Contents: 1. Main Objectives. 2. Useful Websites. 4.Word Wall Cards. 3.Vocabulary Cards. 5.Glossary. 6.Key Question Cards. 7.Prior Learning Diagram
|
|
|
- Luke Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MODERN AGE
2 Contents: 1. Main Objectives 2. Useful Websites 4.Word Wall Cards 3.Vocabulary Cards 5.Glossary 6.Key Question Cards 7.Prior Learning Diagram 8.Hands-On Activities 9.Reading Comprehension Text 10.Final Activity
3 Main Objectives: 1. To situate the Modern Age period on the time line. 2. To use the vocabulary related to the content. 3. To know how technical advances in navigation favoured the new trade routes. 4. To understand reasons for and consequences of the Discovery of America. 5. To value the importance of the Spanish Empire in the sixteenth Century. 6. To appreciate the importance of the Spanish Golden Age. 7. To demonstrate their understanding of life during the Modern Age through a piece of creative writing.
4 Useful websites Information about Renaissance and the main figures of that time. Interactive links to other interesting sites Lots of information, activities and links about Christopher Columbus and the Discovery of America. Site to know who the most important discoverers and explorers of the Modern Age were. A complete calendar about Golden Age.
5 Chronological information about the development of the Absolute Monarchy in Spain, France and England. The main events of the History of Spain.
6 MODERN AGE
7 Renaissance classical culture
8 patron
9 authoritarian monarchy absolute monarchy
10 navigation
11 caravel compass
12 astrolabe sextant
13 portolan charts
14 silk spices
15 Discovery colonisation
16 nobleman nobility
17 bourgeoisie bourgeois
18 craftsman
19 peasant clergy
20 Golden Age
21 architect painter
22 sculptor
23 literature writer
24 decline (decadence)
25 the Enlightenment
26 Vocabulary Cards Modern Age n. the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). During the Modern Age there were many changes in the European society. Renaissance Classical culture n. means re-birth. A cultural movement that spanned roughly from the 14 th Century to the 17 th Century. It began in Italy and it later spread to the rest of Europe. During the Renaissance people were interested in all aspects of Greek and Roman cultures. n. name given to the influence of Ancient Greek or Roman civilizations on language, philosophy, art throughout the Renaissance period.
27 n. a person who supports and gives money to artists, writers or musicians. patron Lorenzo de Medici, called Lorenzo the Magnificent, was patron to the Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo. n. the politic system in which the kings in 15 th century have all the power. authoritarian monarchy Catholic monarchs of Spain, Isabella and Ferdinand, were the most representative example of authoritarian monarchy in Europe. absolute monarchy n. form of government where the king or queen has absolute power on all aspects of his or her subjects life. Charles I of Spain (Holy Roman Emperor) and his son, Philip II, were the most powerful monarchs in 16 th Century. French absolute Monarchy was the most powerful monarchy in Europe in 17 th and 18 th centuries.
28 n. the guidance of ships from place to place. navigation The appearance of technical advances in navigation and the building of bigger ships favoured the discovery of new trade routes. caravel n. a light sailing ship with two or three masts and lateen sails used by the Spanish and Portuguese in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. La Pinta and La Niña were the two caravels used by Columbus in this first voyage to America. The other ship was a carrack called Santa María. n. an instrument that is used for finding directions. It has a dial and a magnetic needle that always points to the North. compass The use of the compass greatly improved the safety and efficiency of travelling, especially in ocean travel.
29 astrolabe n. ancient instrument used by navigators and astronomers to determine latitude, longitude and time of day. It also determines the altitude of the Sun, planets, stars and Moon. sextant The word astrolabe comes from the Greek and means stars seeker. n. navigational instrument used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon and to determine its latitude and longitude. Navigators replaced the astrolabe for the sextant because it was more precise. n. European navigational maps, based on realistic descriptions of harbours and coasts. portolan charts Portolan charts were created in the 13 th Century and developed in 14 th and 15 th centuries.
30 n. valuable/delicate cloth made from the fine treads produced by certain insect larvae. silk The Silk Road was the most important cultural and commercial communication link between Southern Europe and Asia. n. any of a variety of pungent or aromatic vegetable substances used to for seasoning food. spice From the 11 th Century, as a consequence of the Crusades, spices such cinnamon, pepper, cardamom, ginger, turmeric were used for seasoning food and also for medical reasons. n. the act of discovering a place or a thing. Discovery The Discovery of America marked the beginning of a new age.
31 n. the act or process of establishing colonies. colonisation For more than 300 years, the Spaniards colonised a vast territory stretching from the line between California and Florida to the Southernmost part of the American continent. n. the inhabitant of walled towns, formed by craftsmen, merchants bourgeois In the Modern Age the bourgeois became rich with trade development. n. a man who makes things skilfully with his hands. craftsman Craftsmen associated themselves in trade groups, called guilds, according with their jobs: blacksmiths, silversmiths, shoemakers, tailors
32 n. a person who works on the land. peasant Peasants were the poorest social class in this time. Many of them emigrated to America looking for a better future. n. the official leaders of a religious belief. clergy Golden Age The clergy had big influence in the society. Many of them went to America and founded missions where they taught religion, reading, writing and even farming. n. a flourishing period in arts and literature that took place in Spain during the 16 th and 17 th Centuries. During Spain s Golden Age there were very important artists like El Greco, Velázquez, Murillo and great writers like Cervantes, Lope de Vega, Calderón de la Barca, Quevedo
33 n. a person who designs buildings. architect The most important Spanish architect in Modern Age was Juan de Herrera who designed the San Lorenzo de El Escorial Monastery. n. an artist who paints. painter Diego Velázquez was the official painter of the Spanish Court in the seventeenth Century. n. a person who creates sculptures. sculptor Spanish sculptures in the Golden Age were made of wood and marble. The sculptures were used for decorate churches and the cathedrals.
34 n. name given to all creative writing of recognised artistic value. literature The seventeenth century was the most brilliant period for literature in Spain. n. a person who writes books, stories or articles as a job. writer decline The writer Miguel de Cervantes was born in Alcalá de Henares and wrote many novels. The most famous of which was Don Quixote de la Mancha. n. period when something approaches an end. For many and different reasons (bad harvest, epidemics, lost battles, droughts, high mortality, emigration to America ) the Spanish Empire begin to decline in the 17 th Century.
35 The Enlightenment n. a philosophical and cultural movement in the eighteenth Century that stressed human reasoning over blind faith and encouraged scientific thinking. Charles III was the most important king of the Enlightenment. He carried out many significant social and economic changes in Spain. He was called The best Mayor of Madrid for all the important monuments he built during his reign.
36 Glossary absolute monarchy: n. form of government where the king or queen has absolute power on all aspects of his or her subjects life. architect: n. a person who designs buildings. astrolabe: n. ancient instrument used by navigators and astronomers to determine latitude, longitude and time of day. It also determines the altitude of the Sun, planets, stars and Moon. authoritarian monarchy: n. the politic system in which the kings in 15 th Century have all the power. bourgeois: n. the inhabitant of walled towns, formed by craftsmen, merchants caravel: n. a light sailing ship with two or three masts and lateen sails used by the Spanish and Portuguese in the 15 th and 16 th Centuries. Classical culture: n. name given to the influence of Ancient Greek or Roman civilizations on language, philosophy, art in the Renaissance. clergy: n. the official leaders of a religious belief. colonisation: n. the act or process of establishing colonies.
