Activities to do at Home with 4 th and 5 th Grade Students
|
|
|
- Godfrey Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Activities to do at Home with 4 th and 5 th Grade Students (Standards Based Review Activities) by Jennifer Davis 1
2 Table of Contents Number Sense 7 Place Value Millions 8 Know the Basics 8 Make the Biggest Number - Place Value Millions 9 Number Line Fractions and Decimals 10 Know the Basics 10 Sidewalk Chalk Number Line Locating Fractions and Decimals 11 Integers Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line 12 Know the Basics 12 The Money Game Understanding Negative Numbers 13 Basic Fractions 14 Know the Basics 14 Fractions in our Environment Identifying Fractions 15 Standard Algorithms Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division 16 Know the Basics 16 Making Numbers Using standard algorithms. 17 Word Problems Multiplication and Division 18 Know the Basics 18 Word Problems Multiplication and Division 19 Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions 20 Know the Basics 20 The Match Game Matching Equivalent Fractions, Decimals, and Percents 21 Finding the Percent of a whole Number 22 Know the Basics 22 How much are you Saving? I Finding the Percent of a Whole Number 23 Adding and Subtracting Decimals 24 Know the Basics 24 Beat the Budget I Adding with Decimals 25 Beat the Budget II Subtracting with Decimals 26 Multiply with Decimals 27 Know the Basics 27 How much are you Saving? II Multiplying Decimals 28 Divide with Decimals 29 Know the Basics 29 How much do I Owe? Dividing with Decimals 30 Adding Integers 31 Know the Basics 31 Integer Circle Puzzles Adding and Subtracting Integers 32 Subtracting Integers 33 Know the Basics 33 See Integer Circle Puzzles Adding and Subtracting Integers 33 Adding and Subtracting Fractions with answers in the Simplest Form 34 Know the Basics 34 Blackjack 1 Adding and Reducing Fractions 35 Algebra and Functions 36 2
3 Expressions with Parentheses 37 Know the Basics 37 Order of Operations 38 Know the Basics 38 Mighty Memorization Memorizing the Order of Operations 39 Graphing Ordered Pairs 40 Know the Basics 40 Ordered Pair Battleship Graphing Ordered Pairs 41 Measurement and Geometry 42 Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Triangle 43 Know the Basics 43 Color the Polygons Measuring the Angles in a Triangle 43 Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Quadrilateral 44 Know the Basics 44 Color the Polygons Measuring the Angles in a Quadrilateral 45 Reading 47 Synonyms 47 Know the Basics 47 The List Game - Synonyms 48 Antonyms 49 Know the Basics 49 Say the Opposite - Antonyms 49 Multiple Meaning Words and Homographs 50 Know the Basics 50 Draw the Meaning - Multiple Meaning Words and Homographs 51 Similes, Metaphors, Hyperbole 52 Know the Basics 52 Figurative Language Search Similes, Metaphors, and Hyperbole 52 Idioms 53 Know the Basics 53 Draw Both Figurative and Literal Meanings of Idioms 53 Compare and Contrast 54 Know the Basics 54 The Great Cookie Comparison Compare and Contrast 55 Main Idea 56 Know the Basics 56 Suggestions for Practice Finding the Main Idea 56 Generalizations 57 Know the Basics 57 What s True of the Group Making Generalizations 57 Multiple Step Instructions 58 Know the Basics 58 Suggestions for Practice - Following Multiple Step Directions 58 Writing 59 Encouraging Writing 60 Written and Oral Language Conventions 61 3
4 Verbs Action and Linking Verbs 61 Know the Basics 61 What s Happening Identifying Linking and Action Verbs 62 Regular and Irregular Verbs 63 Know the Basics 63 Past or Present Tense? - Identifying Regular and Irregular Verbs 63 Adverbs 64 Know the Basics 64 Adverb Charades 64 Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases 65 Know the Basics 65 Where is it? Using Prepositional Phrases 66 Appositives 67 Know the Basics 67 Combining Sentences Using Appositives 67 Independent and Dependent Clauses 68 Know the Basics 68 Finish the Thought - Independent and Dependent Clauses 69 Appendix 70 Math Resources 71 Make the Biggest Number Game Board 72 Beat the Budget I Game Board 73 Beat the Budget II Game Board 74 The Money Game Game Board 75 The Money Game Game Cards 76 Match Game - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions Game Set-up 77 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions 78 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions (continued) 79 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions (continued) 80 Integer Circle Puzzles - Adding and Subtracting Integers 81 Word Puzzle Evaluating Expressions 82 Hundreds Counting Chart 83 Multiplication Table through Battleship Game Boards Graphing Ordered Pairs 85 Extra Battleship Game Boards Graphing Ordered Pairs 86 Reading Resources 87 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards 88 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards Continued 89 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards Continued 90 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Board 91 Adverb Charades Word Lists 92 4
5 What s the Big Idea Finding the Main Idea 93 What s the Big Idea Finding the Main Idea Continued 94 References 96 5
6 Math Activities 6
7 Number Sense Place Value Negative Numbers Using a Number Line Standard Algorithms Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division Word Problems Decimals and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions Finding the Percent of a Whole Number Decimals Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division Adding and Subtracting Negative Integers Adding and Subtracting Fractions Simplest Form Adding and Subtracting Whole Numbers - Simplest Form 7
8 Place Value Millions We use a decimal based number system. Know the Basics The value of each digit is determined by it s position in the number. Each place has a value of ten times the place to the right of it. When we write numbers in standard from, we separate the digits into groups of three using a comma. These groups are called periods. This helps us to read the number correctly. o Example: Standard Form - 4,328,921 Word Form - Four million three hundred twenty-eight thousand nine hundred twenty-one Periods Table Millions Thousands Units Decimals Hundreds Tens Ones Hundreds Tens Ones Hundreds Tens Ones. Tenths Hundredths Thousandths Place Value Table Millions Hundred Thousands Ten Thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones 8
9 Make the Biggest Number - Place Value Millions Materials: Dice (1 die for each player) Objective: Game board (See appendix) Pencils Make the largest number possible using the number rolled during each turn. Directions: 1. The first player rolls the die once. 2. Record the number in one of the place value columns. 2. Pass the die to the next player. 3. The next player rolls and records his or her number, then passes the die. 4. After each column has been filled, each player writes his or her number in standard form and then reads his or her number out loud. Compare numbers to see who has the greatest (largest) number. Example: Roll the die to fill in your grid. Millions Hundred Thousands Ten Thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Write your number in standard form. 6,735,221 Read your number aloud to the other players. Six million seven hundred thirty-five thousand, two hundred and one Suggestions: You can also play to see who can make the smallest number. Have your student practice putting the numbers in order from greatest to least (biggest to smallest) or least to greatest (smallest to biggest). 9
10 Number Line Fractions and Decimals Know the Basics In addition to positive and negative whole numbers, you can also identify positive and negative fractions and decimals on the number line /2 0 1/ / Positive decimals that do not include a whole number fall between 0 and 1 on the number line. Proper fractions fall between 0 and 1 on the number line. 10
11 Sidewalk Chalk Number Line Locating Fractions and Decimals Materials: Sidewalk Chalk Objective: Student will identify fractions and decimals on the number line. Directions: 1. Using sidewalk chalk draw a number line. (See the example below.) 2. Only include the whole numbers -2, -1, 0, 1, and Work together to fill in the following fractions and their equivalent decimal numbers on the number line. a. ½ and.5 b. ¼ and.25 c. -3/4 and -.75 d. ¾ and.75 e. -1/2 and.5 f. 1 ½ and 1.5 Example: Draw you number line to look like this one. Not all of the lines will be filled in using the numbers above. Note: For an extra challenge you can fill identify all of the lines
12 Integers Positive and Negative Numbers on the Number Line Know the Basics Integers are whole numbers on the number line that are either greater than 0 (positive numbers) or less than 0 (negative numbers). The 0 is often referred to as the origin. For each positive integer, there is a negative integer that is the same distance from 0. - is the negative sign and + is the positive sign If a number does not have a sign it is usually a positive number. On a number line, numbers to the right of the 0 are positive and the numbers to the left are negative. 12
13 The Money Game Understanding Negative Numbers Materials: The Money Game - Game Board (see appendix) The Money Game Game Cards (see appendix) Game Pieces (pennies, buttons, etc.) Tape or Glue Scissors Objective: Explore negative and positive numbers on a number line. Directions: 1. Assemble the game board and cut out the game cards. (Follow the directions in the appendix.) 2. Player one draws a game card and reads it aloud. If the game card indicates that the player has earned, collected, or found money, the player moves his or her piece to the right (to the positive) according to the amount of money indicated on the card. If the card indicates that the player has lost, spent, or given money away, the player moves his or her piece to the left (to the negative) as indicated buy the amount of money on the card. 3. Each player takes a turn drawing a card and moving his or her piece. 4. Play continues until one player reaches the $25.00 goal. 5. If you run out of game cards reshuffle the pile to use again. Suggestions: Use sidewalk chalk to draw the game board on the ground outside. Make the space large enough for players to stand in. Use play money and IOU notes to help players keep track of their earning and spending. 13
14 Basic Fractions Know the Basics Fraction - A fraction is made up of two parts. o The top number is the numerator. The numerator tells us how many parts of the whole we are working with. o The bottom number is the denominator. The denominator tells us how may pieces the whole is divided into. Proper Fraction - In a proper fraction the numerator is less than the denominator. o Example 1/2 Improper Fraction An improper fraction has a numerator that is larger than the denominator. o Example 4/3 Mixed Number A mixed number is made up of a whole number and a fraction. o Example 5 ½ Equivalent Fraction Equivalent fractions are fractions that represent the same number. o Example 1/2, 2/4, 3/6, 5/10 Reciprocal The inverse or reciprocal of a fraction is simply that fraction turned over. o Example - If the original fraction is 3/5 the reciprocal would be 5/3. Fractions are division problems that have not yet been divided. Every fraction can be turned into a decimal by dividing. In addition to whole numbers fractions can also be located on a number line. 14
