Color Theory. Chapter 2 Color Basics
|
|
|
- Edmund Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Color Basics Color Theory Intrinsic Value Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Strict vs. Chromatic Neutral, Tint, Shade, Tone Analogous/Adjacent Local vs. Atmospheric Clr Color & temperature Pigment vs. Light Primaries Surface qualities Transparency/alpha
2 Last Class: Color is fundamentally? Visible light is only one portion of? From a physics/physical point of view, red is different from green due to? Rainbows and sunsets are largely due to what light-color phenomena? White light is?
3 Three dimensions of color Just as a point is space can be defined by is position in the three special dimensions (height, width, depth), color also has its own three dimensions. Any single color can be described by its three dimensions. Hue Chroma Value
4 For Next Class: Read from Text: p (Color Mixing) Read from The Acrylic Book ; p (see syllabus for web link to PDF) ylicbook.pdf Have painting supplies here.
5 Basic terms & concepts: Color as light The visible spectrum wavelengths White light Reflection, Transmission, Absorption, Refraction Additive Color vs. Subtractive Color Light Primaries vs. Pigment Primaries
6 Color as Light Every color you have ever seen was due to colored light. Your eye sees only light never the surface, never a pigment, paint or dye, and never the object. The nerves at the back of our eye are photosensors they respond to light. Since we see light, but we most often mix pigment in paint, or ink, or dyes we must understand both color as light and color as pigment. That is, we must understand additive color (light) and subtractive color (pigment)
7 Visible light spectrum
8 White-Light to Colored objects/surfaces: Absorption is the main way that materials become colored subtracting some colors from white light, and either reflecting or transmitting colored light.
9 Three dimensions of color - Munsell s color model
10 Intrinsic Value or Natural Value Every hue has its own intrinsic value. This is the value of the undiluted hue at full chroma. In practical terms, think of the strait from the tube color yellow is very light in value, violet is very dark in value, blue and red are middle values.
11 Intrinsic Value or Natural Value red red-violet blue blue-violet violet
12 Color/Pigment Value Chart
13 Intrinsic Value: each hue has its own native territory of value.
14 Intrinsic Value: each hue has its own native territory of value.
15 Subtractive Primaries, Secondaries, Tertiaries Primaries (3) R, Y, B Secondaries Tertiaries
16 Secondary Color In theory, a hue that is mixed by equal proportions of two (adjacent) primary colors. In traditional color mixing, there are three secondary colors however, there will be as many secondary colors in a color model as there are primary colors.
17 Subtractive Primaries, Secondaries, Tertiaries Primaries Secondaries (3) G, O, V Tertiaries
18 Tertiary Color In theory, a hue that is mixed by equal proportions of a primary color and an adjacent secondary color. In traditional color mixing, there are six tertiary colors however, there will be as many tertiary colors in a color model as there are primary AND secondary colors, combined.
19 Subtractive Primaries, Secondaries, Tertiaries Primaries Secondaries Tertiaries (6) YO, RO, RV, BV, BG, YG
20 Neutral Color A neutral is a color that has no chroma so it has no discernable hue at all. True neutrals are black, white and the grays. In practice, we refer to many colors as neutrals when their chroma is quite low browns, along with warm and cool grays are usually called neutrals though, strictly speaking, they are near-neutrals.
21 Strict vs. Near Neutrals (Chromatic Neutrals) We will speak of strict neutrals or true neutrals when referring to grays that have no hue whatsoever. But when speaking of neutrals, we will often include near neutrals, the browns and near-grays.
22 Neutrals vs. Chromatic Hues True Neutrals have no chroma, or zero- Chroma. Near-neutrals have very little chroma. Chromatic hues are the opposite they have higher chroma (more color, higher saturation, a more apparent hue)
23 Tint A high-value form of a hue. In practice, a tint is a color that has had white added to it. For instance, pink is a tint of red. A pure, primary red might be mixed with white. The result is a light red a tint of red. +
24 Constant Hue Charts
25 Shade A low-value form of a hue. In practice, a color that has had black added to it. Maroon is a shade of red a pure, primary red might be mixed with black (or dark brown, or dark gray). The result is a dark red a shade of red. +
26 Warm and Cool Colors Warms: reds, yellows, oranges -- fire colors. Cool: blues, violets, some greens. Note that every color is warm compared to some colors and cool compared to others. Temperature is relative to surroundings.
27 Adjacent (or Analogous) Hues that are near each other on a color wheel. Colors that are similar in hue. Colors that have some dominant hue in common.
