ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF POROUS SILICON PREPARED BY PHOTOCHEMICAL ETCHING ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Vivian Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF POROUS SILICON PREPARED BY PHOTOCHEMICAL ETCHING A. M. Ahmmed 1, A. M. Alwan 1, N. M. Ahmed 2 1 School of Applied Science/ University of Technology, Baghdad-IRAQ 2 School of physics/ Universiti Sains Malaysia/ 11800/ Pinang ABSTRACT In this work, electrical properties of porous silicon (PS) structure fabricated by using the photochemical etching process in HF acid under different etching times was investigated. (111) n-type silicon wafers with two different resistivities (ρ 1 = 3.25 x 10-4 Ωcm and ρ 2 = Ωcm) were used. The wafers were etched in 40% HF acid by using 100 W quartz tungsten halogen lamp integral with ditchroic ellipsoidal mirror for two different etching times (t 1 = 1800 s and t 2 = 5400 s). The current-voltage characteristics for all Al/PS/n-Si/Al structures show a rectifying behavior with different values of ideality factor and barrier height. The forward and reverse current show Schottky-like behavior and the presence of an inflection point in reverse a characteristic is explained by energy band gap difference between porous silicon and crystalline silicon substrates. INTRODUCTION Porous silicon (PS) has been identified as a potential optoelectronic material, compatible with silicon technology after the discovery of strong room temperature photoluminescense (PL) from high porosity in 1990 [1]. Electriluminescense (EL) is also observed from a PS layer prepared by photochemical etching (Laser induced etching) and electrochemical etching under forward and reverse biasing [2-4]. PS consists of a network of nanometer-sized silicon regions surrounded by void space. Many groups of researchers studied the electrical properties of PS prepared by electrochemical etching. According to Dimitrov [5], the I-V characteristics of porous silicon prepared by electrochemical etching is due to the existence of Schottky Junction between metal and PS interface while Pulsford et al. [7] and Ray et al. [8] believed that the I-V characteristics are due to heterojunction between PS and its silicon substrate. M. Ben-Chorin [6] et al. discussed the band alignment of p-type PS heterojunction in the light of PS/bulk silicon interface behaving like a Schottky diode, where the PS itself plays the role of metal. The photochemical etching (laser induced-etching (L.I.E.) technique is electrodeless without external potential, photon source as high power density laser is used to supply the required holes in the irradiated area of silicon wafer to initiate the etching [9]. Spectroscopic investigations of PS prepared by L.I.E were established to determine the silicon nanocrystallites sizes, size distribution and PL spectral [10, 11]. In this study, the electrical properties of porous silicon prepared using this technique have been investigated for Al/PS/n-Si/Al structure. The structures are 160
2 based for different voltages and the resulting I-V characteristics have Schottky Junction-like behavior with different values of ideality factor and barrier height. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE Photochemical etching technique is used in this study to prepare PS layer. Detailed information of this technique can be found elsewhere [12]. A commercially available n- type (111) oriented silicon wafer of two different resistivities (ρ 1 = 3.25 x 10-4 Ωcm and ρ 2 = Ωcm) was rinsed with acetone and ethanol to remove grease and dirt and then immersed in electronic grade 40% HF acid. The mount of the wafer is in such a way that is explained in Ref. [12]. In this electrode less photochemical etching process, there was no applied bias. The light beam of quartz tungsten halogen lamp integral with dichroic ellipsoidal mirror, has been focused on a silicon wafer to a circular spot (1.13cm 2 area), the distance between the halogen lamp and the wafer about (4cm). Bubbles were observed during the etching process. Wafer were etching with different etching times, after which they were rinsed with ethanol and dried with nitrogen gas. The porous layer was formed on the side of wafer illuminated by halogen lamp. Al electrodes are thermally deposited on the (3 x 3 mm 2 ) area of the irradiated surface of the wafers and on all back surface of the wafer. Electrical measurements are established in dark condition. The side view of the final device is shown in Figure.(1). For current-voltage measurements, two Keithley (616) digital electrometer and (50V) power supply are used. C-V measurements are achieved using a Fluke PM 6306 programmable automatic RCL meter. During capacitance measurements, the reverse voltage is varied from 0 to 5 V and the frequency is maintained at 1 MHz. Aluminum Figure 1: Sectional-view of the final device. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION n-porous n-type si Aluminum I-V characteristics in dark conditions are done at room temperature on a number of Al/PS/n-Si/Al structures. Figure.(2) shows the I-V characteristics at two different etching times (t 1 = 1800 s and 5400 s) for silicon substrate resistivity of ρ 1. The characteristics show a rectifying behavior with different rectifying ratios. The forward part of the measured I-V characteristics is similar to a Schottky diode characteristics, and may be analyzed using thermionic emission model [13]. From the slope of the semi-log I-V curve (not shown here), the ideality factor is larger than unity. The values of ideality factor are interpreted in [5] where its relation with the interface 161
