Improvements on rotating coil systems at CERN
|
|
|
- Charles Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 20th IMEKO TC4 International Symposium and 18th International Workshop on ADC Modelling and Testing Research on Electric and Electronic Measurement for the Economic Upturn Benevento, Italy, September 1517, 2014 Improvements on rotating coil systems at CERN Lucio Fiscarelli 1, Olaf Dunkel 1, Stephan Russenschuck 1 1 CERN, Route de Meyrin,Geneva,CH, lucio.fiscarelli@cern.ch Abstract A large variety of magnetic measurement requirements arises from the multiple accelerator projects at CERN, such as MedAustron, SESAME, HIEISOLDE, ELENA, and Linac4. Limited resources and a narrow time scale impose optimized procedures and instrumentations. Standardization of measurement equipment becomes essential in order to increase efficiency in terms of installation time and workflow. This paper gives an overview of the ongoing effort to optimize CERN measurement resources by keeping a suitable measurement quality. A flexible control and acquisition software, a standard drive unit, rotating coil systems with standard assembly of tangential search coils, and multipurpose measurement benches are described as main elements of an optimized development of highprecision magnetic measurement systems. I. INTRODUCTION Quality assurance of magnets is an important task in the development and installation process of an accelerator machine. In general, the beam characteristics of an accelerator are closely related to the field quality and the tuning of the magnet system. The requirements for the magnetic measurements are often determined by a conservative approach rather than the effective needs. In the design phase of a new accelerator machine, beam dynamic experts and magnet designers must agree on the magnet system requirements. Beam physics experts base their request on past experience and on simulation tools. On the other hand, magnet designers are interested in a deep knowledge of the magnet performances to improve their design tools. Therefore highprecision measurements are constantly on demand and, as a consequence, a continuous development of the measurement techniques is required. At present, a large variety of projects is underway at CERN. The MedAustron project is an iontherapy and research center, based on a synchrotron accelerator complex, located in Austria. The Synchrotron light for Experimental Science and Applications in the Middle East (SESAME) is a joint project launched in 2003 by countries in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East to build a synchrotron light source in Jordan. The HIEISOLDE project aims at greatly expanding the physics programme compared to that of the already existing REXISOLDE at CERN. HIEISOLDE forms part of the European nuclear physics strategy and its science case covers the majority of the key questions in nuclear structure pursued by the scientific community. ELENA is a compact ring for cooling and further deceleration of 5.3 MeV antiprotons delivered by the CERN Antiproton Decelerator (AD). The AD physics program is focused on trapping antiprotons and producing antihydrogen after recombination with positrons. The ultimate physics goal is to perform spectroscopy on antihydrogen atoms at rest and to investigate the effect of the gravitational force on matter and antimatter. The Linac4 project is a 160 MeV H linear accelerator replacing Linac2 as injector to the PS Booster (PSB). The new linac is expected to increase the beam brightness of the PSB by a factor of 2, making possible an upgrade of the LHC injectors for higher intensity and eventually an increase of the LHC luminosity. Table 1 gives a summary of the magnets, more than 230 in total, to be measured with the rotating coil systems. Quadrupoles, sextupoles, as well as the corrector magnets for these projects have a magnetic length of up to 80 cm and straight aperture bores. The required measurement relative precision depends on the magnet type and its final use in the machine. In general it ranges from 10 3 for correctors to 10 5 for lattice quadrupoles. Rotating coil technique is the most suitable method for measuring such magnets [1]. A large number of magnets for different projects ( Figure 1 ) requires a strong synergy in the development of the measurement tools. Highly efficient test equipment and procedures have to be devised to accomplish the measurement task within the given time. Userfriendliness, robustness and reliability are additional characteristics required for such systems. Based on the experience gained previously during the LHC development, an R&D program was launched to construct standard rotating coils benches for a full characterization (field strength, filed angle, magnetic center, and field quality) of relatively short magnets by reducing the measurement time. II. THE BENCH DESIGN A bench for rotating coil measurements is composed of four main elements: the magneticmeasurement shaft, a ISBN14:
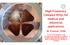
2 Table 1. Magnets requiring rotating coil measurements. Project Quadruples Sextupoles H/V dipoles MedAustron 9 64 SESAME HIEISOLDE ELENA Linac motor drive unit, the support structure, and the data acquisition system. A brief description of each component will be given in this section. A. The magneticmeasurement shaft Magneticmeasurement shafts with a standard length of 1.20 m and different diameters have been designed on the basis of a standardized crosssection (Figure 2)[2]. For the accurate measurement of the multipole field errors it is common practice to suppress the contribution of some field components from the signal of the main measurement coil. In the proposed design, five rectangular sensing coils with an equal surface are used. Two external coils are positioned on the opposite sides of the shaft at a radius maximised with respect to the aperture diameter of the magnet. The intermediate coils, used for compensating (bucking) the signal, are placed at half distance and are centered with respect to the rotation axis. The compensation coils are maintained in position by the same centering pins that fix the external coils. This setup allows for the bucking of the quadrupole component, by connecting in series the external coil with the two intermediate coils with the proper polarity. The residual dipole component can be bucked by further connecting the central coil with inverse polarity. Ease of manufacturing, stiffness requirements, and cost issues have driven the selection of glassreinforced epoxy (EPGM 203) as material for tube support and coil core [3]. In addition, glassfibre epoxy is completely nonmagnetic and nonconducting. The coils are wound on supports by hand. Each coil is then calibrated individually and matched to other coils of the same assembly to achieve the highest possible compensation ratio. The external coils are mounted onto reference surfaces machined along the outside of the shaft support tube and fixed to it with precise dowel pins. Flatness and parallelism of this fitting is the range of ±20 µm. The sensitivity factors of a tangential coil (intercepting the radial component of the magnetic flux density) to a multipole error of order n depend on the opening angle of the coil. A nominal opening angle of 28.8 degrees 694 Fig. 1. Some examples of different types of magnets being measured. was selected in order to have zero sensitivity to the harmonic order between 12 and 13. The shaft thus allows to measure, with a good sensitivity, low order multipoles for n < 10 and the "allowed" multipoles (n = 6, 10, 14) in quadrupoles. The shaft is equipped with a specific mechanical connector to adapt it to the drive unit and to allow a suitable angular stiffness. The mechanical connector includes the electrical connections for signals of coils and tilt sensor in order to facilitate the operations of assembling/disassembling of the shaft from the motor unit. Two ceramic ball bearings are placed on the ends of shaft and are held by aluminium cylinders; see Figure 3. B. The drive unit The magneticmeasurement shaft is driven by a compact motor drive, referred to as the Micro Rotating Unit (MRU). The unit includes a DC motor with 15:1 reduction gearbox, able to achieve a maximum rotation speed of 8 turns per second with variations smaller than 3%. The power driver for the motor is shielded from the signal cables, so that the coil signal is not affected by noise. The operation of the unit is remotely controlled by the acquisition software. The angular position of the shaft is given by an angular encoder with counts per revolution plus an index pulse on a separate channel. For the connection of the signal cables a multichannel slipring is used. This configuration allows measurements with a continuous rotation of the shaft at maximum speed.
