FEMTOSMART. Benefits. Features
|
|
|
- Barrie McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FEMTOSMART Extremely large space under the objective For in vivo studies Field upgradability Patented imaging technologies Flexible scanning methods Maximal photon collection Elevated, column-based body XYZ positioning Tilting objective High level of modularity Galvanometric, resonant, or both scanning possibilities Travelling detector system 3P ready transmission range upon request
2 FemtoS-Galvo/Technology Technology/FemtoS-Galvo The FemtoSmart series is the next step in Femtonics product evolution, fully customizable two-photon microscopes, which are primarily used in in vivo studies. Their special feature is the elevated body which can move in X, Y, and Z directions, providing ample room under the objective for optimal positioning of your sample. This feature makes them suitable for model organisms ranging from zebra fish larvae, through mice navigating in virtual reality to even non-human primates. Extreme positioning freedom Superior imaging technology Modularity The FemtoS-Galvo is a galvanometric scanner-based two-photon microscope which enables in vivo and in vitro functional imaging to be focused on the region of interest (ROI). The scanner consists of two galvanometer-based motor-driven mirrors, meaning that the focal spot can be positioned where required. The high accuracy and this positioning freedom support flexible approaches for ROI creation. In contrast to sampling all pixels in images, ROI scanning (e.g. along a predefined line) restricts scanning to the regions which are relevant for the scientist, resulting in faster recording, and elimination of background noise. This helps to reveal cellular signaling and action potentials. The column-based X-Y-Z moving body of the FemtoSmart houses the scanner unit, control circuits, and internal light path. The leg is 600 mm long and custom size is also available, and its footprint is only 250 mm 250 mm; the distance between the objective and the surface is 360 mm. The design enables the objective to move in a 50 mm range in the Z-direction and the microscope body can also move in 50 mm range in the XY directions around the base. The Tilting objective, as an upgrade module, can further increase mobility. The optomechanical design of FemtoSmart is based on the established technology of Femtonics. The fine-tuned optical construction allows imaging to a depth of 850 μm, and wavelength range from visible to the infrared regime allowing even 3p excitation. The high-quality scanners delivering the highest resolution currently available. Detection is performed by our patented travelling detector system, where the highest quality GaAsP PMTs and associated optical elements are mounted on the objective arm which helps to keep the photon collection ratio high. The microscope s modular nature allows us to assemble the components, and recombine and upgrade the system to perfectly fit the customer s needs. Multiple lasers can be built into the microscope, either for imaging or photoactivation. Galvo and/or resonant scanner direct the beam. The detection is performed by multiple high-sensitivity GaAsP photomultipliers. The system can be equipped with a lot of optional modules enabling it to be adapted for a wide range of biological applications. Key features For in vivo functional imaging in deep tissues Each cell body, axon, dendrite and spine can be measured separately Flexible imaging modes, patented solutions for fast imaging only on the regions of interest High signal to noise ratio Intelligent control software Advanced 2D scanning methods The advantages of the galvo scanner combined with the intelligent, user-friendly control software enables the user to use many scanning patterns covering the ROIs distributed across the field of view. These patterns have been developed based on the most frequent requests by neuroscientists. For example, multiple frame scanning focuses on cell bodies, multiple line scanning enables us to follow action potentials along dendrites, and random-access point scanning allows measurement or photostimulation of subcellular components of the highest temporal resolution. Many features of the software, such as real-time display, analysis functions, F/F calculations and integrated parallel data acquisition of electrical recordings promote greater understanding of the physiological processes under the focus of your research. raster multiple frame multiple line folded frame random-access point stimulus patterns