3 states and to the possible thin insulator layer presented at the metal semiconductor interface is given in the form: n = δ δqd s S (1) w i i where Ds is the density of localized states at the metal/ps boundary, w is the width of semiconductor space charge region and ε S and ε i are the dielectric constants of the interface and semiconductor region respectively. The I-V characteristics of Al/PS/n- Si/Al have been analyzed by a way similar to that described in [15]. We calculate the density of metal/porous silicon interface states by taking the values of ε S = ε i and δ = 25 o as in [14, 15]. The obtained values for the ideality factor and barrier height are close to those given in [5, 16] for porous silicon prepared by electrochemical etching. The dependence of the I-V characteristics on the etching time is related to the formation of pores of porous silicon, where the pore diameter in porous silicon structure may be increased by increasing the etching time where the etching power is constant, which is led to increase the resistivity of porous silicon due to the carrier trapping at pores wall [6]; also the increasing of the etching time from t = 1800 s to t = 5400 s will lead to increase the thicknesses of the PS layer, where, a simple investigation under optical microscopy, allowed us to estimate the thickness of light-etched PS layer. We estimate a maximum depth of about 44 µm for etching time 1800 s and 78 µm for etching time 5400 s. the increasing in PS layer thickness will lead to increase the resistivity of PS layer [17]. Figure.(3) shows the current-voltage characteristics at two used resistivities (ρ 1 and ρ 2 ) and etching time of 1800 s. The dependence of (I-V) characteristics on the wafer resistivity is related to the effective charge carrier in PS layer after the etching process at a constant etching time and etching power. Results from I-V characteristics are summarized in Table (1). The reverse saturation current (I S ) is also tabulated in this table. When we apply a forward bias to metal-semiconductor junction (metal side is positive and semiconductor side is negative), electron energy levels on the semiconductor side will increase by q(v bi -V), where V bi denotes to the built-in voltage and V denotes to the applied forward bias voltage between metal and semiconductor. Therefore the Fermi energy level of semiconductor should be increased by the value of ev as well. Thus, barrier height for electrons passing from semiconductor to metal will be decreased by ev. As a result, current flow from semiconductor to metal will be increased by exp(ev/kt) at a constant etching time. 162
4 80 50 Dark Current Density (ma/cm 2 t = 1800 s 60 t = 5400 s Dark Current Density (ma/cm ohm.cm ohm.cm Bias Voltage (V) -50 Bias Voltage (V) Figure (2): I-V characteristics of Al/PS/n-Si/Al structure at 1800 s etching time for two used resistivities. The reverse current-voltage characteristics Table (1) of Al/PS/n-Si/Al structures are sensitive to the preparation condition for the wafers. The dark current is related to the recombination-generation process associated with space charge region of Schottky Junction formed between the metal electrode and the porous silicon layer [5]. This current is observed even in the case of almost (PtSi-Si) Schottky diodes [18, 19]. The values of the current due to recombination-generation process depends only on the width of the depleted space-charge region (w) and described by: J = B V (2) V bi where ni 2 s B = q τ o qn D o 1/ 2 (2) 163
5 Table (1): Values obtained from I-V measurements. Etching time (s) Resistivity Ωcm I S (µa/cm 2 ) n Φ bn (ev) Ds(cm -2 ev -1 ) x x x x x Reciprocal of C 2 against V is plotted in Figure.(4). The plot is illustrated as a straight line which indicates an abrupt type. The effective carrier density (N D ) and depletion layer width (W) that is calculated from this curve is listed in Table (2) t = 1800 s t =5400 s C -2 x10 21 (F -2.cm 4 ) 2.00 C -2 x10 21 (F -2.cm 4 ) 1.00 (a) Reverse Voltage (V) (b) Reverse Voltage (V) 0.15 t = 1800 s C -2 x10 21 (F -2.cm 4 ) (c) Reverse Voltage (V) Figure 3: C -2 -V plot; (a) and (b) for ρ 1 and (c) for ρ
6 Table :2 Values obtained from C-V measurements Etching time (s) Resistivity Ωcm N(cm -3 ) W ( µ m) x x x x x CONCLUSIONS The Al/PS/n-Si/Al structure in this work is a Schottky-like junction with high ideality factor due to the formation of high density of interface states at PS boundaries. The junction is an abrupt type. REFERENCES [1]. Canham, L. (1990); Appl. Phys. Lett. 57, [2]. Koshida, N. and Koyama, H. (1992); Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 347. [3]. Halimaoui, A., Oules, C. and Bomchil, G. (1991); Appl. Phys. Lett. 59, 304. [4]. Yamamoto, N., Sumiya, A. and Takai, H. (2000) Mate. Sci. and Eng. B6-70, 205. [5]. Dimotrov, D. (1995); Phys. Rev. B51, [6]. Chorin, M., Moller, F. and Koch, F. (1995); J. Appl. Phys. 77(9), [7]. Pulsford, N., Rikken, J. and Kessener, Y., Lous, E. and Verhuizen, A. (1994); J. Appl. Phys.75, 636. [8]. Ray, A., Mabrook, M. and Nabok, A. (1998); J. Appl. Phys.84(6), [9]. Choy, C. and Cheah, K. (1995); J. Appl. Phys. A(61), 45. [10]. S. Mavi, H., Rasheed, B. and Shukla, A. (2001); J. Non-crystalline solid. 286, 162. [11]. Mavi, H., Rasheed, B. and Jain, K. (2002); J. Phys. D., Appl. Phys. 34, 292. [12]. Ahmed, A., Alwan, A. and Alrawi, N., Proceedings of XXII Regional Conference on solid State Science and Technology, December, 2005, Malaysia. [13]. Sze, S. (1980); Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 2 nd ed. Wiley, New York, ch. 12. [14]. Card, H. and Rhoderick, E. (1971); J. Phys. D., Appl. Phys. 4, [15]. Card, H. (1974); Solid State Commun. 14, [16]. Maruska, H., Namavar, F. and Kalhoran, N. (1992); Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, [17]. Anderson, R., Muller, R. and Tobias, C. (1991); J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, [18]. Zheng, J., Liau, K. and Shen, W. (1992); Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, [19]. Wittmer, M. (1990); Phys. Rev. B42,
Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes
 Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes Abstract We report the fabrication and testing of a GaAs-based high-speed resonant cavity enhanced (RCE) Schottky photodiode. The
Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes Abstract We report the fabrication and testing of a GaAs-based high-speed resonant cavity enhanced (RCE) Schottky photodiode. The
Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices Kay Thi Soe 1, Moht Moht Than 2 and Win Win Thar 3 Abstract This study
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Investigation of Photovoltaic Properties of In:ZnO/SiO 2 /p- Si Thin Film Devices Kay Thi Soe 1, Moht Moht Than 2 and Win Win Thar 3 Abstract This study
Lecture 18: Photodetectors
 Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Photovoltaic Properties of Pb(Zr x,ti 1-x )O 3 /n-si and Pb(Zr x,ti 1-x )O 3 /n-ps Hetero junction Solar Cell
 International Journal of Physics, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 3, 82-86 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/3/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijp-5-3-3 Photovoltaic Properties of Pb(Zr
International Journal of Physics, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 3, 82-86 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/3/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijp-5-3-3 Photovoltaic Properties of Pb(Zr
NAME: Last First Signature
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit
 9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS
 CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 9.1 INTRODUCTION The phthalocyanines are a class of organic materials which are generally thermally stable and may be deposited as thin films by vacuum evaporation
CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 9.1 INTRODUCTION The phthalocyanines are a class of organic materials which are generally thermally stable and may be deposited as thin films by vacuum evaporation
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Author(s) Osamu; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri,
 TitleCryogenic InSb detector for radiati Author(s) Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Osamu; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS (2 2533-2536 Issue Date 2002-07 URL
TitleCryogenic InSb detector for radiati Author(s) Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Osamu; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS (2 2533-2536 Issue Date 2002-07 URL
Unless otherwise specified, assume room temperature (T = 300 K).
 ECE 3040 Dr. Doolittle Homework 4 Unless otherwise specified, assume room temperature (T = 300 K). 1) Purpose: Understanding p-n junction band diagrams. Consider a p-n junction with N A = 5x10 14 cm -3
ECE 3040 Dr. Doolittle Homework 4 Unless otherwise specified, assume room temperature (T = 300 K). 1) Purpose: Understanding p-n junction band diagrams. Consider a p-n junction with N A = 5x10 14 cm -3
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
 LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). The emission intensity as a function of the diode
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). The emission intensity as a function of the diode
Title detector with operating temperature.
 Title Radiation measurements by a detector with operating temperature cryogen Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Author(s) Osamu; Murase, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Masaki Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS
Title Radiation measurements by a detector with operating temperature cryogen Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Author(s) Osamu; Murase, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Masaki Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS
CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a pn junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a pn junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
value of W max for the device. The at band voltage is -0.9 V. Problem 5: An Al-gate n-channel MOS capacitor has a doping of N a = cm ;3. The oxi
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
Depletion width measurement in an organic Schottky contact using a Metal-
 Depletion width measurement in an organic Schottky contact using a Metal- Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Arash Takshi, Alexandros Dimopoulos and John D. Madden Department of Electrical and Computer
Depletion width measurement in an organic Schottky contact using a Metal- Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Arash Takshi, Alexandros Dimopoulos and John D. Madden Department of Electrical and Computer
Problem 4 Consider a GaAs p-n + junction LED with the following parameters at 300 K: Electron diusion coecient, D n = 25 cm 2 =s Hole diusion coecient
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 7 This homework is due on November 8. Problem 1 An optical power density of 1W/cm 2 is incident on a GaAs sample. The photon energy is 2.0 ev and there is
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 7 This homework is due on November 8. Problem 1 An optical power density of 1W/cm 2 is incident on a GaAs sample. The photon energy is 2.0 ev and there is
Electronic devices-i. Difference between conductors, insulators and semiconductors
 Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Dynamics of Charge Carriers in Silicon Nanowire Photoconductors Revealed by Photo Hall. Effect Measurements. (Supporting Information)
 Dynamics of Charge Carriers in Silicon Nanowire Photoconductors Revealed by Photo Hall Effect Measurements (Supporting Information) Kaixiang Chen 1, Xiaolong Zhao 2, Abdelmadjid Mesli 3, Yongning He 2*
Dynamics of Charge Carriers in Silicon Nanowire Photoconductors Revealed by Photo Hall Effect Measurements (Supporting Information) Kaixiang Chen 1, Xiaolong Zhao 2, Abdelmadjid Mesli 3, Yongning He 2*
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination
 Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
In-nSiC schottky photodiode ; Fabrication and Study
 Khalid Z. Yahiya* Ammar H. Jraiz** & Abdulla Khudiar Abass** Received on:9/3/2008 Accepted on:6/3/2008 Abstract In the present work, schottky photodiode have been mode on n-type SiC by depositing of thin
