INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT & COST
|
|
|
- Lynn Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Pelawat Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka 7 INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT & COST Some parts of these presentation are taken from Chapter-1
2 MANAGEMENT Technique, practice or science of managing or controlling; the skillful use of resources and time; the specific treatment of a disease or disorder. Function that organizes the execution of today s business. The process of getting activities completed efficiently and effectively with and through other people. Traditionally, the term "management" refers to the set of activities, and often the group of people, involved in four general functions, including planning, organizing, leading and coordinating activities. (Note that the four functions recur throughout the organization and are highly integrated.)
3 MANAGEMENT Some writers, teachers and practitioners assert that the previous view is rather outmoded and that management needs to focus more on leadership skills, e.g., establishing vision and goals, communicating the vision and goals, and guiding others to accomplish them. They also assert that leadership must be more facilitative, participative and empowering in how visions and goals are established and carried out. Some people assert that this really isn't a change in the management functions, rather it's re-emphasizing emphasizing certain aspects of management.
4 MANAGEMENT Management functions: Planning Organizing Staffing Directing Coordinating Reporting Budgeting The people who administer a company, create policies, and provide the support necessary to implement the owners' business objectives.
5 Management roles: MANAGEMENT Interpersonal roles Figurehead, Leader, Liaison Informational roles: Monitor, Disseminator, Spokesperson Decisional roles Entrepreneur, Disturbance handler, Resource allocator,, Negotiator
6 What Is Management? Management the process of coordinating work activities so that they are completed efficiently and effectively with and through other people elements of definition ProcessProcess - represents ongoing functions or primary activities engaged in by managers Coordinating - distinguishes a managerial position from a non-managerial one
7 What is Management? (cont.) Management (cont.) Efficiency - getting the most output from the least amount of inputs doing things right concerned with means Effectiveness - completing activities so that organizational goals are attained doing the right things concerned with ends
8 Efficiency and Effectiveness in Management Efficiency (Means) Effectiveness (Ends) Resource Usage Goal Attainment Low Waste High Attainment Management Strives For: Low resource waste (high efficiency) High goal attainment (high effectiveness)
9 Who Are Managers? Manager someone who works with and through other people by coordinating their work activities in order to accomplish organizational goals changing nature of organizations and work has blurred the clear lines of distinction between managers and non-managerial employees
10 UNIVERSAL NEED FOR MANAGEMENT
11 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION The major inventions of the Industrial Revolution American - British and European the Industrial Revolution defined was the widespread replacement of manual labor by new inventions or machinery. Industrial Revolution, widespread replacement of manual labor by machines that began in Britain in the 18th century and is still continuing in some parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution was the result of many fundamental, interrelated changes that transformed agricultural economies into industrial ones. The most immediate changes were in the nature of production: what was produced, as well as where and how.
12 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Newcomen Steam Engine and the Industrial Revolution In 1712, Thomas Newcomen together with John Calley built their first steam engine on top of a water filled mine shaft and used it to pump water out of the mine. The Newcomen steam engine was the predecessor to the Watt steam engine and it was one of the most interesting pieces of technology developed during the 1700's. The invention of engines, the first being steam engines, was very important to the industrial revolution.
13 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1733 Flying Shuttle, Automation of Textile Making & The Industrial Revolution In 1733, John Kay invented the flying shuttle, an improvement to looms that enabled weavers to weave faster. By using a flying shuttle, a single weaver could produce a wide piece of cloth. The original shuttle contained a bobbin on to which the weft (weaving term for the crossways yarn) yarn was wound. It was normally pushed from one side of the warp (weaving term for the the series of yarns that extended lengthways in a loom) to the other side byb hand. Before the flying shuttle wide looms needed two or more weavers to throw the shuttle.
14 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Increased Yarn & Thread Production During Industrial Revolution In 1764, a British carpenter and weaver named James Hargreaves invented an improved spinning jenny, a hand- powered multiple spinning machine that was the first machine to improve upon the spinning wheel by making it possible to spin more than one ball of yarn or thread.{p] ] Spinner machines like the spinning wheel and the spinning jenny made the threads and yarns used by weavers in their looms. As weaving looms became faster, inventors had to find ways for spinners to keep up.
15 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION James Watt's Improved Steam Engine Powers the Industrial Revolution James Watt was sent a Newcomen steam engine to repair that led him to invented improvements for steam engines. Steam engines were now true reciprocating engine and not atmospheric engines. Watt added a crank and flywheel to his engine so that it could provide rotary motion. Watt's steam engine machine was four times more powerful than those engines based on Thomas Newcomen's steam engine design
16 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Spinning Frame or Water Frame Richard Arkwright patented the spinning frame or water that could produce stronger threads for yarns. The first models were powered by waterwheels so the device came to be first known as the water frame. It was the first powered, automatic, and continuous textile machine and enabled the move away from small home manufacturing towards factory production of textiles. The water frame was also the first machine that could spin cotton threads.
17 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Spinning Mule Increased Variety in Threads & Yarns In 1779, Samuel Crompton invented the spinning mule that combined the moving carriage of the spinning jenny with the rollers of the water frame. The spinning mule gave the spinner great control over the weaving process. Spinners could now make many different types of yarn. Finer cloths could now be made.
18 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Power Loom's Effect on the Women of the Industrial Revolution The power loom was a steam-powered, mechanically-operated version of a regular loom. A loom is a device that combined threads to make cloth. When the power loom became efficient, women replaced most men as weavers in the textile factories
19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPACT RESULTED (POSITIVE) The social changes brought about by the Industrial Revolution were significant. As economic activities in many communities moved from agriculture to manufacturing, production shifted from its traditional locations in the home and the small workshop to factories. Large portions of the population relocated from the countryside to the towns and cities where manufacturing centers were found. The overall amount of goods and services produced expanded dramatically, and the proportion of capital invested per worker grew.
20 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPACT RESULTED (POSITIVE) New groups of investors, businesspeople, and managers took financial risks and reaped great rewards. In the long run the Industrial Revolution has brought economic improvement for most people in industrialized societies. Many enjoy greater prosperity and improved health, especially those in the middle and the upper classes of society.
