Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality
|
|
|
- Jasmine Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Sensation and Perception Are skills we need For hearing, feeling And helping us to see I will begin with A few definitions This way confusion Has some prevention Sensation notices Various stimuli Of what is out there In reality 2
3 Perception in contrast Happens in the brain It in no way is Something mundane Exactly how it works Is a mystery Because it s different For you and for me An external stimulus Has energy But Some have molecules Like a cup of tea This Outside energy is translated Into (neural) signals That are somewhat graded Gustav Fechner created psychophysics These were like Sense system yardsticks This process is called TRANSDUCTION 2
4 Absolute thresholds Are the minimums Of what gets in To sensory Systems 3
5 Like a candle flame On a starless night From 30 miles away is within our sight 4
6 Or the tick of a clock From 30 feet 5
7 Or the weight of a fly s wing Falling on your cheek 6
8 A single drop of perfume Diffused in six rooms 7
9 Or two gallons of water Sugared with a teaspoon 8
10 These are thresholds Of our sense systems Is it there or is it not That is the question 9
11 Thresholds are also About differences Kinda like the taste Of different kisses The minimal difference Is the JND It s not the same For you and me But Weber s Law Gave us some guidance For weight and sound and Taste and brightness 10
12 Just Noticeable Difference 10
13 Sometimes our world Seems very cluttered (Signal) Detection theory Is the new buzzword Everyone makes Different decisions What we see Comes from motivations 11
14 A saving grace is Sensory adaptation Over time Senses have less action 12
15 Like getting used To a blinding light 13
16 Or adjusting to The dark at night 14
17 When it comes to vision A good place to start Is the creation Of the Snellen chart This chart is famous As you can see It helps your doctor Find acuity 15
18 But first we must Take a look at light Its unique properties Determine our sight Light waves have Three properties These determine Exactly what we see 16
19 The length of a light wave Determines its hue 17
20 The brightness of colors Is due to amplitude 18
21 The richness of color Is known as purity It is due to Light s complexity 19
22 But Not all light is seen by the eye The wavelength spectrum shows us why Some of these waves Are too short to see Unless you happen To see like a bee Other waves are way too long But not too long To carry a song Refers to radio waves 20
23 The human eye Is an amazing thing Its various parts Work like a team 21
24 To focus light On the retina Color and detail In the fovea To Focus too close Is myopia Focus too far and hyperopia 22
25 Either way These Problems are correctable Corrective lenses Make things visible 23
26 But the real miracle is Light transduction This is how the Retina functions Rods and cones are Photoreceptors 24
27 Rods see black and white 25
28 But Cones see colors 26
29 Rods are for low light And see shades of gray Cones in the fovea: Details of the day Rods and cones also Differ in number More rods than cones But it s not a blunder 27
30 Image processing Begins in the retina This is done By retinal ganglia 28
31 These cells have Different receptive fields Center on or center off Determine neural yields 29
32 Color vision requires Cones in three types They respond to Different colored lights 30
33 Mixing these colors Gives variety To all the colors That we can see 31
34 But cones get tired A sort of fatigue This makes (after)images You can barely see 32
35 But The real stuff of vision Is in the human brain Different parts collaborate Let me explain 33
36 Some cells are programmed To see certain things Like lines at an angle 34
37 Or birds on the wing 35
38 The brain is the computer To help us to see Things complex Or simple like a G 36
39 The gestalt psychologists Did a lot of research To help understand How perception works They developed Perceptual organization These principles are Part of our doctrine 37
40 Sometimes figures are ambiguous Figure or ground May confuse us 38
41 Perceiving depth Requires many cues Some are for one eye And others are for two 39
42 Relative size uses Familiarity 40
43 3D images need (Binocular) disparity 41
44 We can tell what is near or what is far Sometimes while Riding in a moving car 42
45 Like the Linear perspective of rail road tracks 43
46 or the texture gradient of dry river cracks 44
47 Sometimes objects Block One another 45
48 Or the relative heights Of a bunch of flowers 46
49 This Understanding of How perception works Can help to make Some interesting quirks The Ames Room plays With relative heights 47
50 Or we can see motion In blinking lights 48
51 Our visual system is simply Amazing Its complexity leaves me Quaking 49
52 But also remarkable: The Ability to hear! Audition is more Than what meets the ear 50
53 To understand hearing You have to know sound Here are some basics To give us common ground Sound waves have three Properties Pitch depends on Frequencies 51
54 Loudness is due to Amplitude Like a musician With an attitude 52
55 And sounds may be pure Or very complex Like what we hear In a multiplex 53
56 The ear itself is Very Marvelous From outer to inner It s incredulous 54
57 From the ear drum to the cochlea too much sound and you ve got trauma Sound waves are read By the basilar membrane 55
58 Which sends signals Up into the brain Actually, hair cells are stimulated by vibrations in the basilar membrane. These are actually dendritic terminals, which send the messages to their cell bodies which relay them to other cells in the brain. 56
59 Having two ears Detects the source of sound Loudness and timing Help us look around 57
60 The bodily senses are More than skin deep The skin itself is Something to keep Under the skin are many Receptors They detect pain And sometimes pleasures 58
