Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
|
|
|
- Steven Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due to the use of the full amplitude modulation, which is extremely inefficient in terms of power as we have seen previously. The use of full AM permits the use of the simple and cheap envelope detector in the AM radio demodulator. In fact, the AM demodulator available in the market is slightly more complicated than a simple envelope detector. The block diagram below shows the construction of a typical AM receiver and the plots below show the signals in frequency domain at the different parts of the radio. Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver Signal a(t) at the output of the Antenna: The antenna of the AM radio receiver receives the whole band of interest. So it receives signals ranging in frequency from around 530 khz to 1650 khz as shown by a(t) in the figure. Each channel in this band occupies around 10 khz of bandwidth and the different channels have center frequencies of 540, 550, 560,., 1640 khz. Signal b(t) at the output of the RF (Radio Frequency) Stage: The signal at the output of the antenna is extremely week in terms of amplitude. The radio cannot process this signal as it is, so it must be amplified. The amplification does not amplify the whole spectrum of the AM band and it does not amplify a single channel, but a range of channels is amplified around the desired channel that we would like to receive. The reason for using a BPF in this stage although the desired channel is not completely separated from adjacent channels is to avoid possible interference of some channels later in the demodulation process if the whole band was allowed to pass (assume the absence of this BPF and try demodulating the two channels at the two edges of the AM band, you will see that one of these cannot be demodulated). Also, the reason for not extracting the desired channel alone is that extracting only that channel represents a big challenge since the filter that would have to extract it must have a constant bandwidth of 10 khz and a center frequency in the range of 530 khz to 1650 khz. Such a filter is extremely difficult to design since it has a high Q factor (center frequency/bandwidth) let alone the fact that its center frequency is variable. Therefore, the process of extracting only one channel is
2 left for the following stages where a filter with constant center frequency may be used. Note in the block diagram above that the center frequency of the BPF in the RF stage is controlled by a variable capacitor with a value that is modified using a knob in the radio (the tuning knob). Signal c(t) at the output of the Local Oscillator: This is simply a sinusoid with a variable frequency that is a function of the carrier frequency of the desired channel. The purpose of multiplying the signal b(t) by this sinusoid is to shift the center frequency of b(t) to a constant frequency that is called IF (intermediate frequency). Therefore, assuming that the desired channel (the channel you would like to listen to) has a frequency of f RF and the IF frequency that we would like to move that channel to is f IF, one choice for the frequency of the local oscillator is to be f RF + f IF. The frequency of the local oscillator is modified in the radio using a variable capacitor that is also controlled using the same tuning knob as the variable capacitor that controls the center frequency of the BPF filter in the RF stage. The process of controlling the values of two elements such as two variable capacitors using the same knob by placing them on the same shaft is known as GANGING. Signal d(t) at the output of the Multiplier (Usually called frequency converter or mixer): The signal here should contain the desired channel at the constant frequency f IF regardless of the original frequency of the desired channel. Remember that this signal does not only contain the desired channel but it contains also several adjacent channels and also contain images of these channels at the much higher frequency 2f RF + f IF (since multiplying by a cosine shifts the frequency of the signal to the left and to the right). When this type of radios was first invented, a standard was set for the value for the IF frequency to be 455 khz. There is nothing special about this value. A range of other values can be used. Signal e(t) at the output of the IF Stage: Now that the desired channel is located at the IF frequency, a relatively simple to create BP filter with BW of 10 khz and center frequency of f IF can be used to extract only the desired channel and reject all adjacent channels. This filter has a constant Q factor of about 455/10 = 45.5 (which is not that difficult to create), but more importantly has a constant center frequency. Therefore the output of this stage is the desired channel alone located at the IF frequency. This stage also contains a filter that amplifies the signal to a level that is sufficient for an envelope detector to operate on. Signal f(t) at the output of the Envelope Detector: The signal above is input to an envelope detector that extracts the original unmodulated signal from the modulated signal and also rejects any DC that is present in that signal. The output of that stage becomes the original signal with relatively low power. Signal g(t) at the output of the Audio Stage (Power Amplifier): Since the output of the envelope detector is generally weak and is not sufficient to drive a large speaker, the use of an amplifier that increases the power in the signal is necessary. Therefore, the output of that stage is the original audio signal with relatively high power that can directly be input to a speaker.
