thin lens equatin is: i Therere, i we measure the bject istance an the image istance we can etermine the cal length the lens. Prceure:. Place the bject at sme pint away rm the lens. (Start at arun 60 cm.) Recr the bject istance (istance rm lens t bject). 2. Using a white piece paper as a screen, mve the screen until a sharp image the bject (the bulb ilament) appears n the screen. Recr the image istance (istance rm lens t the screen). 3. Repeat steps ne an tw until a ttal three ierent psitins have been lcate. Observatins: Create an apprpriate ata table t rganise yur results. Analysis:. Calculate the cal length r each psitin an then in an average result. Shw all wrk an calculatins. 2. Draw scale ray iagrams r each psitin shwing the rmatin each image. R.L. & A.K. 9 2//203
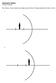
f f d o FIGURE 1 - Light ray diagram
 Lab 10 Thin Lenses What Yu Nee T Knw: The Physics Frm last week s lab, Reflectin an Refractin, yu shul alreay be familiar with the fllwing terms: principle axis, fcal pint, fcal length, f, cnverging lens
Lab 10 Thin Lenses What Yu Nee T Knw: The Physics Frm last week s lab, Reflectin an Refractin, yu shul alreay be familiar with the fllwing terms: principle axis, fcal pint, fcal length, f, cnverging lens
Student Exploration: Ray Tracing (Lenses)
 G T: www.explrelearning.cm r use te Explre Learning App n te ipad Class Cde: BAHPGNUHVR Name: Date: Student Explratin: Ray Tracing (Lenses) Vcabulary: cncave lens, cnvex lens, cal pint, image, magniicatin,
G T: www.explrelearning.cm r use te Explre Learning App n te ipad Class Cde: BAHPGNUHVR Name: Date: Student Explratin: Ray Tracing (Lenses) Vcabulary: cncave lens, cnvex lens, cal pint, image, magniicatin,
Physics 11b Lecture #20
 Physics 11b Lecture #20 Lenses, Mirrrs, and Images S&J Chapter 36 What We Did Last Time Law relectin: Huygens principle Index reractin θ = θ 1 1 Wavelength is aected Snell s law reractin: n = c v> λ n
Physics 11b Lecture #20 Lenses, Mirrrs, and Images S&J Chapter 36 What We Did Last Time Law relectin: Huygens principle Index reractin θ = θ 1 1 Wavelength is aected Snell s law reractin: n = c v> λ n
EXPERIMENT 10 Thin Lenses
 Objectives ) Measure the power and focal length of a converging lens. ) Measure the power and focal length of a diverging lens. EXPERIMENT 0 Thin Lenses Apparatus A two meter optical bench, a meter stick,
Objectives ) Measure the power and focal length of a converging lens. ) Measure the power and focal length of a diverging lens. EXPERIMENT 0 Thin Lenses Apparatus A two meter optical bench, a meter stick,
Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing
 Name: Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different converging lenses, one diverging lens, screen, lighted object, three stands, meter stick, two letter
Name: Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different converging lenses, one diverging lens, screen, lighted object, three stands, meter stick, two letter
Optics Practice. Version #: 0. Name: Date: 07/01/2010
 Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
10.2 Images Formed by Lenses SUMMARY. Refraction in Lenses. Section 10.1 Questions
 10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
Physics II. Chapter 23. Spring 2018
 Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
From Perspectivities to Perspective Collineations
 Frm erspectivities t erspective Cllineatins Given distinct planes π and π 0 in extended Euclidean space E3, and a pint n neither plane, the assciated ne-pint prjectin with center maps π bijectively nt
Frm erspectivities t erspective Cllineatins Given distinct planes π and π 0 in extended Euclidean space E3, and a pint n neither plane, the assciated ne-pint prjectin with center maps π bijectively nt
Look at the text on page 426 for the answer.
 ur butterflies, but nly ne is real! The thers small, large, upright, and turned upside dwn are images that result frm reflectin and refractin in a single piece f glass. What must be the shape f the glass?
ur butterflies, but nly ne is real! The thers small, large, upright, and turned upside dwn are images that result frm reflectin and refractin in a single piece f glass. What must be the shape f the glass?
