Exercises The Color Spectrum (pages ) 28.2 Color by Reflection (pages )
|
|
|
- Eugenia Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercises 28.1 The Spectrum (pages ) 1. was the first person to do a systematic study of color. 2. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about Newton s study of color. a. He studied sunlight. b. He passed sunlight through triangular-shaped pieces of glass. c. He observed that sunlight was broken into a rainbow-like pattern of colors. d. He showed that sunlight is yellow light. 3. A spread of colors is called a. 4. List the colors of the visible spectrum in the correct order. 5. Is the following sentence true or false? Sunlight is a combination of all colors. 6. A white object appears when illuminated by white light. 7. Explain this statement: White and black are not actually colors. 8. Is the following sentence true or false? Black objects that you can see absorb all light that falls on them by Reflection (pages ) 9. Circle the letter that best describes the color of an opaque object. a. An opaque object is the color it absorbs. b. An opaque object is the color of the light that shines on it. c. An opaque object is the color it reflects. d. An opaque object is the color of white light. 10. Different materials have different for absorbing and emitting radiation. 11. Describe what happens when the frequency of the light shining on an object resonates with the object s natural frequency. 12. Describe what happens when the frequency of the light shining on an object is higher or lower than the object s natural frequency. 13. Is the following sentence true or false? When an object reemits the light that shines on it, absorption occurs. Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook 239
2 14. Circle the letter that best explains why cells containing chlorophyll are green. a. They absorb green light. b. They produce food. c. They reflect green light. d. They are very small. 15. Is the following sentence true or false? Different sources of light produce light made up of different frequencies by Transmission (page 558) 16. What determines the color of a transparent object? 17. The illustration below shows what happens when sunlight shines on a piece of blue glass. Describe what happens to the sunlight as it passes through the glass. 18. A is a material in glass that selectively absorbs colored light. 19. Circle the letter that explains what the energy from the light absorbed by a piece of glass does to the glass. a. The energy hardens the glass. b. The energy warms the glass. c. The energy darkens the glass. d. The energy has no effect on the glass Sunlight (page 559) 20. Is the following sentence true or false? Human vision is most sensitive to colors in the red-orange part of the visible spectrum. 21. The graphical distribution of brightness versus frequency in sunlight is called the. 240 Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
3 Use the graph of brightness versus frequency of sunlight to answer Questions 22 and Is the following sentence true or false? The brightness of sunlight is directly proportional to frequency. 23. What is the brightest portion of the spectrum of sunlight? 28.5 Mixing ed Light (pages ) 24. What color of light is produced when red, blue, and green light of equal brightness overlap?. Match the name of each color of light to the mixture of colors that produces it. of Light Mixtures That Produce the 25. magenta a. mixture of green and blue 26. yellow b. mixture of red and blue 27. cyan c. mixture of red and green 28. Is the following sentence true or false? By mixing red, blue, and green light and adjusting the brightness of each, virtually any color can be formed. 29. Red, blue, and green light are known as the colors. 30. Explain how a color television produces a wide range of colors on its screen. Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook 241
4 28.6 Complementary s (pages ) 31. Two colors of light that when added together produce white are known as. Match each color in the left column with its complementary color in the right column. Complementary 32. magenta a. red 33. yellow b. green 34. cyan c. blue 35. Circle the letter that best describes the light that results when a color is subtracted from white light. a. black b. magenta c. muddy brown d. the complementary color to the subtracted color 28.7 Mixing ed Pigments (pages ) 36. Is the following sentence true or false? The mixing of colored paints yields similar results as mixing the same colors of light. 37. Explain what happens when paints or dyes are mixed. 38. What color(s) are absorbed by blue paint? 39. What color(s) are absorbed by yellow paint? 40. If white light shines on a mixture of blue and yellow paint, what color is not absorbed? 41. The mixing of pigments, paints, or dyes is known as color mixing by. 42. Magenta, yellow, and cyan are the colors used in printing illustrations in full color. 43. Describe the process used to print a color image in a book. 242 Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook
5 28.8 Why the Sky Is Blue (pages ) 44. Circle the letter of the process in which sound or light is absorbed and reemitted in all directions. a. reflection b. resonance c. scattering d. stimulated emission 45. Is the following sentence true or false? Atoms and molecules can behave like optical tuning forks, reemitting light waves that shine on them. 46. Describe the relationship between the size of a particle in the atmosphere and the frequency of the light it scatters. 47. Is the following sentence true or false? The sky appears blue because particles in the atmosphere scatter low-frequency light. 48. Although violet light is scattered more than blue light, our eyes see the sky as blue. Explain. 49. Circle the letter that describes what occurs when many particles larger than oxygen and nitrogen molecules are in the atmosphere. a. The sky appears darker blue. b. The sky appears black. c. The sky appears whitish. d. The sky appears green. 50. Is the following sentence true or false? The presence of water droplets in the atmosphere does not affect how much light is scattered or what frequencies of light are scattered. 51. Explain why many clouds appear white. 52. A cloud containing many large water droplets appears Why Sunsets Are Red (pages ) 53. Circle the letter of the color of light that is scattered the least as it passes through the atmosphere. a. red b. orange c. yellow d. blue 54. Is the following sentence true or false? At sunset, light reaches Earth s surface through a shorter path than at noon. 55. As the path of sunlight through the atmosphere increases, what color of light is scattered more? Conceptual Physics Reading and Study Workbook 243
28 Color. The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them.
 The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 27: COLOR This lecture will help you understand: Color in Our World Selective Reflection Selective Transmission Mixing Colored Light Mixing Colored Pigments Why
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 27: COLOR This lecture will help you understand: Color in Our World Selective Reflection Selective Transmission Mixing Colored Light Mixing Colored Pigments Why
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points
 WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History
 Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History In Lecture 5 we discussed the two different ways of talking about
Lecture 6 6 Color, Waves, and Dispersion Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 7 Colors, Section I, II, III 6.1 Overview and History In Lecture 5 we discussed the two different ways of talking about
Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
Section 18.3 Behavior of Light
 Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Light and Color (pages )
 Light and Color (pages 106 111) When Light Strikes an Object (page 107) Key Concept: When light strikes an object, the light can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Materials can be transparent, translucent,
Light and Color (pages 106 111) When Light Strikes an Object (page 107) Key Concept: When light strikes an object, the light can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Materials can be transparent, translucent,
color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric!
 for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
for ages 12-17 color & dye chemisty Explore in a scientific way! Learn how and why we see color, and how dye chemically reacts with fabric! objectives and materials what is color? types of color how reactive
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
 Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths.
 Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Color Concept Basis Color Concept What is Color? In a physical sense, there really is no such thing as color, just light waves of different wavelengths. Color comes from light. The human eye can distinguish
Light. Light: Rainbow colors: F. Y. I. A type of energy that travels as a wave Light Experiments.notebook. May 19, 2015
 Light Light: A type of energy that travels as a wave F. Y. I. Light is different from other kinds of waves. Other kinds of waves, such as sound waves must travel through matter. Light waves do not need
Light Light: A type of energy that travels as a wave F. Y. I. Light is different from other kinds of waves. Other kinds of waves, such as sound waves must travel through matter. Light waves do not need
Light, Color, Spectra 05/30/2006. Lecture 17 1
 What do we see? Light Our eyes can t t detect intrinsic light from objects (mostly infrared), unless they get red hot The light we see is from the sun or from artificial light When we see objects, we see
What do we see? Light Our eyes can t t detect intrinsic light from objects (mostly infrared), unless they get red hot The light we see is from the sun or from artificial light When we see objects, we see
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Color. PHY205H1F Summer Physics of Everyday Life Class 10: Colour, Optics. Recall from Chapters 25 and 26
 PHY205H1F Summer Physics of Everyday Life Class 10: Colour, Optics Color in Our World Mixing Colored Light Why the Sky Is Blue Why Sunsets Are Red Law of Reflection Virtual Image Formation Image Reversal