15 Fractions in our Environment Identifying Fractions Materials: No Materials Needed Objective: Students will locate and identify fractions in environment. Directions: 1. Look around your environment. 2. Find 5 examples of proper fractions and 5 examples of mixed numbers. Suggestions: Try looking for fractions at the gas station, in cook books, in the financial section of the newspaper, and on television. 15
16 Standard Algorithms Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division Using a Multiplication Table Know the Basics The numbers along the left side of the table and the numbers along the tope of the table are called factors. The numbers inside the table are called the products. (5 x 6 = 30, factor X factor = product) Use the multiplication chart to find the product of two numbers by locating the first number along the left side of the table and the second number along the top edge of the table. Find product in the box inside the table where the row and columns meet. Example: 8 x 5 = 40 Put your finger on the number 8 row along the left side of the chart. Put a different finger on the number 5 along the top column of the chart. Slide your finger across the number 8 row and down the number 5 column until they come together. The box where the row and column come together is the product of the two numbers. 16
17 Making Numbers Using standard algorithms. Materials: pencil and eraser lined or graph paper calculator timer must keep track of minutes Objective: Directions: Use standard algorithms for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division in order to create a variety of equations that equal the same number. 1. Fold your paper in half. You should have two long sections on the front and two long sections on the back. Label each section of the paper with a different operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division). Note: If you are playing with other people, each person will need his or her own sheet of paper. 2. Choose a number between 1 and 100. Write the number at the top of your paper. 3. In the addition section on your page, think of as many different combinations of numbers that equal the chosen number as possible in 3 minutes. Record your combinations. 4. Do this for each operation listed on your paper. 5. If you are playing with other people, compare your lists to share ideas. Example: 25 Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division 20+5= = = = = =25 1 x 25 = 25 5 x 5 = / 4 = / 2 = / 1 =25 Suggestions: You may want to start out with longer amounts of time for each section when trying this activity for the first time. Try combining operations and using your knowledge of the order of operations to create more complicated combinations. Try using larger three or four-digit numbers. 17
18 Word Problems Multiplication and Division Know the Basics Key Words for Decoding Word Problems Addition increased by combined sum in all more than total of added together Subtraction minus less than reduced by difference of difference between fewer than decreased by how many are left Multiplication of times multiplied by product of factor of Division per ratio quotient of percent (divided by 100) out of Equals is are was were will be gives yields Steps for Solving Word Problems 1. Understand Use the key words above to help understand what the question is asking. 2. Plan Make a plan for how to solve the problem. 3. Solve Solve the problem using the plan you decided upon. Word Problem Strategies Write a number sentence to represent the problem. Draw a picture to represent the problem. 18
19 Word Problems Multiplication and Division Materials: lined paper pencil with eraser Objective: Read and solve words problems containing multiplication or division. Directions: 1. Write word problems for your student that involves multiplying and dividing as part of the solution. 2. Discuss how to determine if the problem requires multiplication or division. 3. Practice drawing the picture to with word problem. Suggestions: Take turns writing and solving word problems. Discuss how the problems are written Use the student s textbook for sample problems. 19
20 Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions Know the Basics Fractions, decimals, and percents are all ways to refer to the parts of a whole. Any fraction can be turned into an equivalent decimal by simply dividing the fraction. o Example: ½ means the same as 1 divided by 2 1 divided by 2 equals.5 so.5 = ½ Percents can be found by multiplying a decimal by 100 and adding the percent sign (%). o Example: 100 x.5 = 50% Equivalent Reference Chart Word Form Decimal Percent Fraction one half.5 50% ½ one third.333 repeating decimal 33.33% 1/3 two thirds.666 repeating decimal 66.66% 2/3 one fourth.25 25% ¼ three fourths.75 75% ¾ one fifth.20 20% 1/5 two fifths.40 40% 2/5 three fifths.60 60% 3/5 four fifths.80 80% 4/5 one sixth.1666 repeating decimal 16.66% 1/6 one eighth % 1/8 one ninth.111 repeating decimal 11.11% 1/9 one tenth.1 10% 1/10 one one- hundredth.01 1% 1/100 one one-thousandth.001.1% 1/
21 The Match Game Matching Equivalent Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Materials: cut game cards (see appendix) reference card to check your pairs Objective: Recognize and match equivalent fractions, decimals, and percents. Directions: 1. Cut out game cards from the pages in the appendix. 2. Lay cards out on a flat surface with the number sides down. 3. Pick two cards from the group. Compare the two items. The cards are a pair if you make any of the following combinations. a. word form equivalent fraction, percent, or decimal b. fraction equivalent word form, percent, or decimal c. percent equivalent fraction, word form, or decimal d. decimal equivalent percent, fraction, or word form. 4. Check the reference card to make sure you have made a correct pair. If the cards do not match, place them back in the spaces from which they came, face down. 5. If you are playing with other players, it would then be the next players turn. 6. If a player makes a match, his or her turn continues until he or she does not make a match. Suggestions: Glue game cards to index cards and store in a plastic sandwich bag so that they can be used again. Practice reading the cards out loud to help remember the equivalents. These game cards can also be used to play a Go Fish style game. Simply distribute the cards to each player and practice asking for the equivalent by reading the cards. 21
22 Finding the Percent of a whole Number Know the Basics Percent means out of 100 or divided by 100. The symbol for percent is %. Percents can always be written as a decimal by moving the decimal point two places to the left. To convert a decimal to a percent, move the decimal point two places to the right. To convert a percent to a decimal, move the decimal point two places to the left. Formula for finding the percent of a whole number: percent (decimal) x whole number = the percent of the whole number. o Example: Find 15% of $ x $150 = $
23 How much are you Saving? I Finding the Percent of a Whole Number Materials: Mail Order Catalog or Retail Store Advertisement Paper Pencil and eraser Calculator Objective: Use the formula for finding the percent of a whole number to calculate the possible amount of savings. Directions: 1. Pick and item from the catalog or advertisement that you might consider buying. 2. Round the number to the nearest whole number. (Example: $22.89 would round up to $23.00). 3. Use the formula for calculating percentages to figure how much money you would save if the item was marked down 10%, 15%, 30%, 50%, and 65%. 4. Use the calculator to check you work. Example: Suggestion: Item Discount Savings College Logo Sweatshirt Original price $ % $54.00 x.10 = $ % $54.00 x.15 = $ % $54.00 x.30 = $ % $54.00 x.50 = $ % $54.00 x.65 = $35.10 To practice multiplication with decimals, try calculating the discount without rounding the original price to the nearest whole number. Use graph paper to help keep numbers lined up in the correct columns. 23
24 Adding and Subtracting Decimals Know the Basics The most important thing to remember when adding and subtracting decimals is to always keep the decimal points lined up. After lining up the decimals add and subtract as you would any whole numbers. Use 0s as placeholders if there are extra spaces at the end of the numbers. 24
25 Beat the Budget I Adding with Decimals Materials: Grocery store add Game board (See appendix) Pencil and eraser Objective: Use addition and to work with decimals. Directions: 1. Set a spending goal. A good starting goal is $ Look through the grocery store add and pick items that you would like to buy. 3. On your game board, start with $ Add each item to your game board. Calculate your new spending balance each time you add an item. 5. The player that gets closest to the spending goals without going over wins. Example: Item Name Balance + Item Price = New Balance Bananas $ $0.59 = $0.59 Cheerios $ $3.99 = $ Liter 7-up $ $1.50 = $6.08 Suggestions: Use scratch paper to figure problems before entering the information into the grid. Check the calculations with a calculator. Make sure that the decimals are always lined up when adding decimals. 25
26 Beat the Budget II Subtracting with Decimals Materials: Grocery store flyer Game board (See appendix) Pencil and eraser Objective: Use subtraction to work with decimals. Directions: 1. Set a budget. A good starting budget is $ Look through the grocery store add and pick items that you would like to buy. 3. On your game board, start with $ One item at a time, write the name of the item you would like to buy on your game board and calculate how much you have spent. 5. If you are playing with other people, take turns purchasing items. The player that gets closest to the entire $50.00 without going over the budget wins. Example: Suggestions: Item Name Balance - Item Price = New Balance Bananas $ $0.59 = $49.41 Cheerios $ $3.99 = $ Liter 7-up $ $1.50 = $43.92 Use scratch paper to figure problems before entering the information into the grid. Check the calculations with a calculator. Make sure that the decimals are always lined up when subtracting decimals. 26
27 Multiply with Decimals Know the Basics Unlike adding and subtracting decimals, DO NOT line up the decimals when multiplying decimals. Line up numbers at the right. Multiply the numbers just a you would multiply whole numbers. Count the decimal places in the numbers that were multiplied. Place the decimal in your answer by starting at the right and moving the decimals the same number of places. 27
28 How much are you Saving? II Multiplying Decimals Materials: Mail Order Catalog or Retail Store Advertisement Paper Pencil and eraser Calculator Objective: Multiply decimals in order to calculate the amount of savings on a discounted item. Directions: 1. Pick and item from the catalog or advertisement that you might consider buying. 2. Use the formula for calculating percentages to figure how much money you would save if the item was marked down 10%, 15%, 30%, 50%, and 65%. 3. Use the calculator to check you work. Example: Suggestion: Item Discount Savings College Logo Sweatshirt Original price $54.00 Use graph paper to help keep numbers lined up in the correct columns. 10% $54.00 x.10 = $ % $54.00 x.15 = $ % $54.00 x.30 = $ % $54.00 x.50 = $ % $54.00 x.65 = $
29 Divide with Decimals Know the Basics When dividing decimals the first step is to move the decimal to the right of the ones column in order to make a whole number. Move the decimal in the dividend to the right the same number of places. Divide as usual until the answer either terminates or repeats. Place the decimal point directly above the decimal point in the dividend. 29
