TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
|
|
|
- Lee Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/19 (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (51) Int Cl.: G02B 6/32 ( ) B23K 26/08 ( ) G02B 27/28 ( ) (86) International application number: PCT/JP2012/ (87) International publication number: WO 2013/ ( Gazette 2013/01) (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR (30) Priority: JP (71) Applicant: Furuuchi Chemical Corporation Tokyo (JP) (72) Inventor: HOSOKAWA Tadatoshi Sayama-shi Saitama (JP) (74) Representative: Baumgärtel, Gunnar et al Patentanwälte Maikowski & Ninnemann Postfach Berlin (DE) (54) COLLIMATOR AND OPTICAL ISOLATOR WITH COLLIMATOR (57) An optical isolator with a collimator which is used at the tip end of a laser beam transmitting fiber utilized in a laser processing. The optical isolator can provide solutions to the problems how to make return lights to be isolated from an incident light path and how to prevent the light energy from being conducted to an incident fiber, a laser oscillator, the collimator, and the optical isolator. The solutions comprise light-receiving fibers (22 and 23) disposed at focal points of a collimator lens (5) to which reflected lights from a workpiece return through the optical isolator. The return lights are then led to a ceramic tube (24) where the return light energy is converted to thermal energy and dissipated. EP A1 Printed by Jouve, PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP A1 2 Description FIELD OF THE INVENTION [0001] This invention relates to an optical isolator with an optical collimator which is set at the tip end of a light transmitting fiber conveying a fiber laser light energy to a workpiece to be processed by, for example, cutting, marking or soldering. This optical isolator with the optical collimator is used to prevent return lights reflected from the object from entering into the light transmitting fiber and a laser light source. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION [0002] Solid-state YAG lasers were previously used for a laser welding, cutting, or marking of metals in metal processing. Fiber lasers were recently developed and begun to be used practically in the wavelength region between 1.0 micrometer and 1.1 micrometers. The fiber lasers are paid attention as a replacement of YAG lasers. [0003] Optical reflectivity of metals is very high in these wavelength regions, especially the optical reflectivity of gold, silver, copper, and aluminum are more than 90%. Although iron, nickel, and cobalt metals have relatively low optical reflectivity and suit for laser processing in these wavelength regions, the optical reflectivity of these metals is more than 50%. It must be taken into consideration that a considerable amount of the laser light energy returns to the laser light source, though all of the radiated energy does not return to the laser light source because the surface of the metal workpiece is not always mirror finished surface. [0004] Resonant material of a YAG solid-state laser is crystal and that of a fiber laser is quartz glass which has less power damage threshold than crystals. For this reason, a return light to the laser light source and particularly an incident light normal-incidence to the light source have to be avoided. The use of an optical isolator is ultimately effective in cases of fiber lasers wherein the optical polarization plane can always be changed arbitrary. The polarization independent optical isolators are especially useful. [0005] The polarization independent optical isolator is an optical device composed of two optical polarizers made of birefringent crystal and a Faraday rotator. The polarization independent optical isolators are classified into two types with its crystal polarizer type. One optical isolator is using birefringent crystal plane plate polarizers, and the other is using birefringent crystal wedge polarizers. [0006] In the case of the birefringent crystal plane plate type optical isolator, one incident collimated optical beam is separated into two parallel beams after passing through the plane plate polarizer. The two parallel beams propagate through the Faraday rotator whose area of cross section needs at least 2ϕ that is twice large of the diameter ϕ of the incident beam. On the other hand, in the case of the birefringent crystal wedge type optical isolator, the incident beam is separated into two beams, i.e. a normal light beam and an abnormal light beam, at a definite angle θ after passing through the polarizer. The diameter of the Faraday rotator needs ϕ + d x tan θ, where d denotes the distance of two wedge polarizers. The numerical values of these parameters, namely, beam diameter ϕ, distance between polarizers d, and the beam separation angle θ determines which type of isolator is more advantageous. It can generally be said that the wedge isolator has an advantage, because the required Faraday rotator cross sections do not increase as a beam diameter increases. In the case of the plane plate type optical isolator, the more power of the fiber laser, the more beam diameter increases practically. In view of this fact, it is expected that there will be an increase in demand for the wedge type optical isolators and that the high durability to the high power fiber laser will be needed for the wedge type optical isolators. PRIOR ART PATENT DOCUMENTS [0007] JP, ,B(1983) JP, ,B(1986) JP, ,B US5,408,354A US7,306,376B2 US7,426,325B2 JP, ,A SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED BY THE INVENTION [0008] It must be aware that there is a difference in a character of the optical isolator used for fiber lasers in laser processing such as welding, cutting, or marking processing, from that of optical isolators previously used for optical communications. The optical isolator for laser processing needs measures to release safely the thermal energy of return light to protect the laser system from thermal damage, because the return light energy is very high. [0009] In wedge type optical isolators, the return light focuses at two points which are apart by a distance f x tan θ from the incident point, where f is the focal length of the lens, θ is the return angle mentioned in the previous section. [0010] For optical isolators used for optical communications, it is important to determine focal length f and angle θ of return beam angle of the inline optical isolator so that the focal points may have a sufficient distance wherein the return light does not couple with the core of the incident light fiber. The core diameter is only about 2