PHY205H1F Summer Physics of Everyday Life Class 10: Colour, Optics Color in Our World Mixing Colored Light Why the Sky Is Blue Why Sunsets Are Red Law of Reflection Virtual Image Formation Image Reversal
Fill in the blanks. Reading Skill: Compare and Contrast - questions 3, 17
 Light and Color Lesson 9 Fill in the blanks Reading Skill: Compare and Contrast - questions 3, 17 How Do You Get Color From White Light? 1 A(n) is a triangular piece of polished glass that refracts white
Light and Color Lesson 9 Fill in the blanks Reading Skill: Compare and Contrast - questions 3, 17 How Do You Get Color From White Light? 1 A(n) is a triangular piece of polished glass that refracts white
Light waves. VCE Physics.com. Light waves - 2
 Light waves What is light? The electromagnetic spectrum Waves Wave equations Light as electromagnetic radiation Polarisation Colour Colour addition Colour subtraction Interference & structural colour Light
Light waves What is light? The electromagnetic spectrum Waves Wave equations Light as electromagnetic radiation Polarisation Colour Colour addition Colour subtraction Interference & structural colour Light
Color Theory. Chapter 2 Color Basics. Color as Light. Light as Color
 Color Theory Chapter 2 Color Basics Color as Light Light as Color Last Class: Color Coding & Color as Communication Color as cultural & personal expression Current technology driving color availability
Color Theory Chapter 2 Color Basics Color as Light Light as Color Last Class: Color Coding & Color as Communication Color as cultural & personal expression Current technology driving color availability
2. Pixels and Colors. Introduction to Pixels. Chapter 2. Investigation Pixels and Digital Images
 2. Pixels and Colors Introduction to Pixels The term pixel is a truncation of the phrase picture element which is exactly what a pixel is. A pixel is the smallest block of color in a digital picture. The
2. Pixels and Colors Introduction to Pixels The term pixel is a truncation of the phrase picture element which is exactly what a pixel is. A pixel is the smallest block of color in a digital picture. The
Light waves interact with materials.
 Page of 7 KEY CONCEPT Light waves interact with materials. BEFORE, you learned Mechanical waves respond to a change in medium Visible light is made up of EM waves EM waves interact with a new medium in
Page of 7 KEY CONCEPT Light waves interact with materials. BEFORE, you learned Mechanical waves respond to a change in medium Visible light is made up of EM waves EM waves interact with a new medium in
Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS
 Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
Test 1: Example #2. Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, Note: * indicates the correct answer.
 Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Notes: Light and Optics. Reflection. Refraction. Law of Reflection. Light goes straight 12/13/2012
 Notes: Light and Optics Light goes straight Light travels in a straight line unless it interacts with a medium. The material through which a wave travels is called a medium. Light can be reflected, refracted
Notes: Light and Optics Light goes straight Light travels in a straight line unless it interacts with a medium. The material through which a wave travels is called a medium. Light can be reflected, refracted
CHAPTER 26: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT 02/19/18
 CHAPTER 26: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT 02/19/18 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES At the end of last chapter, there was a more general statement of Faraday s Law: o Faraday s Law: An electric field is created in any region
CHAPTER 26: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT 02/19/18 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES At the end of last chapter, there was a more general statement of Faraday s Law: o Faraday s Law: An electric field is created in any region
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
Color Studies for Kids
 Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Color Studies for Kids By C.L. Swanner 2011 C.L. Swanner All rights reserved. Special Thanks To: God, who designed me with a great love for His creation and gave me the ability to explore His creation
Mastery. Chapter Content. What is light? CHAPTER 11 LESSON 1 C A
 Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Chapter Content Mastery What is light? LESSON 1 Directions: Use the letters on the diagram to identify the parts of the wave listed below. Write the correct letters on the line provided. 1. amplitude 2.
Preview. Light and Reflection Section 1. Section 1 Characteristics of Light. Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Section 3 Curved Mirrors
 Light and Reflection Section 1 Preview Section 1 Characteristics of Light Section 2 Flat Mirrors Section 3 Curved Mirrors Section 4 Color and Polarization Light and Reflection Section 1 TEKS The student
Light and Reflection Section 1 Preview Section 1 Characteristics of Light Section 2 Flat Mirrors Section 3 Curved Mirrors Section 4 Color and Polarization Light and Reflection Section 1 TEKS The student
Wright Field Scale Modelers. Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong.
 Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Wright Field Scale Modelers Color Mixing: Everything you thought you knew about color is wrong. Sources http://www.huevaluechroma.com/ Written by a color scientist, Dr. Briggs. It is a bit technical. Principles
Selective Reflection
 PHY205H1F Summer Physics of Everyday Life Class 10: Colour, Optics Color in Our World Mixing Colored Light Why the Sky Is Blue Why Sunsets Are Red Law of Reflection Virtual Image Formation Image Reversal
PHY205H1F Summer Physics of Everyday Life Class 10: Colour, Optics Color in Our World Mixing Colored Light Why the Sky Is Blue Why Sunsets Are Red Law of Reflection Virtual Image Formation Image Reversal
Light and Applications of Optics
 UNIT 4 Light and Applications of Optics Topic 4.1: What is light and how is it produced? Topic 4.6: What are lenses and what are some of their applications? Topic 4.2 : How does light interact with objects
UNIT 4 Light and Applications of Optics Topic 4.1: What is light and how is it produced? Topic 4.6: What are lenses and what are some of their applications? Topic 4.2 : How does light interact with objects
Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception. Chapter 27 Color
 Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception Chapter 27 Color 4-Nov-10 The Eye As light enters the eye, it moves through the transparent cover, the cornea, which does about 70% of the necessary
Lecture 30 Chapter 26 The Human Eye & Visual Perception Chapter 27 Color 4-Nov-10 The Eye As light enters the eye, it moves through the transparent cover, the cornea, which does about 70% of the necessary
Term Info Picture. A wave that has both electric and magnetic fields. They travel through empty space (a vacuum).
 Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
10.2 Color and Vision
 10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
10.2 Color and Vision The energy of light explains how different colors are physically different. But it doesn't explain how we see colors. How does the human eye see color? The answer explains why computers
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS
 UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT. Physics 5 th Six Weeks
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT Physics 5 th Six Weeks What are Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves Sound and water waves are examples of waves resulting from energy being transferred from particle
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT Physics 5 th Six Weeks What are Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves Sound and water waves are examples of waves resulting from energy being transferred from particle
Section 1: Sound. Sound and Light Section 1
 Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Chapter: Sound and Light
 Table of Contents Chapter: Sound and Light Section 1: Sound Section 2: Reflection and Refraction of Light Section 3: Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye Section 4: Light and Color 1 Sound Sound When an object
Table of Contents Chapter: Sound and Light Section 1: Sound Section 2: Reflection and Refraction of Light Section 3: Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye Section 4: Light and Color 1 Sound Sound When an object
Physics for Kids. Science of Light. What is light made of?
 Physics for Kids Science of Light What is light made of? This is not an easy question. Light has no mass and is not really considered matter. So does it even exist? Of course it does! We couldn't live
Physics for Kids Science of Light What is light made of? This is not an easy question. Light has no mass and is not really considered matter. So does it even exist? Of course it does! We couldn't live
Black is the absence of all visible light. Black is NOT a color!!!
 Black is the absence of all visible light. Black is NOT a color!!! This is why white colored clothing is cooler in summer. White fabric re emits light, while black fabric absorbs light. Why do we see this
Black is the absence of all visible light. Black is NOT a color!!! This is why white colored clothing is cooler in summer. White fabric re emits light, while black fabric absorbs light. Why do we see this
Chapter 22Light and Color
 Chapter 22Light and Color Television brings you images of objects and places that you may not otherwise have ever seen. What s more, the images move with full sound and color as if you really were there.
Chapter 22Light and Color Television brings you images of objects and places that you may not otherwise have ever seen. What s more, the images move with full sound and color as if you really were there.
Ch 16: Light. Do you see what I see?