21 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPACT RESULTED (NEGATIVE) There have been costs, however. In some cases, the lower classes of society have suffered economically. Industrialization has brought factory pollutants and greater land use, which have harmed the natural environment. In particular, the application of machinery and science to agriculture has led to greater land use and, therefore, extensive loss of habitat for animals and plants. In addition, drastic population growth following industrialization has contributed to the decline of natural habitats and resources. These factors, in turn, have caused many species to become extinct or endangered.
22 Changes in Industry Continuous-Process Manufacturing An important American development was continuousprocess manufacturing. In continuous-process manufacturing, large quantities of the same product, such as cigarettes or canned food, are made in a nonstop operation. The process runs continuously, except for repairs to or maintenance of the machinery used. Continuous-Process Manufacturing In the late 18th century, inventor Oliver Evans of Delaware created a remarkable waterpowered flour mill. In Evans s mill, machinery elevated the grain to the top of the mill and then moved it mechanically through various processing steps, eventually producing flour at the bottom of the mill. The process greatly reduced the need for manual labor and cut milling costs dramatically. Mills modeled after Evans s were built along the Delaware and Brandywine rivers and Chesapeake Bay, and by the time of the American Revolution ( ) they were arguably the most productive in the world. Similar milling technology was also used to grind snuff and other tobacco products in the same region.
23 Changes in Industry The American System by the mid-19th century American manufacturers shaped a set of techniques later known as the American system of production. This system involved using special-purpose machines to produce large quantities of similar, sometimes interchangeable, parts that would then be assembled into a finished product. The American system extended the idea of division of labor from workers to specialized machines. Instead of a worker making a small part of a finished product, a machine made the part, speeding the process and allowing manufacturers to produce goods more quickly. This method also enabled goods of much more uniform quality than those made by hand labor.
24 Changes in Industry The Second Industrial Revolution As American manufacturing technology spread to new industries 1. The first had come on a wave of new inventions in iron making, in textiles, in the centrally powered factory, and in new ways of organizing business and work. 2. In the latter 19th century, a second wave of technical and organizational advances carried industrial society to new levels. While Great Britain had been the birthplace of the first revolution, the second occurred most powerfully in the United States.
25 FORDIANISM Changes in Industry It was in the automobile industry that continuous-process methods and the American system combined to greatest effect. In 1903 American industrialist Henry Ford founded the Ford Motor Company. His production innovation was the moving assembly line which brought together many mass-produced parts to create automobiles. Ford s s moving assembly line gave the world the fullest expression yet of the Second Industrial Revolution, and his production triumphs in the second decade of the 20th century signaled the crest of the new industrial age.
26 Changes in Industry Organization and Work-Taylorism Just as important as advances in manufacturing technology was a wave of changes in how business was structured and work was organized. Engineers studied and modified production, seeking the most efficient ways to lay out a factory, move materials, route jobs, and control work through precise scheduling. Industrial engineer Frederick Taylor and his followers sought both efficiency and contented workers. They believed that they could achieve those results through precise measurement and analysis of each aspect of a job.
27 INDUSTRIAL PROGRESS & ISSUES
28 Stages of Economic Development Features Pre- Use of Standard dominant human Unit of of living Society Game activity labor social life e measure Structure Technology Pre- Against Agriculture Raw Extended Sub- Routine Simple hand Industrial Nature Mining muscle household sistence Traditional tools power Authoritative Industrial Against Goods Machine Individual Quantity Bureaucratic Machines fabricated production tending of goods Hierarchical nature Post- Among Services Artistic Community Quality of Inter- Information industrial Persons Creative life in terms dependent Intellectual ectual of health, Global education, recreation
29 Faster Growth and More Good Jobs Once an economy reaches the middle income level of development, service industries become a more important source of job growth than manufacturing
30 Trends in U.S. Employment by Sector Proportation of total employement Service Manufacturing Agriculture Year
31 Percent Service Employment for Selected Industrialized Nations Country United States Canada Japan France Israel Italy China
32 Faster Growth and More Good Jobs Once an economy reaches the middle income level of development, service industries become a more important source of job growth than manufacturing
33 Percent of U.S. Labor Force by Industry Percent of U.S. Labor Force Year Source: Survey of Current Business, April 1998, Table B.8, July 1988, Table 6.6B, and July 1992, Table 6.4C; Eli Ginzberg and George J. Vojta, The Service Sector of the U.S. Economy, Scientific American, 244,3 (1981): Services Manufacturing Mining & Agriculture
34 Percent of U.S. Gross Domestic Product by Industry Percent of GDP Year Source: Survey of Current Business, August 1996, Table 11, April 1998, Table B.3; Eli Ginzberg and George J. Vojta, The Service Sector of the U.S. Economy, Scientific American, 244,3 (1981): Services Manufacturing Mining & Agriculture
The Industrial Revolution
 Importance of the Agricultural Revolution The Industrial Revolution Agricultural Revolution Before the Industrial Revolution, most people were farmers. Wealthy landowners owned most of the land, and families
Importance of the Agricultural Revolution The Industrial Revolution Agricultural Revolution Before the Industrial Revolution, most people were farmers. Wealthy landowners owned most of the land, and families
The Industrial Revolution Making Cloth: The Industrial Revolution Begins
 Non-fiction: Making Cloth:The Industrial Revolution Begins The Industrial Revolution Making Cloth: The Industrial Revolution Begins The Industrial Revolution got its start in the textile industry. Before
Non-fiction: Making Cloth:The Industrial Revolution Begins The Industrial Revolution Making Cloth: The Industrial Revolution Begins The Industrial Revolution got its start in the textile industry. Before
Innovation during the Industrial Revolution
 Innovation during the Industrial Revolution 1. Innovations in Energy Sources: Human, Animal, Wood and Water Power to Coal Before the Industrial Revolution Before the Industrial Revolution, the main sources
Innovation during the Industrial Revolution 1. Innovations in Energy Sources: Human, Animal, Wood and Water Power to Coal Before the Industrial Revolution Before the Industrial Revolution, the main sources
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution In the early 1700s large landowners across Great Britain bought much of the land once owned by poor farmers. They introduced new methods of farming, using the latest agricultural
The Industrial Revolution In the early 1700s large landowners across Great Britain bought much of the land once owned by poor farmers. They introduced new methods of farming, using the latest agricultural
Chapter 12, Section 1 The Industrial Revolution in America