28 Complementary Hues that are opposite each other on a color wheel. Note that there are several color wheels or color models. Precise complementary pairs differ according to the color model. In general, complementary hues are as different as hues can be -- and so offer a powerful visual contrast for design purposes.
29 Local Color vs. Atmospheric Color Local Color is the color of a surface, material, fabric, or light source under ideal white light and undisturbed viewing conditions. Atmospheric Color is the color that a surface, material, etc. appears to be due to lighting conditions, atmospheric mist and dust, and distance.
30 Local Color surface color. The local color of this bathtub is White. This is the color that a surface is under perfectly balanced white light, with no glare, no shadows, and no mist, fog or smoke obscuring our view. Local color is the color of the surface itself undisturbed by atmosphere and irregular lighting..
31 Atmospheric Color: Local Color altered by light/shadow, etc. For the interior designer, especially, local color (swatches and paint samples, for instance) are only a part of the color planning lighting is the other essential component of color design. Lighting conditions always alter the appearance of local color.
32 Atmospheric Color: Local Color altered by light/shadow, etc. Question: What color is the Ferrari? Answer: lots of colors. (modeling/angles of surfaces with respect to light source, and reflected sky/environment influence color.) What is the local color of the Ferrari? Answer: Red. (hue: Red, value: middle/5, chroma: high)
33 Atmospheric Color The color a surface appears to be when lighting, shadows, fog or mist and other moderating factors are taken into account.
34 Atmospheric Color In practice, all color that you and I see is atmospheric in that every color we perceive depends on the conditions we see it in We see the effects of light sources, shadows, glare, dust, moisture, reflections, etc. however, we paint, apply and specify local colors!
35 Atmospheric Color Dust and moisture between the viewer and the subject, scatter sunlight, cause distant surfaces to be closer to sky color -- which is fully due to sunlight scattered by dust, moisture, gases and pollutants.
36 Atmospheric Color Bierstadt The Haying Atmospheric perspective, also called Aerial perspective, is a reliable technique artists use to create an illusion of depth or distance. Colors of distant objects are lower in chroma, usually lighter in value and more bluish in hue.
37 Local Color vs. Atmospheric Color Architects, Interior Designers and stage designers, especially, must distinguish between the colors that are specified, and the colors that the viewer sees. Light, shadow, and surface characteristics alter color dramatically, generally expanding the range of color in the design.
38 Emmanuel chapel p. 161
39 Emmanuel chapel p. 161 Local colors (paint, carpet, wood ) are altered by lighting and surface qualities. In Interiors and Architecture, we specify local colors, but plan atmospheric colors.
40 Color as Pigment A pigment is any material used to provide the actual color to a paint, a dye, an ink or other colored medium. Pigment is the colored matter within the substance we color with. Each pigment absorbs certain colors of light and reflects other colors. The characteristics of selective absorption and reflection determine the color of the pigment.
41 Paint, Dye and Ink The media we apply color with have three basic ingredients. Pigment Binder Solvent
42 Paint, Dye and Ink Pigment The coloring agent the actual colored substance. Note that there are many kinds of pigments with distinctive characteristics. Pigments vary in coloring power, opacity, light-fastness, and permanence.
43 Paint, Dye and Ink Binder Binder is the glue that enables pigments to adhere and stay where you put them. Each medium has is own binder. (linseed oil, glcyerine, acrylic polymer, etc.) In general, the various media are distinguised primarily by their binder. Note that not all pigments are use with all binders/media -- the binder and solvent can chemically react with some pigments.
44 Paint, Dye and Ink Solvent The solvent keeps the paint moist and fluid until it dries. In watercolors, tempera and acrylics, water is the solvent. In oil paint, turpentine provides liquidity. The pigment must be able to suspend or float in the solvent and binder.
45 Subtracting Colors by Adding Pigments Whenever we mix two pigments together, the colors absorbed (subtracted) by each color continue to be absorbed and so, less light reflects and a new hue results. So, the resulting color is a bit darker in value than might be expected.
46 The traditional Subtractive primaries Red Yellow Blue
47 Pigment Primaries & Secondaries Secondaries Orange Violet Green As color/pigment is added, we get closer to black. (each added color subtracts FROM reflected light.)
48 The traditional Subtractive Mixed together, they should create black theoretically. In practice a dark muddy gray usually results. primaries
49 Light/Additive Primary Colors The primaries for lightcolor mixing and pigment-color mixing are NOT the same. Red Green Blue
50 The Additive Primaries RGB Red Green Blue Colors of the phosphors on a television or computer monitor (RGB). When combined (all are glowing) these light primaries produce white - even though they don t overlap (optical mixing). The absence of light is black darkness.