3 Fig. 2. Cross section of the tangential coil shaft. Fig. 4. The bench used for the MedAustron project. Fig. 3. Standard bench for measuring corrector magnets. C. The support structure The requirements of the support structure are mainly related to the mechanical stability under the stress of the magnet weight, the adjustable shaft position to fit the magnet dimensions, and the absence of magnetic material, which could disturb the magnetic measurement. The adopted solution is a modular aluminium frame (Figure 4). It is sustained by six adjustable feet allowing the leveling of the magnet under test up to 1200 kg. The drive unit and shaft are held by two xy adjustable tables. The repeatability of the shaft positioning is assured by two vshaped supports for the cylinders housing the shaft ball bearings. The acquisition system The acquisition system is based on a PXI crate with a blade computer, an encoder interface, two integrator cards (Fast Digital Integrator [4]), and a standard acquisition card. The software application is generated by the Software Framework for Measurement Applications (SFMA) [5] and a testspecific script. An online data processing contributes to the reduction of the measurement time. The integrators are triggered by the angular encoders connected to the shaft through the encoder interface. The integrated voltage signals delivered by the integrators are equal to the flux changes between two adjacent angular steps. This reparametrization of the signal (with respect to the angular position) makes the signal (flux) independent of time and variations in the rotation velocity. The current is measured by using a DC Current Transformer (DCCT) and acquired by the acquisition card synchronously with the flux increments. III. MEASUREMENT RESULTS Four benches have been produced and are operational. About 50 magnets have been already measured for the MedAustron project, 10 for Linac4, together with preseries and prototype magnets for other projects. Results obtained for a HIEISOLDE preseries quadrupole are given as an example. Table 2. Measurement results on main field. System D. Single Stretched Wire R Gdl (Tm/m) Rotating coils Relative difference σ The first result of interest is the integrated gradient along the magnet aperture. The integrated gradient is defined as the average field, dived by the measurement radius and multiplied by the effective measurement length of the shaft. The results obtained (see Table 2) by using the new 695
4 units of 10 4 at R ref = 20 mm units of 10 4 at R ref = 20 mm multipole order Fig. 5. Measured multipoles on a quadrupole multipole order Fig. 6. Standard deviations of measured multipoles computed on ten measurements. rotating coil bench is analysed in terms of repeatability or relative standard deviation (σ) of ten consecutive measurements, the calibration error, or the difference with respect to the Single Stretched Wire system, which can be taken as a reference [6]. The precision of the system results to be excellent. A residual calibration error is present due to a possible coil nonhomogeneity in longitudinal direction (sausaging). An in situ calibration should be able to further improve the results [7]. For the measurement of the magnetic multipoles, the results are reported as relative value to the main field (normalization) and expressed in units of 10 4 (0.01%). The reference radius used to express the multipoles is 20 mm. The measured multipoles are only evaluated in terms of repeatability because it is difficult to have a reference for such quantities. In Figure 5, the measured normal and skew normalized multipoles are shown. Their amplitude is b n a n b n a n drawn with logarithmic scale in order to make visible the high order multipoles with small amplitude. In this way two important properties of harmonic fields are visualized: The RiemannLebesque lemma that states that higher order harmonics in a periodic signal must converge to zero, and the Cauchy estimat for Taylor coefficients, which states that in a conservative field, the multipole field errors must scale with 1/r n, where r is the reference radius and n the multipole error. Any obvious deviation of these rules can be attributed to measurement errors. The multipoles of the qudrupole magnet are well noticeable (b 6, b 10, b 14 ). These multipole field errors are due to the finite length of the pole surfaces and are therefore present in the field even if the magnets were built without manufacturing tolerances. These field harmonics are therefore known as the allowed field harmonics, unlike the nonallowed terms which must be attributed to asymmetries resulting from manufacturing tolerances. The linear decreasing slope proves that the results are not limited by the precision of the measurement system [8]. In Figure 6, the repeatability of the measurements of multipoles is given. It further confirms the very low noise of 0.3 ppm. The multipoles of order 12 and 13 are most affected by noise because the shaft has a low sensitivity this range due to its opening angle. The repeatability on measurements of the magnetic center has been also investigated. The shaft was first positioned in the magnetic center of the magnet (minimization of feeddown effect), then removed and replaced several times by repeating the measurement. With a certain care during the operations, a repeatability in the range of ±20 µm has been assessed on the magnetic center coordinates. IV. CONCLUSIONS A set of new rotating coil benches has been developed at CERN in order to respond to the measurement needs of the new projects. An effort in terms of standardization ad flexibility of the tools has been made to assure a short development time. New magneticmeasurement shafts and support structures have been designed, produced and tested. The performance in terms of measurement quality has demonstrated to be suitable for the most demanding requirements. REFERENCES [1] K. N. Henrichsen, Classification of magnetic measurement methods, in CERN Accelerator School, Magnetic Measurement and Alignment, Montreux, 1620 March 1992 (CERN, Montreux, 1992), pp , [2] O. Dunkel, Standardization of the CERN Equipment to cope with the Magnetic Measurement Requests from a Variety of Accelerator Projects, 18th International Magnetic Measurement Workshop (IMMW18), 696
5 June , Upton NY, USA [3] M. Buzio, Fabrication and calibration of search coils, in CERN Accelerator School CAS 2009: Specialised Course on Magnets, Bruges, 1625 June 2009 (CERN, Bruges, 2009), pp , [4] P. Arpaia, L. Bottura, L. Fiscarelli, L. Walckiers, Performance of a fast digital integrator in onfield magnetic measurements for particle accelerators, Review of Scientific Instruments 83, (2012), doi: / [5] P. Arpaia, M. Buzio, L. Fiscarelli, V. Inglese, A software framework for developing measurement applications under variable requirements, Review of Scientific Instruments 83, (2012), doi: / [6] L. Walckiers, Magnetic measurement with coils and wires, in CERN Accelerator School CAS 2009: Specialised Course on Magnets, Bruges, June 2009 (CERN, Bruges, 2009), pp , [7] P. Arpaia, M. Buzio, G. Golluccio, L. Walckiers, In situ calibration of rotating sensor coils for magnet testing, Review of Scientific Instruments, 83, (2012), doi: / [8] S. Russenschuck, Field Computation for Accelerator Magnets: Analytical and Numerical Methods for Electromagnetic Design and Optimization, Wiley March 2010, ISBN:
ARotating Coil Array in Mono Bloc Printed Circuit Technology for Small Scale Harmonic Measurements
 ARotating Coil Array in Mono Bloc Printed Circuit Technology for Small Scale Harmonic Measurements Olaf DUNKEL (Dep. TE MSC MM) On behalf of Rui DE OLIVEIRA (Dep. TE MPE EM) Lucette Gaborit, Ricardo Beltron