3 3 EP A1 4 10mm. The return light may go back to fiber clad of 125mm diameter, which is acceptable. [0011] However, in isolators for high power fiber laser processing, return light power is so high that the return light must be configured not to couple with the core of the incident light fiber and that the value of f x tan θ must be determined to be sufficiently large enough for the return light not to go back to clad of the fiber. Or, otherwise, the thermal energy will heat the fiber, surrounding polymer material, ferrule, or the inner wall of the optical isolator and result in destroying the collimator or the laser oscillator itself, at last end. [0012] One of the previous solutions for this issue is found in the U. S. Patent No. 7,426,325, for instance, showing an inline polarization independent optical isolator equipped with special optical collimators which are monolithically composed of fibers, an end cap or a lens with end cap such as shown in the U.S. Patent No. 7,306,376. By using this collimator, the return light does not return to a laser oscillator, nor damage fibers or collimators. [0013] In the previous solution, the return light energy however diverges to the surroundings such as collimator holders and isolator holders around the collimator and heats them. This means that a temperature increase occurs in magnets, components of the isolator. Since the magnet has such properties that its magnetic field intensity depends upon temperature, characteristics of the isolator change with the change of temperature of magnets. If the workpiece under laser processing is a high reflective material, the isolator needs water cooling. In the case that the reflectivity of the workpiece is very high, the use of the isolator in the laser processing will be restricted. [0014] The purpose of this invention is to supply a mechanism to safely isolate the return light from the collimator, the surrounding holder, and the isolator without accumulating the return light energy, change the light energy to thermal energy and evacuate the thermal energy to dissipate it. MEANS FOR SOLVING THE PROBLEM [0015] In order to resolve the above mentioned problem, the inventor fabricated such a mechanism that optical fibers receive the return light from an optical isolator to separate the light from the collimator, optical isolator and the laser oscillator, and change the light energy to thermal energy to safely dissipate it. [0016] Three optical fibers are aligned in parallel with the same distance apart. The center fiber is used to emanate light from laser oscillator and the emanated light is led to optical isolator through a lens. Two outside fibers are used to receive return light from the optical isolator. The received light is led to a heat-resistant article such as ceramics placed apart from the laser source in order to change the light energy to the thermal energy. Then the thermal energy is cooled by water or air in the ceramics. To fix the three fibers, a three-hole ferrule or a threeline grooved plate with grooves arranged at the same distance apart can be used. [0017] The whole system is schematically drawn in Figure 1. Light emitted from a fiber laser 1 is led to a first fiber 2 fixed at the center of the three fibers. The light is emanated from an end of the fiber 2 to a lens 5. It is desirable for the light passing area at the end of the fiber 2 to be large in order to protect the end area from high power damage. For this purpose, it is desirable to enlarge a core of the fiber 2 at the end area or weld an end cap of pure fused silica glass to the end area of the fiber 2. The light passing through the lens 5 becomes a collimated beam. After passing through a wedge polarizer type optical isolator, the collimated beam passes through a condense lens 14 and then focuses at a focal point 16 on a workpiece 15. [0018] All the irradiated light is not absorbed as the energy for processing into the workpiece under processing. Part of the light is reflected at a reflection rate determined by the workpiece material. The reflected light becomes collimated beam when returning through a second lens 14. When the collimated beam returns through the isolator, the return beams make some angle θ with the incident beam. The angle θ is determined by the wedge angle of the isolator. As is shown in Figure 2, the backward light beams are focused on two points 19 and 20 which are f x tan θ away from the end of the first fiber. If ends of two fibers 22 and 23 are disposed at these focusing points, then the energy of reflection light from the workpiece under processing can be effectively captured. The return light never returns to the first fiber 2 or the laser oscillator 1. It is desirable for core diameters of the second and third fibers 22 and 23 to be larger than that of the first fiber 2 because the role of the second and third fibers is only to receive the light. It is desirable for the ends of the core of the second and third fibers to be expanded or to have