37 compass: n. an instrument that is used for finding directions. It has a dial and a magnetic needle that always points to the North. craftsman: n. a man who makes things skilfully with his hands. decline: n. the period when something approaches an end. Discovery: n. the act of discovering a place or a thing. Golden Age: n. a flourishing period in arts and literature that took place in Spain during the 16 th and 17 th Centuries. literature: n. name given to all creative writing of recognised artistic value. Modern Age: n. the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). navigation: n. the guidance of ships from place to place. painter: n. an artist who paints. patron: n. a person who supports and gives money to artists, writers or musicians. peasant: n. a person who works on the land. portolan charts: n. European navigation maps based on realistic descriptions of harbours and coasts.
38 Renaissance: n. means re-birth. A cultural movement that spanned roughly from the 14 th Century to the 17 th Century. It began in Italy and it later spread to the rest of Europe. sculptor: n. a person who creates sculptures. sextant: n. navigational instrument used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon and to determine its latitude and longitude. silk: n. valuable/delicate cloth made from the fine treads produced by certain insect larvae. spice: n. any of a variety of pungent or aromatic vegetable substances used to for seasoning food. writer: n. a person who writes books, stories or articles as a job. The Enlightenment: n. a philosophical and cultural movement in the eighteenth century that stressed human reasoning over blind faith and encouraged scientific thinking.
39 When does the Modern Age begin?
40 When does the Modern Age end?
41 What does Renaissance mean?
42 What were the people of Renaissance most interested in?
43 Who supported artists, writers or musicians during the Renaissance?
44 What were the names of the Catholic Monarchs?
45 Who were the absolute monarchs in Spain during 16 th Century?
46 The three most important navigational instruments of 15 th and 16 th Centuries were
47 Where was Christopher Columbus born?
48 On what date did Christopher Columbus discover America?
49 What were the names of Christopher Columbus ships in his first voyage?
50 Did Christopher Columbus know that he had discovered a new continent?
51 What was the name of the Trade Route between Southern Europe and Asia?
52 Can you name three different types of spices?
53 What part of America did Spanish Empire conquer in the 16 th Century?
54 The richest social class in the Modern Age was
55 Can you name three jobs that craftsmen did in the Modern Age?
56 The poorest social class in this period was
57 Who had a big influence in the society during the Modern Age?
58 The period when the arts and literature flourished in Spain was called
59 Can you name three Spanish artists from the Golden Age?
60 Can you name three Spanish writers from the Golden Age?
61 Which is the most famous piece of Spanish literature?
62 Who wrote Don Quixote of La Mancha?
63 Where was Miguel de Cervantes born?
64 Who was the main architect of San Lorenzo de El Escorial?
65 In which province of Spain is San Lorenzo de El Escorial situated?
66 The official painter of the Spanish Court in the 17 th Century was
67 What were the sculptures made of?
68 Can you name three reasons for The Spanish Empire s decline?
69 In what century did The Enlightenment take place?
70 The most important Spanish king of The Enlightenment was
71 What do you know about Modern Age? Fill in the diagram with as many things as you can remember about Modern Age MODERN AGE
72 Hands on Activity 1 Benefits after the Discovery of America Exchange of products between Europe and America Objectives 1. To describe what products passed from Europe to America and from America to Europe after the Discovery of America. 2. To value and describe the importance that the exchange of these products (food, animal farming, agriculture, trade ) had for life in those days. Introduction In this activity children will use the picture cards and place them on a map of the world to learn about what products crossed over from one continent to the other. Development The teacher should cut and laminate the picture cards. In a physical wall of the world map, the pupils must draw an arrow between Europe and America and another arrow between America and Europe. They must stick each picture card in the correct direction in order to understand what types of products passed from Europe to America and vice versa. Plenary Once the pupils have finished the task, they should be able to write some conclusions and to answer several comprehension questions.
73 Products that passed over from Europe to America wheat grapes olives melon
74 Products that passed over from Europe to America sugar rice oranges lemons
75 Products that passed over from Europe to America garlic onions apples coffee
76 Products that passed over from Europe to America cattle pigs horses poultry
77 Products that passed over from Europe to America sheep goats roses carnations
78 Products that passed over from America to Europe potatoes corn tomatoes peppers
79 Products that passed over from America to Europe sunflowers peanuts cocoa pineapples
80 Products that passed over from America to Europe avocados beans vanilla pumpkins
81 Products that passed over from America to Europe custard apples yucca turkeys tobacco
82 Comprehension questions 1. Can you name five farming products that crossed over from Europe to America? 2. Can you name five farming products that crossed over from America to Europe? 3. What animals crossed from Europe to America? 4. And from America to Europe? 5. What other products crossed over from Europe? 6. And from America? 7. Do you think the diet of both continents changed? Why?
83 8. And the way of life? Why? 9. Write a few sentences with some conclusions about what you have learned in this activity.
84
85
86 Hands on Activity 2 Learning about three Modern Age masterpieces Main Objectives 1. To learn about three artistic masterpieces of the Modern Age and their authors. 2. To appreciate and describe the progress in some of the Fine Arts (architecture, sculpture and painting) during this period in History. Resources needed: - Web sites - Interactive board - Encyclopaedias masterpieces/work-card/obra/the-family-of-felipe-iv-or-las-meninas/ Introduction In this activity children learn about three artistic masterpieces from the 16 th and 17 th Centuries. They represent three of the Fine Arts: - Architecture: Monastery of San Lorenzo of El Escorial. Juan de Herrera (Madrid) - Sculpture: The Pieta. Michelangelo. Vatican (Rome) - Painting: Las Meninas. Velázquez. Prado Museum (Madrid)
87 Development Project the images in the IWB (Interactive White Board) and encourage the pupils to observe each one carefully. Ask them to brainstorm and say what these images mean to them and to share whatever all they already know about them. Give a short explanation on the importance and value of these masterpieces and give the children the websites. They will need to consult these websites to find out more information on each of the masterpieces. They can either do this at home or in the computer room in school. Once the children have found the information, they must answer the different questions that follow the pictures Plenary The teacher projects the images again and all the pupils check with the teacher that they have answered the questions correctly.
88 Palace Monastery of San Lorenzo de El Escorial (Madrid) Juan de Herrera
89 San Lorenzo de El Escorial Answer these questions: 1. What king ordered the construction of this building? 2. What did he want commemorate? 3. What architect designed it? Who continued the work? 4. Where is it located? 5. Can you name the main parts of the building? 6. Why is it a palace and a monastery at the same time? 7. What does the Royal Pantheon contain? 8. What shape does the building have? For what reason?
90 The Meninas- Diego Velázquez Las Meninas Diego Velázquez
91 Las Meninas Answer these questions: 1. What is the name of the main figure? 2. Who were her parents? 3. Where are they in the picture? 4. What is the name of the palace they are in? 5. What room of the palace are they in? 6. How many people appear in the picture? 7. Who are the people that surround Margaret? 8. Where does the light in the picture come from?