51 Light & Primaries & Secondaries Secondaries Yellow Magenta Cyan (note - these are the primary inks/colors in CMYK printing) As color/lights are added, the result is closer to white
52 Pigment vs. Light Primaries & Secondaries
53 Pigment vs. Light Primaries & Secondaries Light (additive) primaries are very similar to pigment (subtractive) secondaries.
54 Pigment vs. Light Primaries & Secondaries Pigment (subtractive) primaries are very similar to light (additive) secondaries. In fact, the most true and reliable pigment primaries may be derived from light-secondaries. (e.g. CMYK)
55 Adding Color by Adding Light Whenever two colored lights are shined on the same spot, a new color is created. If a red light and a green light (additive primaries) shine on the same spot, they add up to yellow a much lighter and brighter color.
56 Adding Color by Adding Light If a red light and a green light (additive primaries) shine on the same spot, they add up to yellow a much lighter and brighter color. Blue and Red = Magenta Blue and Green = Cyan. All 3 = white. Note CMYK
57 Adding Color by Adding Light When all colored lights are added up, or combined, the result is white light. This is the opposite of what we usually see a prism do though a prism can be positioned to rejoin colored light into white.
58 Adding Color by Adding Light Note the color of partially shaded areas -- which colors of light are illuminating those spots?
59 We always work with both additive and subtractive color Because we most often select and mix pigmented colors under paricular lighting conditions, we must pay attention to both additive and subtractive models of color and light. Perceived color is a product of both phenomena.
60 finis
61 The color we see the color of illumination ALL color depends on light. If no there is no illumination, there IS no color.
62 The color we see light sources vary in color additive color (light) RGB primaries
63 Light Sources Our perception of color is always altered by the colors of the light (or lights) that illuminate the objects we see. Ambient light is rarely color-balanced (true white), but is, instead, shifted toward one hue or another that is, the illumination itself has a color. The color of illumination alters the appearance of the local color; lighting changes perceived color.
64 Common Light Sources
65 Dominant Hue of Light Sources Most light sources project many colors of light. But one color/hue will dominate.
66 What color is White? Kelvin temperature/ratings Some typical color temperatures are: 1500 K Candlelight 2680 K 40 W incandescent lamp 3000 K 200 W incandescent lamp 3200 K Sunrise/sunset 3400 K Tungsten lamp 3400 K 1 hour from dusk/dawn K Xenon lamp/light arc 5500 K Sunny daylight around noon K Electronic photo flash K Overcast sky K Blue sky
67 What color is White? Kelvin temperature/ratings Standard unit for color temperature is Kelvin (K). Technically, color temperature refers to the temperature to which one would have to heat a theoretical "black body" source to produce light of the same visual color.
68 Black Bodies In physics, a black body is an object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation that falls onto it. No radiation passes through it and none is reflected. the amount and wavelength (color) of electromagnetic radiation they emit is directly related to their temperature. Black bodies below around 700 K (430 C) produce very little radiation at visible wavelengths and appear black (hence the name). Black bodies above this temperature however, produce radiation at visible wavelengths starting at red, going through orange, yellow, and white before ending up at blue as the temperature increases. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/black_body
69 Temperature by Color Molten bronze at ~2200 deg F. Foundry workers can read the temperature of molten metals by the color.
70 Temperature by Color Foundry workers read the temperature of molten metals by the color.
71 Kelvin Color Temperature, Black Bodies & Your Monitor This is a C.I.E. Chromaticity Diagram it is one of the most widely used color models used for measuring and specifying color in many contexts such as the color of white in your computer monitor. Astronomers also use it to measure the temperature of black bodies depending on how hot something is, it will radiate energy at a particular wavelength. In case you re wondering Kelvin= (Fahrenheit + 459) x 5/9 273K = 32F Kelvin = Celsius + 273
72 Lighting Temperature & Kelvin Illumination: 2800 Kelvin (warm light) Illumination: 4700 Kelvin (cool light)
73 Lighting Temperature & Kelvin Illumination: 2800 Kelvin (warm light) Illumination: 4700 Kelvin (cool light)
74 Lighting Temperature & Kelvin Illumination: 2950 Kelvin (warm light) Illumination: 4700 Kelvin (cool light)
75 Suffused/Aggregate Color Most surfaces and even many paints, have several colors in them. Fabrics often have several colors. Artists sometimes choose to not fully mix their paints, but let several colors remain visible. In short, most surfaces we see have several colors present in varied proportions. The designer must consider the overall color, as well as the impact of the constituent colors.