3 FemtoS-Galvo/Technology Applications/FemtoS-Galvo Multiple line scanning Photostimulus patterns Deep brain imaging Calcium imaging Multiple line scanning has been developed for researchers who want to resolve dendritic and even spine activity of neurons approaching near real-time measurement mode. During this scanning mode, the X and Y mirrors direct the laser beam flexible along straight lines or complex curves. The scanner spends most of its time collecting signals from these lines, while the intermediate sections between the lines are skipped. In this way, the scanning speed and the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the signals sampled from the multisite ROIs increases 3- to 4-fold compared to frame scanning. Uncaging, optogenetics, and other photostimulation techniques are also supported by our unique scanning patterns and their combinations. Random-access point scanning can be used for stimulation in femtoliter volumes near dendritic spines where the duration of the stimulation, can be set from microseconds to seconds precisely to the experiment. The evoked signals can be followed along the dendrite by line scanning near simultaneously with the photostimulation. The microsecond-scale switching time between the stimulation and imaging is achieved by using of a Pockels cell and gated detectors. Thanks to two-photon laser technology and our optical developments, you can study cell bodies and dendrites at a high spatial resolution down to a depth of 850 μm with no photodamage. The 3D slicer module of the control software implements XZ or YZ sectioning and projection of the Z-stacks and enables 2D visualization of 3D stacks projected to any of the three axes. The fast scanning speed on user-defined, separated regions ensures precise and repeatable measurements of rapid changes in the Ca 2+ -level of neurons and their dendrites. The ratio-imaging software tool offers algorithms for eliminating background noise, and determinates the relative fluorescence changes, displaying them as transient curves as a function of time. The batch analysis tool contains efficient tools for analyzing entire multi-roi measurement sets conveniently; it also implements the grouped analysis of imaging data at multiple regions. Folded frame scanning High signal-to-noise ratio This patented method enables imaging of a Subtle changes in the evoked signals can be confined area along a line, where the shape of revealed because of the following features: the selected regions can be straight or curved. scanning only the relevant part of the field-ofview, and skipping the background, result in a This advanced scanning method is useful for imaging single cell bodies in different regions of very high signal-to-noise ratio, the specimen, or following events along winding photon collection efficiency is enhanced thanks dendrites with their protrusions, even while the to our patented travelling detector system, tissue is moving. which uses the shortest possible optical path, the most sensitive GaAsP photomultipliers available (quantum efficiency >40%) collect scattered photons. Specification in vivo deep brain imaging down to 850 μm 800 μm 800 μm FOV (with a 20x obj.) 2D scanning modes point and random access point with 200 μs/point free hand line and multiple line: 40 lines/5 ms frame with 4.1 fps at 512 x 512 pixel, 750 μm x 750 μm folded frame, multiple folded frame pixel dwell time adjustable: 0.5 μs - 10 ms, pixel-based averaging minimized optical path length by patented travelling detector system non-descanned, ultrasensitive GaAsP PMT (>40% quantum efficiency) high signal-to-noise ratio simultaneous detection of multiple wavelength custom-designed optical elements for maximal transmission efficiency MATLAB-based control software with analysis and upgrade possibilities F/F, G/R calculation parallel recording and analysis of electrophysiological data CMOS camera compatibility with extended IR wavelength range Intravital imaging Parallel electrophysiology The infrared excitation laser can penetrate Hardware and software tools help parallel twophoton imaging and aligned electrophysiological thick specimens, enabling living cell behavior in intact tissues and organs to be visualized at recordings. Precise triggering the external high resolution for extended periods with no recording ensures time aligned measurement phototoxicity: essential for morphological studies. of the electrophysiology and imaging, providing The metaprotocol module of the control software different aspects for studying the neuronal cell and automates these measurements on a timescale network activity. Software module helps automatic of seconds by letting you run freely composed importing recorded traces for parallel analysis. sequences of image acquisition. Figure shows Figure shows calcium imaging and patch-clamp renal morphology (red: blood vessels, green: tubule walls, blue: nuclei, yellow: tubular cavities). recording in an OGB-1 and Alexa-594 filled hippocampal neuron.
