Introduction to Vision. Alan L. Yuille. UCLA.
|
|
|
- Tiffany Hodges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Vision Alan L. Yuille. UCLA.
2 IPAM Summer School weeks of online lectures on Vision. What papers do I read in computer vision? There are so many and they are so different.
3 Main Points of this Talk (I) Vision is extremely hard. Humans are vision experts, Vision is very complex and only partially understood. (III) Why is vision hard? Complexity of images, ambiguity of images, complexity of visual tasks. (IV) Taxonomy: Low-, middle-, high-level vision. Course structure.
4 The Purpose of Vision To Know What is Where by Looking. Aristotle. ( BC). Information Theory: receive a signal by light rays and decode its information to understand the three-dimensional scene. Vision appears deceptively simple to humans, but this is highly misleading.
5 Humans can understand very complex images We can get the gist of an image in about 150 msec, the time to blink an eye.
6 But we make mistakes: Accidental alignments fool us. Other accidental alignment images.
7 We are subject to Attention blindness. Change blindness. ok_zfy Policeman was sent to jail because he was chasing a criminal and didn t stop to break up a fight. Was he guilty?
8 We don t agree on what we see The dress illusion: This is an example of colour constancy. The colour that reaches our eye is a product of the colour of the object and of the lighting. We don t know the colour of the lighting, so our eyes guess it and sometimes are wrong.
9 But we can get information from very little From dots to people: biological motion ndex.html But computer vision can do better (3d from single image). Also juggler.
10 But we can perform many visual tasks And so can our relatives: a5ypdq Why waste our brain power (takes 25% of our total energy) to do vision? Maybe our ancestors evolved because they could do vision? For hunting, for foraging, for social interactions.
11 Vision and the Brain Humans appear to understand images effortlessly. But this is only because of the enormous amount of our brains that we devote to visual tasks. It is estimated that 40-50% of neurons in the cortex are involved in doing vision. Humans are very visual. We get much more information from our eyes than other animals.
12 The Human and Monkey Visual System The visual cortex is roughly percent of the size of our cortex (the intelligent part of the brain)
13 Vision and the Brain: complexity The number of nerve cells in brain 100,000,000,000 is about the number of trees in the Amazon rainforest. The number of nerve cell connections 1,000,000,000,000,000 is about the number of leaves in rainforest. The number of connections in the world s telephone system (biggest machine on the planet). The brain is the most complicated (known) system in the Universe. The neurons in your brain would reach to the moon and back.
14 Why is Vision hard? The main difficulty of vision is due to the complexity of images, the local ambiguity of images, and the complexity of visual tasks. Artificial Intelligence researchers were too ambitious in the 1960 s. Solve vision in the summer. Now we have computer power, and are developing the theories, to deal with complexity. The twenty-first century will be the century of complexity S.W. Hawking (2000).
15 The Raw Input Image Patterns The raw input is a set of numbers (bottom left). The image patterns are very complex. The patterns are very different even for similar objects (same bike and tree changed viewpoint).
16 Vision can be very hard Hidden object: n/index.html Motion can help.
17 The Complexity of Images The set of all images is practically infinite. Only a tiny fraction of all possible images have been seen by humans. The number of visual scenes is also enormous. There are 30,000 different types of objects. They can be arranged into 1,000 scene categories. This can be done in an exponential number of ways.
18 The Local Ambiguity of Images Airplane Car Boat Sign Building
19 The Complexity of Visual Tasks Humans can easily detect the fox, the tree trunk, the grass and the background twigs. And can also estimate the shape of the fox s legs and head, its type fur, what it is doing, is it old or young, is this winter or summer? But the local regions are highly ambiguous.
20 Visual Tasks and Image Detail Interpret images, reason about them, predict the future, estimate danger. Small details (feet, hands) can be very important.
