Design, Implementation and Comparison of Different QAM Techniques using Cadence 180nm Technology
|
|
|
- Arron Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
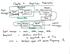
1 Design, Implementation and Comparison of Different QAM Techniques using Cadence 180nm Technology Chandra Shekar P*, Karthik M**, Maram Reddy Jahnavi***, Pallavi B S**** and Rubiya Sultana***** Asst. professor & students, Department of Electronics and Communication, ATME College of Engineering, Mysore, VTU Belgaum, Karnataka, India. chandrashekar1910@gmail.com, karthikm0045@gmail.com, maramreddyjahnavi@gmail.com pallavibs095@gmail.com, rubiyasultana23@gmail.com Abstract: Modulation is one of the fundamental technique required for communication applications. High bit rate, better constellation diagram and effective utilization of bandwidth are the important properties which will be considered in selecting a modulation technique. One such modulation technique which has these properties is QAM technique. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is a combination of two basic modulation techniques amplitude modulation and phase modulation. QAM is widely used in communication applications which come under radio frequency range (such as modems over telephone lines, satellite communications, HD television broadcasting and wireless communications etc) because of its high bit rate, better constellation diagram and effective utilization of bandwidth. Different types of QAM techniques are studied. Designing and implementation of different types of QAMs (16, 32 & 64-QAM) are carried out. In these QAM designs the basic components used are the MOSFETs. The circuit is analyzed at each stage and resulting waveforms are obtained. The bit rate of each QAM is calculated and the comparison is done for different QAMs that are designed. The whole design and implementation of these circuits are carried out using cadence virtuoso software, stimulations are done using spectre circuit simulator and the technology used is CMOS 180nm. Keywords: Modulation, Constellation diagram, QAM technique, MOSFETs, Cadence virtuoso software, Spectre. Introduction Communication is the process of sending and receiving information between 2 or more people. Communication is the basic need for every human being. When the exchange of information takes place between 2 or more people who are separated by certain distance is carried out by sending the information in the form of electrical signals through wired or wireless communication devices such as mobile, telephone, internet etc. One of the fundamental system or technique used in communication system is Modulation technique. Modulation is also called as heart of communication system. Modulation is the process of enhancing the signal frequency and it is also defined as varying the properties of carrier signal with respect to message signal. Transmission of message signal over a band-pass communication channel requires a shift of the range of frequency range suitable for transmission, and a corresponding shift back to the original frequency range after reception. Modulation has several advantages such as protecting the information signal from loss of information or wrong information due to noise addition, reducing the cost of communication system by reducing the size of the antenna, increasing the rate of transmission of the information signal and so on. Nowadays QAM is one of the trending modulation technique used in the communication field because of its high bit rate, effective bandwidth utilization and better constellation diagram. QAM stands for Quadrature Amplitude Modulation. QAM has become fast dominant modulation mechanism for high speed digital signals. The QAM technique is the combination of ASK and PSK. QAM performs 2 ASK modulation (with respect to the message signal) using 2 carrier signals which have a phase difference of 90 and the output of these ASK modulators are summed up using a summer, the output of this summer is called as QAM output. Here we can see that the 2 ASK modulation has been performed using phase shifted waves and summed up at the end, hence the summed signal has both amplitude and phase difference. The information signal is split into 2 parts as I-phase and Q-phase data streams. QAM is widely used in practically world. It has many applications in the communication field due to its faster transmission rate and bandwidth efficiency. Block Diagram of QAM The block diagram of QAM is as shown in the fig. 1, it consist of Information source, splitter & synchronization circuit, carrier source, 90 deg phase shifter, 2 ASK modulators (I-phase modulator and q-phase modulator) and signal summer.
2 502 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing Communication and Automation - ICSIPCA Fig.1: Block diagram of QAM modulator Information Source Information source produces the message signal which has to be transmitted. The message signal may be a video, audio or a text message. The real world circuit is in analog or continuous form in nature. This signal is converted into digital signal which is actually the input to our QAM circuit (Digital QAM). The analog form signal (voice, video or text) can be converted using Analog to Digital conversion (ADC) block which is used just before splitter circuit. We have made use of V-pulse in Cadence virtuoso software as information source (data input) for our QAM circuit which is already in digital form. Hence we don t require any ADC for QAM circuit. If analog input is used as information we should use ADC, since it is a digital QAM. SOURCE Analog signal ADC Digital signal SPLITTER Fig.2: Block diagram of information source Splitter QAM performs 2-ASK operations simultaneously using 2 different ASK modulators whose carrier wave has 90 degree out of Phase with respect to each other and the output of these ASK modulators are summed up. We have single information source and 2 different ASK modulators (I-phase and Q-phase modulators), hence the information bits are split into 2 parts and are given as input to these Modulators. First the serial bits are converted to parallel form as per order of QAM (for 2 n n parallel bits) and these parallel bits are split as per the order of QAM. Fig.3 shows the block diagram of splitter using D-Flip Flop. Fig.3: Block diagram of splitternumber of d-latch usage depends on the order of QAM. Splitter is designed to split the input bits equally or unequally as per the requirement. In 16-QAM and 64-QAM the splitting of the bits takes place equally (since n is even) and in 32-QAM (since n is odd) splitting of the bits takes place unequally. The splitter circuit requires a synchronization circuit since the input bits to selection circuit of I-phase and Q-phase modulators should be synchronized.
