Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Status of Space Segment definition
|
|
|
- Daisy Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Status of Space Segment definition Donny M. Aminou a, D. Lamarre a, Hendrik Stark a, Paul Blythe a Gary Fowler b, S. Gigli b, Rolf Stuhlmann b, Sergio Rota b a European Space Agency, ESTEC, Directorate of the Earth Observation Programmes, Earth Observation Future Programmes Department P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands. b European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) Eumetsat allee 1, D Darmstadt, Germany. ABSTRACT ESA and EUMETSAT have initiated joint preparatory activities for the formulation and definition of the Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) geostationary system to ensure the future continuity, and enhancement, of the current Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) system. The MTG programmatics are being established to ensure a seamless transition between the conclusion of the successful MSG operational system and the start of the new MTG operational system, with particular emphasis on continuity of the imagery missions. The MTG phase A studies were successfully concluded in December 2008 with a subsequent consolidation phase continuing from January to July These studies were devoted to the MTG concept definition and requirements consolidation for meeting the User needs in the field of Nowcasting and Very Short Term Weather Forecasting (NWC), Medium/Short Range global and regional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP), Climate, Air Quality and Composition Monitoring. The following missions have been analysed, measurement techniques studied and preliminary concepts established: - High Resolution Fast Imagery Mission (improved successor to MSG SEVIRI HRV mission) - Full Disk High Spectral Resolution Imagery Mission (improved successor to SEVIRI) - Lightning Imagery Mission - IR Sounding Mission - UV-VIS-NIR Sounding Mission Both space segment architecture and preliminary satellite and instrument concepts were investigated in the course of these studies, and a dual satellite configuration established comprising the Imaging satellite (MTG-I) and the sounding satellite (MTG-S). The study covered all elements to a level of detail allowing to establish a technical baseline, conclude on the feasibility of the system requirements and undertake preliminary programmatic evaluation. Riders to the Phase A studies have been placed to further consolidate the satellite and payload definition and development, prior to the release of the Invitation To Tender (ITT) for the full space segment implementation in July This paper provides an overview of the conclusions of those MTG space segment studies. It summarises the conclusions reached for the satellites, and associated instruments relating to Imaging, IR Sounding and Lightning missions, with respect to achievable performances, including Radiometry and Image Navigation and Registration aspects. Keywords: Meteorology, Meteosat, Imagery, Infrared Sounding, Lightning, NWP, MTG.
2 1. INTRODUCTION The MTG mission capitalises on the continuation and enhancement of the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) capabilities with respect to nowcasting, global and regional numerical weather prediction, climate and atmospheric chemistry monitoring. The MTG system will provide Europe s National Meteorological Services and, by extension, the International Users and Science Community, with an advanced operational satellite system, providing improved imaging and new infrared sounding capabilities for both meteorological and climate applications. This system will facilitate enhanced capabilities for monitoring and prediction of meteorological phenomena and the monitoring of climate and air composition through operational applications for the period of time between 2017 and The objective of the MTG System is to provide continuous high spatial and temporal resolution observations and geophysical parameters of the Earth System derived from direct measurements of its emitted and reflected radiation using satellite based sensors from the geo-stationary orbit. The MTG space segment supports the following payloads and associated missions and services: Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) missions, allowing to scan either the full disc in 16 channels every 10 minutes with a Spatial Sampling Distance (SSD) in the range 1-2km, i.e. Full Disc High Spectral resolution Imagery (FDHSI) in support of the Full Disc Scanning Service (FCI- FDSS) or a quarter of the Earth every 2.5 minutes with 4 channels at improved SSD of km (High spatial Resolution Fast Imagery (HRFI) in support of the Rapid Scanning Service (FCI-RSS). InfraRed Sounding (IRS) mission covering the full disc, providing hyper-spectral sounding information in two bands, a Long Wave InfraRed (LWIR: cm-1) and Mid Wave InfraRed (MWIR: cm-1) band with a SSD = 4 km. Lightning Imagery (LI) mission, detecting continuously over almost the full Earth disc, the lightning discharges taking place in clouds or between cloud and ground with a sampling distance around 10 km. Ultraviolet, Visible & Near-infrared (UVN) sounding mission, covering Europe every hour taking measurements in three spectral bands (UV: nm; VIS: nm, NIR: nm) with SSD of 8 km. The UVN mission is implemented with the GMES Sentinel- 4/UVN payload accommodated in the MTG-S satellites. Search and Rescue (SAR) Relay Service allowing the continuation of the MSG geostationary search and rescue (GEOSAR) service as part of the Cospas-Sarsat international system, whose aim is to provide distress alert and location information to appropriate rescue authorities for maritime, aviation and land users in distress. Data Collection System (DCS) mission which involves, as a continuity of the MSG mission, the collection and transmission of observations and data from surface, buoy, ship, balloon or airborne Data Collection Platforms (DCP). The competition between potential suppliers of the satellites/instruments being still on-going, does not allow in fairness to discuss any design in this paper, constraining us to explain the challenges ahead to meet the end user requirements. This paper addresses an overview of the outcome of the MTG space segment progress accomplished so far in the frame of the phase A and its extension phase (mission needs in terms of payload/satellite). It highlights the requirements evolution for the Imaging and Sounding Missions, shows the status of Image Navigation and Registration (INR) aspects and introduces the progress towards the implementation of the MTG development programme.
3 2. MTG SPACE SEGMENT STATUS TOWARDS THE ITT RELEASE The MTG user requirements have been discussed extensively elsewhere 1-7. In this paper, we will focus only on the updated specifications. The twin configuration, comprising the MTG imaging satellite, called MTG-I, and the MTG sounding satellite, called MTG-S, has been selected and consolidated as baseline. Both MTG-I and MTG-S satellites will be based on a common three-axis stabilised platform.. This platform will be derived from standard geostationary telecommunication bus making maximum use of heritage equipments wherever practicable with the necessary adaptations for the MTG mission. EUMETSAT, in coordination with ESA and industry, have established priorities vis-à-vis of the overall mission. The highest priority being for the Imaging missions (HRFI + FDHSI), which will provide continuity to the current MSG mission. The infrared sounding mission and the lightning imagery mission are the second priority. The UVN instrument, to be embarked on MTG-S will be provided to MTG by the GMES programme. The target date for the operational deployment of the MTG space segment element, ensuring continuity of the the imagery mission, is now end This requires a launch in late 2016 with a one year commissioning phase anticipated for the the new MTG system, including ground and space segments. Figure 1 shows the baseline MTG deployment strategy. This has a direct impact on the envisaged overall mission development and deployment schedule. High mission and satellite reliability and availability are required combined with the nominal and extended mission lifetime for both the MTG-I and MTG-S satellites. Figure 1: MTG mission nominal deployment plan. The payload complement of both MTG-I and MTG-S have been presented in last year papers (6, 7). The imagery mission will consist 4 MTG-I satellites, whereas the sounding mission will be fulfilled with 2 MTG-S satellites. The MTG-I spacecraft will embark the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) and the Lightning Imager (LI) to fulfil the user needs in delivering the imagery services. The selection of a Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) is driven by the end users needs to meet the first two imagery mission requirements. The FCI will be operated in an exclusive way to satisfy either FDHSI or HRFI missions.. Only with 2 satellites can both the Local Area Coverage (LAC) elaborated for the HRFI mission and the Full Disc Coverage (FDC) tailored for the FDHSI mission, be met. It is also required that all the channels are delivered in FDHSI and HRFI for the FCI-FDSS. In addition to the optical payloads, the MTG-I satellite series will embark the Data Collection System (DCS) and Search and Rescue (GEOSAR). For the sounding missions of MTG-S, the users have defined two missions: The Infrared Sounding (IRS) mission focusing on operational meteorology (water vapour tracking & profiling, and temperature profiling), with some relevance to atmospheric chemistry as a secondary application (thanks to the UVN contribution); The UV/VIS/NIR sounding (UVN) mission (also called Sentinel 4) is dedicated to atmospheric chemistry and Air Quality. In combination with the IRS, the UVN mission will complement the atmospheric chemistry mission needed by the users.
