Chapter 9. Amplitude Modulation
|
|
|
- Gerard Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9. Amplitude Modulation 1
2 Goals Modulate and demodulate the double sideband-suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) amplitude modulation (AM) signals. Investigate the effects of frequency and phase errors on the demodulation performance. Modulate and demodulate AM signals by using the sampling and band pass filter (BPF) technique.
3 Double side-band suppressed carrier(dsb-sc) Amplitude modulations(am) DSB-SC, DSB-LC, SSB, VSB, etc. DSB-SC Modulated signal (tt)=ff tt cos(ωω cc tt) ff tt : information signal cos ωω cc tt : carrier signal, ωω cc = carrier frequency. Transmitter(modulator) structure ff tt (tt)=ff tt cos(ωω cc tt) cos ωω cc tt Spectrum of DSB-SC F tt = F tt = F ff tt cos(ωω cc tt) = 1 FF ωω + ωω cc + 1 FF ωω ωω cc Recall that multiplying sinusoid = frequency shift 3
4 Double side-band suppressed carrier(dsb-sc) DSB-SC Receiver (demodulator) structure (tt)=ff tt cos(ωω cc tt) gg(tt) LPF 1 ff tt : demodulated signal [CH19.B9] Proof: cos ωω cc tt :local carrier signal gg tt = tt cos ωω cc tt = ff tt cos(ωω cc tt) = ff(tt) 1+cos(ωω cctt) = 1 ff tt + 1 ff tt cos(ωω cctt) GG(ωω)= 1 FF ωω FF ωω ωω cc FF ωω + ωω cc Here, let us define LPF[x]: LPF[x] Ideal(Perfectly flat magnitude response within BW, no delay) LPF output of x. Then, LPF[GG(ωω)]= 1 FF ωω FF ωω ωω cc = 1 FF ωω FF ωω + ωω cc LPF gg tt = LPF 1 ff tt + 1 ff tt cos(ωω cctt) = 1 ff(tt) 4
5 Waveforms and Spectra of DSB-SC cos ωω cc tt LPF [CH9.1F4~1F6]If the BW of LPF is larger than W, noise power in the demodulated signal increases. [CH9.1F4~1F6]If the BW of LPF is smaller than W, the demodulated information is distorted. 5
6 Effect of phase error What if there exists a phase error between the carrier and the local carrier? Say, local carrier =cos ωω cc tt + θθ not cos ωω cc tt. Then, gg tt = tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ = ff tt cos(ωω cc tt)cos ωω cc tt + θθ = ff(tt) 1 cos ωω cctt + θθ + cos θθ = 1 ff tt cos ωω cctt + θθ + 1 ff tt cos θθ [CH9.A4] the demodulated signal(lpf output in the receiver) is given as: LPF gg tt = LPF 1 ff(tt) cos ωω cctt + θθ + 1 ff(tt)cos θθ =LPF 1 ff(tt) cos ωω cctt + θθ +LPF 1 ff(tt)cos θθ = 1 ff tt cos(θθ) Phase error results in decreased amplitude of the demodulated signal by the factor of cos(θθ). Special case: if θθ = ππ, then the signal disappears. 6
7 Effect of phase error [CH9.B]Consider the background noise nn tt is added to the received signal ff tt cos(ωω cc tt): Then, the multiplier output in the receiver gg tt = ff tt cos ωω cc tt + nn(tt) cos ωω cc tt + θθ = ff tt cos ωω cc tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ + nn(tt) cos ωω cc tt + θθ nn tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ = the noise component in gg tt. We denote nn θθ tt = nn tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ. [CH9.B10a] ACF of nn θθ tt IF ττ=0, RR nnθθ ττ = 0 = lim lim TT TT TT TT TT nn tt cos ωωcc tt+θθ dddd TT TT Two sample cases of nn θθ tt nn tt cos ωωcc tt+θθ nn tt cos ωω cc tt+θθ dddd =Power of nn θθ tt nn tt TT θθ = 0 = θθ = ππ/3 cos ωω cc tt + θθ nn θθ tt = nn tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ These samples illustrate that Power of nn θθ tt = Power of nn tt Power of cos(ωωtt+θθ), where power of cos(ωωtt+θθ) =1/ irrespective of θθ. RR nnθθ ττ = 0 =0.5 RR nn ττ = 0 7
8 Effect of phase error [CH9.B10a] (continued) ACF of nn θθ tt RR nnθθ ττ = Correlation between nn tt cos ωω cc tt + θθ and nn tt + ττ cos(ωω cc (tt + 8