 Chapter 12, Section 1 The Industrial Revolution in America Pages 384-389 In the early 1700s making goods depended on the hard work of humans and animals. It had been that way for hundreds of years. Then
Chapter 12, Section 1 The Industrial Revolution in America Pages 384-389 In the early 1700s making goods depended on the hard work of humans and animals. It had been that way for hundreds of years. Then
Domestic industry and craftsmen
 Domestic industry and craftsmen Up to 1700s most products made at home or by craftsmen in workshops Carpenters, potters, blacksmiths, bakers Spinners, weavers, tailors Domestic Industry versus Factories
Domestic industry and craftsmen Up to 1700s most products made at home or by craftsmen in workshops Carpenters, potters, blacksmiths, bakers Spinners, weavers, tailors Domestic Industry versus Factories
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Industrialization and Nationalism Lesson 1 The Industrial Revolution
 and Study Guide Lesson 1 The Industrial Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK Content Vocabulary
and Study Guide Lesson 1 The Industrial Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK Content Vocabulary
Module 2: Origin of city in history Lecture 8: The Industrial Revolution and the Rise of the Gesellschaft Part I
 The Lecture Contains: Industrial Revolution Changes at the core of Industrial Revolution Changes within Technology Labour Urbanization Environment Reference file:///d /NPTL%20WORK/Dr.%20Anindita%20Chakrabarti/UrbanSociology/lecture8/8_1.htm
The Lecture Contains: Industrial Revolution Changes at the core of Industrial Revolution Changes within Technology Labour Urbanization Environment Reference file:///d /NPTL%20WORK/Dr.%20Anindita%20Chakrabarti/UrbanSociology/lecture8/8_1.htm
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution Enduring Understanding: The global spread of democratic ideas and nationalist movement occurred during the nineteenth century. To understand the effects of nationalism, industrialism,
The Industrial Revolution Enduring Understanding: The global spread of democratic ideas and nationalist movement occurred during the nineteenth century. To understand the effects of nationalism, industrialism,
AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society
 AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE: The previous chapter describes the dramatic political changes that followed the American and French
AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE: The previous chapter describes the dramatic political changes that followed the American and French
AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION?
 *COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
*COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
Sample file. Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution. What Was the Industrial Revolution? Student Handouts, Inc.
 Page2 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution An ancient Greek or Roman would have been just as comfortable living in Europe in 1700 as during
Page2 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution An ancient Greek or Roman would have been just as comfortable living in Europe in 1700 as during
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution Enduring Understanding: The global spread of democratic ideas and nationalist movement occurred during the nineteenth century. To understand the effects of nationalism, industrialism,
The Industrial Revolution Enduring Understanding: The global spread of democratic ideas and nationalist movement occurred during the nineteenth century. To understand the effects of nationalism, industrialism,
Section 13-1: The Industrial Revolution and America
 Name: Date: Chapter 13 Study Guide Section 13-1: The Industrial Revolution and America 1. The Industrial Revolution was a major period of economic change in which manufacturing gradually shifted from small
Name: Date: Chapter 13 Study Guide Section 13-1: The Industrial Revolution and America 1. The Industrial Revolution was a major period of economic change in which manufacturing gradually shifted from small
Early Industry and Inventions
 Lesson: Early Industry and Inventions How did the Industrial Revolution change America? Lauren Webb. 2015. {a social studies life} Name Date Social Studies The Industrial Revolution Early Industry and
Lesson: Early Industry and Inventions How did the Industrial Revolution change America? Lauren Webb. 2015. {a social studies life} Name Date Social Studies The Industrial Revolution Early Industry and
The Beginnings of Industrialization. Text Summary Worksheet with student directions
 The Beginnings of Industrialization Text Summary Worksheet with student directions Standards Alignment California State Standards for Grade 10 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution
The Beginnings of Industrialization Text Summary Worksheet with student directions Standards Alignment California State Standards for Grade 10 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution
The Making of Industrial Society. Chapter 30
 The Making of Industrial Society Chapter 30 The Making of Industrial Society Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. Demographic changes Urbanization Imperialism
The Making of Industrial Society Chapter 30 The Making of Industrial Society Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. Demographic changes Urbanization Imperialism
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 The Industrial Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary labor
Lesson 1 The Industrial Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary labor
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution Discussion Question What factors caused the Industrial Revolution to begin in England? Causes of the Industrial Revolution Favorable natural resources Agricultural Revolution
The Industrial Revolution Discussion Question What factors caused the Industrial Revolution to begin in England? Causes of the Industrial Revolution Favorable natural resources Agricultural Revolution
Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section
 ECON 30423 Economic History of the Europe to the Industrial Revolution John Lovett Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section Readings: Yorke, Stan (2005). The Industrial Revolution Explained:
ECON 30423 Economic History of the Europe to the Industrial Revolution John Lovett Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section Readings: Yorke, Stan (2005). The Industrial Revolution Explained:
The old ways will burn in the fires of industry
 Aka ISENGARD The old ways will burn in the fires of industry JRR Tolkien Waitaminute. A Major Change agrarian handmade goods rural industrial machine-made goods urban Putting Out System Fun for the whole
Aka ISENGARD The old ways will burn in the fires of industry JRR Tolkien Waitaminute. A Major Change agrarian handmade goods rural industrial machine-made goods urban Putting Out System Fun for the whole
Section 1: Industrial Revolution in America
 The North Section 1: The Industrial Revolution in America Section 2: Changes in Working Life Section 3: The Transportation Revolution Section 4: More Technological Advances Section 1: Industrial Revolution
The North Section 1: The Industrial Revolution in America Section 2: Changes in Working Life Section 3: The Transportation Revolution Section 4: More Technological Advances Section 1: Industrial Revolution
A Bit More on Windmill Drive Pumps + The Beginning of the Industrial Age - the Industrial Revolution The Mechanization of the Textile Industry
 Science A 52 Lecture 7 Feb. 27, 2006 A Bit More on Windmill Drive Pumps + The Beginning of the Industrial Age - the Industrial Revolution The Mechanization of the Textile Industry Spring 2006 Science A