ARotating Coil Array in Mono Bloc Printed Circuit Technology for Small Scale Harmonic Measurements Olaf DUNKEL (Dep. TE MSC MM) On behalf of Rui DE OLIVEIRA (Dep. TE MPE EM) Lucette Gaborit, Ricardo Beltron
Rotating Coil Measurement Errors*
 Rotating Coil Measurement Errors* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA 2 nd Workshop on Beam Dynamics Meets Magnets (BeMa2014) December 1-4,
Rotating Coil Measurement Errors* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA 2 nd Workshop on Beam Dynamics Meets Magnets (BeMa2014) December 1-4,
Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB
 Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB Y. Arimoto (KEK) IMMW 20 @ Diamond Light Source 2017/Jun/8 SuperKEKB Final focus magnet system Magnetic field measurement
Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB Y. Arimoto (KEK) IMMW 20 @ Diamond Light Source 2017/Jun/8 SuperKEKB Final focus magnet system Magnetic field measurement
Printed Circuit Fluxmeter to Measure the Bending Magnets of the MedAustron Synchrotron
 Printed Circuit Fluxmeter to Measure the Bending Magnets of the MedAustron Synchrotron A. Beaumont 1, M. Buzio 2, R. De Oliveira 2, O. Dunkel 2, M. Stockner 1, T. Zickler 2 1 MedAustron, Austria 2 CERN,
Printed Circuit Fluxmeter to Measure the Bending Magnets of the MedAustron Synchrotron A. Beaumont 1, M. Buzio 2, R. De Oliveira 2, O. Dunkel 2, M. Stockner 1, T. Zickler 2 1 MedAustron, Austria 2 CERN,
RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS
 CBN 14-01 March 10, 2014 RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS Alexander Mikhailichenko Abstract. The results of measurements with a gradient magnet, arranged
CBN 14-01 March 10, 2014 RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS Alexander Mikhailichenko Abstract. The results of measurements with a gradient magnet, arranged
RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT OF VIBRATING WIRE ALIGNMENT TECHNIQUE FOR HEPS
 RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT OF VIBRATING WIRE ALIGNMENT TECHNIQUE FOR HEPS WU Lei,WANG Xiaolong, LI Chunhua, QU Huamin IHEP,CAS.19B Yuanquan Road,Shijingshan District,Beijing,100049 Abstract The alignment tolerance
RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT OF VIBRATING WIRE ALIGNMENT TECHNIQUE FOR HEPS WU Lei,WANG Xiaolong, LI Chunhua, QU Huamin IHEP,CAS.19B Yuanquan Road,Shijingshan District,Beijing,100049 Abstract The alignment tolerance
CERN-EC SUPPORT FOR SESAME MAGNETS
 1. PUBLISHABLE SUMMARY CERN-EC SUPPORT FOR SESAME MAGNETS WP1 Project Management and Technical Coordination A complex preparation involving several CERN offices (Director-General, Legal service, Procurement
1. PUBLISHABLE SUMMARY CERN-EC SUPPORT FOR SESAME MAGNETS WP1 Project Management and Technical Coordination A complex preparation involving several CERN offices (Director-General, Legal service, Procurement
Emilia Cruz. September 21, 2015
 Designing the interaction regions of the upgrades of the LHC Emilia Cruz September 21, 2015 7/7/2016 1 About me Guadalajara, Mexico 7/7/2016 2 About me Bachelors degree: National Autonomous University
Designing the interaction regions of the upgrades of the LHC Emilia Cruz September 21, 2015 7/7/2016 1 About me Guadalajara, Mexico 7/7/2016 2 About me Bachelors degree: National Autonomous University
A ferrimagnetic resonance (FMR) marker for fast ramped, non uniform field
 A ferrimagnetic resonance (FMR) marker for fast ramped, non uniform field P Arpaia 1, M Buzio 2, F Caspers 2, D Giloteaux 2, G Golluccio 12, D Oberson 2 1 Universita del Sannio, Benevento, Italy, 2 CERN,
A ferrimagnetic resonance (FMR) marker for fast ramped, non uniform field P Arpaia 1, M Buzio 2, F Caspers 2, D Giloteaux 2, G Golluccio 12, D Oberson 2 1 Universita del Sannio, Benevento, Italy, 2 CERN,
ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS. J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers.
 295 ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers. CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction Electromagnets
295 ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers. CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction Electromagnets
A Data Reduction Algorithm for Magnetic Measurement Pre-processing at CERN
 A Data Reduction Algorithm for Magnetic Measurement Pre-processing at CERN P. Arpaia 1,2, M. Buzio 2, V. Inglese 2,3 1 Department of Engineering, University of Sannio, Corso Garibaldi 107, 82100 Benevento,
A Data Reduction Algorithm for Magnetic Measurement Pre-processing at CERN P. Arpaia 1,2, M. Buzio 2, V. Inglese 2,3 1 Department of Engineering, University of Sannio, Corso Garibaldi 107, 82100 Benevento,
XVIII IMEKO WORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17 22, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
 XVIII IMEKO WORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17 22, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil METROLOGICAL CHARATERIZATION OF A FAST DIGITAL INTEGRATOR FOR MAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AT
XVIII IMEKO WORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17 22, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil METROLOGICAL CHARATERIZATION OF A FAST DIGITAL INTEGRATOR FOR MAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS AT
SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SWISS LIGHT SOURCE
 1 SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SWISS LIGHT SOURCE F.Q. Wei, K. Dreyer, U. Fehlmann, J.L. Pochon and A. Wrulich SLS / Paul Scherrer Institute CH5232 Villigen PSI Switzerland ABSTRACT The Swiss Light Source
1 SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SWISS LIGHT SOURCE F.Q. Wei, K. Dreyer, U. Fehlmann, J.L. Pochon and A. Wrulich SLS / Paul Scherrer Institute CH5232 Villigen PSI Switzerland ABSTRACT The Swiss Light Source
AUTOMATION OF 3D MEASUREMENTS FOR THE FINAL ASSEMBLY STEPS OF THE LHC DIPOLE MAGNETS
 IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 AUTOMATION OF 3D MEASUREMENTS FOR THE FINAL ASSEMBLY STEPS OF THE LHC DIPOLE MAGNETS M. Bajko, R. Chamizo, C. Charrondiere, A. Kuzmin 1, CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 AUTOMATION OF 3D MEASUREMENTS FOR THE FINAL ASSEMBLY STEPS OF THE LHC DIPOLE MAGNETS M. Bajko, R. Chamizo, C. Charrondiere, A. Kuzmin 1, CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
TEST AND CALIBRATION FACILITY FOR HLS AND WPS SENSORS
 IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 TEST AND CALIBRATION FACILITY FOR HLS AND WPS SENSORS Andreas Herty, Hélène Mainaud-Durand, Antonio Marin CERN, TS/SU/MTI, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 1. ABSTRACT
IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 TEST AND CALIBRATION FACILITY FOR HLS AND WPS SENSORS Andreas Herty, Hélène Mainaud-Durand, Antonio Marin CERN, TS/SU/MTI, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 1. ABSTRACT
Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring*
 Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 17 th International Magnetic Measurement Workshop
Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 17 th International Magnetic Measurement Workshop
Physics Requirements Document Document Title: SCRF 1.3 GHz Cryomodule Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7
 Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
Proposal of test setup
 Proposal of test setup Status of the study The Compact Linear collider (CLIC) study is a site independent feasibility study aiming at the development of a realistic technology at an affordable cost for
Proposal of test setup Status of the study The Compact Linear collider (CLIC) study is a site independent feasibility study aiming at the development of a realistic technology at an affordable cost for
Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project. Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, Dec.
 Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, 01-04 Dec. 2014 MAX IV 3 GeV ring magnets key aspects: Relatively small magnet aperture
Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, 01-04 Dec. 2014 MAX IV 3 GeV ring magnets key aspects: Relatively small magnet aperture
200 MHz 350 MHz 750 MHz Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz 0.5 MeV /m Weight : 1000 kg/m Ext. diameter : 45 cm
 M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
Status and Upgrade. P. Elleaume. XVIII ESLS Workshop, November P. Elleaume, ESRF. Slide: 1
 ESRF Status and Upgrade P. Elleaume Slide: 1 Statistics 2008-2010 Availability (%) Mean time between failures (hrs) Mean duration of a failure (hrs) 2008 2009 2010* 98.30 99.04 98.83 64.50 75.80 70.80
ESRF Status and Upgrade P. Elleaume Slide: 1 Statistics 2008-2010 Availability (%) Mean time between failures (hrs) Mean duration of a failure (hrs) 2008 2009 2010* 98.30 99.04 98.83 64.50 75.80 70.80
INDUSTRIAL CONTROLS FOR TEST SYSTEMS FROM SUPERCONDUCTING STRANDS TILL MAGNET FIDUCIALISATION IN THE TUNNEL FOR THE LHC PROJECT
 INDUSTRIAL CONTROLS FOR TEST SYSTEMS FROM SUPERCONDUCTING STRANDS TILL MAGNET FIDUCIALISATION IN THE TUNNEL FOR THE LHC PROJECT ABSTRACT A. Rijllart, C. Charrondière, B. Khomenko, M. Marchesotti, E. Michel,
INDUSTRIAL CONTROLS FOR TEST SYSTEMS FROM SUPERCONDUCTING STRANDS TILL MAGNET FIDUCIALISATION IN THE TUNNEL FOR THE LHC PROJECT ABSTRACT A. Rijllart, C. Charrondière, B. Khomenko, M. Marchesotti, E. Michel,
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique
 A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
Chapter 9. Magnet System. 9.1 Magnets in the Arc and Straight Sections
 Chapter 9 Magnet System This chapter discusses the parameters and the design of the magnets to use at KEKB. Plans on the magnet power supply systems, magnet installation procedure and alignment strategies
Chapter 9 Magnet System This chapter discusses the parameters and the design of the magnets to use at KEKB. Plans on the magnet power supply systems, magnet installation procedure and alignment strategies
Non-invasive Beam Profile Measurements using an Electron-Beam Scanner
 Non-invasive Beam Profile Measurements using an Electron-Beam Scanner W. Blokland and S. Cousineau Willem Blokland for the Spallation Neutron Source Managed by UT-Battelle Overview SNS Accelerator Electron
Non-invasive Beam Profile Measurements using an Electron-Beam Scanner W. Blokland and S. Cousineau Willem Blokland for the Spallation Neutron Source Managed by UT-Battelle Overview SNS Accelerator Electron
Maurizio Vretenar Linac4 Project Leader EuCARD-2 Coordinator
 Maurizio Vretenar Linac4 Project Leader EuCARD-2 Coordinator Every accelerator needs a linac as injector to pass the region where the velocity of the particles increases with energy. At high energies (relativity)
Maurizio Vretenar Linac4 Project Leader EuCARD-2 Coordinator Every accelerator needs a linac as injector to pass the region where the velocity of the particles increases with energy. At high energies (relativity)
Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland. Introduction
 THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
The European Spallation Source. Dave McGinnis Chief Engineer ESS\Accelerator Division IVEC 2013
 The European Spallation Source Dave McGinnis Chief Engineer ESS\Accelerator Division IVEC 2013 Overview The European Spallation Source (ESS) will house the most powerful proton linac ever built. The average
The European Spallation Source Dave McGinnis Chief Engineer ESS\Accelerator Division IVEC 2013 Overview The European Spallation Source (ESS) will house the most powerful proton linac ever built. The average
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES.
 COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES. Isaac Vasserman, Shigemi Sasaki Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439, USA Abstract The magnetic measurement system at APS was upgraded.
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES. Isaac Vasserman, Shigemi Sasaki Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439, USA Abstract The magnetic measurement system at APS was upgraded.
CERN (The European Laboratory for Particle Physics)
 462 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 48, NO. 2, APRIL 1999 The Measurement Challenge of the LHC Project Gunnar Fernqvist Abstract In 2005, CERN is planning to commission its next
462 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 48, NO. 2, APRIL 1999 The Measurement Challenge of the LHC Project Gunnar Fernqvist Abstract In 2005, CERN is planning to commission its next
Smart off axis absolute position sensor solution and UTAF piezo motor enable closed loop control of a miniaturized Risley prism pair
 Smart off axis absolute position sensor solution and UTAF piezo motor enable closed loop control of a miniaturized Risley prism pair By David Cigna and Lisa Schaertl, New Scale Technologies Hall effect
Smart off axis absolute position sensor solution and UTAF piezo motor enable closed loop control of a miniaturized Risley prism pair By David Cigna and Lisa Schaertl, New Scale Technologies Hall effect
Preliminary Design of the n2edm Coil System
 Preliminary Design of the n2edm Coil System Christopher Crawford, Philipp Schmidt-Wellenburg 2013-07-03 1 Introduction This report details progress towards the design of an electromagnetic coil package
Preliminary Design of the n2edm Coil System Christopher Crawford, Philipp Schmidt-Wellenburg 2013-07-03 1 Introduction This report details progress towards the design of an electromagnetic coil package
Results of FE65-P2 Pixel Readout Test Chip for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades
 for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades R. Carney, K. Dunne, *, D. Gnani, T. Heim, V. Wallangen Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, USA e-mail: mgarcia-sciveres@lbl.gov A. Mekkaoui Fermilab, Batavia, USA
for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades R. Carney, K. Dunne, *, D. Gnani, T. Heim, V. Wallangen Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, USA e-mail: mgarcia-sciveres@lbl.gov A. Mekkaoui Fermilab, Batavia, USA
MEASUREMENT OF BEAM LOSSES USING OPTICAL FIBRES AT THE AUSTRALIAN SYNCHROTRON
 MEASUREMENT OF BEAM LOSSES USING OPTICAL FIBRES AT THE AUSTRALIAN SYNCHROTRON E. Nebot del Busto (1,2), M. J. Boland (3,4), E. B. Holzer (1), P. D. Jackson (5), M. Kastriotou (1,2), R. P. Rasool (4), J.
MEASUREMENT OF BEAM LOSSES USING OPTICAL FIBRES AT THE AUSTRALIAN SYNCHROTRON E. Nebot del Busto (1,2), M. J. Boland (3,4), E. B. Holzer (1), P. D. Jackson (5), M. Kastriotou (1,2), R. P. Rasool (4), J.