61 Maintaining balance Is part of the picture In the ear is a System vestibular 59
62 Chemical senses add Flavor to our lives 60
63 Like Smelling pheromones And tasting good wines 61
64 Wouldn t it be nice If we were synesthetes That way we taste The things that we see 62
65 Speaking of seeing I see that I am done In rhyming this chapter I think that I have won! I m done, I m out! I m Professor Hal! 63
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Sensory and Perception. Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague
 Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Sensory and Perception Team 4: Amanda Tapp, Celeste Jackson, Gabe Oswalt, Galen Hendricks, Harry Polstein, Natalie Honan and Sylvie Novins-Montague Our Senses sensation: simple stimulation of a sense organ
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 5.1 How Do Sensation and Perception Affect
CHAPTER 4. Sensation & Perception. Lecture Overview. Introduction to Sensation & Perception PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Understanding Sensation
 CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
CHAPTER 4 Sensation & Perception How many senses do we have? Name them. Lecture Overview Understanding Sensation How We See & Hear Our Other Senses Understanding Perception Introduction to Sensation &
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Sensation and Perception PSY 100: Foundations of Contemporary Psychology Basic Terms Sensation: the activation of receptors in the various sense organs Perception: the method by which the brain takes all
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception
 Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Chapter 4: Sensation & Perception 30? ThEcOwgAvecOla TheCowGaveCola rat eht saw tac eht The cat saw the rat The cat was the rat The cat was the tar Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
Sensation v. Perception Sensation and Perception Chapter 5 Vision: p. 135-156 Sensation vs. Perception Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience & interpretation Example vision research
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Lecture Outline. Basic Definitions
 Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
Lecture Outline Sensation & Perception The Basics of Sensory Processing Eight Senses Bottom-Up and Top-Down Processing 1 Basic Definitions Sensation: stimulation of sense organs by sensory input Transduction:
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
Chapter 4/8 Sensation and Perception Sensation: stimulation of sense organs Ex. Absorbing sound waves from band Perception: the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Ex. Enjoying
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 5 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow Sensation and Perception: What s the difference Sensory systems with specialized receptors respond to (transduce) various forms
Unit 4. Sensation and. Perception. 6-8% (7-9% in past) College Board - Acorn Book Course Description. Unit IV. Sensaton and.
 Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Unit 4. Sensation and College Board - Acorn Book Course Description 6-8% (7-9% in past) Overview A. Thresholds B. Sensory Mechanisms C. Attention D. Perceptual Processes A. Thresholds Threshold Absolute
Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception 8 th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception What are the function of THERMORECPTORS? Thermoreceptors are responsible for the sensation of non-painful warmth or cold sensations. They have ion channels that change
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahg6qcgoay4 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION THE DIFFERENCE Stimuli: an energy source that causes a receptor to become alert to information (light, sound, gaseous molecules, etc)
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Visual Perception. Jeff Avery
 Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Sensation is the stimulation of the sense organs. Perception is the selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input. Light waves vary in amplitude, that is, their
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Sensation and perception
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6
 Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Psychology Study Guide Chapter 6 Sensation: process by which our sensory responses and nervous system receive and repeat stimulus from our environment. Perception: process organizing and interpreting sensory
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Sensation and perception. Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects
 Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Sensation and perception Definitions Sensation The detection of physical energy emitted or reflected by physical objects Occurs when energy in the external environment or the body stimulates receptors
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of responses by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Feeding human senses through Immersion
 Virtual Reality Feeding human senses through Immersion 1. How many human senses? 2. Overview of key human senses 3. Sensory stimulation through Immersion 4. Conclusion Th3.1 1. How many human senses? [TRV
Virtual Reality Feeding human senses through Immersion 1. How many human senses? 2. Overview of key human senses 3. Sensory stimulation through Immersion 4. Conclusion Th3.1 1. How many human senses? [TRV
Unit IV Sensation Perception
 Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
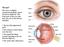 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Advanced Version Vision Lab - Overview In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight at is the one extent
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
the human chapter 1 the human Overview Perception Limitations of poor interface design Why do we need to understand users?