National Curriculum Programme of Study:
 Natinal Curriculum Prgramme f Study: Cunt in steps f 2, 3, and 5 frm 0, and in tens frm any number, frward and backward. Recall and use multiplicatin and divisin facts fr the 2, 5 and 10 multiplicatin
Natinal Curriculum Prgramme f Study: Cunt in steps f 2, 3, and 5 frm 0, and in tens frm any number, frward and backward. Recall and use multiplicatin and divisin facts fr the 2, 5 and 10 multiplicatin
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses
 PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
Part 1 Investigating Snell s Law
 Geometric Optics with Lenses PURPOSE: To observe the refraction of light off through lenses; to investigate the relationship between objects and images; to study the relationship between object distance,
Geometric Optics with Lenses PURPOSE: To observe the refraction of light off through lenses; to investigate the relationship between objects and images; to study the relationship between object distance,
Unit #3 - Optics. Activity: D21 Observing Lenses (pg. 449) Lenses Lenses
 ist10_ch11.qxd Unit #3 - Optics 11.3 Lenses 7/22/09 3:53 PM Page 449 Night vision goggles use lenses to ocus light onto a device called an image intensiier. Inside the intensiier, the light energy releases
ist10_ch11.qxd Unit #3 - Optics 11.3 Lenses 7/22/09 3:53 PM Page 449 Night vision goggles use lenses to ocus light onto a device called an image intensiier. Inside the intensiier, the light energy releases
Converging Lens. Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image.
 Converging Lens Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image. Lab Preparation The picture on the screen in a movie
Converging Lens Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image. Lab Preparation The picture on the screen in a movie
LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction Read Hewitt Chapters 28 and 29 What to learn and explore Please read this! When light rays reflect off a mirror surface or refract through
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction Read Hewitt Chapters 28 and 29 What to learn and explore Please read this! When light rays reflect off a mirror surface or refract through
3. What kind of mirror could you use to make image distance less than object distance?
 REFLETION REVIEW hoose one o the ollowing to answer questions 7-24. A response may be used more than once. a. plane mirror e. plane mirror or convex mirror b. concave mirror. concave mirror or convex mirror
REFLETION REVIEW hoose one o the ollowing to answer questions 7-24. A response may be used more than once. a. plane mirror e. plane mirror or convex mirror b. concave mirror. concave mirror or convex mirror
LENSES. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
13. Optical Instruments*
 13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
ECE 3829: Advanced Digital System Design with FPGAs A Term 2017
 ECE 3829: Advanced Digital System Design with FPGAs A Term 2017 Lab 2- VGA display and Light Sensr interface Reprt due at start f class Friday September 15 th Use the prvided Ambient Light Sensr mdule
ECE 3829: Advanced Digital System Design with FPGAs A Term 2017 Lab 2- VGA display and Light Sensr interface Reprt due at start f class Friday September 15 th Use the prvided Ambient Light Sensr mdule
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #8: Thin Lenses
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #8: Thin Lenses Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 2/4/5/6, 2018 Background In the previous lab
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #8: Thin Lenses Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 2/4/5/6, 2018 Background In the previous lab
The Mathematics of the Rubik s Cube
 In this lessn, students will explre the pssible number ways the pieces f a Rubik's Cube can be arranged, and still fit the criteria fr a Rubik's Cube. Clrs are riented in a set way, s sme pieces (such
In this lessn, students will explre the pssible number ways the pieces f a Rubik's Cube can be arranged, and still fit the criteria fr a Rubik's Cube. Clrs are riented in a set way, s sme pieces (such
Instructions. To run the slideshow:
 Instructions To run the slideshow: Click: view full screen mode, or press Ctrl +L. Left click advances one slide, right click returns to previous slide. To exit the slideshow press the Esc key. Optical
Instructions To run the slideshow: Click: view full screen mode, or press Ctrl +L. Left click advances one slide, right click returns to previous slide. To exit the slideshow press the Esc key. Optical
Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its colour components.