3
4
5
6
7
Topic Advanced Radio Receivers. Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity;
 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
OBJECTIVES EQUIPMENT LIST
 1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGIES
 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGIES Course : EET 24 Communications Electronics Module : AM Tx and
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGIES Course : EET 24 Communications Electronics Module : AM Tx and
Receiver Architectures
 Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
CHAPTER 13 TRANSMITTERS AND RECEIVERS
 CHAPTER 13 TRANSMITTERS AND RECEIVERS Frequency Modulation (FM) Receiver Frequency Modulation (FM) Receiver FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) RECEIVER Superheterodyne Receiver Heterodyning The word heterodyne
CHAPTER 13 TRANSMITTERS AND RECEIVERS Frequency Modulation (FM) Receiver Frequency Modulation (FM) Receiver FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) RECEIVER Superheterodyne Receiver Heterodyning The word heterodyne
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Chapter 5 AM Receivers
 Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang. General Outline
 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
Analog & Digital Communication
 Analog & Digital Communication UNIT I Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver Outline Basic Receiver TRF block diagram Advantages Disadvantages Basic receiver -1 Basic receiver -2 If there are many stations then
Analog & Digital Communication UNIT I Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver Outline Basic Receiver TRF block diagram Advantages Disadvantages Basic receiver -1 Basic receiver -2 If there are many stations then
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages.
 Figure 3-1 Simple radio receiver block diagram. Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages. Jeffrey
Figure 3-1 Simple radio receiver block diagram. Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver (TRF) The most elementary receiver design, consisting of RF amplifier stages, detector and audio amplifier stages. Jeffrey
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1. General Outline Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang
 1. General Outline 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang The invention and mass application of radio broadcast was triggered in the first decade of the nineteenth century by
1. General Outline 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang The invention and mass application of radio broadcast was triggered in the first decade of the nineteenth century by
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
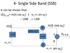 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9)
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Chapter 3. Question Mar No
 Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
Definitions. Spectrum Analyzer
 SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation
 ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
THE SPECTRUM ANALYZER AND SPECTRAL CONTENT
 ECE 351 OBJECTIVE: EQUIPMENT: EXPERIMENT EM4 THE SPECTRUM ANALYZER AND SPECTRAL CONTENT The purpose of this experiment is to introduce the student to the spectrum analyzer and to demonstrate the activity
ECE 351 OBJECTIVE: EQUIPMENT: EXPERIMENT EM4 THE SPECTRUM ANALYZER AND SPECTRAL CONTENT The purpose of this experiment is to introduce the student to the spectrum analyzer and to demonstrate the activity
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Costas Loop. Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier
 Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Chapter-15. Communication systems -1 mark Questions
 Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
COMM 704: Communication Systems
 COMM 704: Communication Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg Course Objective Give an introduction to the basic concepts of electronic communication systems
COMM 704: Communication Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg Course Objective Give an introduction to the basic concepts of electronic communication systems
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
8.5 Modulation of Signals
 8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
4 Receiver Design. A radio receiver must simultaneously complete two tasks:
 0/3/007 Receiver notes / 4 Receiver Design We re finally done studying microwave components! We can now take our palette of components and construct useful radio systems specifically, a microwave receiver.
0/3/007 Receiver notes / 4 Receiver Design We re finally done studying microwave components! We can now take our palette of components and construct useful radio systems specifically, a microwave receiver.
LABORATORY MANUAL COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EE 321
 LABORATORY MANUAL COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EE 321 K. Rad October 26, 2005 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES K. Rad Experiment 1 Part 1: Exercise
LABORATORY MANUAL COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EE 321 K. Rad October 26, 2005 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES K. Rad Experiment 1 Part 1: Exercise
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6
 Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Does Your Receiver have an IQ?
