EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/40
|
|
|
- Jacob Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP A1 (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01P 7/04 ( ) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (84) Designated Contracting States: AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR Designated Extension States: AL BA HR LV MK YU (71) Applicant: MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC INDUSTRIAL CO., LTD. Osaka (JP) (72) Inventors: Müller, Johannes Hamburg (DE) Höft, Michael, Dr Asendorf (DE) (74) Representative: UEXKÜLL & STOLBERG Patentanwälte Beselerstrasse Hamburg (DE) (54) Microwave band- pass filter (57) The present invention relates to a microwave band- pass filter comprising a plurality of coupled resonators including at least one coaxial resonator (1). For suppression of higher order or spurious pass- bands the filter is characterised in that a central hole (9) extends from the upper end of the inner conductor (6) of said at least one coaxial resonator through at least part of the length of the inner conductor, the central hole (9) forming a wave guide section, the cut- off frequency of which being above the pass- band of the band- pass filter, and in that the wave guide section contains in an upper portion (11) thereof a low loss dielectric material with a dielectric constant sufficiently high so that the cut- off frequency of the wave guide section is below the first higher order response of the band- pass filter, and in that the lower end portion (10) of the central hole (9) contains a lossy material. EP A1 Printed by Jouve, PARIS (FR)
2 Description [0001] The present invention relates to a microwave band- pass filter comprising a plurality of coupled resonators including at least one coaxial resonator. [0002] The microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum finds widespread use in various fields of technology. Exemplary applications include wireless communication systems, such as mobile communication and satellite communication systems, as well as navigation and radar technology. The growing number of microwave applications increases the possibility of interference occurring within a system or between different systems. Therefore, the microwave region is divided into a plurality of distinct frequency bands. To ensure, that a particular device only communicates within the frequency band assigned to this device, microwave filters are utilized to perform band- pass and band reject functions during transmission and/or reception. Accordingly, the filters are used to separate the different frequency bands and to discriminate between wanted and unwanted signal frequencies so that the quality of the received and of the transmitted signals is largely governed by the characteristics of the filters. Commonly, the filters have to provide for a small bandwidth and a high filter quality. [0003] For example, in communications networks based on cellular technology, such as the widely used GSM system, the coverage area is divided into a plurality of distinct cells. Each cell is assigned to a base station which comprises a transceiver that has to communicate simultaneously with a plurality of mobile devices located within its cell. This communication has to be handled with minimal interference. Therefore, the frequency range utilized for the communications signals associated with the cells are divided into a plurality of distinct frequency bands by the use of microwave filters. Due to the usually small size of the cells and the large number of mobile devices potentially located within a single cell at a time, the width of a particular band is chosen to be as small as possible. Moreover, the filters must have a high attenuation outside their pass- band and a low pass- band insertion loss in order to satisfy efficiency requirements and to preserve system sensitivity. Thus, such communication systems require an extremely high frequency selectivity in both the base stations and the mobile devices which often approaches the theoretical limit. [0004] Commonly, microwave filters include a plurality of resonant sections which are coupled together in various configurations. Each resonant section constitutes a distinct resonator and usually comprises a space contained within a closed or substantially closed conducting surface. Upon suitable external excitation, an oscillating electromagnetic field may be maintained within this space. The resonant sections exhibit marked resonance effects and are characterized by the respective resonant frequency and band- width. In order for the filter to yield the desired filter characteristics, it is essential that the distinct resonators coupled together to form the filter have a predetermined resonant frequency and band width or pass- band. The pass- band is usually defined as the frequency range between the frequencies at which a 3 db attenuation compared to the central resonant frequency is observed. [0005] A general problem of band- pass filters is that they have many unwanted (or "spurious") pass- bands. They occur due to the fact that the resonators have higher order resonances which are also named (Eigen-) modes of the corresponding structure. Accordingly, there are periodic higher order pass- bands at higher frequencies. For many applications such higher order pass- bands are not acceptable. [0006] One solution to overcome the problem is the utilization of an additional low- pass filter. This is the most commonly applied technique which, however, is accompanied by additional costs and additional space required for the low- pass filter, as well as by an increased insertion loss. [0007] Furthermore, there are techniques to disperse or to damp the spurious responses of the band- pass filter, as for example described in "A capacitively coupled wave guide