4 FemtoS-Resonant/Technology Applications/FemtoS-Resonant 3D volume scanning Time-lapse imaging In the FemtoS-Resonant microscope, Femtonics combines high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging of living tissues by using a fast resonant scanner. Resonant-scanner-based raster scanning acquires images of the entire field-of-view ~5 times faster than galvanometric-based scanning: it is therefore the most appropriate choice for imaging the entire field-of-view at high frame rate. Key features Uninterrupted high-speed imaging The fast XY-scanning, combined with fast Z-movement, ensures near real-time measurement of a 3D volume which enables us to study activity changes in 3D cellular networks or the morphology of organs. The fast Z movement can be performed by a Piezo objective positioner or a Liquid lens objective. While two-photon excitation ensures deep penetration and fine spatial resolution, the high frame scanning rate of the resonant scanner provides high temporal resolution. This feature means that the microscope is suitable for measuring rapid events in living cells, neuronal networks, or other circuits. For in vivo high-speed functional imaging in deep tissues Rapid image acquisition Long-term measurements Time-lapse imaging 3D volume scanning upgrade Intelligent control software The resonant scanner consists of a fast oscillating mirror for x-axis deflection and a galvanometric mirror for y-axis sweep. Thanks to the 8 khz oscillating speed of the fast x mirror, the microscope is capable of gathering images at 31 frames per second for hours. High scanning rate with no image distortion The velocity of the resonant scanner is non-linear: the speed is different in the center and at the edges of the frame. In the microscope, Pockels cell limits the scanning range to that portion where the scanning velocity is near linear, avoiding photobleaching/photodamage at the two sides of the image. Scan electronics performs dynamic pixel dwelling for data linearization and to cancel out image distortion. Long-term measurements Photostimulation Specification in vivo deep brain imaging down to 850 μm 600 μm 600 μm FOV (with a 20x obj.) scanning modes raster scanning with 31 fps at 512x512 pixels and 500 fps at 512x32 pixels lines/sec (straight, parallel with x-axis) 3D volume scanning with 3 Hz by Piezo objective positioner dynamic pixel dwell time to avoid image distorsion minimized optical path length by patented travelling detector system non-descanned, ultrasensitive GaAsP PMT (>40% quantum efficiency) high signal-to-noise ratio simultaneous detection of multiple wavelength custom-designed optical elements for maximal transmission efficiency C++-based control software with analysis and upgrade possibilities dedicated software efficiently handling large datasets nearly unlimited measurement times F/F calculation parallel recording and analysis of electrophysiological data CMOS camera compatibility with extended IR wavelength range The high frame scanning rate and the unlimited video streaming combined with the possibility of automated measurement, support long-term studies such as following learning processes, memory retrieval, associative learning, development of model organisms, etc. The middle figure shows an early stage of the development of a zebrafish embryo, whose ontogenesis was followed and recorded over a day from the low cell state. Full-field illumination from an LED light source enables cell populations to be stimulated in different locations of a specimen while the resonant scanner simultaneously images the evoked signals. The selective stimulation of the cells can be ensured by targeted expression of photosensitive molecules such as channelrhodopsin or halorhodopsin (optogenetics).
5 FemtoS-Dual FemtoS-Bridge The FemtoS-Dual microscope contains both galvanometric and resonant scanners, providing all advantages of the two types of imaging technique. For example, follow activity on a large field of view using resonant scanner, then zoom to selected ROIs or finish with a high-resolution z-stack using the galvo scanner. GALVO DUAL Resonant The FemtoS-Bridge is a special edition of the FemtoSmart microscope which is designed to provide extreme freedom in positioning of the body. It involves all the advantages of the FemtoSmart series but it has been extended, making it particularly beneficial to studies which need a very large space for the sample or accessories by enabling functional brain imaging in head-fixed mice navigating in a large mobile cage. Photostimulation and imaging Using the two scanners function in tandem is a perfect solution for photostimulation. The galvanometric scanner directs the laser to cells or subcellular components selectively. The selectivity is established by scanning along arbitrary line patterns placed on cell bodies or dendritic segments. With the resonant scanner, you can follow the changes in the cells of a neural network collecting imaging data simultaneously by high-speed frame scanning of the surrounding area. Timing of photostimulation and gating of the detectors are controlled by protocols designed on user-friendly GUI. Unique features Stimulation along ROIs using spiral scanning pattern with galvo scanner on ChR2 expressing neurons Full field imaging by resonant scanner Offline ROI selection 200% ΔF/F 4 s Calcium responses from the selected ROIs The foot is replaced with a lifting apparatus which moves the head vertically. Moving range: 50 cm Coarse Z adjustment: 1 mm Fine adjustments: by the objective holding arm in a 50 mm range of the Z direction, Piezo objective positioner for moving the objective with fast Z positioning in a range of a few hundred micrometers, an XY actuator moves the body relative to the column in the X and Y directions (±25 mm range, step size: 1 μm), our Tilting objective further increases accessibility to the lateral parts of the brain.