Khalid Z. Yahiya* Ammar H. Jraiz** & Abdulla Khudiar Abass** Received on:9/3/2008 Accepted on:6/3/2008 Abstract In the present work, schottky photodiode have been mode on n-type SiC by depositing of thin
Electrical Characterization
 Listing and specification of characterization equipment at ISC Konstanz 30.05.2016 Electrical Characterization µw-pcd (Semilab) PV2000 (Semilab) - spatially resolved minority charge carrier lifetime -diffusion
Listing and specification of characterization equipment at ISC Konstanz 30.05.2016 Electrical Characterization µw-pcd (Semilab) PV2000 (Semilab) - spatially resolved minority charge carrier lifetime -diffusion
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
 LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). Using a photodetector, the emission intensity
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). Using a photodetector, the emission intensity
Organic Electronics. Information: Information: 0331a/ 0442/
 Organic Electronics (Course Number 300442 ) Spring 2006 Organic Field Effect Transistors Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp Information: Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/course/c30 http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/course/c30
Organic Electronics (Course Number 300442 ) Spring 2006 Organic Field Effect Transistors Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp Information: Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/course/c30 http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/course/c30
Proposal of Novel Collector Structure for Thin-wafer IGBTs
 12 Special Issue Recent R&D Activities of Power Devices for Hybrid ElectricVehicles Research Report Proposal of Novel Collector Structure for Thin-wafer IGBTs Takahide Sugiyama, Hiroyuki Ueda, Masayasu
12 Special Issue Recent R&D Activities of Power Devices for Hybrid ElectricVehicles Research Report Proposal of Novel Collector Structure for Thin-wafer IGBTs Takahide Sugiyama, Hiroyuki Ueda, Masayasu
High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors
 High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors Veerendra Dhyani 1, and Samaresh Das 1* 1 Centre for Applied Research in Electronics, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi-110016,
High-Speed Scalable Silicon-MoS 2 P-N Heterojunction Photodetectors Veerendra Dhyani 1, and Samaresh Das 1* 1 Centre for Applied Research in Electronics, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi-110016,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Photon-triggered nanowire transistors Jungkil Kim, Hoo-Cheol Lee, Kyoung-Ho Kim, Min-Soo Hwang, Jin-Sung Park, Jung Min Lee, Jae-Pil So, Jae-Hyuck Choi,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Photon-triggered nanowire transistors Jungkil Kim, Hoo-Cheol Lee, Kyoung-Ho Kim, Min-Soo Hwang, Jin-Sung Park, Jung Min Lee, Jae-Pil So, Jae-Hyuck Choi,
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism;
 Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Low-field behaviour of source-gated transistors
 Low-field behaviour of source-gated transistors J. M. Shannon, R. A. Sporea*, Member, IEEE, S. Georgakopoulos, M. Shkunov, Member, IEEE, and S. R. P. Silva Manuscript received February 5, 2013. The work
Low-field behaviour of source-gated transistors J. M. Shannon, R. A. Sporea*, Member, IEEE, S. Georgakopoulos, M. Shkunov, Member, IEEE, and S. R. P. Silva Manuscript received February 5, 2013. The work
King Mongkut s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Bangkok 10520, Thailand b Thai Microelectronics Center (TMEC), Chachoengsao 24000, Thailand
 Materials Science Forum Online: 2011-07-27 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 695, pp 569-572 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.695.569 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland DEFECTS STUDY BY ACTIVATION ENERGY
Materials Science Forum Online: 2011-07-27 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 695, pp 569-572 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.695.569 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland DEFECTS STUDY BY ACTIVATION ENERGY
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits 2nd Devices
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective The Devices The Diode The diodes are rarely explicitly used in modern integrated circuits However, a MOS transistor contains at least two reverse biased
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective The Devices The Diode The diodes are rarely explicitly used in modern integrated circuits However, a MOS transistor contains at least two reverse biased
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Review of Semiconductor Physics
 Review of Semiconductor Physics k B 1.38 u 10 23 JK -1 a) Energy level diagrams showing the excitation of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resultant free electron can freely
Review of Semiconductor Physics k B 1.38 u 10 23 JK -1 a) Energy level diagrams showing the excitation of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resultant free electron can freely
Lecture 16 - Metal-Semiconductor Junction (cont.) October 9, 2002
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Fall 2002 Lecture 16-1 Lecture 16 - Metal-Semiconductor Junction (cont.) October 9, 2002 Contents: 1. Schottky diode 2. Ohmic contact Reading assignment:
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Fall 2002 Lecture 16-1 Lecture 16 - Metal-Semiconductor Junction (cont.) October 9, 2002 Contents: 1. Schottky diode 2. Ohmic contact Reading assignment:
Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices
 В. Jayant Baliga Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices 4y Spri ringer Contents Preface vii Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ideal and Typical Power Switching Waveforms 3 1.2 Ideal and Typical Power Device
В. Jayant Baliga Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices 4y Spri ringer Contents Preface vii Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ideal and Typical Power Switching Waveforms 3 1.2 Ideal and Typical Power Device