Computer Numeric Control
 Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
n Measuring range ,02 N m to N m n Clockwise and counter-clockwise torque n Low linearity deviation of ± 0.05 % F.S.
 Precision Torque Sensor Non-contact transmission for rotating applications Optional measurement of angle and speed Model 8661 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 2-3 weeks 24 months Application The 8661 precision
Precision Torque Sensor Non-contact transmission for rotating applications Optional measurement of angle and speed Model 8661 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 2-3 weeks 24 months Application The 8661 precision
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
A novel solution for various monitoring applications at CERN
 A novel solution for various monitoring applications at CERN F. Lackner, P. H. Osanna 1, W. Riegler, H. Kopetz CERN, European Organisation for Nuclear Research, CH-1211 Geneva-23, Switzerland 1 Department
A novel solution for various monitoring applications at CERN F. Lackner, P. H. Osanna 1, W. Riegler, H. Kopetz CERN, European Organisation for Nuclear Research, CH-1211 Geneva-23, Switzerland 1 Department
DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT
 DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT Ji-Gwang Hwang, Tae-Keun Yang, Seon Yeong Noh Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences,
DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT Ji-Gwang Hwang, Tae-Keun Yang, Seon Yeong Noh Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences,
Cavity BPMs for the NLC
 SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
Unbalance Detection in Flexible Rotor Using Bridge Configured Winding Based Induction Motor
 Unbalance Detection in Flexible Rotor Using Bridge Configured Winding Based Induction Motor Natesan Sivaramakrishnan, Kumar Gaurav, Kalita Karuna, Rahman Mafidur Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Unbalance Detection in Flexible Rotor Using Bridge Configured Winding Based Induction Motor Natesan Sivaramakrishnan, Kumar Gaurav, Kalita Karuna, Rahman Mafidur Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Technical overview drawing of the Roadrunner goniometer. The goniometer consists of three main components: an inline sample-viewing microscope, a high-precision scanning unit for
Supplementary Figure 1 Technical overview drawing of the Roadrunner goniometer. The goniometer consists of three main components: an inline sample-viewing microscope, a high-precision scanning unit for
T10FS. Data Sheet. Torque Flange. Special features. Installation example T10FS. B en
 T10FS Torque Flange Data Sheet Special features Nominal (rated) torques: 100 NVm, 200 NVm, 500 NVm, 1 knvm, 2 knvm, 3 knvm, 5 knvm, 10 knvm Nominal speed from 12,000 rpm to 24,000 rpm Low rotor weights
T10FS Torque Flange Data Sheet Special features Nominal (rated) torques: 100 NVm, 200 NVm, 500 NVm, 1 knvm, 2 knvm, 3 knvm, 5 knvm, 10 knvm Nominal speed from 12,000 rpm to 24,000 rpm Low rotor weights
Roman Pots. Marco Oriunno SLAC, PPA. M.Oriunno, SLAC
 Roman Pots Marco Oriunno SLAC, PPA The Roman Pot technique 1. The Roman Pot, an historically successful technique for near beam physics: ISR, SPS, TEVATRON, RICH, DESY 2. A CERN in-house technology: ISR,
Roman Pots Marco Oriunno SLAC, PPA The Roman Pot technique 1. The Roman Pot, an historically successful technique for near beam physics: ISR, SPS, TEVATRON, RICH, DESY 2. A CERN in-house technology: ISR,
Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS. By Mark Jaski
 Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS By Mark Jaski Outline What is an Undulator IEX device Analysis Prototypes Final device EMVPU Device Analysis Prototypes Final device 2 What
Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS By Mark Jaski Outline What is an Undulator IEX device Analysis Prototypes Final device EMVPU Device Analysis Prototypes Final device 2 What
FAST RF KICKER DESIGN
 FAST RF KICKER DESIGN David Alesini LNF-INFN, Frascati, Rome, Italy ICFA Mini-Workshop on Deflecting/Crabbing Cavity Applications in Accelerators, Shanghai, April 23-25, 2008 FAST STRIPLINE INJECTION KICKERS
FAST RF KICKER DESIGN David Alesini LNF-INFN, Frascati, Rome, Italy ICFA Mini-Workshop on Deflecting/Crabbing Cavity Applications in Accelerators, Shanghai, April 23-25, 2008 FAST STRIPLINE INJECTION KICKERS
RF System Models and Longitudinal Beam Dynamics
 RF System Models and Longitudinal Beam Dynamics T. Mastoridis 1, P. Baudrenghien 1, J. Molendijk 1, C. Rivetta 2, J.D. Fox 2 1 BE-RF Group, CERN 2 AARD-Feedback and Dynamics Group, SLAC T. Mastoridis LLRF
RF System Models and Longitudinal Beam Dynamics T. Mastoridis 1, P. Baudrenghien 1, J. Molendijk 1, C. Rivetta 2, J.D. Fox 2 1 BE-RF Group, CERN 2 AARD-Feedback and Dynamics Group, SLAC T. Mastoridis LLRF
ANALYSIS OF 3RD OCTAVE BAND GROUND MOTIONS TRANSMISSION IN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION FACILITY SOLARIS Daniel Ziemianski, Marek Kozien
 ANALYSIS OF 3RD OCTAVE BAND GROUND MOTIONS TRANSMISSION IN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION FACILITY SOLARIS Daniel Ziemianski, Marek Kozien Cracow University of Technology, Institute of Applied Mechanics, al. Jana
ANALYSIS OF 3RD OCTAVE BAND GROUND MOTIONS TRANSMISSION IN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION FACILITY SOLARIS Daniel Ziemianski, Marek Kozien Cracow University of Technology, Institute of Applied Mechanics, al. Jana
TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM. W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18480 Introduction TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany In 2001
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18480 Introduction TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany In 2001
Angle Encoder Modules
 Angle Encoder Modules May 2015 Angle encoder modules Angle encoder modules from HEIDENHAIN are combinations of angle encoders and high-precision bearings that are optimally adjusted to each other. They
Angle Encoder Modules May 2015 Angle encoder modules Angle encoder modules from HEIDENHAIN are combinations of angle encoders and high-precision bearings that are optimally adjusted to each other. They
CERN PS, SL & ST Divisions
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH ORGANISATION EUROPÉENNE POUR LA RECHERCHE NUCLÉAIRE CERN PS, SL & ST Divisions CERN-PS-2002 CERN-SL-2002 CERN-ST-2002 1 st February 2002 TOWARDS A COMMON MONITORING