6 FemtoSmart Product line/optional modules Vessel pattern visualization Green illumination Full field photostimulation LED light source Uncaging/Optogenetics Multiple beam path Optional modules/femtosmart Product line Free rotation of the objective Tilting objective Fast Z-stack and 3D imaging Piezo objective positioner Fast 3D imaging Liquid lens objective Green illumination from an Full-field illumination using a The optomechanical design of LED light source allows highcontrast visualization of blood molecules and cells to be more beams into the microscope, selected LED source allows the light path enables us to direct vessels, helping to navigate on stimulated over the whole FOV utilizing the same light path. We the surface of any organs under homogeneously. Combine this offer secondary, fine-tuned laser in vivo conditions and position a module with gated detectors to sources for a wide range of patch pipette for bulk loading or achieve millisecond switching biophotonics applications. patch clamping. between stimulation and imaging. excitation wavelength at nm ~100 μm penetration depth 3 sec switching time between camera and two-photon modes detection by CMOS camera adjustable brightness, contrast and gamma parameters equipped on the objective arm built-in PMT protection during operation high-contrast visualization precise overlap in XYZ between camera and twophoton recorded field of view locate your chronic imaging spot within the craniotomy VIS light stimulation by LED typical wavelengths: 430, 450, 480, 590 nm, others on special request precisely timed and highly repeatable impulses ~200 μm penetration depth PMT protection during the stimulation by built-in gating system software controlled equipped on the objective arm simultaneous stimulation over the entire FOV optimized for optogenetics studies: precise spatiotemporal activation of ChR2 and/or NpHR millisecond switching between stimulation and detection additional IR or CW laser(s) coupled to the existing light path light path optimized for all wavelengths full optical engineering photostimulation with IR or visible light flexible stimulation patterns supporting stimulation of selected regions two-photon uncaging studies visible light optogenetics: ChR2 activation with 473 nm laser NpHR activation with 561 nm laser The motorized tilting module A Piezo objective positioner The Liquid lens objective contains rotates the objective, giving a enables the microscope to a carefully chosen objective and higher level of freedom to reach change the focal point by a fast-focusing element which the sample from different angles. mechanically moving the utilizes electrically controlled The module also includes a Piezo objective. With this module the shape-changing membrane. objective positioner, ensuring microscope is able to collect This flexible membrane enables additional movement of the signals from different depths with the objective to switch quickly objective in the Z direction. up to 200 Hz, resolving activity in between focal planes. 180º rotation around the horizontal axis 100º rotation around the vertical axis speed of rotation: 4º/sec unidirectional repeatability: < 0.02 mrad (~2 μm) Z movement with piezo: up to 400 μm flexible objective positioning with high precision highly stable in all positions minimized optical path to the detectors fixed on the tilting unit useful for in vivo experiments, intravital imaging, and deep brain imaging in rodents or even non-human primates 3D samples. positions objectives in the Z direction with nanometer resolution travelling range up to 400 μm up to 200 Hz frequency in resonant mode millisecond step-and-settle any types of objectives can be attached no influence on the optical path 3D trajectory scanning using galvo scanner is able to collect signals from dendrites arbored in the 3D tissue fast enough to resolve biological activity 3D volume scanning using resonant or galvo scanners is able to collect signals from a 3D volume, revealing activity of the neural network or other cell groups fine positioning along the tilted axis when using tilting objective module focuses with nanometer precision 200 μm focal range 10 ms focal-plane switching time fast settling time transmission 90% at 800 nm aperture 10 mm comes with a 40 magnification Nikon objective no mechanical perturbation fast switch between the focal planes 3D volume scanning: is able to collect signals from a 3D volume, revealing activity of the neural network or other cell groups imaging at multiple tissue depths near simultaneously
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Optimized Bessel foci for in vivo volume imaging.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimized Bessel foci for in vivo volume imaging. (a) Images taken by scanning Bessel foci of various NAs, lateral and axial FWHMs: (Left panels) in vivo volume images of YFP + neurites
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimized Bessel foci for in vivo volume imaging. (a) Images taken by scanning Bessel foci of various NAs, lateral and axial FWHMs: (Left panels) in vivo volume images of YFP + neurites
Opterra. Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity. Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging
 Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
Life Science Instrumentation. New Generation. Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope. Alph
 Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Using Autofocus in NIS-Elements
 Using Autofocus in NIS-Elements Overview This technical note provides an overview of the available autofocus routines in NIS-Elements, and describes the necessary steps for using the autofocus functions.
Using Autofocus in NIS-Elements Overview This technical note provides an overview of the available autofocus routines in NIS-Elements, and describes the necessary steps for using the autofocus functions.