end caps in order to protect the core ends from high power light energy. The other ends of second and third fibers are led to a high temperature durable ceramic tube 24 whose one end is closed. Moreover, the ceramic tube is covered with a stainless tube 25 whose one end is closed. The stainless tube is cooled by water or air. TECHNICAL EFFECT OF THE INVENTION [0019] As is described in previous section, some amount of light is reflected without absorbed into the processing workpiece. The reflected light energy is completely isolated with the optical isolator and the triple fiber collimator of this invention from the first fiber and the laser oscillator. The reflected light energy is led with the second and the third fibers to the high temperature durable tube and changed to thermal energy. The reflected light energy thus gives no damages to the laser oscillator and the transmitting fiber. 3
4 5 EP A1 6 BREAF DISCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0020] Fig.1: the whole scheme of this invention Fig.2: a detailed explanation of light pass of the incident beam and return light beam near the triple fiber collimator and the first wedge polarizer of the optical isolator of this invention Fig.3: a cross section of the triple fiber collimator and the optical isolator of this invention Fig.4A: a cross section of the three holes zirconia ferrule with three fibers of this invention. Fig.4B: a right side view of the three holes zirconia ferrule with three fibers of this invention. A MODE FOR EMBODYING THE INVENTION [0021] Zirconia ferrules are conventionally used devices to fix fibers positioning precisely. Zirconia ferrules with several holes precisely positioned are recently marketed. An example of this invention using a three-hole zirconia ferrule is shown below. WORKING EXAMPLE [0022] Figure 3 shows the cross section of an embodiment of this invention. A collimator composed of a three core zirconia ferrule with three fibers and a lens 5 is combined with an optical isolator whose polarizers 6 and 11 are Rochon prisms as a kind of birefringent crystal wedge polarizer. [0023] Figures 4A and 4B show details of the collimator. Three fibers 2, 22, and 23 are fixed in the three holes of the zirconia ferrule 21 mounted on plug 31. The first fiber 2 has a clad diameter of 125 micrometers. The core diameter of the end of the first fiber is expanded from initial 10 micrometer to 20 micrometers. The numerical aperture NA of this core expanded fiber is The core diameter of both the second fiber 22 and the third fiber 23 is 62.5 micrometers and the clad diameter is 125 micrometers. The core diameter of the second and the third fibers is larger than the core diameter of the first fiber so as to receive the return light easily. Zirconia ferrule with 2.5 mm diameter has a hole with 125 micrometers diameter in the center and two holes with 125 micrometers diameter on both sides of the center hole. As is shown in Figure 4B for the right side view of the ferrule 21, three fibers have their ends aligned straight in the figure. The distances between the first fiber 2 and the second fiber 22 and between the first fiber 2 and the third fiber 23 are equally 250 micrometers, respectively. [0024] As is shown in figure 3, the plug 31 is positionally fixed with respect to the lens 5 of the focus length of 8mm by means of a holder 32. The collimator is composed of the ferrule 21 and the lens 5 with the ends of the fibers exposed to the end of the ferrule 21 being positioned at focal points of the lens, respectively. The three fibers and one lens substantially provide a collimator which emanates one central collimated outgoing beam and receives two collimated return beams inclined by an angle of 1.8 degrees on both sides of the central collimated outgoing beam. This collimator is attached to the optical isolator. [0025] The optical isolator using birefringent crystal wedge type polarizers employed in the present invention is similar to that used in the inventor s JP B (equivalent to US5,408,354A) and JP ,894A. The present invention uses Rutile Rochon prisms as wedge polarizers 6 and 11. [0026] Magnets 10 are composed of five magnets. Polarities of adjacent magnets are faced with N to N and with S to S. The first polarizer 6 is a rutile Rochon prism and the second polarizer 11 is also a rutile Rochon prism. Faraday rotator 9 is a TGG crystal. Birefringent crystal plate 12 is a beam combiner which is disposed outside of Rochon prisms. The isolator has a tube shaped chuck 33 for a collimator holder 32. The inner diameter of the tube shaped chuck 33 is a little larger than the outer diameter of the collimator holder 32. Three sets of two screws, six screws in total, are attached at every 120 degrees around the tube shaped chuck. The angle, the position, and the angular displacement position of the collimator can be adjusted by using these 6 screws. [0027] The Rochon prism uses rutile prism of the angle of 6 degrees and 45 minutes. The return light from the optical isolator is composed of two collimated beams. The beam of the return light from the optical isolator angles by 1.8 degrees to the incident beam. The reflected light from the processing workpiece propagates through the optical isolator and enters into the collimator to the centers of the second and third fibers which are just 250 micrometers apart from the first fiber. [0028] The accuracy of a prism angle is very important to receive the return light with the second and the third fibers. As is described above, the prism angle is decided as 6 degrees and 45 minutes for the return light angle 1.8 degrees. If the prism angle, for instance, is 6 degrees and 15 minutes with a 30 minutes displacement, then the return light angle becomes 1.64 degrees. The position of the return light with the