Modulator: a crucial part of any communication systems
|
|
|
- Dina Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fourier Transform and Communication Systems 116 Introductory concepts in communications Modulator: a crucial part of any communication systems 117 Modulation The term baseband is used to designate the band of frequencies of the signal delivered by the source. Modulation is a process that causes a shift in the range of frequencies in a signal. Motivation Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) and Frequency-Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Reasonable antenna size for effective radiation of power over a radio link Communication channel matching (avoiding frequencies that suffer from large attenuation/distortion)
2 Frequency-Shift Property of Suppose we have a signal whose content is concentrated at. Multiply this signal by a complex-exponential signal: The product is Frequency-Shift Property: Multiplying by a complexexponential signal of frequency shifts the frequency content of the original signal by. The original content at will now occur at If, the original content is shifted to the right by. 118 If, the original content is shifted to the left by. Modulation Property of Multiplying by a complex-exponential signal of frequency shifts the frequency content of the original signal by : 119 What about multiplication by a cosine? Recall that Therefore,.
3 Important Properties of x y t xytd xtyd Convolution Properties: Shifting Properties: Modulation: x y X Y x y X Y j ft t f g t e G j fct e g t G f fc Note that the magnitude of this is simply 120 g t t G f G f f f f c c c Practice Problems (Another Revisit) t f t f t t f 121
4 Simple Modulation: Freq. Domain Message (modulating signal) f t c Modulator 122 g t t G f G f f f f c c c c c c xt mt ft M f f M f f M f fc M f f c Simple Modulation: Time Domain 123
5 Simple Modulation Message (modulating signal) f t Modulator c 124 Fourier Transform and Communication Systems So, which frequencies do we actually use? Radio-frequency spectrum 125
6 Electromagnetic Spectrum 3 MHz 3 GHz 100 m 10 cm [Gosling, 1999, Fig 1.1 and 1.2] c f Wavelength Frequency 126 [ Radio-frequency spectrum Commercially exploited bands 127 c f Wavelength Frequency Note that the freq. bands are given in decades; the VHF band has 10 times as much frequency space as the HF band.
7 128 Analog (Old) terrestrial TV in BKK VHF.(Low Band) Channel Picture Bandwidth.. Carrier. Audio Carrier VHF.(Hight Band) Channel. Bandwidth. Picture Carrier. Audio Carrier UHF.(Band 4) Channel. Bandwidth. Picture Carrier. Audio Carrier ( ) UHF.(Band 5) Channel Picture Bandwidth.. Carrier. Audio Carrier Terrestrial TV in BKK VHF.(Low Band) Channel Picture Bandwidth.. Carrier. Audio Carrier VHF.(Hight Band) Channel. Bandwidth. Picture Carrier. Audio Carrier UHF.(Band 4) Channel. ( ) Bandwidth. Picture Carrier. Audio Carrier MUX 1 MUX 2 MUX 3 MUX 4 MUX 5 UHF.(Band 5) Channel Picture Bandwidth.. Carrier. Audio Carrier
8 130 Announced on September 12, Released on November 3, Cellular Support in iphone X FDD-LTE (Bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 13, 17, 18, 19, 20, 25, 26, 28, 29, 30, 66) TD-LTE (Bands 34, 38, 39, 40, 41) UMTS/HSPA+/DC-HSDPA (850, 900, 1700/2100, 1900, 2100 MHz) GSM/EDGE (850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz) Additionally, only in models A1865 TD-SCDMA 1900 (F), 2000 (A) CDMA EV-DO Rev. A (800, 1900, 2100 MHz) Model A FDD and TDD LTE frequency bands FDD LTE frequency band allocations TDD LTE frequency band allocations [
9 Operating bands specified for LTE in 3GPP below 1 GHz 132 [Dahlman, Parkvall, and Skold, 2016] Operating bands specified for LTE in 3GPP above 1 GHz 133 [Dahlman, Parkvall, and Skold, 2016]
10 Spectrum Allocation Spectral resource is limited. Most countries have government agencies responsible for allocating and controlling the use of the radio spectrum. Commercial spectral allocation is governed globally by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is responsible for radio communication. in the U.S. by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in Europe by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in Thailand by the National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC; ;.) Blocks of spectrum are now commonly assigned through spectral auctions to the highest bidder [