ChromoFlex. The flexibility of four colour multiphoton imaging. Experts in Electrophysiology & Imaging
 Experts in Electrophysiology & Imaging 1 Multiphoton Imaging ChromoFlex The flexibility of four colour multiphoton imaging www.scientifica.uk.com/chromoflex www.scientifica.uk.com 2 ChromoFlex Multiple
Experts in Electrophysiology & Imaging 1 Multiphoton Imaging ChromoFlex The flexibility of four colour multiphoton imaging www.scientifica.uk.com/chromoflex www.scientifica.uk.com 2 ChromoFlex Multiple
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 . Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics and characterization of our AO two-photon fluorescence microscope. (a) Essential components of our AO two-photon fluorescence microscope: Ti:Sapphire laser; optional
. Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics and characterization of our AO two-photon fluorescence microscope. (a) Essential components of our AO two-photon fluorescence microscope: Ti:Sapphire laser; optional
Rapid Adaptive Optical Recovery of Optimal Resolution over Large Volumes
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Rapid Adaptive Optical Recovery of Optimal Resolution over Large Volumes Kai Wang, Dan Milkie, Ankur Saxena, Peter Engerer, Thomas Misgeld, Marianne E. Bronner, Jeff Mumm, and Eric
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Rapid Adaptive Optical Recovery of Optimal Resolution over Large Volumes Kai Wang, Dan Milkie, Ankur Saxena, Peter Engerer, Thomas Misgeld, Marianne E. Bronner, Jeff Mumm, and Eric
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Microscopy Tracks Living Cells
 from photonics.com: 04/01/2012 http://www.photonics.com/article.aspx?aid=50654 Dynamic Phase-Shifting Microscopy Tracks Living Cells Dr. Katherine Creath, Goldie Goldstein and Mike Zecchino, 4D Technology
from photonics.com: 04/01/2012 http://www.photonics.com/article.aspx?aid=50654 Dynamic Phase-Shifting Microscopy Tracks Living Cells Dr. Katherine Creath, Goldie Goldstein and Mike Zecchino, 4D Technology
contents TABLE OF The SECOM platform Applications - sections Applications - whole cells Features Integrated workflow Automated overlay
 S E C O M TABLE OF contents The SECOM platform 4 Applications - sections 5 Applications - whole cells 8 Features 9 Integrated workflow 12 Automated overlay ODEMIS - integrated software Specifications 13
S E C O M TABLE OF contents The SECOM platform 4 Applications - sections 5 Applications - whole cells 8 Features 9 Integrated workflow 12 Automated overlay ODEMIS - integrated software Specifications 13
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM
 More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
LASU - Laser Applied Stimulation & Uncaging
 Built with neuroscience in mind Optogenetics & Uncaging 1 LASU - Laser Applied Stimulation & Uncaging Optogenetics & Uncaging www.scientifica.uk.com/lasu www.scientifica.uk.com 2 LASU - Laser Applied Stimulation
Built with neuroscience in mind Optogenetics & Uncaging 1 LASU - Laser Applied Stimulation & Uncaging Optogenetics & Uncaging www.scientifica.uk.com/lasu www.scientifica.uk.com 2 LASU - Laser Applied Stimulation
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules
 Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal
 Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal
 Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal Todays Goal: Introduce some additional functionalities of the Leica SP8 confocal HyD vs. PMT detectors Dye Assistant Scanning By
Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal Todays Goal: Introduce some additional functionalities of the Leica SP8 confocal HyD vs. PMT detectors Dye Assistant Scanning By
Simultaneous two-photon calcium imaging at different depths with spatiotemporal multiplexing
 Nature Methods Simultaneous two-photon calcium imaging at different depths with spatiotemporal multiplexing Adrian Cheng, J Tiago Gonçalves, Peyman Golshani, Katsushi Arisaka & Carlos Portera-Cailliau
Nature Methods Simultaneous two-photon calcium imaging at different depths with spatiotemporal multiplexing Adrian Cheng, J Tiago Gonçalves, Peyman Golshani, Katsushi Arisaka & Carlos Portera-Cailliau
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
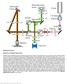 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8. 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software:
 Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
FemtoFAB. Femtosecond laser micromachining system. tel fax Konstitucijos ave. 23C LT Vilnius, Lithuania
 FemtoFAB Femtosecond laser micromachining system Konstitucijos ave. 23C LT-08105 Vilnius, Lithuania tel. +370 5 272 57 38 fax +370 5 272 37 04 info@wophotonics.com www.wophotonics.com INTRODUCTION FemtoFAB
FemtoFAB Femtosecond laser micromachining system Konstitucijos ave. 23C LT-08105 Vilnius, Lithuania tel. +370 5 272 57 38 fax +370 5 272 37 04 info@wophotonics.com www.wophotonics.com INTRODUCTION FemtoFAB
LMT F14. Cut in Three Dimensions. The Rowiak Laser Microtome: 3-D Cutting and Imaging
 LMT F14 Cut in Three Dimensions The Rowiak Laser Microtome: 3-D Cutting and Imaging The Next Generation of Microtomes LMT F14 - Non-contact laser microtomy The Rowiak laser microtome LMT F14 is a multi-purpose
LMT F14 Cut in Three Dimensions The Rowiak Laser Microtome: 3-D Cutting and Imaging The Next Generation of Microtomes LMT F14 - Non-contact laser microtomy The Rowiak laser microtome LMT F14 is a multi-purpose
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
Introduction of New Products
 Field Emission Electron Microscope JEM-3100F For evaluation of materials in the fields of nanoscience and nanomaterials science, TEM is required to provide resolution and analytical capabilities that can
Field Emission Electron Microscope JEM-3100F For evaluation of materials in the fields of nanoscience and nanomaterials science, TEM is required to provide resolution and analytical capabilities that can
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
Nikon. King s College London. Imaging Centre. N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING KING S COLLEGE LONDON
 N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
NIS-Elements C (For CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE A1) Instructions (Ver. 4.40)
 M487E 15.4.NF.17 (1/4) *M487EN17* NIS-Elements C (For CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE A1) Instructions (Ver. 4.40) Preface Thank you for purchasing the Nikon products. This instruction manual has been prepared for
M487E 15.4.NF.17 (1/4) *M487EN17* NIS-Elements C (For CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE A1) Instructions (Ver. 4.40) Preface Thank you for purchasing the Nikon products. This instruction manual has been prepared for
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, EL6000 fluorescent light source for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, EL6000 fluorescent light source for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm
 TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Section 1: Sound. Sound and Light Section 1
 Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Invitation for a walk through microscopy. Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner
 Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
A 4 Megapixel camera with 6.5μm pixels, Prime BSI captures highly. event goes undetected.