4 More discussions are provided in a paper by G. Balzagette (4) from SPIEEurope 2008 conference. The UVN instrument (4) will target its observations in latitude range 30 o N/65 o N, longitude 30 o W/45 o E (at 40 o N), with a repeat cycle of 0.5 hour (goal) / 1 hour (Threshold). A self-standing paper on MTG critical technology pre-developments is presented at the 2009 SPIEEurope conference. For cost efficiency, and risk mitigation, it is envisaged to utilise many of the technologies and equipments developed for commercial telecommunication platforms as the basis for the MTG platform. Several platform concepts have been analysed in the frame the ESA Space Segment Phase A. A dual-wing satellite (see Figure 2) has been selected, ensuring a better balanced configuration in terms of solar panel effective area and centre of solar pressure, despite the drawback of loosing a clear field of view to cold space which could be brought by a single solar array spacecraft.. This decision has been taken primarily due to the simplification of the Attitude Orbit and Control System implementation requiring significantly less reaction wheel off-loading manoeuvres and thus reducing potential disturbances to the satellite pointing stability and risk of associated degradation or outages in mission data. The loss of instrument radiating capabilities will be mitigated by the implementation of active coolers... The target mass for the MTG-I and MTG-S satellite is presently kept to the launch capabilities of Soyuz in Kourou to allow later flexibility in the potential selection of the European launcher, i.e. Ariane 5 or Soyuz.. In addition, both spacecraft will be designed to allow the launch with a nonequatorial launcher, i.e. enabling a super-synchronous transfer into the geostationary orbit if necessary. Cold panel Spacecraft Coordinate System One of the SC axis shall be perpendicular to the Launcher I/F plane. +P sc +X sc +S sc Earth Warm panel +Z sc +Y sc The two other axes shall be within the Launcher I/F plane, (one) perpendicular to a platform panel. +P sc +S sc Cold panel North Warm panel North +P sc +S sc +Y sc +X sc +Z sc +Y sc Yaw equinox +Z sc +X sc Northern Hemisphere Winter Northern Hemisphere Summer Figure 2: MTG dual wing configuration and coordinate system It is planned to use a common bus design for the MTG-I and MTG-S satellites with local adaptations as required per mission. It is expected that the following bus subsystems will be largely common for both satellite types: Structure (separate mechanical interfaces are foreseen for the two payload complements), Thermal (conventional thermal control design envisaged), Attitude and Orbit Control (similar design approach for both satellites), Propulsion (based on a chemical propulsion system),
5 Electrical Power (being modular to adapt the power needs as required per satellite type), Command and Data Handling (similar design envisaged for both satellites with adaptation per satellite), Telemetry, Tracking and Command (heritage of existing conventional S-band systems). Extensive discussions have been carried out between ESA, EUMETSAT and Industries, with the aim at fulfilling the user needs without leading the space system into an over-design, thus avoiding risks and unsustainable cost impacts. For example, it is now agreed that the imagery mission provides data at level 1c (after image rectification) whilst a clear need of having the IRS data at level 1b (before image rectification) has been adopted. For the IRS data delivered at level 1b, ESA has ensured that algorithm delivering IRS data at level 1c is also available for IRS imaging performance assessment. The discussions which focused on the geometric performances took into account image deformations induced by the satellite and instruments pointing, thermo-elastic aspects and micro-vibrations. Thanks to extensive Image Navigation and Registration (INR) simulations, industries were able to provide during phase A and its extension, preliminary analyses including fine modelling of thermo-elastic deformation (minimised by design), correction using observables from star trackers, gyros and landmarks, that allow to consolidate the imagery and sounding achievable geometric performances. The FCI radiometric and spectral requirements remained as presented in referenced papers (6, 7), with the only exception being a relaxation of channel VIS0.8 which central wavelength changed from 860 nm to 865 nm with a bandwidth of 50 nm instead of 70 nm.). For the FCI, the updated spectral channels and their bandwidth requirements are depicted in Table 1. Table 1: Channel specification for the FCI imager. The channels VIS 0.6, NIR 2.2, IR 3.8 and IR 10.5 are delivered in FDHSI spatial sampling and HRFI spatial sampling configurations. The spatial sampling and spectral requirements for the HRFI sampling configuration are indicated by #1. The fire application channels are marked with #2. All other channels are delivered in FDHSI sampling configuration. In total, up to 22 image colours and sampling configurations could be delivered by each image cycle, covering all the needs. In the nominal imaging mode, the FDHSI covers the full Earth disk with a 10 minutes Baseline Repeat Cycle (BRC). Rapid Scan Services (RSS) are provided thanks to coverage equivalent to BRC/n referred to as Local Area Coverage (LAC). The LAC coverage can be variably placed anywhere over the Earth (this shall be taken into account for the scan mechanism qualification). In particular for the FCI, coverage, as depicted in Figure 3, will be used for the RSS. The images will be delivered with the following considerations: Imagery data will now be delivered to the users at level 1c, e.g. after image rectification; Co-registration error is specified at level 1b as knowledge; The end performances are to be determined after image rectification; In-flight absolute and relative image geometric quality of FCI will be assessed after image rectification, so that high accuracy landmark processing can be fully applied;
6 The image quality process will be applied also for the IRS data, only for in-flight performance verification. However, the sounding data will be delivered to the users before rectification. The various data level was fully described in previous papers (3, 5). The radiometric aspects, the number of channels for both the FCI and IRS missions and all other specifications remain unchanged from previous papers (5-7). Figure 3: Example of Rapid Scanning Services for the FCI. One of the challenging requirements of the MTG-I remains the Inter-Channel Co-registration Accuracy (ICRA). The contributors to the ICRA characterisation include at instrument level: - Detectors (spatial response uniformity of each pixel, pitch uniformity, dispersion and alignment) - Optics (relay optics magnification, field distortion, alignment, stray light) - Scan mechanism (actual scan rate and direction, scan rate stability) - Integration (alignment) - Satellite (launch stability, thermal stability, ageing, pointing stability in terms of drift and microvibrations, master-clock jitter). A definition for ICRA was described in the last year s papers (6, 7). The IRS Mission will cover the spectral domain from 700 to 2175 cm -1 at design level (for the sake of simplification at detectors level), but the useful bands (extended bands) will cover the limits depicted in Table 2. Table 2: MTG IRS reference mission bands and required SSD. The IRS instrument will be designed such that the part of extended bands which is not in the specified band is also retrievable. The spectral sampling (Δν) for both IRS bands LWIR and MWIR shall be better or equal to 0.625cm - 1, with FWHM of the instrument line shape to be better than cm -1. To cover the extended bandwidth and meet all the spectral characterisation requirements, it has been agreed to use an Optical Path Difference (OPD) of 8.8 mm, leading to a tighter spectral sampling (0.568 cm -1 ), thus allowing an apodisation function to take care of meeting the FWHM of the ILS (0.754 cm -1 ). The IRS data will, however, be made available to end users, unapodised,. Over the complete spectral bands, resampling to a fixed spectral channel grid common to all spatial samples will be performed on the basis of the spectral calibration algorithm results. For coverage, one of the IRS potential operational scenarios is depicted in Figure 4, allowing interleaved scanning pattern to cover the whole Earth. Similarly to FCI, the IRS will cover the area depicted in Figure 4, down to latitude CD=22 N which may lead to BRC/3 temporal coverage of 20 minutes instead of the classical 15 minutes. Due to the operational nature of MTG, the availability of the observational missions is required to be >96% with a minimum number of operational interventions and limited outages and a reliability (per mission element) of >0.75 eat the end of life. This is applicable during the entire MTG mission lifetime of 20 years. To achieve this it was concluded that each satellite shall be designed with nominal in-orbit lifetime of at least 8.5 years each.