11 Thailand Freq. Allocations 136 [ ] 137 [ nbtc.go.th/spectrum_management//.aspx ]
12 National Table of Frequency Allocation 138 [ nbtc.go.th/spectrum_management/â  n / µ µ ε ºÉ ªµ É n µ.aspx ] Thailand Freq. Allocations Chart 139
13 Spectrum Allocation Spectrum is a scarce resource. Radio spectrum will be the first of our finite resources to run out, long before oil, gas or mineral deposits. Spectrum is allocated in chunks in frequency domain. Chunks are licensed to (cellular/wireless) operators. Within a single cellular operator, the chunk is further divided into many channels. Each channel has its own band of frequency. 140 Oct 2012: Thailand 2.1GHz Auction 4.5bn baht per license (freq chunk) 1 license (chunk) = 5 MHz (UL) + 5 MHz (DL) 450 million baht per MHz 30 million baht per MHz per year 141
14 Nov 2015: Thailand 1800MHz Auction 40bn baht 15 MHz (UL) + 15 MHz (DL) 1.3 billion baht per MHz 74 million baht per MHz per year ( 2.5) (15 years) (18 years) 142 Dec 2015: Thailand 900MHz Auction 76bn baht 10 MHz (UL) + 10 MHz (DL) 3.8 billion baht per MHz 250 million baht per MHz per year ( 3) Nov years Dec years (forfeit) 143
15 Digital TV License Auction in 2012 Channels for variety TV in high definition (HD) and standard definition (SD) 144 [ ] Digital TV License Auction in 2012 News and children's/family channels 145 [ ]
16 Cognitive radios: Motivation Traditional Rule: Allow predetermined licensed users the right to transmit at given frequencies. Frequency bands were sold at auction, bringing considerable revenue to the government. Unlicensed users are regarded as harmful interference. Radio-frequency resources are not fully utilized There exists a large number of frequency bands that have considerable, and sometimes periodic, idle time intervals. For example, some TV stations do not work at night. Spectrum holes. 146 Cognitive radios A revolutionary communication paradigm that can utilize the existing wireless spectrum resources more efficiently. New Assumption: Users are intelligent and have the ability to observe, learn, and act to optimize their performance. Game theory has been recognized as an important tool in studying, modeling, and analyzing the cognitive interaction process. 147
17 Game Theory A branch of applied mathematics as well as of applied sciences. A formal framework with a set of mathematical tools To study the complex interactions analyze competition and cooperation among interdependent rational players (having individual selfinterests.) For more than half a century, game theory has led to revolutionary changes in economics. Three Nobel Prizes have been given in the economic sciences for work primarily in game theory. 148 John Nash June 13, 1928 May 23, 2015 an American mathematician Share the 1994 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with game theorists Reinhard Selten and John Harsanyi. In 1959, Nash began showing clear signs of mental illness, and spent several years at psychiatric hospitals being treated for paranoid schizophrenia. His struggles with his illness and his recovery became the basis for Sylvia Nasar's biography, A Beautiful Mind, as well as a film of the same name starring Russell Crowe. 149 [ [
18 150 Fourier Transform and Communication Systems Demodulation 151
19 Message (modulating signal) DSB-SC Channel f t Modulator c f t c LPF Demodulator 152 Key equation: LPF mt fct fct xt vt mt In the time domain 153 Note the oscillation at twice the carrier frequency
20 Scaling and Suppressing Frequency Components 154 Important Properties of :A Revisit x y t xytd xtyd Convolution Properties: Shifting Properties: Modulation: x y X Y x y X Y j ft t f g t e G j fct e g t G f fc Note that the magnitude of this is simply 155 g t t G f G f f f f c c c
21 Filter Property of x y t xytd xtyd Convolution Properties: Time Domain View: Filter xt x ht x y X Y x y X Y Frequency Domain View: Filter X f X f H f DSB-SC [Demo_DSBSC_Sound_ReadWAV.m] 157