 Ch 16: Light Do you see what I see? Light Fundamentals What is light? How do we see? A stream of particles emitted by a source? Wavelike behavior as it bends and reflects Today we know light is dual in
Ch 16: Light Do you see what I see? Light Fundamentals What is light? How do we see? A stream of particles emitted by a source? Wavelike behavior as it bends and reflects Today we know light is dual in
Color Theory. Additive Color
 Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Color Theory A primary color is a color that cannot be made from a combination of any other colors. A secondary color is a color created from a combination of two primary colors. Tertiary color is a combination
Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
 Type of wave Travel in Vacuum? Speed Speed vs. Medium Light Sound vs. Sound Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
Type of wave Travel in Vacuum? Speed Speed vs. Medium Light Sound vs. Sound Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
11. What happens if two complementary colors are projected together at the correct intensities onto a white screen?
 PreAP Physics Review Chapter 14 & 15 09 Name: Date: Period: _ Use the diagram to answer questions 1 13. The diagram represents three overlapping circles of equally intense light of different pure colors.
PreAP Physics Review Chapter 14 & 15 09 Name: Date: Period: _ Use the diagram to answer questions 1 13. The diagram represents three overlapping circles of equally intense light of different pure colors.
How is Light Absorbed and Transmitted?
 How is Light Absorbed and Transmitted? Description: Students will examine the absorption and transmission of light by color filters with the help of a light source and a diffraction grating. Student Materials
How is Light Absorbed and Transmitted? Description: Students will examine the absorption and transmission of light by color filters with the help of a light source and a diffraction grating. Student Materials
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors.
 Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 2: Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
It s a Colorful Life
 It s a Colorful Life Dr. Lawrence D. Woolf General Atomics San Diego CA 92121 Presented at the 2000 Southeastern College Art Conference/Mid-America College Art Association Meeting Foundations in Art Theory
It s a Colorful Life Dr. Lawrence D. Woolf General Atomics San Diego CA 92121 Presented at the 2000 Southeastern College Art Conference/Mid-America College Art Association Meeting Foundations in Art Theory
Hue Do You Think Hue Are?
 Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
Hue Do You Think Hue Are? The Properties of Color There are three fundamental properties by which color is characterized: hue, value and chroma. We ve been discussing value. Now Introducing Hue! Who What
L 32 Light and Optics [2] The rainbow. Why is it a rain BOW? Atmospheric scattering. Different colors are refracted (bent) by different amounts
![L 32 Light and Optics [2] The rainbow. Why is it a rain BOW? Atmospheric scattering. Different colors are refracted (bent) by different amounts L 32 Light and Optics [2] The rainbow. Why is it a rain BOW? Atmospheric scattering. Different colors are refracted (bent) by different amounts](/thumbs/77/75013139.jpg) L 32 Light and Optics [2] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky and red sunsets Mirrors
L 32 Light and Optics [2] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky and red sunsets Mirrors
PHYSICS - Chapter 16. Light and Color and More
 PHYSICS - Chapter 16 Light and Color and More LIGHT-fundamentals 16.1 Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum runs from long Radio and TV waves to short
PHYSICS - Chapter 16 Light and Color and More LIGHT-fundamentals 16.1 Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum runs from long Radio and TV waves to short
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves What is an Electromagnetic Wave? An EM Wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a field. A field is a area around an object where the object can apply a force on another
Electromagnetic Waves What is an Electromagnetic Wave? An EM Wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a field. A field is a area around an object where the object can apply a force on another
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
 Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Color Theory. Chapter 2 Color Basics
 Chapter 2 Color Basics Color Theory Intrinsic Value Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Strict vs. Chromatic Neutral, Tint, Shade, Tone Analogous/Adjacent Local vs. Atmospheric Clr Color & temperature Pigment vs.
Chapter 2 Color Basics Color Theory Intrinsic Value Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Strict vs. Chromatic Neutral, Tint, Shade, Tone Analogous/Adjacent Local vs. Atmospheric Clr Color & temperature Pigment vs.