76 Suffused Color surface qualities Local color is altered by the character of the surface -- is it rough, is it smooth, is it matte, is it glossy?
77 Suffused Color surface qualities
78 Suffused Color surface qualities Different surfaces reflect light differently, and since color is a by-product of light, different surfaces of the same color produce a different variety of colors. Consider wood finishes, metal surfaces.
79 Aggregate Color Many colors are in most surfaces and materials. The designer must consider the overall color the color chord as well as the individual colors present.
80 Aggregate Color Each color is relates to those around it. At different distances, the impact of an aggregate color changes -- far away the details blend into a single color impression.
81 Aggregate Color Wood, marble and granite, for instance, often have several distinct colors sometimes in very fine textures so that the constituent colors don t fully show themselves except on close inspection.
82 Aggregate Color
83 Material Qualities The color of a surface is effected by the kind of reflective and refractive properties the surface material has.
84 Material Qualities Polished metal, for instance, is highly reflective gold may have a local color of yellow-orange, but the viewer always sees that yellow color mixed with reflections of whatever else in nearby.
85 Material Qualities Plastics and glass will transmit light through the surface, as well as reflecting light off of the surface. This combination reflection, diffusion, refraction, and absorption enables glass to be fascinating material.
86 Naturalistic Color
87 Deep color -- layered and suspended pigments Pearls and pearlescent paint both reflect and refract light echoing the colors nearby, while softening the colors and contrasts. Glass and gloss varnishes or laquer s transmit light and refract it light is bent and, to some extent, divided into constituent colors.
88 Surface Qualities Local color and lighting alone do not determine the final color of an object. A surface color may well reflect other colors from nearby objects. Glass often has a polished surface that reflects light (and so colors), but also transmit and refracts much of the light.
89 Color terms & concepts: Color as light The visible spectrum, wavelengths White light Reflection, Transmission, Absorption, Refraction Additive Color vs. Subtractive Color Light Primaries vs. Pigment Primaries
90 Color terms & concepts: Intrinsic value, binder, local color, aggregate color, atmospheric color, Complementary, Analogous, Warm, Cool, Neutrals and Near Neutrals
91 For Next Class: Read from Text: p (Color Mixing) Read from The Acrylic Book ; p (see syllabus for web link to PDF) ylicbook.pdf Have painting supplies here.
Color Theory. Chapter 2 Color Basics. Color as Light. Light as Color
 Color Theory Chapter 2 Color Basics Color as Light Light as Color Last Class: Color Coding & Color as Communication Color as cultural & personal expression Current technology driving color availability
Color Theory Chapter 2 Color Basics Color as Light Light as Color Last Class: Color Coding & Color as Communication Color as cultural & personal expression Current technology driving color availability
Color theory Quick guide for graphic artists
 Quick guide for graphic artists We can talk about color using two kinds of terminology: Color generation systems. Color harmony system. Graphic artists and photographers certainly have to understand color
Quick guide for graphic artists We can talk about color using two kinds of terminology: Color generation systems. Color harmony system. Graphic artists and photographers certainly have to understand color
COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT
 COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
COLOR COLOR AS A DESIGN ELEMENT Color is one of the most important elements of design. It can evoke action and emotion. It can attract or detract attention. I. COLOR SETS COLOR HARMONY Color Harmony occurs
Test 1: Example #2. Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, Note: * indicates the correct answer.
 Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Color is a property of light.
 Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
Color Theory I Color is a property of light. -Objects have no color of their own, they just reflect a particular wavelength from the color spectrum. (For example a blue object absorbs all of the wavelengths,
In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths.
 Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Elements Of Art Study Guide
 Elements Of Art Study Guide General Elements of Art- tools artists use to create artwork; Line, shape, color, texture, value, space, form Composition- the arrangement of elements of art to create a balanced
Elements Of Art Study Guide General Elements of Art- tools artists use to create artwork; Line, shape, color, texture, value, space, form Composition- the arrangement of elements of art to create a balanced
Fundamentals of color. Color temperature
 Fundamentals of color Color temperature color temperature, such as 3400 K for halogen lamps, 4200 K for certain fluorescent tubes (Temperature is measured in Kelvin, which is a scale that has its zero
Fundamentals of color Color temperature color temperature, such as 3400 K for halogen lamps, 4200 K for certain fluorescent tubes (Temperature is measured in Kelvin, which is a scale that has its zero
Art 177 :: Creative Photography. Color & Color Theory
 Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
Art 177 :: Creative Photography Color & Color Theory Color I never met a color I didn t like. Dale Chihuly Color [electromagnetic spectrum] The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of all forms of electromagnetic
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition. Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout.