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells
 LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
MSE 410/ECE 340: Electrical Properties of Materials Fall 2016 Micron School of Materials Science and Engineering Boise State University
 MSE 410/ECE 340: Electrical Properties of Materials Fall 2016 Micron School of Materials Science and Engineering Boise State University Practice Final Exam 1 Read the questions carefully Label all figures
MSE 410/ECE 340: Electrical Properties of Materials Fall 2016 Micron School of Materials Science and Engineering Boise State University Practice Final Exam 1 Read the questions carefully Label all figures
photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited by
 Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
Solid State Devices- Part- II. Module- IV
 Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS
 SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS Erik C. Garnett, Craig Peters, Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui and Mike McGehee Stanford Univeristy, Department of Materials Science, Stanford, CA, USA ABSTRACT Silicon nanowire
SILICON NANOWIRE HYBRID PHOTOVOLTAICS Erik C. Garnett, Craig Peters, Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui and Mike McGehee Stanford Univeristy, Department of Materials Science, Stanford, CA, USA ABSTRACT Silicon nanowire
semiconductor p-n junction Potential difference across the depletion region is called the built-in potential barrier, or built-in voltage:
 Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
Chapter four The Equilibrium pn Junction The Electric field will create a force that will stop the diffusion of carriers reaches thermal equilibrium condition Potential difference across the depletion
- Near Field Scanning Optical Microscopy - Electrostatic Force Microscopy - Magnetic Force Microscopy
 - Near Field Scanning Optical Microscopy - Electrostatic Force Microscopy - Magnetic Force Microscopy Yongho Seo Near-field Photonics Group Leader Wonho Jhe Director School of Physics and Center for Near-field
- Near Field Scanning Optical Microscopy - Electrostatic Force Microscopy - Magnetic Force Microscopy Yongho Seo Near-field Photonics Group Leader Wonho Jhe Director School of Physics and Center for Near-field
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
Solid State Device Fundamentals
 Solid State Device Fundamentals 4.4. Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) ENS 463 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 4N101b 1 Field-effect transistor (FET)
Solid State Device Fundamentals 4.4. Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) ENS 463 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 4N101b 1 Field-effect transistor (FET)
Instruction manual and data sheet ipca h
 1/15 instruction manual ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Instruction manual and data sheet ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Broad area interdigital photoconductive THz antenna with microlens array and hyperhemispherical silicon
1/15 instruction manual ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Instruction manual and data sheet ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Broad area interdigital photoconductive THz antenna with microlens array and hyperhemispherical silicon
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic illustration of fabrication procedure of MoS2/h- BN/graphene heterostructures. a, c d Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic illustration of fabrication procedure of MoS 2 /hon a 300- BN/graphene heterostructures. a, CVD-grown b, Graphene was patterned into graphene strips by oxygen monolayer
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic illustration of fabrication procedure of MoS 2 /hon a 300- BN/graphene heterostructures. a, CVD-grown b, Graphene was patterned into graphene strips by oxygen monolayer
THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES
 THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES Thermionic and gaseous state (vacuum tube) diodes Thermionic diodes are thermionic-valve devices (also known as vacuum tubes, tubes, or valves), which are arrangements
THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES Thermionic and gaseous state (vacuum tube) diodes Thermionic diodes are thermionic-valve devices (also known as vacuum tubes, tubes, or valves), which are arrangements
Solar-energy conversion and light emission in an atomic monolayer p n diode
 Solar-energy conversion and light emission in an atomic monolayer p n diode Andreas Pospischil, Marco M. Furchi, and Thomas Mueller 1. I-V characteristic of WSe 2 p-n junction diode in the dark The Shockley
Solar-energy conversion and light emission in an atomic monolayer p n diode Andreas Pospischil, Marco M. Furchi, and Thomas Mueller 1. I-V characteristic of WSe 2 p-n junction diode in the dark The Shockley
10/14/2009. Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell
 PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
Tests of monolithic CMOS SOI pixel detector prototype INTPIX3 MOHAMMED IMRAN AHMED. Supervisors Dr. Henryk Palka (IFJ-PAN) Dr. Marek Idzik(AGH-UST)
 Internal Note IFJ PAN Krakow (SOIPIX) Tests of monolithic CMOS SOI pixel detector prototype INTPIX3 by MOHAMMED IMRAN AHMED Supervisors Dr. Henryk Palka (IFJ-PAN) Dr. Marek Idzik(AGH-UST) Test and Measurement
Internal Note IFJ PAN Krakow (SOIPIX) Tests of monolithic CMOS SOI pixel detector prototype INTPIX3 by MOHAMMED IMRAN AHMED Supervisors Dr. Henryk Palka (IFJ-PAN) Dr. Marek Idzik(AGH-UST) Test and Measurement
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
Introduction to Photovoltaics
 Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
Introduction to Photovoltaics PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 24, 2015 Only solar energy Of all the possible sources
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell?