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 13 13 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 13: Light 13.1: The Behavior of Light 13.2: Light and Color 13.3: Producing Light 13.4: Using Light 13.1 The Behavior of Light Light and Matter
13 13 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 13: Light 13.1: The Behavior of Light 13.2: Light and Color 13.3: Producing Light 13.4: Using Light 13.1 The Behavior of Light Light and Matter
UBT128X Colour theory
 UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
UBT128X Colour theory Unit reference number: L/507/5481 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring the concepts and theories of colour. Learners will develop the knowledge
Reading Preview. Key Terms transparent material translucent material opaque material primary colors secondary color complementary colors pigment
 Section 1 Light and Color 1 Light and Color Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to O.4.1.1 State what happens to the light that strikes an object. O.4.1.2 Describe what determines the color
Section 1 Light and Color 1 Light and Color Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to O.4.1.1 State what happens to the light that strikes an object. O.4.1.2 Describe what determines the color
Color & Graphics. Color & Vision. The complete display system is: We'll talk about: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain
 Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
Color & Graphics The complete display system is: Model Frame Buffer Screen Eye Brain Color & Vision We'll talk about: Light Visions Psychophysics, Colorimetry Color Perceptually based models Hardware models
 CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
CHAPTER 11 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory
 Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
Part I: Color Foundations The Basic Principles of COLOUR theory Colour Systems Available colour systems are dependent on the medium with which a designer is working. When painting, an artist has a variety
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry. Lecture 2. Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics
 FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
KS3 revision booklet Physics
 NAME KS3 revision booklet Physics Use this booklet to help you revise the physics you have studied in Key Stage 3. There are some ideas about how you can test yourself in the back of this booklet. Why
NAME KS3 revision booklet Physics Use this booklet to help you revise the physics you have studied in Key Stage 3. There are some ideas about how you can test yourself in the back of this booklet. Why
Characteristic Primary Color Primary Pigment. Colors red, green, blue magenta, cyan, yellow
 Light Energy Chapter 14 You can use a compare and contrast table to show how two or more items are alike and how they are different. Look at the example shown below for primary colors and primary pigments.
Light Energy Chapter 14 You can use a compare and contrast table to show how two or more items are alike and how they are different. Look at the example shown below for primary colors and primary pigments.
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Light enables organisms
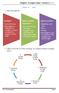 Chapter 15. Light 1. What does light do? Sunlight causes the day. Moonlight is a reflection of Sunlight. It shines to dispel the darkness of the night. Light enables organisms to see during day and night.
Chapter 15. Light 1. What does light do? Sunlight causes the day. Moonlight is a reflection of Sunlight. It shines to dispel the darkness of the night. Light enables organisms to see during day and night.
Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light
 Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
Optics B. Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET. THIS IS AN TEST SET.
 Optics B Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida 1 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET. THIS IS AN TEST SET. Part I: General Body Knowledge Questions 2 1) (3 PTS) For much of the
Optics B Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida 1 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET. THIS IS AN TEST SET. Part I: General Body Knowledge Questions 2 1) (3 PTS) For much of the
Physical Science Physics
 Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
Unit 8: Light and Optics
 Objectives Unit 8: Light and Optics Explain why we see colors as combinations of three primary colors. Explain the dispersion of light by a prism. Understand how lenses and mirrors work. Explain thermal
Objectives Unit 8: Light and Optics Explain why we see colors as combinations of three primary colors. Explain the dispersion of light by a prism. Understand how lenses and mirrors work. Explain thermal
Test Review # 8. Physics R: Form TR8.17A. Primary colors of light
 Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Light. In this unit: 1) Electromagnetic Spectrum 2) Properties of Light 3) Reflection 4) Colors 5) Refraction
 Light In this unit: 1) Electromagnetic Spectrum 2) Properties of Light 3) Reflection 4) Colors 5) Refraction Part 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum and Visible Light Remember radio waves are long and gamma rays
Light In this unit: 1) Electromagnetic Spectrum 2) Properties of Light 3) Reflection 4) Colors 5) Refraction Part 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum and Visible Light Remember radio waves are long and gamma rays
Thursday, May 19, 16. Color Theory
 Color Theory Which colours is white light made of? Did you know?! Your eyes have only 3 types of cells that can recognize millions of colours.! When you observe a colour, it is because different combinations
Color Theory Which colours is white light made of? Did you know?! Your eyes have only 3 types of cells that can recognize millions of colours.! When you observe a colour, it is because different combinations
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals
 color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
color basics theory & application Fall 2013 Ahmed Ansari Communication Design Fundamentals Presentation 7 Tom Fraser + Adam Banks Designer's Color Manual Johannes Itten The Art of Color Ellen Lupton &
Test Review # 9. Physics R: Form TR9.15A. Primary colors of light
 Physics R: Form TR9.15A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics R: Form TR9.15A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Waves
 A Waves in air, fluids and solids 1. The diagrams below show two types of wave produced on a slinky spring. A B a. Which one is a transverse wave? (1) Wave B b. What is the name of the other type of wave?
