Amplitude Modulation
|
|
|
- Corey Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Amplitude Modulation Manasvi Grover Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Maninder Bir Singh Gulshan Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Amrita Kaul Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Abstract Amplitude modulation is process of superimposing of message or baseband signal over carrier signal, so that signal will travel effectively fast and secure through long distance communication. In this paper, we will study about various methods of AM waves and their generations techniques. The main idea behind this paper is to compare power, spectrum, efficiency and modulation techniques of AM. I.INTRODUTION Amplitude Modulation: The maximum amplitude of carrier signal is made proportional to the instantaneous value of amplitude of modulating or baseband signal in system. According to the definition, There are three types of AM : 1. DSB-FC or AM(Double Sideband Full Carrier) 2. DSB-SC(Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) 3. SSB-SC(Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) II.MATHEMATICAL EXPRESSIONS DSB-FC : Double Sideband Full Carrier Also know to be Amplitude Modulation. Let a message signal or baseband signal be m(t) for single tone, or (1) And the carrier signal be c(t), or... (2) The modulated signal be s(t),.(3) Modulated signal s(t) is (1+ ) times c(t). where, = Amplitude of baseband signal (volts / V) = Amplitude of carrier signal (volts / V) = Angular frequency of message signal (rad / s) = Angular frequency of carrier signal (rad / s) = Amplitude sensitivity factor Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN:
2 Substituting eqn. (1) in eqn.(3), =,, = where is Modulation Index. =, Power of DSB-FC or AM :, from the above eqn. Therefore, Frequency Spectrum (for single tone), DSB-FCcontains (Single tone): 1. Carrier Signal c(t) at. 2. One Upper Sideband at. 3. One Lower Sideband at Techniques for the Generation of DSB-FC are: 1. Square Law Modulator XFG1 D1 The Square law modulator circuit contains: (a). A non-linear device (SLD) Diode (b). A band pass filter (BPF) (c). A carrier source and modulating signal V 1 is voltage before D1 and V 2 is voltage after D1. V 0 is output voltage across R. m(t) c(t) XFG2 1N4446 C 0.1µF T1 10:1 R 0.5Ω Idealized input-output relation After passing through BPF, Comparing above eqn. with s(t), ; V 0 ; Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN: V 1
3 2. Switching Modulator XFG1 D1 m(t) c(t) XFG2 1N4446 Load 0.5Ω Idealized input-output relation After passing through BPF, Comparing above eqn. with s(t), where,. DSB-SC : Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier Let a message signal or baseband signal be m(t) for single tone, or (1) No carrier signal as it is suppressed. The modulated signal be s(t),..(2) Modulated signal s(t) is times c(t). where, = Amplitude of baseband signal (volts / V) = Amplitude of carrier signal (volts / V) = Angular frequency of message signal (rad / s) = Angular frequency of carrier signal (rad / s) = Amplitude sensitivity factor Substituting eqn. (1) in eqn.(2), =, = where is Modulation Index as,, Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN:
4 Power of DSB-SC:, from the above eqn.. Therefore, Frequency Spectrum (for single tone), DSB-SC contains (Single tone): 1. One Upper Sideband at. 2. One Lower Sideband at Techniques for the Generation of DSB-SC are: 1. Balanced Modulator The balanced modulator is used to suppress the unwanted carrier in an AM wave. The carrier and modulating signals are applied to the inputs of the balanced modulator and we get the DSB signal with suppressed carrier at the output of the balanced modulator. Block diagram of Balanced Modulator ; where, and are the output signals of respective AM s and is output for DSB-SC. 2. Ring Modulator or Chopper Modulator Ring modulation is a signal-processing function in electronics, an implementation of amplitude modulation or frequency mixing, performed by multiplying two signals, where one is typically a sine wave or another simple waveform. Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN:
5 SSB-SC : Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier An AM signal with no carrier and one sideband is called a single sideband. The upper and lower sidebands contain the same information, and is not preferred over the other. Let a message signal or baseband signal be m(t) for single tone, or. (1) No carrier signal as it is suppressed. The modulated signal be s(t),.(2) Modulated signal s(t) is times c(t). where, = Amplitude of baseband signal (volts / V) = Amplitude of carrier signal (volts / V) = Angular frequency of message signal (rad / s) = Angular frequency of carrier signal (rad / s) = Amplitude sensitivity factor Substituting eqn. (1) in eqn.(2), =, = where is Modulation Index as,, After passing through Band Pass Filter either will pass or will pass, OR Power of SSB-SC:, from the above eqns. Therefore,. OR SSB-SC contains (Single tone): One Upper Sideband at ( ) OR One Lower Sideband at ( ) Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN:
6 Techniques for the Generation of SSB-SC are: 1. Frequency Discrimination Method One way to generate SSB is to first generate DSB-SC and the suppress the side bands by filtering. ( Derived from DSB-SC) After multiplying and, After passing through the Band Pass Filter, we get, For Upper Sideband, For Lower Sideband, 2. Phase Discrimination Method It is possible to generate SSB by proper phasing of signals. The method essentially uses two product modulators to create two DSB-SC signals that are phase shifted by 90. The two DSB signals are then combined to cancel one of the side bands. REFERENCES [1] Dr. Sanjay Sharma, Communication Systems, 6 th Edition: 2016, pp. 197 [2] Simon Haykin, Communication Systems,4 th Edition: United States of America, pp. 90, 91 Volume 1 Issue 2 - April ISSN:
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad
 Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
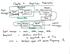 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II)
 Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis
 CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation
 Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems
 CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
World Journal of Engineering Research and Technology WJERT
 wjert, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 2, 185-197 Original Article ISSN 2454-695X Susanchi et al. WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.326 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER MODEL USING
wjert, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 2, 185-197 Original Article ISSN 2454-695X Susanchi et al. WJERT www.wjert.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.326 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER MODEL USING
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
3.1 Introduction 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3 Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier Modulation 3.4 Quadrature-Carrier Multiplexing 3.