7 Figure 4: MTG IRS operational scenario scanning pattern 3. MTG PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS AND DISCUSSIONS The MTG achievable performances (radiometric and geometric) have been presented in several previous papers (5-7), resulting from phase A analyses. The analyses of the FCI and IRS radiometric performances have always shown promising results. It has been anticipated that most of the requirements will be met with the available technologies. Only the LWIR bands were showing shortage in terms of dark current noise, leading to cooling down to 55K. For the IRS, radiometric requirement can be met with a 60 minutes repeat cycle (full Earth disc coverage). It is shown that photonic noise and ROIC noise are the most dominant noise contributions that are to be carefully handled for any potential improvement. For that the radiometric noise requirement of the IRS has been updated (Figure 5) to cope with limitations due to photonic noise, thus favoring rather feasible technology for simplification purposes. The FCI noise requirement remained the same (#1 indicating HRFI sampling configuration, #2 representing Fire Application). Figure 5: Radiometric noise requirement for FCI and Noise template for IRS. Based on event triggered readout electronics, the LI instrument could be a single camera or a 4-headed camera (on-going trade-off). The instrument will be optimised for capturing events (spatially expanding between less than 10 up to 100 km) at 45 N with a Detection Efficiency of DE 90%, whereas elsewhere on Earth, DE 70% is required, days and nights. With such an instrument, false alarm rate (FAR) of 350 per second could be achieved at raw data level. Thanks to on-ground processing of the data, including background scene tracking and removal, thresholding, event detection at level 1b processing, we expect to achieve a FAR 2 Hz. The level 1b processing will perform filtering of false events, geolocate the lightning, time-tag the samples (UTC convention) and convert to radiances the acquired data by applying pre-launch calibration factors. The navigation of FCI observations will use MSG heritage and GOES-N satellites series lessons learned. The navigation of the LI will be based on images taken (background images) by the LI detecting landmarks wherever clear sky is available, and thanks to star tracking, the LI could navigate
8 properly for geolocating LI detected events. The IRS will use its own imaging capabilities for day and night navigation. The UVN will use both the capabilities of MTG-S satellite navigation capabilities, in addition to its own imaging mode (to be investigated). 4. CONCLUSION The Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) mission will substantially enhance the European capability in operational meteorology and climate applications with the implementation of five observation missions described in this paper. The MTG mission requirements for the space segment have been reviewed and updated in line with achievable performances and remain fully consistent the end user needs. The preliminary work performed on the MTG mission conceptual design has traded-off the possible designs and achievable performances of the 3 main payloads (FCI, LI and IRS) embarked on 3-axis stabilised satellites. The UVN/Sentinel-4 instrument (provided by the GMES programme) will also be embarked on MTG-S satellite series. For each mission and associated instrument concept, trade-off s have been carried out, parametric analysis performed and critical areas identified. Major findings are on the focal plane array technology that is the main development axis to focus on and applicable to both FCI and IRS instruments. Associated cryogenic cooling technoloigies, and related implications at Spacecraft level are also highlighted (namely the accuracy and stability of satellite pointing and its related Image Navigation & Registration). Whilst ESA has launched technology pre-development activities on LWIR detectors and coolers,, the MTG missions present highly challenging performance requirements, which lead to complex optical instruments and overall spacecraft system. The required performances are confirmed by the feasibility studies to be achievable; however substantial effort in technology development is yet necessary to retire all identified risks. The MTG phase A (and its extension) activities included a review of the technical requirements, selection of a system concept, assessment of feasibility and cost estimate and have been concluded successfully. The MTG ITT for phase B2-C/D has been released in July The start of phase B2-C/D activities should commence in early ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The overall concept studies were performed in parallel by two industrial teams led by EADS Astrium GmbH (Germany) and Thales Alenia Space (France) to whom the phase A and B1 contracts were awarded by ESA. The authors would like to thank the MTG team for their contributions to the overall analyses and implementations of the MTG Programme. REFERENCES 1. of Future Programmes/Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) 2. Jean-Loup Bézy, Donny M. A. Aminou, P. Bensi, R. Stuhlmann, S. Tjemkes, A. Rodriguez Meteosat Third Generation: User requirements and Sensors Concept Symposium on Remote Sensing 2004, Denver Colorado. 3. Donny M. Aminou, J.L. Bézy, P. Bensi, R. Stuhlmann, S. Tjemkes, A. Rodriguez Meteosat Third Generation: Preliminary Design of the Imaging Radiometers and Sounding Instruments. Proceedings of SPIE, Europto Series, Vol. 5570, pages 81-92, September G. Bazalgette Courrèges-Lacoste, Marco Arcioni, Yasjka Meijer, Jean-Loup Bézy, Paolo Bensi, Jöerg Langen; ESA contribution to the GMES atmosphere monitoring missions, SPIE Europe 2008, Paper Donny M. Aminou, H. Stark, W. Schumann, R. Stuhlmann, G. Fowler, S. Gigli Meteosat Third Generation: Meteosat Third Generation Phase A Optical Payload Consolidation Proceedings of SPIE, Europto Series, Florence, Italy Donny M. Aminou, H. Stark, W. Schumann, R. Stuhlmann, G. Fowler, S. Gigli, A. Rodriguez Meteosat Third Generation: Meteosat Third Generation: Progress on Space Segment System Feasibility Studies: Payload Aspects. Proceedings of SPIE, Europto Series, Cardiff, Wales Donny M. Aminou, H. Stark, W. Schumann, R. Stuhlmann, G. Fowler, S. Gigli, A. Rodriguez Meteosat Third Generation: Mission Payload Concept at the end of pre-phase A EUMETSAT Meteorological Conference, Darmstadt 2008.
Status of Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Pre-Phase A System Architecture Studies
 Status of Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Pre-Phase A System Architecture Studies Paolo Bensi, Earth Observation Future Programme Department European Space Agency Planning: Meteosat Third Generation (MTG)
Status of Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Pre-Phase A System Architecture Studies Paolo Bensi, Earth Observation Future Programme Department European Space Agency Planning: Meteosat Third Generation (MTG)
Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Lightning Imager (LI) instrument on-ground and in-flight calibration
 Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Lightning Imager (LI) instrument on-ground and in-flight calibration Marcel Dobber, Stephan Kox EUMETSAT (Darmstadt, Germany) 1 Contents of this presentation Meteosat Third
Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Lightning Imager (LI) instrument on-ground and in-flight calibration Marcel Dobber, Stephan Kox EUMETSAT (Darmstadt, Germany) 1 Contents of this presentation Meteosat Third
STATUS OF THE SEVIRI LEVEL 1.5 DATA
 STATUS OF THE SEVIRI LEVEL 1.5 DATA Christopher Hanson (1), Johannes Mueller (1) EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany, Email: hanson@eumetsat.de (2) VEGA IT GmbH, Hilpertstraβe, 20A,
STATUS OF THE SEVIRI LEVEL 1.5 DATA Christopher Hanson (1), Johannes Mueller (1) EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany, Email: hanson@eumetsat.de (2) VEGA IT GmbH, Hilpertstraβe, 20A,
MTG Imager Consolidating Priorities and Open Issues March 2004 at EUMETSAT Darmstadt
 1 st Meteosat Third Generation Mission Team Meeting MTG Imager Consolidating Priorities and Open Issues MTG Mission Team and Invited Experts 8. - 9. March 2004 at EUMETSAT Darmstadt P Based on the assessment
1 st Meteosat Third Generation Mission Team Meeting MTG Imager Consolidating Priorities and Open Issues MTG Mission Team and Invited Experts 8. - 9. March 2004 at EUMETSAT Darmstadt P Based on the assessment
Meteosat Third Generation (MTG): Status and Mechanisms Challenges
 Meteosat Third Generation (MTG): Status and Mechanisms Challenges Donny Aminou European Space Agency ESTEC, Noordwijk Earth Observation Project Department Meteosat Third Generation Programme MTG Payload
Meteosat Third Generation (MTG): Status and Mechanisms Challenges Donny Aminou European Space Agency ESTEC, Noordwijk Earth Observation Project Department Meteosat Third Generation Programme MTG Payload
AMIPAS. Advanced Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmosphere Sounding. Concepts and Technology for Future Atmospheric Chemistry Sensors
 Earth Observation, Navigation & Science Concepts and Technology for Future Atmospheric Chemistry Sensors AMIPAS Advanced Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmosphere Sounding Markus Melf, Winfried Posselt,
Earth Observation, Navigation & Science Concepts and Technology for Future Atmospheric Chemistry Sensors AMIPAS Advanced Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmosphere Sounding Markus Melf, Winfried Posselt,
Industry Day of the Copernicus Sentinel-5 and Jason-CS Projects
 Industry Day of the Copernicus Sentinel-5 and Jason-CS Projects With the present announcement, the European Space Agency and Astrium GmbH Satellites (Germany) inform the EMITS Users (European Companies