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH ORGANISATION EUROPÉENNE POUR LA RECHERCHE NUCLÉAIRE CERN PS, SL & ST Divisions CERN-PS-2002 CERN-SL-2002 CERN-ST-2002 1 st February 2002 TOWARDS A COMMON MONITORING
T40B. Torque Flange. Special features. Data sheet. Overall concept
 T40B Torque Flange Special features - Nominal (rated) torques 50 N m, 0 N m, 200 N m, 500 N m, 1 kn m, 2 kn m, 3 kn m, 5 kn m and kn m - Nominal rated rotational speed up to 24000 rpm (depending on nominal
T40B Torque Flange Special features - Nominal (rated) torques 50 N m, 0 N m, 200 N m, 500 N m, 1 kn m, 2 kn m, 3 kn m, 5 kn m and kn m - Nominal rated rotational speed up to 24000 rpm (depending on nominal
Rotary Encoder System Compact Model Range
 we set the standards RIK Rotary Encoder System Compact Model Range 2 Incremental rotary encoder Features Compact design, consisting of scanning head with round cable, 15pin D-sub connector and grating
we set the standards RIK Rotary Encoder System Compact Model Range 2 Incremental rotary encoder Features Compact design, consisting of scanning head with round cable, 15pin D-sub connector and grating
CTOF Magnetic Shield Test Plan with FROST Magnet
 CTOF Magnetic Shield Test Plan with FROST Magnet D.S. Carman, Jefferson Laboratory A. Ni, Kyungpook National University shield-test.tex May 21, 2015 Abstract This document outlines the test plan for the
CTOF Magnetic Shield Test Plan with FROST Magnet D.S. Carman, Jefferson Laboratory A. Ni, Kyungpook National University shield-test.tex May 21, 2015 Abstract This document outlines the test plan for the
n Measurable displacements between n Linearity: max. ± 0.05 % n Housing diameter 12.9 mm n Service life: 10 8 movements
 Potentiometric Displacement Sensor Miniature design Model 8709 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 8709 EN ex stock 24 months Application Potentiometric displacement sensors are used for direct, precise measurement
Potentiometric Displacement Sensor Miniature design Model 8709 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 8709 EN ex stock 24 months Application Potentiometric displacement sensors are used for direct, precise measurement
Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components
 Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components Thomas J. Dunn, Robert Michaels, Simon Lee, Mark Tronolone, and Andrew Kulawiec; Corning Tropel
Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components Thomas J. Dunn, Robert Michaels, Simon Lee, Mark Tronolone, and Andrew Kulawiec; Corning Tropel
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Laboratory for Particle Physics FIELD MEASUREMENTS. L. Bottura, K.N. Henrichsen
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Laboratory for Particle Physics Divisional Report CERN LHC/2002-20 (MTA) FIELD MEASUREMENTS L. Bottura, K.N. Henrichsen The measurement of the magnetic field
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Laboratory for Particle Physics Divisional Report CERN LHC/2002-20 (MTA) FIELD MEASUREMENTS L. Bottura, K.N. Henrichsen The measurement of the magnetic field
SIGNAL TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEAM POSITION MONITOR
 SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position monitor (BP) system is under development
SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position monitor (BP) system is under development
MAGNETOSCOP Measurement of magnetic field strengths in the range 0.1 nanotesla to 1 millitesla
 MAGNETOSCOP Measurement of magnetic field strengths in the range 0.1 nanotesla to 1 millitesla Extremely high sensitivity of 0.1 nanotesla with field and gradient probe Measurement of material permeabilities
MAGNETOSCOP Measurement of magnetic field strengths in the range 0.1 nanotesla to 1 millitesla Extremely high sensitivity of 0.1 nanotesla with field and gradient probe Measurement of material permeabilities
HIGH POWER PULSED TESTS OF A BETA=0.5 5-CELL 704 MHZ SUPERCONDUCTING CAVITY
 HIGH POWER PULSED TESTS OF A BETA=0.5 5-CELL 704 MHZ SUPERCONDUCTING CAVITY G. Devanz, D. Braud, M. Desmons, Y. Gasser, E. Jacques, O. Piquet, J. Plouin, J.- P. Poupeau, D. Roudier, P. Sahuquet, CEA-Saclay,
HIGH POWER PULSED TESTS OF A BETA=0.5 5-CELL 704 MHZ SUPERCONDUCTING CAVITY G. Devanz, D. Braud, M. Desmons, Y. Gasser, E. Jacques, O. Piquet, J. Plouin, J.- P. Poupeau, D. Roudier, P. Sahuquet, CEA-Saclay,
The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker and its Electronic Readout
 The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker and its Electronic Readout Markus Friedl Dissertation May 2001 M. Friedl The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker and its Electronic Readout 2 Introduction LHC Large Hadron Collider:
The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker and its Electronic Readout Markus Friedl Dissertation May 2001 M. Friedl The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker and its Electronic Readout 2 Introduction LHC Large Hadron Collider:
RGH34 encoder system. Data sheet L A. RGH34 readhead and RGI34 interface: RGS40 scale:
 L-9517-978-01-A The Renishaw RGH34 series is a non-contact optical encoder system, providing highly-reliable positional feedback. This modular miniaturised encoder consists of an RGH34 readhead that reads
L-9517-978-01-A The Renishaw RGH34 series is a non-contact optical encoder system, providing highly-reliable positional feedback. This modular miniaturised encoder consists of an RGH34 readhead that reads
two pairs of dipole steering windings that t inside the quadrupole yoke an RF beam position monitor (BPM) consisting of a pill box RF cavity,
 Chapter 6 Quadrupole Package The quadrupole package is shown in Fig. 6.1. It consists of a superferric quadrupole doublet powered in series enclosed in a stainless steel vessel and cooled by 4 K LHe; two
Chapter 6 Quadrupole Package The quadrupole package is shown in Fig. 6.1. It consists of a superferric quadrupole doublet powered in series enclosed in a stainless steel vessel and cooled by 4 K LHe; two
QPLL a Quartz Crystal Based PLL for Jitter Filtering Applications in LHC
 QPLL a Quartz Crystal Based PLL for Jitter Filtering Applications in LHC Paulo Moreira and Alessandro Marchioro CERN-EP/MIC, Geneva Switzerland 9th Workshop on Electronics for LHC Experiments 29 September
QPLL a Quartz Crystal Based PLL for Jitter Filtering Applications in LHC Paulo Moreira and Alessandro Marchioro CERN-EP/MIC, Geneva Switzerland 9th Workshop on Electronics for LHC Experiments 29 September
Title Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn.