30 How much do I Owe? Dividing with Decimals Materials: Grocery or Restaurant Receipts Paper Pencil and eraser Calculator to check your work Objective: Students will divide decimal numbers. Directions: 1. Divide the total from your receipt by the number of people in your family or by the number of people that attended the meal. 2. Practice dividing the totals from any receipts you can find. 3. Use the calculator to check you work. 30
31 Adding Integers Know the Basics When adding a positive integer, you move to the right on the number line. Example: o = 11 Both 4 and 7 are positive integers. On the number line, you would start at positive 4 and move to the right 7 units. o = 3 Start at -4 and move 7 units to the right. When adding a negative integer, you move to the left of the number line. Example: o -3 + (-2) = -5-2 is a negative integer. On the number line, start at -3 and move to the left 2 units. o 3 + (-2) = 1 Start at 3 and move 2 units to the left. 31
32 Integer Circle Puzzles Adding and Subtracting Integers Materials: Integer Circle Puzzles worksheet from the Appendix Pencil and eraser Calculator to check your work Objective: Students will add and subtract integers to complete the integer puzzles. Directions: 1. Add the number in the center of the addition wheel to the number in the second ring of the addition wheel. 2. Write your answer in the outside ring of the wheel. 3. Use the calculator to check you work. 32
33 Subtracting Integers Know the Basics When adding a positive integer, you move to the right on the number line. Example: o 4-7 = -3 4 is a positive integer and -7 is a negative integer. Start on 4 and move to the left 7 units. o -4 (-7) = 3 is the same as = 3-4 is a negative integer. When a subtraction sign precedes a negative integer the result is in the opposite function. See Integer Circle Puzzles Adding and Subtracting Integers 33
34 Adding and Subtracting Fractions with answers in the Simplest Form Know the Basics In order to add or subtract fractions they must have the same, or a common denominator. Example: Unlike denominators: ¼ + ½ Common denominators: ¼ + ¾ Once you have determined a common denominator, you need to make sure that you multiply the numerator by the same number you multiplied to the denominator. Add or subtract only the numerators. The denominators Will remain the same. Reduce the answer to the simplest form. Least Common Multiple List the common multiples of both denominators until a common multiple is identified. The least common multiple of 2 and 4 is 4. Remember whatever you do to the denominator you must also do to the numerator. Multiples of 2 and
35 Blackjack 1 Adding and Reducing Fractions Materials: Fraction Card Reference List from the Appendix Pencil and eraser Scratch Paper 3 x5 index cards Objective: Students will add and reduce fractions to their simplest form in order to get closest to 1. Directions: 1. Make 2 sets of fraction cards for each player using 3 x 5 index cards and the list of fractions that appears in the Appendix. 2. Instead of trying to get to 21 the goal is to get to 1 without going over. 3. Each player is dealt 2 cards to start. Add the fractions and reduce to see how close you are to If a player requires an additional card they must say Hit me. If the player does not require an additional card they may simply say I stand. 5. Each time a player turns a card the fraction on the card is added to the previous card. Reduce the sum of the fraction cards to the simplest form and compare to The player that gets closest to 1 without going over wins that hand. 35
36 Algebra and Functions Expressions with Parentheses Order of Operations Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Graphing Ordered Pairs Linear Functions 36
37 Expressions with Parentheses Know the Basics In an algebraic expression, letters can be used to represent numbers. They are called variables. Evaluating an expression To evaluate an expression means giving the variables in the expression a specific value and the performing the prescribed operations. Steps for Evaluating an Expression First, place replace each variable with the number or value that has been assigned to it. o Place the inserted values in parentheses to help make them easy to identify. o the value that is assigned to a variable will remain the same until the problem is solved. Next, complete the operations following the order of operations. This skill is best practiced by working together on problems out of the textbook. 37
38 Order of Operations Know the Basics The order of operations are the rules that are followed when evaluating an expression or solving an equation. Operations should be solved in the following order: 1. P arentheses 2. E xponents or roots 3. M ultiplication (from left to right) 4. D ivision (from left to right) 5. A ddition (from left to right) 6. S ubtraction (from left to right) Hint: a helpful way to remember the order of operations is to learn the following pneumonic device: P lease E xcuse M y D ear A unt S ally 38
39 Mighty Memorization Memorizing the Order of Operations Materials: Pencil and eraser Lined Paper Objective: Students will create a pneumonic device to help aide in the memorization of the Order of Operations Directions: 1. Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally is a commonly used pneumonic device that helps people to remember the steps in the Order of Operations. 2. Use the first letter from each step P-E-M-D-A-S to create your own pneumonic device to help you remember the Order of Operations. P arentheses Operation Write Your Own Pneumonic Device Each word must start with the first letter of the Example: Please operation that it corresponds with. E xponents or roots Example: Excuse M ultiplication (from left to right) Example: My D ivision (from left to right) Example: Dear A ddition (from left to right) Example: Aunt S ubtraction (from left to right) Example: Sally 39
40 Graphing Ordered Pairs Know the Basics Coordinate Plane - The coordinate plane is formed by two intersecting number lines. The first number line is horizontal and is called the x-axis. The other is vertical, and is known as the y-axis. The x-axis is also known as the input. The y-axis is also known as the output. Two numbers known as an ordered pair can identify each point on the coordinate plane. o Example (6,5) or (x,y) The first number in the ordered pair is called the x-coordinate. It identifies the horizontal position of a point on the plane. The second number is the y-coordinate. The y-coordinate identifies the vertical position of the point on the plane. To graph these points, first locate the x-coordinate on the grid. Next, locate the y-coordinate on the grid. Mark the point at which the two gridlines intersect. 40
41 Ordered Pair Battleship Graphing Ordered Pairs Materials: Battleship Game Boards Pencil and eraser Objective: Students will identify the ordered pairs for given points in order to locate points on a coordinate plane. Directions: 1. Make 2 copies of the Battleship Game Board for each player. One copy will be for plotting you own ships and the other for recording your guesses on the enemy ships. 2. Plot all of your ships by drawing and outline of each ship on the grid according to its size. Ships my not overlap. Keep your ships hidden from the other players. 3. Take turns taking shots at your enemy s ships by calling out ordered pairs (Example: (-5,-7). Mark an X on your grid for points that hit your enemy s ships and use a dot to mark on your grid for points that miss. 4. When the enemy takes shots at your ships you say hit or miss and mark your hit ships with an X when they are hit. When your ship is sunk, you must say You sank my! (Fill in the blank with the name of the ship that was sunk.) 5. The first person to sink all of their enemy s ships is the winner. Ships: (Points indicate the number of points covered on the coordinate grid.) Aircraft Carrier Battleship Cruiser Patrol Boat Submarine (5 points) (4 points) (3 points) (2 points) (3 points) Example: Cruiser Coordinates (1,2) (2,2) (3,2) If all three of these coordinates are called the ship is sunk. 41
42 Measurement and Geometry Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Triangle Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Quadrilateral 42
43 Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Triangle Know the Basics Triangles have 3 angles. The sum of these angles is always 180 degrees. When given the measurements of two angles of a triangle, add the two angles and subtract from 180 degrees to find the measurement of the third angle. Color the Polygons Measuring the Angles in a Triangle Materials: Blank white paper or construction paper markers, colored pencils, or crayons Protractor pencil and eraser ruler Objective: Students will use a protractor to measure the angles of triangles. Directions: 1. Use a ruler to draw several lines that cross and intersect on your blank paper. Make lines that run from right to left as well as up and down. When you are done you should have a design made up of three and four sided polygons. 2. Pick one polygon at a time and measure and find the sum of the angles. Make sure to label the measurement of each angle. 3. If the sum of the angles for a polygon is equal to 180 degrees then color the polygon. If it does not then leave it blank. 4. When you are done you should have a beautiful piece of art work. All of the triangles should be colored. 43
44 Finding the Sum of the Angles in a Quadrilateral Know the Basics Quadrilaterals have 4 sides and four angles. The sum of these angles is always 360 degrees. When given the measurements of three of the angles of a quadrilateral, add the three angles and subtract from 360 degrees to find the measurement of the fourth angle. Polygon A polygon is a closed plane figure that has three or more line segments. A quadrilateral is a polygon that has 4 sides and 4 angles. The sum of the 4 angles is 360 degrees. When given 3 of the 4 angles, the measurement for the fourth angle can be found by adding the 3 measurements together and subtracting the sum from 360 degrees. If the quadrilateral is a regular polygon and you know one of the angles, the other 3 angles have the same measurement. 44
45 Color the Polygons Measuring the Angles in a Quadrilateral Materials: Blank white paper or construction paper markers, colored pencils, or crayons Protractor pencil and eraser ruler Objective: Students will use a protractor to measure the angles of quadrilateral. Directions: 1. Use a ruler to draw several lines that cross and intersect on your blank paper. Make lines that run from right to left as well as up and down. When you are done you should have a design made up of three and four sided polygons. 2. Pick one polygon at a time and measure and find the sum of the angles. Make sure to label the measurement of each angle. 3. If the sum of the angles for a polygon is equal to 360 degrees then color the polygon. If it does not then leave it blank. 4. When you are done you should have a beautiful piece of art work. All of the quadrilaterals should be colored. 45
46 Language Arts Activities 46
47 Reading Synonyms Know the Basics Definition Words that have similar or the meanings. Examples tired/sleepy young/youthful ran/jogged 47