angle of 1.64 degrees is 223 micrometer from the center of first fiber. The positional difference is only 21 micrometer, which is sufficiently within the core diameter of 62.5 micrometers of the receiving fiber. The tolerance of angle 30 minutes is an easy value, for ordinary prism manufacturing technology. Thus, it is not difficult to optically couple this three fiber collimator with the optical isolator. [0029] In order to receive the return light in alignment, rotating the collimator around its axis is required to adjust the center of the second and third fibers so as to coincide with the position of the return light beams. When the second and third fibers are adjusted within the range of 15.6 micrometers which corresponds to half of the radius of micrometers of these fibers, the collimator must be rotated by 3.8 degrees, which correspond to arctan (16.5/250). This adjustment accuracy of 3.8 degrees is 4
5 7 EP A1 8 easy for an ordinary fiber adjustment technology. Thus it is shown from the numerical point of view that it is not difficult to fabricate and adjust the set of the triple fiber collimator and the optical isolator of this invention. [0030] In this detailed description of the invention, Rochon prisms are used as polarizers. These polarizers are also replaceable with the set of glass prism and wedge polarizers which was used in the examples of JP A. End-capped fibers are also available for preventing the high power damage instead of the core end expanded fibers. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY [0031] This invention makes it possible to isolate the return light from the laser oscillator. With the use of this invention the return light does not heat the optical isolator. Thus this invention can be used for high power fiber lasers. EXPLANATION OF LETTERS AND NUMBERS [0032] 1. Fiber laser oscillator 2. Optical fiber (first) for laser light delivery 3. End of delivery fiber 4. Light emanated by fiber impinging to lens 5. first lens 6. Frist birefringent crystal wedge polarizer 7. One light beam between the first wedge polarizer and the second polarizer 8. Another light beam between the first wedge polarizer and the second polarizer 9. Faraday rotator 10. Magnet 11. Second birefringent crystal wedge polarizer 12. Birefringent crystal plate 13. Combined beam 14. Condense lens 15. Workpiece 16. Focus point on the processing workpiece 17. One return light 18. Another return light 19. Fiber end of the one return light 20. Fiber end of another return light 21. Ferrule or V-groove device for fixing fibers 22. One optical fiber (second) for receiving return light 23. The other optical fiber (third) for receiving return light 24. Ceramics tube whose one end is closed 25. Stainless tube whose one end is closed 26. Fiber core 27. Fiber clad 28. Enlarged cross section for light passing through part 29. Optical isolator holder Claims 30. Collimator adjustment screw 31. Plug 32. Collimator holder 33. Collimator holder chuck 1. A collimator employing three optical fibers comprising; a first optical fiber; a second and a third optical fibers having core diameters larger than the core diameter of the first optical fiber; a ceramic, glass or metal ferrule having three holes arranged in parallel such that the distance between a center hole and one of side holes is the same as the distance between the center hole and the other of the side holes, or a ceramic, glass or metal plate having three grooves formed on the plate surface and arranged such that the distance between a center groove and one of side grooves is the same as the distance between the center groove and the other of the side grooves; the three optical fibers being configured to be passed through the holes of the ferrule or fixed in the grooves of the plate such that the end of the three optical fibers are neatly aligned; and a lens configured to collimate a light beam come from the first optical fiber disposed in the center of the three optical fibers. 2. An optical isolator combined with a collimator comprising: a collimator employing three optical fibers according to claim 1; and an optical isolator employing wedge polarizers made of birefringent crystal; wherein a collimated beam formed through the lens of the collimator from the light beam come from said first optical fiber at the center of the three optical fibers is incident in the forward direction of the optical isolator, and wherein two return lights come from the optical isolator are focused on with the lens of the collimator and received at said second and third optical fibers. 5
6 EP A1 6
7 EP A1 7
8 EP A1 8
9 EP A1 9
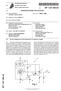
10 EP A1 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Patent documents cited in the description JP B [0007] JP B [0007] JP B [0007] [0025] US A [0007] [0025] US B2 [0007] US B2 [0007] JP A [0007] [0025] [0030] US B [0012] US B [0012] 10
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/51
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
TEPZZ 8 5ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/09
 (19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 ( ) B21D 41/00 ( ) B62D 1/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 ( ) G01B 11/24 ( ) G01N 21/47 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
TEPZZ Z47794A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
(19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
TEPZZ 76 84_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
(19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
TEPZZ 7545 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/29
 (19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
(19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B29B 15/12 ( ) B32B 5/26 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
