Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
|
|
|
- Doris Powers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI 1 Monday, June 08, 2015
2 Syllabus Introduction of technique of baseband signal transmission - the definition of baseband signal - typical techniques are applied to transmitted signal - The role of modulation technology in signal transmission theory. Linear- modulation -amplitude modulation (AM) - DSB-SC modulation - SSB-SC modulation - VSB-SC modulation Demodulation - AM demodulation envelope detection coherent demodulation - DSB-SC demodulation - SSB-SC demodulation - VSB-SC demodulation 2 Monday, June 08, 2015
3 Syllabus Non linear modulation - frequency modulation (FM) direct FM indirect FM - phase modulation (PM) Demodulation - FM demodulation slope discriminator phase discriminator ratio discriminator PLL discriminator - PM demodulation the applications of modulation techniques - BeiDou Navigation Satellite System - AM decoder (NE567) - stereo FM transmitter - LM1596 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator - advanced technology Software Defined Ratio 3 Monday, June 08, 2015
4 Theme : baseband signal transmission Introduction of technique of baseband signal transmission Recently, there are dramatically evolutions of information techniques, such as cellphone, computer and network etc, along with the development of technology. Particularly, in the electronic and wireless transmission fields, for instance, the speed of network is much higher than before. Even though, the most popular way to transmit baseband signal is based on the digital technique, such as, improving the channel transmission or develop the digital elements, I would like to study the analog signal transmission in the free space according to the analog techniques. The following graph illustrates the basic architecture of baseband transmission between receiver and transmitter. 4 Monday, June 08, 2015
5 The modulation and demodulation techniques are applied to baseband signal transmission What are not shown in the picture Filter amplifier 5 Monday, June 08, 2015
6 Definition for baseband signal A signal is baseband if it has a very narrow frequency range, i.e. a spectral magnitude that is nonzero only for frequencies in the vicinity of the origin (termed f = 0) and negligible elsewhere. Compared with RF signal, it has rather low frequency. Baseband signals always represent basic information voice image audio.etc 6 Monday, June 08, 2015
7 Typical techniques are applied to transmitted signal baseband transmission applied to computer inner parallel buses, most Local Area Network such as, Ethernet and Token Ring Benefits: convenient for short transmission; low attenuation ; high speed transmission low error probability no need of M-DeM cells Drawback: not suitable for long transmission since it has many AC components 7 Monday, June 08, 2015
8 Typical techniques are applied to transmitted signal Pass-band transmission Passband transmission technique is related to transmitting signal directly inner channels and based on the modulation and demodulation technologies. Benefits: high radiation capability capability for long-distance transmission Drawback: low speed, high error probability 8 Monday, June 08, 2015
9 Typical techniques are applied to transmitted signal broadband transmission Broadband transmissions are divided into multiple bands or channels by multiplexers using a multiplexing scheme such as frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). Benefits: high bandwidth (>128Kbps typical) high speed Drawback: strict requirements complex structure 9 Monday, June 08, 2015
10 Linear modulation Amplitude Modulation (AM) Definition: the amplitude of a high frequency sine wave (usually at a radio frequency) is varied in direct proportion to that of a modulating signal AM radio transmitter system 10 Monday, June 08, 2015
11 Linear modulation Mathematic model m(t) modulating signal A 0 is additional DC component X c (t) = cos (ω c t) called carrier s AM (t) called AM signal or modulated signal Mathematic expression: From the spectrum : Center frequency at ω=±ω C AM bandwidth: 2B m (2f H ) 11 Monday, June 08, 2015
12 Linear modulation AM parameters: Power p AM No DC component for m(t) <m(t)> t =0 <cos 2 (ω c t)> t =< 1 2 cos 2ω ct > t=1/2 finally, P AM =A 02 /2+ <m 2 (t)> t /2 =P C + P S with carrier power P C and sideband power P S Modulation efficiency ή AM definition: ή AM =Ps/P AM =<m 2 (t)> t /(A 02 +<m 2 (t)> t ) < 1 always! 12 Monday, June 08, 2015
13 Linear modulation Modulation index m : Modulation index m is defined as the maximum changes of modulated signal marked as ΔV AM (t) max also could be expressed with (V M -V m )/(V M +V m ) m= (V M -V m )/(V M +V m ) or ΔV AM (t) max Interpolation of m: m=1 is called full-modulated; m>1 is called overmodulated. general case : 0<m<1 13 Monday, June 08, 2015
14 Linear modulation Example of voice signal modulation: Human voice : Frequency range from 300 to 20,000 hertz 14 Monday, June 08, 2015
15 Linear modulation DSB-SC modulation: Mathematic expression: Notation: m(t)=v m cos(ω m t) called modulating signal V c cos( c t)=x c (t) called carrier 15 Monday, June 08, 2015
16 Linear modulation DSB-SC modulation: Spectrum analysis: no carrier component amplitude attenuation 1/2 What about DSB-SC in time domain? 16 Monday, June 08, 2015