92 9. Does Velázquez appear in the picture? 10. Where is he? 11. What is he doing? 12. Can you describe one of the three meninas?
93 La Pieta Michelangelo Buonarroti ( )
94 La Pieta Michelangelo was relatively unknown to the world as an artist. He was only in his early twenties when he was commissioned in 1498 to do a life size sculpture of the Virgin Mary holding her son in her arms. It would be the first of four that he would create, but this was the only one he finished completely. It was to be unveiled in St. Peter's Basilica by In less than two years, Michelangelo carved it from a single slab of marble; the most magnificent sculpture ever created. His interpretation of the Pieta was far different from others created previously by other artists. Michelangelo decided to create a youthful, serene and celestial Virgin Mary instead of a broken hearted and somewhat older woman. When it was unveiled, a proud Michelangelo stood by and watched as people admired the beautiful Pieta. His pride was turned into anger as he overheard a group of people attributing the work to other artists of his time. That anger caused Michelangelo to add one last thing to his sculpture. Going down the sash on the Virgin Mary, Michelangelo carved his name. Later he regretted that his emotions had overwhelmed him and promised not to sign any of his works again. Answer these questions: Anthony Parente 1. How old was Michelangelo when he created the Pieta? 2. How many sculptures of the Pieta did Michelangelo do in all his life? 3. Where was the sculpture to be unveiled? 4. How long did it take him to carve it?
95 5. What is it made of? 6. Why was this sculpture of the Pieta different from the others? 7. What happened when the sculpture was unveiled? 8. What did Michelangelo carve on Virgin Mary s sash*? 9. What did he promise himself? 10. Look carefully at the picture and write some sentences describing it. * sash: long band of cloth or other material worn over one shoulder.
96 Hands on Activity 3 Christopher Columbus and the Discovery of America Objectives 1. To discuss the reasons of Christopher Columbus project. 2. To describe the importance of his heroic deed travelling towards the unknown. Resources needed Interactive White Board/Digital Projector Relevant word wall cards Relevant key question cards PowerPoint presentation Activity 3 Development The PowerPoint presentation will help the pupils understand the reasons and the facts of the Discovery of America. In the last slide there is a button that links with a web site that will provide them more information about Christopher Columbus life and voyages. After watching the PowerPoint presentation and the web site, the students must answer some questions related to it. Plenary The pupils can see the PowerPoint again and check that they have answered the questions correctly.
97 Hands on Activity 3 Christopher Columbus and the Discovery of America Answer these questions: 1. When was Columbus born? Where? 2. At what age did he start sailing? 3. What did he want to find? 4. What monarchs did he manage to persuade? 5. What where the names of the three ships? 6. What did the sailors use to measure time? 7. What instruments did they use for navigation? 8. What date did the expedition arrive to land?
98 9. At what age did Columbus die? 10. Can you name the three first lands where they arrived at in the new continent? Do you know their actual names?
99 Comprehension text The first circumnavigation around the world ( ) Ferdinand Magellan was born in 1480 in Portugal. At the age of 12, he was appointed as queen s messenger in the royal court. At the court, he learned about many famous explorers and the most important information about navigating ships. He started sailing when he was 25 years old. He thought that the Earth was round and he wanted to go to the Spice Islands (also known as Moluccas Islands) by the West route because the trade with spices was very important. He asked the King of Portugal to support his journey, but he refused. After that, he begged the King of Spain, Charles I, to support his journey. The king was interested in his plan since Spain was looking for a better sea route to Asia, rather than the Portuguese route around the southern tip of Africa. He began to look for sailors but it was a very difficult task. None of the Spanish sailors wanted to sail with him because he was Portuguese. He would have to take anybody who signed on, whether they were good seamen or not. Parts of his crew were prisoners, released from jail in return for sailing with him, but the captains of the ships were Spanish. In September of 1519, he sailed from Sanlúcar de Barrameda with five ships the Trinidad, the Concepcion, the Santiago, the San Antonio and the Victoria. At the beginning, all went well. The small fleet sailed across the Atlantic Ocean and reached South America. They stocked up with goods and sailed down the coastline looking for a passage through this continent. They sailed further and further south, sailing into every river and bay they came upon. The weather was getting colder, and they were running out of supplies, so the crew revolted against Magellan and the other captains. Magellan managed to put down the revolt and after that, they continued the journey. Later the Santiago was sunk in a storm. Finally, in October of 1520, they found a strait, that would later become the Strait of Magellan. It took 38 days to sail through the dangerous strait. They finally arrived at the ocean that Núñez de Balboa had discovered several years before. They named it the Pacific Ocean because of its calm waters.
100 They sailed for weeks across this ocean with no trace of land. The drinking water stunk and started to get slimy. All the crew had to eat rats. Most of the crew suffered from scurvy because of the lack of vegetables and fruits in their diet. One of the other captains deserted him and sailed the San Antonio back to Spain. On March of 1521, they arrived in Guam, an island in the Pacific. From there, they headed for the Moluccas islands. He never managed to get to the Spice Islands. He was caught in a war in the Philippine islands. They faced a group of natives who killed Magellan with a poisoned arrow in his foot and a spear through his heart. After he died, his crew burned the Conception because of its poor condition. Only two ships finally reached the Spice Islands. The crew loaded both ships with a rich cargo of spices and headed back for Spain. On the way home, the Portuguese, who had claimed the Spice Islands, captured the Trinidad. The Victoria, which was commanded by Juan Sebastian Elcano, was the only ship to make it safely back to Spain. Crossing the sea was not easy. There were many storms near the Cape of Good Hope and part of the crew died due to scurvy and starvation. Some desertions took place. Finally, the Victoria arrived at Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Spain, on September 6 th, Of the five ships that begun the journey, only one ship made the voyage around the world. Out of 250 men, only 18 survived. In that date, Juan Sebastián Elcano was the first person to circumnavigate the world after sailing nautical miles ( kilometres) almost twice the equatorial diameter of The Earth, having proved that it was round.
101 Reading Comprehension The first Circumnavigation around the World Answer these questions: 1. Where was Fernando Magellan born? 2. Where did he learn about navigation? 3. At what age did he start to sail? 4. Where did he want to go? 5. Who did he ask to support his journey at first? 6. Who supported the journey really? 7. When and where did the expedition start? 8. What were the names of the ships? 9. Where did the expedition head to? 10. What happened in October 1520?
102 11. How many days did the crew need to sail through the strait? 12. How did they call the ocean? Why? 13. Why did the crew suffer from scurvy? 14. What happened in the Philippine Islands? 15. What did the crew do when they arrived at the Spice Islands? 16. Who commanded the Victoria? 17. What happened on the way home? 18. When and where did the Victoria arrive? 19. How many people started and how many people arrive? 20. What did Juan Sebastian Elcano prove with this voyage?
103 Final activity Notes for the teacher This activity aims to give the children an opportunity to demonstrate what they have learnt about the topic through imaginative writing. Each child should assume the character of a Modern Age character, and write about their life. Before the writing starts, you can use the word bank to make sure children have the words they need and the correct spelling, and the writing organiser for those children who find difficult to put their ideas in order.