21 Vision is the full AI Problem Understanding of objects, scenes, and events. Reasoning about functions and roles of objects, goals and intentions of agents, predicting the outcomes of events. The full Artificial Intelligence problem. Visual Turing Tests: can computers answer all questions that a human can about images (or do it better)? (D. Geman and S. Geman).
22 How to Address Vision? One strategy divide vision up into many subtasks that can be studied separately. In this course, we will study subtasks in a unified way that will enable them to be integrated into a complete visual system and which takes complexity into account (research program).
23 Vision as Inverse Inference Helmholtz More recently: inverse computer graphics. Vision must invert the forward process (CG) to discover the causal factors that have generated the images. But only for the tasks that we care about attention, change blindness.
24 Richard Gregory "Perception (vision) as hypotheses. Perception is not just a passive acceptance of stimuli, but an active process involving memory and other internal processes. Humans have internal representations we see images when we dream, we can imagine what animals and people will do, we can hallucinate.
25 Bayesian Decision Theory Bayes Theorem is a conceptual framework for inverse inference problems. We can infer the state S of the world from the image I using prior knowledge. P(S I) = P(I S)P(S)/P(I). Rev. T. Bayes P(I S) likelihood, P(S) prior
26 Inverse Problems are hard There are an infinite number of ways that images can be formed. Why do we see a cube? The likelihood P(I S) rules out some interpetations S Prior P(S) cubes are more likely than other shapes consistent with the image.
27 Inverse inference requires priors Humans use prior knowledge about the world (obtained through experience). Often correct but can fail occasionally. Flying carpet? Levitate? Play ball-in-box.
28 Taxonomy of Vision Hierarchy Low-, Middle-, High-level vision. This gives a way to roughly taxonomize visual problems. Relates to theories of the human visual system. E.g., Poggio, Marr, Ullman.
29 Figure Marr s Taxonomy
30 Low-, Mid-, and High-Level Vision Vision can be broken down into low-, mid-, and high-level vision (very roughly). Low-level vision local image operations which have limited knowledge of the world. Mid-level vision semi-local operations which know about surfaces and geometry. High-level vision non-local operations knowing about objects and scene structures. From generic to specify. From local to global.
31 Low-level vision Image processing. Filtering, denoising, enhancement. Edge detection. Image segmentation. Right: ideal segmentation (followed by labeling).
32 Mid-Level Vision: Depth Estimation of 3D surfaces: E.g., binocular stereo, structure from motion, Figure: Images, Depth, Segmentation. (Blue close, red far).
33 Stereo: Correspondence and Trigonometry The correspondence problem and depth estimation: There are no good one-eyed sportsplayers.
34 Mid-Level Vision: Grouping Kanisza. Humans have a strong tendency to group image structures as surfaces which can partially occlude each other.
35 More Kanisza From Michael Bach: Kansiza with other cues.
36 High-Level Vision Object detection and Scene Understanding. Example: detect objects and object parts.
37 Feedforward and Feedback How do these levels interact? Feedforward from low-, to mid-, to high. Feedback high to low -- analysis by synthesis. Low-level vision makes proposals which are validated by high-level vision.
38 Does high-level always beat Tanz Illusion: mid-level? 7d8LQw Inverted Face Mask: We see it as a real face, but it isn t.
39 Hierarchical Compositional Models Compositional models represent objects and scenes in terms of compositions of elementary shared parts. This offers a possible solution to the complexity problem of vision.
40 Summary The key challenges of vision are complexity of images, local ambiguity of images, and complexity of visual tasks. Vision is organized into a hierarchical structure. This leads to a rough taxonomy into low-, mid-, and high-level vision. Inverse inference, pattern theory, representation, inference and learning. Visual Turing tests drive computer vision forward.
41 More Illusions A few more: M4wfyZI
Digital image processing vs. computer vision Higher-level anchoring
 Digital image processing vs. computer vision Higher-level anchoring Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Cybernetics Center for Machine Perception
Digital image processing vs. computer vision Higher-level anchoring Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Cybernetics Center for Machine Perception
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception
 Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Artificial Intelligence. What is AI?