Industry Day of the Copernicus Sentinel-5 and Jason-CS Projects With the present announcement, the European Space Agency and Astrium GmbH Satellites (Germany) inform the EMITS Users (European Companies
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014
 Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Spectral and Radiometric characteristics of MTG-IRS. Dorothee Coppens, Bertrand Theodore
 Spectral and Radiometric characteristics of MTG-IRS Dorothee Coppens, Bertrand Theodore 1 ECMWF workshop on Assimilation of Hyper-spectral Geostationary Satellite Observations 22-25 May 2017 Outlines 1)
Spectral and Radiometric characteristics of MTG-IRS Dorothee Coppens, Bertrand Theodore 1 ECMWF workshop on Assimilation of Hyper-spectral Geostationary Satellite Observations 22-25 May 2017 Outlines 1)
MR-i. Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements
 MR-i Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements FT-IR Spectroradiometry Applications Spectroradiometry applications From scientific research to
MR-i Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements FT-IR Spectroradiometry Applications Spectroradiometry applications From scientific research to
Satellite Technology for Future Applications
 Satellite Technology for Future Applications WSRF Panel n 4 Dubai, 3 March 2010 Guy Perez VP Telecom Satellites Programs 1 Commercial in confidence / All rights reserved, 2010, Thales Alenia Space Content
Satellite Technology for Future Applications WSRF Panel n 4 Dubai, 3 March 2010 Guy Perez VP Telecom Satellites Programs 1 Commercial in confidence / All rights reserved, 2010, Thales Alenia Space Content
MR-i. Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements
 MR-i Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements FT-IR Spectroradiometry Applications Spectroradiometry applications From scientific research to
MR-i Hyperspectral Imaging FT-Spectroradiometers Radiometric Accuracy for Infrared Signature Measurements FT-IR Spectroradiometry Applications Spectroradiometry applications From scientific research to
Remote Sensing Platforms
 Types of Platforms Lighter-than-air Remote Sensing Platforms Free floating balloons Restricted by atmospheric conditions Used to acquire meteorological/atmospheric data Blimps/dirigibles Major role - news
Types of Platforms Lighter-than-air Remote Sensing Platforms Free floating balloons Restricted by atmospheric conditions Used to acquire meteorological/atmospheric data Blimps/dirigibles Major role - news
Compact High Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (CHRIS) siraelectro-optics
 Compact High Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (CHRIS) Mike Cutter (Mike_Cutter@siraeo.co.uk) Summary CHRIS Instrument Design Instrument Specification & Performance Operating Modes Calibration Plan Data
Compact High Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (CHRIS) Mike Cutter (Mike_Cutter@siraeo.co.uk) Summary CHRIS Instrument Design Instrument Specification & Performance Operating Modes Calibration Plan Data
METimage an innovative imaging radiometer for Post-EPS
 METimage an innovative imaging radiometer for Post-EPS Dr. Christian Brüns 1, Dr. Matthias Alpers 1, Dr. Alexander Pillukat 2 1 DLR German Space Agency, Königswinterer Straße 522-524, D-53227 Bonn, Germany
METimage an innovative imaging radiometer for Post-EPS Dr. Christian Brüns 1, Dr. Matthias Alpers 1, Dr. Alexander Pillukat 2 1 DLR German Space Agency, Königswinterer Straße 522-524, D-53227 Bonn, Germany
Low Cost Earth Sensor based on Oxygen Airglow
 Assessment Executive Summary Date : 16.06.2008 Page: 1 of 7 Low Cost Earth Sensor based on Oxygen Airglow Executive Summary Prepared by: H. Shea EPFL LMTS herbert.shea@epfl.ch EPFL Lausanne Switzerland
Assessment Executive Summary Date : 16.06.2008 Page: 1 of 7 Low Cost Earth Sensor based on Oxygen Airglow Executive Summary Prepared by: H. Shea EPFL LMTS herbert.shea@epfl.ch EPFL Lausanne Switzerland
AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration
 AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration Jörg Ackermann, Remote Sensing and Products Division 1 Workshop`Radiometric Calibration for European Missions, 30/31 Aug. 2017`,Frascati (EUM/RSP/VWG/17/936014) AVHRR/3
AVHRR/3 Operational Calibration Jörg Ackermann, Remote Sensing and Products Division 1 Workshop`Radiometric Calibration for European Missions, 30/31 Aug. 2017`,Frascati (EUM/RSP/VWG/17/936014) AVHRR/3
Wind Imaging Spectrometer and Humidity-sounder (WISH): a Practical NPOESS P3I High-spatial Resolution Sensor
 Wind Imaging Spectrometer and Humidity-sounder (WISH): a Practical NPOESS P3I High-spatial Resolution Sensor Jeffery J. Puschell Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems, El Segundo, California Hung-Lung Huang
Wind Imaging Spectrometer and Humidity-sounder (WISH): a Practical NPOESS P3I High-spatial Resolution Sensor Jeffery J. Puschell Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems, El Segundo, California Hung-Lung Huang
Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager: A Next Generation GEO Imager for MTSAT-1R
 Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager: A Next Generation GEO Imager for MTSAT-1R Jeffery J. Puschell 1 Raytheon Electronic Systems, Santa Barbara Remote Sensing ABSTRACT The Japanese Advanced Meteorological
Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager: A Next Generation GEO Imager for MTSAT-1R Jeffery J. Puschell 1 Raytheon Electronic Systems, Santa Barbara Remote Sensing ABSTRACT The Japanese Advanced Meteorological
GMES Sentinel-2. The Optical High Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services
 GMES Sentinel-2 The Optical High Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services Philippe Martimort GMES Sentinel-2 Mission and Payload Manager, ESA/ESTEC 15 October 2007, AGRISAR Workshop, Noordwijk
GMES Sentinel-2 The Optical High Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services Philippe Martimort GMES Sentinel-2 Mission and Payload Manager, ESA/ESTEC 15 October 2007, AGRISAR Workshop, Noordwijk
Advanced Meteorological Imager (AMI) Development for GEO-KOMPSAT-2A
 1 st KMA International Meteorological Satellite Conference Advanced Meteorological Imager (AMI) Development for GEO-KOMPSAT-2A 16 November 2015 Koon-Ho YANG Korea Aerospace Research Institute 1 Agenda
1 st KMA International Meteorological Satellite Conference Advanced Meteorological Imager (AMI) Development for GEO-KOMPSAT-2A 16 November 2015 Koon-Ho YANG Korea Aerospace Research Institute 1 Agenda
METimage Calibration & Performance Verification. Xavier Gnata ICSO 2016
 METimage Calibration & Performance Verification Xavier Gnata ICSO 2016 METimage factsheet Mission Passive imaging radiometer (multi-spectral) 20 spectral channels (443 13.345nm) Global coverage within
METimage Calibration & Performance Verification Xavier Gnata ICSO 2016 METimage factsheet Mission Passive imaging radiometer (multi-spectral) 20 spectral channels (443 13.345nm) Global coverage within
Sentinel-2 Products and Algorithms
 Sentinel-2 Products and Algorithms Ferran Gascon (Sentinel-2 Data Quality Manager) Workshop Preparations for Sentinel 2 in Europe, Oslo 26 November 2014 Sentinel-2 Mission Mission Overview Products and
Sentinel-2 Products and Algorithms Ferran Gascon (Sentinel-2 Data Quality Manager) Workshop Preparations for Sentinel 2 in Europe, Oslo 26 November 2014 Sentinel-2 Mission Mission Overview Products and
MicroCarb Mission: A new space instrumental concept based on dispersive components for the measurement of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere
 International Conference on Space Optics 2012 MicroCarb Mission: A new space instrumental concept based on dispersive components for the measurement of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere Véronique PASCAL
International Conference on Space Optics 2012 MicroCarb Mission: A new space instrumental concept based on dispersive components for the measurement of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere Véronique PASCAL
ASSESSMENT BY ESA OF GCOS CLIMATE MONITORING PRINCIPLES FOR GMES
 Prepared by ESA Agenda Item: III.5 Discussed in WG3 ASSESSMENT BY ESA OF GCOS CLIMATE MONITORING PRINCIPLES FOR GMES The ESA Sentinel missions are being designed for the GMES services, with special emphasis
Prepared by ESA Agenda Item: III.5 Discussed in WG3 ASSESSMENT BY ESA OF GCOS CLIMATE MONITORING PRINCIPLES FOR GMES The ESA Sentinel missions are being designed for the GMES services, with special emphasis
THE SPACE TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VEHICLE 2 MEDIUM WAVE INFRA RED IMAGER
 THE SPACE TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VEHICLE 2 MEDIUM WAVE INFRA RED IMAGER S J Cawley, S Murphy, A Willig and P S Godfree Space Department The Defence Evaluation and Research Agency Farnborough United Kingdom
THE SPACE TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VEHICLE 2 MEDIUM WAVE INFRA RED IMAGER S J Cawley, S Murphy, A Willig and P S Godfree Space Department The Defence Evaluation and Research Agency Farnborough United Kingdom
Information furnished in conformity with the Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space
 United Nations Secretariat Distr.: General 9 September 2003 Original: English Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Information furnished in conformity with the Convention on Registration of Objects
United Nations Secretariat Distr.: General 9 September 2003 Original: English Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Information furnished in conformity with the Convention on Registration of Objects
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing. Mads Olander Rasmussen
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
TopSat: Brief to Ground Segment Coordination. Presenter Ian Pilling. By : W.A. Levett. Co author: E.J. Baxter.