(19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
(51) Int Cl.: G03B 37/04 ( ) G03B 21/00 ( ) E04H 3/22 ( ) G03B 21/60 ( ) H04N 9/31 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
(19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 5496_6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 ( ) H02M 7/493 (2007.
 (19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/35
 (19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
(19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
(19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/48
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( ) G06F 3/0482 (2013.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
(19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/02 ( ) G01S 5/14 ( ) H04L 12/28 (2006.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
(19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
TEPZZ Z7Z7 5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H01F 30/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/50
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
TEPZZ 674Z48A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ 9746 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/06 ( ) G01S 5/02 (2010.
 (19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
(19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/40
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 708 303 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/40 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 708 303 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/40 (51) Int Cl.:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/33
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
(51) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
(19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04B 1/40 ( ) H04W 52/02 (2009.
 (19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
(19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 ( ) B25J 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ Z_89_5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2016/19
 (19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 ( ) G01S 13/78 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/37
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 498 162 A1 (43) Date of publication: 12.09.2012 Bulletin 2012/37 (51) Int Cl.: G05F 3/24 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11368007.8 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 498 162 A1 (43) Date of publication: 12.09.2012 Bulletin 2012/37 (51) Int Cl.: G05F 3/24 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11368007.8 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 ( ) B25J 9/00 ( ) (54) Robotic system for laser, plasma, water jet, milling etc. machining or processing of parts
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
(51) Int Cl.: G07D 9/00 ( ) G07D 11/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/06 ( ) (54) Combined current and voltage measurement transformer of the capacitor bushing type
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
TEPZZ Z 8867A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/18
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ _79748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 ( ) B60Q 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
(19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04N 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
(19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
(51) Int Cl.: G10L 19/24 ( ) G10L 21/038 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B23K 9/095 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
TEPZZ 5Z 8 9B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 52/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ _64_69B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
(19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
(54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE FOR USE IN THE COLORIMETRIC ANALYSIS OF A SAMPLE FLUID, APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COLORIMETRIC ANALYSIS OF A SAMPLE FLUID
 (19) TEPZZ _79 _A_T (11) EP 3 179 231 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/2 (06.01) (21) Application number: 162482.2 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _79 _A_T (11) EP 3 179 231 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/2 (06.01) (21) Application number: 162482.2 (22) Date of
APSI WIFI, LLC. Company S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070
 APSI WIFI, LLC Address 9121 S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070 Publication number WO/2015/161133 Application number PCT/US2015/026259 Publication date 2015-10-22 Filing Date 2015-04-16 Publication
APSI WIFI, LLC Address 9121 S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070 Publication number WO/2015/161133 Application number PCT/US2015/026259 Publication date 2015-10-22 Filing Date 2015-04-16 Publication
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
TEPZZ 755Z44A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 ( ) G01S 13/93 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7Z44A_T (11) EP 2 7 044 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/ (06.01) G01S 13/93 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1311322.8
(19) TEPZZ 7Z44A_T (11) EP 2 7 044 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/ (06.01) G01S 13/93 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1311322.8
III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II
 (19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
TEPZZ _74 6 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2002/33
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2004/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