 Chapter 21 Clurs (A) Dispersin 1. Define dispersin. Dispersin is the splitting f white light int its clur cmpnents. 2. What is the clur that sunlight appears t be? White 3. State the seven clurs in sunlight
Chapter 21 Clurs (A) Dispersin 1. Define dispersin. Dispersin is the splitting f white light int its clur cmpnents. 2. What is the clur that sunlight appears t be? White 3. State the seven clurs in sunlight
Refraction and Lenses
 Reraction and Lenses The most common application o reraction in science and technology is lenses. The kind o lenses we typically think o are made o glass or plastic. The basic rules o reraction still apply
Reraction and Lenses The most common application o reraction in science and technology is lenses. The kind o lenses we typically think o are made o glass or plastic. The basic rules o reraction still apply
PHYS 160 Astronomy. When analyzing light s behavior in a mirror or lens, it is helpful to use a technique called ray tracing.
 Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Geometric Optics Practice Problems. Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror.
 Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS
 REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
LENSES. a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses.
 Purpose Theory LENSES a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses. formation by thin spherical lenses s are formed by lenses because of the refraction
Purpose Theory LENSES a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses. formation by thin spherical lenses s are formed by lenses because of the refraction
Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror
 Physics 41 Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror Objective: Apply the thin-lens equation and the mirror equation to determine the focal length of a converging (biconvex) lens and
Physics 41 Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror Objective: Apply the thin-lens equation and the mirror equation to determine the focal length of a converging (biconvex) lens and
Physics 197 Lab 7: Thin Lenses and Optics
 Physics 197 Lab 7: Thin Lenses and Optics Equipment: Item Part # Qty per Team # of Teams Basic Optics Light Source PASCO OS-8517 1 12 12 Power Cord for Light Source 1 12 12 Ray Optics Set (Concave Lens)
Physics 197 Lab 7: Thin Lenses and Optics Equipment: Item Part # Qty per Team # of Teams Basic Optics Light Source PASCO OS-8517 1 12 12 Power Cord for Light Source 1 12 12 Ray Optics Set (Concave Lens)
PhotoVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide
 PhtVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide PhtVu, LLC 2450 Central Ave, #G1 Bulder, CO 80301 USA www.phtvu.cm/supprt Versin: 1.0 Table f Cntents Getting Started... 3 Determine Yur Generatin f PhtVu
PhtVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide PhtVu, LLC 2450 Central Ave, #G1 Bulder, CO 80301 USA www.phtvu.cm/supprt Versin: 1.0 Table f Cntents Getting Started... 3 Determine Yur Generatin f PhtVu
Geometric Optics. This equation is known as the mirror equation or the thin lens equation, depending on the setup.
 Geometric Optics Purpose (Write the purposes at the beginning of each problem.) Problem 1: find the focal length of a concave mirror to verify the mirror equation; Problem 2: find the focal length of a
Geometric Optics Purpose (Write the purposes at the beginning of each problem.) Problem 1: find the focal length of a concave mirror to verify the mirror equation; Problem 2: find the focal length of a
O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope
 O5. 1 O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope Introduction In this experiment, you will study converging lenses and the lens equation. You will make several measurements of the focal length of lenses and
O5. 1 O5: Lenses and the refractor telescope Introduction In this experiment, you will study converging lenses and the lens equation. You will make several measurements of the focal length of lenses and
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
Lenses. A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope
 SNC2D Lenses A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope Reading stones used by monks, nuns, and scholars ~1000 C.E. Lenses THERE ARE
SNC2D Lenses A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope Reading stones used by monks, nuns, and scholars ~1000 C.E. Lenses THERE ARE
LO - Lab #05 - How are images formed from light?