3 Design, Implementation and Comparison of Different QAM Techniques using Cadence 180nm Technology 503 The splitter circuit is the combination of D-Flip Flops. Synchronization block is also included in the splitter block itself to ensure that process of splitting is been synchronized. Synchronization circuit is also designed using D-Flip Flops. Output from the splitter will be given to the multiplexer (MUX) through selection circuit. Modulator The modulator is the heart of the QAM. QAM requires 2 ASK modulators. The modulator circuit is a combination of selection circuit and analog MUX. The inputs to the modulator circuit are the message signal and carrier signal.the block diagram of modulator is as shown below in Fig.5. Fig.5: Internal modulator block diagram Selection Circuit Modulator task is to send the corresponding carrier wave as output with respect to the input message signal. The selection circuit will help in turning on or triggering any one of the switch of Analog-MUX with respect to the message signal. The selection circuit is a digital circuit. The selection circuit is made up of using AND gates and Inverters. The number of AND gates used (example 2-input, 3-input etc) and number or inverters vary with respect to the order of QAM. The block connection diagram of selection circuit with splitter and MUX is as shown in Fig.4 Fig.4: selection circuit Multiplexer A multiplexer (MUX) is a device that selects one signal among several input signals and forwards it to the single output line. A MUX of 2 n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line which has to be connected to the output line. Multiplexers are mainly used to increase the amount of data that can be sent over the network within a certain amount of time and bandwidth. In any order of QAM the input Phases of carrier signal will have 4 different phases for all the orders of QAM but number of different amplitude used will change with respect to the order of QAM. We require two Analog MUXs for the QAM circuit, since we have two different ASK Modulators in QAM circuit. The MUX is designed using op-amp along with MOSFETs as switches. Here we use negative feedback to increase the stability. Over-all gain of the op-amp used is unity. Signal summer The basic function of the summer is to add two or more signals. The signal summer used here is for analog signals since the output of both the modulators are in the Analog form. Analog summer is designed using op-amp to sum the analog signals. Here we use negative feedback to increase the stability. The output of I-phase modulator and Q-phase modulator is given as input to the op-amp through resistors as shown in the below circuit. Over-all gain of the op-amp is unity. The summer circuit is as shown in fig.6. Fig. 6: The signal summer circuit
4 504 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing Communication and Automation - ICSIPCA Implementation of QAM circuits using Cadence gpdk 180nm technology Implementation of 16-QAM The 16-QAM implemented circuit is as shown in fig. 7. The incoming serial bits are grouped 4 bits at a time and converted to parallel form. These 4 bits are split into 2 equal parts (2 bits each) and these split bits sent to the message inputs of I-phase and Q-phase modulators. Both I-phase and Q-phase modulators are implemented using 4:1 Analog MUX. The Carrier signal inputs for I-phase Modulator are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 0 deg), (5 mv, 180 deg), (10 mv, 0 deg) and (10 mv, 180 deg) and the Carrier signal inputs for Q-phase Modulator are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 90 deg), (5 mv, 270 deg), (10 mv, 90 deg) and (10 mv, 270 deg). The output of 16-QAM consist of 16 different combinations of phase and amplitude. Fig.7: Implementation of 16-QAM circuit Implementation of 32-QAM The 32-QAM implemented circuit is as shown in fig. 8. The incoming serial bits are grouped 5 bits at a time and converted to parallel form. These 4 bits are split into 2 un-equal parts (3 bits for I-phase modulator and 2-bits for Q-phase modulator) and these split bits are sent to the message inputs of I-phase and Q-phase modulators. I-phase is implemented using 8:1 Analog MUX and the Q-phase modulator is implemented using 4:1 MUX. The Carrier signal inputs for I-phase Modulator are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 0 deg), (5 mv, 180 deg), (10 mv, 0 deg), (10 mv, 180 deg), (15 mv, 0 deg), (15 mv, 180 deg), (20 mv, 0 deg) and (20 mv, 180 deg) and the Carrier signal inputs for Q-phase Modulator are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 90 deg), (5 mv, 270 deg), (10 mv, 90 deg) and (10 mv, 270 deg). The output of 32-QAM consist of 32 different combinations of phase and amplitude. Fig. 8: Implementation of 32-QAM circuit
5 Design, Implementation and Comparison of Different QAM Techniques using Cadence 180nm Technology 505 Implementation of 64-QAM The 64-QAM implemented circuit is as shown in fig. 9. The incoming serial bits are grouped 4 bits at a time and converted to parallel form. These 4 bits are split into 2 equal parts (3 bits each) and these split bits are sent to the message inputs of I- phase and Q-phase modulators. Both I-phase and Q-phase modulators are implemented using 8:1 Analog MUX. The Carrier signal inputs for I-phase Modulators are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 0 deg), (5 mv, 180 deg), (10 mv, 0 deg), (10 mv, 180 deg), (15 mv, 0 deg), (15 mv, 180 deg), (20 mv, 0 deg) and (20 mv, 180 deg) and the Carrier signal inputs for Q-phase Modulators are continuous signal having amplitude and phase (5 mv, 90 deg), (5 mv, 270 deg), (10 mv, 90 deg), (10 mv, 270 deg) (15 mv, 90 deg), (15 mv, 270 deg), (20 mv, 90 deg) and (20 mv, 270 deg). The output of 64-QAM consist of 64 different combinations of phase and amplitude. Results 16-QAM: Waveform Fig.9: Implementation of 64-QAM circuit Bit rate calculation The obtained bit rate from the output waveform of 16-QAM f c = 10 Mhz. 250k Hz = 4 bits T = 1/f = 4u 4 us = 4 bits 1 s = x (f b ) Fig.10: 16-QAM output waveform