Science A 52 Lecture 7 Feb. 27, 2006 A Bit More on Windmill Drive Pumps + The Beginning of the Industrial Age - the Industrial Revolution The Mechanization of the Textile Industry Spring 2006 Science A
Factories are buildings or sets of buildings in which manufactured
 4 The First Factories Factories are buildings or sets of buildings in which manufactured goods are made from raw materials on a large scale. Work in factories is usually accomplished with laborsaving machinery
4 The First Factories Factories are buildings or sets of buildings in which manufactured goods are made from raw materials on a large scale. Work in factories is usually accomplished with laborsaving machinery
An Economic Revolution
 cultivation, fertilization, careful seeding, and crop rotation all made farms much more productive. The agriculture of France and other European countries was backward in comparison. With enclosure, the
cultivation, fertilization, careful seeding, and crop rotation all made farms much more productive. The agriculture of France and other European countries was backward in comparison. With enclosure, the
The Industrial Revolution
 Journal: Complete the chart on technological inventions: Modern day invention: What life was like before it: What has changed because of it: The Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution The greatly
Journal: Complete the chart on technological inventions: Modern day invention: What life was like before it: What has changed because of it: The Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution The greatly
AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society
 AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE: The previous chapter describes the dramatic political changes that followed the American and French
AP World History (Povletich) CHAPTER 30 OUTLINE The Making of Industrial Society BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE: The previous chapter describes the dramatic political changes that followed the American and French
The Industrial Revolution. The Revolution that changed the world forever
 The Industrial Revolution The Revolution that changed the world forever Industrial Having to do with industry, business or manufacturing Revolution a huge change or a change in the way things are done
The Industrial Revolution The Revolution that changed the world forever Industrial Having to do with industry, business or manufacturing Revolution a huge change or a change in the way things are done
The invention of new machines in Great Britain led to the beginning of the Industrial
 Chapter 12: The North The industrial revolution The invention of new machines in Great Britain led to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution: a period of rapid growth in using machines for manufacturing
Chapter 12: The North The industrial revolution The invention of new machines in Great Britain led to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution: a period of rapid growth in using machines for manufacturing
Chapter 13 Section Review Packet
 Name: Date: Section 13-1: The Industrial Revolution and America Chapter 13 Section Review Packet 1. Industrial Revolution 2. Textiles 3. Richard Awkwright 4. Samuel Slater 5. Technology 6. Eli Whitney
Name: Date: Section 13-1: The Industrial Revolution and America Chapter 13 Section Review Packet 1. Industrial Revolution 2. Textiles 3. Richard Awkwright 4. Samuel Slater 5. Technology 6. Eli Whitney
LEQ: What industry was first affected by the Industrial Revolution?
 LEQ: What industry was first affected by the Industrial Revolution? Power loom weaving is shown in this illustration titled, The Interior of a Cotton Mill. This painting by Thomas Allom (1804-1872) is
LEQ: What industry was first affected by the Industrial Revolution? Power loom weaving is shown in this illustration titled, The Interior of a Cotton Mill. This painting by Thomas Allom (1804-1872) is
The Rise of Industrial Revolution. Innovations and Individuals that Changed the World
 The Rise of Industrial Revolution Innovations and Individuals that Changed the World How did it start? Spinning Jenny & Steam Engine Allowed people to make goods more efficiently (faster and cheaper with
The Rise of Industrial Revolution Innovations and Individuals that Changed the World How did it start? Spinning Jenny & Steam Engine Allowed people to make goods more efficiently (faster and cheaper with
Why not Industrial Revolution?
 Industrialization Why not Industrial Revolution? Areas industrialized at different times, while Revolution implies sudden change. Revolution suggests sharp break from past, but industrialization was a
Industrialization Why not Industrial Revolution? Areas industrialized at different times, while Revolution implies sudden change. Revolution suggests sharp break from past, but industrialization was a
Chapter 11. Industry
 Chapter 11 Industry Industry In this Chapter, Industry refers to the manufacturing of goods in a factory. Key Issue #1 Where is industry distributed? Manufacturing Value Added Fig. 11-1: The world s major
Chapter 11 Industry Industry In this Chapter, Industry refers to the manufacturing of goods in a factory. Key Issue #1 Where is industry distributed? Manufacturing Value Added Fig. 11-1: The world s major
How it Was. In the 1700s, most people wore clothes that were made by hand at home. Can you imagine having no choice but to make your own clothes?
 How it Was In the 1700s, most people wore clothes that were made by hand at home. Can you imagine having no choice but to make your own clothes? All of this changed in 1790 with the start of the Industrial
How it Was In the 1700s, most people wore clothes that were made by hand at home. Can you imagine having no choice but to make your own clothes? All of this changed in 1790 with the start of the Industrial
The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30)
 The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30) Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. It also had enormous effects on the economic, domestic, and social
The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30) Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. It also had enormous effects on the economic, domestic, and social
AP EURO. Unit #5 Nationalism of 19 th Century. Lesson #501 Foundations of Industrial Revolution
 AP EURO Unit #5 Nationalism of 19 th Century Lesson #501 Foundations of Industrial Revolution Essential Questions 1. Why is the Industrial Revolution so revolutionary? 2. Why did it start in Britain, and
AP EURO Unit #5 Nationalism of 19 th Century Lesson #501 Foundations of Industrial Revolution Essential Questions 1. Why is the Industrial Revolution so revolutionary? 2. Why did it start in Britain, and
The North and the South Take Different Paths. Chapter 11
 The North and the South Take Different Paths Chapter 11 Section 1 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION A Revolution in Technology Before 1800s- most Americans worked on farms and things were made by hand Industrial
The North and the South Take Different Paths Chapter 11 Section 1 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION A Revolution in Technology Before 1800s- most Americans worked on farms and things were made by hand Industrial
Student Reading 12.2: The Industrial Revolution: From Farms to Factories. Can you imagine what it would be like to live without cars, electricity,
 Student Reading 12.2: The Industrial Revolution: From Farms to Factories Can you imagine what it would be like to live without cars, electricity, refrigerators, iphones, televisions, and computers? Life
Student Reading 12.2: The Industrial Revolution: From Farms to Factories Can you imagine what it would be like to live without cars, electricity, refrigerators, iphones, televisions, and computers? Life
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution. What was the Industrial Revolution?