48 The List Game - Synonyms Materials: Blank Paper Pencils Thesaurus Objective: List the as many synonyms as possible for the given words. Directions: 1. Fold a blank piece of paper into 3 columns. 2. Pick a word from the word bank. 3. In the first column, write the word you chose at the top of your paper. If you are playing with other people, everyone should use the same word from the word bank. 4. Making sure that no other player can see your list, list as many synonyms for the word as you can in 2 minutes. 5. Compare your list to the other players. Any words that are on more than one players list get crossed out. The player with the most remaining words wins. 6. If you are playing alone, save the list and try and beat your score the next time you play. ugly said slow Word Bank fast unhappy pretty ran bad good Example: happy Column 2 Column 3 glad cheerful content joyful joyous 48
49 Antonyms Know the Basics Definition Words that have opposite meanings. Examples young/old nice/mean beautiful/ugly Say the Opposite - Antonyms Materials: Thesaurus (to look up any challenges) Objective: List the as many synonyms as possible for the given words. Directions: 1. Player One says a word. 2. Player Two must quickly come up with an antonym. 3. Player One continues to come up with a new word until Player Two can no longer come up with an antonym. 4. Switch rolls 49
50 Multiple Meaning Words and Homographs Definition Multiple Meaning Words Know the Basics Multiple meaning words are words that have more than one meaning depending on how they are used is a sentence. Examples swing Swing can be used as a noun meaning a mechanical device used as a plaything to support someone swinging back and forth Swing can also be used as a verb. When used as a verb it means to move in a curve or arc, usually with the intent of hitting Definition Homographs Words that have the same spelling but have different pronunciations and different meanings. Homographs are similar to multiple meaning words Examples wind - The wind was blowing hard. In this sentence the word wind is a noun. It is pronounced with the short i sound. wind The snake will wind himself around the branch. In this sentence with the word is pronounced with the long i sound and it is verb. It tells what the snake is going to do. 50
51 Draw the Meaning - Multiple Meaning Words and Homographs Materials: Dictionary Crayons, Colored Pencils, or Markers Blank Drawing Paper Objective: Illustrate the different meanings of multiple meaning words. Directions: 1. Fold a blank piece of drawing paper in half. 2. Pick a word from the word bank. 3. Look up the word in the dictionary to find the different meanings. 4. Write one definition on one half of the page and another definition on the other half of the page. 5. Write a sentence for each definition and draw a picture to go with your sentence. 6. Keep the page in a safe place and make a collection of your multiple meaning word illustrations. 7. Note There are many other multiple meaning words that are not included on this word list. Example: Word Bank pet dance crash cut dread post string smell fire wish fight love color shape shot spring Multiple Meaning Word - swing Your Drawing Sentence 1 - James fell off of the swing. Definition 1 - noun - mechanical device used as a plaything to support someone swinging back and forth Multiple Meaning Word - swing Your Drawing Sentence 2 - I am going to swing the bat. Definition 2 -verb move in a curve or arc, usually with the intent of hitting 51
52 Similes, Metaphors, Hyperbole Know the Basics Definitions Simile - A part of speech that compares two unlike things by using the words like or as. Examples The girl was as quiet as a mouse. Metaphor A part of speech that compares two unlike things without using the words like or as. Examples The pancake was drowning in maple syrup. Hyperbole An over exaggeration used as a part of speech. Examples The cake was a big as the house. Figurative Language Search Similes, Metaphors, and Hyperbole Materials: Books or Magazines Lined Paper Pencils Objective: Identify and create examples of similes, metaphors, and hyperbole Directions: Option A: 1. Pick some poems from books or magazines at your reading level. 2. Take turns looking for examples where the author has used similes, metaphors, or hyperboles. 3. Discuss what things are being compared and which type of figurative language was used. Option B 1. With a partner write examples of similes, metaphors, and hyperboles. 2. Exchange examples and try to identify which two items are being compared and what type of figurative language is being used. 52
53 Idioms Know the Basics Definition An idiom is a phrase in which the literal meaning of the words does not provide clues as to the figurative meaning of the phrase. Example kick the bucket The literal meaning of this phrase is to use your foot to physically kick a bucket. The figurative meaning of this phrase means to die. Draw Both Figurative and Literal Meanings of Idioms Materials: Blank Paper Pencil and Eraser Crayons, Markers, or Colored Pencils Objective: Students will identify both the literal and the figurative meanings of commonly used idioms. Directions: 1. Fold a piece of blank paper in half from top to bottom. 2. Pick an idiom from the included list. 3. Write the idiom at the top of both sides of the paper. 4. On the left side, draw a picture of the literal meaning (what the words actually mean) of the idiom. 5. Discuss with your parents or another grown-up the figurative meaning (the way we use the saying). 6. On the right side of the paper draw the figurative meaning of the idiom. 53
54 Compare and Contrast Know the Basics Definition When you compare two or more items you look for things that the items have in common or that are the same. When you contrast two pr more items you look for the things that are different about the two items, or things that are not the same. Example In the Venn Diagram below the circle on the left is for details that are only about butterflies. The circle on the right is for details that are only about moths. The section in the middle where the circles overlap is for details that the butterfly and the moth have in common. 54
55 The Great Cookie Comparison Compare and Contrast Materials: Blank Paper Pencil and Eraser Two different types of cookies Objective: Students will use a Venn Diagram to compare familiar objects. Directions: DO NOT TASTE THE COOKIES UNTIL YOU HAVE MADE ALL THE OTHER COMPARISONS. 1. Draw a Venn Diagram on a blank piece of paper. Be sure to leave enough room to write in each section of the diagram. 2. Place two different types of cookies next to each other on a paper towel. 3. Start by looking for the things that are different about the two cookies. 4. Next, look for things that are the same about the two cookies. 5. Then, taste the two cookies and add to your Venn Diagram. 6. Finally, discuss the things that are the same and different with someone else. 55
56 Main Idea Know the Basics The main idea of a paragraph tells what all or most of the sentences in that paragraph are going to be about. Main idea sentences help people to remember what they are reading about. The other sentences in the paragraph are details and provide extra information about the main idea. The main idea of a paragraph is usually found in the topic sentence, or the first sentence in the paragraph. Suggestions for Practice Finding the Main Idea Practice reading short articles from the newspaper. Use a highlighter to highlight the main idea of each paragraph. What is the main idea for the whole story 56
57 Generalizations Know the Basics A generalization is a statement about a group of people or things that is true about most of the group most of the time. What s True of the Group Making Generalizations Materials: Blank Paper Pencil and Eraser Glue Scissors Objective: Students will make generalizations about a group of similar items. Directions: Collect a group of similar pictures from a magazine. o Example: Several pictures of different shirts. Several pictures of different people. Several pictures of the same kind of furniture. Look closely at the group of pictures that you have collected. Consider the following: o What is true of most of the pictures? Look for things that are the same about all of the pictures. Maybe most of them have the same shape or color. Make a generalization about the group of pictures that you collected. 57
58 Multiple Step Instructions Know the Basics The most important part of this concept is that students be able to read and follow directions with multiple steps. This type of text is commonly found in instruction manuals, product assembly documents, How To guides, driving directions, and recipes. Suggestions for Practice - Following Multiple Step Directions With a parent, follow a recipe to make part of a meal. Print driving directions from a source such as MapQuest and help navigate a family trip. With adult supervision, follow the assembly directions for a younger siblings toy. Pick an activity that you do well or often. Write multiple step directions for someone else to follow so that they can be successful at the same activity. 58
59 Writing 59
60 Encouraging Writing Read your student s writing for enjoyment and talk about what they have written. You do not always need to read correct your students work. Provide a place for your student to write. Keep lots of crayons, paper, pencils, erasers, stickers, and anything that your student likes to write with. Play words games such as Scrabble, Dictionary, and Hangman Involve your student in making grocery lists or filling out calendars and planners If there is a computer available, encourage your student to use it as a writing tool. Read with your student as much as possible. Write notes to your child and encourage you student to write Christmas cards, thank you notes, and other notes to family. Write together. Have your student start a story. Take turns adding to the story to make it more interesting. Keep a collection of your student s best writing. With your student, decide which pieces of his or her writing should be included in the collection. 60
61 Written and Oral Language Conventions Verbs Action and Linking Verbs Know the Basics Definition A verb is a word that describes an action or a state of being (linking verbs). Action verbs Describe an action. Linking Verbs Describe a state of being. These verbs link a noun or adjective to the subject of the sentence. Rule for Use Adverbs help answer for questions. How? When? Where? and to what extent? Examples Action Verbs (describe an action): eat walk swim love sleep run think hate Linking Verbs (describe a state of being): was is to be sound are am being feel Verbs in sentences I am going to eat corn at the fair. - Eat is an action verb. The baby grows everyday. Grows is an action verb. Her name is Nancy. Is, is a linking verb. She was sad. Was is a linking verb. 61
62 What s Happening Identifying Linking and Action Verbs Materials: Magazines, Newspapers, Books, or Family Photo Album Lined Paper Pencils Objective: Identify, discuss, and write action and linking verbs Directions: 1. Pick 5 pictures out of a magazine, newspaper, book, or family photo album. 2. Talk about what is happening in each picture. 3. Write at least 1 sentence about what is happening in the picture. 4. Circle the verbs in each sentence. 5. Label each verb as an action verb or linking verb. 62