9 Effect of phase error Demodulated signal (LPF output) = signal term + noise term = 1 ff tt cos(θθ) + LPF[nn θθ tt ] Signal amplitude decreases by the factor of cos θθ Signal power decreases by the factor of cos θθ On the other hand, noise power is constant irrespective of θθ [CH9.B4] Signal to Noise power Ratio (SNR) Signal power SNR(θθ) = Noise power =cos θθ SNR(θθ = 0) 1 Power of ff tt cos(θθ) = Power of LPF[nn θθ tt ] = cos θθ Power of 1 ff tt Power of LPF[nn θθ tt ] Phase error results in SNR decrease by the factor of cos θθ [CH9.B5] SNR loss =cos θθ =10llllll 10 cos θθ db 9
10 Effect of frequency error Now we consider the case when local carrier =cos ωω cc + ωω tt not cos ωω cc tt. We can rewrite local carrier = cos ωω cc tt + ωωtt =cos ωω cc tt + θθ where θθ= ωωtt. This implies that the frequency error results in linearly increasing phase error. [CH9.C1] So, we only need to change θθ into ωωtt in all the derivations for the phase error case. For example : demodulated signal= 1 ff tt cos( ωωtt) So, Signal to Noise power Ratio (SNR) SNR( ωωtt) =cos ωωtt SNR ωω = 0 SNR is time varying according to cos ωωtt. [CH9.C,C3,C6,C7] Even with a very tiny frequency error, cos ωωtt periodically changes from 0 to 1. [CH9.C,C3,C6,C7] Whenever cos ωωtt approaches 0, SNR instantaneously becomes 0. Critical problem! 10
11 Generating AM signal without Oscillator To generate carrier signal cos(ωω cc tt), we need an oscillator which is expensive. [CH9.3B] DSB-SC is equal to frequency shifting to center frequencies = ±ωω cc Recall, in chapter 7, frequency shifting is possible by sampling and BPF technique if we properly set the sampling frequency and properly design BPF. Sampling of ff tt by a periodic signal pp(tt) BPF nω 0 P1 ω 0 P n P 0 P 1 nω P 0 P 1 ω P n 0 0 BPF output =Spectrum of DSB-SC nω 0 P 0 P1 Pn BPF output spectrum=pp nn XX ωω + nnωω 0 + PP nn XX ωω nnωω 0 BPF output signal= ff(tt) PP nn cos nnωω 0 tt + θθ PPnn = DSB-SC modulated signal with a carrier signal = PP nn cos nnωω 0 tt + θθ PPnn [CH9.3B4] Parameter setting Condition 1: nnωω 0 =carrier frequency ωω cc, n=positive integer Condition : The sampling frequency ωω 0 Bandwidth of ff tt. Possible sampling frequency ωω 0 SSSSSSSSSSSS oooooo oooo ωω cc, ωω cc cc cc 3 4 under the condition 11
Chapter 10. Quadrature Multiplexing and Frequency Division Multiplexing
 Chapter 10. Quadrature Multiplexing and Frequency Division Multiplexing 1 Goals Design a modulation and demodulation system for quadrature multiplexing (QM) amplitude modulation (AM). Design a frequency
Chapter 10. Quadrature Multiplexing and Frequency Division Multiplexing 1 Goals Design a modulation and demodulation system for quadrature multiplexing (QM) amplitude modulation (AM). Design a frequency
ANGLE MODULATION. U1. PHASE AND FREQUENCY MODULATION For angle modulation, the modulated carrier is represented by
 [4.1] ANGLE MODULATION U1. PHASE AND FREQUENCY MODULATION For angle modulation, the modulated carrier is represented by xx cc (tt) = AA cccccc[ωω cc tt + φφ(tt)] (1.1) Where A ω c are constants the phase
[4.1] ANGLE MODULATION U1. PHASE AND FREQUENCY MODULATION For angle modulation, the modulated carrier is represented by xx cc (tt) = AA cccccc[ωω cc tt + φφ(tt)] (1.1) Where A ω c are constants the phase
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad
 Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Communication Engineering I Lab (EELE 3170) Eng. Adam M. Hammad EXPERIMENT #5 DSB-SC AND SSB MODULATOR Theory The amplitude-modulated signal is
The performance of AM and FM receivers. Editor: Xuanfeng Li Teacher: Prof. Xiliang Luo
 The performance of AM and FM receivers Editor: Xuanfeng Li Teacher: Prof. Xiliang Luo The performance of AM receivers using Envelop Detection In a full AM signal, both sidebands and the carrier wave are