 Slide 1 Slide 2 Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution An ancient Greek or Roman would have been just as comfortable in Europe in 1700 because daily life was not much different agriculture
Slide 1 Slide 2 Historical Significance of the Industrial Revolution An ancient Greek or Roman would have been just as comfortable in Europe in 1700 because daily life was not much different agriculture
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 8 Activity Page page 9 Practice Pages page 10 11 Answer Key pages 12 13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask:
The Industrial Revolution Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 8 Activity Page page 9 Practice Pages page 10 11 Answer Key pages 12 13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask:
Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section
 ECON 40970 Economic History of the Modern Europe John Lovett Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section Readings: Yorke, Stan (2005). The Industrial Revolution Explained: Steam, Sparks, and
ECON 40970 Economic History of the Modern Europe John Lovett Study questions for the Textile Manufacturing section Readings: Yorke, Stan (2005). The Industrial Revolution Explained: Steam, Sparks, and
Chapter 11 A Nation Grows and Prospers Powerpoint Questions Instructions:
 Chapter 11 A Nation Grows and Prospers Powerpoint Questions Instructions: Use the Powerpoint presentation, American Nation textbook pages 328-355 and your class notes to answer these questions. 1. How
Chapter 11 A Nation Grows and Prospers Powerpoint Questions Instructions: Use the Powerpoint presentation, American Nation textbook pages 328-355 and your class notes to answer these questions. 1. How
The Making of Industrial Society
 The Making of Industrial Society Chapter 30 FA for this chapter on Monday The Making of Industrial Society Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. Demographic changes
The Making of Industrial Society Chapter 30 FA for this chapter on Monday The Making of Industrial Society Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. Demographic changes
Unit #2 PA History- Lesson #4- PA Economical History A Diversity of Industries
 Unit #2 PA History- Lesson #4- PA Economical History A Diversity of Industries The Edgar Thomson Steel Works, by William Rau, Braddock, PA, 1891 The Rustbelt runs right through Pennsylvania, the former
Unit #2 PA History- Lesson #4- PA Economical History A Diversity of Industries The Edgar Thomson Steel Works, by William Rau, Braddock, PA, 1891 The Rustbelt runs right through Pennsylvania, the former
LET S REVIEW CHAPTER 12. Study your notes from ALL of chapter 12 (two pages) and your two reading checks.
 LET S REVIEW CHAPTER 12 Study your notes from ALL of chapter 12 (two pages) and your two reading checks. In the mid-1800s, most of America s industry was located in the A) Northeast. B) South C) West.
LET S REVIEW CHAPTER 12 Study your notes from ALL of chapter 12 (two pages) and your two reading checks. In the mid-1800s, most of America s industry was located in the A) Northeast. B) South C) West.
Factories and Workers
 The Industrial Revolution Factories and Workers Main Idea The transition from cottage industries changed how people worked in factories, what life was like in factory towns, labor conditions, and eventually
The Industrial Revolution Factories and Workers Main Idea The transition from cottage industries changed how people worked in factories, what life was like in factory towns, labor conditions, and eventually
Museu Industrial del Ter, Manlleu, Catalonia (photo taken by Maria del Roser Pujadas Jubany)
 Museu Industrial del Ter, Manlleu, Catalonia (photo taken by Maria del Roser Pujadas Jubany) 1. Read the sentences about the cotton industry and tick the answers you think you know. a. Cotton is a white
Museu Industrial del Ter, Manlleu, Catalonia (photo taken by Maria del Roser Pujadas Jubany) 1. Read the sentences about the cotton industry and tick the answers you think you know. a. Cotton is a white
Do Now What were some of the important advancements of the Scientific Revolution?
 Do Now What were some of the important advancements of the Scientific Revolution? Objective Students will understand the technological advancements of the Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution
Do Now What were some of the important advancements of the Scientific Revolution? Objective Students will understand the technological advancements of the Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution
STAAR Questions of the Day. Volume 1: Pages Questions #1-5 Volume 2: Pages Questions #1-4 KAMICO: Pages Questions #6-10
 STAAR Questions of the Day Volume 1: Pages 12-13 Questions #1-5 Volume 2: Pages 12-13 Questions #1-4 KAMICO: Pages 27-29 Questions #6-10 USE STRATEGIES!!! STAAR QUESTION OF THE DAY #69. The Industrial
STAAR Questions of the Day Volume 1: Pages 12-13 Questions #1-5 Volume 2: Pages 12-13 Questions #1-4 KAMICO: Pages 27-29 Questions #6-10 USE STRATEGIES!!! STAAR QUESTION OF THE DAY #69. The Industrial
Answer Key. linen c. Initially it was mixed either with woollen or worsted yarn. cotton
 1. Read the sentences about the cotton industry and tick the answers you think you know. a. Cotton is a white fibrous substance composed of the hairs surrounding the seeds of the cotton plant. tree. seeds.
1. Read the sentences about the cotton industry and tick the answers you think you know. a. Cotton is a white fibrous substance composed of the hairs surrounding the seeds of the cotton plant. tree. seeds.
An Introduction to Human Geography The Cultural Landscape, 8e James M. Rubenstein. Chapter 11. Industry. PPT by Abe Goldman
 An Introduction to Human Geography The Cultural Landscape, 8e James M. Rubenstein Chapter 11 Industry PPT by Abe Goldman Origin and Diffusion of the Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution Diffusion
An Introduction to Human Geography The Cultural Landscape, 8e James M. Rubenstein Chapter 11 Industry PPT by Abe Goldman Origin and Diffusion of the Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution Diffusion
2.1 The Industrial Revolution
 2.1 The Industrial Revolution Students will: 2.1.1. Know, understand and be able to explain the new ideas and innovations which led to the Industrial Revolution. 2.1.2. Analyze elements of social change/conflict
2.1 The Industrial Revolution Students will: 2.1.1. Know, understand and be able to explain the new ideas and innovations which led to the Industrial Revolution. 2.1.2. Analyze elements of social change/conflict
Study Questions for our Scientific and Industrial Revolution Reading
 Study Questions for our Scientific and Industrial Revolution Reading Readings: Merriman. Chapter 16: The Industrial Revolution, 1800-1850 1. Rank the following regarding how proximately (i.e. directly,
Study Questions for our Scientific and Industrial Revolution Reading Readings: Merriman. Chapter 16: The Industrial Revolution, 1800-1850 1. Rank the following regarding how proximately (i.e. directly,
MECHANICAL HANDLOOM MACHINE
 MECHANICAL HANDLOOM MACHINE J.P.RAMESH, K.ARUMUGAM, M.SARAVANAN, M. VIGNESH, M.RAJKAPOOR, V.SUTHARSAN VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE Abstract:This project MECHANICAL HANDLOOM MACHINE is for weaving the
MECHANICAL HANDLOOM MACHINE J.P.RAMESH, K.ARUMUGAM, M.SARAVANAN, M. VIGNESH, M.RAJKAPOOR, V.SUTHARSAN VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE Abstract:This project MECHANICAL HANDLOOM MACHINE is for weaving the
The Industrial Revolution was a period that began in England in the 1700 s when humanity really began to turn to machines to do their work for them.