 2 Artificial Intelligence What is AI? Some Definitions of AI The scientific understanding of the mechanisms underlying thought and intelligent behavior and their embodiment in machines American Association
2 Artificial Intelligence What is AI? Some Definitions of AI The scientific understanding of the mechanisms underlying thought and intelligent behavior and their embodiment in machines American Association
Occlusion. Atmospheric Perspective. Height in the Field of View. Seeing Depth The Cue Approach. Monocular/Pictorial
 Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Spring 2018 CS543 / ECE549 Computer Vision. Course webpage URL:
 Spring 2018 CS543 / ECE549 Computer Vision Course webpage URL: http://slazebni.cs.illinois.edu/spring18/ The goal of computer vision To extract meaning from pixels What we see What a computer sees Source:
Spring 2018 CS543 / ECE549 Computer Vision Course webpage URL: http://slazebni.cs.illinois.edu/spring18/ The goal of computer vision To extract meaning from pixels What we see What a computer sees Source:
What you see is not what you get. Grade Level: 3-12 Presentation time: minutes, depending on which activities are chosen
 Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Optical Illusions What you see is not what you get The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to basic principles of visual processing. Much of the lesson revolves around the use of visual illusions
Computational and Biological Vision
 Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Some necessary administrivia Lecturer : Ohad Ben-Shahar Email address : ben-shahar@cs.bgu.ac.il
Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Some necessary administrivia Lecturer : Ohad Ben-Shahar Email address : ben-shahar@cs.bgu.ac.il
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Artificial Intelligence
 Torralba and Wahlster Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1: Introduction 1/22 Artificial Intelligence 1. Introduction What is AI, Anyway? Álvaro Torralba Wolfgang Wahlster Summer Term 2018 Thanks to Prof.
Torralba and Wahlster Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1: Introduction 1/22 Artificial Intelligence 1. Introduction What is AI, Anyway? Álvaro Torralba Wolfgang Wahlster Summer Term 2018 Thanks to Prof.
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Artificial Intelligence: An overview
 Artificial Intelligence: An overview Thomas Trappenberg January 4, 2009 Based on the slides provided by Russell and Norvig, Chapter 1 & 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that act like
Artificial Intelligence: An overview Thomas Trappenberg January 4, 2009 Based on the slides provided by Russell and Norvig, Chapter 1 & 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that act like
The Visual System. Computing and the Brain. Visual Illusions. Give us clues as to how the visual system works
 The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
The Visual System Computing and the Brain Visual Illusions Give us clues as to how the visual system works We see what we expect to see http://illusioncontest.neuralcorrelate.com/ Spring 2010 2 1 Visual
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS kersten.org
 How big is it? Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS 2009 kersten.org NIH R01 EY015261 NIH P41 008079, P30 NS057091 and the MIND Institute Huseyin Boyaci Bilkent
How big is it? Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS 2009 kersten.org NIH R01 EY015261 NIH P41 008079, P30 NS057091 and the MIND Institute Huseyin Boyaci Bilkent
Introduction to AI. What is Artificial Intelligence?