(51) Int Cl.: B42D 25/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_8868 B_T (11) EP 1 886 83 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.08.201 Bulletin 201/33 (1) Int Cl.: B42D 2/00 (2014.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ_8868 B_T (11) EP 1 886 83 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.08.201 Bulletin 201/33 (1) Int Cl.: B42D 2/00 (2014.01) (21)
(51) Int Cl.: B60J 10/00 ( ) B60P 3/34 ( ) F16J 15/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
(19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Intel e B60M 1/13. Bayonne, New Jersey (US) Holborn London EC1N2QP (GB)
 (19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
(19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
TEPZZ _48_45A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
(19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T (11) EP 2 871 760 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.0.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 13192249.4 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/42 (07.01) H02M 1/32 (07.01)
(19) TEPZZ 87_76ZA_T (11) EP 2 871 760 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.0.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 13192249.4 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/42 (07.01) H02M 1/32 (07.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/39
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56857 A_T (11) EP 2 568 572 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/11 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12183666.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 56857 A_T (11) EP 2 568 572 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/11 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 17/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12183666.2 (22)
TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B21J 5/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/35
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 362 70 A2 (43) Date of publication: 31.08.11 Bulletin 11/3 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 1/22 (06.01) H04L 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 098.4 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 362 70 A2 (43) Date of publication: 31.08.11 Bulletin 11/3 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 1/22 (06.01) H04L 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 098.4 (22) Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
TEPZZ 45A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/01
 (19) TEPZZ 45A_T (11) EP 3 113 345 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (21) Application number: 15174720.1 (22) Date of filing: 01.07.2015 (51) Int
(19) TEPZZ 45A_T (11) EP 3 113 345 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (21) Application number: 15174720.1 (22) Date of filing: 01.07.2015 (51) Int
(51) Int Cl.: G02B 21/00 ( ) G02B 21/32 ( ) G02B 21/36 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6_8_97B_T (11) EP 2 618 197 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 11824911.9
(19) TEPZZ 6_8_97B_T (11) EP 2 618 197 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 11824911.9
(51) Int Cl.: A23G 9/04 ( ) A23G 9/22 ( ) A23G 1/00 ( ) A23G 1/20 ( ) A23G 3/02 ( ) A23G 9/26 (2006.
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 767 099 A1 (43) Date of publication: 28.03.2007 Bulletin 2007/13 (21) Application number: 06076699.5 (51) Int Cl.: A23G 9/04 (2006.01) A23G 9/22 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 767 099 A1 (43) Date of publication: 28.03.2007 Bulletin 2007/13 (21) Application number: 06076699.5 (51) Int Cl.: A23G 9/04 (2006.01) A23G 9/22 (2006.01)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B23K 26/14 ( ) B23K 28/02 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 666579A_T (11) EP 2 666 579 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.11.2013 Bulletin 2013/48 (51) Int Cl.: B23K 26/14 (2006.01) B23K 28/02 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 666579A_T (11) EP 2 666 579 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.11.2013 Bulletin 2013/48 (51) Int Cl.: B23K 26/14 (2006.01) B23K 28/02 (2006.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/041 ( ) H03K 17/96 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
(19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T (11) EP 2 806 286 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.11.14 Bulletin 14/48 (21) Application number: 13168943.2 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/34 (06.01) G01S 13/93
(19) TEPZZ 8Z6 86A_T (11) EP 2 806 286 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.11.14 Bulletin 14/48 (21) Application number: 13168943.2 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/34 (06.01) G01S 13/93
~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) ~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 843 043 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: E01B 31/17 20.05.1998
(19) J (12) ~ mi ii ii ii iii i mi m i n i u m European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 843 043 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: E01B 31/17 20.05.1998
Will contain image distance after raytrace Will contain image height after raytrace
 Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1
 USOO6525828B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1 Grosskopf (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 25, 2003 (54) CONFOCAL COLOR 5,978,095 A 11/1999 Tanaami... 356/445 6,031,661. A 2/2000 Tanaami...
USOO6525828B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1 Grosskopf (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 25, 2003 (54) CONFOCAL COLOR 5,978,095 A 11/1999 Tanaami... 356/445 6,031,661. A 2/2000 Tanaami...