 LO - Lab #05 - Helpful Definitions: The normal direction to a surface is defined as the direction that is perpendicular to a surface. For example, place this page flat on the table and then stand your
LO - Lab #05 - Helpful Definitions: The normal direction to a surface is defined as the direction that is perpendicular to a surface. For example, place this page flat on the table and then stand your
Thin Lens and Image Formation
 Pre-Lab Quiz / PHYS 4 Thin Lens and Image Formation Name Lab Section. What do you investigate in this lab?. The ocal length o a bi-convex thin lens is 0 cm. To a real image with magniication o, what is
Pre-Lab Quiz / PHYS 4 Thin Lens and Image Formation Name Lab Section. What do you investigate in this lab?. The ocal length o a bi-convex thin lens is 0 cm. To a real image with magniication o, what is
Thin Lenses. Physics 227 Lab. Introduction:
 Introduction: From last week's lab, Reflection and Refraction, you should already be familiar with the following terms: principle axis, focal point, focal length,f, converging lens (f is +), and diverging
Introduction: From last week's lab, Reflection and Refraction, you should already be familiar with the following terms: principle axis, focal point, focal length,f, converging lens (f is +), and diverging
Assignment X Light. Reflection and refraction of light. (a) Angle of incidence (b) Angle of reflection (c) principle axis
 Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
 1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
PRINCIPLE PROCEDURE ACTIVITY. AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit.
 ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit
 Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit 5.1.1 Oscillatins - time fr ne scillatin - number f scillatins per secnd Equatin Pendulum Mass n a Spring PRACTICE Regents Physics 1. A pendulum is timed as it mves
Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit 5.1.1 Oscillatins - time fr ne scillatin - number f scillatins per secnd Equatin Pendulum Mass n a Spring PRACTICE Regents Physics 1. A pendulum is timed as it mves
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light
 AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1974-3 (Geometric Optics) An object 1.0 cm high is placed 4 cm away from a converging lens having a focal length of 3 cm. a. Sketch a principal ray diagram for
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1974-3 (Geometric Optics) An object 1.0 cm high is placed 4 cm away from a converging lens having a focal length of 3 cm. a. Sketch a principal ray diagram for
PAPER SPACE AND LAYOUTS
 PAPER SPACE AND LAYOUTS There are tw distinct wrking envirnments in AutCAD namely: Mdel Space and Paper space. Prjects can be develped by either wrking in the mdel space thrugh the use f MVSETUP r PAPER
PAPER SPACE AND LAYOUTS There are tw distinct wrking envirnments in AutCAD namely: Mdel Space and Paper space. Prjects can be develped by either wrking in the mdel space thrugh the use f MVSETUP r PAPER
A2: Aperture, DOF, & Focus
 Art 205 A2: Aperture, DOF, & Fcus Original RAW Shts Due: Crit Date: Requires 2 Ink Jet Prints (50 pints) Objectives: 1. T understand hw apertures like f-16 & f-22 have a large DOF r range f fcus. 2. T
Art 205 A2: Aperture, DOF, & Fcus Original RAW Shts Due: Crit Date: Requires 2 Ink Jet Prints (50 pints) Objectives: 1. T understand hw apertures like f-16 & f-22 have a large DOF r range f fcus. 2. T
How Do I Use Ray Diagrams to Predict How an Image Will Look?
 How Do I Use Ray Diagrams to Predict How an Image Will Look? Description: Students will create ray diagrams to predict the type o image ormed. Student Materials (per group): Ray Diagrams Worksheet Ruler
How Do I Use Ray Diagrams to Predict How an Image Will Look? Description: Students will create ray diagrams to predict the type o image ormed. Student Materials (per group): Ray Diagrams Worksheet Ruler
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems
 Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Algebra Based Physics. Reflection. Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66. Slide 3 / 66. Slide 4 / 66. Slide 5 / 66. Slide 6 / 66.