63 Regular and Irregular Verbs Definitions Know the Basics Regular Verbs Regular verbs can be changed from the present tense to the past tense by simply by adding ed or d. Irregular Verbs Irregular verbs are verbs that have unpredictable past tense forms. Rule for Use Examples - Regular Verbs: jump - jumped walk - walked Irregular Verbs sleep slept eat ate love - loved hate - hated do - did - done is was slip - slipped jog - jogged break - broke swim swam Past or Present Tense? - Identifying Regular and Irregular Verbs Materials: Magazines, Newspapers, Books Lined Paper Dictionary Pencils Objective: Identify and write regular and irregular verbs in the past and present tenses. Directions: 1. Look through a newspaper, magazine, or book and find 5 examples of regular verbs and 5 examples of irregular verbs. 2. Write each verb in the past and present tenses. 3. Look up the words in the dictionary to check your work. 63
64 Adverbs Know the Basics Definition An adverb describes verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They help to give a clearer and more accurate description. Rule for Use Adverbs help answer for questions. How? When? Where? and To what extent? Examples quickly, late, very, slow, fast, faster, fastest The fox jumped quickly over the fence. Quickly is describing the verb jumped. The very short ladder was not helpful. Very is describing the adjective short. The hamster ran surprisingly fast. Surprisingly is describing the adverb fast. Adverb Charades Materials: 3 x 5 index cards labeled with the adverbs and verbs from the following list. Objective: Students will act out and a variety of verbs and adverbs. Directions 1. Make the game cards for this game using the lists of verbs and adverbs located in the Appendix. 2. Make one index cards for each verb and adverb. a. NOTE: Use two different colors to easily identify verbs and adverbs. 3. Player one picks a card from the Verb pile and silently acts out the verb listed on the card until the verb is guessed. 4. Once the verb has been guessed, Player One draws a card from the Adverb pile and silently acts out the adverb in relationship to the original verb. i. NOTE: Some of the combinations of verbs and adverbs may be silly. 5. Once the verb and adverb have been guessed, it becomes the next player s turn. 64
65 Prepositions and Prepositional Phrases Know the Basics Definition Preposition - A preposition usually tells where something is, where something is going, or when something is happening. Examples about over onto into outside under before without since Prepositional Phrase Prepositional phrases are groups of two or more words that begin with a preposition and end with a noun or pronoun. Examples We played under the bridge. The cat was in the tree. She went before me. The penny fell between the cushions. Rule for Use The noun or pronoun at the end of the prepositional phrase is the object of the preposition. 65
66 Where is it? Using Prepositional Phrases Materials: No Materials Needed Objective: Students will use prepositional phrases to locate objects within their environment. Directions: 1. Player one picks an object that they can see within the current environment, keeping the object a secret. 2. The other players take turns guessing the object and it s location by asking questions about the specific location (using prepositional phrases) until the object and it s location have been identified. 3. Player one can only answer by saying yes or no. Examples: Is the object under the table? Is the object inside the kitchen? 66
67 Appositives Know the Basics Definition Appositives follow nouns, pronouns, or phrases in clauses that they describe. They help to clarify and provide additional information about the subject in which they are describing. Rule for Use Appositives are separated from the main clause or sentence by commas. Examples Julia, my sister, is younger than me. Hesperia, California, is in the desert. Spike, the dog next door, chased the cat. Combining Sentences Using Appositives Materials: Game Board (See Appendix) Game Pieces (make your own) Game Cards (See Appendix) Objective: Students will combine sentences using appositives. Directions: 1. Each player will take turns drawing a card and reading the two related sentences on the card aloud. 2. To move forward on the game board each player must correctly combine the two sentences on his or her card using an appositive. Example: o Sentence 1 - Amanda is a excellent gymnast. o Sentence 2 Amanda had crowd cheering wildly. o Combined Sentence - Amanda, an excellent gymnast, had the crowd cheering wildly. 67
68 Independent and Dependent Clauses Know the Basics Definitions- Independent Clause - An independent clause can stand alone as a complete sentence. Dependent Clause A dependent clause tells about or modifies the idea or information related to the independent clause. Rule for Use Independent clauses can stand alone as complete sentences. Dependent clauses are not complete sentences. They must be combined with an independent clause to complete a thought or give more meaning to a sentence. Examples Independent Clauses I like apples. The horse was sick. The boy played soccer. Dependent clauses because they are sweet. after he ate the sweet grass. after school. Combined Independent and Dependent Clauses I like apples because they are sweet. The horse was sick after he ate the sweet grass. The boy played soccer after school. 68
69 Finish the Thought - Independent and Dependent Clauses Materials: Lined Paper Pencils and erasers Objective: Students write using both dependent and independent clauses. Directions: 1. Each person writes a complete sentence on his or her paper. 2. Switch papers and add a dependent clause to the end of each sentence to make a silly sentence. 3. Share the new sentences aloud. Examples: Independent Clause: I went to the beach. Dependent Clause: to kiss a jellyfish New sentence I went to the beach to kiss a jellyfish. 69
70 Appendix 70
71 Math Resources 71
72 Make the Biggest Number Game Board Millions Hundred Thousands Ten Thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Game 1 Game 2 Game 3 Game 4 Game 5 Millions Hundred Thousands Ten Thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Game 1 Game 2 Game 3 Game 4 Game 5 72
73 Beat the Budget I Game Board Item Name Balance + Item Price = New Balance $ $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. Item Name Balance + Item Price = New Balance $ $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. $. + $. = $. 73
74 Beat the Budget II Game Board Item Name Balance - Item Price = New Balance $ $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. Item Name Balance - Item Price = New Balance $ $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. $. - $. = $. 74
75 The Money Game Game Board Game Board and Card Directions Step 1: Cut out both pieces of the game board. Step 2: Tape or glue the pieces together so that the 0 covers the black star. Step 3: Cut out the game cards. 75
76 You found $3.00 on your way home from school. You gave $1.00 to your little sister. The Money Game Game Cards You lost $5.00 when you lost your wallet. You gave $3.00 to a local charity. You earned $1.00 for taking out the trash. You spent $6.00 on lunch. Your found $5.00 while walking your brother home from school. You collected $6.00 for delivering the newspapers this week. You gave $4.00 to your mom for helping you with your chores. You lost $4.00 in the washing machine. You earned $4.00 for an A+ on your math test. You lost $1.00 through a hole in your pocket. You earned $1.00 for washing the dishes after dinner. You spent $6.00 on toys at the toy store. You found $400 when you cleaned under your bed. You gave your little brother $2.00 for his school fundraiser. You paid $5.00 to register your bike. You gave a friend $2.00 for his pet spider. You earned $2.00 for washing the dog. You spent $1.00 on a soda at the park. You found $3.00 in your jacket pocket. You spent $5.00 on a new comic book. You earned $7.00 for turning in all of your homework for a month. You earned $2.00 for walking the neighbor s dog. 76
77 Match Game - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions Game Set-up Game Set-up Step 1: Cut out the matching cards for the Match Game. Step 2: To make the cards sturdier they can be glued to index cards. Step 3: Lay out the cards face down on the table and begin the game. 77
78 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions one half.5 50% 1/2 one half.5 50% 1/2 one third.333 repeating decimal 33.33% 1/3 two thirds.666 repeating decimal 66.66% 2/3 78
79 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions (continued) three fourths.75 75% 3/4 one fifth.20 20% 1/5 two fifths.40 40% 2/5 three fifths.60 60% 3/5 one fourth.25 25% 1/4 79
80 Match Game Cards - Decimal and Percent Equivalents for Common Fractions (continued) four fifths.80 80% 4/5 one sixth.1666 repeating decimal 16.66% 1/6 one eighth % 1/8 one ninth.111 repeating decimal 11.11% 1/9 one tenth.1 10% 1/10 80
81 Integer Circle Puzzles - Adding and Subtracting Integers *This activity was downloaded from the Scholastic.com web site. 81
82 Word Puzzle Evaluating Expressions QuickTime and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. *This activity was downloaded from the Scholastic.com web site. 82
83 Hundreds Counting Chart 83
84 Multiplication Table through 12 84
85 Battleship Game Boards Graphing Ordered Pairs 85
86 Extra Battleship Game Boards Graphing Ordered Pairs 86
87 Reading Resources 87
88 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards 1. Rita is a good friend of mine. Rita works as a police officer. 2. My dog has spots. My dog is an Irish Setter. 3. Around the barnyard Eric ran squealing. Eric is our pig. 4. Our sailboat has two sails. Our sailboat is The Betsy. 5. Ellen s favorite exercise is walking. Ellen gave up her favorite exercise following her accident. 6. Our group left the museum early. Our group is Ike, Phoebe and I. 88
89 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards Continued 7. Kiwi fruit is a brown furry fruit with green flesh. Kiwi was originally called Chinese gooseberry. 8. Our city newspaper is published every day. Our city newspaper is The Independent Journal. 9. Amanda had the crowd cheering wildly. Amanda is an excellent gymnast. 10. John s dog liked only one other person. John s dog liked me. 11. The neighbor boys are twins. The neighbor boys are excellent baseball players. 12. My sister lives in Arizona. My sister s name is Pat. 89
90 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Cards Continued 13. The girl is the best actress. The girl is wearing a red dress. 14. My friend is Matt Matson. Matt Mason collects stamps. 15. Her dog likes to chase rabbits. Her dog is named Rusty. 16. The first man on the moon has become a legend. The first man on the moon was Neil Armstrong. 90
91 Combining Sentences with Appositives Game Board 91
2011 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math
 Name 0 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math Rachel Carson Elementary PACKET MUST INCLUDE COVER SHEET WITH THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CLEARLY PRINTED Students Name (first & last) 0-0 Homeroom
Name 0 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math Rachel Carson Elementary PACKET MUST INCLUDE COVER SHEET WITH THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CLEARLY PRINTED Students Name (first & last) 0-0 Homeroom
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
First Name: Last Name: Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator in completing this packet.