 TopSat: Brief to Ground Segment Coordination Board Presenter Ian Pilling By : W.A. Levett Co author: E.J. Baxter Contents Space Division overview The TopSat mission Overview Development Programme Launch
TopSat: Brief to Ground Segment Coordination Board Presenter Ian Pilling By : W.A. Levett Co author: E.J. Baxter Contents Space Division overview The TopSat mission Overview Development Programme Launch
Remote Sensing Platforms
 Remote Sensing Platforms Remote Sensing Platforms - Introduction Allow observer and/or sensor to be above the target/phenomena of interest Two primary categories Aircraft Spacecraft Each type offers different
Remote Sensing Platforms Remote Sensing Platforms - Introduction Allow observer and/or sensor to be above the target/phenomena of interest Two primary categories Aircraft Spacecraft Each type offers different
Cover. DLR-ESA Workshop on ARTES-11. SGEO: Implementation of of Artes-11. Dr. Andreas Winkler
 Cover DLR-ESA Workshop on ARTES-11 SGEO: Implementation of of Artes-11 Dr. Andreas Winkler June June29, 29, 2006 2006 Tegernsee, Tegernsee, Germany Germany Slide 1 Table Table of of Contents - Introduction
Cover DLR-ESA Workshop on ARTES-11 SGEO: Implementation of of Artes-11 Dr. Andreas Winkler June June29, 29, 2006 2006 Tegernsee, Tegernsee, Germany Germany Slide 1 Table Table of of Contents - Introduction
AstroBus S, the high performance and competitive Small Satellites platform for Earth Observation
 AstroBus S, the high performance and competitive Small Satellites platform for Earth Observation Dr. Jean Cheganças 10th IAA Symposium on Small Satellites for Earth Observation April 20-24, 2015 Berlin,
AstroBus S, the high performance and competitive Small Satellites platform for Earth Observation Dr. Jean Cheganças 10th IAA Symposium on Small Satellites for Earth Observation April 20-24, 2015 Berlin,
Status of Air Liquide Space Pulse Tube Cryocoolers
 Status of Air Liquide Space Pulse Tube Cryocoolers T. Trollier, J. Tanchon, J. Buquet and A. Ravex AIR LIQUIDE Advanced Technology Division, AL/DTA Sassenage, France ABSTRACT Air Liquide Advanced Technology
Status of Air Liquide Space Pulse Tube Cryocoolers T. Trollier, J. Tanchon, J. Buquet and A. Ravex AIR LIQUIDE Advanced Technology Division, AL/DTA Sassenage, France ABSTRACT Air Liquide Advanced Technology
EPS Bridge Low-Cost Satellite
 EPS Bridge Low-Cost Satellite Results of a Concept Study being performed for Dr. Hendrik Lübberstedt OHB-System AG OpSE Workshop Walberberg 8th November 2005 EPS Bridge Key System Requirements Minimum
EPS Bridge Low-Cost Satellite Results of a Concept Study being performed for Dr. Hendrik Lübberstedt OHB-System AG OpSE Workshop Walberberg 8th November 2005 EPS Bridge Key System Requirements Minimum
The Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) Mission Status and Early Results
 The Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) Mission Status and Early Results M. C. Edwards (University of Leicester, UK) D. Llewellyn-Jones (University of Leicester, UK) D. L. Smith (Rutherford
The Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) Mission Status and Early Results M. C. Edwards (University of Leicester, UK) D. Llewellyn-Jones (University of Leicester, UK) D. L. Smith (Rutherford
Future Concepts for Galileo SAR & Ground Segment. Executive summary
 Future Concepts for Galileo SAR & Ground Segment TABLE OF CONTENT GALILEO CONTRIBUTION TO THE COSPAS/SARSAT MEOSAR SYSTEM... 3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY... 3 ADDED VALUE OF SAR PROCESSING ON-BOARD G2G SATELLITES...
Future Concepts for Galileo SAR & Ground Segment TABLE OF CONTENT GALILEO CONTRIBUTION TO THE COSPAS/SARSAT MEOSAR SYSTEM... 3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY... 3 ADDED VALUE OF SAR PROCESSING ON-BOARD G2G SATELLITES...
The CarbonSat candidate mission - Radiometric and Spectral Performances over Spatially Heterogeneous Scenes
 The CarbonSat candidate mission - Radiometric and Spectral Performances over Spatially Heterogeneous Scenes J. Caron, B. Sierk, J.-L. Bézy, A. Loescher, Y. Meijer ESA-Estec (Netherlands) Earth Observation
The CarbonSat candidate mission - Radiometric and Spectral Performances over Spatially Heterogeneous Scenes J. Caron, B. Sierk, J.-L. Bézy, A. Loescher, Y. Meijer ESA-Estec (Netherlands) Earth Observation
Mission requirements and satellite overview
 Mission requirements and satellite overview E. BOUSSARIE 1 Dual concept Users need Defence needs Fulfil the Defence needs on confidentiality and security Civilian needs Fulfillment of the different needs
Mission requirements and satellite overview E. BOUSSARIE 1 Dual concept Users need Defence needs Fulfil the Defence needs on confidentiality and security Civilian needs Fulfillment of the different needs
Miguel A. Aguirre. Introduction to Space. Systems. Design and Synthesis. ) Springer
 Miguel A. Aguirre Introduction to Space Systems Design and Synthesis ) Springer Contents Foreword Acknowledgments v vii 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Aim of the book 2 1.2. Roles in the architecture definition
Miguel A. Aguirre Introduction to Space Systems Design and Synthesis ) Springer Contents Foreword Acknowledgments v vii 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Aim of the book 2 1.2. Roles in the architecture definition
INTRODUCTION The validity of dissertation Object of investigation Subject of investigation The purpose: of the tasks The novelty:
 INTRODUCTION The validity of dissertation. According to the federal target program "Maintenance, development and use of the GLONASS system for 2012-2020 years the following challenges were determined:
INTRODUCTION The validity of dissertation. According to the federal target program "Maintenance, development and use of the GLONASS system for 2012-2020 years the following challenges were determined:
Mission Overview. 1 Word & PDF U. Schull Astrium GmbH 1 Word & PDF U. Schäfer Astrium GmbH 1 Word & PDF T. Knigge Astrium GmbH
 DL Mission Overview Distribution List Quantity Type * Name Company / Department 1 PDF J-L. Bezy ESA 1 PDF M. Aguirre ESA 1 PDF F. Gascon ESA 1 Word & PDF U. Schull Astrium GmbH 1 Word & PDF U. Schäfer
DL Mission Overview Distribution List Quantity Type * Name Company / Department 1 PDF J-L. Bezy ESA 1 PDF M. Aguirre ESA 1 PDF F. Gascon ESA 1 Word & PDF U. Schull Astrium GmbH 1 Word & PDF U. Schäfer
The Biomass Mission, status of the satellite system
 The Biomass Mission, status of the satellite system M. Arcioni, P. Bensi, M. Fehringer, F. Fois, F. Heliere, K. Scipal PolInSAR/Biomass Meeting 2015, ESRIN 29/01/2015 1. Key facts (lifetime, duty cycle
The Biomass Mission, status of the satellite system M. Arcioni, P. Bensi, M. Fehringer, F. Fois, F. Heliere, K. Scipal PolInSAR/Biomass Meeting 2015, ESRIN 29/01/2015 1. Key facts (lifetime, duty cycle
Status of the CNES / MicroCarb small
 Status of the CNES / MicroCarb small satellite for CO 2 measurements D. Jouglet on behalf of the MicroCarb team (F. Buisson, D. Pradines, V. Pascal, C. Pierangelo, C. Buil, S. Gaugain, C. Deniel, F.M.
Status of the CNES / MicroCarb small satellite for CO 2 measurements D. Jouglet on behalf of the MicroCarb team (F. Buisson, D. Pradines, V. Pascal, C. Pierangelo, C. Buil, S. Gaugain, C. Deniel, F.M.
OPAL Optical Profiling of the Atmospheric Limb
 OPAL Optical Profiling of the Atmospheric Limb Alan Marchant Chad Fish Erik Stromberg Charles Swenson Jim Peterson OPAL STEADE Mission Storm Time Energy & Dynamics Explorers NASA Mission of Opportunity
OPAL Optical Profiling of the Atmospheric Limb Alan Marchant Chad Fish Erik Stromberg Charles Swenson Jim Peterson OPAL STEADE Mission Storm Time Energy & Dynamics Explorers NASA Mission of Opportunity
Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications
 Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications Cecilia Cappellin, Knud Pontoppidan TICRA Læderstræde 34 1201 Copenhagen Denmark Email:cc@ticra.com, kp@ticra.com
Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications Cecilia Cappellin, Knud Pontoppidan TICRA Læderstræde 34 1201 Copenhagen Denmark Email:cc@ticra.com, kp@ticra.com
1 st IFAC Conference on Mechatronic Systems - Mechatronics 2000, September 18-20, 2000, Darmstadt, Germany
 1 st IFAC Conference on Mechatronic Systems - Mechatronics 2000, September 18-20, 2000, Darmstadt, Germany SPACE APPLICATION OF A SELF-CALIBRATING OPTICAL PROCESSOR FOR HARSH MECHANICAL ENVIRONMENT V.
1 st IFAC Conference on Mechatronic Systems - Mechatronics 2000, September 18-20, 2000, Darmstadt, Germany SPACE APPLICATION OF A SELF-CALIBRATING OPTICAL PROCESSOR FOR HARSH MECHANICAL ENVIRONMENT V.