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 lgebra ased Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 lgebra ased Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION 1. List four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror. Properties of image formed by a plane mirror: 1. It is always virtual and erect. 2. Its size is equal to that
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION 1. List four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror. Properties of image formed by a plane mirror: 1. It is always virtual and erect. 2. Its size is equal to that
Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. ... (1) What word can be used to describe this type of lens? ... (1)
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
PreLab5 Temperature-Controlled Fan (Due Oct 16)
 PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION
 LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions for lenses and mirrors Spherical mirrors
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions for lenses and mirrors Spherical mirrors
Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics)
 1 Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics) 1. A convex glass lens (refractive index = 3/2) has a focal length of 8 cm when placed in air. What is the focal length of the lens when it is immersed in water
1 Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics) 1. A convex glass lens (refractive index = 3/2) has a focal length of 8 cm when placed in air. What is the focal length of the lens when it is immersed in water
Optics: Lenses & Mirrors
 Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 Light. In each of the following sentences, fill in the bracket the appropriate word or words given below.
 JPN Pahang Physics Module orm 4 HAPTER 5: LIGHT In each of the following sentences, fill in the bracket the appropriate word or words given below. solid, liquid, gas, vacuum, electromagnetic wave, energy
JPN Pahang Physics Module orm 4 HAPTER 5: LIGHT In each of the following sentences, fill in the bracket the appropriate word or words given below. solid, liquid, gas, vacuum, electromagnetic wave, energy
Refraction by Spherical Lenses by
 Page1 Refraction by Spherical Lenses by www.examfear.com To begin with this topic, let s first know, what is a lens? A lens is a transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both the surfaces
Page1 Refraction by Spherical Lenses by www.examfear.com To begin with this topic, let s first know, what is a lens? A lens is a transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both the surfaces
Manual Zeiss Axio Zoom.V16 microscope and ZEN 2 Pro software
 Manual Zeiss Axi Zm.V16 micrscpe and ZEN 2 Pr sftware 15-9-2015 Fred Hartjes EMS 3 Caxial illum. Ring illum. Starting up Pwer n Actuate the knb n the EMS 3 cntrl unit Switch n the caxial illuminatin Switch
Manual Zeiss Axi Zm.V16 micrscpe and ZEN 2 Pr sftware 15-9-2015 Fred Hartjes EMS 3 Caxial illum. Ring illum. Starting up Pwer n Actuate the knb n the EMS 3 cntrl unit Switch n the caxial illuminatin Switch
Figure 1: A Battleship game by Pogo
 CSCI 2312-002: Object Oriented Prgramming Final Prject Assigned: Octber 17, 2017 Design Due: Octber 24, 2017 IN CLASS (Graded as ne hmewrk grade) Final prject Due: Nvember 16, 2017 at 11:59 PM Fr many
CSCI 2312-002: Object Oriented Prgramming Final Prject Assigned: Octber 17, 2017 Design Due: Octber 24, 2017 IN CLASS (Graded as ne hmewrk grade) Final prject Due: Nvember 16, 2017 at 11:59 PM Fr many
Desktop Teller Exception User Guide
 Desktp Teller Exceptin User Guide Jammed Dcuments If a dcument jams during the scanning prcess, the scanner will stp, and a message bx will display a Device Errr Message, as shwn belw: Click OK t allw
Desktp Teller Exceptin User Guide Jammed Dcuments If a dcument jams during the scanning prcess, the scanner will stp, and a message bx will display a Device Errr Message, as shwn belw: Click OK t allw
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Final Reg Optics Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
lens Figure 1. A refractory focusing arrangement. Focal point
 Laboratory 2 - Introduction to Lenses & Telescopes Materials Used: A set o our lenses, an optical bench with a centimeter scale, a white screen, several lens holders, a light source (with crossed arrows),
Laboratory 2 - Introduction to Lenses & Telescopes Materials Used: A set o our lenses, an optical bench with a centimeter scale, a white screen, several lens holders, a light source (with crossed arrows),
Geometric Optics. This is a double-convex glass lens mounted in a wooden frame. We will use this as the eyepiece for our microscope.
 I. Before you come to lab Read through this handout in its entirety. II. Learning Objectives As a result of performing this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use the thin lens equation to determine the focal
I. Before you come to lab Read through this handout in its entirety. II. Learning Objectives As a result of performing this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use the thin lens equation to determine the focal
SIMPLE LENSES. To measure the focal lengths of several lens and lens combinations.