 The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
The Elements of Art: Photography Edition Directions: Copy the notes in red. The notes in blue are art terms for the back of your handout. The elements of art a set of 7 techniques which describe the characteristics
Exercises The Color Spectrum (pages ) 28.2 Color by Reflection (pages )
 Exercises 28.1 The Spectrum (pages 555 556) 1. was the first person to do a systematic study of color. 2. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about Newton s study of color. a. He studied sunlight.
Exercises 28.1 The Spectrum (pages 555 556) 1. was the first person to do a systematic study of color. 2. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about Newton s study of color. a. He studied sunlight.
Color Theory. Additive Color
 Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
Color Wheel. Warm Colors. Cool Colors
 Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Color Wheel Warm Colors Cool Colors How we see color: the light source gives a full spectrum of wavelengths (All 6 colors). The cup absorbs every wave length of color except Blue. Blue is reflected back
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 27: COLOR This lecture will help you understand: Color in Our World Selective Reflection Selective Transmission Mixing Colored Light Mixing Colored Pigments Why
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 27: COLOR This lecture will help you understand: Color in Our World Selective Reflection Selective Transmission Mixing Colored Light Mixing Colored Pigments Why
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory
 Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
NEWTONIAN COLOR THEORY
 THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
THEORY 2D Design Color Crash Course NEWTONIAN THEORY Color in a picture is like enthusiasm in life. -incent an Gogh In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1726) passed a beam of light through a prism and proved
UBT128X Colour theory
 UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
H10: Description of Colour
 page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
page 1 of 7 H10: Description of Colour Appearance of objects and materials Appearance attributes can be split into primary and secondary parts, as shown in Table 1. Table 1: The attributes of the appearance
Color Theory and Mixing
 MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
MODULE 4 Color Theory and Mixing? What is explored in this module? In this module, we ll look at basic color theory and mixing colors. You ll find that color theory and mixing is not a perfect science.
Hue Do You Think Hue Are?
 Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
Color Studies for Kids
 Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR
 THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes
 Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Choose Paint Colors and Schemes When you re decorating your home, choosing the right paint colors is the most important decision you ll make. As fun as choosing colors can be, this part of the planning
Chapter Objectives. Color Management. Color Management. Chapter Objectives 1/27/12. Beyond Design
 1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
1/27/12 Copyright 2009 Fairchild Books All rights reserved. No part of this presentation covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26
 skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red.
 Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Hue Hue is what makes a color identifiable and different from any other color, e.g. orange, red-orange, red. Hues are determined (and can be measured) by a color's wavelength. There are millions of hues
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2.
 Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
Principles of Architectural Design Lec. 2. The Complementary Elements of design. The complementary elements characterize the natural elements, creating means of comparison for the primary elements used
Notes on colour mixing
 INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS
 LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
LIGHTIG FOR INTERIORS COLORS LIGHTING Interior Design Department Third grade/ Fall semester Siba nazem Kady COLORS THEORIES OF COLOR DESIGN Review The Hue REVIEW HUE,VALUE, AND SATURATION - Gradation of
color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric!
 for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
Line Line Characteristic of Line are: Width Length Direction Focus Feeling Types of Line: Outlines Contour Lines Gesture Lines Sketch Lines
 Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
28 Color. The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them.
 The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
Color Theory: Defining Brown
 Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
Color Theory: Defining Brown Defining Colors Colors can be defined in many different ways. Computer users are often familiar with colors defined as percentages or amounts of red, green, and blue (RGB).
What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes.
 Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Chapter 7: COLOR What is Color? The element of art derived from reflected light. Light reflects off objects, sending colors back to our eyes. I. Color Spectrum Color Spectrum: The bands of color created
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART
 Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Name: Period: THE ELEMENTS OF ART Name: Period: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with
Wright Field Scale Modelers. Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong.
 Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
The Principles of Chromatics
 The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
The Principles of Chromatics 03/20/07 2 Light Electromagnetic radiation, that produces a sight perception when being hit directly in the eye The wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm 1 03/20/07 3 Visible
check it out online at
 check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
check it out online at www.belyea.com/svc/all_about_color.pdf Who am I? I got the blues Experience and Emotions through color PASSION JOY Depression HARMONY CREATIVITY PEACE MOURNING It s a bird, it s
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg
 Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
Understanding Color Theory Excerpt from Fundamental Photoshop by Adele Droblas Greenberg and Seth Greenberg Color evokes a mood; it creates contrast and enhances the beauty in an image. It can make a dull
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
Art & Design visual elements
 Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
Make your own colour scheme Which 20 colours suit you best? Choose 20 of your favourite colours out of the different stacks on the tables. Make sure to group harmonious colours together. Discuss the place
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
 Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with
 DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
DESIGNING FLOWER BEDS with Good flower bed designs incorporate many different features Relative surface feel or look On plants, texture comes from Leaves Twigs Bark Texture also comes from Rocks Pavement
Hot or Cold? Warm Colors: Yellow, Orange, Red (excitement) Cool Colors: Green, Blue, Violet (calmness)
 Art Basics The Color Wheel Primary Colors: a group of colors from which all other colors can be obtained by mixing. Ex: Yellow, Red, and Blue Secondary Colors: a color resulting from the mixing of two
Art Basics The Color Wheel Primary Colors: a group of colors from which all other colors can be obtained by mixing. Ex: Yellow, Red, and Blue Secondary Colors: a color resulting from the mixing of two
Multimedia Systems and Technologies
 Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
Multimedia Systems and Technologies Faculty of Engineering Master s s degree in Computer Engineering Marco Porta Computer Vision & Multimedia Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History
 Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History In Lecture 5 we discussed the two different ways of talking about
Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History In Lecture 5 we discussed the two different ways of talking about
elements of design worksheet
 elements of design worksheet Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed
elements of design worksheet Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed
Section 18.3 Behavior of Light
 Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Color and Color Model. Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin
 Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
Color and Color Model Chap. 12 Intro. to Computer Graphics, Spring 2009, Y. G. Shin Color Interpretation of color is a psychophysiology problem We could not fully understand the mechanism Physical characteristics
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS
 UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
Design and Colour. Jacquie Wilson
 Design and Colour Jacquie Wilson The colours of the spectrum violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red Colour range for questionnaire violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red black, white Colour
Design and Colour Jacquie Wilson The colours of the spectrum violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red Colour range for questionnaire violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange, red black, white Colour
Introduction. The Spectral Basis for Color
 Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Introduction Color is an extremely important part of most visualizations. Choosing good colors for your visualizations involves understanding their properties and the perceptual characteristics of human
Light Sources. Hard VS Soft
 Light Sources This article is provided to you as a courtesy of The Pro Doodler. www.theprodoodler.com your best source for all of your graphic design needs. Copyright 2009 by The Pro Doodler. In the beginning
Light Sources This article is provided to you as a courtesy of The Pro Doodler. www.theprodoodler.com your best source for all of your graphic design needs. Copyright 2009 by The Pro Doodler. In the beginning
Color is derived from Reflected Light.
 How We See Color Color is derived from Reflected Light. White light from the sun is actually a combination of all colors. When light passes through a prism, a wedge-shaped glass, the beam of light bends
How We See Color Color is derived from Reflected Light. White light from the sun is actually a combination of all colors. When light passes through a prism, a wedge-shaped glass, the beam of light bends
Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018
 Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018 Definition: What is a Line? Definition: Line is the most basic design tool. A line has length, width, tone, and texture. It may divide space, define a form, describe contour,
Art 2D Mid-Term Review 2018 Definition: What is a Line? Definition: Line is the most basic design tool. A line has length, width, tone, and texture. It may divide space, define a form, describe contour,
Light waves interact with materials.
 Page of 7 KEY CONCEPT Light waves interact with materials. BEFORE, you learned Mechanical waves respond to a change in medium Visible light is made up of EM waves EM waves interact with a new medium in
Page of 7 KEY CONCEPT Light waves interact with materials. BEFORE, you learned Mechanical waves respond to a change in medium Visible light is made up of EM waves EM waves interact with a new medium in
Value. Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page.
 Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Value Value-It is the lightness or darkness of an object, regardless of color. Value is relative to the background color and other items on the page. Value is created by a light source that shines on an
Coloured pencils are easy to work with step-by-step to avoid making mistakes. It is easy to correct mistakes once happen using an eraser.
 Coloured pencil technique What makes this medium so special and supersedes pencil in drawing? Human beings eye adores both colour and light. Coloured pencils are portable and a good medium to start with
Coloured pencil technique What makes this medium so special and supersedes pencil in drawing? Human beings eye adores both colour and light. Coloured pencils are portable and a good medium to start with
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception. Chapter 27 Color
 Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception Chapter 27 Color 4-Nov-10 The Eye As light enters the eye, it moves through the transparent cover, the cornea, which does about 70% of the necessary
Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception Chapter 27 Color 4-Nov-10 The Eye As light enters the eye, it moves through the transparent cover, the cornea, which does about 70% of the necessary
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle.