6 506 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing Communication and Automation - ICSIPCA X (f b ) = 1s*4/4u Bit-rate = f b = 1 Mbps Baud rate = f b /N N=number of bits per symbol Baud-rate (f b1 ) = 250 khz. The fastest rate of change frequency and highest fundamental frequency at both balanced modulators (f a ) = 125 khz. Upper frequency = f c + f a = Mhz. Lower frequency = f c - f a = Mhz. Bandwidth = Upper frequency Lower frequency = 250 khz f b (bit rate) in terms of bandwidth. f b = Bandwidth*N f b =Bandwidth*4 32 QAM: Waveform Fig.11: 32-QAM output waveform Bit rate calculation The obtained bit rate from the output waveform of 32-QAM f c = 10 Mhz. 250k Hz = 5 bits T = 1/f = 4 us 4 us = 5 bits 1 s = x (f b ) X (f b ) = 1s*5/4us Bit-rate = f b = 1.25 Mbps Baud-rate = f b /N N=number of bits per symbol Baud-rate (f b1 ) = 250 khz. The fastest rate of change frequency and highest fundamental frequency at both balanced modulators (f a ) = 125 khz. Upper frequency = f c + f a = Mhz. Lower frequency = f c - f a = Mhz. Bandwidth = Upper frequency Lower frequency = 250 khz f b (bit rate) in terms of bandwidth. f b = Bandwidth*N f b =Bandwidth*5
7 64-QAM: Waveform Design, Implementation and Comparison of Different QAM Techniques using Cadence 180nm Technology 507 Fig.12:64-QAM output waveform Bit rate calculation The obtained bit rate from the output waveform of 64-QAM f c = 10 Mhz. 250 khz = 6 bits T = 1/f = 4 us 4 us = 6 bits 1 s = x(f b ) X(f b) = 1s*6/4us bit rate = f b = 1.5 Mhz baud-rate = f b /N N=number of bits per symbol Baud-rate (f b1 ) = 250 khz. The fastest rate of change frequency and highest fundamental frequency at both balanced modulators(f a ) = 125 khz. Upper frequency = f c + f a = Mhz. Lower frequency = f c - f a = Mhz. Bandwidth = Upper frequency Lower frequency = 250 khz f b (bit rate) in terms of bandwidth. f b = Bandwidth*N fb= Bandwidth*6 Comparison of Bit-rate Table 1: bit-rate comparison table QAM Technique Bandwidth in terms of Hz Bit rate in terms of bits/s Bit rate in terms of Bandwidth 16-QAM 250 k 1 M 4 * BW 32-QAM 250 k 1.25 M 5 * BW 64-QAM 250 k 1.5 M 6 * BW
8 508 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing Communication and Automation - ICSIPCA Fig.13: Comparison of bit rates in terms of bandwidth Conclusion This work describes the design and implementation of the transmitter part of Quadrature Amplitude Modulation scheme of 16, 32, 64-bits using Cadence Tool. The output at each stage of QAM is analyzed. This design can be practically implemented as it uses MOSFETs for its circuit which minimizes the cost and decrease the size. The efficiency of the circuit is high due to the CMOS technology used. The data rate of each QAM is calculated for a channel frequency. Data transmission rate of each QAM technique is compared and it has shown that as the order of QAM increases, the data rate also increases. The future work can be carried out on the study of SNR (signal to noise ratio) and Shannon s channel capacity formula for these QAM circuits and modifying the QAM circuit for acceptable SNR ratio. The work can be continued to obtain the layouts for the schematics of different QAM techniques. Once the layout is obtained, the fabrication process can be done for these circuits. This will greatly help in many of the communication applications, as QAM techniques play an important role in it. Acknowledgement We take this opportunity to acknowledge my profound gratitude to Dr. L Basavaraj, Principal, ATME college of Engineering, Mysuru for all the Infrastructure and facilities provided during my study in the institution. We sincerely thank Dr. Mahesh M K, Professor and Head, Dept. of ECE, ATME college of Engineering, Mysuru for his suggestions and support for completion of this work. We would like to thank Mr. Abilash G and Mr. Chandra Shekar P, Asst. professors, Dept. of ECE, ATME college of Engineering, Mysuru for their guidance, help and useful suggestions in this work. Finally we would like to thank our Parents and all our beloved ones for supporting us in many ways that meant a lot for us. References [1] "Quadrature Amplitude Modulation: A simulation study" K.Kisiel, D.Sahota, G.Swaminathan, School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University, Canada, Nov [2] "Design and ASIC Implementation of 64-QAM Modulator and Demodulator for High Data Rate Wireless Communication System, D.V.Narasimha Rao, VSD (FT-2007). [3] Raghunandan Swain and Ajit Kumar Panda,"Design of 16-QAM Transmitter and Receiver: Review of Methods of Implementation in FPGA",International journal of Engineering and Science ISSN: , Vol. 1,Issue 9 (Nov 2012) PP [4] Luke Vercimakand Karl Weyeneth, "Software defined Radio", Bradley University, [5] Maria Wikstrom, "Survey of Modulation Classification Methods for QAM Signals, sponsored by 'Swedish Armed Forces'. [6] Sareka Jeevane Dowrla1, K. Jhansi Rani2,"VLSI Implementation and Design of Digital Modulation Using Xilinx", International Journal of Research in Computer and Communication Technology, Vol 2, Issue 9, September [7] Paul Tobin, "PSpice for Digital Communications Engineering", School of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Dublin Institute of technology, Ireland. [8] Bit-rate calculations in Digital modulation retrieved from [9] CMOS Analog Electronic circuit by Neil H.E. West. [10] Next generation wireless LANs by Eldad Perahia and Robert Stacey. [11] Comparative study of digital modulation techniques in WIMAX paper submitted by Umesh Sharma in IJEIT, volume 2, issue 2, August [12] Analog & digital modulation techniques paper submitted by H.Verma.