 PRODUCT DATASHEET Prime BSI SCIENTIFIC CMOS CAMERA Can a camera single-handedly differentiate your product against competitors? With the Prime BSI, the answer is a resounding yes. Instrument builders no
PRODUCT DATASHEET Prime BSI SCIENTIFIC CMOS CAMERA Can a camera single-handedly differentiate your product against competitors? With the Prime BSI, the answer is a resounding yes. Instrument builders no
NanoSpective, Inc Progress Drive Suite 137 Orlando, Florida
 TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes
 Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Swept-Field User Guide
 Swept-Field User Guide Note: for more details see the Prairie user manual at http://www.prairietechnologies.com/resources/software/prairieview.html Please report any problems to Julie Last (jalast@wisc.edu)
Swept-Field User Guide Note: for more details see the Prairie user manual at http://www.prairietechnologies.com/resources/software/prairieview.html Please report any problems to Julie Last (jalast@wisc.edu)
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
Nikon Instruments Europe
 Nikon Instruments Europe Recommendations for N-SIM sample preparation and image reconstruction Dear customer, We hope you find the following guidelines useful in order to get the best performance out of
Nikon Instruments Europe Recommendations for N-SIM sample preparation and image reconstruction Dear customer, We hope you find the following guidelines useful in order to get the best performance out of
 07 Setting Place a specimen, and select a fluorescence dye. The FV10i automatically selects the most suitable imaging conditions based on the fluorescence dye selection. Set Image mapping menu Just click
07 Setting Place a specimen, and select a fluorescence dye. The FV10i automatically selects the most suitable imaging conditions based on the fluorescence dye selection. Set Image mapping menu Just click
High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS
 CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS Prime BSI delivers the perfect balance between high resolution imaging and sensitivity with an optimized pixel design and
CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS Prime BSI delivers the perfect balance between high resolution imaging and sensitivity with an optimized pixel design and
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Ionscope SICM. About Ionscope. Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy. Ionscope A brand of Openiolabs Limited
 SICM About is a brand of openiolabs Ltd, headquartered in Cambridge UK, is the world-leader in (SICM), a rapidly emerging Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) technique which allows nanoscale topographical
SICM About is a brand of openiolabs Ltd, headquartered in Cambridge UK, is the world-leader in (SICM), a rapidly emerging Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) technique which allows nanoscale topographical
Systematic Workflow via Intuitive GUI. Easy operation accomplishes your goals faster than ever.
 Systematic Workflow via Intuitive GUI Easy operation accomplishes your goals faster than ever. 16 With the LEXT OLS4100, observation or measurement begins immediately once the sample is placed on the stage.
Systematic Workflow via Intuitive GUI Easy operation accomplishes your goals faster than ever. 16 With the LEXT OLS4100, observation or measurement begins immediately once the sample is placed on the stage.