22 DSB-SC (Zoomed in time) Note how the baseband signal becomes the envelope of the modulated signal. Note the delay caused by the LPF. 158 (Zoomed in time) 159
23 In the time domain we expect 160 Note the oscillation at twice the carrier frequency In the time domain When the sampling rate is not fast enough, 161
24 The problem with sampling rate This is the plot of when we don t connect the dots 162 The problem with sampling rate 163
25 BW Inefficiency in Our System (1) Conjugate symmetry property of Fourier transform: Recall If. is real-valued, then 164 Bandwidth The bandwidth (BW) of a signal is usually calculated from the differences between two frequencies (called the bandwidth limits). Absolute bandwidth: Use the highest frequency and the lowest frequency in the positive-f part of the signal s nonzero magnitude spectrum. Half-power bandwidth (3-dB bandwidth): Use the frequencies where the signal power starts to decrease by 3 db (1/2). Null-to-null bandwidth: Use the signal spectrum s first set of zero crossings. Occupied bandwidth: Consider the frequency range in which X% (for example, 99%) of the energy is contained in the signal s bandwidth. 165
26 BW Inefficiency (2) Message bandwidth and the transmitted signal bandwidth The DSB spectrum has two sidebands: the upper sideband (USB) and the lower sideband (LSB), both containing complete information about the base-band signal m(t). As a result, DSB signals occupy twice the bandwidth required for the baseband. 166 Fourier Transform and Communication Systems Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) 167
27 QAM Send two messages over the same bandwidth of 2B Hz. m t v t H f LP m t f t c f t c f t c x t ht y t f t c m t v t H f m LP t 168 A more general formula: g t t G f G f f f f c c c j j gt fct Gf fce Gf fce 169
28 QAM Demodulation When, B f c x t fct m t x t fct m t 170 c m t ft c m t fct ft c m t ft c m t fct ft c m t f t m t f t v t x t f t c c m t fc t c m t m t f t Complex form of QAM x t m t fct m t fct j fct mte where. 171 : complex envelope or complex baseband signal : in-phase component : quadrature(-phase) component
29 QAM vs. DSB-SC Key Equations DSB-SC Key Equation LPF mt fct fct x t mt QAM Key Equation LPF j ft c j ft c mt e e x t mt 172 Derivation of the QAM Key Equation (1) Recall that. Find and simplify the Fourier transform of. Find and simplify the Fourier transform of. 173
30 Derivation of the QAM Key Equation (2) LPF j ft c j ft c mt e e x t mt 174
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction
 ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.3 Spectrum Allocation 1 Dr.Prapun prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Tuesday 14:20-15:20 Wednesday 14:20-15:20 Friday 9:15-10:15 Electromagnetic
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.3 Spectrum Allocation 1 Dr.Prapun prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Tuesday 14:20-15:20 Wednesday 14:20-15:20 Friday 9:15-10:15 Electromagnetic
Fourier transform ( ) LED Audio Spectrum Analyzer. Fourier transform: Example. Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong
 ICT Elementary for Embedded Systems Signal/Electronic Fundamental Fourier Transform and Communication Systems Fourier transform ( ) The Fourier transform is a frequency domain representation of the original
ICT Elementary for Embedded Systems Signal/Electronic Fundamental Fourier Transform and Communication Systems Fourier transform ( ) The Fourier transform is a frequency domain representation of the original
1.4 Spectrum Allocation Office Hours: BKD Monday 9:20-10:20 Wednesday 9:20-10:20
 ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.4 Spectrum Allocation 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:20-10:20 Wednesday 9:20-10:20 Electromagnetic Spectrum [Gosling, 1999, Fig 1.1] 2 8 3 10 m/s c f Frequency
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.4 Spectrum Allocation 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:20-10:20 Wednesday 9:20-10:20 Electromagnetic Spectrum [Gosling, 1999, Fig 1.1] 2 8 3 10 m/s c f Frequency
EC Talk. Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong.