System Generator Based Implementation of QAM and Its Variants
 System Generator Based Implementation of QAM and Its Variants Nilesh Katekar *1, Prof. G. R. Rahate*2 *1 Student of M.E. VLSI & Embedded system, PCCOE Pune, Pune University, India *2 Astt. Prof. in Electronics
System Generator Based Implementation of QAM and Its Variants Nilesh Katekar *1, Prof. G. R. Rahate*2 *1 Student of M.E. VLSI & Embedded system, PCCOE Pune, Pune University, India *2 Astt. Prof. in Electronics
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4. Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A
 COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
Design and Implementation of 4-QAM Architecture for OFDM Communication System in VHDL using Xilinx
 Design and Implementation of 4-QAM Architecture for OFDM Communication System in VHDL using Xilinx 1 Mr.Gaurang Rajan, 2 Prof. Kiran Trivedi 3 Prof.R.M.Soni 1 PG student (EC), S.S.E.C., Bhavnagar-Gujarat
Design and Implementation of 4-QAM Architecture for OFDM Communication System in VHDL using Xilinx 1 Mr.Gaurang Rajan, 2 Prof. Kiran Trivedi 3 Prof.R.M.Soni 1 PG student (EC), S.S.E.C., Bhavnagar-Gujarat
Analysis of New Dynamic Comparator for ADC Circuit
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Analysis of New Dynamic Comparator for ADC Circuit B. Shiva Kumar *, Fazal Noorbasha**, K. Vinay Kumar ***, N. V. Siva Rama Krishna. T**** * (Student of VLSI Systems Research
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Analysis of New Dynamic Comparator for ADC Circuit B. Shiva Kumar *, Fazal Noorbasha**, K. Vinay Kumar ***, N. V. Siva Rama Krishna. T**** * (Student of VLSI Systems Research
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
Optimized BPSK and QAM Techniques for OFDM Systems
 I J C T A, 9(6), 2016, pp. 2759-2766 International Science Press ISSN: 0974-5572 Optimized BPSK and QAM Techniques for OFDM Systems Manikandan J.* and M. Manikandan** ABSTRACT A modulation is a process
I J C T A, 9(6), 2016, pp. 2759-2766 International Science Press ISSN: 0974-5572 Optimized BPSK and QAM Techniques for OFDM Systems Manikandan J.* and M. Manikandan** ABSTRACT A modulation is a process
Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short Questions notes
 Department of Electrical (POWER) Engineering Swedish College of Engineering & Technology Rahim yar khan Subject: Communication systems Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short
Department of Electrical (POWER) Engineering Swedish College of Engineering & Technology Rahim yar khan Subject: Communication systems Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short
(Refer Slide Time: 2:23)
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11B Multiplexing (Contd.) Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexing
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11B Multiplexing (Contd.) Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexing
DESIGN OF A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR QUADRATURE PHASE SHIFT KEYING USING MODEL SIM SIMULATOR FOR BROADCAST COMMUNICATION RELEVANCE S
 DESIGN OF A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR QUADRATURE PHASE SHIFT KEYING USING MODEL SIM SIMULATOR FOR BROADCAST COMMUNICATION RELEVANCE S Thota Markandeyulu 1, S.Siva Sankar Reddy 2 1 M.Tech (VLSI) Scholar,
DESIGN OF A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR QUADRATURE PHASE SHIFT KEYING USING MODEL SIM SIMULATOR FOR BROADCAST COMMUNICATION RELEVANCE S Thota Markandeyulu 1, S.Siva Sankar Reddy 2 1 M.Tech (VLSI) Scholar,
POWER LINE COMMUNICATION. A dissertation submitted. to Istanbul Arel University in partial. fulfillment of the requirements for the.