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites. The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning
 Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
UPDATE ON COMS PROGRAM
 Prepared by KMA Agenda Item: C.2 Discussed in Plenary UPDATE ON COMS PROGRAM This document is to update the COMS program as a part of CGMS-34-WMO-WP-25. Currently, the integration of COMS system has been
Prepared by KMA Agenda Item: C.2 Discussed in Plenary UPDATE ON COMS PROGRAM This document is to update the COMS program as a part of CGMS-34-WMO-WP-25. Currently, the integration of COMS system has been
of the Small Satellite Mission Systematic Image Processing Eckehard Lorenz, DLR Berlin Ilmenau, Klaus Briess, TU Berlin 49th IWK
 Ilmenau, 27.-30.09. 2004 49th IWK Eckehard Lorenz, DLR Berlin Klaus Briess, TU Berlin Astro- und Feinwerktechnik Adlershof GmbH Systematic Image Processing of the Small Satellite Mission BIRD Optical Information
Ilmenau, 27.-30.09. 2004 49th IWK Eckehard Lorenz, DLR Berlin Klaus Briess, TU Berlin Astro- und Feinwerktechnik Adlershof GmbH Systematic Image Processing of the Small Satellite Mission BIRD Optical Information
IMAGING RADIOMETER METimage FOR FUTURE OPERATIONAL EARTH OBSERVATION PLATFORMS IN POLAR ORBITS. Dr. A. Pillukat*, Dr. H.-P. Nothaft**, Dr. C.
 IMAGING RADIOMETER METimage FOR FUTURE OPERATIONAL EARTH OBSERVATION PLATFORMS IN POLAR ORBITS Dr. A. Pillukat*, Dr. H.-P. Nothaft**, Dr. C. Brüns*** * e-mail: alexander.pillukat@jena-optronik.de, phone:
IMAGING RADIOMETER METimage FOR FUTURE OPERATIONAL EARTH OBSERVATION PLATFORMS IN POLAR ORBITS Dr. A. Pillukat*, Dr. H.-P. Nothaft**, Dr. C. Brüns*** * e-mail: alexander.pillukat@jena-optronik.de, phone:
ESA Human Spaceflight Capability Development and Future Perspectives International Lunar Conference September Toronto, Canada
 ESA Human Spaceflight Capability Development and Future Perspectives International Lunar Conference 2005 19-23 September Toronto, Canada Scott Hovland Head of Systems Unit, System and Strategy Division,
ESA Human Spaceflight Capability Development and Future Perspectives International Lunar Conference 2005 19-23 September Toronto, Canada Scott Hovland Head of Systems Unit, System and Strategy Division,
Chapter 8. Remote sensing
 1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
Sensor Technologies and Sensor Materials for Small Satellite Missions related to Disaster Management CANEUS Indo-US Cooperation
 Sensor Technologies and Sensor Materials for Small Satellite Missions related to Disaster Management CANEUS Indo-US Cooperation Suraj Rawal, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Co., USA G. Mohan Rao, Indian
Sensor Technologies and Sensor Materials for Small Satellite Missions related to Disaster Management CANEUS Indo-US Cooperation Suraj Rawal, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Co., USA G. Mohan Rao, Indian
Geospatial Vision and Policies Korean Industry View 26 November, 2014 SI Imaging Services
 Geospatial Vision and Policies Korean Industry View 26 November, 2014 SI Imaging Services Distribution Limitation, SI Imaging Services Proprietary Data : The data contained in this document, without the
Geospatial Vision and Policies Korean Industry View 26 November, 2014 SI Imaging Services Distribution Limitation, SI Imaging Services Proprietary Data : The data contained in this document, without the
GEO-OCULUS: A MISSION FOR REAL-TIME MONITORING THROUGH HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGING FROM GEOSTATIONARY ORBIT
 GEO-OCULUS: A MISSION FOR REAL-TIME MONITORING THROUGH HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGING FROM GEOSTATIONARY ORBIT Ulrich Schull, Thiemo Knigge Astrium GmbH, 88039 Friedrichshafen, Germany Contact: Ulrich Schull;
GEO-OCULUS: A MISSION FOR REAL-TIME MONITORING THROUGH HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGING FROM GEOSTATIONARY ORBIT Ulrich Schull, Thiemo Knigge Astrium GmbH, 88039 Friedrichshafen, Germany Contact: Ulrich Schull;
Cross Track Infrared Sounder (CrIS) Flight Model 1 Test Results
 May 6, 2009 Ronald Glumb, Joseph P. Predina, Robert Hookman, Chris Ellsworth, John Bobilya, Steve Wells, Lawrence Suwinski, Rebecca Frain, and Larry Crawford For Publication at the ASS-FTS14 Conference
May 6, 2009 Ronald Glumb, Joseph P. Predina, Robert Hookman, Chris Ellsworth, John Bobilya, Steve Wells, Lawrence Suwinski, Rebecca Frain, and Larry Crawford For Publication at the ASS-FTS14 Conference
detected by Himawari-8 then the location will be uplinked to approaching Cubesats as an urgent location for medium resolution imaging.
 Title: Cubesat constellation for monitoring and detection of bushfires in Australia Primary Point of Contact (POC) & email: siddharth.doshi2@gmail.com Co-authors: Siddharth Doshi, David Lam, Himmat Panag
Title: Cubesat constellation for monitoring and detection of bushfires in Australia Primary Point of Contact (POC) & email: siddharth.doshi2@gmail.com Co-authors: Siddharth Doshi, David Lam, Himmat Panag
General Support Technology Programme (GSTP) Period 6 Element 3: Technology Flight Opportunities (TFO)
 General Support Technology Programme (GSTP) Period 6 Element 3: Technology Flight Opportunities (TFO) Open Call for Technology Flight Demonstrators and Carrier Flight Opportunities Introduction The Agency
General Support Technology Programme (GSTP) Period 6 Element 3: Technology Flight Opportunities (TFO) Open Call for Technology Flight Demonstrators and Carrier Flight Opportunities Introduction The Agency
ARTES Competitiveness & Growth Full Proposal. Requirements for the Content of the Technical Proposal
 ARTES Competitiveness & Growth Full Proposal Requirements for the Content of the Technical Proposal Part 3C (DDVP) Statement of Applicability and Proposal Submission Requirements Applicable Domain(s) Space
ARTES Competitiveness & Growth Full Proposal Requirements for the Content of the Technical Proposal Part 3C (DDVP) Statement of Applicability and Proposal Submission Requirements Applicable Domain(s) Space
Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager
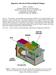 Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager Jeffery J. Puschell Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems 2000 East El Segundo Boulevard, EO/E01/C150 El Segundo, CA 90245-0902 UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Abstract:
Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager Jeffery J. Puschell Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems 2000 East El Segundo Boulevard, EO/E01/C150 El Segundo, CA 90245-0902 UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Abstract:
The Sentinel-1 Constellation
 The Sentinel-1 Constellation Evert Attema, Sentinel-1 Mission & System Manager AGRISAR and EAGLE Campaigns Final Workshop 15-16 October 2007 ESA/ESTECNoordwijk, The Netherlands Sentinel-1 Programme Sentinel-1
The Sentinel-1 Constellation Evert Attema, Sentinel-1 Mission & System Manager AGRISAR and EAGLE Campaigns Final Workshop 15-16 October 2007 ESA/ESTECNoordwijk, The Netherlands Sentinel-1 Programme Sentinel-1
Polar Communications & Weather (PCW) Mission. Guennadi Kroupnik, Canadian Space Agency
 Polar Communications & Weather (PCW) Mission Guennadi Kroupnik, Canadian Space Agency Mission Objectives Reliable communications and navigations services in the high latitudes (North of 70º) to ensure:
Polar Communications & Weather (PCW) Mission Guennadi Kroupnik, Canadian Space Agency Mission Objectives Reliable communications and navigations services in the high latitudes (North of 70º) to ensure:
A SYNERGETIC USE OF REMOTE-SENSED DATA TO ASSESS THE EVOLUTION OF BURNT AREA BY WILDFIRES IN PORTUGAL
 A SYNERGETIC USE OF REMOTE-SENSED DATA TO ASSESS THE EVOLUTION OF BURNT AREA BY WILDFIRES IN PORTUGAL Teresa J. Calado and Carlos C. DaCamara CGUL, Faculty of Sciences, University of Lisbon, Campo Grande,
A SYNERGETIC USE OF REMOTE-SENSED DATA TO ASSESS THE EVOLUTION OF BURNT AREA BY WILDFIRES IN PORTUGAL Teresa J. Calado and Carlos C. DaCamara CGUL, Faculty of Sciences, University of Lisbon, Campo Grande,
CGMS-37, NOAA-WP-33 Prepared by NOAA Agenda Item: IV/1 Discussed in WG IV
 Prepared by NOAA Agenda Item: IV/1 Discussed in WG IV NOAA-WP-33 provides a status of its Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite Series R (GOES-R). and polar-orbiting satellite constellations.
Prepared by NOAA Agenda Item: IV/1 Discussed in WG IV NOAA-WP-33 provides a status of its Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite Series R (GOES-R). and polar-orbiting satellite constellations.
