Sensation & Perception. Chapter 6 Perception. Myers PSYCHOLOGY. Attention: Theoretical Issues. Perception Outline
|
|
|
- Baldric Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Myers PSYCHOLOGY C6:1 Sensation & Perception C6:2 Chapter 6 Perception Sensation - Process by which sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energy (+1) Perception - Process of organizing and interpreting sensory information to recognize meaningful objects and events - Subject to host of psychological influences (+2) Visual Information Processing C6:3 C6:4 Hastorf & Cantril (1954) Classic case study on role of values in perception. Selective perception of 1951 football game between Dartmouth and Princeton. Princeton won. A very rough game, many penalties. Princeton quarterback, All-American in last college game, left in 2 nd quarter with broken nose and mild concussion. In 3 rd quarter Dartmouth quarterback's leg broken. A week later, Hastorf and Cantril had Dartmouth and Princeton psychology students fill out questionnaire, and authors analyzed answers of those who had seen either the game or movie of game. Two other groups viewed film of game and tabulated number of infractions seen. Question: "Which team do you feel started the rough play?" Pr Da Both Neither/No Answer Dartmouth Students Princeton Students Question: "Do you believe game was clean and fairly played or unnecessarily rough and dirty?" C&F R&F R&D Don t Know Dartmouth Students Princeton Students When shown film, Princeton students "saw" Dartmouth team make over 2x as many infractions as were seen by Dartmouth students. Perception Outline Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual Organization - Form Perception - Depth Perception - Motion Perception - Perceptual Constancy C6:5 Perceptual Interpretation - Sensory Deprivation and Restored Vision - Perceptual Adaptation - Perceptual Set - Perception and the Human Factor Is there Extrasensory Perception? - Claims of ESP - Premonitions or Pretensions? - Putting ESP to Experimental Test Attention: Theoretical Issues Attention: ability to perceive part of environment, and ignore rest Number of fundamental issues - Early vs. Late selection - Mechanisms (analogies) Attention as Filter Attentional Spotlight Attention as Limited Resource - Do unattended stimuli have an influence? C6:6 1
2 Attention: Findings Binocular Rivalry Ambiguous stimuli - Necker Cube, Old/Young Woman,... Consciously experience only one object at a time Attention a limited capacity system C6:7 Necker Cube X C6:8 Box on left can be seen in two ways - By one interpretation, X is at center of front wall, which faces down to left - By other interpretation, X is at center of back wall, and front wall faces up to right Old or Young Woman? C6:9 Auditory Attention Findings Cocktail Party Effect - Dichotic Listening or Shadowing task Hear two different messages in headphones, one to each ear (+1) - What known about message to ignored ear? Identify gender, loudness Not language, content But something particularly salient (e.g., your name) may be noticed C6:10 Shadowing Task C6:11 Selective Attention: Stroop C6:12 2
3 C6:13 Fascinating Finding Neisser basketball game film - Unaware of woman with umbrella crossing screen or even person in ape suit Change Blindness Change Blindness: 1 2 C6:14 People fail to notice pronounced changes in perceptual stimuli, even introduction of completely different person into conversation 3 Subliminal Perception C6:15 Can unattended stimuli affect us? Natural observations or myths - Eat Popcorn / Drink Coca-Cola Hoax Denied by owner, Factual errors 1/24th sec duration not subliminal Subliminal Experimental Studies Shadowing messages, heard tunes in other ear - Recognition at chance level - Implicit memory (familiarity) > chance Processing ambiguous stimuli - Homonyms: We stood by the bank. - Affected by context in unattended ear: river, money Salient stimuli - If someone at loud party says your name, then you attend... but how? Name must have registered at some, subliminal level. C6:16 Perception Outline Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual Organization - Form Perception - Depth Perception - Motion Perception - Perceptual Constancy C6:17 Perceptual Interpretation - Sensory Deprivation and Restored Vision - Perceptual Adaptation - Perceptual Set - Perception and the Human Factor Is there Extrasensory Perception? - Claims of ESP - Premonitions or Pretensions? - Putting ESP to Experimental Test C6:18 Illusions Perceptual illusions - Many based on interplay between visual stimulation and contextual cues (e.g., about distance) - Can involve quite complex computations that we are unaware of - Vertical-Horizontal Illusion St. Louis landmark Vertical=Horizontal 3
4 Size/Distance Illusion C6:19 Size & Ponzo Illusions C6:20 Small figure at front is same size as figure at back, as are two arrows. Front figures appear much smaller. If figures dragged from back to front, would appear to shrink. Ponzo Illusion C6:21 Muller-Lyer Illusion C6:22 AB BC Muller-Lyer Illusion C6:23 Inward pointing arrows appear on edges extending towards us Outward pointing arrows appear on edges receding away 2 lines, same image on retina; one (>-- <) appears further away than other (<- ->) must be longer. Seen as so! Perceptual Illusions C6:24 4