 POWER LINE COMMUNICATION A dissertation submitted to Istanbul Arel University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor's Degree Submitted by Egemen Recep Çalışkan 2013 Title in all caps
POWER LINE COMMUNICATION A dissertation submitted to Istanbul Arel University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor's Degree Submitted by Egemen Recep Çalışkan 2013 Title in all caps
Lecture (07) Digital Modulation Digital data transmission through analog signals
 Lecture (07) Digital Modulation Digital data transmission through analog signals Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Agenda Aspects of Digital Modulation Amplitude Shift Keying Frequency Shift Keying Phase Shift Keying
Lecture (07) Digital Modulation Digital data transmission through analog signals Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Agenda Aspects of Digital Modulation Amplitude Shift Keying Frequency Shift Keying Phase Shift Keying
DESIGN OF CMOS BASED FM MODULATOR USING 90NM TECHNOLOGY ON CADENCE VIRTUOSO TOOL
 DESIGN OF CMOS BASED FM MODULATOR USING 90NM TECHNOLOGY ON CADENCE VIRTUOSO TOOL 1 Parmjeet Singh, 2 Rekha Yadav, 1, 2 Electronics and Communication Engineering Department D.C.R.U.S.T. Murthal, 1, 2 Sonepat,
DESIGN OF CMOS BASED FM MODULATOR USING 90NM TECHNOLOGY ON CADENCE VIRTUOSO TOOL 1 Parmjeet Singh, 2 Rekha Yadav, 1, 2 Electronics and Communication Engineering Department D.C.R.U.S.T. Murthal, 1, 2 Sonepat,
Chapter 5 Analog Transmission
 5-1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Chapter 5 Analog Transmission Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal depending on the information in digital
5-1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Chapter 5 Analog Transmission Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal depending on the information in digital
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering. Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT
 BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 Semester 2 & 2017 Semester 1 Resit Examinations for BEE/12/FT
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 Semester 2 & 2017 Semester 1 Resit Examinations for BEE/12/FT
Design of High Gain Two stage Op-Amp using 90nm Technology
 Design of High Gain Two stage Op-Amp using 90nm Technology Shaik Aqeel 1, P. Krishna Deva 2, C. Mahesh Babu 3 and R.Ganesh 4 1 CVR College of Engineering/UG Student, Hyderabad, India 2 CVR College of Engineering/UG
Design of High Gain Two stage Op-Amp using 90nm Technology Shaik Aqeel 1, P. Krishna Deva 2, C. Mahesh Babu 3 and R.Ganesh 4 1 CVR College of Engineering/UG Student, Hyderabad, India 2 CVR College of Engineering/UG
Hardware/Software Co-Simulation of BPSK Modulator and Demodulator using Xilinx System Generator
 www.semargroups.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.02,Issue.10, September-2013, Pages:984-988 Hardware/Software Co-Simulation of BPSK Modulator and Demodulator using Xilinx System Generator MISS ANGEL
www.semargroups.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.02,Issue.10, September-2013, Pages:984-988 Hardware/Software Co-Simulation of BPSK Modulator and Demodulator using Xilinx System Generator MISS ANGEL
DESIGN OF QAM MODULATOR AND GENERATION OF QAM SEQUENCE FOR ISI FREE COMMUNICATION Chethan B 1, Ravisimha B N 2, Dr. M Z Kurian 3
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume VI, Issue I, April 14 www.ijcea.com ISSN 2321 3469 DESIGN OF QAM MODULATOR AND GENERATION OF QAM SEQUENCE FOR ISI FREE COMMUNICATION
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume VI, Issue I, April 14 www.ijcea.com ISSN 2321 3469 DESIGN OF QAM MODULATOR AND GENERATION OF QAM SEQUENCE FOR ISI FREE COMMUNICATION
Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash ADC with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology
 Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology A.Nandhini PG Scholar, Dept of ECE Kumaraguru College of Technology Coimbatore -641 049 M.Shanthi Associate
Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology A.Nandhini PG Scholar, Dept of ECE Kumaraguru College of Technology Coimbatore -641 049 M.Shanthi Associate
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
Basic Concepts in Data Transmission
 Basic Concepts in Data Transmission EE450: Introduction to Computer Networks Professor A. Zahid A.Zahid-EE450 1 Data and Signals Data is an entity that convey information Analog Continuous values within
Basic Concepts in Data Transmission EE450: Introduction to Computer Networks Professor A. Zahid A.Zahid-EE450 1 Data and Signals Data is an entity that convey information Analog Continuous values within
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Lecture 01
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29
 Scoring: 1 point per problem, 29 points total. ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29 1. For the system of figure 14-1, give the binary code output that will result for each of the following
Scoring: 1 point per problem, 29 points total. ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29 1. For the system of figure 14-1, give the binary code output that will result for each of the following
Digital Modulation Lecture 01. Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Introduction to Communications Part Two: Physical Layer Ch5: Analog Transmission. Goals of This Class. Warm Up. Outline of the Class
 Introduction to Communications Part Two: Physical Layer Ch5: Analog Transmission Kuang Chiu Huang TCM NCKU Spring/2008 2009/4/11 KuangChiu Huang 1 Goals of This Class Through the lecture of analog transmission,
Introduction to Communications Part Two: Physical Layer Ch5: Analog Transmission Kuang Chiu Huang TCM NCKU Spring/2008 2009/4/11 KuangChiu Huang 1 Goals of This Class Through the lecture of analog transmission,
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security. Examinations for Semester 1
 BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security Cohort: BCNS/15B/FT Examinations for 2015-2016 Semester 1 MODULE: DATA COMMUNICATIONS MODULE CODE: CAN1101C Duration: 2 Hours Instructions to Candidates:
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security Cohort: BCNS/15B/FT Examinations for 2015-2016 Semester 1 MODULE: DATA COMMUNICATIONS MODULE CODE: CAN1101C Duration: 2 Hours Instructions to Candidates:
ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 DIGITAL MODULATIONS INTRODUCTION In many digital communication systems, cable (as for data
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 DIGITAL MODULATIONS INTRODUCTION In many digital communication systems, cable (as for data
CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics
 Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics Dr. Kemal Akkaya E-mail: kemal@cs.siu.edu Kemal Akkaya Mobile & Wireless Computing
Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale CS441 Mobile & Wireless Computing Communication Basics Dr. Kemal Akkaya E-mail: kemal@cs.siu.edu Kemal Akkaya Mobile & Wireless Computing
Electronics Interview Questions
 Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
The Last Mile Problem