 EC Talk Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday 14:40-16:00 Outline Courses ECS 452: Digital Communication
EC Talk Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday 14:40-16:00 Outline Courses ECS 452: Digital Communication
1.2 Fourier Transform and Communication System Office Hours: BKD Wednesday 15:30-16:30 Friday 9:30-10:30
 ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.2 Fourier Transform and Communication System 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Wednesday 15:30-16:30 Friday 9:30-10:30 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 Spectrum of Digital Data (4/4) C
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.2 Fourier Transform and Communication System 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Wednesday 15:30-16:30 Friday 9:30-10:30 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 Spectrum of Digital Data (4/4) C
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, Introduction to EECS 2
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review
 ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.4 Spectrum Allocation 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 9:30-10:30 Tuesday 13:30-14:30 Thursday 13:30-14:30 Electromagnetic
ECS 455 Chapter 1 Introduction & Review 1.4 Spectrum Allocation 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 9:30-10:30 Tuesday 13:30-14:30 Thursday 13:30-14:30 Electromagnetic
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6
 AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Lecture 15. Signal Transmission Radio Spectrum. Duplexing Channel Sharing or Multiplexing Modulation. Elec 1200
 Signal Transmission- Modulation Lecture 15 Signal Transmission Radio Spectrum Multiple Users Duplexing Channel Sharing or Multiplexing Modulation Elec 1200 Signal Transmission In a communications system
Signal Transmission- Modulation Lecture 15 Signal Transmission Radio Spectrum Multiple Users Duplexing Channel Sharing or Multiplexing Modulation Elec 1200 Signal Transmission In a communications system
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation
 Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang 09/6/2012 Outline Admin and recap Frequency domain examples Basic concepts of modulation Amplitude modulation Amplitude demodulation frequency
Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang 09/6/2012 Outline Admin and recap Frequency domain examples Basic concepts of modulation Amplitude modulation Amplitude demodulation frequency
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
Page 1. Overview : Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE
 Overview 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/
Overview 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 9: OFDM, WiMAX, LTE Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Chapter 5 OFDM. Office Hours: BKD Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30
 Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 2 OFDM: Overview Let S 1, S 2,, S N be the information symbol. The discrete baseband OFDM modulated symbol can be expressed
Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 2 OFDM: Overview Let S 1, S 2,, S N be the information symbol. The discrete baseband OFDM modulated symbol can be expressed
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Communications and Signals Processing
 Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
ECS455: Chapter 5 OFDM
 ECS455: Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong www.prapun.com Office Hours: Library (Rangsit) Mon 16:20-16:50 BKD 3601-7 Wed 9:20-11:20 OFDM Applications 802.11 Wi-Fi: a/g/n/ac versions DVB-T (Digital Video
ECS455: Chapter 5 OFDM 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong www.prapun.com Office Hours: Library (Rangsit) Mon 16:20-16:50 BKD 3601-7 Wed 9:20-11:20 OFDM Applications 802.11 Wi-Fi: a/g/n/ac versions DVB-T (Digital Video
I-Q transmission. Lecture 17
 I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX
 PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002
 Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems
 CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems Wireless Foundation: Modulation and Demodulation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 208A Watson Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs434/
CS434/534: Topics in Networked (Networking) Systems Wireless Foundation: Modulation and Demodulation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 208A Watson Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs434/
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE ADVANCED SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE LUO Chapter18.1 and Introduction to OFDM
 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE ADVANCED SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE LUO Chapter18.1 and 18.2 Introduction to OFDM 2013/Fall-Winter Term Monday 12:50 Room# 1-322 or 5F Meeting Room Instructor: Fire Tom Wada, Professor 12/9/2013
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE ADVANCED SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE LUO Chapter18.1 and 18.2 Introduction to OFDM 2013/Fall-Winter Term Monday 12:50 Room# 1-322 or 5F Meeting Room Instructor: Fire Tom Wada, Professor 12/9/2013
! Amplitude of carrier wave varies a mean value in step with the baseband signal m(t)
 page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad
 Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Fading & OFDM Implementation Details EECS 562
 Fading & OFDM Implementation Details EECS 562 1 Discrete Mulitpath Channel P ~ 2 a ( t) 2 ak ~ ( t ) P a~ ( 1 1 t ) Channel Input (Impulse) Channel Output (Impulse response) a~ 1( t) a ~2 ( t ) R a~ a~
Fading & OFDM Implementation Details EECS 562 1 Discrete Mulitpath Channel P ~ 2 a ( t) 2 ak ~ ( t ) P a~ ( 1 1 t ) Channel Input (Impulse) Channel Output (Impulse response) a~ 1( t) a ~2 ( t ) R a~ a~
Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = 1 T. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt.
![Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = 1 T. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt. Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = 1 T. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt.](/thumbs/76/74238457.jpg) Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang Admin and recap Basic concepts o modulation Amplitude demodulation requency shiting 09/6/202 2 Admin First assignment to be posted by this
Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang Admin and recap Basic concepts o modulation Amplitude demodulation requency shiting 09/6/202 2 Admin First assignment to be posted by this
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer. Bird s Eye View. Outline. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
Digital Communication System
 Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at required rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth, power requirements
Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at required rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth, power requirements
COMM 704: Communication Systems
 COMM 704: Communication Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg Course Objective Give an introduction to the basic concepts of electronic communication systems
COMM 704: Communication Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg Course Objective Give an introduction to the basic concepts of electronic communication systems
HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM
 Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Chapter-15. Communication systems -1 mark Questions
 Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. G[k] = 1 T. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt.
![Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. G[k] = 1 T. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt. Outline. Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation. Admin. Page 1. G[k] = 1 T. g(t)e j2πk t dt. G[k] = = k L. ) = g L (t)e j2π f k t dt.](/thumbs/89/97558237.jpg) Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang Admin and recap Basic concepts o modulation Amplitude modulation Amplitude demodulation requency shiting 9/6/22 2 Admin First assignment
Outline Wireless PHY: Modulation and Demodulation Y. Richard Yang Admin and recap Basic concepts o modulation Amplitude modulation Amplitude demodulation requency shiting 9/6/22 2 Admin First assignment
Music 171: Amplitude Modulation
 Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research PDF-document.
 Mansor, Z. B., Nix, A. R., & McGeehan, J. P. (2011). PAPR reduction for single carrier FDMA LTE systems using frequency domain spectral shaping. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Postgraduate Symposium
Mansor, Z. B., Nix, A. R., & McGeehan, J. P. (2011). PAPR reduction for single carrier FDMA LTE systems using frequency domain spectral shaping. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Postgraduate Symposium
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing. Cartoon View 1 A Wave of Energy
 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
EE228 Applications of Course Concepts. DePiero
 EE228 Applications of Course Concepts DePiero Purpose Describe applications of concepts in EE228. Applications may help students recall and synthesize concepts. Also discuss: Some advanced concepts Highlight
EE228 Applications of Course Concepts DePiero Purpose Describe applications of concepts in EE228. Applications may help students recall and synthesize concepts. Also discuss: Some advanced concepts Highlight
Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp
 Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0
Planning of LTE Radio Networks in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0
Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
 Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
ECE 457 Communication Systems. Selin Aviyente Assistant Professor Electrical & Computer Engineering
 ECE 457 Communication Systems Selin Aviyente Assistant Professor Electrical & Computer Engineering Announcements Class Web Page: http://www.egr.msu.edu/~aviyente/ece 457.htm M, W, F 10:20-11:10 a.m. Office
ECE 457 Communication Systems Selin Aviyente Assistant Professor Electrical & Computer Engineering Announcements Class Web Page: http://www.egr.msu.edu/~aviyente/ece 457.htm M, W, F 10:20-11:10 a.m. Office
ITM 1010 Computer and Communication Technologies
 ITM 1010 Computer and Communication Technologies Lecture #14 Part II Introduction to Communication Technologies: Digital Signals: Digital modulation, channel sharing 2003 香港中文大學, 電子工程學系 (Prof. H.K.Tsang)
ITM 1010 Computer and Communication Technologies Lecture #14 Part II Introduction to Communication Technologies: Digital Signals: Digital modulation, channel sharing 2003 香港中文大學, 電子工程學系 (Prof. H.K.Tsang)
2.4GHz & 900MHz UNLICENSED SPECTRUM COMPARISON A WHITE PAPER BY INGENU
 2.4GHz & 900MHz UNLICENSED SPECTRUM COMPARISON A WHITE PAPER BY INGENU 2.4 GHZ AND 900 MHZ UNLICENSED SPECTRUM COMPARISON Wireless connectivity providers have to make many choices when designing their
2.4GHz & 900MHz UNLICENSED SPECTRUM COMPARISON A WHITE PAPER BY INGENU 2.4 GHZ AND 900 MHZ UNLICENSED SPECTRUM COMPARISON Wireless connectivity providers have to make many choices when designing their
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications
 EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics
 Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics Dr. Kemal Akkaya E-mail: kemal@cs.siu.edu Kemal Akkaya Mobile & Wireless Computing
Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics Dr. Kemal Akkaya E-mail: kemal@cs.siu.edu Kemal Akkaya Mobile & Wireless Computing
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
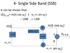 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Technician License Course Chapter 2. Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth
 Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
2012 LitePoint Corp LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved.
 LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
Some key functions implemented in the transmitter are modulation, filtering, encoding, and signal transmitting (to be elaborated)
 1 An electrical communication system enclosed in the dashed box employs electrical signals to deliver user information voice, audio, video, data from source to destination(s). An input transducer may be
1 An electrical communication system enclosed in the dashed box employs electrical signals to deliver user information voice, audio, video, data from source to destination(s). An input transducer may be
Telecommunications Regulation & Trends Lectures 2-4: Spectrum Management Fundamentals
 Telecommunications Regulation & Trends Lectures 2-4: Spectrum Management Fundamentals ) ديغم فاضل ( Digham Dr. Fadel R&D Executive Director National Telecom Regulatory Authority (NTRA), Egypt The radio
Telecommunications Regulation & Trends Lectures 2-4: Spectrum Management Fundamentals ) ديغم فاضل ( Digham Dr. Fadel R&D Executive Director National Telecom Regulatory Authority (NTRA), Egypt The radio
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation
 Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
ECE513 RF Design for Wireless
 1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels
 Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class)
 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2015/1 HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class) Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do
ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2015/1 HW 6 Due: November 3, 10:39 AM (in class) Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) ONE part of a question will be graded (5 pt). Of course, you do
CME312- LAB Manual DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Experiment 6. Experiment 6. Experiment. DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation
 Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques
 6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques The quality of analog transmission is S/N (signal to noise ratio). signal power S/N = ---------------------------- baseband noise power S/N can be greater than
6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques The quality of analog transmission is S/N (signal to noise ratio). signal power S/N = ---------------------------- baseband noise power S/N can be greater than
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Requirements on 5G Development Device manufacturer s perspective
 Requirements on 5G Development Device manufacturer s perspective ECC 5G Mobile Communications Workshop Mainz, Nov. 2 4 2016 Quan Yu, Chief Strategy Officer, Huawei Wireless Product Line 1 Europe s 5G Action
Requirements on 5G Development Device manufacturer s perspective ECC 5G Mobile Communications Workshop Mainz, Nov. 2 4 2016 Quan Yu, Chief Strategy Officer, Huawei Wireless Product Line 1 Europe s 5G Action
1 Introduction 1.1 RADIO: WHAT AND WHY...
 1 Introduction 1.1 RADIO: WHAT AND WHY... Radio is the use of unguided propagating electromagnetic fields in the frequency range 3 khz and 300 GHz to convey information. Propagating electromagnetic fields
1 Introduction 1.1 RADIO: WHAT AND WHY... Radio is the use of unguided propagating electromagnetic fields in the frequency range 3 khz and 300 GHz to convey information. Propagating electromagnetic fields
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
3250 Series Spectrum Analyzer
 The most important thing we build is trust ADVANCED ELECTRONIC SOLUTIONS AVIATION SERVICES COMMUNICATIONS AND CONNECTIVITY MISSION SYSTEMS 3250 Series Spectrum Analyzer > Agenda Introduction
The most important thing we build is trust ADVANCED ELECTRONIC SOLUTIONS AVIATION SERVICES COMMUNICATIONS AND CONNECTIVITY MISSION SYSTEMS 3250 Series Spectrum Analyzer > Agenda Introduction
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 16 Orthogonal Frequency Division Medium Access (OFDM)
 Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 16 Orthogonal Frequency Division Medium Access (OFDM) 1 4G File transfer at 10 Mbps High resolution 1024 1920 pixel hi-vision picture
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 16 Orthogonal Frequency Division Medium Access (OFDM) 1 4G File transfer at 10 Mbps High resolution 1024 1920 pixel hi-vision picture