 Does Your Receiver have an IQ? A Brief Presenta-on of how Radio Receivers have Evolved over the Decades of Radio, and Describing how some Modern SDR Receivers work using the Quadrature Sampling Detector,
Does Your Receiver have an IQ? A Brief Presenta-on of how Radio Receivers have Evolved over the Decades of Radio, and Describing how some Modern SDR Receivers work using the Quadrature Sampling Detector,
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Problem Sheet for Amplitude Modulation
 Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Technician License Course Chapter 3. Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits The Basic Transceiver Combination of transmitter and receiver Abbreviated XCVR (X = trans) Antenna switched between transmitter
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits The Basic Transceiver Combination of transmitter and receiver Abbreviated XCVR (X = trans) Antenna switched between transmitter
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK UNIT IV PART-A
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
Fig. VII-1. Block diagram of experimental i-f discriminator unit. VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION
 VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION Prof. E. J. Baghdady M. Barash D. D. Weiner Prof. J. B. Wiesner R. J. McLaughlin L. D. Shapiro A. REGENERATIVE FEEDBACK AROUND THE LIMITER An experimental study is being conducted
VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION Prof. E. J. Baghdady M. Barash D. D. Weiner Prof. J. B. Wiesner R. J. McLaughlin L. D. Shapiro A. REGENERATIVE FEEDBACK AROUND THE LIMITER An experimental study is being conducted
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
 EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE
 RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
RFS21 December 1991 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO APPARATUS: VHF LAND MOBILE SERVICE USING AMPLITUDE MODULATION WITH 12.5 khz CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION Communications Division Ministry of Commerce
4/29/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Signals and Emissions. SignalSignals and Emissionsissions. Subelement G8
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam
 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study material 2017 South India Amateur Radio Society, Chennai CHAPTER 4 1 Chapter 4 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study Material Chapter
Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study material 2017 South India Amateur Radio Society, Chennai CHAPTER 4 1 Chapter 4 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study Material Chapter
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
Introduction. In the frequency domain, complex signals are separated into their frequency components, and the level at each frequency is displayed
 SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver. Dr. Mohammed Hawa. Electrical Engineering Department, University of Jordan
 Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance
 DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance N5RFX 4/21/08 Introduction The purpose of this initial paper is to describe and show the results of DStar co-channel and adjacent channel interference
DStar Co-channel and Adjacent Channel Performance N5RFX 4/21/08 Introduction The purpose of this initial paper is to describe and show the results of DStar co-channel and adjacent channel interference
FT-897 Alignment. Local Oscillator Adjustment. PLL Adjustment
 FT-897 Local Oscillator Adjustment Reference Frequency Adjustment a. Connect a frequency counter to TP1032. b. Adjust the trimmer capacitor (TC5001) for 67.875000MHz ±5Hz on the frequency counter. c. Connect
FT-897 Local Oscillator Adjustment Reference Frequency Adjustment a. Connect a frequency counter to TP1032. b. Adjust the trimmer capacitor (TC5001) for 67.875000MHz ±5Hz on the frequency counter. c. Connect
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation
 Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 5 (March 9, 2016)
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 5 (March 9, 2016)
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
ECE513 RF Design for Wireless
 1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
 UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation
 Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Television and video engineering
 Television and video engineering Unit-4 Television Receiver systems Objectives: To learn the requirements of TV receiver Study of monochrome and Colour TV receivers. To learn functions of Tuning circuits
Television and video engineering Unit-4 Television Receiver systems Objectives: To learn the requirements of TV receiver Study of monochrome and Colour TV receivers. To learn functions of Tuning circuits
RF Communications : Systems & Circuits
 ELEN 665 RF Communications : Systems & Circuits Edgar Sánchez-Sinencio sanchez@ece.tamu.edu Analog and Mixed-Signal Center,Texas A&M University Fall 2009 1 WHAT ARE THE MAIN TOPICS INVOLVED TO FULLY UNDERSTAND
ELEN 665 RF Communications : Systems & Circuits Edgar Sánchez-Sinencio sanchez@ece.tamu.edu Analog and Mixed-Signal Center,Texas A&M University Fall 2009 1 WHAT ARE THE MAIN TOPICS INVOLVED TO FULLY UNDERSTAND
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
Wideband Receiver for Communications Receiver or Spectrum Analysis Usage: A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion
 A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
STUDIO TO TRANSMITTER LINKING SYSTEM