104 WORD BANK Before you start your writing, think of words you might need to use. Check for spelling in the dictionary. Ask your teacher how to say them in English. Nouns Verbs Adjectives Adverbs
105 Writing Organizer Write down ideas to organize your writing. Paragraph 1: Introduction. What is your name? Who are you? How old are you? Where do you live? What is the date? Paragraph 2: Explain your activities on a regular day. Do you work? What is your job? Do you study? Do you have free time? Paragraph 3: Explain what culture you belong to. Where do you come from? Who is the king at your time? What language do you speak? Paragraph 4: Conclusion. Is your life easy or hard? Why?
106 Think about all that you have learned throughout this topic. Imagine you are a child living in the Modern Age in Spain. Write about your life. Think about your name, where you live, what you eat, how you dress and what activities you do during the day. Choose amongst these people possible character: A Renaissance artist (painter, sculptor, architect, writer ) or A sailor in one of Columbus voyages.
107 My Life as Modern Age Artist
108 My Life as Sailor
109 Final Activity Can you link each work or works of art with a monarch? Are there any monarchs who can not be linked with any work of art? What conclusions does this bring to your mind? Charles I of Spain and V of Germany ( ) Philip V ( ) Philip II ( ) Ferdinand VI ( ) Philip III ( ) Charles III ( ) Philip IV ( ) Charles II ( Charles IV ( )
110 Yuste Monastery 1556 Casón of El Buen Retiro ( ) El Greco Palace Monastery of San Lorenzo of ElEscorial ( ) Alcalá Gate ( ) Main Square Madrid (1619) Palace of Charles V- Granada 1526 Velázquez ( ) Royal Palace of Madrid ( ) Salesas Reales ( ) House of the Prince-Aranjuez ( ) Goya ( )
111 Link with arrows Monarchs Works of art Charles I Philip II Philip III Philip IV CharlesII Philip V Ferdinand VI Charles III Charles IV Royal Palace of Madrid Goya Alcala Gate Salesas Reales Palace of Charles V House of the Prince Velázquez Monastery of El Escorial Main Square El Greco Yuste Monastery Casón of El Buen Retiro Write down your conclusions :
112 Final Activity CROSSWORD PUZZLE A B C D E F G H I J K L M N Ñ O P Q R
113 CROSSWORD PUZZLE 1. The person who writes books, stories or articles as a job. 2. The man who makes things skilfully with his hands. 3. The person who supports and gives money to artists, writers or musicians. 6. Navigational instrument used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon and to determine its latitude and longitude. 9. The guidance of ships from place to place. 11. Any of a variety of pungent or aromatic vegetable substances used for flavouring food. 13. The act or process of establishing colonies. 14. The instrument that is used for finding directions. It has a dial and a magnetic needle that always points to the North. 15. The person who creates sculptures. 17. Name given to all creative writing of recognised artistic value.. A. The person who works on the land. D. Name of the Ocean that Christopher Columbus crossed over. E. The light sailing ship with two or three masts and lateen sails used by the Spanish and Portuguese in the 15 th and 16 th Centuries. F. Means re-birth. A cultural movement that spanned roughly from the 14 th Century to the 17 th Century. It began in Italy and it later spread to the rest of Europe. I. Valuable/delicate cloth made from the fine treads produced by certain insect larvae. L. The person who designs buildings. M. The artist who paints. Ñ. The period when something approaches an end. P. The term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). R. The official leaders of a religious belief.
114 Final Activity CROSSWORD PUZZLE -SOLUTIONS A B C D E F G H I J K L M N Ñ O P Q R W R I T E R A E C R A F T S M A N P A T R O N C O E A H D D A A I I E E C S T S E X T A N T C R L A L S E L N E N A A S C I A R T N N A V I G A T I O N G G T C L E E Y S P I C E K P C A A R C O L O N I S A T I O N C O M P A S S N V S C U L P T O R E E L I T E R A T U R E
115 CROSSWORD PUZZLE 1. The person who writes books, stories or articles as a job. 2. The man who makes things skilfully with his hands. 3. The person who supports and gives money to artists, writers musicians. 6. Navigational instrument used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon and to determine its latitude and longitude. 9. The guidance of ships from place to place. 11. Any of a variety of pungent or aromatic vegetable substances used for flavouring food. 13. The act or process of establishing colonies. 14. The instrument that is used for finding directions. It has a dial and a magnetic needle that always points to the North. 15. The person who creates sculptures. 17. Name given to all creative writing of recognised artistic value.. A. The person who works on the land. D. Name of the Ocean that Christopher Columbus crossed over. E. The light sailing ship with two or three masts and lateen sails used by the Spanish and Portuguese in the 15 th and 16 th Centuries. F. Means re-birth. A cultural movement that spanned roughly from the 14 th Century to the 17 th Century. It began in Italy and it later spread to the rest of Europe. I. Valuable/delicate cloth made from the fine treads produced by certain insect larvae. L. The person who designs buildings. M. The artist who paints. Ñ. The period when something approaches an end. P. The term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). R. The official leaders of a religious belief.
116 1492 DISCOVERY OF AMERICA 1516 Charles I of Spain and V of Germany 1522 First Circumnavigation of Magellan and Elcano 1598 Philip II Spanish Empire 1605 First Edition of Don Quixote de La Mancha 1700 Philip V Borbon Dinasty 1759 Charles III 1789 FRENCH REVOLUTION MODERN AGE HISTORY
Vocabulary Cards. n. the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution).
 Vocabulary Cards Modern Age n. the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). During the Modern Age there were many changes
Vocabulary Cards Modern Age n. the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution). During the Modern Age there were many changes
Final activity. Notes for the teacher
 Final activity Notes for the teacher This activity aims to give the children an opportunity to demonstrate what they have learnt about the topic through imaginative writing. Each child should assume the
Final activity Notes for the teacher This activity aims to give the children an opportunity to demonstrate what they have learnt about the topic through imaginative writing. Each child should assume the
7th Chapter 11 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
The use of perspective allowed artists to Vernacular
 Journal 02-25-19 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Journal 02-25-19 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Vikings & European Explorers Ponce de Leon
 Non-fiction: Vikings & European Explorers Ponce de Leon Vikings & European Explorers Ponce de Leon In 1513, a Spanish explorer named Juan Ponce de Leon landed on the east coast of Florida. He was the first
Non-fiction: Vikings & European Explorers Ponce de Leon Vikings & European Explorers Ponce de Leon In 1513, a Spanish explorer named Juan Ponce de Leon landed on the east coast of Florida. He was the first
The use of perspective allowed artists to Vernacular
 Journal 02-26-18 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Journal 02-26-18 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
 Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
 Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning ( )
 1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
Bonnie Rose Hudson
 Copyright 2014 by Bonnie Rose Hudson Select graphics used courtesy of EduClips. All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or transmitted by any means, including graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
Copyright 2014 by Bonnie Rose Hudson Select graphics used courtesy of EduClips. All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or transmitted by any means, including graphic, electronic, or mechanical,
THE RENAISSANCE. A time period of great change in European society. Video Introduction
 THE RENAISSANCE 1450 1700 A time period of great change in European society Video Introduction What Does Renaissance Mean? Definition: Renaissance the French word for rebirth. The Renaissance time period
THE RENAISSANCE 1450 1700 A time period of great change in European society Video Introduction What Does Renaissance Mean? Definition: Renaissance the French word for rebirth. The Renaissance time period
What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential?
 Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning ( )
 1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance
 This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance I am Mr. Lanni, Art Teacher at Columbia Middle School. I will lead you through this presentation which highlights a few artists from this period.
This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance I am Mr. Lanni, Art Teacher at Columbia Middle School. I will lead you through this presentation which highlights a few artists from this period.
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People
 April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
Home work. Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers. THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE
 Date: 1 THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE The Renaissance is the r of Europe, a period when scholars became more interested in studying the w around them, when a became more *l f l k, and when Europeans began to e
Date: 1 THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE The Renaissance is the r of Europe, a period when scholars became more interested in studying the w around them, when a became more *l f l k, and when Europeans began to e
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy
 The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
The Renaissance Florence During the Renaissance
 Non-fiction: The Renaissance Florence During the Renaissance The Renaissance Florence During the Renaissance Florence 1, in the North of Italy, was the center of the Renaissance. Florence was a city-state.
Non-fiction: The Renaissance Florence During the Renaissance The Renaissance Florence During the Renaissance Florence 1, in the North of Italy, was the center of the Renaissance. Florence was a city-state.
Chapter Living History. A statue of King David from a medieval cathedral
 Chapter 3 Sculptors are artists who make statues using stone, metal or wood. In the Middle Ages, sculptors worked in the great Gothic churches that we read about on page 141. They carved the statues of
Chapter 3 Sculptors are artists who make statues using stone, metal or wood. In the Middle Ages, sculptors worked in the great Gothic churches that we read about on page 141. They carved the statues of
The Renaissance It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them.
 The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
The Renaissance. Europe 1300s 1600s
 The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
Contents: 1. Main Objectives. 2. Useful Websites. 4.Word Wall Cards. 3.Vocabulary Cards. 5.Glossary. 6.Key Question Cards. 7.Prior Learning Diagram
 CONTEMPORARY AGE Contents: 1. Main Objectives 2. Useful Websites 4.Word Wall Cards 3.Vocabulary Cards 5.Glossary 6.Key Question Cards 7.Prior Learning Diagram 8.Hands-On Activities 9.Reading Comprehension
CONTEMPORARY AGE Contents: 1. Main Objectives 2. Useful Websites 4.Word Wall Cards 3.Vocabulary Cards 5.Glossary 6.Key Question Cards 7.Prior Learning Diagram 8.Hands-On Activities 9.Reading Comprehension
Chapter 22 AP Art History
 Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
SS.7 Kelley_Renaissance Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SS.7 Kelley_Renaissance Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2804BD 1 Use the list below to answer the question. Characteristics of the Renaissance Cultural achievements were financed
SS.7 Kelley_Renaissance Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2804BD 1 Use the list below to answer the question. Characteristics of the Renaissance Cultural achievements were financed
Silk Road. Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE
 Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity
 Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
Homeroom. Turn in SIGNED interims. Picture of PINK before electives
 Homeroom Turn in SIGNED interims Picture of PINK before electives Welcome Back! Happy Spirit Week! Need: NOTEBOOKS, New Warm Up Sheet, and Lost Colony story map **Turn in CURRENT EVENTS AND WARM UPS from
Homeroom Turn in SIGNED interims Picture of PINK before electives Welcome Back! Happy Spirit Week! Need: NOTEBOOKS, New Warm Up Sheet, and Lost Colony story map **Turn in CURRENT EVENTS AND WARM UPS from
LEQ: What area is known as the Crossroads between Asia and Europe?
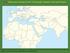 LEQ: What area is known as the Crossroads between Asia and Europe? Europe is at the top left of this map. Asia is on the top right of this map. Africa is at the bottom left of this map. This image is courtesy
LEQ: What area is known as the Crossroads between Asia and Europe? Europe is at the top left of this map. Asia is on the top right of this map. Africa is at the bottom left of this map. This image is courtesy
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe?
 Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
Art of the Renaissance
 Art of the Renaissance Changes in Art & Learning The rise of Humanism can be seen in paintings created by Renaissance artists. During the Medieval period, art and learning were centered on the church and
Art of the Renaissance Changes in Art & Learning The rise of Humanism can be seen in paintings created by Renaissance artists. During the Medieval period, art and learning were centered on the church and
Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju
 Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs 48-60 http://www.cleanvideosearch.com/media /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju All the world is full of knowing men, of most learned schoolmasters, and vast libraries; and
Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs 48-60 http://www.cleanvideosearch.com/media /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju All the world is full of knowing men, of most learned schoolmasters, and vast libraries; and
Spain s Empire and European Absolutism. Chapter 21, Section 1
 Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Chapter 21, Section 1 Section Opener During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. Philip II of Spain May 21 1527
Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Chapter 21, Section 1 Section Opener During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. Philip II of Spain May 21 1527
Chapter 15. The Renaissance in Europe
 Chapter 15 The Renaissance in Europe 15-1 THE ITALIAN STATES What is a Renaissance? It means rebirth After feudalism & the Plague Europe needed to rebuild The renaissance begins in Italy Five Italian States
Chapter 15 The Renaissance in Europe 15-1 THE ITALIAN STATES What is a Renaissance? It means rebirth After feudalism & the Plague Europe needed to rebuild The renaissance begins in Italy Five Italian States
THE HISTORY OF THE MARITIME INDUSTRY
 THE HISTORY OF THE MARITIME INDUSTRY NAMEPA s Mission Preserve and protect the marine environment Demonstrate maritime commitment to environmental protection and pollution prevention Support the marine
THE HISTORY OF THE MARITIME INDUSTRY NAMEPA s Mission Preserve and protect the marine environment Demonstrate maritime commitment to environmental protection and pollution prevention Support the marine
Art of the Italian Renaissance
 Art of the Italian Renaissance A time of great change for art and architecture I want to thank a fellow teacher, Susan M. Pojer of Horace Greeley High School in Chappaqua, New York who created a PowerPoint
Art of the Italian Renaissance A time of great change for art and architecture I want to thank a fellow teacher, Susan M. Pojer of Horace Greeley High School in Chappaqua, New York who created a PowerPoint
7/8 World History. Week 26. The Renaissance
 7/8 World History Week 26 The Renaissance Tuesday Do Now Thinking back through all the past societies you've studied, what are some of the reasons that a society enters a golden age or period of prosperity?
7/8 World History Week 26 The Renaissance Tuesday Do Now Thinking back through all the past societies you've studied, what are some of the reasons that a society enters a golden age or period of prosperity?
Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance?
 Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance? Examine the diagram above and then answer the following questions. 1. In this Renaissance plant which root grows straight up? Which roots
Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance? Examine the diagram above and then answer the following questions. 1. In this Renaissance plant which root grows straight up? Which roots
The Renaissance. Time of Rebirth ( )
 The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27: The Renaissance Begins. Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27: The Renaissance Begins Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation Understanding the political geography of Europe during the 1300s to the 1600s will give you
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27: The Renaissance Begins Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation Understanding the political geography of Europe during the 1300s to the 1600s will give you
Warmup. What is her name? Mona Lisa. Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503
 Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Artists: Michelangelo
 Artists: Michelangelo By Biography.com Editors and A+E Networks, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 851 Level 1060L A portrait of Michelangelo by Jacopino del Conte. Wikimedia Commons Synopsis:
Artists: Michelangelo By Biography.com Editors and A+E Networks, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 851 Level 1060L A portrait of Michelangelo by Jacopino del Conte. Wikimedia Commons Synopsis:
In the fifteenth century, Italy was not the unified country we know today. At that time the boot-shaped peninsula was divided into many small
 The Renaissance The Renaissance occurred between 1400 A.D. and 1600 A.D. It began in the city states of Italy. Renaissance means "rebirth" in French. The art of this period reflected back to the classical
The Renaissance The Renaissance occurred between 1400 A.D. and 1600 A.D. It began in the city states of Italy. Renaissance means "rebirth" in French. The art of this period reflected back to the classical
The Renaissance. THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE Use the online notes guide to find the correct answers.
 THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE Use the online notes guide to find the correct answers. The Renaissance is the r of Europe, a period when scholars became more interested in studying the w around them, when a became
THE DAWN OF A NEW AGE Use the online notes guide to find the correct answers. The Renaissance is the r of Europe, a period when scholars became more interested in studying the w around them, when a became
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and. the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activityengage the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson What can we learn
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activityengage the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson What can we learn
TCI Lesson 27 - The Renaissance Begins. Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation
 TCI Lesson 27 - The Renaissance Begins Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation Understanding the political geography of Europe during the 1300s to the 1600s will give you a foundation
TCI Lesson 27 - The Renaissance Begins Setting the Stage - Europe s Renaissance and Reformation Understanding the political geography of Europe during the 1300s to the 1600s will give you a foundation
I. The Renaissance was the period that followed the Middle Ages. It was a time of renewed interest in things of this world.
 Renaissance I. The Renaissance was the period that followed the Middle Ages. It was a time of renewed interest in things of this world. A. Human beings and their conditions B. Education, art, literature,
Renaissance I. The Renaissance was the period that followed the Middle Ages. It was a time of renewed interest in things of this world. A. Human beings and their conditions B. Education, art, literature,
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty
 Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 3 Starter Jan 11th and 12th Draw a picture of a landscape on the paper attached to the bottom of your desk Renaissance Architecture 1. Revival of Greek and Roman
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 3 Starter Jan 11th and 12th Draw a picture of a landscape on the paper attached to the bottom of your desk Renaissance Architecture 1. Revival of Greek and Roman
Contents. Introduction 4. Leonardo da Vinci 7. Christopher Wren 21. Antoni Gaudí 33. Pablo Picasso 47. Frida Kahlo 59. Glossary 71
 Contents Introduction 4 Leonardo da Vinci 7 Christopher Wren 21 Antoni Gaudí 33 Pablo Picasso 47 Frida Kahlo 59 Glossary 71 Leonardo da Vinci 1452 1519 the man who painted the Mona Lisa I had many careers
Contents Introduction 4 Leonardo da Vinci 7 Christopher Wren 21 Antoni Gaudí 33 Pablo Picasso 47 Frida Kahlo 59 Glossary 71 Leonardo da Vinci 1452 1519 the man who painted the Mona Lisa I had many careers
The Renaissance and Reformation. Unit 7
 The Renaissance and Reformation Unit 7 Unit 7 The Renaissance & Reformation set up a new table of contents on INB 134 134. New Table of Contents 135. Unit 7 Cover Page 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. I ve given
The Renaissance and Reformation Unit 7 Unit 7 The Renaissance & Reformation set up a new table of contents on INB 134 134. New Table of Contents 135. Unit 7 Cover Page 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. I ve given
WARM-UP. What would you create? Why?
 WARM-UP You are a 35 year old adult. You ve been working your whole life, doing okay, but usually too busy to enjoy life during the weekdays. Suddenly, a wealthy citizen from Austin offers you a paycheck
WARM-UP You are a 35 year old adult. You ve been working your whole life, doing okay, but usually too busy to enjoy life during the weekdays. Suddenly, a wealthy citizen from Austin offers you a paycheck
How did the collapse of the Roman Empire affect the Silk Roads?
 Journal A JOURNAL 02-20-18 How did the collapse of the Roman Empire affect the Silk Roads? A. Pirates constantly raided ships in the Mediterranean Sea. B. Traffic on the roads throughout Italy increased.
Journal A JOURNAL 02-20-18 How did the collapse of the Roman Empire affect the Silk Roads? A. Pirates constantly raided ships in the Mediterranean Sea. B. Traffic on the roads throughout Italy increased.
Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE
 Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE INTRODUCTION Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), a Florentine artist, one of the great masters of the High Renaissance, is celebrated as a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer,
Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE INTRODUCTION Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), a Florentine artist, one of the great masters of the High Renaissance, is celebrated as a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer,
Other Artists. Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael. Renowned painter, accomplished architect
 Other Artists Raphael Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael Renowned painter, accomplished architect Most famous work, The School of Athens, fresco painting made on fresh, moist plaster Also well known
Other Artists Raphael Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael Renowned painter, accomplished architect Most famous work, The School of Athens, fresco painting made on fresh, moist plaster Also well known
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA. The Northern Renaissance
 Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona
 Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
Read pages Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab
 Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
10A. Chapter 1 Section1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
 10A Chapter 1 Section1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance The Renaissance Renaissance is the period of time in which a movemnet caused an explosion of creativity in art and writing Renaissance means
10A Chapter 1 Section1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance The Renaissance Renaissance is the period of time in which a movemnet caused an explosion of creativity in art and writing Renaissance means
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
Leonardo da Vinci. by Owen Mitchell April 8, 2012
 Leonardo da Vinci by Owen Mitchell April 8, 2012 Leonardo da Vinci was a wonderful inventor and artist. His inventions concepts are still used today and his art still inspires many people in the modern
Leonardo da Vinci by Owen Mitchell April 8, 2012 Leonardo da Vinci was a wonderful inventor and artist. His inventions concepts are still used today and his art still inspires many people in the modern
The Renaissance and Reformation
 The Renaissance and Reformation The Italian Renaissance Renaissance rebirth Italian Renaissance rebirth of ancient Greek & Roman worlds Characteristics Secular Urban society (City-states) Age of Recovery
The Renaissance and Reformation The Italian Renaissance Renaissance rebirth Italian Renaissance rebirth of ancient Greek & Roman worlds Characteristics Secular Urban society (City-states) Age of Recovery
To receive maximum points students must exceed expectations
 Introduction: Today we will be learning about some of the most famous and accomplished artists of all time those of the Renaissance. Amazingly, some of their art will be coming to our school for a gallery
Introduction: Today we will be learning about some of the most famous and accomplished artists of all time those of the Renaissance. Amazingly, some of their art will be coming to our school for a gallery
Art Masterpiece Project Procedure Form
 Art Masterpiece Project Procedure Form Artist: Name of Print: Project: Objective: Description: Diego Rivera Mother s Helper Mural of Moms Drawing from memory and depicting characteristic features Talk
Art Masterpiece Project Procedure Form Artist: Name of Print: Project: Objective: Description: Diego Rivera Mother s Helper Mural of Moms Drawing from memory and depicting characteristic features Talk
 Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
Station A: Advances in Architecture and Engineering
 a Station A: Advances in Architecture and Engineering The Site: You are at the cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore. 1. Read Section 3 in History Alive! The Medieval World and Beyond. Answer Questions 1
a Station A: Advances in Architecture and Engineering The Site: You are at the cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore. 1. Read Section 3 in History Alive! The Medieval World and Beyond. Answer Questions 1
Terms, People, and Places
 Terms, People, and Places Renaissance: Medici: Perspective: Renaissance Man Niccolo Machiavelli: The Prince Humanism: Humanities: Johann Gutenberg: The Printing Press: Lesson Objectives: Describe the characteristics
Terms, People, and Places Renaissance: Medici: Perspective: Renaissance Man Niccolo Machiavelli: The Prince Humanism: Humanities: Johann Gutenberg: The Printing Press: Lesson Objectives: Describe the characteristics
What Was the Renaissance?