 Introduction to AI Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? Views of AI fall into four categories: Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Acting Humanly Acting Rationally The
Introduction to AI Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? Views of AI fall into four categories: Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Acting Humanly Acting Rationally The
Artificial Intelligence. Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University
 Artificial Intelligence Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University What is AI? What is Intelligence? The ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills (definition
Artificial Intelligence Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University What is AI? What is Intelligence? The ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills (definition
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects
 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Artificial Intelligence for Engineers. EE 562 Winter 2015
 Artificial Intelligence for Engineers EE 562 Winter 2015 1 Administrative Details Instructor: Linda Shapiro, 634 CSE, shapiro@cs.washington.edu TA: ½ time Bilge Soran, bilge@cs.washington.edu Course Home
Artificial Intelligence for Engineers EE 562 Winter 2015 1 Administrative Details Instructor: Linda Shapiro, 634 CSE, shapiro@cs.washington.edu TA: ½ time Bilge Soran, bilge@cs.washington.edu Course Home
Vision V Perceiving Movement
 Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Vision V Perceiving Movement Overview of Topics Chapter 8 in Goldstein (chp. 9 in 7th ed.) Movement is tied up with all other aspects of vision (colour, depth, shape perception...) Differentiating self-motion
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Humans used a web interface to say same person or different person for a large set of faces. Several computer programs made the same comparisons
 OPTO 6124 Perception Scott Stevenson Image Segmentation What is really behind so many perception demos? Perception demos show us that our visual understanding of the world involves a lot of filling in
OPTO 6124 Perception Scott Stevenson Image Segmentation What is really behind so many perception demos? Perception demos show us that our visual understanding of the world involves a lot of filling in
COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall Lecture 1: Intro
 COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Lecture 1: Intro Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan Today s Agenda Defining intelligence and AI state-of-the-art, goals Course outline AI by introspection
COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Lecture 1: Intro Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan Today s Agenda Defining intelligence and AI state-of-the-art, goals Course outline AI by introspection
Making Representations: From Sensation to Perception
 Making Representations: From Sensation to Perception Mary-Anne Williams Innovation and Enterprise Research Lab University of Technology, Sydney Australia Overview Understanding Cognition Understanding
Making Representations: From Sensation to Perception Mary-Anne Williams Innovation and Enterprise Research Lab University of Technology, Sydney Australia Overview Understanding Cognition Understanding
Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by
 Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Fun with visual illusions. Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic
 Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Perceptual Ideas Perception Selective Attention: focus of conscious
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Application Areas of AI Artificial intelligence is divided into different branches which are mentioned below:
 Week 2 - o Expert Systems o Natural Language Processing (NLP) o Computer Vision o Speech Recognition And Generation o Robotics o Neural Network o Virtual Reality APPLICATION AREAS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Week 2 - o Expert Systems o Natural Language Processing (NLP) o Computer Vision o Speech Recognition And Generation o Robotics o Neural Network o Virtual Reality APPLICATION AREAS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
LECTURE 1: OVERVIEW. CS 4100: Foundations of AI. Instructor: Robert Platt. (some slides from Chris Amato, Magy Seif El-Nasr, and Stacy Marsella)
 LECTURE 1: OVERVIEW CS 4100: Foundations of AI Instructor: Robert Platt (some slides from Chris Amato, Magy Seif El-Nasr, and Stacy Marsella) SOME LOGISTICS Class webpage: http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/rplatt/cs4100_spring2018/index.html
LECTURE 1: OVERVIEW CS 4100: Foundations of AI Instructor: Robert Platt (some slides from Chris Amato, Magy Seif El-Nasr, and Stacy Marsella) SOME LOGISTICS Class webpage: http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/rplatt/cs4100_spring2018/index.html
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Computational Vision and Picture. Plan. Computational Vision and Picture. Distal vs. proximal stimulus. Vision as an inverse problem
 Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Computational Vision and Picture Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer
Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Computational Vision and Picture Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer
Plan. Vision Solves Problems. Distal vs. proximal stimulus. Vision as an inverse problem. Unconscious inference (Helmholtz)
 The Art and Science of Depiction Vision Solves Problems Plan Vision as an cognitive process Computational theory of vision Constancy, invariants Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Intro to Visual