(51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/16 ( ) B29K 55/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
(12) United States Patent
 USOO948471 OB2 (12) United States Patent Yoshino et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.484,710 B2 Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) SEMCONDUCTOR LASER DEVICE Applicant: USHIO DENKI KABUSHIKI KAISHA, Tokyo
USOO948471 OB2 (12) United States Patent Yoshino et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.484,710 B2 Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) SEMCONDUCTOR LASER DEVICE Applicant: USHIO DENKI KABUSHIKI KAISHA, Tokyo
Office europeen des Publication number : EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Office europeen des brevets @ Publication number : 0 465 1 36 A2 @ EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION @ Application number: 91305842.6 @ Int. CI.5 : G02B 26/10 (22) Date of filing : 27.06.91 ( ) Priority : 27.06.90
Office europeen des brevets @ Publication number : 0 465 1 36 A2 @ EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION @ Application number: 91305842.6 @ Int. CI.5 : G02B 26/10 (22) Date of filing : 27.06.91 ( ) Priority : 27.06.90
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
TEPZZ 87_554A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 87_554A_T (11) EP 2 871 554 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.05.2015 Bulletin 2015/20 (21) Application number: 14192721.0 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/01 (2006.01) G06F
(19) TEPZZ 87_554A_T (11) EP 2 871 554 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.05.2015 Bulletin 2015/20 (21) Application number: 14192721.0 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/01 (2006.01) G06F
-i. DDs. (12) United States Patent US 6,201,214 B1. Mar. 13, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: aeeeeeeea. Duffin
 (12) United States Patent Duffin USOO62O1214B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2001 (54) LASER DRILLING WITH OPTICAL FEEDBACK (75) Inventor: Jason E. Duffin, Leicestershire (GB) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Duffin USOO62O1214B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2001 (54) LASER DRILLING WITH OPTICAL FEEDBACK (75) Inventor: Jason E. Duffin, Leicestershire (GB) (73) Assignee:
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/52
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001609947A1* (11) EP 1 609 947 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.12.2005 Bulletin 2005/52
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001609947A1* (11) EP 1 609 947 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.12.2005 Bulletin 2005/52
Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) νlh, where ν, L, and H are as defined below. ν: the Verdet Constant, a property of the
 Aspheric Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) Function An optical isolator is a passive magneto-optic device that only allows light to travel in one direction. Isolators are used to protect a source
Aspheric Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) Function An optical isolator is a passive magneto-optic device that only allows light to travel in one direction. Isolators are used to protect a source
(51) Int Cl.: C03C 27/06 ( ) E06B 3/663 ( ) E06B 3/66 ( ) E06B 3/677 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8_ ZB_T (11) EP 2 81 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.01.17 Bulletin 17/01 (21) Application number: 13790324.1 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 8_ ZB_T (11) EP 2 81 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.01.17 Bulletin 17/01 (21) Application number: 13790324.1 (22)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/11
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm
 An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
TEPZZ 8 7Z9B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 7Z9B_T (11) EP 2 282 709 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (21) Application number: 08779272.7
(19) TEPZZ 8 7Z9B_T (11) EP 2 282 709 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (21) Application number: 08779272.7
TEPZZ B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
WO 2008/ A3 PCT. (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau
 (12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
TEPZZ _99976A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _99976A_T (11) EP 3 199 976 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 02.08.17 Bulletin 17/31 (21) Application number: 16326.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/93 (06.01) G01S 7/03 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ _99976A_T (11) EP 3 199 976 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 02.08.17 Bulletin 17/31 (21) Application number: 16326.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 13/93 (06.01) G01S 7/03 (06.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/21
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0013367A1* (11) EP 1 33 67 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.0.200 Bulletin 200/21 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0013367A1* (11) EP 1 33 67 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.0.200 Bulletin 200/21 (1) Int
TEPZZ 94 78A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 94 78A_T (11) EP 2 942 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.11.1 Bulletin 1/46 (21) Application number: 1446127. (1) Int Cl.: C09D 11/32 (14.01) B41M 3/14 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 94 78A_T (11) EP 2 942 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.11.1 Bulletin 1/46 (21) Application number: 1446127. (1) Int Cl.: C09D 11/32 (14.01) B41M 3/14 (06.01)