The performance of AM and FM receivers Editor: Xuanfeng Li Teacher: Prof. Xiliang Luo The performance of AM receivers using Envelop Detection In a full AM signal, both sidebands and the carrier wave are
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
ELE636 Communication Systems
 ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals
 Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Manasvi Grover Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Maninder Bir Singh Gulshan Electronics and Communications Department Northern
Amplitude Modulation Manasvi Grover Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Maninder Bir Singh Gulshan Electronics and Communications Department Northern
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis
 CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators
 55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems
 Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems 1. The diodes and capacitors in the circuit shown are ideal. The voltage v(t) across the diode DD 1 is CC 1 DD 2 cos(ωωωω) AC DD 1 CC 1 (a) cos(ωωωω) 1 (b) sin(ωωωω)
Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems 1. The diodes and capacitors in the circuit shown are ideal. The voltage v(t) across the diode DD 1 is CC 1 DD 2 cos(ωωωω) AC DD 1 CC 1 (a) cos(ωωωω) 1 (b) sin(ωωωω)
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems
 CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
CME312- LAB Manual DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Experiment 6. Experiment 6. Experiment. DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation
 Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
multiplier input Env. Det. LPF Y (Vertical) VCO X (Horizontal)
 Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
Spectrum Analyzer Objective: The aim of this project is to realize a spectrum analyzer using analog circuits and a CRT oscilloscope. This interface circuit will enable to use oscilloscopes as spectrum
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
EE 464 Short-Time Fourier Transform Fall and Spectrogram. Many signals of importance have spectral content that
 EE 464 Short-Time Fourier Transform Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter 4.9. and Spectrogram Many signals of importance have spectral content that changes with time. Let xx(nn), nn = 0, 1,, NN 1 1 be a discrete-time
EE 464 Short-Time Fourier Transform Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter 4.9. and Spectrogram Many signals of importance have spectral content that changes with time. Let xx(nn), nn = 0, 1,, NN 1 1 be a discrete-time
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Music 171: Amplitude Modulation
 Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
Microphonics. T. Powers
 Microphonics T. Powers What is microphonics? Microphonics is the time domain variation in cavity frequency driven by external vibrational sources. A 1.5 GHz structure 0.5 m long will change in frequency
Microphonics T. Powers What is microphonics? Microphonics is the time domain variation in cavity frequency driven by external vibrational sources. A 1.5 GHz structure 0.5 m long will change in frequency
1-B.P. Lathi, Modern Digital and Communication Systems, Fourth Edition, Oxfodr university press, 2009.
 Items : 1-Introduction to Communication Systems 2-Amplitude Modulation 3- Angle Modulation 4-Detectors and Receivers. 5- Pulse Modulation. 6-Noise in Communication Systems 7- Transmission Line Theory.
Items : 1-Introduction to Communication Systems 2-Amplitude Modulation 3- Angle Modulation 4-Detectors and Receivers. 5- Pulse Modulation. 6-Noise in Communication Systems 7- Transmission Line Theory.