ESA UNCLASSIFIED - Releasable to the Public. ESA Workshop: Research Opportunities on the Deep Space Gateway
 ESA Workshop: Research Opportunities on the Deep Space Gateway Prepared by James Carpenter Reference ESA-HSO-K-AR-0000 Issue/Revision 1.1 Date of Issue 27/07/2017 Status Issued CHANGE LOG ESA Workshop:
ESA Workshop: Research Opportunities on the Deep Space Gateway Prepared by James Carpenter Reference ESA-HSO-K-AR-0000 Issue/Revision 1.1 Date of Issue 27/07/2017 Status Issued CHANGE LOG ESA Workshop:
RECONNAISSANCE PAYLOADS FOR RESPONSIVE SPACE
 3rd Responsive Space Conference RS3-2005-5004 RECONNAISSANCE PAYLOADS FOR RESPONSIVE SPACE Charles Cox Stanley Kishner Richard Whittlesey Goodrich Optical and Space Systems Division Danbury, CT Frederick
3rd Responsive Space Conference RS3-2005-5004 RECONNAISSANCE PAYLOADS FOR RESPONSIVE SPACE Charles Cox Stanley Kishner Richard Whittlesey Goodrich Optical and Space Systems Division Danbury, CT Frederick
PROPOSAL FOR A NEW HYPER SPECTRAL IMAGING MICRO SATELLITE: SVALBIRD
 PROPOSAL FOR A NEW HYPER SPECTRAL IMAGING MICRO SATELLITE: SVALBIRD Fred Sigernes 1, Udo Renner 2, Stephan Roemer 2, Jörn-Hendrik Bleif 2, Dag Arne Lorentzen 1, Stefan Claes 1, Reidar Nordheim 3, Frank
PROPOSAL FOR A NEW HYPER SPECTRAL IMAGING MICRO SATELLITE: SVALBIRD Fred Sigernes 1, Udo Renner 2, Stephan Roemer 2, Jörn-Hendrik Bleif 2, Dag Arne Lorentzen 1, Stefan Claes 1, Reidar Nordheim 3, Frank
Galileo Programme Update
 Galileo Programme Update Pieter De Smet, European Commission ICTP Conference, Prague, 10 November, 2014 1 December 2014 The European GNSS Programmes 2 Secure Foundations ü A stable 7 years perspective
Galileo Programme Update Pieter De Smet, European Commission ICTP Conference, Prague, 10 November, 2014 1 December 2014 The European GNSS Programmes 2 Secure Foundations ü A stable 7 years perspective
P1.53 ENHANCING THE GEOSTATIONARY LIGHTNING MAPPER FOR IMPROVED PERFORMANCE
 P1.53 ENHANCING THE GEOSTATIONARY LIGHTNING MAPPER FOR IMPROVED PERFORMANCE David B. Johnson * Research Applications Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.53 ENHANCING THE GEOSTATIONARY LIGHTNING MAPPER FOR IMPROVED PERFORMANCE David B. Johnson * Research Applications Laboratory National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
SOME ASPECT AND PERSPECTIVES OF IMPLEMENTATION OF THE NATIONAL POLICY IN THE FIELD OF EXPLORATION AND PEACEFUL USES OF OUTER SPACE
 SOME ASPECT AND PERSPECTIVES OF IMPLEMENTATION OF THE NATIONAL POLICY IN THE FIELD OF EXPLORATION AND PEACEFUL USES OF OUTER SPACE 1 Folie 1 NKS Raumfahrt, Dr. Adrian klein Background National Academy
SOME ASPECT AND PERSPECTIVES OF IMPLEMENTATION OF THE NATIONAL POLICY IN THE FIELD OF EXPLORATION AND PEACEFUL USES OF OUTER SPACE 1 Folie 1 NKS Raumfahrt, Dr. Adrian klein Background National Academy
PLATO Preliminary Requirements Review Technical Report
 PLATO Preliminary Requirements Review Technical Report Prepared by Review Team Reference SRE-F/2013.075/ Issue 1 Revision 1 Date of Issue 16/12/2013 Status Issued Document Type Distribution Title Issue
PLATO Preliminary Requirements Review Technical Report Prepared by Review Team Reference SRE-F/2013.075/ Issue 1 Revision 1 Date of Issue 16/12/2013 Status Issued Document Type Distribution Title Issue
The Sounding Instruments on Second Generation of Chinese Meteorological Satellite FY-3
 The Sounding Instruments on Second Generation of Chinese Meteorological Satellite FY-3 DONG Chaohua ZHANG Wenjian National Satellite Meteorological Center China Meteorological Administration Beijing 100081,
The Sounding Instruments on Second Generation of Chinese Meteorological Satellite FY-3 DONG Chaohua ZHANG Wenjian National Satellite Meteorological Center China Meteorological Administration Beijing 100081,
THE OFFICINE GALILEO DIGITAL SUN SENSOR
 THE OFFICINE GALILEO DIGITAL SUN SENSOR Franco BOLDRINI, Elisabetta MONNINI Officine Galileo B.U. Spazio- Firenze Plant - An Alenia Difesa/Finmeccanica S.p.A. Company Via A. Einstein 35, 50013 Campi Bisenzio
THE OFFICINE GALILEO DIGITAL SUN SENSOR Franco BOLDRINI, Elisabetta MONNINI Officine Galileo B.U. Spazio- Firenze Plant - An Alenia Difesa/Finmeccanica S.p.A. Company Via A. Einstein 35, 50013 Campi Bisenzio
EARTH OBSERVATION WITH SMALL SATELLITES
 EARTH OBSERVATION WITH SMALL SATELLITES AT THE FUCHS-GRUPPE B. Penné, C. Tobehn, M. Kassebom, H. Lübberstedt OHB-System GmbH, Universitätsallee 27-29, D-28359 Bremen, Germany www.fuchs-gruppe.com ABSTRACT
EARTH OBSERVATION WITH SMALL SATELLITES AT THE FUCHS-GRUPPE B. Penné, C. Tobehn, M. Kassebom, H. Lübberstedt OHB-System GmbH, Universitätsallee 27-29, D-28359 Bremen, Germany www.fuchs-gruppe.com ABSTRACT
Comprehensive Vicarious Calibration and Characterization of a Small Satellite Constellation Using the Specular Array Calibration (SPARC) Method
 This document does not contain technology or Technical Data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations. Comprehensive Vicarious
This document does not contain technology or Technical Data controlled under either the U.S. International Traffic in Arms Regulations or the U.S. Export Administration Regulations. Comprehensive Vicarious
CIRiS: Compact Infrared Radiometer in Space August, 2017
 1 CIRiS: Compact Infrared Radiometer in Space August, 2017 David Osterman PI, CIRiS Mission Presented by Hansford Cutlip 10/8/201 7 Overview of the CIRiS instrument and mission The CIRiS instrument is
1 CIRiS: Compact Infrared Radiometer in Space August, 2017 David Osterman PI, CIRiS Mission Presented by Hansford Cutlip 10/8/201 7 Overview of the CIRiS instrument and mission The CIRiS instrument is
remote sensing? What are the remote sensing principles behind these Definition
 Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
Airbus DS ESA Phase-0 L5 Spacecraft/Orbital Concept Overview. Emanuele Monchieri 6 th March 2017
 Airbus DS ESA Phase-0 L5 Spacecraft/Orbital Concept Overview Emanuele Monchieri 6 th March 2017 Airbus DS ESA Phase-0 L5 Spacecraft/Orbital Concept Overview Contents L5 Mission Outline Mission Concept
Airbus DS ESA Phase-0 L5 Spacecraft/Orbital Concept Overview Emanuele Monchieri 6 th March 2017 Airbus DS ESA Phase-0 L5 Spacecraft/Orbital Concept Overview Contents L5 Mission Outline Mission Concept
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS
 Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS. Introduction
 An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
P5.15 ADDRESSING SPECTRAL GAPS WHEN USING AIRS FOR INTERCALIBRATION OF OPERATIONAL GEOSTATIONARY IMAGERS
 P5.15 ADDRESSING SPECTRAL GAPS WHEN USING AIRS FOR INTERCALIBRATION OF OPERATIONAL GEOSTATIONARY IMAGERS Mathew M. Gunshor 1*, Kevin Le Morzadec 2, Timothy J. Schmit 3, W. P. Menzel 4, and David Tobin
P5.15 ADDRESSING SPECTRAL GAPS WHEN USING AIRS FOR INTERCALIBRATION OF OPERATIONAL GEOSTATIONARY IMAGERS Mathew M. Gunshor 1*, Kevin Le Morzadec 2, Timothy J. Schmit 3, W. P. Menzel 4, and David Tobin
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural
 The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural Luxembourg, 12.03.2014 r. Tomasz Milewski NUTS for Poland: NUTS 1 macro-regions (grup of province, voivodships) (6), NUTS 2 - regions (province,
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural Luxembourg, 12.03.2014 r. Tomasz Milewski NUTS for Poland: NUTS 1 macro-regions (grup of province, voivodships) (6), NUTS 2 - regions (province,
Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors
 Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors S. Roose, A. Cucchiaro & D. de Chambure* Centre Spatial de Liège, Avenue du Pré-Aily, B-4031 Angleur-Liège, Belgium *ESTEC, Planck project, Keplerlaan
Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors S. Roose, A. Cucchiaro & D. de Chambure* Centre Spatial de Liège, Avenue du Pré-Aily, B-4031 Angleur-Liège, Belgium *ESTEC, Planck project, Keplerlaan