 SIMPLE LENSES PURPOSE: To measure the ocal lengths o several lens and lens combinations. EQUIPMENT: Three convex lenses, one concave lens, lamp, image screen, lens holders, meter stick. INTRODUCTION: Combinations
SIMPLE LENSES PURPOSE: To measure the ocal lengths o several lens and lens combinations. EQUIPMENT: Three convex lenses, one concave lens, lamp, image screen, lens holders, meter stick. INTRODUCTION: Combinations
EEEE 381 Electronics I
 EEEE 381 Electrnics I Lab #4: MOSFET Differential Pair with Active Lad Overview The differential amplifier is a fundamental building blck in electrnic design. The bjective f this lab is t examine the vltage
EEEE 381 Electrnics I Lab #4: MOSFET Differential Pair with Active Lad Overview The differential amplifier is a fundamental building blck in electrnic design. The bjective f this lab is t examine the vltage
Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses
 Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses Name Section Introduction. In this lab, you will study converging lenses. There are a number of different types of converging lenses, but all of them are thicker in the middle
Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses Name Section Introduction. In this lab, you will study converging lenses. There are a number of different types of converging lenses, but all of them are thicker in the middle
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
COMP 110 INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING WWW
 COMP 110 INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING WWW http://cmp110www.web.unc.edu Fall 2011 Hmewrk 3 Submissin Deadline: 10:59 AM, Oct 24 Overview Validating Multiple Chess Mves n a Chessbard Fr this assignment yu
COMP 110 INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING WWW http://cmp110www.web.unc.edu Fall 2011 Hmewrk 3 Submissin Deadline: 10:59 AM, Oct 24 Overview Validating Multiple Chess Mves n a Chessbard Fr this assignment yu
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction
 Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: ( ),( )
 Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: (442-462),(482-487) Spherical curved mirrors : a mirror that has the shape of
Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: (442-462),(482-487) Spherical curved mirrors : a mirror that has the shape of
Experiment 7. Thin Lenses. Measure the focal length of a converging lens. Investigate the relationship between power and focal length.
 Experiment 7 Thin Lenses 7.1 Objectives Measure the focal length of a converging lens. Measure the focal length of a diverging lens. Investigate the relationship between power and focal length. 7.2 Introduction
Experiment 7 Thin Lenses 7.1 Objectives Measure the focal length of a converging lens. Measure the focal length of a diverging lens. Investigate the relationship between power and focal length. 7.2 Introduction
Converging and Diverging Surfaces. Lenses. Converging Surface
 Lenses Sandy Skoglund 2 Converging and Diverging s AIR Converging If the surface is convex, it is a converging surface in the sense that the parallel rays bend toward each other after passing through the
Lenses Sandy Skoglund 2 Converging and Diverging s AIR Converging If the surface is convex, it is a converging surface in the sense that the parallel rays bend toward each other after passing through the
Name. Light Chapter Summary Cont d. Refraction
 Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 12(Sem. 2) Name Light Chapter Summary Cont d with a smaller index of refraction to a material with a larger index of refraction, the light refracts towards the normal line. Also,
Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 12(Sem. 2) Name Light Chapter Summary Cont d with a smaller index of refraction to a material with a larger index of refraction, the light refracts towards the normal line. Also,
Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24
 5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
Big Kahuna Assembly Instructions
 Big Kahuna Assembly Instructins Thank yu fr purchasing a d-it-yurself pergla kit frm Average Je s Pergla Dept. We appreciate yur business, and we are here t help yu in any way pssible. Read this entire
Big Kahuna Assembly Instructins Thank yu fr purchasing a d-it-yurself pergla kit frm Average Je s Pergla Dept. We appreciate yur business, and we are here t help yu in any way pssible. Read this entire
KITCHEN FIELD TRIP LESSON PLAN
 KITCHEN FIELD TRIP LESSON PLAN 1/2 3/4 2/16 Grade 4 Mathematics Unit 8 Grade 4 Mathematics (Unit 8) UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION: Hw can yu use mdels t cmpare custmary units f length? Hw can yu use mdels t
KITCHEN FIELD TRIP LESSON PLAN 1/2 3/4 2/16 Grade 4 Mathematics Unit 8 Grade 4 Mathematics (Unit 8) UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION: Hw can yu use mdels t cmpare custmary units f length? Hw can yu use mdels t
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 10 Thin Lenses Name: Lab Partner: Section: 10.1 Purpose In this experiment, the formation of images by concave and convex lenses will be explored. The application of the thin lens equation and
Chapter 10 Thin Lenses Name: Lab Partner: Section: 10.1 Purpose In this experiment, the formation of images by concave and convex lenses will be explored. The application of the thin lens equation and