 Title Measurements of Magnetic Field Harm Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn Amemiya, Naoyuki; Mizuta, Shingo; N Author(s) Ogitsu, Toru; Orikasa, Tomofumi; Ku Tetsuhiro; Noda, Koji Citation IEEE Transactions
Title Measurements of Magnetic Field Harm Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn Amemiya, Naoyuki; Mizuta, Shingo; N Author(s) Ogitsu, Toru; Orikasa, Tomofumi; Ku Tetsuhiro; Noda, Koji Citation IEEE Transactions
Cylindrical rotor inter-turn short-circuit detection
 Cylindrical rotor inter-turn short-circuit detection by Kobus Stols, Eskom A strayflux probe is commonly used in the industry to determine if any inter-turn short-circuits are present in the field winding
Cylindrical rotor inter-turn short-circuit detection by Kobus Stols, Eskom A strayflux probe is commonly used in the industry to determine if any inter-turn short-circuits are present in the field winding
PeakVue Analysis for Antifriction Bearing Fault Detection
 Machinery Health PeakVue Analysis for Antifriction Bearing Fault Detection Peak values (PeakVue) are observed over sequential discrete time intervals, captured, and analyzed. The analyses are the (a) peak
Machinery Health PeakVue Analysis for Antifriction Bearing Fault Detection Peak values (PeakVue) are observed over sequential discrete time intervals, captured, and analyzed. The analyses are the (a) peak
HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning
 Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer 27 th April, Erice, Sicily, Italy HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning Kazuo Hiramoto Energy & Environmental Systems Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Contents
Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer 27 th April, Erice, Sicily, Italy HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning Kazuo Hiramoto Energy & Environmental Systems Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Contents
LHC ARC DIPOLE STATUS REPORT
 LHC ARC DIPOLE STATUS REPORT C.Wyss, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland # Abstract The LHC, a 7 Tev proton collider presently under construction at CERN, requires 1232 superconducting (SC) dipole magnets, featuring
LHC ARC DIPOLE STATUS REPORT C.Wyss, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland # Abstract The LHC, a 7 Tev proton collider presently under construction at CERN, requires 1232 superconducting (SC) dipole magnets, featuring
Nmark AGV-HPO. High Accuracy, Open Frame, Thermally Stable Galvo Scanner. Highest accuracy scanner available attains singledigit,
 Nmark AGV-HPO Galvanometer Nmark AGV-HPO High Accuracy, Open Frame, Thermally Stable Galvo Scanner Highest accuracy scanner available attains singledigit, micron-level accuracy over the field of view Optical
Nmark AGV-HPO Galvanometer Nmark AGV-HPO High Accuracy, Open Frame, Thermally Stable Galvo Scanner Highest accuracy scanner available attains singledigit, micron-level accuracy over the field of view Optical
A HALL PLATE BASED INSTRUMENT TO MEASURE THE SNAPBACK IN THE LARGE HADRON COLLIDER SUPERCONDUCTING DIPOLE MAGNETS
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 1068 A HALL PLATE BASED INSTRUMENT TO MEASURE THE SNAPBACK IN THE LARGE
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 1068 A HALL PLATE BASED INSTRUMENT TO MEASURE THE SNAPBACK IN THE LARGE
The LHCb Vertex Locator : Marina Artuso, Syracuse University for the VELO Group
 The LHCb Vertex Locator : status and future perspectives Marina Artuso, Syracuse University for the VELO Group The LHCb Detector Mission: Expore interference of virtual new physics particle in the decays
The LHCb Vertex Locator : status and future perspectives Marina Artuso, Syracuse University for the VELO Group The LHCb Detector Mission: Expore interference of virtual new physics particle in the decays
Evaluation Kit: MPS 160 ASIC. Magneto Encoder ASIC
 Evaluation Kit: MPS 160 ASIC Magneto Encoder ASIC Table of Contents 1. Overview 2. Mounting Instructions 2.1. Sensor Orientation 2.2. Pitch Radius 2.3. Air Gap 3. Magnetic Target 4. Output 4.1. Optional
Evaluation Kit: MPS 160 ASIC Magneto Encoder ASIC Table of Contents 1. Overview 2. Mounting Instructions 2.1. Sensor Orientation 2.2. Pitch Radius 2.3. Air Gap 3. Magnetic Target 4. Output 4.1. Optional
CONTROLLING THE OSCILLATIONS OF A SWINGING BELL BY USING THE DRIVING INDUCTION MOTOR AS A SENSOR
 Proceedings, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7,, Dubrovnik, Croatia Proceedings, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7,, Dubrovnik, Croatia XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in the rd Millennium June 7,,
Proceedings, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7,, Dubrovnik, Croatia Proceedings, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7,, Dubrovnik, Croatia XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in the rd Millennium June 7,,
PART 2 - ACTUATORS. 6.0 Stepper Motors. 6.1 Principle of Operation
 6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II
 Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II Peter Röjsel MAX-lab, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Abstract. The MAX II is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source. The first beamline is in operation
Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II Peter Röjsel MAX-lab, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Abstract. The MAX II is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source. The first beamline is in operation
Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs. Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory
 Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Hybrid Insertion Devices Inclusion of Iron Simple hybrid example Top Array e - Bottom Array 2 Lines of Magnetic
Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Hybrid Insertion Devices Inclusion of Iron Simple hybrid example Top Array e - Bottom Array 2 Lines of Magnetic
1. This is an integrated product combining a bearing with a rotation sensor that detects the speed and direction of rotation.
 1. This is an integrated product combining a bearing with a rotation sensor that detects the speed and direction of rotation. 2. With a wide variety of models and advanced functions available, these bearings
1. This is an integrated product combining a bearing with a rotation sensor that detects the speed and direction of rotation. 2. With a wide variety of models and advanced functions available, these bearings
Application of SLOFEC and Laser Technology for Testing of Buried Pipes
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Application of SLOFEC and Laser Technology for Testing of Buried Pipes Gerhard SCHEER 1 1 TMT - Test Maschinen Technik GmbH, Schwarmstedt, Germany
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Application of SLOFEC and Laser Technology for Testing of Buried Pipes Gerhard SCHEER 1 1 TMT - Test Maschinen Technik GmbH, Schwarmstedt, Germany
MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM CHAMBER
 Frascati Physics Series Vol. X (1998), pp. 371-378 14 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop, Frascati, Oct. 20-25, 1997 MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM
Frascati Physics Series Vol. X (1998), pp. 371-378 14 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop, Frascati, Oct. 20-25, 1997 MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM
3 General layout of the XFEL Facility
 3 General layout of the XFEL Facility 3.1 Introduction The present chapter provides an overview of the whole European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser (XFEL) Facility layout, enumerating its main components and
3 General layout of the XFEL Facility 3.1 Introduction The present chapter provides an overview of the whole European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser (XFEL) Facility layout, enumerating its main components and
Zettlex. Precision in the Extreme
 Zettlex is a sensors company. We design, make and sell sensors & sensor components for position and speed measurement. Flow metering Our company motto is signifying that even in harsh environments, our