Large format 17µm high-end VOx µ-bolometer infrared detector
 Large format 17µm high-end VOx µ-bolometer infrared detector U. Mizrahi, N. Argaman, S. Elkind, A. Giladi, Y. Hirsh, M. Labilov, I. Pivnik, N. Shiloah, M. Singer, A. Tuito*, M. Ben-Ezra*, I. Shtrichman
Large format 17µm high-end VOx µ-bolometer infrared detector U. Mizrahi, N. Argaman, S. Elkind, A. Giladi, Y. Hirsh, M. Labilov, I. Pivnik, N. Shiloah, M. Singer, A. Tuito*, M. Ben-Ezra*, I. Shtrichman
UNCLASSIFIED R-1 ITEM NOMENCLATURE FY 2013 OCO
 Exhibit R-2, RDT&E Budget Item Justification: PB 2013 Air Force DATE: February 2012 BA 3: Advanced Development (ATD) COST ($ in Millions) Program Element 75.103 74.009 64.557-64.557 61.690 67.075 54.973
Exhibit R-2, RDT&E Budget Item Justification: PB 2013 Air Force DATE: February 2012 BA 3: Advanced Development (ATD) COST ($ in Millions) Program Element 75.103 74.009 64.557-64.557 61.690 67.075 54.973
1. INTRODUCTION. GOCI : Geostationary Ocean Color Imager
 1. INTRODUCTION The Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute (KORDI) releases an announcement of opportunity (AO) to carry out scientific research for the utilization of GOCI data. GOCI is the world
1. INTRODUCTION The Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute (KORDI) releases an announcement of opportunity (AO) to carry out scientific research for the utilization of GOCI data. GOCI is the world
OVERVIEW OF THE ALOS SATELLITE SYSTEM
 OVERVIEW OF THE ALOS SATELLITE SYSTEM Presented to The Symposium for ALOS Data Application Users @Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan Mar. 27, 2001 Takashi Hamazaki Senior Engineer ALOS Project National
OVERVIEW OF THE ALOS SATELLITE SYSTEM Presented to The Symposium for ALOS Data Application Users @Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan Mar. 27, 2001 Takashi Hamazaki Senior Engineer ALOS Project National
Part I. The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing
 Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
Hyperspectral goes to UAV and thermal
 Hyperspectral goes to UAV and thermal Timo Hyvärinen, Hannu Holma and Esko Herrala SPECIM, Spectral Imaging Ltd, Finland www.specim.fi Outline Roadmap to more compact, higher performance hyperspectral
Hyperspectral goes to UAV and thermal Timo Hyvärinen, Hannu Holma and Esko Herrala SPECIM, Spectral Imaging Ltd, Finland www.specim.fi Outline Roadmap to more compact, higher performance hyperspectral
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
 QuikSCAT Mission Status QuikSCAT Follow-on Mission 2 QuikSCAT instrument and spacecraft are healthy, but aging June 19, 2009 will be the 10 year launch anniversary We ve had two significant anomalies during
QuikSCAT Mission Status QuikSCAT Follow-on Mission 2 QuikSCAT instrument and spacecraft are healthy, but aging June 19, 2009 will be the 10 year launch anniversary We ve had two significant anomalies during
Greg Mandt. AMS 90 th Annual Meeting 6th Annual Symposium on Future National Operational Environmental Satellite Systems NPOESS and GOES R
 An Overview of the GOES R Program Greg Mandt System Program Director AMS 90 th Annual Meeting 6th Annual Symposium on Future National Operational Environmental Satellite Systems NPOESS and GOES R January19
An Overview of the GOES R Program Greg Mandt System Program Director AMS 90 th Annual Meeting 6th Annual Symposium on Future National Operational Environmental Satellite Systems NPOESS and GOES R January19
Leveraging Commercial Communication Satellites to support the Space Situational Awareness Mission Area. Timothy L. Deaver Americom Government Services
 Leveraging Commercial Communication Satellites to support the Space Situational Awareness Mission Area Timothy L. Deaver Americom Government Services ABSTRACT The majority of USSTRATCOM detect and track
Leveraging Commercial Communication Satellites to support the Space Situational Awareness Mission Area Timothy L. Deaver Americom Government Services ABSTRACT The majority of USSTRATCOM detect and track
GEOMETRIC RECTIFICATION OF EUROPEAN HISTORICAL ARCHIVES OF LANDSAT 1-3 MSS IMAGERY
 GEOMETRIC RECTIFICATION OF EUROPEAN HISTORICAL ARCHIVES OF LANDSAT -3 MSS IMAGERY Torbjörn Westin Satellus AB P.O.Box 427, SE-74 Solna, Sweden tw@ssc.se KEYWORDS: Landsat, MSS, rectification, orbital model
GEOMETRIC RECTIFICATION OF EUROPEAN HISTORICAL ARCHIVES OF LANDSAT -3 MSS IMAGERY Torbjörn Westin Satellus AB P.O.Box 427, SE-74 Solna, Sweden tw@ssc.se KEYWORDS: Landsat, MSS, rectification, orbital model
Performance status of IASI on MetOp-A and MetOp-B
 Performance status of IASI on MetOp-A and MetOp-B E. Jacquette (1), E. Péquignot (1), J. Chinaud (1), C. Maraldi (1), D. Jouglet (1), S. Gaugain (1), L. Buffet (1), C. Villaret (1), C. Larigauderie (1),
Performance status of IASI on MetOp-A and MetOp-B E. Jacquette (1), E. Péquignot (1), J. Chinaud (1), C. Maraldi (1), D. Jouglet (1), S. Gaugain (1), L. Buffet (1), C. Villaret (1), C. Larigauderie (1),
NASTER System Definition Proposal
 Remote Sensing Team NASTER System Definition Proposal All rights reserved. - 7/14/03 Page 1 Overview Review and comment the mid-ir requirements Presentation of ABB s current platform technology Proposed
Remote Sensing Team NASTER System Definition Proposal All rights reserved. - 7/14/03 Page 1 Overview Review and comment the mid-ir requirements Presentation of ABB s current platform technology Proposed
EGS-CC. System Engineering Team. Commonality of Ground Systems. Executive Summary
 System Engineering Team Prepared: System Engineering Team Date: Approved: System Engineering Team Leader Date: Authorized: Steering Board Date: Restriction of Disclosure: The copyright of this document
System Engineering Team Prepared: System Engineering Team Date: Approved: System Engineering Team Leader Date: Authorized: Steering Board Date: Restriction of Disclosure: The copyright of this document
CAL/VAL ACTIVITIES IN ROSHYDROMET. GSICS Executive Panel 14, Tokyo, 15 July. 2013
 CAL/VAL ACTIVITIES IN ROSHYDROMET GSICS Executive Panel 14, Tokyo, 15 July. 2013 Future CAL/VAL system deployment in Roshydromet Roshydromet has started the deployment of ground-based calibration/validation
CAL/VAL ACTIVITIES IN ROSHYDROMET GSICS Executive Panel 14, Tokyo, 15 July. 2013 Future CAL/VAL system deployment in Roshydromet Roshydromet has started the deployment of ground-based calibration/validation
CubeSat Integration into the Space Situational Awareness Architecture
 CubeSat Integration into the Space Situational Awareness Architecture Keith Morris, Chris Rice, Mark Wolfson Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company 12257 S. Wadsworth Blvd. Mailstop S6040 Littleton, CO
CubeSat Integration into the Space Situational Awareness Architecture Keith Morris, Chris Rice, Mark Wolfson Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company 12257 S. Wadsworth Blvd. Mailstop S6040 Littleton, CO
NASA s X2000 Program - an Institutional Approach to Enabling Smaller Spacecraft
 NASA s X2000 Program - an Institutional Approach to Enabling Smaller Spacecraft Dr. Leslie J. Deutsch and Chris Salvo Advanced Flight Systems Program Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
NASA s X2000 Program - an Institutional Approach to Enabling Smaller Spacecraft Dr. Leslie J. Deutsch and Chris Salvo Advanced Flight Systems Program Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
The EU Satellite Navigation programmes status Applications for the CAP
 The EU Satellite Navigation programmes status Applications for the CAP Michaël MASTIER European Commission DG ENTR GP3 GNSS Applications, Security and International aspects GPS Workshop 2010 Montpellier
The EU Satellite Navigation programmes status Applications for the CAP Michaël MASTIER European Commission DG ENTR GP3 GNSS Applications, Security and International aspects GPS Workshop 2010 Montpellier