 The Industrial Revolution was a period that began in England in the 1700 s when humanity really began to turn to machines to do their work for them. I. Factors of Production A. Factors of production are
The Industrial Revolution was a period that began in England in the 1700 s when humanity really began to turn to machines to do their work for them. I. Factors of Production A. Factors of production are
Technology and theories of economic development: Neo-Schumpeterian approach (Techno-economic Paradigms)
 Technology and theories of economic development: Neo-Schumpeterian approach (Techno-economic Paradigms) Freeman, C. & Perez, C. (1988) (Structural Crises of Adjustment. in G. Dosi et al. (eds.), Technical
Technology and theories of economic development: Neo-Schumpeterian approach (Techno-economic Paradigms) Freeman, C. & Perez, C. (1988) (Structural Crises of Adjustment. in G. Dosi et al. (eds.), Technical
WEAVING TECHNOLOGY II
 WEAVING TECHNOLOGY II Chapter2: History of Weaving Classification of Weaving Machinery 1 Horizontal loom HISTORY OF WEAVING (EVOLUTION OF WEAVING) Backstrap loom Egyptians made woven fabrics some 6000years
WEAVING TECHNOLOGY II Chapter2: History of Weaving Classification of Weaving Machinery 1 Horizontal loom HISTORY OF WEAVING (EVOLUTION OF WEAVING) Backstrap loom Egyptians made woven fabrics some 6000years
The Industrial Revolution Phase II CHAPTER 11 SECTION 1
 The Industrial Revolution Phase II CHAPTER 11 SECTION 1 The First Industrial Revolution Focus on the introduction of: Textile Industry Railroad construction Iron production And coal extraction and use
The Industrial Revolution Phase II CHAPTER 11 SECTION 1 The First Industrial Revolution Focus on the introduction of: Textile Industry Railroad construction Iron production And coal extraction and use
Downloaded from
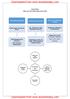 CHAPTER 5 THE AGE OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Proto-Industrialization Coming Up Of Factories The Pace of Industrial Change Hand Labour and Steam Power Age of Indian Textiles- Factories Come Up Small Scale Industries
CHAPTER 5 THE AGE OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Proto-Industrialization Coming Up Of Factories The Pace of Industrial Change Hand Labour and Steam Power Age of Indian Textiles- Factories Come Up Small Scale Industries
AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry
 AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry Name: Period: Complete the graphic organizer as you read Chapter 22. DO NOT simply hunt for the answers; doing so will leave holes
AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry Name: Period: Complete the graphic organizer as you read Chapter 22. DO NOT simply hunt for the answers; doing so will leave holes
Industrialization Spreads Close Read
 Industrialization Spreads Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Industrialization Spreads Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Markets for New Technology
 Markets for New Technology Robert M. Coen Professor Emeritus of Economics Northwestern Alumnae Continuing Education February 16, 2017 Smith Was Pessimistic About Future of Market Systems Deadening effects
Markets for New Technology Robert M. Coen Professor Emeritus of Economics Northwestern Alumnae Continuing Education February 16, 2017 Smith Was Pessimistic About Future of Market Systems Deadening effects
Additional Research 1.1
 Additional Research 1.1 The Industrial Revolution and the Age of would not have been possible without the contributions of some remarkable people. The list below is a catalogue of some of the more famous
Additional Research 1.1 The Industrial Revolution and the Age of would not have been possible without the contributions of some remarkable people. The list below is a catalogue of some of the more famous
Ch. 9 Life in the Industrial Age. a British engineer who developed a new process for making steel from iron in 1856
 Ch. 9 Life in the Industrial Age Ch. 9.1 The Industrial Revolution Spreads a British engineer who developed a new process for making steel from iron in 1856 a Swedish chemist who invented dynamite in 1866
Ch. 9 Life in the Industrial Age Ch. 9.1 The Industrial Revolution Spreads a British engineer who developed a new process for making steel from iron in 1856 a Swedish chemist who invented dynamite in 1866
The Age of Industrialisation
 The Age of Industrialisation 5 CHAPTER Tips and Tricks Introduction: Glorification of machines and technology. Before the Industrial Revolution (i) Proto-industrialisation. (ii) The Coming up of the Factory
The Age of Industrialisation 5 CHAPTER Tips and Tricks Introduction: Glorification of machines and technology. Before the Industrial Revolution (i) Proto-industrialisation. (ii) The Coming up of the Factory
Chapter 5 The Age of Industrialisation
 Chapter 5 The Age of Industrialisation Before the Industrial Revolution Proto-industrialisation: There was large-scale industrial production for an international market not based on factories. It was controlled
Chapter 5 The Age of Industrialisation Before the Industrial Revolution Proto-industrialisation: There was large-scale industrial production for an international market not based on factories. It was controlled
CHAPTER 6 Raw Material, Quality and Usage Pattern
 CHAPTER 6 Raw Material, Quality and Usage Pattern Most of the textile production in the state is made out of cotton yarns and, therefore, cotton yarn is the dominant raw material. The usage of manmade
CHAPTER 6 Raw Material, Quality and Usage Pattern Most of the textile production in the state is made out of cotton yarns and, therefore, cotton yarn is the dominant raw material. The usage of manmade
Chapter 5 Notes: The Industrial Age. The railroad system expanded rapidly in the late 1800s, building large fortunes for some wealthy businesspeople.