The Art and Science of Depiction Vision Solves Problems Plan Vision as an cognitive process Computational theory of vision Constancy, invariants Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Intro to Visual
CMSC 372 Artificial Intelligence. Fall Administrivia
 CMSC 372 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2017 Administrivia Instructor: Deepak Kumar Lectures: Mon& Wed 10:10a to 11:30a Labs: Fridays 10:10a to 11:30a Pre requisites: CMSC B206 or H106 and CMSC B231 or permission
CMSC 372 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2017 Administrivia Instructor: Deepak Kumar Lectures: Mon& Wed 10:10a to 11:30a Labs: Fridays 10:10a to 11:30a Pre requisites: CMSC B206 or H106 and CMSC B231 or permission
Multi-Robot Teamwork Cooperative Multi-Robot Systems
 Multi-Robot Teamwork Cooperative Lecture 1: Basic Concepts Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il 2 Why Robotics? Basic Science Study mechanics, energy, physiology, embodiment Cybernetics: the mind (rather than
Multi-Robot Teamwork Cooperative Lecture 1: Basic Concepts Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il 2 Why Robotics? Basic Science Study mechanics, energy, physiology, embodiment Cybernetics: the mind (rather than
Outline. Introduction to AI. Artificial Intelligence. What is an AI? What is an AI? Agents Environments
 Outline Introduction to AI ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture #1 What is an AI? Russell & Norvig, chapter 1 Agents s Russell & Norvig, chapter 2 ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence
Outline Introduction to AI ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture #1 What is an AI? Russell & Norvig, chapter 1 Agents s Russell & Norvig, chapter 2 ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence
What is AI? Artificial Intelligence. Acting humanly: The Turing test. Outline
 What is AI? Artificial Intelligence Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that act like humans Systems that act rationally Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Chapter 1 3 Outline Acting
What is AI? Artificial Intelligence Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that act like humans Systems that act rationally Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Chapter 1 3 Outline Acting
CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Outline
 CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Rajesh Rao (Instructor) Ravi Kiran (TA) http://www.cs.washington.edu/473 UW CSE AI faculty Goals of this course Logistics What is AI? Examples Challenges Outline 2
CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Rajesh Rao (Instructor) Ravi Kiran (TA) http://www.cs.washington.edu/473 UW CSE AI faculty Goals of this course Logistics What is AI? Examples Challenges Outline 2
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Perception: Pattern and object recognition. Chapter 3
 Perception: Pattern and object recognition Chapter 3 Pattern recognition theories How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Why is object perception so difficult for computers? Start simple: How
Perception: Pattern and object recognition Chapter 3 Pattern recognition theories How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Why is object perception so difficult for computers? Start simple: How
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Location-Based Activity Recognition
 Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Location-Based Activity Recognition Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz Activity Recognition Based on L. Liao, D. J. Patterson, D. Fox,
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Location-Based Activity Recognition Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz Activity Recognition Based on L. Liao, D. J. Patterson, D. Fox,
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
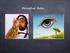
 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Texas Hold em Inference Bot Proposal. By: Brian Mihok & Michael Terry Date Due: Monday, April 11, 2005
 Texas Hold em Inference Bot Proposal By: Brian Mihok & Michael Terry Date Due: Monday, April 11, 2005 1 Introduction One of the key goals in Artificial Intelligence is to create cognitive systems that
Texas Hold em Inference Bot Proposal By: Brian Mihok & Michael Terry Date Due: Monday, April 11, 2005 1 Introduction One of the key goals in Artificial Intelligence is to create cognitive systems that
4D-Particle filter localization for a simulated UAV
 4D-Particle filter localization for a simulated UAV Anna Chiara Bellini annachiara.bellini@gmail.com Abstract. Particle filters are a mathematical method that can be used to build a belief about the location
4D-Particle filter localization for a simulated UAV Anna Chiara Bellini annachiara.bellini@gmail.com Abstract. Particle filters are a mathematical method that can be used to build a belief about the location
Optical Illusions ONLINE EYE CHECKUP TEST LINKS:
 ONLINE EYE CHECKUP TEST LINKS: Our eyes are our most important sensory organ. That's why optimum vision is an absolute must. When was the last time you had your eyes tested? Many people don't have their
ONLINE EYE CHECKUP TEST LINKS: Our eyes are our most important sensory organ. That's why optimum vision is an absolute must. When was the last time you had your eyes tested? Many people don't have their
TenMarks Curriculum Alignment Guide: EngageNY/Eureka Math, Grade 7
 EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
Intelligent Systems. Lecture 1 - Introduction
 Intelligent Systems Lecture 1 - Introduction In which we try to explain why we consider artificial intelligence to be a subject most worthy of study, and in which we try to decide what exactly it is Dr.