Zettlex is a sensors company. We design, make and sell sensors & sensor components for position and speed measurement. Flow metering Our company motto is signifying that even in harsh environments, our
HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION
 HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION K.V. Zolotarev *, A.M. Batrakov, S.V. Khruschev, G.N. Kulipanov, V.H. Lev, N.A. Mezentsev, E.G. Miginsky, V.A. Shkaruba,
HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION K.V. Zolotarev *, A.M. Batrakov, S.V. Khruschev, G.N. Kulipanov, V.H. Lev, N.A. Mezentsev, E.G. Miginsky, V.A. Shkaruba,
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
High Resolution Sensor Bearing with an Index Signal
 Technical Article High Resolution Sensor Bearing with an Index Signal NTN NTN-SNR Hiroyoshi ITO Toru TAKAHASHI Pascal DESBIOLLES Cyril PETERSCHMITT Shintarou UENO This bearing with a rotation sensor is
Technical Article High Resolution Sensor Bearing with an Index Signal NTN NTN-SNR Hiroyoshi ITO Toru TAKAHASHI Pascal DESBIOLLES Cyril PETERSCHMITT Shintarou UENO This bearing with a rotation sensor is
MIG Encoders BEGE MIG NOVA+ Your drive, our (trans)mission. BEGE Power Transmission
 MIG Encoders BEGE MIG NOVA+ BEGE Power Transmission Anton Philipsweg 30 2171 KX Sassenheim The Netherlands T: +31 252-220 220 E: bege@bege.nl W: www.bege.nl Your drive, our (trans)mission Mounting a conventional
MIG Encoders BEGE MIG NOVA+ BEGE Power Transmission Anton Philipsweg 30 2171 KX Sassenheim The Netherlands T: +31 252-220 220 E: bege@bege.nl W: www.bege.nl Your drive, our (trans)mission Mounting a conventional
rotary encoder system
 L-9517-9466-01-B TONiC DSi dual readhead rotary encoder system DSi brings higher accuracy to rotary axes whilst propoz technology offers a selectable reference mark position. Using two readheads on an
L-9517-9466-01-B TONiC DSi dual readhead rotary encoder system DSi brings higher accuracy to rotary axes whilst propoz technology offers a selectable reference mark position. Using two readheads on an
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report
 Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
STRETCHED-WIRE TECHNIQUES AND MEASUREMENTS FOR THE ALIGNMENT OF A 15GHz RF-BPM FOR CLIC
 STRETCHED-WIRE TECHNIQUES AND MEASUREMENTS FOR THE ALIGNMENT OF A 15GHz RF-BPM FOR CLIC S. Zorzetti, N. Galindo Munoz, M. Wendt, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland L. Fanucci, Universitá di Pisa, Pisa, Italy Abstract
STRETCHED-WIRE TECHNIQUES AND MEASUREMENTS FOR THE ALIGNMENT OF A 15GHz RF-BPM FOR CLIC S. Zorzetti, N. Galindo Munoz, M. Wendt, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland L. Fanucci, Universitá di Pisa, Pisa, Italy Abstract
Investigating the Electromechanical Coupling in Piezoelectric Actuator Drive Motor Under Heavy Load
 Investigating the Electromechanical Coupling in Piezoelectric Actuator Drive Motor Under Heavy Load Tiberiu-Gabriel Zsurzsan, Michael A.E. Andersen, Zhe Zhang, Nils A. Andersen DTU Electrical Engineering
Investigating the Electromechanical Coupling in Piezoelectric Actuator Drive Motor Under Heavy Load Tiberiu-Gabriel Zsurzsan, Michael A.E. Andersen, Zhe Zhang, Nils A. Andersen DTU Electrical Engineering
PoS(VERTEX2015)008. The LHCb VELO upgrade. Sophie Elizabeth Richards. University of Bristol
 University of Bristol E-mail: sophie.richards@bristol.ac.uk The upgrade of the LHCb experiment is planned for beginning of 2019 unitl the end of 2020. It will transform the experiment to a trigger-less
University of Bristol E-mail: sophie.richards@bristol.ac.uk The upgrade of the LHCb experiment is planned for beginning of 2019 unitl the end of 2020. It will transform the experiment to a trigger-less
A high resolution bunch arrival time monitor system for FLASH / XFEL
 A high resolution bunch arrival time monitor system for FLASH / XFEL K. Hacker, F. Löhl, F. Ludwig, K.H. Matthiesen, H. Schlarb, B. Schmidt, A. Winter October 24 th Principle of the arrival time detection
A high resolution bunch arrival time monitor system for FLASH / XFEL K. Hacker, F. Löhl, F. Ludwig, K.H. Matthiesen, H. Schlarb, B. Schmidt, A. Winter October 24 th Principle of the arrival time detection
CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES This section provides the first-time photomultiplier tube users with general information on how to choose the ideal photomultiplier tube (often
CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES This section provides the first-time photomultiplier tube users with general information on how to choose the ideal photomultiplier tube (often
Set Up and Test Results for a Vibrating Wire System for Quadrupole Fiducialization
 LCLS-TN-06-14 Set Up and Test Results for a Vibrating Wire System for Quadrupole Fiducialization Michael Y. Levashov, Zachary Wolf August 25, 2006 Abstract A vibrating wire system was constructed to fiducialize
LCLS-TN-06-14 Set Up and Test Results for a Vibrating Wire System for Quadrupole Fiducialization Michael Y. Levashov, Zachary Wolf August 25, 2006 Abstract A vibrating wire system was constructed to fiducialize
GSP303D 3-Axis Digital Magnetic Field Transmitter
 Digital Handheld Magnetic Transmitter Transmitter Field Transmitter GSP303D 3-Axis Digital Magnetic Field Transmitter Digital Output (RS485) Accuracy Based on Reading (Not Range) Wide Supply Power: 5 to
Digital Handheld Magnetic Transmitter Transmitter Field Transmitter GSP303D 3-Axis Digital Magnetic Field Transmitter Digital Output (RS485) Accuracy Based on Reading (Not Range) Wide Supply Power: 5 to
CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010
 CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010 Yan Wang Deputy Group Leader of the Operations Group Outline CEBAF Timeline Machine Overview Injector Linear Accelerators Recirculation Arcs Extraction Systems Beam Specifications
CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010 Yan Wang Deputy Group Leader of the Operations Group Outline CEBAF Timeline Machine Overview Injector Linear Accelerators Recirculation Arcs Extraction Systems Beam Specifications
SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC
 SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC Y. Iwata *, K. Noda, T. Shirai, T. Murakami, T. Fujita, T. Furukawa, K. Mizushima, Y. Hara, S. Suzuki, S. Sato, and K. Shouda, NIRS, 4-9-1 Anagawa,
SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC Y. Iwata *, K. Noda, T. Shirai, T. Murakami, T. Fujita, T. Furukawa, K. Mizushima, Y. Hara, S. Suzuki, S. Sato, and K. Shouda, NIRS, 4-9-1 Anagawa,
CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS
 CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS R. Geithner #, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany & Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany T. Stöhlker, Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany
CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS R. Geithner #, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany & Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany T. Stöhlker, Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany
Vibrating Wire R&D for Alignment of Multipole Magnets in NSLS-II
 Vibrating Wire R&D for Alignment of Multipole Magnets in NSLS-II 10 th International Workshop on Accelerator Alignment February 11-15, 2008, Tsukuba, Japan Animesh Jain for the NSLS-II magnet team Collaborators
Vibrating Wire R&D for Alignment of Multipole Magnets in NSLS-II 10 th International Workshop on Accelerator Alignment February 11-15, 2008, Tsukuba, Japan Animesh Jain for the NSLS-II magnet team Collaborators
Chapter 5. Tracking system with MEMS mirror
 Chapter 5 Tracking system with MEMS mirror Up to now, this project has dealt with the theoretical optimization of the tracking servo with MEMS mirror through the use of simulation models. For these models
Chapter 5 Tracking system with MEMS mirror Up to now, this project has dealt with the theoretical optimization of the tracking servo with MEMS mirror through the use of simulation models. For these models