5 Ames Room: Size-Distance Relation C6:25 Perception Outline Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual Organization - Form Perception - Depth Perception - Motion Perception - Perceptual Constancy C6:26 Perceptual Interpretation - Sensory Deprivation and Restored Vision - Perceptual Adaptation - Perceptual Set - Perception and the Human Factor Is there Extrasensory Perception? - Claims of ESP - Premonitions or Pretensions? - Putting ESP to Experimental Test Form Perception Gestalt - An organized whole - Tend to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes Figure-Ground - Perceive objects against background - Illustrated on next few slides C6:27 Form: Figure Ground Grouping of elements and other processes lead to classification of shapes as figures and ground - Figure: coherent, structured object - Ground: background, context for objects Gestalt principles applied to figure-ground problem C6:28 C6:29 Figure-Ground Gestalt principles Closure: prefer shape that is closed as figure Relative size: see smaller shape as figure against larger ground Surroundedness: Figure / Ground effects enhanced if ground shape surrounds figure Symmetry: symmetry enhances grouping and perception of figure Ambiguous Vase/Faces Figure and Ground - Organization of visual field into objects (Figures) that stand out from their surroundings (Ground) - In ambiguous Figure / Ground stimuli, ambiguous which part is figure and which ground C6:30 5
6 Figure/Ground: Ambiguous Images C6:31 C6:32 Gestalt Laws: principles that govern / describe how perceptual system groups together stimulus pieces in environment (see below and next few slides) - Proximity: group nearby figures together - Similarity: group figures that are similar - Continuity: perceive continuous patterns - Closure: fill in gaps - Connectedness: spots, lines and areas are seen as unit when connected Grouping C6:33 Gestalt principle: Proximity Proximity one of most important factors for perceptual organization Here elements grouped as columns, dots, and rows depending on spacing (proximity) C6:34 Gestalt principle: Similarity C6:35 Gestalt principle: Continuity C6:36 Things that look similar tend to be grouped together The dots image now appears to be rows What makes images similar is empirical issue - In circular image task is to identify odd quadrant of circle, easier for leftmost of two images: distinctiveness? Left we see straight line figure as two separate lines crossing at rather than other configurations, such as kissing beaks Right, proximity, similarity and continuity interact to yield same image structure 6
7 Gestalt Principles: Closure C6:37 C6:38 Parts of occluded objects are completed by visual system The Law of Common Fate Elements that move together seen as forming common object - Animals may blend into background (above), until they move. Suddenly visible. - As an example, next few slides and ovement/dots3.mov Common Fate Example - 1 C6:39 Depth Perception C6:43 Perception of Depth and Distance - Ability to see objects in three dimensions - Allows us to judge distance Motion and Depth: Kinetic Depth Two primary types of cues - Binocular and Monocular Cues - Development Depth Perception Binocular cues - Require use of two eyes - Retinal Disparity Images from the two eyes differ Closer object, larger the disparity (right) - Convergence Neuromuscular cue Two eyes move inward for near objects (+1) C6:44 Convergence The larger the angle represented by A and B in figure, nearer the object C6:45 7
8 Depth Perception Monocular Cues - Relative size: Smaller image more distant (+1) - Interposition: Closer object blocks distant object (+2) - Relative clarity: Hazy object seen as more distant (+3 +4) - Texture: Coarse close, Fine distant (+5) C6:46 Depth Perception: Relative Size C6:47 C6:48 Depth Perception: Clarity C6:49 Depth Perception: Interposition Clarity and Perceived Distance C6:50 Depth Perception: Texture Texture gradient - Stimuli that are nearer have coarser texture. C6:51 8
9 Depth Perception C6:52 Parallax C6:53 More Monocular Cues - Relative height: Higher objects seen as more distant - Relative motion (motion parallax): Closer objects seem to move faster (+1) - Linear perspective: Parallel lines converge with distance (+2) - Light and Shadow: Closer objects appear brighter (+3) Near objects move faster than distant objects Demonstration: MotionParallax Depth Perception: Perspective C6:54 Monocular Cues: Shading Major light sources tend to come from above, so shading is another source of depth information. Objects shaded lighter on top seen as sticking out towards us. Here, crater (top) becomes mound (bottom) when picture turned upside down. C6:55 Development of Depth Perception Visual Cliff: Used by Gibson & Walk to study depth perception in infants and animals C6:56 Infant on Visual Cliff C6:57 Research on infants and animals indicates that certain cues for depth/distance are innate and do not depend on experience, whereas other cues are learned and do not operate without experience 9