Intelligent Systems Lecture 1 - Introduction In which we try to explain why we consider artificial intelligence to be a subject most worthy of study, and in which we try to decide what exactly it is Dr.
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 9: Motion perception Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT. Ways to create movement
 PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang
 A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
Fundamentals of Computer Vision
 Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Fundamentals of Computer Vision COMP 558 Course notes for Prof. Siddiqi's class. taken by Ruslana Makovetsky (Winter 2012) What is computer vision?! Broadly speaking, it has to do with making a computer
Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion
 Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
Vision Research 42 (2002) 2731 2735 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Modulating motion-induced blindness with depth ordering and surface completion Erich W. Graf *, Wendy J. Adams, Martin Lages Department
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
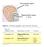 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
ES 492: SCIENCE IN THE MOVIES
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA ES 492: SCIENCE IN THE MOVIES LECTURE 5: ROBOTICS AND AI PRESENTER: HANNAH BECTON TODAY'S AGENDA 1. Robotics and Real-Time Systems 2. Reacting to the environment around them
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA ES 492: SCIENCE IN THE MOVIES LECTURE 5: ROBOTICS AND AI PRESENTER: HANNAH BECTON TODAY'S AGENDA 1. Robotics and Real-Time Systems 2. Reacting to the environment around them
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
Prof. Greg Francis 5/27/08
 Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Visual Perception : Motion IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Dr. Francis Lecture 11 Motion Motion is of tremendous importance for survival (Demo) Try to find the hidden bird in the figure below (http://illusionworks.com/hidden.htm)
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion
 Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
Chapter 8: Perceiving Motion Motion perception occurs (a) when a stationary observer perceives moving stimuli, such as this couple crossing the street; and (b) when a moving observer, like this basketball
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence (Sistemas Inteligentes) Pedro Cabalar Depto. Computación Universidade da Coruña, SPAIN Chapter 1. Introduction Pedro Cabalar (UDC) ( Depto. AIComputación Universidade da Chapter
Artificial Intelligence (Sistemas Inteligentes) Pedro Cabalar Depto. Computación Universidade da Coruña, SPAIN Chapter 1. Introduction Pedro Cabalar (UDC) ( Depto. AIComputación Universidade da Chapter
Elements of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems
 Elements of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems Master in Data Science for Economics, Business & Finance Nicola Basilico Dipartimento di Informatica Via Comelico 39/41-20135 Milano (MI) Ufficio
Elements of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems Master in Data Science for Economics, Business & Finance Nicola Basilico Dipartimento di Informatica Via Comelico 39/41-20135 Milano (MI) Ufficio
Digital Image Processing
 Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Part 1: Course Introduction Achim J. Lilienthal AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapters 1 & 2 2011-04-05 Contents 1. Introduction
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality Marc Erich Latoschik AI & VR Lab Artificial Intelligence Group University of Bielefeld Virtual Reality (or VR for short) Virtual Reality (or VR for short)
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality Marc Erich Latoschik AI & VR Lab Artificial Intelligence Group University of Bielefeld Virtual Reality (or VR for short) Virtual Reality (or VR for short)
CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
 CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Rajesh Rao (Instructor) Jennifer Hanson (TA) Evan Herbst (TA) http://www.cs.washington.edu/473 Based on slides by UW CSE AI faculty, Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew
CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Rajesh Rao (Instructor) Jennifer Hanson (TA) Evan Herbst (TA) http://www.cs.washington.edu/473 Based on slides by UW CSE AI faculty, Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline Course overview What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 Administrivia Class home page: http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs188 for
Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline Course overview What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 Administrivia Class home page: http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs188 for
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation
 Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation Hiroshi Ishiguro Department of Information Science, Kyoto University Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-01, Japan E-mail: ishiguro@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation Hiroshi Ishiguro Department of Information Science, Kyoto University Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-01, Japan E-mail: ishiguro@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Philosophical Foundations
 Philosophical Foundations Weak AI claim: computers can be programmed to act as if they were intelligent (as if they were thinking) Strong AI claim: computers can be programmed to think (i.e., they really
Philosophical Foundations Weak AI claim: computers can be programmed to act as if they were intelligent (as if they were thinking) Strong AI claim: computers can be programmed to think (i.e., they really
Outline. What is AI? A brief history of AI State of the art
 Introduction to AI Outline What is AI? A brief history of AI State of the art What is AI? AI is a branch of CS with connections to psychology, linguistics, economics, Goal make artificial systems solve
Introduction to AI Outline What is AI? A brief history of AI State of the art What is AI? AI is a branch of CS with connections to psychology, linguistics, economics, Goal make artificial systems solve
PERCEIVING SCENES. Visual Perception
 PERCEIVING SCENES Visual Perception Occlusion Face it in everyday life We can do a pretty good job in the face of occlusion Need to complete parts of the objects we cannot see Slide 2 Visual Completion
PERCEIVING SCENES Visual Perception Occlusion Face it in everyday life We can do a pretty good job in the face of occlusion Need to complete parts of the objects we cannot see Slide 2 Visual Completion
Goals of this Course. CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence. AI as Science. AI as Engineering. Dieter Fox Colin Zheng
 CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence Dieter Fox Colin Zheng www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/cse473/08au Goals of this Course To introduce you to a set of key: Paradigms & Techniques Teach you to identify
CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence Dieter Fox Colin Zheng www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/cse473/08au Goals of this Course To introduce you to a set of key: Paradigms & Techniques Teach you to identify
The Three Laws of Artificial Intelligence
 The Three Laws of Artificial Intelligence Dispelling Common Myths of AI We ve all heard about it and watched the scary movies. An artificial intelligence somehow develops spontaneously and ferociously
The Three Laws of Artificial Intelligence Dispelling Common Myths of AI We ve all heard about it and watched the scary movies. An artificial intelligence somehow develops spontaneously and ferociously
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: cs580
 Office: Nguyen Engineering Building 4443 email: zduric@cs.gmu.edu Office Hours: Mon. & Tue. 3:00-4:00pm, or by app. URL: http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ zduric/ Course: http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ zduric/cs580.html
Office: Nguyen Engineering Building 4443 email: zduric@cs.gmu.edu Office Hours: Mon. & Tue. 3:00-4:00pm, or by app. URL: http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ zduric/ Course: http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ zduric/cs580.html
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 19. Brightness illusions
 Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
The first topic I would like to explore is probabilistic reasoning with Bayesian
 Michael Terry 16.412J/6.834J 2/16/05 Problem Set 1 A. Topics of Fascination The first topic I would like to explore is probabilistic reasoning with Bayesian nets. I see that reasoning under situations
Michael Terry 16.412J/6.834J 2/16/05 Problem Set 1 A. Topics of Fascination The first topic I would like to explore is probabilistic reasoning with Bayesian nets. I see that reasoning under situations
CS 131 Lecture 1: Course introduction
 CS 131 Lecture 1: Course introduction Olivier Moindrot Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 olivierm@stanford.edu 1 What is computer vision? 1.1 Definition Two definitions
CS 131 Lecture 1: Course introduction Olivier Moindrot Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 olivierm@stanford.edu 1 What is computer vision? 1.1 Definition Two definitions
Manipulation. Manipulation. Better Vision through Manipulation. Giorgio Metta Paul Fitzpatrick. Humanoid Robotics Group.