17 Linear modulation DSB-SC modulation: In time domain m(t)=0 Parameters analysis: power P DSB =<m 2 (t)> t /2 is the same as AM ME ή DSB =100% improve the modulation efficiency 17 Monday, June 08, 2015
18 Linear modulation SSB-SC modulation: Basic idea: since both sidebands carry the same information, we can only keep one sideband (upper or lower)component to save resource expression in time domain: How can we create the SSB-SC signal? 1. using a sideband filter, which can be HPF or LPF HPF or LPF can be applied to remove one of the sideband, leaving only either the upper sideband (USB) or the lower sideband (LSB) according to which sideband we want to keep. Assuming both sidebands are symmetric, no information is lost in the process and the effective power output is greater than in normal AM. method model Where H SSB (ω) is the transfer function of sideband filter 18 Monday, June 08, 2015
19 Linear modulation SSB-SC modulation: Requirements: need a dramatic cut-off characteristic at f cut-off LPF Lower sideband Benefit: rather easy way to create SSB Drawbacks: difficult to make such kinds of filters (very steep filter) HPF upper sideband 19 Monday, June 08, 2015
20 Linear modulation SSB-SC modulation: How to create SSB-SC signal 2. Phase-shift method Parameter analysis: bandwidth Notation: H h (ω) is the transfer function of Hilbert transform filter, which translates all the components coming from m(t) with phase shift - 90 o Drawbacks: big problem for obtaining such kinds filters with a strict -90 o phase shift. BW SSB = 1 2 BW DSB=B m =f H Power modulation efficiency ή SSB =100% 20 Monday, June 08, 2015
21 Linear modulation VSB-SC modulation: VSB-SC is called Vestigial Sideband suppression carrier. The idea is designing a kind of filter called VSB filter to filter one sideband and keeps a little part of the other one Requirement: H VSB (ω+ω C )+H VSB (ω-ω C )=constant for ω <=ω H. This is derived from VSB demodulation techniques. H VSB (ω) is reciprocal around carrier frequency ω c 21 Monday, June 08, 2015
22 Linear modulation VSB-SC modulation: Expression: 2 cases according to SSB-SC principle Benefits: we could make VSB filter without the strict requirement like SSB However we still have some requirement. Now, let s have a look at the demodulation techniques 22 Monday, June 08, 2015
23 demodulation AM demodulation envelope detection coherent demodulation DSB-SC demodulation SSB-SC demodulation VSB-SC demodulation 1. envelope detection Detector: rectifier and a LPF Diode rectifier condition :1/ω c <<RC<<1/ω H Output: m o (t)=a 0 +m(t) No distortion when A 0 >= m(t) max 23 Monday, June 08, 2015
24 1. envelope detection demodulation Bridge circuit with diodes rectifying circuit process of envelop detection 24 Monday, June 08, 2015
25 demodulation 2. coherent demodulation applying the mixer with inputs s AM (t) and x c (t) can recover the modulating signal m(t). Output: m o (t) = 1/2[A o +m(t)]. PLL applied reference signal. stable frequency component ω called 25 Monday, June 08, 2015
26 demodulation DSB-SC demodulation Only coherent demodulation method can be used, since the DSB envelope is not corresponding with the shape of m(t) The structure is the same as AM one. From the LPF, we can get m o (t)= 1 2 m(t) 26 Monday, June 08, 2015
27 demodulation SSB-SC demodulation With the same factor as DSB-SC, the coherent demodulation is also applied for SSB-SC demodulation process with the same principle circuit The output from mixer is The output from LPF is m o (t) = 1 4 m(t) 27 Monday, June 08, 2015
28 demodulation VSB-SC demodulation Coherent technique is applied: Output from the multiplier Spectrum domain: From LPF we get: 28 Monday, June 08, 2015
29 demodulation VSB-SC demodulation From above equation, we can conclude that in order to get the modulating signal m (t) without distortion from VSB-SC signal, we have H VSB (ω+ω C )+H VSB (ω-ω C )=constant for ω <=ω H Up to now, we have analyzed some kinds of the linear modulation and demodulation techniques Comparison among these AM, DSB-SC, SSB-SC, VSB-SC 29 Monday, June 08, 2015
30 Comparison chart Modulation type Demodulation methods benefits drawbacks AM Envelope detector and coherent demodulation Simple structure for demodulation process; envelope detection can be applied; Low modulation efficiency; Large band is occupied DSB-SC Coherent demodulation No carrier power; High modulation efficiency Large band is occupied SSB-SC Coherent demodulation No carrier power; High modulation efficiency; Few band occupied; Difficult to realize steep sideband filter; VSB-SC Coherent demodulation No carrier power; High modulation efficiency; Few band occupied; Strict condition limited 30 Monday, June 08, 2015
31 Non-linear modulation Non-linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM): frequency variation of carrier Δω c is proportional to modulating signal m(t). Phase modulation (PM): phase variation of carrier ΔΦ is proportional to modulating signal m(t). Frequency modulation (FM): encoding information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave and keep the amplitude constant. 31 Monday, June 08, 2015