filter with wide stop- band", 33rd European Microwave Conference 2003, Munich, Germany, pages The dispersion of the spurious responses may for example be done by using different resonant structures for each single resonator of the band- pass. Therefore, higher order eigenmodes occur at different frequencies and the spurious band- pass transmissions of the filter will be reduced. [0008] Another possibility is to add waveguides outside of the resonator cavities which have a cut- off frequency above the pass- band of the filter and which have placed at their end absorbers of lossy material. Such a technique is described in "Wave guide band- pass filters with attenuation of higher order pass- bands", 32rd European Microwave Conference 1993, Madrid, Spain, pages by W. Menzel et al. for a rectangular wave guide band- pass. In between the resonators of the filter there are placed smaller rectangular waveguides having a cut- off frequency above the pass- band of the filter. In this arrangement, only fields with frequencies above the cut- off frequency of the smaller waveguides can penetrate the smaller waveguides, and are thereby damped by the lossy material at the end of the added waveguides. A disadvantage of this arrangement is the extra space needed for the added smaller waveguides which are placed in between adjacent resonators of the filter. [0009] It is an object of the present invention to provide a microwave filter comprising a plurality of resonators including at least one coaxial resonator which allows for a sufficient suppression of spurious or higher order pass- bands without needing space for extra components. [0010] This object is achieved by a microwave filter as defined in claim 1. Preferred embodiments of the microwave filter are set out in the dependent claims. 2
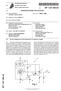
3 [0011] The microwave filter has a plurality of coupled resonators including at least one coaxial resonator. Coaxial resonators have a cylindrical inner conductor which is mounted on the base of the resonator cavity and which extends to a predetermined height, leaving a gap between its upper end and the inner surface of the top cover of the cavity. Such coaxial resonators are also referred to as combline resonators. According to the present invention, the inner conductor of the at least one coaxial resonator is provided with a central hole extending from the top end of the inner conductor over at least part of its height. This central hole forms a waveguide section which has a cut- off frequency above the pass- band of the filter. This is so because the transverse or cross- sectional dimension of the central hole of the inner conductor is smaller than the inner diameter of the coaxial resonator cavity. The waveguide section is further adapted, as will be explained below, to have a cut- off frequency below the first higher order resonance of the filter. [0012] The lower portion of the central hole contains a lossy material which may be a lossy dielectric material, e.g. silicon carbide ceramics, or a lossy magnetic material, e.g. a resin matrix material filled with magnetic material. [0013] With this arrangement electromagnetic fields with frequencies above the cut- off frequency of the waveguide section, which is below the first higher order or spurious pass- band frequency of the filter, will enter the central hole of the inner conductor and will be damped or attenuated by the lossy material at the bottom of the central hole. On the other hand, for frequencies within the pass- band the lossy material at its bottom is "invisible", since these electromagnetic fields cannot enter the central hole but are decaying exponentially. Thus, the central hole with its lossy material does not affect the transmission performance of the filter within the pass- band. [0014] A combline resonator has a height of lower than λ/ 4 - typically λ/ 8 - where λ is the wavelength corresponding to the center of the pass- band. The short (electrical connection between inner conductor and base plate) at the bottom of the resonator is transformed to an inductance at the top of the resonator, which together with the capacitive gap at the top of the resonator create the fundamental resonance. If only transversal electromagnetic (TEM-) waves are considered, the first higher order or spurious pass- band would be in a frequency area approximately 3 to 5 times larger than the fundamental pass- band frequency. Besides the TEM- waves, also the transversal electric (TE-) and transversal magnetic (TM-) modes of the resonator have to be considered - which in contrast to the TEM- modes have a strong dependency on the resonator diameters. Therefore, the spurious pass- band might even lie closer to the intended passband. To keep the TE- and TM- modes at higher frequencies, the outer diameter of the resonator should be kept small - typically much smaller than λ/ 2 of the fundamental pass- band frequency. The ratio of the outer diameter of the resonator to the outer diameter of the inner conductor should lie around 3.6 to guarantee a high quality factor of the resonator, since at this ratio the damping constant of the corresponding coaxial line is minimal. [0015] The central hole needs to be adapted in order to be able to have a cut- off frequency below the first higher order pass- band. The cut- off frequency ν cut of the central hole corresponds to a wavelength λ cut =2.61 r 0, where r 0 is the radius of the air- filled central hole. At frequencies larger than ν cut, the first mode, i.e. the TM 01 -mode will be able to propagate. If the frequency is further increased, other modes have to be taken into account as well. This ν cut, if the central hole were filled with air as the resonator cavity, would generally correspond to a frequency many times higher than the resonance frequency in the pass- band. Since