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
CS 544 Human Abilities
 CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
CS 544 Human Abilities Color Perception and Guidelines for Design Preattentive Processing Acknowledgement: Some of the material in these lectures is based on material prepared for similar courses by Saul
Input-output channels
 Input-output channels Human Computer Interaction (HCI) Human input Using senses Sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell Sight, hearing & touch have important role in HCI Input-Output Channels Human output
Input-output channels Human Computer Interaction (HCI) Human input Using senses Sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell Sight, hearing & touch have important role in HCI Input-Output Channels Human output
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
SENSES. Educator s Guide OUR AN IMMERSIVE EXPERIENCE. amnh.org/our-senses-educators INSIDE ONLINE. Are these rows straight or tilted?
 Educator s Guide Are these rows straight or tilted? OUR SENSES AN IMMERSIVE EXPERIENCE amnh.org/our-senses-educators human vision simulated butterfly vision simulated bee vision INSIDE Map of the Exhibition
Educator s Guide Are these rows straight or tilted? OUR SENSES AN IMMERSIVE EXPERIENCE amnh.org/our-senses-educators human vision simulated butterfly vision simulated bee vision INSIDE Map of the Exhibition
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version
 Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Vision: How does your eye work? Student Version In this lab, we will explore some of the capabilities and limitations of the eye. We will look Sight is one at of the extent five senses of peripheral that
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
1. What are the components of your nervous system? 2. How do telescopes and human eyes work?
 Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Chapter 18 Vision and Hearing Although small, your eyes and ears are amazingly important and complex organs. Do you know how your eyes and ears work? Scientists have learned enough about these organs to
Overview of Human Cognition and its Impact on User Interface Design (Part 2)
 Overview of Human Cognition and its Impact on User Interface Design (Part 2) Brief Recap Gulf of Evaluation What is the state of the system? Gulf of Execution What specific inputs needed to achieve goals?
Overview of Human Cognition and its Impact on User Interface Design (Part 2) Brief Recap Gulf of Evaluation What is the state of the system? Gulf of Execution What specific inputs needed to achieve goals?
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Lecture 26. PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Finalities. Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Introduction to Visual Perception
 The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
The Art and Science of Depiction Introduction to Visual Perception Fredo Durand and Julie Dorsey MIT- Lab for Computer Science Vision is not straightforward The complexity of the problem was completely
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a frequency analyzer. Chris Darwin
 Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a analyzer Chris Darwin Frequency: -Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude against -..5 Time (s) Waveform Amplitude against time amp Hz Frequency: 5-Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude
Hearing and Deafness 2. Ear as a analyzer Chris Darwin Frequency: -Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude against -..5 Time (s) Waveform Amplitude against time amp Hz Frequency: 5-Hz Sine Wave. Spectrum Amplitude
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night.
 Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Light intensities range across 9 orders of magnitude. A piece of white paper can be 1,000,000,000 times brighter in outdoor sunlight than in a moonless night. But in a given lighting condition, light ranges
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Biology 9 Senses Lab
 Biology 9 Senses Lab Objectives: To understand the anatomy and physiology of several of our senses both through observation and by means of some simple experiments and examinations. PART 1: The Eye 1.
Biology 9 Senses Lab Objectives: To understand the anatomy and physiology of several of our senses both through observation and by means of some simple experiments and examinations. PART 1: The Eye 1.
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych
 Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych Perception: is the study of how we integrate sensory information into percepts of objects and how we then use these percepts to get around in the world (a percept is
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Light and Colour. Sir Isaac Newton The Founder of Colour Science
 Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Slide 1 the Rays to speak properly are not coloured. In them there is nothing else than a certain Power and Disposition to stir up a Sensation of this or that Colour Sir Isaac Newton (1730) Slide 2 Light
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Chapter Introduction. Chapter Wrap-Up. and the Eye
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Sound Light Chapter Wrap-Up Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye How do sound and light waves travel and interact with matter? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Sound Light Chapter Wrap-Up Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye How do sound and light waves travel and interact with matter? What do you think? Before you begin,
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
1 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) 2 of 10 9/19/2013 11:53 AM Focusing,
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2005 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics
 CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception and Ergonomics Human Computer Interaction SS 2006 Ute Schmid (lecture) Emanuel Kitzelmann (practice) Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University CogSysIII Lecture 2: Perception
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