10 Culture and Depth Perception C6:58 Motion Perception Size of objects - Looming objects moving towards us - Critical for various activities: driving, flying plane, catching ball,... Phi phenomenon - Apparent motion - Similar to common fate example, but faster timing (+1) Motion illusions (above) - Focus on dot, move head forward and backward - Motion After-Effect C6:59 C6:60 C6:61 Perceptual Constancy Perceptual Constancy - Perceive objects as unchanged despite changes in retinal image Shape (above) Size Color (right) Brightness (+1) Brightness (Lightness) Constancy C6:62 Relative Nature of Brightness C6:63 White paper looks white whether in sunlight or shadow Brightness viewed not in absolute terms, but relative to brightness of context. When cloud passes over, everything gets less bright and, as a result, nothing really seems to change. - See next few slides 10
11 Brightness Constancy C6:64 Perception Outline Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual Organization - Form Perception - Depth Perception - Motion Perception - Perceptual Constancy C6:65 Perceptual Interpretation - Sensory Deprivation and Restored Vision - Perceptual Adaptation - Perceptual Set - Perception and the Human Factor Is there Extrasensory Perception? - Claims of ESP - Premonitions or Pretensions? - Putting ESP to Experimental Test Sensory Deprivation and Restored C6:66 Vision Restored vision - Figure-Ground, sensed colours, not object identification Rearing animals with deprived visual input - Color, Brightness, but not Form - Held & Hein: vertical stripes (+1) Critical period for sensory development - Rationale for corrective surgery for cataracts early (few months) - Similar effect of cochlear implants Sensory Restriction C6:67 Blakemore & Cooper, 1970 Kittens raised without exposure to horizontal lines later had difficulty perceiving horizontal bars. Learning can also be studied by Perceptual observing how people or animals adapt to modified Adaptation perceptual experience - e.g., surgery, distorting prisms Displacing goggles contain prisms - Humans adapt quickly given visual-motor experience with feedback - Upside-down prism: Stratton (1896) - Adaptation varies across species Some species unable to adapt: chicks In some species (owls), depends on early infant experience C6:68 Perceptual Set C6:69 Predisposition to see one thing and not another (+1) - Expectations developed on basis of context Visual - Loch Ness monster or log, space ships or clouds, ambiguous figure Auditory - Cheer Up Satanic messages in backward tapes - -eel is on the wagon -eel is on the orange 11
12 Expectations and Set C6:70 Set (and Illusion) C6:71 Does front monster appear frightened and back one ferocious? Actually, exactly the same expression (also same size). More examples of set Interpretation of neutral facial expression - Prior Image Interpretation dead woman soup playing child sad thoughtful happy C6:72 C6:73 - Mental representation of concepts based on past experience important for effect of set - Myer s discussion of schemas Organized, mental representation of objects in external world (e.g., face) Children s schemas quite primitive, basic Play sad or happy music - People asked to interpret homophones mourning/morning, die/dye, pain/pane C6:74 Representation of Concepts Person without mental concept of Dalmatian or Cow is unlikely to perceive these images as objects Concept Representation Parts of occluded objects completed by visual system. Requires representations (+1) C6:75 12
13 C6:76 Schemas for Faces Face schemas exert influence on perception - C6:78 Perception and Human Factors C6:80 C6:77 Below, exaggerated version of Michael J. Fox recognized better than actual image Inverted faces present perceptual difficulties (+1) Culture and Context Effects Airplane Accidents C6:79 C6:81 Many applied implications - Medical Procedures Critical periods and corrective surgery - Human Factors Research Design of instruments, appliances, etc.: Right stove below allows more natural interpretation of controls Airplane accidents (+1) 13
14 Perception Outline Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual Organization - Form Perception - Depth Perception - Motion Perception - Perceptual Constancy C6:82 Perceptual Interpretation - Sensory Deprivation and Restored Vision - Perceptual Adaptation - Perceptual Set - Perception and the Human Factor Is there Extrasensory Perception? - Claims of ESP - Premonitions or Pretensions? - Putting ESP to Experimental Test Is there Extrasensory Perception? C6:83 Extrasensory Perception - Claim that perception can occur without normal sensory input Telepathy: mind-to-mind communication Clairvoyance: perceive distant objects/events Precognition: perceive event in future Parapsychology - The study of paranormal phenomena ESP Psychokinesis: mental bending/moving of objects C6:84 Natural Observations of ESP Apparent success Vague predictions: Nostradamus Chance - Two students in different classes taught by same instructor are partners - but, 40 x 60 = 2400 pairs of students, and many possible relationships Fraud, post-diction Little success for psychic predictions Newspaper psychics Police departments Spontaneous visions/dreams - Lindbergh baby: only 4/1300 dreams involved body in trees C6:85 Experimental Studies of ESP Myers quote - A reproducible ESP phenomenon has never been discovered, nor has anyone produced any individual who can convincingly demonstrate psychic ability. USA