 The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
The Color Wheel is a visual representation of color theory. It is the color spectrum wrapped onto a circle. It creates an orderly progression of color that helps us understand color balance and harmony.
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHOD
 ABSTRACT This research project aims to investigate and illustrate the effects a light source s spectral distribution and colour temperature has on photographic image colour reproduction, and how this often
ABSTRACT This research project aims to investigate and illustrate the effects a light source s spectral distribution and colour temperature has on photographic image colour reproduction, and how this often
Color Theory. Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map. Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff
 Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map Color Theory Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff Munsell color notation (HVC) HC color mapping HV color mapping Strait Line Mixing (2clr/3clr Y ) 1st
Color Mixing Intro (ch. 7 pp. 77ff) Liquitex Color Map Color Theory Value Staff Intrinsic Value Staff Munsell color notation (HVC) HC color mapping HV color mapping Strait Line Mixing (2clr/3clr Y ) 1st
Light. Light: Rainbow colors: F. Y. I. A type of energy that travels as a wave Light Experiments.notebook. May 19, 2015
 Light Light: A type of energy that travels as a wave F. Y. I. Light is different from other kinds of waves. Other kinds of waves, such as sound waves must travel through matter. Light waves do not need
Light Light: A type of energy that travels as a wave F. Y. I. Light is different from other kinds of waves. Other kinds of waves, such as sound waves must travel through matter. Light waves do not need
CUT the wheel vertically IN HALF: WARM (right) AND COOL COLORS (left)
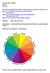 COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
COLOR CHEAT SHEET! Simons Arts123 The following information has been collected from a number of websites. See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrjpau Karen Kavet http://www.color-wheel-pro.com/color-schemes.html
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II
 GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
GRAPHICS TECHNOLOGY II COLORS ARE PART OF OUR LIFE From the clothes we wear, to the things around us, the food we eat, the things we use- everything. Colors are said to activate the right brain for emotions.
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
Designing Flower Beds with Colors
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Archived Publications Archived USU Extension Publications 1-1-2005 Designing Flower Beds with Colors Larry A. Sagers Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_histall
Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
Art Vocabulary Assessment
 Art Vocabulary Assessment Name: Date: Abstract Artwork in which the subject matter is stated in a brief, simplified manner; little or no attempt is made to represent images realistically, and objects are
Art Vocabulary Assessment Name: Date: Abstract Artwork in which the subject matter is stated in a brief, simplified manner; little or no attempt is made to represent images realistically, and objects are
Christoph Wagner Colour Theory
 Colour Theory Hue, Saturation and Lightness (HSL) This model is one of the most intuitive ones in describing colour and I find it most useful for our purposes. There are other models, but we'll focus on
Colour Theory Hue, Saturation and Lightness (HSL) This model is one of the most intuitive ones in describing colour and I find it most useful for our purposes. There are other models, but we'll focus on
Elements and Principals of Design. Unit 1: Drawing
 Elements and Principals of Design Unit 1: Drawing Elements of Design Art works are composed of the basic elements of design: Dot - Tone Line - Value Shape - Space Form - Colour Texture The elements of
Elements and Principals of Design Unit 1: Drawing Elements of Design Art works are composed of the basic elements of design: Dot - Tone Line - Value Shape - Space Form - Colour Texture The elements of
This chapter will cover the following topics: Colour terminology. The colour spectrum. The colour wheel. Organisation of colour.