 What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
Study of irradiated 3D detectors. University of Glasgow, Scotland. University of Glasgow, Scotland
 Department of Physics & Astronomy Experimental Particle Physics Group Kelvin Building, University of Glasgow Glasgow, G12 8QQ, Scotland Telephone: ++44 (0)141 339 8855 Fax: +44 (0)141 330 5881 GLAS-PPE/2002-20
Department of Physics & Astronomy Experimental Particle Physics Group Kelvin Building, University of Glasgow Glasgow, G12 8QQ, Scotland Telephone: ++44 (0)141 339 8855 Fax: +44 (0)141 330 5881 GLAS-PPE/2002-20
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2011. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201101677 Contact Resistance and Megahertz Operation of Aggressively Scaled
Copyright WILEY VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2011. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201101677 Contact Resistance and Megahertz Operation of Aggressively Scaled
THE METAL-SEMICONDUCTOR CONTACT
 THE METAL-SEMICONDUCTOR CONTACT PROBLEM 1 To calculate the theoretical barrier height, built-in potential barrier, and maximum electric field in a metal-semiconductor diode for zero applied bias. Consider
THE METAL-SEMICONDUCTOR CONTACT PROBLEM 1 To calculate the theoretical barrier height, built-in potential barrier, and maximum electric field in a metal-semiconductor diode for zero applied bias. Consider
Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in
 Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in semiconductor material Pumped now with high current density
Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in semiconductor material Pumped now with high current density
Integrated High Speed VCSELs for Bi-Directional Optical Interconnects
 Integrated High Speed VCSELs for Bi-Directional Optical Interconnects Volodymyr Lysak, Ki Soo Chang, Y ong Tak Lee (GIST, 1, Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712, Korea, T el: +82-62-970-3129, Fax: +82-62-970-3128,
Integrated High Speed VCSELs for Bi-Directional Optical Interconnects Volodymyr Lysak, Ki Soo Chang, Y ong Tak Lee (GIST, 1, Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712, Korea, T el: +82-62-970-3129, Fax: +82-62-970-3128,
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 16
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 16 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 16.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 16 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 16.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Supporting Information. Vertical Graphene-Base Hot-Electron Transistor
 Supporting Information Vertical Graphene-Base Hot-Electron Transistor Caifu Zeng, Emil B. Song, Minsheng Wang, Sejoon Lee, Carlos M. Torres Jr., Jianshi Tang, Bruce H. Weiller, and Kang L. Wang Department
Supporting Information Vertical Graphene-Base Hot-Electron Transistor Caifu Zeng, Emil B. Song, Minsheng Wang, Sejoon Lee, Carlos M. Torres Jr., Jianshi Tang, Bruce H. Weiller, and Kang L. Wang Department
Effect of Silicon Nanowire on Crystalline Silicon Solar Cell Characteristics
 Journal of Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials https://jufgnsm.ut.ac.ir Vol. 49, No.1, June 2016, pp. 43-47 Print SSN: 2423-6845 Online SSN: 2423-6837 DO: 10.7508/jufgnsm.2016.01.07 Effect of
Journal of Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials https://jufgnsm.ut.ac.ir Vol. 49, No.1, June 2016, pp. 43-47 Print SSN: 2423-6845 Online SSN: 2423-6837 DO: 10.7508/jufgnsm.2016.01.07 Effect of
Front-Wall Illumination of Spray-Deposited PbS-Si HJ Detector. Kadhim A. Hubeatir* Received on: Accepted on:
 Front-Wall Illumination of Spray-Deposited PbS-Si HJ Detector Kadhim A. Hubeatir* Received on: Accepted on: ABSTRACT (n-p) PbS-Si HJ detector has been fabricated by pyrolytic spraying of PbS heterolayer
Front-Wall Illumination of Spray-Deposited PbS-Si HJ Detector Kadhim A. Hubeatir* Received on: Accepted on: ABSTRACT (n-p) PbS-Si HJ detector has been fabricated by pyrolytic spraying of PbS heterolayer
UV/EUV CONTINUOUS POSITION SENSOR
 UV/EUV CONTINUOUS POSITION SENSOR ODD-SXUV-DLPSD FEATURES Submicron position resolution Stable response after exposure to UV/EUV 5 mm x 5 mm active area TO-8 windowless package RoHS ELECTRO-OPTICAL CHARACTERISTICS
UV/EUV CONTINUOUS POSITION SENSOR ODD-SXUV-DLPSD FEATURES Submicron position resolution Stable response after exposure to UV/EUV 5 mm x 5 mm active area TO-8 windowless package RoHS ELECTRO-OPTICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Nanoscale Systems for Opto-Electronics
 Nanoscale Systems for Opto-Electronics 675 PL intensity [arb. units] 700 Wavelength [nm] 650 625 600 5µm 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95 Energy [ev] 2.00 2.05 1 Nanoscale Systems for Opto-Electronics Lecture 5 Interaction
Nanoscale Systems for Opto-Electronics 675 PL intensity [arb. units] 700 Wavelength [nm] 650 625 600 5µm 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95 Energy [ev] 2.00 2.05 1 Nanoscale Systems for Opto-Electronics Lecture 5 Interaction
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES by J. P. Colinge Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis C. A. Colinge Department of Electrical
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES by J. P. Colinge Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis C. A. Colinge Department of Electrical
Forward bias operation of irradiated silicon detectors A.Chilingarov Lancaster University, UK
 1 st Workshop on Radiation hard semiconductor devices for very high luminosity colliders, CERN, 28-30 November 2001 Forward bias operation of irradiated silicon detectors A.Chilingarov Lancaster University,
1 st Workshop on Radiation hard semiconductor devices for very high luminosity colliders, CERN, 28-30 November 2001 Forward bias operation of irradiated silicon detectors A.Chilingarov Lancaster University,
Analysis of the Current-voltage Curves of a Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 Thin-film Solar Cell Measured at Different Irradiation Conditions
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 14, No. 4, December 2010, pp. 321-325 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2010.14.4.321 Analysis of the Current-voltage Curves of a Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 Thin-film Solar Cell Measured
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 14, No. 4, December 2010, pp. 321-325 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2010.14.4.321 Analysis of the Current-voltage Curves of a Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 Thin-film Solar Cell Measured
Intrinsic Semiconductor
 Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits
 Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Research Article Room Temperature Direct Band Gap Emission from Ge p-i-n Heterojunction Photodiodes
 OptoElectronics Volume 22, Article ID 96275, 4 pages doi:.55/22/96275 Research Article Room Temperature Direct Band Gap Emission from Ge p-i-n Heterojunction Photodiodes E. Kasper, M. Oehme, T. Arguirov,
OptoElectronics Volume 22, Article ID 96275, 4 pages doi:.55/22/96275 Research Article Room Temperature Direct Band Gap Emission from Ge p-i-n Heterojunction Photodiodes E. Kasper, M. Oehme, T. Arguirov,
Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography
 Proceedings of the Korea Nuclear Society Autumn Meeting Seoul, Korea, October 2001 Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography S.W Kwak 1), H.K Kim 1), Y. S Kim 1), S.C Jeon 1), G.