 5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
Operation Target. Round Number Sentence Target How Close? Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses.
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 5. OA.1 2 Operation Target Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses. Materials: digit cards (0-9) and a recording sheet per player Number of Players:
Operations and Algebraic Thinking 5. OA.1 2 Operation Target Building Fluency: creating equations and the use of parentheses. Materials: digit cards (0-9) and a recording sheet per player Number of Players:
5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work
 NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards
 Mathematical Resource Package For Number Sense and Numeration, Grades 4 to 6 Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards Made For Teachers By Teachers Developed By: J. Barretto-Mendoca, K. Bender, A. Conidi, T.
Mathematical Resource Package For Number Sense and Numeration, Grades 4 to 6 Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards Made For Teachers By Teachers Developed By: J. Barretto-Mendoca, K. Bender, A. Conidi, T.
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook
 Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
This book belongs to
 This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 4 course. The instructions for each
This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 4 course. The instructions for each
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Summer Math Calendar
 Going into Third Grade Directions: Follow the daily activities to practice different math concepts. Feel free to extend any of the activities listed. When the work is completed, have a parent initial the
Going into Third Grade Directions: Follow the daily activities to practice different math concepts. Feel free to extend any of the activities listed. When the work is completed, have a parent initial the
Coin Combinations. Crayons. 1. Mark the coins you need to buy an eraser. 2. Mark the coins you need to buy a box of crayons. $0.70.
 HOME LINK 8 1 Coin Combinations 88 89 Family Note In the next lesson, we will extend our work with money to include dollars. In preparation for this, we have been practicing counting coins. If your child
HOME LINK 8 1 Coin Combinations 88 89 Family Note In the next lesson, we will extend our work with money to include dollars. In preparation for this, we have been practicing counting coins. If your child
MATH GAMES THAT SUPPORT SINGAPORE MATH GRADES
 Box Cars and One-Eyed Jacks MATH GAMES THAT SUPPORT SINGAPORE MATH GRADES 3-5 JOHN FELLING SMART TRAINING SCOTTSDALE, AZ July 9, 2015 john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 / 1-780-440-6284
Box Cars and One-Eyed Jacks MATH GAMES THAT SUPPORT SINGAPORE MATH GRADES 3-5 JOHN FELLING SMART TRAINING SCOTTSDALE, AZ July 9, 2015 john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 / 1-780-440-6284
Suggested Games and Activities MathShop: Cartesian Coordinate Mat
 Cartesian Coordinates Suggested Games and Activities MathShop: Cartesian Coordinate Mat Gr. 1 Curriculum Expectations Geometry and Spatial Sense Overall Expectations Describe the relative locations of
Cartesian Coordinates Suggested Games and Activities MathShop: Cartesian Coordinate Mat Gr. 1 Curriculum Expectations Geometry and Spatial Sense Overall Expectations Describe the relative locations of
Shapes. Practice. Family Note. Unit. show 3-sided, 4-sided, 5-sided, and 6-sided shapes. Ask an adult for permission first. Add.
 Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Year 4 Homework Activities
 Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
Roll & Make. Represent It a Different Way. Show Your Number as a Number Bond. Show Your Number on a Number Line. Show Your Number as a Strip Diagram
 Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
I Can Read. (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds.
 1 I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. I can find and
1 I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. I can find and
Acing Math (One Deck At A Time!): A Collection of Math Games. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Introduction to Acing Math page 5 Card Sort (Grades K - 3) page 8 Greater or Less Than (Grades K - 3) page 9 Number Battle (Grades K - 3) page 10 Place Value Number Battle (Grades 1-6)
Table of Contents Introduction to Acing Math page 5 Card Sort (Grades K - 3) page 8 Greater or Less Than (Grades K - 3) page 9 Number Battle (Grades K - 3) page 10 Place Value Number Battle (Grades 1-6)
+ 4 ~ You divided 24 by 6 which equals x = 41. 5th Grade Math Notes. **Hint: Zero can NEVER be a denominator.**
 Basic Fraction numerator - (the # of pieces shaded or unshaded) denominator - (the total number of pieces) 5th Grade Math Notes Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions When converting a mixed number into
Basic Fraction numerator - (the # of pieces shaded or unshaded) denominator - (the total number of pieces) 5th Grade Math Notes Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions When converting a mixed number into
Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5
 Unit 13 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5 Introduction In this unit, students will develop fluency in addition and subtraction within 5. By this point, they have learned several methods
Unit 13 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5 Introduction In this unit, students will develop fluency in addition and subtraction within 5. By this point, they have learned several methods
Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 7 5 6 Lesson 7 Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe patterns within the coordinate pairs. Suggested Lesson Structure
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 7 5 6 Lesson 7 Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe patterns within the coordinate pairs. Suggested Lesson Structure
Math Matters! Fifth Grade Summer Practice Packet. Colonial School District
 Math Matters! Fifth Grade Summer Practice Packet Colonial School District Promoting a Culture of Collaboration, Innovation and Inspiration June 2017 Dear Parents/Guardians, First, we would like to thank
Math Matters! Fifth Grade Summer Practice Packet Colonial School District Promoting a Culture of Collaboration, Innovation and Inspiration June 2017 Dear Parents/Guardians, First, we would like to thank
Cheetah Math Superstars
 PARENTS: You may read the problem to your child and demonstrate a similar problem, but he/she should work the problems. Please encourage independent thinking and problem solving skills. SCORING: 20 paw
PARENTS: You may read the problem to your child and demonstrate a similar problem, but he/she should work the problems. Please encourage independent thinking and problem solving skills. SCORING: 20 paw
 OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M. K-6 www.ewing.k12.nj.us
OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M. K-6 www.ewing.k12.nj.us
Maths games and activities to help your child s learning Enjoy!
 Maths games and activities to help your child s learning Enjoy! DICE GAMES Dice games are fun! They are also one of the oldest of all kinds of games: there are records of dice being played over 5,000 years
Maths games and activities to help your child s learning Enjoy! DICE GAMES Dice games are fun! They are also one of the oldest of all kinds of games: there are records of dice being played over 5,000 years
GRADE 4. M : Solve division problems without remainders. M : Recall basic addition, subtraction, and multiplication facts.
 GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
Reading and Writing Decimals
 Reading and Writing Decimals Home Link - Use the place-value chart below to complete Problems 8. Ones s s. Tenths 0.s _ 0 s Hundredths 0.0s _ 00 s Thousandths 0.00s _,000 s 7-9 Write each decimal in words..98
Reading and Writing Decimals Home Link - Use the place-value chart below to complete Problems 8. Ones s s. Tenths 0.s _ 0 s Hundredths 0.0s _ 00 s Thousandths 0.00s _,000 s 7-9 Write each decimal in words..98
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING
 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-1000 ThinkMath 2017 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 The Mathematical relational skills
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-1000 ThinkMath 2017 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 The Mathematical relational skills
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
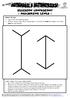 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros
 L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros A. Here are the steps for subtracting 3-digit numbers across zeros. Complete the example. 7 10 12 8 0 2 2 3 8 9 1. Subtract the ones column. 2 8 requires regrouping. 2.
L_sson 9 Subtracting across zeros A. Here are the steps for subtracting 3-digit numbers across zeros. Complete the example. 7 10 12 8 0 2 2 3 8 9 1. Subtract the ones column. 2 8 requires regrouping. 2.
Dear Parents,
 Dear Parents, This packet of math activities was created to help your child engage with and become excited about Math over the summer months. All projects in this packet are based upon the Connecticut
Dear Parents, This packet of math activities was created to help your child engage with and become excited about Math over the summer months. All projects in this packet are based upon the Connecticut
Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts
 NCTM 206 San Francisco, California Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts -5 Sandra Niemiera Elizabeth Cape mathtrailblazer@uic.edu 2 4 5 6 7 Game Analysis Tool of Game Math Involved in the Game This game
NCTM 206 San Francisco, California Meaningful Ways to Develop Math Facts -5 Sandra Niemiera Elizabeth Cape mathtrailblazer@uic.edu 2 4 5 6 7 Game Analysis Tool of Game Math Involved in the Game This game
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
These are skills that we have covered within our math outcomes this year
 Patterns & Relationships Whole Number Multiplication & Division Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Measurement, Data, and Geometry Word Problem Analysis These are skills that we have covered within our
Patterns & Relationships Whole Number Multiplication & Division Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Measurement, Data, and Geometry Word Problem Analysis These are skills that we have covered within our
Minute Simplify: 12( ) = 3. Circle all of the following equal to : % Cross out the three-dimensional shape.
 Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Multiplication and Division
 E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
MATH NUMBER SENSE 3 Performance Objective Task Analysis Benchmarks/Assessment Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers.
 Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
Spell Well! Letter Tiles
 Spell Well! Selected Spelling Activities For Practice at School or at Home Letter Tiles Use the letter tiles to spell out your spelling words. After you have arranged the letters, check to see that you
Spell Well! Selected Spelling Activities For Practice at School or at Home Letter Tiles Use the letter tiles to spell out your spelling words. After you have arranged the letters, check to see that you
Write silly sentences using a popcorn word in each sentence. Please underline your popcorn words! Write neatly!