32 FM modulation Instantaneous phase and frequency introduction: a(t) Am cos (t) is called the total phase (t) t Relationship between phase and frequency t ω t ω Non-linear modulation dt 0 0 t d (t) dt ω c called instantaneous radius and φ 0 called initial phase. t instantaneous phase: t ω t d t 0 x m (t) is called transmitted signal. sinusoidal carrier: x c (t) = A c cos (2πf c t) 0 32 Monday, June 08, 2015
33 FM modulation Non-linear modulation f(τ) is the instantaneous frequency of local oscillator and f Δ is the frequency deviation, which represents the maximum shift away from f c in one direction, assuming x m (t) is limited to the range ±1 namely, x m (t)=sin(2πf m t). expression for y(t) simplifies to Modulation index: Δf is the maximum deviation of the instantaneous frequency f m : highest frequency component 33 Monday, June 08, 2015
34 FM modulation Non-linear modulation When h<<1, narrowband FM otherwise wideband FM. The realization of FM circuit 1. Direct FM modulation circuit FM circuit with var-diode Crystal oscillator FM circuit Reactance tube FM circuit 2. Indirect FM modulation circuit Direct FM modulation circuit Basic idea: control the output frequency for resonance circuit with modulating signal m (t) f r = 1 2π LC 34 Monday, June 08, 2015
35 Direct modulation FM circuit with var-diode Non-linear modulation Basic steps: 1. Integrating m(t) 2. phase modulation Finally, we get the resonance frequency ( x ) 1 LC j u ( t) c(1 ) V V Crystal oscillator FM circuit D 2 (1 x ) 2 c Q Using m(t) controls resonance frequency 35 Monday, June 08, 2015
36 Direct modulation Non-linear modulation Reactance tube FM circuit Reactance tube which is the same as var-diode is also voltage control device Modulating signal M(t) Indirect FM modulation circuit First, do the integration for modulating signal m(t) and after that do the phase modulation. 36 Monday, June 08, 2015
37 indirect modulation Non-linear modulation output Carrier in M(t) Integrator isolation resistors: R 1,R 2 and R 3 Three capacitors: short circuit for high frequency and open circuit for modulating signal m(t) 37 Monday, June 08, 2015
38 Non-linear modulation PM modulation Analysis: phase Φ is the integration of angle frequency ω technique is quite similar with FM modulation PM modulation using modulating signal m(t) controls the phase of carrier, thus the carrier phase variation ΔΦ is proportional to m(t). The expression is : u U cos ω t k u (t) Δ instantaneous phase: k p :proportion coefficient, (t)called instantaneous phase shift. p PM cm c p Ω (t) ω t k u (t) ω t Δ (t) c p Ω c p instantaneous frequency: d ( t) du ( t) ( t) c kp c p( t) dt dt with du ( t) p( t) kp dt 38 Monday, June 08, 2015
39 Non-linear modulation PM modulation Modulation index :m p Δ p t max maximum phase shift bandwidth: 2(m p + 1)f M with f M =ω m /2π PM circuits correspond to the FM circuits. when doing FM, we get PM as well. 39 Monday, June 08, 2015
40 demodulation FM demodulation FM demodulation process is called frequency detector or discriminator 1. Modifying FM to AM or pulses with different duty cycle 2. Applying AM demodulation methods Fig. basic principle for FM demodulation process 40 Monday, June 08, 2015
41 demodulation FM demodulation Discriminator transconductance : CONSTANT 1. Slope discriminator Circuit : double loop detuning frequency discriminator f 1 <f c f 2 >f c When f c -f 1 =f 2 -f c 41 Monday, June 08, 2015
42 FM demodulation demodulation 2. Phase discriminator Phase discriminator is based on the phase-frequency curve for resonance circuit to change the FM signal to AM signal. Another idea is using steep filter to transfer FM to AM basic circuit equivalent circuit Output voltage : K d called voltage transmission coefficient 42 Monday, June 08, 2015
43 FM demodulation demodulation 3. Ratio discriminator Clipping to avoid the parasitic signal Ratio discriminator has both discrimination function and clipping function 43 Monday, June 08, 2015
44 FM demodulation demodulation 4. PLL-discriminator Recalling the behavior of PLL, we can use certain region F p =F po +KM(t) there is full F p spectrum in the lock range marked with L and V C (t) is proportional to M(t) 44 Monday, June 08, 2015
45 The applications of modulation techniques BeiDou Navigation Satellite System I-Q demodulation 45 Monday, June 08, 2015
46 The applications of modulation techniques AM decoder: NE567 IC 46 Monday, June 08, 2015
47 The applications of modulation techniques AM decoder: NE567 IC Configuration PLL cell 47 Monday, June 08, 2015
48 The applications of modulation techniques stereo FM transmitter: Rohm BA1404 maximum voltage <3V battery can be used 7805 Regulator with a couple of 1N4001 diodes can drive this IC reducing supply voltage to about 2.8 V 48 Monday, June 08, 2015
49 The applications of modulation techniques LM1596/LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator Applications: suppressed- carrier modulation, AM, syn-detection, FM or PM detection. 49 Monday, June 08, 2015
50 The applications of modulation techniques LM1596/LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator 50 Monday, June 08, 2015
51 The applications of modulation techniques Advanced technique-software Defined Radio (SDR) Software structure instead of hardware components (e.g. mixer filter amplifier modulator,etc.) Based on computers or embedded systems Benefits: Increasing capacity Reducing interference to others Software defined antenna 51 Monday, June 08, 2015