on the other hand, as mentioned above, the first higher order pass- band may already occur at 3 times of the pass- band frequency, it is necessary to lower the cut- off frequency of the central hole. This can be done by disposing a low loss dielectric material in an upper portion of the central hole, such as for example a ceramic material, which has a relative dielectric constant sufficiently high so that the cut- off frequency of the central hole can be brought to lower frequencies closer to the pass- band frequency so that already the first higher order resonance of the filter is above the cut- off frequency of the central hole. The cut- off frequency depends on properties of the material in the waveguide section as (ε r r ) -1/2 (ε r being the relative dielectric constant and r being the relative permeability of the material). Thus, using a material with ε r being about 100, r being of the order of 1, would lower the cut- off frequency of the central hole by a factor 1/10 compared to an air filled waveguide section. [0016] A dielectric material is further characterized by a dissipation factor D or a loss tangent tan δ which are identical. [0017] This is the quantity representative for the energy loss characteristic of the material. Materials which have a value of tan δ of above 0,1 are characterized as lossy materials. On the other hand, dielectric materials with tan δ below 0,01 are considered to be low loss dielectric materials. They are electrical insulators. Dielectric properties of these materials show relatively little variation with the frequency over the microwave range. It is preferred that the low- loss dielectric materials have a loss tangent below 0,001. [0018] The property of the central hole to have a cut- off frequency above the pass- band is defined herein in the usual manner to mean that the cut- off frequency is above the 3 db corner frequency of the pass- band of the filter. [0019] It will be appreciated that with the design of the present invention higher order pass- bands of the filter may be suppressed without needing any extra space or additional components. Therefore, such filter design allows to provide very efficient and compact microwave filters. [0020] The invention will in the following be described in connection with the embodiments shown in the drawings, in which Figure 1 is a schematical perspective representation of a four pole band- pass filter; 3
4 Figure 2 is a perspective schematical representation of a coaxial resonator as used in the filter according to the invention; and Figure 3 shows the frequency dependent response of the filter in terms of the ratio of outgoing to incoming power with and without spurious mode suppression. [0021] Figure 1 shows a microwave filter comprising four coaxial resonators 1 being coupled in series. This filter has a capacitive input coupling 20 and a capacitive output coupling 21. Tuning screws for tuning frequencies and couplings are not shown. In general, there will be more than a series of resonators but rather a two- dimensional arrangement of coupled resonators. [0022] Figure 2 shows an individual coaxial resonator which is to be used in a filter comprising a plurality of coupled resonators according to the invention. This coaxial resonator 1 comprises a hollow cylindrical housing 2. The housing 2 is formed by a disc- shaped base 3, a side- wall 4 extending upwardly from the base 3, and a disc- shaped cover 5 secured to the upper end of the side- wall 4. The resonator 1 further includes a cylindrical inner conductor 6 which is centrally located inside the interior of the housing 2 and which is attached with its lower end 7 to the base 3. The inner conductor 6 extends upwardly from the base 3 along the longitudinal axis of the cylindrical housing 2. Its length is lower than the height of the housing 2 so that a capacitive gap is formed between the upper end 8 of the inner conductor 6 and the cover 5 of the housing 2. [0023] The inner conductor 2 is provided with a central hole 9 which is extending from its upper end 8 into the inner conductor 6 over a part of the length of the latter. The central hole 9 may for example be drilled into the inner conductor 6. [0024] The lower part 10 of the central hole 9 contains a lossy material which acts as an absorber. Such lossy material may for example be lossy magnetic materials such as magnetically loaded epoxide resins, as the absorber materials provided by Emerson & Cuming Microwave Products, Randolph, MA, USA, under the tradename Eccosorb MF. The material Eccosorb MF190 for example has at 3GHz a dielectric constant ε r of 28 and a magnetic permeability r of 4.5, and loss tangents of tan δ d of 0.04 and tan δ m Alternatively, lossy dielectric materials may be used, such as silicon carbide ceramics which are formed by sintering silicon carbide (SiC) powders. Such silicon carbide ceramics have dielectric constants ε r of typically 30 to 35, and loss tangents tan δ d in the range 0.3 to 0.5. [0025] The lossy material may partially or completely fill the lower end portion of the central hole 9. [0026] The upper part 11 of the central hole 9 contains preferably a low- loss dielectric material (for example a ceramic material as used for dielectric resonators). As has been explained above, this upper low- loss dielectric material is needed to provide a relative dielectric constant ε r within the upper part of the central hole 9 which is sufficiently high to lower the cut- off frequency of the central hole 9 in order to ensure that the first higher order pass- band of the filter is above the cut- off frequency of the central hole 9. Examples for materials which are suitable as low- loss dielectric materials in the upper part of the central hole 9 are listed in table 1 below. Table 1: Low loss Ceramic Materials Material Composition ε r Q*f (f in GHz) Loss