 THE RENAISSANCE What Was the Renaissance? It was a change in thinking about the world and the place people occupy in it A new philosophy called HUMANISM came to dominate people s thinking Humanism emphasizes
THE RENAISSANCE What Was the Renaissance? It was a change in thinking about the world and the place people occupy in it A new philosophy called HUMANISM came to dominate people s thinking Humanism emphasizes
TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS
 MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
Early Renaissance in Europe. Chapter 17-3
 Early Renaissance in Europe Chapter 17-3 Artist: Nuño Gonçalves Title: Saint Vincent with the Portuguese Royal Family Medium: Oil on wood panel Size: 6'9¾" X 4' 2⅝" (2.07 X 1.28 m) Date: c 1465 67 Iberian
Early Renaissance in Europe Chapter 17-3 Artist: Nuño Gonçalves Title: Saint Vincent with the Portuguese Royal Family Medium: Oil on wood panel Size: 6'9¾" X 4' 2⅝" (2.07 X 1.28 m) Date: c 1465 67 Iberian
The Renaissance in Europe Ideas and Art of the Renaissance
 The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
Bellringer. Identify the century for the following years:
 Bellringer Identify the century for the following years: -1778 C.E. -983 C.E. -1215 C.E. -524 B.C.E. Why are the Middle Ages also known as the Dark Ages? Although no organized governments existed during
Bellringer Identify the century for the following years: -1778 C.E. -983 C.E. -1215 C.E. -524 B.C.E. Why are the Middle Ages also known as the Dark Ages? Although no organized governments existed during
Visual Art. Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words. Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words. Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words
 ARTICLE-A-DAY Visual Art 7 Articles Check articles you have read: Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words Forms of Art - Landscape
ARTICLE-A-DAY Visual Art 7 Articles Check articles you have read: Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words Forms of Art - Landscape
Lesson Plans. World History. Grade 10. Mrs. Newgard. Monday, January 18 o Standard: N/A o Objective: N/A Teacher In-Service: NO SCHOOL
 Monday, January 18 o Objective: N/A Teacher In-Service: NO SCHOOL Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Tuesday, January 19 late 18th century to the early 20 th century o Objective: Understand
Monday, January 18 o Objective: N/A Teacher In-Service: NO SCHOOL Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Tuesday, January 19 late 18th century to the early 20 th century o Objective: Understand
Introduction to The Renaissance. Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB
 Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
ON A JOURNEY WITH THE MARQUIS OF CERRALBO
 ON A JOURNEY WITH THE MARQUIS OF CERRALBO FAMILY ITINERARIES Nº 2 THE CERRALBO MUSEUM Text and design: Andrea López Azcona Photographs: Tomás Antelo Mª Jesús del Amo Rodríguez Alberto Otero Illustrations:
ON A JOURNEY WITH THE MARQUIS OF CERRALBO FAMILY ITINERARIES Nº 2 THE CERRALBO MUSEUM Text and design: Andrea López Azcona Photographs: Tomás Antelo Mª Jesús del Amo Rodríguez Alberto Otero Illustrations:
Lesson 53: Art/Museum Exhibitions (20-25 minutes)
 Main Topic 8: Entertainment Lesson 53: Art/Museum Exhibitions (20-25 minutes) Today, you will: 1. Learn useful vocabulary related to Art/Museum Exhibitions. 2. Review Verb Tenses (Basic Present). I. VOCABULARY
Main Topic 8: Entertainment Lesson 53: Art/Museum Exhibitions (20-25 minutes) Today, you will: 1. Learn useful vocabulary related to Art/Museum Exhibitions. 2. Review Verb Tenses (Basic Present). I. VOCABULARY
Jonathan Swift ( )
 (1667-1745) Marina Spiazzi, Marina Tavella, Margaret Layton 2012 1. Swift s life Born in 1667 in Dublin of English parents. Left Ireland for England at the time of the Revolution in 1688. Started to work
(1667-1745) Marina Spiazzi, Marina Tavella, Margaret Layton 2012 1. Swift s life Born in 1667 in Dublin of English parents. Left Ireland for England at the time of the Revolution in 1688. Started to work
The Middle Ages. Written by Rebecca Stark
 The Middle Ages Create-A-Center Written by Rebecca Stark Originally published by Educational Impressions, Inc. 2016 Barbara M. Peller, also known as Rebecca Stark The purchase of this book entitles the
The Middle Ages Create-A-Center Written by Rebecca Stark Originally published by Educational Impressions, Inc. 2016 Barbara M. Peller, also known as Rebecca Stark The purchase of this book entitles the
Bell Ringer Finish Notes 22.3 Discuss the impact of Russia leaving Assign:
 Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, February 8 o Standard: 9-12.2.15 Analyze the global causes, course, and consequences of World War I o Objective: Understand the progression of WWI
Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, February 8 o Standard: 9-12.2.15 Analyze the global causes, course, and consequences of World War I o Objective: Understand the progression of WWI
To receive maximum points students must exceed expectations.
 Introduction: Today we will be learning about some of the most famous and accomplished artists of all time those of the Renaissance. Amazingly, some of their art will be coming to our school for a gallery
Introduction: Today we will be learning about some of the most famous and accomplished artists of all time those of the Renaissance. Amazingly, some of their art will be coming to our school for a gallery
Who was Francisco de Goya?