 The Last Mile Problem LAN, MAN, WAN how to connect private users at home to such networks? Problem of the last mile: somehow connect private homes to the public Internet without laying many new cables
The Last Mile Problem LAN, MAN, WAN how to connect private users at home to such networks? Problem of the last mile: somehow connect private homes to the public Internet without laying many new cables
Year : TYEJ Sub: Digital Communication (17535) Assignment No. 1. Introduction of Digital Communication. Question Exam Marks
 Assignment 1 Introduction of Digital Communication Sr. Question Exam Marks 1 Draw the block diagram of the basic digital communication system. State the function of each block in detail. W 2015 6 2 State
Assignment 1 Introduction of Digital Communication Sr. Question Exam Marks 1 Draw the block diagram of the basic digital communication system. State the function of each block in detail. W 2015 6 2 State
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
Physical Layer. Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS. School of Computing, UNF
 Physical Layer Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF Multiplexing Transmission channels are expensive. It is often that two communicating
Physical Layer Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF Multiplexing Transmission channels are expensive. It is often that two communicating
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
BER Performance Comparison between QPSK and 4-QA Modulation Schemes
 MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2013, pp. 62 66 62 BER Performance Comparison between QPSK and 4-QA Modulation Schemes Manish Trikha ME Scholar
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2013, pp. 62 66 62 BER Performance Comparison between QPSK and 4-QA Modulation Schemes Manish Trikha ME Scholar
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
Data Communications and Networking (Module 2)
 Data Communications and Networking (Module 2) Chapter 5 Signal Encoding Techniques References: Book Chapter 5 Data and Computer Communications, 8th edition, by William Stallings 1 Outline Overview Encoding
Data Communications and Networking (Module 2) Chapter 5 Signal Encoding Techniques References: Book Chapter 5 Data and Computer Communications, 8th edition, by William Stallings 1 Outline Overview Encoding
Presentation Outline. Advisors: Dr. In Soo Ahn Dr. Thomas L. Stewart. Team Members: Luke Vercimak Karl Weyeneth
 Bradley University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Senior Capstone Project Proposal December 6 th, 2005 Team Members: Luke Vercimak Karl Weyeneth Advisors: Dr. In Soo Ahn Dr. Thomas L.
Bradley University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Senior Capstone Project Proposal December 6 th, 2005 Team Members: Luke Vercimak Karl Weyeneth Advisors: Dr. In Soo Ahn Dr. Thomas L.
Design of Rail-to-Rail Op-Amp in 90nm Technology
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 2 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Design of Rail-to-Rail Op-Amp in 90nm Technology P R Pournima M.Tech Electronics
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 2 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Design of Rail-to-Rail Op-Amp in 90nm Technology P R Pournima M.Tech Electronics
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
6. has units of bits/second. a. Throughput b. Propagation speed c. Propagation time d. (b)or(c)
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK
 PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : LINEAR AND DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS Course Code : 13EC1146 L T P C : 4 0 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Electrical and Electronics
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : LINEAR AND DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS Course Code : 13EC1146 L T P C : 4 0 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Electrical and Electronics
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS LAB
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS LAB List of Experiments: 1. PCM Generation and Detection. 2. Differential Pulse Code modulation. 3. Delta modulation. 4. Time Division Multiplexing of 2band Limited Signals. 5. Frequency
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS LAB List of Experiments: 1. PCM Generation and Detection. 2. Differential Pulse Code modulation. 3. Delta modulation. 4. Time Division Multiplexing of 2band Limited Signals. 5. Frequency
Digital Modulation Schemes
 Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES
 1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
Design and Analysis of Low Power Two Stage CMOS Op- Amp with 50nm Technology
 Design and Analysis of Low Power Two Stage CMOS Op- Amp with 50nm Technology Swetha Velicheti, Y. Sandhyarani, P.Praveen kumar, B.Umamaheshrao Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, SSCE, Srikakulam, A.P.,
Design and Analysis of Low Power Two Stage CMOS Op- Amp with 50nm Technology Swetha Velicheti, Y. Sandhyarani, P.Praveen kumar, B.Umamaheshrao Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, SSCE, Srikakulam, A.P.,
Point-to-Point Communications
 Point-to-Point Communications Key Aspects of Communication Voice Mail Tones Alphabet Signals Air Paper Media Language English/Hindi English/Hindi Outline of Point-to-Point Communication 1. Signals basic
Point-to-Point Communications Key Aspects of Communication Voice Mail Tones Alphabet Signals Air Paper Media Language English/Hindi English/Hindi Outline of Point-to-Point Communication 1. Signals basic
CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION
 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
DESIGN, IMPLEMENTATION AND OPTIMISATION OF 4X4 MIMO-OFDM TRANSMITTER FOR
 DESIGN, IMPLEMENTATION AND OPTIMISATION OF 4X4 MIMO-OFDM TRANSMITTER FOR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Abstract M. Chethan Kumar, *Sanket Dessai Department of Computer Engineering, M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced
DESIGN, IMPLEMENTATION AND OPTIMISATION OF 4X4 MIMO-OFDM TRANSMITTER FOR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Abstract M. Chethan Kumar, *Sanket Dessai Department of Computer Engineering, M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced
A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso
 A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso C Ashwini 1, Prof Naveen I G 2, Bhanuteja G 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Sir MVIT College, Bangalore,
A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso C Ashwini 1, Prof Naveen I G 2, Bhanuteja G 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Sir MVIT College, Bangalore,
IES Digital Mock Test
 . The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
. The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
Discussion Chapter#5
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4314: Data Communication Instructor: Dr. Aiman Abu Samra T.A.: Eng. Alaa O. Shama Discussion Chapter#5 Main
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4314: Data Communication Instructor: Dr. Aiman Abu Samra T.A.: Eng. Alaa O. Shama Discussion Chapter#5 Main
Key words: OFDM, FDM, BPSK, QPSK.
 Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analyse the Performance
Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analyse the Performance
Friday 17 June 2016 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 17 June 2016 Morning A2 GCE ELECTRONICS F615/01 Communication Systems *2710852624* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 17 June 2016 Morning A2 GCE ELECTRONICS F615/01 Communication Systems *2710852624* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Chapter-15. Communication systems -1 mark Questions
 Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
FPGA Implementation of QAM and ASK Digital Modulation Techniques
 FPGA Implementation of QAM and ASK Digital Modulation Techniques Anumeha Saxena 1, Lalit Bandil 2 Student 1, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Acropolis Institute of Technology
FPGA Implementation of QAM and ASK Digital Modulation Techniques Anumeha Saxena 1, Lalit Bandil 2 Student 1, Assistant Professor 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Acropolis Institute of Technology
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES
 COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
Analysis and Design of a 1GHz PLL for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition
 Analysis and Design of a 1GHz PLL for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition P. K. Rout, B. P. Panda, D. P. Acharya and G. Panda 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, School of Electrical
Analysis and Design of a 1GHz PLL for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition P. K. Rout, B. P. Panda, D. P. Acharya and G. Panda 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, School of Electrical
Mehmet SÖNMEZ and Ayhan AKBAL* Electrical-Electronic Engineering, Firat University, Elazig, Turkey. Accepted 17 August, 2012
 Vol. 8(34), pp. 1658-1669, 11 September, 2013 DOI 10.5897/SRE12.171 ISSN 1992-2248 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/sre Scientific Research and Essays Full Length Research Paper Field-programmable
Vol. 8(34), pp. 1658-1669, 11 September, 2013 DOI 10.5897/SRE12.171 ISSN 1992-2248 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/sre Scientific Research and Essays Full Length Research Paper Field-programmable
FUJITSU TEN's Approach to Digital Broadcasting
 FUJITSU TEN's Approach to Digital Broadcasting Mitsuru Sasaki Kazuo Takayama 1. Introduction There has been a notable increase recently in the number of television commercials advertising television sets
FUJITSU TEN's Approach to Digital Broadcasting Mitsuru Sasaki Kazuo Takayama 1. Introduction There has been a notable increase recently in the number of television commercials advertising television sets
Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 1 (row 1, column 1)
 Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 1 (row 1, column 1) Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 2 (row 2, column 1) Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 3 (row 3, column 1) ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Pulse Modulation
Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 1 (row 1, column 1) Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 2 (row 2, column 1) Workspace for '6-pulse' Page 3 (row 3, column 1) ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Pulse Modulation
CHAPTER 2. Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication ( )
 CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
Wideband Receiver for Communications Receiver or Spectrum Analysis Usage: A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion
 A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
College of information Technology Department of Information Networks Telecommunication & Networking I Chapter 5. Analog Transmission
 Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
*R. Karthikeyan Research Scholar, Dept. of CSA, SCSVMV University, Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India.