Tangent at 4GHz Temperature Coefficent ppm/ C BaTi 4 O , Ba 2 Ti 9 O , (Zr- Sn) TiO , to +10 Ba (Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 ) O 2 -Ba , to +10 (Zn 1/3 Ta 2/3 ) O 2 BaO- PbO- Nd 2 O 3 -TiO , at 1GHz +10 to -10 MgTiO 3 -CaTiO , to [0027] The transition between the low- loss dielectric material in the upper portion 10 and the lossy material in the lower portion of the central hole could be a discontinuous transition, as shown in the schematic drawings, or preferably be a smooth transition. The latter may be accomplished for example by giving the lossy dielectric material in the lower portion 10 an upper surface which is inclined with respect to the longitudinal axis of the central hole 9, and by giving the low- loss dielectric material a lower surface which is complementary to the upper surface of the lossy dielectric material. This smooth transition is preferred in order to suppress reflections on the transition between the two dielectric materials. Alternatively, a smooth transition may be provided if the low- loss dielectric material and the lossy material are formed in sintering processes in which the powders of the respective materials are mixed in the transition region. [0028] The central hole 9 serves as a cylindrical waveguide. The size (diameter) and its low- loss dielectric filling in 4
5 the upper portion 11 have to be chosen such that the cut- off frequency is above the pass- band of the filter but below the first higher order or spurious pass- band of the filter. In this manner, the central hole is not "visible" for frequencies within the pass- band, and thus does not affect the filter performance in the pass- band. To guarantee that the quality factor of the resonators remains high, the dielectric material in the upper portion 11 should show a low losses as possible. [0029] For frequencies above the cut- off frequency of the central hole, this central hole 9 is able to propagate waves. For such frequencies, the central hole 9 will be able to propagate waves, and the ground of the central hole 9 with its lossy material will be "visible" for electric fields with such frequencies. Since the cut- off frequency of the central hole 9 is adapted to be below the first higher order of spurious pass- band of the filter, all higher order or spurious modes of the filter will be attenuated or suppressed. In this way the stop- band characteristic of the filter is improved. [0030] This is shown in Figure 3 in which the filter performance (ratio of outgoing power to incoming power) is shown for a filter in solid lines which does not employ a higher pass- band suppression according to the present invention. This filter response shows the first pass- band and at higher frequencies undesired higher order or spurious pass- bands. By providing the coaxial resonators with inner conductors with central holes in accordance with the invention the higher order pass- bands are attenuated as shown by the dashed line in Figure 3. Claims Microwave band- pass filter comprising a plurality of coupled resonators including at least one coaxial resonator (1), characterised in that a central hole (9) extends from the upper end of the inner conductor (6) of said at least one coaxial resonator through at least part of the length of the inner conductor, the central hole (9) forming a wave guide section, the cut- off frequency of which being above the pass- band of the band- pass filter, and in that the wave guide section contains in an upper portion (11) thereof a low loss dielectric material with a dielectric constant sufficiently high so that the cut- off frequency of the wave guide section is below the first higher order response of the band- pass filter, and in that the lower end portion (10) of the central hole (9) contains a lossy material. 2. Band- pass filter according to claim 1, characterised in that the lossy material at the lower end portion (10) of the central hole (9) is a lossy dielectric material or a lossy magnetic material Band- pass filter according to claim 1 or 2, characterised in that the low- loss dielectric material has a loss tangent tan δ below 0, Band- pass filter according to claim 2 or 3, characterised in that the lossy material is a lossy dielectric in the form of a silicon carbide (SiC) ceramic. 5. Band- pass filter according to any of the claims 1 to 4, characterised in that the central hole has a cylindrical shape. 6. Band- pass filter according to any of the claims 1 to 5, characterised in that the transition between the low loss material and the lossy material in the central hole (9) is gradual in axial direction of the central hole. 7. Band- pass filter according to claim 6, characterised in that the lossy material has an upper surface which is obliquely oriented with respect to the longitudinal axis of the central hole, and the low loss dielectric material has a complementary lower surface. 8. Band- pass filter according to claim 6, characterised in that the lossy material and the low- loss dielectric material are made of sintered powder materials, and in that the respective powder materials are mixed in the transition region
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Non-patent literature cited in the description A capacitively coupled wave guide filter with wide stop-band. 33rd European Microwave Conference, 2003, [0007] W. MENZEL. Wave guide band-pass filters with attenuation of higher order pass-bands. 32rd European Microwave Conference, 1993, [0008] 10
(51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 ( ) B21D 41/00 ( ) B62D 1/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/02 ( ) G01S 5/14 ( ) H04L 12/28 (2006.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/51
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 5496_6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 ( ) H02M 7/493 (2007.