A Waves in air, fluids and solids 1. The diagrams below show two types of wave produced on a slinky spring. A B a. Which one is a transverse wave? (1) Wave B b. What is the name of the other type of wave?
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26
 skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
UNIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND
 NIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND Primary Colours Luminous Sources of Light Colours sources is divided Secondary Colours includes Illıminated Sources of Light LIGHT Illumination is form Travels in Spaces Shadow Reflection
NIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND Primary Colours Luminous Sources of Light Colours sources is divided Secondary Colours includes Illıminated Sources of Light LIGHT Illumination is form Travels in Spaces Shadow Reflection
Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline. Physical Science minutes. Objectives
 Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline Physical Science 5-12 60-90 minutes Objectives This lesson explores some of the ways in which light can be manipulated to
Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline Physical Science 5-12 60-90 minutes Objectives This lesson explores some of the ways in which light can be manipulated to
LASERS. & Protective Glasses. Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection.
 LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
Ch. 18 Notes 3/28/16
 Section 1 Light & Color: Vocabulary Transparent material: transmits most of the light that strikes it. Light passes through without being scattered, so you can see clearly what is on the other side. Ex.
Section 1 Light & Color: Vocabulary Transparent material: transmits most of the light that strikes it. Light passes through without being scattered, so you can see clearly what is on the other side. Ex.
Take a break: Watch some stop-motion animation Music: Grindin
 Take a break: Watch some stop-motion animation Music: Grindin http://vimeo.com/9625370 1 skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 18 Thursday, March 11 Next week: Chapter 10, start reading.
Take a break: Watch some stop-motion animation Music: Grindin http://vimeo.com/9625370 1 skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 18 Thursday, March 11 Next week: Chapter 10, start reading.
How can we "see" using the Infrared?
 The Infrared Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range
The Infrared Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range
LIGHT. ENERGY FOR LIFE 2 Presented by- Ms.Priya
 LIGHT ENERGY FOR LIFE 2 Presented by- Ms.Priya VOCABULARY 1. Opaque 2. Transparent 3. Translucent 4. Refraction 5. Reflection 6. Ray 7. Image 8. Virtual image 9. Medium 10.Vacuum 11. Lens 12. Spectrum
LIGHT ENERGY FOR LIFE 2 Presented by- Ms.Priya VOCABULARY 1. Opaque 2. Transparent 3. Translucent 4. Refraction 5. Reflection 6. Ray 7. Image 8. Virtual image 9. Medium 10.Vacuum 11. Lens 12. Spectrum
Myth #1. Blue, cyan, green, yellow, red, and magenta are seen in the rainbow.
 Myth #1 Blue, cyan, green, yellow, red, and magenta are seen in the rainbow. a. The spectrum does not include magenta; cyan is a mixture of blue and green light; yellow is a mixture of green and red light.
Myth #1 Blue, cyan, green, yellow, red, and magenta are seen in the rainbow. a. The spectrum does not include magenta; cyan is a mixture of blue and green light; yellow is a mixture of green and red light.