BEAMAGE-3.0 KEY FEATURES BEAM DIAGNOSTICS AVAILABLE MODELS MAIN FUNCTIONS SEE ALSO ACCESSORIES. CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras
 BEAM DIAGNOSTICS BEAM DIAGNOSTICS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER DETECTORS POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras AVAILABLE MODELS
BEAM DIAGNOSTICS BEAM DIAGNOSTICS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER DETECTORS POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras AVAILABLE MODELS
APE Autocorrelator Product Family
 APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
High-sensitivity. optical molecular imaging and high-resolution digital X-ray. In-Vivo Imaging Systems
 High-sensitivity optical molecular imaging and high-resolution digital X-ray In-Vivo Imaging Systems In vivo imaging solutions available in several packages Carestream Molecular Imaging offers a selection
High-sensitivity optical molecular imaging and high-resolution digital X-ray In-Vivo Imaging Systems In vivo imaging solutions available in several packages Carestream Molecular Imaging offers a selection
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
ERS KEY FEATURES BEAM DIAGNOSTICS MAIN FUNCTIONS AVAILABLE MODEL. CMOS Beam Profiling Camera. 1 USB 3.0 for the Fastest Transfer Rates
 POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER DETECTORS CAMERA PROFIL- CMOS Beam Profiling Camera KEY FEATURES ERS 1 USB 3.0 for the
POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER DETECTORS CAMERA PROFIL- CMOS Beam Profiling Camera KEY FEATURES ERS 1 USB 3.0 for the
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain. Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology
 Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser
 880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser The goal of this lab is to give you experience aligning a laser and getting it to lase more-or-less from scratch. There is no write-up
880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser The goal of this lab is to give you experience aligning a laser and getting it to lase more-or-less from scratch. There is no write-up
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
High-speed 1-frame ms scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks
 High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Femtosecond to millisecond transient absorption spectroscopy: two lasers one experiment
 7 Femtosecond to millisecond transient absorption spectroscopy: two lasers one experiment 7.1 INTRODUCTION The essential processes of any solar fuel cell are light absorption, electron hole separation
7 Femtosecond to millisecond transient absorption spectroscopy: two lasers one experiment 7.1 INTRODUCTION The essential processes of any solar fuel cell are light absorption, electron hole separation
The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System
 he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
Multiphoton Detection Unit (MDU)
 Experts in Electrophysiology Microscope Equipment Multiphoton Detection Unit (MDU) For integration with the Scientifica SliceScope Pro motorised microscopy system 2 Multiphoton Detection Unit Two-photon
Experts in Electrophysiology Microscope Equipment Multiphoton Detection Unit (MDU) For integration with the Scientifica SliceScope Pro motorised microscopy system 2 Multiphoton Detection Unit Two-photon
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
Nikon AZ100. Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope. Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin. May 2017.
 Nikon AZ100 Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin May 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Hardware - Startup 2 3 Software/Operation 4 3.1 Multidimensional
Nikon AZ100 Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin May 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Hardware - Startup 2 3 Software/Operation 4 3.1 Multidimensional
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer
 Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Multiphoton confocal microscope. Multiphoton confocal microscope A1R MP
 Multiphoton confocal microscope Multiphoton confocal microscope A1R MP Nikon's provides deeper, faster and sharper imaging. The confocal microscope A1R, which has an excellent reputation for its high speed,
Multiphoton confocal microscope Multiphoton confocal microscope A1R MP Nikon's provides deeper, faster and sharper imaging. The confocal microscope A1R, which has an excellent reputation for its high speed,
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Information & Instructions
 KEY FEATURES 1. USB 3.0 For the Fastest Transfer Rates Up to 10X faster than regular USB 2.0 connections (also USB 2.0 compatible) 2. High Resolution 4.2 MegaPixels resolution gives accurate profile measurements
KEY FEATURES 1. USB 3.0 For the Fastest Transfer Rates Up to 10X faster than regular USB 2.0 connections (also USB 2.0 compatible) 2. High Resolution 4.2 MegaPixels resolution gives accurate profile measurements
Working Simultaneously. The Next Level of TIRF Microscopy. cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence
 cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Four individually aligned illumination beams for simultaneous multi-color TIRF imaging Working Simultaneously The Next Level of TIRF
cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Four individually aligned illumination beams for simultaneous multi-color TIRF imaging Working Simultaneously The Next Level of TIRF
OCT. Optical Coherence Tomography
 OCT Optical Coherence Tomography Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, non-destructive imaging technique that enables high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging of a wide range of highly
OCT Optical Coherence Tomography Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, non-destructive imaging technique that enables high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging of a wide range of highly
taccor Optional features Overview Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser
 taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System
 Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System Outline Opterra design overview Light Path Scan Modes Performance Application data Drosophila larva heart. Courtesy of Nikon
Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System Outline Opterra design overview Light Path Scan Modes Performance Application data Drosophila larva heart. Courtesy of Nikon
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Add CLUE to your SEM. High-efficiency CL signal-collection. Designed for your SEM and application. Maintains original SEM functionality
 Add CLUE to your SEM Designed for your SEM and application The CLUE family offers dedicated CL systems for imaging and spectroscopic analysis suitable for most SEMs. In addition, when combined with other
Add CLUE to your SEM Designed for your SEM and application The CLUE family offers dedicated CL systems for imaging and spectroscopic analysis suitable for most SEMs. In addition, when combined with other
Nikon A1R. Multi-Photon & Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope. Kyle Marchuk Adam Fries Jordan Briscoe Kaitlin Corbin. April 2017.