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
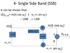 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
 EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
ELG3175: Introduction to Communication Systems. Laboratory II: Amplitude Modulation
 Introduction: ELG3175: Introduction to Communication Systems Laboratory II: Amplitude Modulation In this lab, we shall investigate some fundamental aspects of the conventional AM and DSB-SC modulation
Introduction: ELG3175: Introduction to Communication Systems Laboratory II: Amplitude Modulation In this lab, we shall investigate some fundamental aspects of the conventional AM and DSB-SC modulation
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems
 EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
Studying Noise Contributions in Nonlinear Vector Network Analyzer (NVNA) Measurements
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Studying Noise Contributions in Nonlinear Vector Network Analyzer (NVNA) Measurements Feng Tianyang September 2012 Master s Thesis in Telecommunications
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Studying Noise Contributions in Nonlinear Vector Network Analyzer (NVNA) Measurements Feng Tianyang September 2012 Master s Thesis in Telecommunications
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Problem Sheet for Amplitude Modulation
 Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Accurate Power Conversion Measurements on High Power Motor Drives. Presented by: Ian Walker GMW Associates
 Accurate Power Conversion Measurements on High Power Motor Drives Presented by: Ian Walker GMW Associates ian@gmw.com Motor & Drive Systems; January 21, 2016 Interconnections for the test of a low power
Accurate Power Conversion Measurements on High Power Motor Drives Presented by: Ian Walker GMW Associates ian@gmw.com Motor & Drive Systems; January 21, 2016 Interconnections for the test of a low power
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications
 EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
EEM 306 Introduction to Communications Lecture 5 Department o Electrical and Electronics Engineering Anadolu University April 8, 2014 Lecture 5 1/20 Last Time Bandpass Systems Phase and Group Delay Introduction
1.5 The voltage V is given as V=RI, where R and I are resistance matrix and I current vector. Evaluate V given that
 Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
b) discrete-time iv) aperiodic (finite energy)
 EE 464 Frequency Analysis of Signals and Systems Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter. Study suggestion: Use Matlab to plot several of the signals and their DTFT in the examples to follow. Some types of signal
EE 464 Frequency Analysis of Signals and Systems Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter. Study suggestion: Use Matlab to plot several of the signals and their DTFT in the examples to follow. Some types of signal
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS. College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY RUTGERS College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:322 Principles of Communications Systems Spring Problem Set 3 1. Discovered Angle
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
ECE 421 Introduction to Signal Processing Project 1 - Solutions
 1. (10 credits) Given, xx oooo (tt) = cos (2ππFF cc tt) xx iiii (tt) = cos (2ππππππ) ECE 421 Introduction to Signal Processing Project 1 - Solutions Dror Baron, Spring 2017 The AM modulated output satisfies,
1. (10 credits) Given, xx oooo (tt) = cos (2ππFF cc tt) xx iiii (tt) = cos (2ππππππ) ECE 421 Introduction to Signal Processing Project 1 - Solutions Dror Baron, Spring 2017 The AM modulated output satisfies,
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation
 Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
German Jordanian University. Department of Communication Engineering. Digital Communication Systems Lab. CME 313-Lab. Experiment 8
 German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 8 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 8 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
Jean-Pierre Braun obtained the B.E. degree from the Ecole d'ingénieurs de Genève, Switzerland, in 1980; the M.E.M. degree from the University of
 Jean-Pierre Braun obtained the B.E. degree from the Ecole d'ingénieurs de Genève, Switzerland, in 1980; the M.E.M. degree from the University of Technology Sydney, Australia, in 1993; and the M.Eng.Sc.
Jean-Pierre Braun obtained the B.E. degree from the Ecole d'ingénieurs de Genève, Switzerland, in 1980; the M.E.M. degree from the University of Technology Sydney, Australia, in 1993; and the M.Eng.Sc.
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II)
 Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6
 AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Other Effects in PLLs. Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles
 Other Effects in PLLs Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Example of Up and Down Skew and Width Mismatch Approximating the pulses on the control line by
Other Effects in PLLs Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Example of Up and Down Skew and Width Mismatch Approximating the pulses on the control line by
Homework Assignment Consider the circuit shown. Assume ideal op-amp behavior. Which statement below is true?
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. Consider the circuit shown. Assume ideal op-amp behavior. Which statement below is true? (a) V = VV + = 5 V (op-amp operation)
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. Consider the circuit shown. Assume ideal op-amp behavior. Which statement below is true? (a) V = VV + = 5 V (op-amp operation)
CHAPTER 5. Additional Problems (a) The AM signal is defined by st () = A c. k a A c 1
 CHAPTER 5 Additional Problems 5.7 (a) The AM signal is defined by st () A c ( + k a mt ()) cos( ω c k a A c + ------------ + t cos( ω c To obtain 5% modulation, we choose k a, which results in the modulated
CHAPTER 5 Additional Problems 5.7 (a) The AM signal is defined by st () A c ( + k a mt ()) cos( ω c k a A c + ------------ + t cos( ω c To obtain 5% modulation, we choose k a, which results in the modulated
ECE 359 Spring 2003 Handout # 16 April 15, SNR for ANGLE MODULATION SYSTEMS. v(t) = A c cos(2πf c t + φ(t)) for FM. for PM.