 Chapter 5 Notes: The Industrial Age Section 1: Railroads Lead the Way The railroad system expanded rapidly in the late 1800s, building large fortunes for some wealthy businesspeople. Those who labored,
Chapter 5 Notes: The Industrial Age Section 1: Railroads Lead the Way The railroad system expanded rapidly in the late 1800s, building large fortunes for some wealthy businesspeople. Those who labored,
Chapter 11: Industry
 Chapter 11: Industry The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Where is Industry Distributed? Key Issue 1 Pg 342-249 Origin of industry (pg 345) Began -? From cottage industries to the
Chapter 11: Industry The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Where is Industry Distributed? Key Issue 1 Pg 342-249 Origin of industry (pg 345) Began -? From cottage industries to the
- CENTRAL HISTORICAL QUESTION(S) - WHY DID THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION BEGIN IN GREAT BRITAIN?
 NAME: BLOCK: - CENTRAL HISTORICAL QUESTION(S) - WHY DID THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION BEGIN IN GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON OBJECTIVE(S) 1.) EXPLAIN the primary factors behind Great Britain s industrial revolution
NAME: BLOCK: - CENTRAL HISTORICAL QUESTION(S) - WHY DID THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION BEGIN IN GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON OBJECTIVE(S) 1.) EXPLAIN the primary factors behind Great Britain s industrial revolution
The Industrial Age. Chapter 19 Page 610
 The Industrial Age Chapter 19 Page 610 The Second Industrial Revolution Chapter 19 Section 1 page 614 Breakthroughs in Steel Processing Second Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid growth in U.S. manufacturing
The Industrial Age Chapter 19 Page 610 The Second Industrial Revolution Chapter 19 Section 1 page 614 Breakthroughs in Steel Processing Second Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid growth in U.S. manufacturing
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION California Content Standards: 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, France, Germany, Japan, and the United States. 1. Analyze why England was
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION California Content Standards: 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, France, Germany, Japan, and the United States. 1. Analyze why England was
Chapter 16 Section 1: Railroads Lead the Way
 Chapter 16 Section 1: Railroads Lead the Way Railroads spur the economy standard gauge consolidation railroad barons time zones US8.12 Students analyze the transformation of the American economy and the
Chapter 16 Section 1: Railroads Lead the Way Railroads spur the economy standard gauge consolidation railroad barons time zones US8.12 Students analyze the transformation of the American economy and the
In 1815, the cost of moving goods by land was high. Water transportation was much cheaper, but was limited to the coast or navigable rivers
 Industrialization In 1815, the cost of moving goods by land was high Cost just as much to haul heavy goods by horse-drawn wagons 30 mi. as it did to ship the 3,000 mi. across the Atlantic Ocean Water transportation
Industrialization In 1815, the cost of moving goods by land was high Cost just as much to haul heavy goods by horse-drawn wagons 30 mi. as it did to ship the 3,000 mi. across the Atlantic Ocean Water transportation
Industrialisation. Industrial processes. Industrialisation in developing countries. D Mining in Namibia. Textile in Namibia
 Unit 1 Industrialisation In Module 1 Unit 5 we discussed how rural areas have been affected by development. Now we will look at the industrial development which began in European and North American cities
Unit 1 Industrialisation In Module 1 Unit 5 we discussed how rural areas have been affected by development. Now we will look at the industrial development which began in European and North American cities
Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
 P L A C A R D A The Granger Collection, NYC Inventions of the Industrial Revolution An 1876 print made by American printmakers Currier & Ives showcases an array of inventions developed during the Industrial
P L A C A R D A The Granger Collection, NYC Inventions of the Industrial Revolution An 1876 print made by American printmakers Currier & Ives showcases an array of inventions developed during the Industrial
Announcements: 1: TEST 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly 2: PREAP: Blue books due February 1!
 Announcements: 1: TEST 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly 2: PREAP: Blue books due February 1! Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Copy of The Beginnings of Industrialization 3: Cell phone Bell
Announcements: 1: TEST 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly 2: PREAP: Blue books due February 1! Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Copy of The Beginnings of Industrialization 3: Cell phone Bell
The Industrial Revolution(s): 1750 to 1910 CE
 The Industrial Revolution(s): 1750 to 1910 CE Name: Directions: Using a classroom laptop, desktop computer, or your own device, complete the WebQuest located at http://tinyurl.com/gwnxt3u Follow the instructions
The Industrial Revolution(s): 1750 to 1910 CE Name: Directions: Using a classroom laptop, desktop computer, or your own device, complete the WebQuest located at http://tinyurl.com/gwnxt3u Follow the instructions
THE FIBRE THAT CHANGED THE WORLD
 THE FIBRE THAT CHANGED THE WORLD The Cotton Industry in International Perspective, 1600-1990s EDITED BY AND PASOLD RESEARCH FUND OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS List of Illustrations List of Figures List
THE FIBRE THAT CHANGED THE WORLD The Cotton Industry in International Perspective, 1600-1990s EDITED BY AND PASOLD RESEARCH FUND OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS List of Illustrations List of Figures List
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 20: An Industrial Society, 1860-1914 Section 1: The Growth of Industry Main Idea: The growth of industry during the years 1860 to 1914 transformed life in America. After
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 20: An Industrial Society, 1860-1914 Section 1: The Growth of Industry Main Idea: The growth of industry during the years 1860 to 1914 transformed life in America. After
TRUE STORIES. The VARDHMAN Group: The perfect human machine interface
 TRUE STORIES The VARDHMAN Group: The perfect human machine interface VARDHMAN Company s core business: Yarn spinner, sewing thread producer, weaver, acrylic fi ber producer, dyer for fi ber, tops and yarn
TRUE STORIES The VARDHMAN Group: The perfect human machine interface VARDHMAN Company s core business: Yarn spinner, sewing thread producer, weaver, acrylic fi ber producer, dyer for fi ber, tops and yarn
Student Goal and Planning Form
 Student Goal and Planning Form Name: Hour: Unit Title: The Nation Divides Unit #: 3 Start Date: 01/09/14 End Date: 03/14/14 What I need to learn: What changes occurred in the North during the early 1800s?
Student Goal and Planning Form Name: Hour: Unit Title: The Nation Divides Unit #: 3 Start Date: 01/09/14 End Date: 03/14/14 What I need to learn: What changes occurred in the North during the early 1800s?