 Nikon A1R Multi-Photon & Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Kyle Marchuk Adam Fries Jordan Briscoe Kaitlin Corbin April 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Start-Up 2 3 Imaging 4 3.1 Sample Alignment...........................................
Nikon A1R Multi-Photon & Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Kyle Marchuk Adam Fries Jordan Briscoe Kaitlin Corbin April 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Start-Up 2 3 Imaging 4 3.1 Sample Alignment...........................................
Fiber Optic Device Manufacturing
 Precision Motion Control for Fiber Optic Device Manufacturing Aerotech Overview Accuracy Error (µm) 3 2 1 0-1 -2 80-3 40 0-40 Position (mm) -80-80 80 40 0-40 Position (mm) Single-source supplier for precision
Precision Motion Control for Fiber Optic Device Manufacturing Aerotech Overview Accuracy Error (µm) 3 2 1 0-1 -2 80-3 40 0-40 Position (mm) -80-80 80 40 0-40 Position (mm) Single-source supplier for precision
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
EnFocus Your Upgrade Path to High Performance Intrasurgical OCT
 Your Upgrade Path to High Performance Intrasurgical OCT is FDA 510(k) Cleared > Ultra HD OCT extends your microscope s potential with intrasurgical OCT BRILLIANT IMAGES, SUB-SURFACE KNOWLEDGE is an intrasurgical
Your Upgrade Path to High Performance Intrasurgical OCT is FDA 510(k) Cleared > Ultra HD OCT extends your microscope s potential with intrasurgical OCT BRILLIANT IMAGES, SUB-SURFACE KNOWLEDGE is an intrasurgical
Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano
 Sperm Cell Epithelial Cells I nner Ear Hair Cells I nner Ear Hair Cell Neurons E- Coli Bac teria Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano About ionscope About ionscope The ionscope scanning ion conductance
Sperm Cell Epithelial Cells I nner Ear Hair Cells I nner Ear Hair Cell Neurons E- Coli Bac teria Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano About ionscope About ionscope The ionscope scanning ion conductance
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
11Beamage-3. CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras
 11Beamage-3 CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras Key Features USB 3.0 FOR THE FASTEST TRANSFER RATES Up to 10X faster than regular USB 2.0 connections (also USB 2.0 compatible) HIGH RESOLUTION 2.2 MPixels resolution
11Beamage-3 CMOS Beam Profiling Cameras Key Features USB 3.0 FOR THE FASTEST TRANSFER RATES Up to 10X faster than regular USB 2.0 connections (also USB 2.0 compatible) HIGH RESOLUTION 2.2 MPixels resolution
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
648. Measurement of trajectories of piezoelectric actuators with laser Doppler vibrometer
 648. Measurement of trajectories of piezoelectric actuators with laser Doppler vibrometer V. Grigaliūnas, G. Balčiūnas, A.Vilkauskas Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania E-mail: valdas.grigaliunas@ktu.lt
648. Measurement of trajectories of piezoelectric actuators with laser Doppler vibrometer V. Grigaliūnas, G. Balčiūnas, A.Vilkauskas Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania E-mail: valdas.grigaliunas@ktu.lt
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
HoloMonitor M4. For powerful discoveries in your incubator
 HoloMonitor M4 For powerful discoveries in your incubator HoloMonitor offers unique imaging capabilities that greatly enhance our understanding of cell behavior, previously unachievable by other technologies
HoloMonitor M4 For powerful discoveries in your incubator HoloMonitor offers unique imaging capabilities that greatly enhance our understanding of cell behavior, previously unachievable by other technologies
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal. Quick-Start Guide
 Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal Quick-Start Guide Contents Start-up Preparing for Imaging Part 1 On the scope Part 2 Software interface Part 3 Heat & CO2 incubation Part 4 Other hardware options Shut-down
Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal Quick-Start Guide Contents Start-up Preparing for Imaging Part 1 On the scope Part 2 Software interface Part 3 Heat & CO2 incubation Part 4 Other hardware options Shut-down
Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy
 nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk
 Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer
 Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer 16/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Parts for the THz Kit... 3 1. Delay line... 4 2. Pulse generator and lock-in detector... 5 3. THz antennas... 6
Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer 16/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Parts for the THz Kit... 3 1. Delay line... 4 2. Pulse generator and lock-in detector... 5 3. THz antennas... 6
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