 (19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/48
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T (11) EP 2 728 390 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (21) Application number: 12804964.0
(19) TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T (11) EP 2 728 390 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (21) Application number: 12804964.0
TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
(19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
TEPZZ 8 5ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/09
 (19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( ) G06F 3/0482 (2013.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 674Z48A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B29B 15/12 ( ) B32B 5/26 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
(19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/33
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/50
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
TEPZZ 76 84_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
(19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
(19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/35
 (19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
(19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
TEPZZ Z7Z7 5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H01F 30/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/06 ( ) (54) Combined current and voltage measurement transformer of the capacitor bushing type
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
TEPZZ 7545 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/29
 (19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
(19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04B 1/40 ( ) H04W 52/02 (2009.
 (19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
(19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
TEPZZ Z47794A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
(19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
(51) Int Cl.: G03B 37/04 ( ) G03B 21/00 ( ) E04H 3/22 ( ) G03B 21/60 ( ) H04N 9/31 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
(19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2002/33
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 ( ) G01B 11/24 ( ) G01N 21/47 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G07D 9/00 ( ) G07D 11/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
(19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
TEPZZ Z_89_5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2016/19
 (19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/06 ( ) G01S 5/02 (2010.
 (19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
(19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2004/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H01Q 3/26 ( ) H01Q 21/06 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 469 61 A1 (43) Date of publication: 27.06.12 Bulletin 12/26 (1) Int Cl.: H01Q 3/26 (06.01) H01Q 21/06 (06.01) (21) Application number: 111943.3 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 469 61 A1 (43) Date of publication: 27.06.12 Bulletin 12/26 (1) Int Cl.: H01Q 3/26 (06.01) H01Q 21/06 (06.01) (21) Application number: 111943.3 (22) Date
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 ( ) G01S 13/78 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
(19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
(51) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 ( ) B25J 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 9746 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
TEPZZ _79748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 ( ) B60Q 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
(19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/18
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/39
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 ( ) B25J 9/00 ( ) (54) Robotic system for laser, plasma, water jet, milling etc. machining or processing of parts
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/37
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 498 162 A1 (43) Date of publication: 12.09.2012 Bulletin 2012/37 (51) Int Cl.: G05F 3/24 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11368007.8 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 498 162 A1 (43) Date of publication: 12.09.2012 Bulletin 2012/37 (51) Int Cl.: G05F 3/24 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11368007.8 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04N 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
(19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
TEPZZ _74 6 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G10L 19/24 ( ) G10L 21/038 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B23K 9/095 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56857 A_T (11) EP 2 568 572 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/11 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12183666.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 56857 A_T (11) EP 2 568 572 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/11 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12183666.2 (22)
TEPZZ Z 8867A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
TEPZZ 5Z 8 9B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 52/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ _64_69B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
(19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
Waveguides. Metal Waveguides. Dielectric Waveguides
 Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/52
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001609947A1* (11) EP 1 609 947 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.12.2005 Bulletin 2005/52
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001609947A1* (11) EP 1 609 947 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.12.2005 Bulletin 2005/52
~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) ~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 843 043 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: E01B 31/17 20.05.1998
(19) J (12) ~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 843 043 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: E01B 31/17 20.05.1998
Ceramic Waveguide Filters with Wide Spurious-Free Stopband Response
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 79, 23 31, 2019 Ceramic Waveguide Filters with Wide Spurious-Free Stopband Response Sharjeel Afridi 1, *, Ian Hunter 2, and Yameen Sandhu 1 Abstract This work