military: $20,000,000 on psychic spies - Nothing to show Predicting coin toss - 28,000 people predicted 110,972 tosses, 49.8% right Ganzfeld Procedure (+1) Ganzfeld Experiments Use sensory deprivation to minimize distractions Bem and Honorton (1994) review: 32% vs. 25% - Concerns about some procedures (Susan Blakemore) Milton & Wiseman (1999) - 30 follow-up studies - No statistically significant effect C6:86 C6:87 Critical Scientific Attitude Many such claims - e.g., therapeutic touch: energy fields that practitioners believe are sensed and affected by energy fields of another person Can be VERY difficult to dissuade people - Frustrating for scientist, which can lead to dismissive tone - MANY efforts to demonstrate ESP have failed, yet still many believers Scientific attitude - Extremely critical, skeptical - Important to consider and weigh ALL of evidence - Not out of negativity, but ONLY way to determine whether ideas are valid or not is to subject them to most difficult tests possible - Does not mean close-mindedness OR perpetual openmindedness 14
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Chapter 6: Perception
 Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Chapter 6: Perception Perception The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Selective Attention: the idea that we are
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception. Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Cocktail Party Effect
 Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
5. According to the philosopher, we learn to perceive the world. A) Locke B) Kant C) Gibson D) Walk E) Neisser
 Bryant-Taneda: AP Psychology Test Bank Perception (Chapter 6) 1. If two objects are assumed to be the same size, the object that casts the smaller retinal image is perceived to be: A) more coarsely textured.
Bryant-Taneda: AP Psychology Test Bank Perception (Chapter 6) 1. If two objects are assumed to be the same size, the object that casts the smaller retinal image is perceived to be: A) more coarsely textured.
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Perception. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers. Perception. Chapter 6. Selective Attention. Perceptual Illusions. Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Perception Chapter 6 2 Perception Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Perception Chapter 6 2 Perception Selective Attention Perceptual Illusions Perceptual
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception
 Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception Fritz Perls Father of Gestalt theory and Gestalt Therapy Movement in experimental psychology which began prior to WWI. We perceive objects as well-organized patterns
Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
March 9. Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion?
 March 9 EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion? Agenda: 1. Perception Theories 2. Brain Games Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. Table of Contents: 87. March 9 & 10 88.
March 9 EQ- How do we perceive depth and motion? Agenda: 1. Perception Theories 2. Brain Games Do Now: Explain the Gestalt theory of perception and two examples. Table of Contents: 87. March 9 & 10 88.
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Perceptual Organization. Unit 3 RG 4e
 Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
Perceptual Organization Unit 3 RG 4e Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Perceptual Illusions To understand how perception is organized, illusions
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Unit IV Sensation Perception
 Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Definitions Sensation Sensation and perception Perception
 Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Definitions Sensation and perception Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Module 2. Lecture-1. Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation.
 Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Vision: Distance & Size Perception
 Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation and perception. Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych
 Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception
 Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
CS 559: Computer Vision. Lecture 1
 CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
Optics, perception, cognition. Multimedia Retrieval: Perception. Human visual system. Human visual system
 Multimedia Retrieval: Perception Remco Veltkamp Optics, perception, cognition Be aware of human visual system, perception, and cognition Human visual system Human visual system Optics: Rods for b/w Cones
Multimedia Retrieval: Perception Remco Veltkamp Optics, perception, cognition Be aware of human visual system, perception, and cognition Human visual system Human visual system Optics: Rods for b/w Cones
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
3D Space Perception. (aka Depth Perception)
 3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES?
 Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
the human chapter 1 the human Overview Perception Limitations of poor interface design Why do we need to understand users?