Chapter 18the Electromagnetic Spectrum And Light Calculating
 Chapter 18the Electromagnetic Spectrum And Light Calculating CHAPTER 18THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM AND LIGHT CALCULATING PDF - Are you looking for chapter 18the electromagnetic spectrum and light calculating
Chapter 18the Electromagnetic Spectrum And Light Calculating CHAPTER 18THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM AND LIGHT CALCULATING PDF - Are you looking for chapter 18the electromagnetic spectrum and light calculating
LIGHT BOX & OPTICAL SET CAT NO. PH0615
 LIGHT BOX & OPTICAL SET CAT NO. PH0615 Experiment Guide ACTIVITIES INCLUDED: Diffraction Angle of Reflection Using a Plane Mirror Refraction of Different Shaped Prisms Refraction (Snell's Law) Index of
LIGHT BOX & OPTICAL SET CAT NO. PH0615 Experiment Guide ACTIVITIES INCLUDED: Diffraction Angle of Reflection Using a Plane Mirror Refraction of Different Shaped Prisms Refraction (Snell's Law) Index of
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World
 The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects. We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena
A Colorful Lab in a Bag
 A Colorful Lab in a Bag In this lab you will explore color and color mixing. You will investigate the white light spectrum and examine ways in which color can be combined. One process of mixing color,
A Colorful Lab in a Bag In this lab you will explore color and color mixing. You will investigate the white light spectrum and examine ways in which color can be combined. One process of mixing color,
Additive and Subtractive Color Lab On Line PreAP
 Name Additive and Subtractive Color Lab On Line PreAP Period 1. Go to Explorelearning.com and try to LOG IN with your name. Your user name should be your name: First_LastAHS (example Sally_StudentAHS).
Name Additive and Subtractive Color Lab On Line PreAP Period 1. Go to Explorelearning.com and try to LOG IN with your name. Your user name should be your name: First_LastAHS (example Sally_StudentAHS).
Notes on colour mixing
 INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
INFORMATION SHEET These notes, with the diagrams in colour, can be found on the internet at: http://www.andrewnewland.com/homepage/teaching Notes on colour mixing Andrew Newland T E A C H I N G A R T &
Name: Date: Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum, Sound Waves, and Light Waves Study Guide For Final
 Name: Date: Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum, Sound Waves, and Light Waves Study Guide For Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A disturbance
Name: Date: Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum, Sound Waves, and Light Waves Study Guide For Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A disturbance
Experiment 10. Color. Observe the transmission properties of the three additive primary color filters and the three subtractive primary color filters.
 Experiment 10 Color 10.1 Objectives Observe the transmission properties of the three additive primary color filters and the three subtractive primary color filters. Observe and interpret the color sensations
Experiment 10 Color 10.1 Objectives Observe the transmission properties of the three additive primary color filters and the three subtractive primary color filters. Observe and interpret the color sensations
Instructional Resources/Materials: Light vocabulary cards printed (class set) Enough for each student (See card sort below)
 Grade Level/Course: Grade 7 Life Science Lesson/Unit Plan Name: Light Card Sort Rationale/Lesson Abstract: Light vocabulary building, students identify and share vocabulary meaning. Timeframe: 10 to 20
Grade Level/Course: Grade 7 Life Science Lesson/Unit Plan Name: Light Card Sort Rationale/Lesson Abstract: Light vocabulary building, students identify and share vocabulary meaning. Timeframe: 10 to 20
Psy 280 Fall 2000: Color Vision (Part 1) Oct 23, Announcements
 Announcements 1. This week's topic will be COLOR VISION. DEPTH PERCEPTION will be covered next week. 2. All slides (and my notes for each slide) will be posted on the class web page at the end of the week.
Announcements 1. This week's topic will be COLOR VISION. DEPTH PERCEPTION will be covered next week. 2. All slides (and my notes for each slide) will be posted on the class web page at the end of the week.
Table of Contents. Light and Color
 light and color Table of Contents Light and Color Light Light Sources The Direction of Light Reflection Reflective Surfaces Light Bounces How Do We See? Light Through Objects Refraction Bending Light Experiment
light and color Table of Contents Light and Color Light Light Sources The Direction of Light Reflection Reflective Surfaces Light Bounces How Do We See? Light Through Objects Refraction Bending Light Experiment
TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY SCHOOL
 Page 1 of 7 TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY IN SCHOOL Teachers in public schools are still teaching the wrong color theory to children. Here is a list of reasons why this is done, why it is wrong for teachers
Page 1 of 7 TEACH THE CORRECT COLOR THEORY IN SCHOOL Teachers in public schools are still teaching the wrong color theory to children. Here is a list of reasons why this is done, why it is wrong for teachers
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Do not need matter to transfer energy. Made by vibrating electric charges. When an electric charge vibrates,
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Do not need matter to transfer energy. Made by vibrating electric charges. When an electric charge vibrates,