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
 EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 AMPLITUDE MODULATION PREPARATION...2 theory...3 depth of modulation...4 measurement of m... 5 spectrum... 5 other message shapes.... 5 other generation methods...6 EXPERIMENT...7 aligning the model...7
AMPLITUDE MODULATION PREPARATION...2 theory...3 depth of modulation...4 measurement of m... 5 spectrum... 5 other message shapes.... 5 other generation methods...6 EXPERIMENT...7 aligning the model...7
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
CME312- LAB Manual DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Experiment 6. Experiment 6. Experiment. DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation
 Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (EE-226-F)
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (EE-226-F) LAB MANUAL IV SEMESTER Department Of Electronics & Communication Engg Dronach harya College Of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. NAME OF THE
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (EE-226-F) LAB MANUAL IV SEMESTER Department Of Electronics & Communication Engg Dronach harya College Of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.No. NAME OF THE
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
DSBSC GENERATION. PREPARATION definition of a DSBSC viewing envelopes multi-tone message... 37
 DSBSC GENERATION PREPARATION... 34 definition of a DSBSC... 34 block diagram...36 viewing envelopes... 36 multi-tone message... 37 linear modulation...38 spectrum analysis... 38 EXPERIMENT... 38 the MULTIPLIER...
DSBSC GENERATION PREPARATION... 34 definition of a DSBSC... 34 block diagram...36 viewing envelopes... 36 multi-tone message... 37 linear modulation...38 spectrum analysis... 38 EXPERIMENT... 38 the MULTIPLIER...
! Amplitude of carrier wave varies a mean value in step with the baseband signal m(t)
 page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029
 1 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LAB (EE-226 -F) Communication System Lab (EE-226-F) LAB MANUAL IV SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
1 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM LAB (EE-226 -F) Communication System Lab (EE-226-F) LAB MANUAL IV SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Experiment 1 Design of Conventional Amplitude Modulator
 Name and ID: Preliminary Work Group Number: Date: Experiment 1 Design of Conventional Amplitude Modulator 1. Using the information given in this assignment, design your switching modulator that modulates
Name and ID: Preliminary Work Group Number: Date: Experiment 1 Design of Conventional Amplitude Modulator 1. Using the information given in this assignment, design your switching modulator that modulates
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LAB
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LAB LAB MANUAL (EE-230-F) IV SEM ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING KHENTAWAS, GURGAON-123506
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LAB LAB MANUAL (EE-230-F) IV SEM ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING KHENTAWAS, GURGAON-123506
EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation
 OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 2-1 Student objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules to implement operations
EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 2-1 Student objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules to implement operations
Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation
 1 Communication Systems Chapter Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation In the previous chapter, we have covered, what is modulation, its different types along with its need. Now here in this chapter we
1 Communication Systems Chapter Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation In the previous chapter, we have covered, what is modulation, its different types along with its need. Now here in this chapter we
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
ELE636 Communication Systems
 ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications
 EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS. BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)
 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Fourier Transform And Its Application In Modulation Techniques
 ourier Transform And Its Application In Modulation Techniques Mrs. Supriya Nilesh Thakur Mrs. Megha Kishor Kothawade Assistant Professor, Basic Engineering Science Department, Guru Gobind Singh College
ourier Transform And Its Application In Modulation Techniques Mrs. Supriya Nilesh Thakur Mrs. Megha Kishor Kothawade Assistant Professor, Basic Engineering Science Department, Guru Gobind Singh College
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science. Lab Manual
 Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Engineering 6871 Communication Principles Lab Manual Fall 2014 Lab 1 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: 1. Learn how to use Matlab
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Engineering 6871 Communication Principles Lab Manual Fall 2014 Lab 1 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: 1. Learn how to use Matlab
DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E.