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6
 Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
 1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
1 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June
 An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
Design III CRAFTS SUPPLEMENT
 Design III CRAFTS SUPPLEMENT 4-H MOTTO Learn to do by doing. 4-H PLEDGE I pledge My HEAD to clearer thinking, My HEART to greater loyalty, My HANDS to larger service, My HEALTH to better living, For my
Design III CRAFTS SUPPLEMENT 4-H MOTTO Learn to do by doing. 4-H PLEDGE I pledge My HEAD to clearer thinking, My HEART to greater loyalty, My HANDS to larger service, My HEALTH to better living, For my
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Occlusion. Atmospheric Perspective. Height in the Field of View. Seeing Depth The Cue Approach. Monocular/Pictorial
 Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects
 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 19. Brightness illusions
 Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
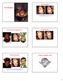 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture
 59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion
 Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION. Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K.
 THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
Regan Mandryk. Depth and Space Perception
 Depth and Space Perception Regan Mandryk Disclaimer Many of these slides include animated gifs or movies that may not be viewed on your computer system. They should run on the latest downloads of Quick
Depth and Space Perception Regan Mandryk Disclaimer Many of these slides include animated gifs or movies that may not be viewed on your computer system. They should run on the latest downloads of Quick
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception
 Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning
 Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES 4.2 AIM 4.1 INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
Static and Moving Patterns
 Static and Moving Patterns Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 7 18.10.2007 Pattern learning People who work with visualizations must learn the skill of seeing patterns in data. In terms of making visualizations
Static and Moving Patterns Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 7 18.10.2007 Pattern learning People who work with visualizations must learn the skill of seeing patterns in data. In terms of making visualizations
MOTION PARALLAX AND ABSOLUTE DISTANCE. Steven H. Ferris NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL RESEARCH LABORATORY NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL CENTER REPORT NUMBER 673
 MOTION PARALLAX AND ABSOLUTE DISTANCE by Steven H. Ferris NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL RESEARCH LABORATORY NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL CENTER REPORT NUMBER 673 Bureau of Medicine and Surgery, Navy Department Research
MOTION PARALLAX AND ABSOLUTE DISTANCE by Steven H. Ferris NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL RESEARCH LABORATORY NAVAL SUBMARINE MEDICAL CENTER REPORT NUMBER 673 Bureau of Medicine and Surgery, Navy Department Research
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
SUBJECTIVE CONTOURS AND APPARENT DEPTH 1
 Psychological Review 1972, Vol. 79, No. 4, 3S9-367 SUBJECTIVE CONTOURS AND APPARENT DEPTH 1 STANLEY COREN * New School for Social Research The phenomenal appearance of contours in the absence of abrupt
Psychological Review 1972, Vol. 79, No. 4, 3S9-367 SUBJECTIVE CONTOURS AND APPARENT DEPTH 1 STANLEY COREN * New School for Social Research The phenomenal appearance of contours in the absence of abrupt
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays
 The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
The Persistence of Vision in Spatio-Temporal Illusory Contours formed by Dynamically-Changing LED Arrays Damian Gordon * and David Vernon Department of Computer Science Maynooth College Ireland ABSTRACT
Auditory Localization
 Auditory Localization CMPT 468: Sound Localization Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November 15, 2013 Auditory locatlization is the human perception
Auditory Localization CMPT 468: Sound Localization Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November 15, 2013 Auditory locatlization is the human perception
GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY
 Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week
 Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 9 5.11.2009 Administrivia Assignment 3 Final projects Static and Moving Patterns IAT814 5.11.2009 Transparency and layering Transparency affords
Static and Moving Patterns (part 2) Lyn Bartram IAT 814 week 9 5.11.2009 Administrivia Assignment 3 Final projects Static and Moving Patterns IAT814 5.11.2009 Transparency and layering Transparency affords
Presentation Design Principles. Grouping Contrast Proportion
 Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object Text Object Object Object Object
Presentation Design Principles Grouping Contrast Proportion Usability Presentation Design Framework Navigation Properties color, size, intensity, metaphor, shape, Object Text Object Object Object Object
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Size perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 22 Why the cars look like toys. Our visual system is useful for identifying the properties of objects in the world Surface (color, texture) Location (depth)
Size perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 22 Why the cars look like toys. Our visual system is useful for identifying the properties of objects in the world Surface (color, texture) Location (depth)
Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by
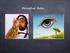 Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Lecture 14. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017
 Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
Motion Perception Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 (chap 6 leftovers) Defects in Stereopsis Strabismus eyes not aligned, so diff images fall on