Proceedings of the Korea Nuclear Society Autumn Meeting Seoul, Korea, October 2001 Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography S.W Kwak 1), H.K Kim 1), Y. S Kim 1), S.C Jeon 1), G.
Physics 160 Lecture 5. R. Johnson April 13, 2015
 Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
Supporting Information. Silicon Nanowire - Silver Indium Selenide Heterojunction Photodiodes
 Supporting Information Silicon Nanowire - Silver Indium Selenide Heterojunction Photodiodes Mustafa Kulakci 1,2, Tahir Colakoglu 1, Baris Ozdemir 3, Mehmet Parlak 1,2, Husnu Emrah Unalan 2,3,*, and Rasit
Supporting Information Silicon Nanowire - Silver Indium Selenide Heterojunction Photodiodes Mustafa Kulakci 1,2, Tahir Colakoglu 1, Baris Ozdemir 3, Mehmet Parlak 1,2, Husnu Emrah Unalan 2,3,*, and Rasit
Study and Measurement of the Main Parameters of a Laser quadrant Detector
 Cairo University National Institute of Laser Enhanced Sciences Laser Sciences and Interactions Study and Measurement of the Main Parameters of a Laser quadrant Detector By Eng. Mohamed Abd-Elfattah Abd-Elazim
Cairo University National Institute of Laser Enhanced Sciences Laser Sciences and Interactions Study and Measurement of the Main Parameters of a Laser quadrant Detector By Eng. Mohamed Abd-Elfattah Abd-Elazim
The Effect of He-Ne and Diode Lasers on the Electrical Characteristics of Silicon Diode
 American Journal of Optics and Photonics 2018; 6(1): 8-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop doi: 10.11648/j.ajop.20180601.12 ISSN: 2330-8486 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8494 (Online) The Effect of He-Ne
American Journal of Optics and Photonics 2018; 6(1): 8-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop doi: 10.11648/j.ajop.20180601.12 ISSN: 2330-8486 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8494 (Online) The Effect of He-Ne
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS
 Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
Grant Soehnel* and Anthony Tanbakuchi
 Simulation and experimental characterization of the point spread function, pixel saturation, and blooming of a mercury cadmium telluride focal plane array Grant Soehnel* and Anthony Tanbakuchi Sandia National
Simulation and experimental characterization of the point spread function, pixel saturation, and blooming of a mercury cadmium telluride focal plane array Grant Soehnel* and Anthony Tanbakuchi Sandia National
Today s Outline - January 25, C. Segre (IIT) PHYS Spring 2018 January 25, / 26
 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 HW #2 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today
Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Outline - January 25, 2018 HW #2 C. Segre (IIT) PHYS 570 - Spring 2018 January 25, 2018 1 / 26 Today
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NPHOTON.212.11 Supplementary information Avalanche amplification of a single exciton in a semiconductor nanowire Gabriele Bulgarini, 1, Michael E. Reimer, 1, Moïra Hocevar, 1 Erik P.A.M. Bakkers,
DOI: 1.138/NPHOTON.212.11 Supplementary information Avalanche amplification of a single exciton in a semiconductor nanowire Gabriele Bulgarini, 1, Michael E. Reimer, 1, Moïra Hocevar, 1 Erik P.A.M. Bakkers,
Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials
 Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials Kjeld Pedersen Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, AAU SEMPEL Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics
Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials Kjeld Pedersen Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, AAU SEMPEL Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline:
 ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
Microscopic Basis for the Mechanism of Carrier Dynamics in an Operating p-n Junction Examined by using Light-Modulated Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Microscopic Basis for the Mechanism of Carrier Dynamics in an Operating p-n Junction Examined by using Light-Modulated Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy Shoji Yoshida, Yuya Kanitani, Ryuji Oshima, Yoshitaka
Microscopic Basis for the Mechanism of Carrier Dynamics in an Operating p-n Junction Examined by using Light-Modulated Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy Shoji Yoshida, Yuya Kanitani, Ryuji Oshima, Yoshitaka
Simulation of silicon based thin-film solar cells. Copyright Crosslight Software Inc.