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE
 TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
1. Give an example of how one can exploit the associative property of convolution to more efficiently filter an image.
 CS 376 Cmputer Visin Spring 2011 Prblem set 1 Out: Tuesday Feb 1 Due: Mnday Feb 14 11:59 PM See the end f this dcument fr submissin instructins. Visit us during ffice hurs t discuss any questins n the
CS 376 Cmputer Visin Spring 2011 Prblem set 1 Out: Tuesday Feb 1 Due: Mnday Feb 14 11:59 PM See the end f this dcument fr submissin instructins. Visit us during ffice hurs t discuss any questins n the
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics EdExcel A Level Physics. Lenses
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES
 Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
Lenses. Optional Reading Stargazer: the life and times of the TELESCOPE, Fred Watson (Da Capo 2004).
 Lenses Equipment optical bench, incandescent light source, laser, No 13 Wratten filter, 3 lens holders, cross arrow, diffuser, white screen, case of lenses etc., vernier calipers, 30 cm ruler, meter stick
Lenses Equipment optical bench, incandescent light source, laser, No 13 Wratten filter, 3 lens holders, cross arrow, diffuser, white screen, case of lenses etc., vernier calipers, 30 cm ruler, meter stick
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Geometric Optics Spring 205 Semester Matthew Jones Sign Conventions > + = Convex surface: is positive for objects on the incident-light side is positive for
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Geometric Optics Spring 205 Semester Matthew Jones Sign Conventions > + = Convex surface: is positive for objects on the incident-light side is positive for
Physics 142 Lenses and Mirrors Page 1. Lenses and Mirrors. Now for the sequence of events, in no particular order. Dan Rather
 Physics 142 Lenses and Mirrors Page 1 Lenses and Mirrors Now or the sequence o events, in no particular order. Dan Rather Overview: making use o the laws o relection and reraction We will now study ormation
Physics 142 Lenses and Mirrors Page 1 Lenses and Mirrors Now or the sequence o events, in no particular order. Dan Rather Overview: making use o the laws o relection and reraction We will now study ormation
A Quick & Dirty Guide to Revising your Novel
 Sz's Revisins, Lessn 4 1 A Quick & Dirty Guide t Revising yur Nvel Lessn 4: Planning the attack. S, yu figured ut what yur Perfect Bk wuld be in Lessn 3. Nw we're ging t take that and apply it t yur nvel.
Sz's Revisins, Lessn 4 1 A Quick & Dirty Guide t Revising yur Nvel Lessn 4: Planning the attack. S, yu figured ut what yur Perfect Bk wuld be in Lessn 3. Nw we're ging t take that and apply it t yur nvel.
Elements and Principles of Design Guided Notes
 Name Perid Date Elements and Principles f Design Guided Ntes DO NOT LOSE THIS PACKET!!! We will be using this packet fr multiple days. Yu will nt get anther packet it yu lse this! Elements & Principles
Name Perid Date Elements and Principles f Design Guided Ntes DO NOT LOSE THIS PACKET!!! We will be using this packet fr multiple days. Yu will nt get anther packet it yu lse this! Elements & Principles
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES 4.2 AIM 4.1 INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
AQA GCSE Physics. Topic 6: Waves. Notes. (Content in bold is for Higher Tier only)
 AQA GCSE Physics Tpic 6: Waves Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Waves Wavelength Amplitude Frequency Perid distance between the same pints n tw cnsecutive waves, distance frm
AQA GCSE Physics Tpic 6: Waves Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Waves Wavelength Amplitude Frequency Perid distance between the same pints n tw cnsecutive waves, distance frm
Physics Worksheet. Topic -Light. Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length.