 RFS37 May 1995 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO LINKING SYSTEM: STUDIO TO TRANSMITTER LINKING SYSTEM USING ANGLE MODULATION WITH CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION BETWEEN 75 AND 500 khz Communications Division
RFS37 May 1995 (Issue 1) SPECIFICATION FOR RADIO LINKING SYSTEM: STUDIO TO TRANSMITTER LINKING SYSTEM USING ANGLE MODULATION WITH CARRIER FREQUENCY SEPARATION BETWEEN 75 AND 500 khz Communications Division
E4332: VLSI Design Laboratory. Columbia University Spring 2005: Lectures
 E4332: VLSI Design Laboratory Nagendra Krishnapura Columbia University Spring 2005: Lectures nkrishna@vitesse.com 1 AM radio receiver AM radio signals: Audio signals on a carrier Intercept the signal Amplify
E4332: VLSI Design Laboratory Nagendra Krishnapura Columbia University Spring 2005: Lectures nkrishna@vitesse.com 1 AM radio receiver AM radio signals: Audio signals on a carrier Intercept the signal Amplify
Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL
 Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
An Introduction to Analog Communications Student Workbook AT02
 LJ Technical Systems An Introduction to Analog Communications AT02 MT191/B LJ Technical Systems This publication is copyright and no part of it may be adapted or reproduced in any material form except
LJ Technical Systems An Introduction to Analog Communications AT02 MT191/B LJ Technical Systems This publication is copyright and no part of it may be adapted or reproduced in any material form except
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL
 CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
NOISE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERSITICS OF DIRECT CONVERSION RECEIVERS
 White Paper NOISE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERSITICS OF DIRECT CONVERSION RECEIVERS January 2012 Austin, Texas Stephen Hicks, N5AC, AAR6AM, VP Engineering, FlexRadio Systems HISTORY AND THE PROBLEM Superheterodyne,
White Paper NOISE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERSITICS OF DIRECT CONVERSION RECEIVERS January 2012 Austin, Texas Stephen Hicks, N5AC, AAR6AM, VP Engineering, FlexRadio Systems HISTORY AND THE PROBLEM Superheterodyne,
Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work. Part I
 Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work Part I Ramón Vargas Patrón rvargas@inictel-uni.edu.pe INICTEL-UNI Regenerative Receivers remain
Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work Part I Ramón Vargas Patrón rvargas@inictel-uni.edu.pe INICTEL-UNI Regenerative Receivers remain
DSP First. Laboratory Exercise #7. Everyday Sinusoidal Signals
 DSP First Laboratory Exercise #7 Everyday Sinusoidal Signals This lab introduces two practical applications where sinusoidal signals are used to transmit information: a touch-tone dialer and amplitude
DSP First Laboratory Exercise #7 Everyday Sinusoidal Signals This lab introduces two practical applications where sinusoidal signals are used to transmit information: a touch-tone dialer and amplitude
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: AM Radio Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment
 EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In this laboratory you will assemble and test a working superheterodyne AM radio consisting of a front-end
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In this laboratory you will assemble and test a working superheterodyne AM radio consisting of a front-end
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER
 LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
LAB Assignment No. 6: TO STUDY GENERATION OF DOUBLE SIDE BAND AMPLITUDE MODULATE (AM) WAVEFORMS, USING DSB/SSB TRANSMITTER APPARATUS: Oscilloscope DSB/SSB Traine Power supply Connecting leads THEORY: A
and RTL-SDR Wireless Systems
 Laboratory 4 FM Receiver using MATLAB and RTL-SDR Wireless Systems TLEN 5830 Wireless Systems This Lab introduces the working of FM Receiver using MATLAB and Software Defined Radio This exercise encompasses
Laboratory 4 FM Receiver using MATLAB and RTL-SDR Wireless Systems TLEN 5830 Wireless Systems This Lab introduces the working of FM Receiver using MATLAB and Software Defined Radio This exercise encompasses
6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory
 6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Spring 2015, Instructor Gim Hom Project Proposal Transmitting, Receiving, and Interpreting ECG Waveforms Daniel Moon (dhmoon@mit.edu) Thipok (Ben) Rak-amnouykit
6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Spring 2015, Instructor Gim Hom Project Proposal Transmitting, Receiving, and Interpreting ECG Waveforms Daniel Moon (dhmoon@mit.edu) Thipok (Ben) Rak-amnouykit
Vintage Radio Alignment: What It Is and How to Do It
 Vintage Radio Alignment: What It Is and How to Do It Copyright 2009 Bret s Old Radios Bret Menassa Member: ARCI, VRPS, OKVRC Presented at Radiofest 2009, Willowbrook,, IL Vibrations A musical instrument
Vintage Radio Alignment: What It Is and How to Do It Copyright 2009 Bret s Old Radios Bret Menassa Member: ARCI, VRPS, OKVRC Presented at Radiofest 2009, Willowbrook,, IL Vibrations A musical instrument
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections , pp Angle Modulation No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c Instantaneous Frequency 2 dt dt No Modulation
 page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
HOMEBREW Q-MULTIPLIER
 HOMEBREW Q-MULTIPLIER This circuit can boost the signal strength in your receiver by 1 or 2 S-units, giving approximately 10 db gain. A Q-multiplier amplifies the Q of the first IF transformer so that
HOMEBREW Q-MULTIPLIER This circuit can boost the signal strength in your receiver by 1 or 2 S-units, giving approximately 10 db gain. A Q-multiplier amplifies the Q of the first IF transformer so that