 Simulation of silicon based thin-film solar cells Copyright 1995-2008 Crosslight Software Inc. www.crosslight.com 1 Contents 2 Introduction Physical models & quantum tunneling Material properties Modeling
Simulation of silicon based thin-film solar cells Copyright 1995-2008 Crosslight Software Inc. www.crosslight.com 1 Contents 2 Introduction Physical models & quantum tunneling Material properties Modeling
CONTENTS. 2.2 Schrodinger's Wave Equation 31. PART I Semiconductor Material Properties. 2.3 Applications of Schrodinger's Wave Equation 34
 CONTENTS Preface x Prologue Semiconductors and the Integrated Circuit xvii PART I Semiconductor Material Properties CHAPTER 1 The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 1.0 Preview 1 1.1 Semiconductor Materials
CONTENTS Preface x Prologue Semiconductors and the Integrated Circuit xvii PART I Semiconductor Material Properties CHAPTER 1 The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 1.0 Preview 1 1.1 Semiconductor Materials
Design of High Performance Lateral Schottky Structures using Technology CAD
 Design of High Performance Lateral Schottky Structures using Technology CAD A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Master of Science (Research) by Linga Reddy
Design of High Performance Lateral Schottky Structures using Technology CAD A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Master of Science (Research) by Linga Reddy
EDC Lecture Notes UNIT-1
 P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
P-N Junction Diode EDC Lecture Notes Diode: A pure silicon crystal or germanium crystal is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. There are not enough free electrons and holes in an intrinsic semi-conductor
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 17 Mar 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 17 Mar 2005 arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.optics] 17 Mar 2005](/thumbs/73/69354164.jpg) Optical modulation at around 1550 nm in a InGaAlAs optical waveguide containing a In- GaAs/AlAs resonant tunneling diode J. M. L. Figueiredo a), A. R. Boyd, C. R. Stanley, and C. N. Ironside Department
Optical modulation at around 1550 nm in a InGaAlAs optical waveguide containing a In- GaAs/AlAs resonant tunneling diode J. M. L. Figueiredo a), A. R. Boyd, C. R. Stanley, and C. N. Ironside Department
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram
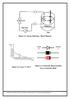 Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
The current density at a forward bias of 0.9 V is J( V) = 8:91 10 ;13 exp 0:06 = 9: :39=961:4 Acm ; 1: 10 ;8 exp 0:05 The current is dominated b
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 000 EECS 30 Solutions to Homework 6 Problem 1 Two dierent processes are used to fabricate a Si p-n diode. The rst process results in a electron-hole recombination time via impurities
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 000 EECS 30 Solutions to Homework 6 Problem 1 Two dierent processes are used to fabricate a Si p-n diode. The rst process results in a electron-hole recombination time via impurities
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) 1. JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET)
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
Radio-frequency scanning tunneling microscopy
 doi: 10.1038/nature06238 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION Radio-frequency scanning tunneling microscopy U. Kemiktarak 1,. Ndukum 2, K.C. Schwab 2, K.L. Ekinci 3 1 Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston,
doi: 10.1038/nature06238 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION Radio-frequency scanning tunneling microscopy U. Kemiktarak 1,. Ndukum 2, K.C. Schwab 2, K.L. Ekinci 3 1 Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston,
Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 11 Detectors
 Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 11 Detectors Warriors of the Net Detector Technologies MSM (Metal Semiconductor Metal) PIN Layer Structure Semiinsulating GaAs Contact InGaAsP p 5x10 18 Absorption InGaAs
Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 11 Detectors Warriors of the Net Detector Technologies MSM (Metal Semiconductor Metal) PIN Layer Structure Semiinsulating GaAs Contact InGaAsP p 5x10 18 Absorption InGaAs
Lecture 4. pn Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 pn junctions 1-1
 Lecture 4 n Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 n junctions 1-1 Agenda Continue n junctions Equilibrium (zero bias) Deletion rejoins Built-in otential Reverse and forward bias I-V characteristics Bias
Lecture 4 n Junctions (Diodes) Wednesday 27/9/2017 n junctions 1-1 Agenda Continue n junctions Equilibrium (zero bias) Deletion rejoins Built-in otential Reverse and forward bias I-V characteristics Bias
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification
 Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Physics of Waveguide Photodetectors with Integrated Amplification J. Piprek, D. Lasaosa, D. Pasquariello, and J. E. Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa
Introduction to Electronic Devices
 Introduction to Electronic Devices (Course Number 300331) Fall 2006 Field Effect Transistors (FETs) Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/dknipp/
Introduction to Electronic Devices (Course Number 300331) Fall 2006 Field Effect Transistors (FETs) Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/dknipp/
A Study on the Electrical Characteristic Analysis of c-si Solar Cell Diodes
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.12, NO.1, MARCH, 212 http://dx.doi.org/1.5573/jsts.212.12.1.59 A Study on the Electrical Characteristic Analysis of c-si Solar Cell Diodes Pyungho Choi,
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.12, NO.1, MARCH, 212 http://dx.doi.org/1.5573/jsts.212.12.1.59 A Study on the Electrical Characteristic Analysis of c-si Solar Cell Diodes Pyungho Choi,