 First write each word in pencil. Then trace over each word three times. Each time you trace, you must use a DIFFERENT color crayon. Trace neatly and you will see a rainbow! Write silly sentences using
First write each word in pencil. Then trace over each word three times. Each time you trace, you must use a DIFFERENT color crayon. Trace neatly and you will see a rainbow! Write silly sentences using
Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions]
![Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions]](/thumbs/84/89643749.jpg) Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Materials: Dice (2 different colored dice, if possible) *It is important to provide students with fractional manipulatives
Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Materials: Dice (2 different colored dice, if possible) *It is important to provide students with fractional manipulatives
Fourth Grade. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators. Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111. Slide 4 / 111. Slide 3 / 111. Slide 6 / 111.
 Slide / Slide / Fourth Grade Fraction Computation 0-- www.njctl.org Slide / Slide / Table of Contents Click on a topic to go to that section. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators Adding Mixed Numbers
Slide / Slide / Fourth Grade Fraction Computation 0-- www.njctl.org Slide / Slide / Table of Contents Click on a topic to go to that section. Adding Fractions with Common Denominators Adding Mixed Numbers
1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b
 1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b Ghetto Blaster Cassette NUMBERS Student Recording Cassette answer sheet 1. On your answer sheet write the following as numbers: Whole numbers: a) eight
1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b Ghetto Blaster Cassette NUMBERS Student Recording Cassette answer sheet 1. On your answer sheet write the following as numbers: Whole numbers: a) eight
 Rising 6 th Grade OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M.
Rising 6 th Grade OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M.
MATH NEWS. 5 th Grade Math. Focus Area Topic A. Grade 5, Module 2, Topic A. Words to know. Things to Remember:
 MATH NEWS Grade 5, Module 2, Topic A 5 th Grade Math Focus Area Topic A Math Parent Letter This document is created to give parents and students a better understanding of the math concepts found in Eureka
MATH NEWS Grade 5, Module 2, Topic A 5 th Grade Math Focus Area Topic A Math Parent Letter This document is created to give parents and students a better understanding of the math concepts found in Eureka
Essentials. Week by. Week. Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient?
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 5 Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient? Is the answer the same for all the calculators in your class?
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 5 Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient? Is the answer the same for all the calculators in your class?
OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION
 Rising 2 nd Grade OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M.
Rising 2 nd Grade OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION 1325 Lower Ferry Rd, Ewing NJ 08618 Don Wahlers, District Supervisor for Curriculum & Instruction Phone 609-538-9800 Ext. 3148 Fax 609-882-8172 S.T.E.M.
Fantastic Fractions. Integrated Unit of Study. Martha A. Ban. Fantastic Fractions
 Fantastic Fractions An Integrated Unit of Study by Martha A. Ban Atlantic Union Conference Teacher Bulletin www.teacherbulletin.org Page 1 of 46 Major Concepts Basic Fractions Fourths, Eights, and Tenths
Fantastic Fractions An Integrated Unit of Study by Martha A. Ban Atlantic Union Conference Teacher Bulletin www.teacherbulletin.org Page 1 of 46 Major Concepts Basic Fractions Fourths, Eights, and Tenths
GRADE 3 TEXAS. Subtraction WORKSHEETS
 GRADE 3 TEXAS Subtraction WORKSHEETS Subtraction mental strategies related facts Knowing one addition fact means you also know two related subtraction facts. Because 7 + 3 = 10 you also know that 10 7
GRADE 3 TEXAS Subtraction WORKSHEETS Subtraction mental strategies related facts Knowing one addition fact means you also know two related subtraction facts. Because 7 + 3 = 10 you also know that 10 7
Instruction Cards Sample
 Instruction Cards Sample mheducation.com/prek-12 Instruction Cards Table of Contents Level A: Tunnel to 100... 1 Level B: Race to the Rescue...15 Level C: Fruit Collector...35 Level D: Riddles in the Labyrinth...41
Instruction Cards Sample mheducation.com/prek-12 Instruction Cards Table of Contents Level A: Tunnel to 100... 1 Level B: Race to the Rescue...15 Level C: Fruit Collector...35 Level D: Riddles in the Labyrinth...41
a. $ b. $ c. $
 LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
Reminder - Practicing multiplication (up to 12) and long division facts are VERY important!
 1 Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 5th Grade Our fourth graders had a busy year learning new math skills. Mastery of all these skills is extremely important in order to develop a
1 Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 5th Grade Our fourth graders had a busy year learning new math skills. Mastery of all these skills is extremely important in order to develop a
5th Grade. Divisibility Rules. Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239. Slide 3 / 239. Slide 4 / 239. Slide 6 / 239. Slide 5 / 239. Division. Division Unit Topics
 Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239 5th Grade Division 2015-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 239 Slide 4 / 239 Division Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Divisibility Rules Patterns in Multiplication
Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239 5th Grade Division 2015-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 239 Slide 4 / 239 Division Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Divisibility Rules Patterns in Multiplication
Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I
 Section 2 Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I Name 1. Complete the two patterns. 448, 458, 468,,, 498,, 518 285, 385, 485, 585,,,,,1085 2. Jackson ate a cookie at 1:00. He ate another cookie every 2½
Section 2 Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I Name 1. Complete the two patterns. 448, 458, 468,,, 498,, 518 285, 385, 485, 585,,,,,1085 2. Jackson ate a cookie at 1:00. He ate another cookie every 2½
Answer Key. Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool
 Answer Key Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool 4 5 6 Telling Time Adding 2-Digits Fractions Subtracting 2-Digits Adding and Subtracting Money A. Draw the hands on each clock face to show the time. 12:20 6:05
Answer Key Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool 4 5 6 Telling Time Adding 2-Digits Fractions Subtracting 2-Digits Adding and Subtracting Money A. Draw the hands on each clock face to show the time. 12:20 6:05
Section 1: Whole Numbers
 Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
This book belongs to
 This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 2 course. The instructions for each
This book belongs to This book was made for your convenience. It is available for printing from the website. It contains all of the printables from Easy Peasy's Math 2 course. The instructions for each
T.G.I.F. Thank Goodness It's Fun! JOHN FELLING BOOS. phone boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.
 T.G.I.F. Thank Goodness It's Fun! JOHN FELLING BOOS boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 1-780-440-6284 BoxCarsEduc BoxcarsEducation For electronic copy send
T.G.I.F. Thank Goodness It's Fun! JOHN FELLING BOOS boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 1-780-440-6284 BoxCarsEduc BoxcarsEducation For electronic copy send
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 1
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 1 Unit 1 Whole Numbers and Algebra MATH 601 Whole Numbers and Algebra INTRODUCTION 3 1. WHOLE NUMBERS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 ROUNDING AND ESTIMATION 7 WHOLE NUMBER OPERATIONS
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 1 Unit 1 Whole Numbers and Algebra MATH 601 Whole Numbers and Algebra INTRODUCTION 3 1. WHOLE NUMBERS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 ROUNDING AND ESTIMATION 7 WHOLE NUMBER OPERATIONS
Example: I predict odd, roll a 5, and then collect that many counters. Play until time is up. The player with the most counters wins.
 Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math
 Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math Did you know that the average American child loses between 1 and 3 months of learning in reading and math each summer? You can continue to love and enjoy your
Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math Did you know that the average American child loses between 1 and 3 months of learning in reading and math each summer? You can continue to love and enjoy your
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
FSA Math Review. **Rounding / Estimating** **Addition and Subtraction** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about
 FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
More Activities to Reinforce and Teach Sight Words
 More Activities to Reinforce and Teach Sight Words Bean Bag Toss Materials: One shower curtain liner divided into 20 boxes with a permanent marker Bean Bag Words on large cards Attach the words to the
More Activities to Reinforce and Teach Sight Words Bean Bag Toss Materials: One shower curtain liner divided into 20 boxes with a permanent marker Bean Bag Words on large cards Attach the words to the
Use the following games to help students practice the following [and many other] grade-level appropriate math skills.
![Use the following games to help students practice the following [and many other] grade-level appropriate math skills. Use the following games to help students practice the following [and many other] grade-level appropriate math skills.](/thumbs/85/92403514.jpg) ON Target! Math Games with Impact Students will: Practice grade-level appropriate math skills. Develop mathematical reasoning. Move flexibly between concrete and abstract representations of mathematical
ON Target! Math Games with Impact Students will: Practice grade-level appropriate math skills. Develop mathematical reasoning. Move flexibly between concrete and abstract representations of mathematical
Core Connections, Course 2 Checkpoint Materials
 Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
T HE M AGIC OF D ECIMALS AND P ERCENTS
 p01_p02.qxd 8/6/02 11:59 AM Page 1 I T HE M AGIC OF D ECIMALS AND P ERCENTS Decimals and percents are everywhere. If you go to the grocery store, you ll find the cost of everything expressed in decimals.
p01_p02.qxd 8/6/02 11:59 AM Page 1 I T HE M AGIC OF D ECIMALS AND P ERCENTS Decimals and percents are everywhere. If you go to the grocery store, you ll find the cost of everything expressed in decimals.
Warm ups PLACE VALUE How many different ways can you make the number 365?
 Warm ups How many different ways can you make the number 365? Write down all you know about the number 24. (It is up to the students to decide how they will display this. They can use numerals, unifix,
Warm ups How many different ways can you make the number 365? Write down all you know about the number 24. (It is up to the students to decide how they will display this. They can use numerals, unifix,
Kindergarten. Counting and Cardinality.
 1 Kindergarten Counting and Cardinality 2016 01 13 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Count Sequence Hundredth Day of School Click on a topic to go to that section Numbers 0 6 Numbers 6 10 Number Writing
1 Kindergarten Counting and Cardinality 2016 01 13 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Count Sequence Hundredth Day of School Click on a topic to go to that section Numbers 0 6 Numbers 6 10 Number Writing
Essentials. Week by. Week. Calculate!
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 7 Calculate! Find two numbers whose product would be between 0 and 50. Can you find more solutions? Find two numbers whose product would be between,500 and,600.