 Manipulation Manipulation Better Vision through Manipulation Giorgio Metta Paul Fitzpatrick Humanoid Robotics Group MIT AI Lab Vision & Manipulation In robotics, vision is often used to guide manipulation
Manipulation Manipulation Better Vision through Manipulation Giorgio Metta Paul Fitzpatrick Humanoid Robotics Group MIT AI Lab Vision & Manipulation In robotics, vision is often used to guide manipulation
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Philosophy. AI Slides (5e) c Lin
 Philosophy 15 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 15 1 15 Philosophy 15.1 AI philosophy 15.2 Weak AI 15.3 Strong AI 15.4 Ethics 15.5 The future of AI AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 15
Philosophy 15 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 15 1 15 Philosophy 15.1 AI philosophy 15.2 Weak AI 15.3 Strong AI 15.4 Ethics 15.5 The future of AI AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 15
CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES?
 Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Academic year 2016/2017 Giorgio Fumera http://pralab.diee.unica.it fumera@diee.unica.it Pattern Recognition and Applications Lab Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Artificial Intelligence Academic year 2016/2017 Giorgio Fumera http://pralab.diee.unica.it fumera@diee.unica.it Pattern Recognition and Applications Lab Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
CS510: Image Computation. Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018
 CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
CS510: Image Computation Ross Beveridge Jan 16, 2018 Class Goals Prepare you to do research in computer vision Provide big picture (comparison to humans) Give you experience reading papers Familiarize
Domain-Specificity versus Expertise in Face Processing
 Domain-Specificity versus Expertise in Face Processing Dan O Shea and Peter Combs 18 Feb 2008 COS 598B Prof. Fei Fei Li Inferotemporal Cortex and Object Vision Keiji Tanaka Annual Review of Neuroscience,
Domain-Specificity versus Expertise in Face Processing Dan O Shea and Peter Combs 18 Feb 2008 COS 598B Prof. Fei Fei Li Inferotemporal Cortex and Object Vision Keiji Tanaka Annual Review of Neuroscience,
Outline. Artificial Neural Network Importance of ANN Application of ANN is Sports Science
 Advances of Neural Networks in Sports Science Aviroop Dutt Mazumder 13 th Aug, 2010 COSC - 460 Sports Science Outline Artificial Neural Network Importance of ANN Application of ANN is Sports Science Modeling
Advances of Neural Networks in Sports Science Aviroop Dutt Mazumder 13 th Aug, 2010 COSC - 460 Sports Science Outline Artificial Neural Network Importance of ANN Application of ANN is Sports Science Modeling
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes.
 CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes. Artificial Intelligence A branch of Computer Science. Examines how we can achieve intelligent
CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes. Artificial Intelligence A branch of Computer Science. Examines how we can achieve intelligent
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Artificial Intelligence Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Outline What is AI? A brief history The state of the art Chapter 1 2 What is AI? Systems that think like humans Systems that think rationally Systems that
Moon Illusion. (McCready, ; 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not
 Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Moon Illusion (McCready, 1997-2007; http://facstaff.uww.edu/mccreadd/index.html) 1. What is Moon Illusion and what it is not 2. Aparent distance theory (SD only) 3. Visual angle contrast theory (VSD) 4.
Contents 1 Motion and Depth
 Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
Contents 1 Motion and Depth 5 1.1 Computing Motion.............................. 8 1.2 Experimental Observations of Motion................... 26 1.3 Binocular Depth................................ 36 1.4
PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8
 Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
Motion 1 Perception (PSY 4204) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. PERCEIVING MOTION CHAPTER 8 Overview of Questions Why do some animals freeze in place when they sense danger? How do films create movement from still