The Big Industrial Innovations: How the Industrial Revolution Began in Great Britain
 The Big Industrial Innovations: How the Industrial Revolution Began in Great Britain We have learned many reasons why industrialization started in Europe and England. But which industry/industries triggered
The Big Industrial Innovations: How the Industrial Revolution Began in Great Britain We have learned many reasons why industrialization started in Europe and England. But which industry/industries triggered
Planning Activity. Theme 1
 Planning Activity Theme 1 This document provides an example of a plan for one topic within Theme 1. This resource goes into more detail than is required in the specification but it provides some background
Planning Activity Theme 1 This document provides an example of a plan for one topic within Theme 1. This resource goes into more detail than is required in the specification but it provides some background
CONVERSIONS FOR PROJECTILE WEAVING MACHINES
 CONVERSIONS FOR PROJECTILE WEAVING MACHINES A new lease of life for your machinery CREALET AG Alte Schmerikonerstrasse 3 8733 Eschenbach/SG Switzerland Tel. +41 (0) 55 286 30 20 Fax +41 (0) 55 286 30 29
CONVERSIONS FOR PROJECTILE WEAVING MACHINES A new lease of life for your machinery CREALET AG Alte Schmerikonerstrasse 3 8733 Eschenbach/SG Switzerland Tel. +41 (0) 55 286 30 20 Fax +41 (0) 55 286 30 29
The Industrial Revolution. Standards Alignment Text with Images Image Analysis Development Cause and Impact Notes Effects Text Scale
 The Industrial Revolution Standards Alignment Text with Images Image Analysis Development Cause and Impact Notes Effects Text Scale Standards Alignment California State Standards for Grade 10 10.3 Students
The Industrial Revolution Standards Alignment Text with Images Image Analysis Development Cause and Impact Notes Effects Text Scale Standards Alignment California State Standards for Grade 10 10.3 Students
Objectives ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER
 9 ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Describe the long-term growth trends in the United States and other countries and regions Identify the main sources of
9 ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Describe the long-term growth trends in the United States and other countries and regions Identify the main sources of
AP Exam Review Unit Six. The Industrial Revolutions and 19 th Century Social Life Ca
 AP Exam Review Unit Six The Industrial Revolutions and 19 th Century Social Life Ca. 1780-1900 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION The industrial revolution began in England in the mid 18th century, but many of
AP Exam Review Unit Six The Industrial Revolutions and 19 th Century Social Life Ca. 1780-1900 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION The industrial revolution began in England in the mid 18th century, but many of
Unit 6 Intro Enlightenment Invention Industrial.notebook April 11, London on Fire
 Unit 6 Revolutions London on Fire Invention - is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product, or a new process for creating an object or
Unit 6 Revolutions London on Fire Invention - is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product, or a new process for creating an object or
Does Russia Need a Tom Sawyer Strategy for Economic Growth?
 Does Russia Need a Tom Sawyer Strategy for Economic Growth? Although they agree about little else, Russia s current leaders and their liberal critics share one firmly-held belief: To secure high growth
Does Russia Need a Tom Sawyer Strategy for Economic Growth? Although they agree about little else, Russia s current leaders and their liberal critics share one firmly-held belief: To secure high growth
Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots.
 The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
iv. Justification: Statement that supports your claim/thesis. 1.
 DO NOW Theme: Technological developments have had both positive and negative effects on the United States economy and on American society. Choose two pieces of technology to write about. (Cotton Gin, Steam
DO NOW Theme: Technological developments have had both positive and negative effects on the United States economy and on American society. Choose two pieces of technology to write about. (Cotton Gin, Steam
Industrialization Presentation
 Industrialization Presentation 2) I can identify, explain, and compare the first and second Industrial Revolutions in the U.S. 3) I can define Industrial Revolution Rapid economic growth primarily driven
Industrialization Presentation 2) I can identify, explain, and compare the first and second Industrial Revolutions in the U.S. 3) I can define Industrial Revolution Rapid economic growth primarily driven
Chapter 8. Technology and Growth
 Chapter 8 Technology and Growth The proximate causes Physical capital Population growth fertility mortality Human capital Health Education Productivity Technology Efficiency International trade 2 Plan
Chapter 8 Technology and Growth The proximate causes Physical capital Population growth fertility mortality Human capital Health Education Productivity Technology Efficiency International trade 2 Plan
Student Handouts, Inc.
 Student Handouts, Inc. What was the Industrial Revolution? The Industrial Revolution was a fundamental change in the way goods were produced, from human labor to machines The more efficient means of production
Student Handouts, Inc. What was the Industrial Revolution? The Industrial Revolution was a fundamental change in the way goods were produced, from human labor to machines The more efficient means of production
Textile Weaving SECTOR UPDATE. JCR-VIS Credit Rating Company Limited. September, Source:
 Textile Weaving SECTOR UPDATE September, 2018 Weaving is defined as the process of conversion of cotton yarn into raw fabric. It can be classified as the third process in the textile value chain illustrated
Textile Weaving SECTOR UPDATE September, 2018 Weaving is defined as the process of conversion of cotton yarn into raw fabric. It can be classified as the third process in the textile value chain illustrated
Revolutions of Industrialization
 Revolutions of Industrialization 1750-1914 AP WORLD HISTORY CHAPTER 17 Life Before the Industrial Revolution Most people lived in rural villages; small communities Farming = major economic sector 1/3 of
Revolutions of Industrialization 1750-1914 AP WORLD HISTORY CHAPTER 17 Life Before the Industrial Revolution Most people lived in rural villages; small communities Farming = major economic sector 1/3 of
Unit 5 - Economic Principles
 Unit 5 - Economic Principles Key Concept: Connections Related Concepts: Resources, Equity Global Context: Globalization and Sustainability Statement of Inquiry Resources have connected our global economy
Unit 5 - Economic Principles Key Concept: Connections Related Concepts: Resources, Equity Global Context: Globalization and Sustainability Statement of Inquiry Resources have connected our global economy
How did early innovations affect the people, economy, and
 Content Claims How did early innovations affect the people, economy, and migration patterns of the United States? Unit Connection This instructional task engages students in content related to the following
Content Claims How did early innovations affect the people, economy, and migration patterns of the United States? Unit Connection This instructional task engages students in content related to the following