 What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
What would the world be like without colour? Colour brings vitality to everything it touches, be it the clothes we wear or the homes we live in and as a painter and decorator, you need to understand colour,
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Communicating Color. Courtesy of: X-Rite Inc Street SE Grand Rapids MI (616)
 Communicating Color Courtesy of: X-Rite Inc 4300 44 Street SE Grand Rapids MI (616) 803-2000 What is Color? Color Perception What influences the perception of color? 1. light source 2. object being viewed
Communicating Color Courtesy of: X-Rite Inc 4300 44 Street SE Grand Rapids MI (616) 803-2000 What is Color? Color Perception What influences the perception of color? 1. light source 2. object being viewed
9/1/2015 Elements and Principles of Design. Color and value
 Color and value Colors are light waves reflected and absorbed by objects. Hues are the names of colors. Primary hues are red, yellow and blue. Secondary hues are green, orange, and violet. Tertiary hues
Color and value Colors are light waves reflected and absorbed by objects. Hues are the names of colors. Primary hues are red, yellow and blue. Secondary hues are green, orange, and violet. Tertiary hues
Colour. Cunliffe & Elliott, Chapter 8 Chapman & Chapman, Digital Multimedia, Chapter 5. Autumn 2016 University of Stirling
 CSCU9N5: Multimedia and HCI 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Cunliffe & Elliott,
CSCU9N5: Multimedia and HCI 1 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Cunliffe & Elliott,
Elements of Art. Define: Line. Shape. Value. Texture. Color. Form. Space
 Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Elements of Art Line Shape Value Texture Color Form Space Directions: When we talk about the parts that make up a picture or work of art, we refer to them as elements. In the space below, draw a picture
Chapter 4. Incorporating Color Techniques
 Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
Chapter 4 Incorporating Color Techniques Color Modes Photoshop displays and prints images using specific color modes A mode is the amount of color data that can be stored in a given file format 2 Color
Properties of Color. Value: Tint: Shade: Tone: Intensity:
 Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
Seeing Color Color and light are inseparable, without light there would be no color When light passes through a prism a spectrum of colors becomes visible Defining Color Hue The name of a color, such
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR
 Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
Unit 2 ART I: UNIT TWO PRINCIPLES OF COLOR CONTENTS INTRODUCTION................................ 1 I. THE COLOR WHEEL........................... 6 Basic Color Mixing.............................. 8 Value
Light and Applications of Optics
 UNIT 4 Light and Applications of Optics Topic 4.1: What is light and how is it produced? Topic 4.6: What are lenses and what are some of their applications? Topic 4.2 : How does light interact with objects
UNIT 4 Light and Applications of Optics Topic 4.1: What is light and how is it produced? Topic 4.6: What are lenses and what are some of their applications? Topic 4.2 : How does light interact with objects
The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements
 Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
Vocabulary The basic tenets of DESIGN can be grouped into three categories: The Practice, The Principles, The Elements 1. The Practice: Concept + Composition are ingredients that a designer uses to communicate
Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART
 Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART TEXTURE IS: the surface quality of a work of art. VISUAL texture that is created to look like something it is not SIMULATED the visual effect of texture without actually
Elements of Art THE WORDS OF ART TEXTURE IS: the surface quality of a work of art. VISUAL texture that is created to look like something it is not SIMULATED the visual effect of texture without actually
10.2 Color and Vision
 10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
ARTS D Design. Project 1: Art Elements. Reading Guide: form. elements of art. line. shape. value. texture. color. principles of organization
 ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
ARTS 101 2-D Design Project 1: Art Elements Reading Guide: form elements of art line shape value texture color principles of organization harmony variety balance proportion dominance movement economy unity
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
 Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier.
 Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier. Color temperature describes the actual temperature of a black
Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier. Color temperature describes the actual temperature of a black
Principles of Design
 Principles of Design Balance A. Stability of an arrangement 1. Arrangement appears secure and stable 2. Balance must be both visual and actual Balance a. visual balance refers to the way an arrangement
Principles of Design Balance A. Stability of an arrangement 1. Arrangement appears secure and stable 2. Balance must be both visual and actual Balance a. visual balance refers to the way an arrangement
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
FIM FUNDAMENTALS OF FILMMAKING CINEMATOGRAPHY
 Color Temperature and Filters SCHOOL OF FILMMAKING 1533 S. Main Street Winston-Salem, North Carolina 27127 FIM 1801 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FILMMAKING CINEMATOGRAPHY So what is color temperature and why is it
Color Temperature and Filters SCHOOL OF FILMMAKING 1533 S. Main Street Winston-Salem, North Carolina 27127 FIM 1801 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FILMMAKING CINEMATOGRAPHY So what is color temperature and why is it
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
Colour. Why/How do we perceive colours? Electromagnetic Spectrum (1: visible is very small part 2: not all colours are present in the rainbow!
 Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
Colour What is colour? Human-centric view of colour Computer-centric view of colour Colour models Monitor production of colour Accurate colour reproduction Colour Lecture (2 lectures)! Richardson, Chapter
LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points
 WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
Naphthol Red Light. Hansa Yellow Medium
 Color Mixing Guide Printer Friendly Version Throughout history, painters and authors have recommended various palettes of color. While some give insight to the painter's working style, others offer a simple
Color Mixing Guide Printer Friendly Version Throughout history, painters and authors have recommended various palettes of color. While some give insight to the painter's working style, others offer a simple