 Physics Worksheet Topic -Light Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length. (Ans: 10 cm) Q2 Calculate the radius of curvature of spherical mirror whose focal length
Physics Worksheet Topic -Light Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length. (Ans: 10 cm) Q2 Calculate the radius of curvature of spherical mirror whose focal length
Algebra Based Physics. Reflection. Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66. Slide 3 / 66. Slide 4 / 66. Slide 5 / 66. Slide 6 / 66.
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
SINGER FUTURA TM Holiday Banner
 SINGER FUTURA TM Hliday Banner Have fun decking the halls with this festive banner! It s s simple t make the HyperFnt sftware and yur SINGER FUTURA machine. Create the base applique right in yur embridery
SINGER FUTURA TM Hliday Banner Have fun decking the halls with this festive banner! It s s simple t make the HyperFnt sftware and yur SINGER FUTURA machine. Create the base applique right in yur embridery
Appendix D. Photography
 Appendix D Phtgraphy 1 I. Taking Phtgraphs Taking phtgraphs is a required NWCA field activity that prvides an imprtant visual recrd f sampling activities at each site. Phtgraphs are taken with a digital
Appendix D Phtgraphy 1 I. Taking Phtgraphs Taking phtgraphs is a required NWCA field activity that prvides an imprtant visual recrd f sampling activities at each site. Phtgraphs are taken with a digital
Spring 06 Assignment 3: Robot Motion, Game Theory
 15-381 Spring 06 Assignment 3: Rbt Mtin, Game Thery Questins t Rng Yan(yanrng@cs.cmu.edu) Out: 2/21/06 Due: 3/7/06 Name: Andrew ID: Please turn in yur answers n this assignment (etra cpies can be btained
15-381 Spring 06 Assignment 3: Rbt Mtin, Game Thery Questins t Rng Yan(yanrng@cs.cmu.edu) Out: 2/21/06 Due: 3/7/06 Name: Andrew ID: Please turn in yur answers n this assignment (etra cpies can be btained
Banner pocket v3 Page 1/7. Banner pocket v3
 Banner pcket v3 Page 1/7 Banner pcket v3 Descriptin Banner pcket will help yu get the printed sheets arranged in the way yu need fr attaching the frnt and back side pckets tgether. It will crp ne sides
Banner pcket v3 Page 1/7 Banner pcket v3 Descriptin Banner pcket will help yu get the printed sheets arranged in the way yu need fr attaching the frnt and back side pckets tgether. It will crp ne sides
Video. Part I. Equipment
 1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation. Lenses Convex Concave. Mirrors Convex Concave. Optical instruments
 Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation Lenses Convex Concave Mirrors Convex Concave Optical instruments Image formation Laws of refraction and reflection can be used to explain how lenses
Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation Lenses Convex Concave Mirrors Convex Concave Optical instruments Image formation Laws of refraction and reflection can be used to explain how lenses
Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors
 1. Plane mirror: Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors Light reflection: It is rebounding (bouncing) light ray in same direction when meeting reflecting surface. The incident ray: The light ray falls
1. Plane mirror: Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors Light reflection: It is rebounding (bouncing) light ray in same direction when meeting reflecting surface. The incident ray: The light ray falls
PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS. Pre-Lab
 PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS Note: Print and complete the separate pre-lab assignment BEFORE the lab. Hand it in at the start of the lab. Pre-Lab Start by reading the entire prelab and lab write-up.
PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS Note: Print and complete the separate pre-lab assignment BEFORE the lab. Hand it in at the start of the lab. Pre-Lab Start by reading the entire prelab and lab write-up.