 ECE 359 Spring 23 Handout # 16 April 15, 23 Recall that for angle modulation: where The modulation index: ag replacements SNR for ANGLE MODULATION SYSTEMS v(t) = A c cos(2πf c t + φ(t)) t 2πk f m(t )dt
ECE 359 Spring 23 Handout # 16 April 15, 23 Recall that for angle modulation: where The modulation index: ag replacements SNR for ANGLE MODULATION SYSTEMS v(t) = A c cos(2πf c t + φ(t)) t 2πk f m(t )dt
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
ECE 4600 Communication Systems
 ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
6. Amplitude Modulation
 6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science. Lab Manual
 Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Engineering 6871 Communication Principles Lab Manual Fall 2014 Lab 1 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: 1. Learn how to use Matlab
Memorial University of Newfoundland Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Engineering 6871 Communication Principles Lab Manual Fall 2014 Lab 1 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Purpose: 1. Learn how to use Matlab
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation
 Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques
 Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Motivations (I) 2 Besides the classical
Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Motivations (I) 2 Besides the classical
Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits
 Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits Dae Hyun Kim EECS Washington State University References John P. Uyemura, Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems, 2002. Chapter 3 Neil H. Weste and David
Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits Dae Hyun Kim EECS Washington State University References John P. Uyemura, Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems, 2002. Chapter 3 Neil H. Weste and David
Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
 Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
8.0 Overview 8.1 The frequency response for a stable system
 8. Frequency Response Analysis 8.0 Overview 8.1 The frequency response for a stable system 8.1.1 Simple system elements 8.1.2 First-order system 8.1.3 Second-order systems 8.1.4 Systems of arbitrary order
8. Frequency Response Analysis 8.0 Overview 8.1 The frequency response for a stable system 8.1.1 Simple system elements 8.1.2 First-order system 8.1.3 Second-order systems 8.1.4 Systems of arbitrary order
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
ANALOG (DE)MODULATION
 ANALOG (DE)MODULATION Amplitude Modulation with Large Carrier Amplitude Modulation with Suppressed Carrier Quadrature Modulation Injection to Intermediate Frequency idealized system Software Receiver Design
ANALOG (DE)MODULATION Amplitude Modulation with Large Carrier Amplitude Modulation with Suppressed Carrier Quadrature Modulation Injection to Intermediate Frequency idealized system Software Receiver Design
Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits Comparators A comparator is a specialized nonlinear op-amp circuit that compares two input voltages and produces an output state that indicates which one is greater.
Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits Comparators A comparator is a specialized nonlinear op-amp circuit that compares two input voltages and produces an output state that indicates which one is greater.
! Amplitude of carrier wave varies a mean value in step with the baseband signal m(t)
 page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 16 Angle Modulation (Contd.) We will continue our discussion on Angle
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 16 Angle Modulation (Contd.) We will continue our discussion on Angle
NOTTCE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 k t Serial Number 827 r 518 Filing Date 28 March 1997 Inventor Keith Y. Williams NOTTCE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
k t Serial Number 827 r 518 Filing Date 28 March 1997 Inventor Keith Y. Williams NOTTCE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Complex Spectrum. Box Spectrum. Im f. Im f. Sine Spectrum. Cosine Spectrum 1/2 1/2 1/2. f C -f C 1/2
 ECPE 364: view o Small-Carrier Amplitude Modulation his handout is a graphical review o small-carrier amplitude modulation techniques that we studied in class. A Note on Complex Signal Spectra All o the
ECPE 364: view o Small-Carrier Amplitude Modulation his handout is a graphical review o small-carrier amplitude modulation techniques that we studied in class. A Note on Complex Signal Spectra All o the
6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation
 1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. Communication Laboratory
 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) & Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) & Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (DQPSK)
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) & Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) & Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (DQPSK)
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL
 CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