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 79, 23 31, 2019 Ceramic Waveguide Filters with Wide Spurious-Free Stopband Response Sharjeel Afridi 1, *, Ian Hunter 2, and Yameen Sandhu 1 Abstract This work
TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B21J 5/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Intel e B60M 1/13. Bayonne, New Jersey (US) Holborn London EC1N2QP (GB)
 (19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
(19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
(54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE FOR USE IN THE COLORIMETRIC ANALYSIS OF A SAMPLE FLUID, APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COLORIMETRIC ANALYSIS OF A SAMPLE FLUID
 (19) TEPZZ _79 _A_T (11) EP 3 179 231 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/2 (06.01) (21) Application number: 162482.2 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _79 _A_T (11) EP 3 179 231 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/2 (06.01) (21) Application number: 162482.2 (22) Date of
Chebyshev Microwave Filter Design by Using Dielectric. Combline Resonators ABSTRACT
 Chebyshev Microwave Filter Design by Using Dielectric Combline Resonators ABSTRACT Microwave filters are important in the design of modern communications systems, military applications and the satellite
Chebyshev Microwave Filter Design by Using Dielectric Combline Resonators ABSTRACT Microwave filters are important in the design of modern communications systems, military applications and the satellite
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF CAVITY RESONATORS
 &2@?%3 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF CAVITY RESONATORS CHAPTER 3 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OFCAVITY RESONATORS 3.1 Introduction In the cavity perturbation techniques, generally rectangular or cylindrical waveguide
&2@?%3 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF CAVITY RESONATORS CHAPTER 3 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OFCAVITY RESONATORS 3.1 Introduction In the cavity perturbation techniques, generally rectangular or cylindrical waveguide
TEPZZ _48_45A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
(19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T (11) EP 2 806 286 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.11.14 Bulletin 14/48 (21) Application number: 13168943.2 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/34 (06.01) G01S 13/93
(19) TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T (11) EP 2 806 286 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.11.14 Bulletin 14/48 (21) Application number: 13168943.2 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/34 (06.01) G01S 13/93
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/35
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 362 70 A2 (43) Date of publication: 31.08.11 Bulletin 11/3 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 1/22 (06.01) H04L 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 098.4 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 362 70 A2 (43) Date of publication: 31.08.11 Bulletin 11/3 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 1/22 (06.01) H04L 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 098.4 (22) Date of filing:
DIELECTRIC RESONATORS
 Operating frequencies in wireless communications have shifted towards high frequency band, and thus frequencies higher than 1 GHz are now commonly utilized. In addition, the microwave frequency spectrum
Operating frequencies in wireless communications have shifted towards high frequency band, and thus frequencies higher than 1 GHz are now commonly utilized. In addition, the microwave frequency spectrum
Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research
 International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
(51) Int Cl.: H01Q 1/36 ( ) (56) References cited:
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 597 794 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 20.08.2008 Bulletin 2008/34 (21) Application number: 03815944.8 (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 597 794 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 20.08.2008 Bulletin 2008/34 (21) Application number: 03815944.8 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: B60J 10/00 ( ) B60P 3/34 ( ) F16J 15/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
(19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
EC Transmission Lines And Waveguides
 EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets A1. Publication number: EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 339 859 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 89303866.1 mt. ci*g11b 23/28 @ Date of filing:
J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 339 859 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 89303866.1 mt. ci*g11b 23/28 @ Date of filing:
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
LENGTH REDUCTION OF EVANESCENT-MODE RIDGE WAVEGUIDE BANDPASS FILTERS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 40, 71 90, 2003 LENGTH REDUCTION OF EVANESCENT-MODE RIDGE WAVEGUIDE BANDPASS FILTERS T. Shen Advanced Development Group Hughes Network Systems Germantown, MD
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 40, 71 90, 2003 LENGTH REDUCTION OF EVANESCENT-MODE RIDGE WAVEGUIDE BANDPASS FILTERS T. Shen Advanced Development Group Hughes Network Systems Germantown, MD
TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T (11) EP 2 871 760 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.0.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 13192249.4 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/42 (07.01) H02M 1/32 (07.01)
(19) TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T (11) EP 2 871 760 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.0.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 13192249.4 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/42 (07.01) H02M 1/32 (07.01)
TEPZZ B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 87_554A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 87_554A_T (11) EP 2 871 554 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.05.2015 Bulletin 2015/20 (21) Application number: 14192721.0 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/01 (2006.01) G06F
(19) TEPZZ 87_554A_T (11) EP 2 871 554 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.05.2015 Bulletin 2015/20 (21) Application number: 14192721.0 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/01 (2006.01) G06F
R.K.YADAV. 2. Explain with suitable sketch the operation of two-cavity Klystron amplifier. explain the concept of velocity and current modulations.
 Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
^^r" Office europeen des brevets. Publication number:
 Europaisches Patentamt fl))j European Patent Office Publication number: 0 066 324 ^^r" Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 82200593.0 Int. CI.3: E 05 G 1/00 @
Europaisches Patentamt fl))j European Patent Office Publication number: 0 066 324 ^^r" Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 82200593.0 Int. CI.3: E 05 G 1/00 @
Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components
 Waveguides Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components BACKGROUND A transmission line can be used to guide EM energy from one point (generator) to another (load). A transmission line can support
Waveguides Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components BACKGROUND A transmission line can be used to guide EM energy from one point (generator) to another (load). A transmission line can support
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and
 Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
Microwave and optical systems Introduction p. 1 Characteristics of waves p. 1 The electromagnetic spectrum p. 3 History and uses of microwaves and optics p. 4 Communication systems p. 6 Radar systems p.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
TEPZZ 755Z44A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 ( ) G01S 13/93 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7Z44A_T (11) EP 2 7 044 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/ (06.01) G01S 13/93 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1311322.8
(19) TEPZZ 7Z44A_T (11) EP 2 7 044 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/ (06.01) G01S 13/93 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1311322.8
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/11
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
Waveguides GATE Problems
 Waveguides GATE Problems One Mark Questions. The interior of a 20 20 cm cm rectangular waveguide is completely 3 4 filled with a dielectric of r 4. Waves of free space wave length shorter than..can be
Waveguides GATE Problems One Mark Questions. The interior of a 20 20 cm cm rectangular waveguide is completely 3 4 filled with a dielectric of r 4. Waves of free space wave length shorter than..can be
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300072 25 May 2017 The below identified patent
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300072 25 May 2017 The below identified patent
Monoconical RF Antenna
 Page 1 of 8 RF and Microwave Models : Monoconical RF Antenna Monoconical RF Antenna Introduction Conical antennas are useful for many applications due to their broadband characteristics and relative simplicity.
Page 1 of 8 RF and Microwave Models : Monoconical RF Antenna Monoconical RF Antenna Introduction Conical antennas are useful for many applications due to their broadband characteristics and relative simplicity.
A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 14, 131 145, 21 A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS C.-Y. Hsiao Institute of Electronics Engineering National
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 14, 131 145, 21 A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS C.-Y. Hsiao Institute of Electronics Engineering National
(51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/16 ( ) B29K 55/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
(74) Representative: Korber, Martin Hans et al
 (19) I Europllsches Patentamt European Patent Office 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 1 739 937 1 (12) EUROPEN PTENT PPLICTION
(19) I Europllsches Patentamt European Patent Office 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 1 739 937 1 (12) EUROPEN PTENT PPLICTION
TEPZZ 66 8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 66 8A_T (11) EP 3 226 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 04..17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 877461.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 66 8A_T (11) EP 3 226 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 04..17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 877461.2 (22)
A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 43, 247 254, 2013 A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER Bao-Qin Lin *, Shao-Hong Zhao, Qiu-Rong Zheng, Meng Zhu, Fan Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 43, 247 254, 2013 A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER Bao-Qin Lin *, Shao-Hong Zhao, Qiu-Rong Zheng, Meng Zhu, Fan Li,
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/041 ( ) H03K 17/96 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
(19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
The below identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300104 25 May 2017 The below identified patent
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY OFFICE OF COUNSEL NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION 1176 HOWELL STREET NEWPORT Rl 02841-1708 IN REPLY REFER TO Attorney Docket No. 300104 25 May 2017 The below identified patent
EC TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES
 TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY 1. Define Characteristic Impedance [M/J 2006, N/D 2006] Characteristic impedance is defined as the impedance of a transmission line measured
TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY 1. Define Characteristic Impedance [M/J 2006, N/D 2006] Characteristic impedance is defined as the impedance of a transmission line measured