52 summary Modulation techniques: Linear-modulation: AM modulation: DSB-SC modulation SSB-SC modulation VSB-SC modulation Non-linear modulation: FM modulation: PM modulation Demodulation techniques: Envelope detection Coherent demodulation FM/PM demodulation circuits Case study: BDS, GPS, NE567,LM1596/LM1496,SDR 52 Monday, June 08, 2015
53 Reference materials 1. <<Fundamentals of Telecommunications>>, published by John Wiley & Sons, <<High frequency electrons>> published by Chen He. 3. Datasheet of LM1596/LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator. 4. Datasheet of IC SI4730 based on broadcast AM/FM/SW/LW radio receiver. 5. 0http:// Monday, June 08, 2015
54 54 Monday, June 08, 2015
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
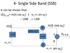 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
Chapter 5. Amplitude Modulation
 Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
3.1 Introduction 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3 Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier Modulation 3.4 Quadrature-Carrier Multiplexing 3.
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
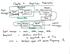 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
ECE513 RF Design for Wireless
 1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
Angle Modulation. Frequency Modulation
 Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER
 LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
Keywords Internet, LabVIEW, Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory, Teaching and Learning process of communication.
 Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
AM, PM and FM mo m dula l ti t o i n
 AM, PM and FM modulation What is amplitude modulation In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed
AM, PM and FM modulation What is amplitude modulation In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]
![Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER] Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]](/thumbs/90/103239233.jpg) Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6
 Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required background (Recall various modulation schemes) Different Multiplexing strategies:
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required background (Recall various modulation schemes) Different Multiplexing strategies:
ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS
 J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
List of Figures. Sr. no.
 List of Figures Sr. no. Topic No. Topic 1 1.3.1 Angle Modulation Graphs 11 2 2.1 Resistor 13 3 3.1 Block Diagram of The FM Transmitter 15 4 4.2 Basic Diagram of FM Transmitter 17 5 4.3 Circuit Diagram
List of Figures Sr. no. Topic No. Topic 1 1.3.1 Angle Modulation Graphs 11 2 2.1 Resistor 13 3 3.1 Block Diagram of The FM Transmitter 15 4 4.2 Basic Diagram of FM Transmitter 17 5 4.3 Circuit Diagram
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
! Amplitude of carrier wave varies a mean value in step with the baseband signal m(t)
 page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS. BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)
 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM)
 EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam
 V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
Communications and Signals Processing
 Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
15.Calculate the local oscillator frequency if incoming frequency is F1 and translated carrier frequency
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
two computers. 2- Providing a channel between them for transmitting and receiving the signals through it.
 1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS. College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS
 PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
 UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6
 AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, Introduction to EECS 2
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals
 Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
General Class License Theory II. Dick Grote K6PBF
 General Class License Theory II Dick Grote K6PBF k6pbfdick@gmail.com 1 Introduction In the first theory class we talked about basic electrical principles and components. Now we will build on this to learn
General Class License Theory II Dick Grote K6PBF k6pbfdick@gmail.com 1 Introduction In the first theory class we talked about basic electrical principles and components. Now we will build on this to learn
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Revision of Previous Six Lectures
 Revision of Previous Six Lectures Previous six lectures have concentrated on Modem, under ideal AWGN or flat fading channel condition Important issues discussed need to be revised, and they are summarised
Revision of Previous Six Lectures Previous six lectures have concentrated on Modem, under ideal AWGN or flat fading channel condition Important issues discussed need to be revised, and they are summarised
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