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 7 Calculate! Find two numbers whose product would be between 0 and 50. Can you find more solutions? Find two numbers whose product would be between,500 and,600.
The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament
 The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament Saturday October 27th, 2018 Grade 6 Test RULES The test consists of 25 multiple choice problems and 5 short answer problems to be done in
The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament Saturday October 27th, 2018 Grade 6 Test RULES The test consists of 25 multiple choice problems and 5 short answer problems to be done in
Reigate Grammar School. 11+ Entrance Examination January 2012 MATHEMATICS
 Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
5-DAY VOCABULARY TEACHING PLAN
 5-DAY VOCABULARY TEACHING PLAN DAY 1 Introduce Target Vocabulary in Context Materials: Concept web, words in context sheet, word smart graphic organizer Introduce vocabulary words and activate prior knowledge
5-DAY VOCABULARY TEACHING PLAN DAY 1 Introduce Target Vocabulary in Context Materials: Concept web, words in context sheet, word smart graphic organizer Introduce vocabulary words and activate prior knowledge
 Geometry 5. G. Number and Operations in Base Ten 5. NBT. Pieces of Eight Building Fluency: coordinates and compare decimals Materials: pair of dice, gameboard, paper Number of Players: - Directions:. Each
Geometry 5. G. Number and Operations in Base Ten 5. NBT. Pieces of Eight Building Fluency: coordinates and compare decimals Materials: pair of dice, gameboard, paper Number of Players: - Directions:. Each
Nine hundred eighty-six One hundred forty-four One thousand, one hundred thirty Eight hundred forty-fi ve
 0-0_5_78537MWVEMC_CM.indd 78537MWVEMC CM 3//09 9:7:8 four hundred six thousand, three hundred fifty-two Number Explosion Number Explosion Objective: Students will use place value to represent whole numbers.
0-0_5_78537MWVEMC_CM.indd 78537MWVEMC CM 3//09 9:7:8 four hundred six thousand, three hundred fifty-two Number Explosion Number Explosion Objective: Students will use place value to represent whole numbers.
Counters in a Cup In and Out. The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup.
 Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Object of the game: to make the standard form of the number for that round. To play:
 0 3 5 9 6 0 7 Go Fish! This variation of Go Fish will reel student pairs into reinforcing number forms! In advance, make four copies of page on tagboard and cut apart the cards. For each game card, program
0 3 5 9 6 0 7 Go Fish! This variation of Go Fish will reel student pairs into reinforcing number forms! In advance, make four copies of page on tagboard and cut apart the cards. For each game card, program
Grade 3: Step Up to Grade 4 Teacher s Guide
 Glenview, Illinois Boston, Massachusetts Chandler, Arizona Shoreview, Minnesota Upper Saddle River, New Jersey Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Printed in the
Glenview, Illinois Boston, Massachusetts Chandler, Arizona Shoreview, Minnesota Upper Saddle River, New Jersey Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Printed in the
TERM 2 MATHS NOTES COMMON FRACTIONS
 1 TERM 2 MATHS NOTES COMMON FRACTIONS Table of Contents DEFINITIONS AND KEY WORDS:... 3 Proper Fractions:... 3 Improper Fractions:... 3 Mixed Fractions:... 3 CONVERTING FRACTIONS... 4 EXERCISE 1... 4 EQUIVALENT
1 TERM 2 MATHS NOTES COMMON FRACTIONS Table of Contents DEFINITIONS AND KEY WORDS:... 3 Proper Fractions:... 3 Improper Fractions:... 3 Mixed Fractions:... 3 CONVERTING FRACTIONS... 4 EXERCISE 1... 4 EQUIVALENT
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS
 MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
4 th Grade Mathematics Learning Targets By Unit
 INSTRUCTIONAL UNIT UNIT 1: WORKING WITH WHOLE NUMBERS UNIT 2: ESTIMATION AND NUMBER THEORY PSSA ELIGIBLE CONTENT M04.A-T.1.1.1 Demonstrate an understanding that in a multi-digit whole number (through 1,000,000),
INSTRUCTIONAL UNIT UNIT 1: WORKING WITH WHOLE NUMBERS UNIT 2: ESTIMATION AND NUMBER THEORY PSSA ELIGIBLE CONTENT M04.A-T.1.1.1 Demonstrate an understanding that in a multi-digit whole number (through 1,000,000),
MATH Learning On The Go!!!!
 MATH Learning On The Go!!!! Math on the Go Math for the Fun of It In this busy world, we spend a lot of time moving from place to place in our cars, on buses and trains, and on foot. Use your traveling
MATH Learning On The Go!!!! Math on the Go Math for the Fun of It In this busy world, we spend a lot of time moving from place to place in our cars, on buses and trains, and on foot. Use your traveling
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
Summer Work th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond:
 Summer Work 208 6 th Grade Math to 7 th Grade Math 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals and fractions - solve
Summer Work 208 6 th Grade Math to 7 th Grade Math 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals and fractions - solve
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Free Math print & Go Pages and centers. Created by: The Curriculum Corner.
 Free Math print & Go Pages and centers Created by: The Curriculum Corner 9 x 3 9 x 10 1x 7 11 x 7 10 x 2 8 x 4 3 x 6 5 x 8 12 x 9 6 x 4 3 x 8 2 x 6 4 x 9 11 x 3 2 x 9 7 x 6 10 x 10 MULTIPLICATION MANIA
Free Math print & Go Pages and centers Created by: The Curriculum Corner 9 x 3 9 x 10 1x 7 11 x 7 10 x 2 8 x 4 3 x 6 5 x 8 12 x 9 6 x 4 3 x 8 2 x 6 4 x 9 11 x 3 2 x 9 7 x 6 10 x 10 MULTIPLICATION MANIA
Working on It Reflecting and Connecting
 Lesson Summary Objectives This lesson will help students to: represent and compare fractions; relate decimal numbers to fractions; compare and order decimal numbers. Curriculum Expectations By the end
Lesson Summary Objectives This lesson will help students to: represent and compare fractions; relate decimal numbers to fractions; compare and order decimal numbers. Curriculum Expectations By the end
THE SULTAN S SCHOOL HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME
 HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
Vocabulary: colon, equivalent ratios, fraction, part-to-part, part-to-whole, ratio
 EE8-39 Ratios and Fractions Pages 144 147 Standards: preparation for 8.EE.B.5 Goals: Students will review part-to-part and part-to-whole ratios, different notations for a ratio, and equivalent ratios.
EE8-39 Ratios and Fractions Pages 144 147 Standards: preparation for 8.EE.B.5 Goals: Students will review part-to-part and part-to-whole ratios, different notations for a ratio, and equivalent ratios.
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
I Can Read. (Reading Foundational Skills)
 I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. RF.3.3 I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. RF.3.3.A I
I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. RF.3.3 I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. RF.3.3.A I
Georgia Department of Education
 Fourth Grade 4.NOP.1 Multiplication and division; Find the factor pairs for a given whole number less than or equal to 100; recognize prime numbers as numbers greater than 1 with exactly one factor pair.
Fourth Grade 4.NOP.1 Multiplication and division; Find the factor pairs for a given whole number less than or equal to 100; recognize prime numbers as numbers greater than 1 with exactly one factor pair.
GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: Read (in standard form) whole numbers. whole numbers Equivalent Whole Numbers
 CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION 1 GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2019 2020 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 MASTER COPY 1 20 19 NUMBER SENSE Whole Numbers 4.NS.1: Read and write whole
CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION 1 GRADE LEVEL: FOURTH GRADE SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2019 2020 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 MASTER COPY 1 20 19 NUMBER SENSE Whole Numbers 4.NS.1: Read and write whole
Lesson 1: Place Value of Whole Numbers. Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions
 Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
December Everyday Math Stations
 December Everyday Math Stations Same or Different: Students were paired up and given a baggie with three craft sticks in it. The sticks were colored red on one side and blue on the other. This is to learn
December Everyday Math Stations Same or Different: Students were paired up and given a baggie with three craft sticks in it. The sticks were colored red on one side and blue on the other. This is to learn
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media. 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. a) 3.6 million b) 6 billion c)
 Master 4.27 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. 3 a) 3.6 million b) 6 billion c) 1 million 4 2 1 d) 2 billion e) 4.25 million f) 1.4 billion 10 2. Use
Master 4.27 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. 3 a) 3.6 million b) 6 billion c) 1 million 4 2 1 d) 2 billion e) 4.25 million f) 1.4 billion 10 2. Use
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media. 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. a) 3.6 million
 Master 4.27 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. a) 3.6 million 3 b) 6 billion 4 c) 1 million 2 1 d) 2 billion 10 e) 4.25 million f) 1.4 billion 2. Use
Master 4.27 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Numbers in the Media 1. Rewrite each number in standard form. a) 3.6 million 3 b) 6 billion 4 c) 1 million 2 1 d) 2 billion 10 e) 4.25 million f) 1.4 billion 2. Use
I Can Read. (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds.
 I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. RF.3.3 I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. RF.3.3.A I
I Can Read (Reading Foundational Skills) I can read words by using what I know about letters and sounds. RF.3.3 I can show what I have learned about letters and sounds by figuring out words. RF.3.3.A I
St Thomas of Canterbury Catholic Primary School Where every child is special
 Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament
 The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament Saturday October 27th, 2018 Grade 6 Test RULES The test consists of 25 multiple choice problems and 5 short answer problems to be done in
The Sixth Annual West Windsor-Plainsboro Mathematics Tournament Saturday October 27th, 2018 Grade 6 Test RULES The test consists of 25 multiple choice problems and 5 short answer problems to be done in