 PVP SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KANURU, VIJAYAWADA-7 DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E. ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS LAB MANUAL Department of Electronics & Communication engineering Prasad V.Potluri Siddhartha Institute
PVP SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KANURU, VIJAYAWADA-7 DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E. ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS LAB MANUAL Department of Electronics & Communication engineering Prasad V.Potluri Siddhartha Institute
 Question 15.1: Which of the following frequencies will be suitable for beyond-the-horizon communication using sky waves? (a) 10 khz (b) 10 MHz (c) 1 GHz (d) 1000 GHz (b) : 10 MHz For beyond-the-horizon
Question 15.1: Which of the following frequencies will be suitable for beyond-the-horizon communication using sky waves? (a) 10 khz (b) 10 MHz (c) 1 GHz (d) 1000 GHz (b) : 10 MHz For beyond-the-horizon
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL
 CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
Keywords Internet, LabVIEW, Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory, Teaching and Learning process of communication.
 Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX
 PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012)
 EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012) I- Audio Transmission of a Single Tone In this part you will modulate a low-frequency audio tone via AM, and transmit it with a carrier also in the audio range. The
EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012) I- Audio Transmission of a Single Tone In this part you will modulate a low-frequency audio tone via AM, and transmit it with a carrier also in the audio range. The
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
Part-I. Experiment 6:-Angle Modulation
 Part-I Experiment 6:-Angle Modulation 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective This experiment deals with the basic performance of Angle Modulation - Phase Modulation (PM) and Frequency Modulation (FM). The student
Part-I Experiment 6:-Angle Modulation 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective This experiment deals with the basic performance of Angle Modulation - Phase Modulation (PM) and Frequency Modulation (FM). The student
EXPERIMENT 4 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION SUBMITTED BY
 EXPERIMENT 4 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION SUBMITTED BY NAME:. STUDENT ID:.. ROOM: INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: The objectives of this laboratory are:. To introduce the spectrum
EXPERIMENT 4 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION SUBMITTED BY NAME:. STUDENT ID:.. ROOM: INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: The objectives of this laboratory are:. To introduce the spectrum
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document
 Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Chapter 9. Amplitude Modulation
 Chapter 9. Amplitude Modulation 1 Goals Modulate and demodulate the double sideband-suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) amplitude modulation (AM) signals. Investigate the effects of frequency and phase errors
Chapter 9. Amplitude Modulation 1 Goals Modulate and demodulate the double sideband-suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) amplitude modulation (AM) signals. Investigate the effects of frequency and phase errors
Communications and Signals Processing
 Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
ES442 Final Project AM & FM De/Modulation Using SIMULINK
 ES442 Final Project AM & FM De/Modulation Using SIMULINK Goal: 1. Understand the basics of SIMULINK and how it works within MATLAB. 2. Be able to create, configure and run a simple model. 3. Create a subsystem.
ES442 Final Project AM & FM De/Modulation Using SIMULINK Goal: 1. Understand the basics of SIMULINK and how it works within MATLAB. 2. Be able to create, configure and run a simple model. 3. Create a subsystem.
OBJECTIVES EQUIPMENT LIST
 1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
multiplier input Env. Det. LPF Y (Vertical) VCO X (Horizontal)
 Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections , pp Angle Modulation No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c Instantaneous Frequency 2 dt dt No Modulation
 page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM
 Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6
 Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Analog Signal Transmission and Reception. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
6. Amplitude Modulation
 6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
1.5 The voltage V is given as V=RI, where R and I are resistance matrix and I current vector. Evaluate V given that
 Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation
 Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation William Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The use of frequency modulation (called FM) is another method of adding intelligence to a carrier signal. While simple
Modulation Methods Frequency Modulation William Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The use of frequency modulation (called FM) is another method of adding intelligence to a carrier signal. While simple
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation
 ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS. College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 10. Digital Modulation
 Digital Modulation Lecture 10 On-Off keying (OOK), or amplitude shift keying (ASK) Phase shift keying (PSK), particularly binary PSK (BPSK) Frequency shift keying Typical spectra Modulation/demodulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 10 On-Off keying (OOK), or amplitude shift keying (ASK) Phase shift keying (PSK), particularly binary PSK (BPSK) Frequency shift keying Typical spectra Modulation/demodulation
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term c Jossy
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term c Jossy
Principles of Communication Systems
 Principles of Communication Systems Course code: EEE351 (3+1) Prerequisites: EEE223 - Signal and Systems Co requisites: - Course Catalog Description: Introduction to communication systems: Fundamental
Principles of Communication Systems Course code: EEE351 (3+1) Prerequisites: EEE223 - Signal and Systems Co requisites: - Course Catalog Description: Introduction to communication systems: Fundamental