 GOYA Who was Francisco de Goya? When and when did he born/ The biography. Resume the main stages. Write about the relation between Goya and Independence War. Why did Goya have to go into exile? Goya anticipated
GOYA Who was Francisco de Goya? When and when did he born/ The biography. Resume the main stages. Write about the relation between Goya and Independence War. Why did Goya have to go into exile? Goya anticipated
Story of a portrait. The Family of Charles IV
 Story of a portrait The Family of Charles IV 1 El Prado para todos Story of a portrait The Family of Charles IV ÁREA DE EDUCACIÓN This story is an educational resource used by The Prado for all, a programme
Story of a portrait The Family of Charles IV 1 El Prado para todos Story of a portrait The Family of Charles IV ÁREA DE EDUCACIÓN This story is an educational resource used by The Prado for all, a programme
Year 3 IPC Topics
 Year 3 IPC Topics 2012 2013 Each unit of work is part of the International Primary Curriculum. This new curriculum sets out very clearly what children will learn the learning goals in three different areas:
Year 3 IPC Topics 2012 2013 Each unit of work is part of the International Primary Curriculum. This new curriculum sets out very clearly what children will learn the learning goals in three different areas:
The European Renaissance
 The European Renaissance Chapter 17 Section 1 1350- mid 16 th century Causes of the Renaissance During the Late middle ages, Europe suffered from both war and plague. Those who survived need something
The European Renaissance Chapter 17 Section 1 1350- mid 16 th century Causes of the Renaissance During the Late middle ages, Europe suffered from both war and plague. Those who survived need something
Lesson Plans. World History. Grade 10. Mrs. Newgard
 Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, February 22 o Objective: Understand the consequences of WWI Study Guide Tuesday, February 23 o Objective: Understand the consequences of WWI Bazinga!
Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, February 22 o Objective: Understand the consequences of WWI Study Guide Tuesday, February 23 o Objective: Understand the consequences of WWI Bazinga!
Photocopiable Resources
 Photocopiable Resources Macmillan Children s Readers Worksheets and Teacher s Notes Contents Kings and Queens Worksheet 1 Kings and Queens Worksheet 2 Kings and Queens Worksheet 3 Kings and Queens Worksheet
Photocopiable Resources Macmillan Children s Readers Worksheets and Teacher s Notes Contents Kings and Queens Worksheet 1 Kings and Queens Worksheet 2 Kings and Queens Worksheet 3 Kings and Queens Worksheet
Reading. 1 Read the text quickly. Then answer the questions. / 0.4 point. a. What is The Thinker? b. Who is Rodin?
 Reading 1 Read the text quickly. Then answer the questions. / 0.4 point a. What is The Thinker? b. Who is Rodin? Rodin originally conceived of The Thinker as the focal point atop his Gates of Hell. At
Reading 1 Read the text quickly. Then answer the questions. / 0.4 point a. What is The Thinker? b. Who is Rodin? Rodin originally conceived of The Thinker as the focal point atop his Gates of Hell. At
RENAISSANCE. Credit: Caroline Mc Corriston. Caroline Mc Corriston
 RENAISSANCE Credit: Caroline Mc Corriston Caroline Mc Corriston Rebirth The renaissance was an era of great advancement in the arts and science The word Renaissance means rebirth A new philosophy called
RENAISSANCE Credit: Caroline Mc Corriston Caroline Mc Corriston Rebirth The renaissance was an era of great advancement in the arts and science The word Renaissance means rebirth A new philosophy called
The sixteenth century, also called the Age of Exploration and Expansion; the Golden Age; and
 Betty Gilson http://www.artistrue.com ARH 1000 01/22/2001 The High Renaissance The sixteenth century, also called the Age of Exploration and Expansion; the Golden Age; and the Age of the High Renaissance,
Betty Gilson http://www.artistrue.com ARH 1000 01/22/2001 The High Renaissance The sixteenth century, also called the Age of Exploration and Expansion; the Golden Age; and the Age of the High Renaissance,
Giuseppe Arcimboldo
 Giuseppe Arcimboldo - 1527-1593 Giuseppe Arcimboldo was born in 1528, the son of a nobleman, in Milan, which is now called Italy. He also signed his name these ways: Josephus, Joseph or Josepho Arcimboldi
Giuseppe Arcimboldo - 1527-1593 Giuseppe Arcimboldo was born in 1528, the son of a nobleman, in Milan, which is now called Italy. He also signed his name these ways: Josephus, Joseph or Josepho Arcimboldi
Sacagawea Noah Remnick
 Sacagawea Sacagawea Noah Remnick In 1804, President Thomas Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis and William Clark on a very difficult expedition. He wanted them to explore the massive 828,000 square miles of
Sacagawea Sacagawea Noah Remnick In 1804, President Thomas Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis and William Clark on a very difficult expedition. He wanted them to explore the massive 828,000 square miles of
1. Robert Tignor, et al., Worlds Together, World Apart: A History of the World. Volume B. New York, WW Norton and Company, 2011.
 William Paterson University Hist-1040-80 Winter Session Syllabus 1. Title of Course and Course Number: History 1040: The Early Modern World, 1200-1800 2. Description of the Course: This course is designed
William Paterson University Hist-1040-80 Winter Session Syllabus 1. Title of Course and Course Number: History 1040: The Early Modern World, 1200-1800 2. Description of the Course: This course is designed
THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN
 23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
What was the Renaissance?
 The Renaissance What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? Began mostly in Italy, and spread to Northern Europe Why Italy? Urban Societies Major Trading Centers Centrally
The Renaissance What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? Began mostly in Italy, and spread to Northern Europe Why Italy? Urban Societies Major Trading Centers Centrally
The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture
 1780-1820 The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture The late 18 th and early 19 th centuries were a time of quick and drastic change in Western society: Revolutions;
1780-1820 The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture The late 18 th and early 19 th centuries were a time of quick and drastic change in Western society: Revolutions;
Lesson Plans. World History. Grade 10. Mrs. Newgard
 Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, April 4 o Objective: Discuss post-wwii Review chapter ABC Booklet Tuesday, April 5 o Objective: Discuss post-wwii Study Guide Wednesday, April 6
Lesson Plans World History Grade 10 Mrs. Newgard Monday, April 4 o Objective: Discuss post-wwii Review chapter ABC Booklet Tuesday, April 5 o Objective: Discuss post-wwii Study Guide Wednesday, April 6
2. The Renaissance represented the rebirth of what two cultures? a. China, Italy b. Scotland, Portugal c. Greece, Rome d.
 WEEKLY QUIZ: WEEK 11: Lower Grammar* ON A SEPARATE PIECE OF PAPER, NUMBER DOWN 1-10. ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BY CHOOSING THE LETTER IN FRONT OF THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITING IT DOWN ON YOUR PAPER. 1. Where
WEEKLY QUIZ: WEEK 11: Lower Grammar* ON A SEPARATE PIECE OF PAPER, NUMBER DOWN 1-10. ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BY CHOOSING THE LETTER IN FRONT OF THE CORRECT ANSWER AND WRITING IT DOWN ON YOUR PAPER. 1. Where
Leonardo da Vinci. Summary. Contents. Jez Uden. Level 4-2. Before Reading Think Ahead During Reading Comprehension... 5
 Level 4-2 Leonardo da Vinci Jez Uden Summary This book is about the life of Leonardo da Vinci and his many paintings, designs, and creations. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During
Level 4-2 Leonardo da Vinci Jez Uden Summary This book is about the life of Leonardo da Vinci and his many paintings, designs, and creations. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During
(D) sfumato (C) Greek temple architecture
 1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
Sacagawea Noah Remnick
 Sacagawea Noah Remnick In 1804, President Thomas Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis and William Clark on a very difficult expedition. He wanted them to explore the massive 828,000 square miles of territory
Sacagawea Noah Remnick In 1804, President Thomas Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis and William Clark on a very difficult expedition. He wanted them to explore the massive 828,000 square miles of territory