 OFDM Signal Improvement Using Radio over Fiber for Wireless System *R. Karthikeyan Research Scholar, Dept. of CSA, SCSVMV University, Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India. rkarthi86@gmail.com Dr. S. Prakasam
OFDM Signal Improvement Using Radio over Fiber for Wireless System *R. Karthikeyan Research Scholar, Dept. of CSA, SCSVMV University, Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, India. rkarthi86@gmail.com Dr. S. Prakasam
Recap of Last 2 Classes
 Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK
 PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Course Code : 13EC1145 L T P C : 4 1 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Information Technology Semester : V Prerequisites
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Course Code : 13EC1145 L T P C : 4 1 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Information Technology Semester : V Prerequisites
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2)
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
FDM- FREQUENCY DIVISION MULTIPLEXING
 FDM- FREQUENCY DIVISION MULTIPLEXING Multiplexing to refer to the combination of information streams from multiple sources for transmission over a shared medium Demultiplexing to refer to the separation
FDM- FREQUENCY DIVISION MULTIPLEXING Multiplexing to refer to the combination of information streams from multiple sources for transmission over a shared medium Demultiplexing to refer to the separation
CATALOG. ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Microcontroller kits Arm controller kits PLC Trainer KITS Regulated Power supplies
 CATALOG ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Microcontroller kits Arm controller kits PLC Trainer KITS Regulated Power supplies UNION INTRUMENTS #17 & 18, 4 th floor, Hanumathra Arcade
CATALOG ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Microcontroller kits Arm controller kits PLC Trainer KITS Regulated Power supplies UNION INTRUMENTS #17 & 18, 4 th floor, Hanumathra Arcade
Design of Low Power Flip Flop Based on Modified GDI Primitive Cells and Its Implementation in Sequential Circuits
 Design of Low Power Flip Flop Based on Modified GDI Primitive Cells and Its Implementation in Sequential Circuits Dr. Saravanan Savadipalayam Venkatachalam Principal and Professor, Department of Mechanical
Design of Low Power Flip Flop Based on Modified GDI Primitive Cells and Its Implementation in Sequential Circuits Dr. Saravanan Savadipalayam Venkatachalam Principal and Professor, Department of Mechanical
Performance Improvement of Delta Sigma Modulator for Wide-Band Continuous-Time Applications
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Improvement of Delta Sigma Modulator for Wide-Band Continuous-Time Applications Parvathy Unnikrishnan 1, Siva Kumari
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Improvement of Delta Sigma Modulator for Wide-Band Continuous-Time Applications Parvathy Unnikrishnan 1, Siva Kumari
OFDM Transceiver using Verilog Proposal
 OFDM Transceiver using Verilog Proposal PAUL PETHSOMVONG ZACH ASAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BRADLEY UNIVERSITY PEORIA, ILLINOIS NOVEMBER 21, 2013 1 Project Outline Orthogonal Frequency Division
OFDM Transceiver using Verilog Proposal PAUL PETHSOMVONG ZACH ASAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BRADLEY UNIVERSITY PEORIA, ILLINOIS NOVEMBER 21, 2013 1 Project Outline Orthogonal Frequency Division
Phase Locked Loop Design for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition
 Phase Locked Loop Design for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition S.Anjaneyulu 1,J.Sreepavani 2,K.Pramidapadma 3,N.Varalakshmi 4,S.Triven 5 Lecturer,Dept.of ECE,SKU College of Engg. & Tech.,Ananthapuramu
Phase Locked Loop Design for Fast Phase and Frequency Acquisition S.Anjaneyulu 1,J.Sreepavani 2,K.Pramidapadma 3,N.Varalakshmi 4,S.Triven 5 Lecturer,Dept.of ECE,SKU College of Engg. & Tech.,Ananthapuramu
 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing & Measurement of its Performance
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 5, Issue. 2, February 2016,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 5, Issue. 2, February 2016,
Wireless Communications
 2. Physical Layer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Periodic Signal Periodic signal: repeats itself in time, that is g(t) = g(t + T ) in which T (given in seconds [s]) is the period of the signal g(t) The number of cycles
2. Physical Layer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Periodic Signal Periodic signal: repeats itself in time, that is g(t) = g(t + T ) in which T (given in seconds [s]) is the period of the signal g(t) The number of cycles
Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling
 Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling, J. Neil Ross & Andrew D. Brown S 1 Outline Introduction ADSL Where is the need for the transformer? What are
Predicting Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in ADSL Transformers using Behavioural Modeling, J. Neil Ross & Andrew D. Brown S 1 Outline Introduction ADSL Where is the need for the transformer? What are
Data Communication (CS601)
 Data Communication (CS601) MOST LATEST (2012) PAPERS For MID Term (ZUBAIR AKBAR KHAN) Page 1 Q. Suppose a famous Telecomm company AT&T is using AMI encoding standard for its digital telephone services,
Data Communication (CS601) MOST LATEST (2012) PAPERS For MID Term (ZUBAIR AKBAR KHAN) Page 1 Q. Suppose a famous Telecomm company AT&T is using AMI encoding standard for its digital telephone services,
Error Probability of Different Modulation Schemes for OFDM based WLAN standard IEEE a
 Error Probability of Different Modulation Schemes for OFDM based WLAN standard IEEE 802.11a Sanjeev Kumar Asst. Professor/ Electronics & Comm. Engg./ Amritsar college of Engg. & Technology, Amritsar, 143001,
Error Probability of Different Modulation Schemes for OFDM based WLAN standard IEEE 802.11a Sanjeev Kumar Asst. Professor/ Electronics & Comm. Engg./ Amritsar college of Engg. & Technology, Amritsar, 143001,
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Department of Systems and Computer Engineering
 CARLETON UNIVERSITY Department of Systems and Computer Engineering SYSC4700 Telecommunications Engineering Winter 2016 Term Exam 10 February 2016 1. NO CELL PHONES. Closed-book exam (with one-page aid-sheet).
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Department of Systems and Computer Engineering SYSC4700 Telecommunications Engineering Winter 2016 Term Exam 10 February 2016 1. NO CELL PHONES. Closed-book exam (with one-page aid-sheet).
Performance Evaluation of Wireless Communication System Employing DWT-OFDM using Simulink Model
 Performance Evaluation of Wireless Communication System Employing DWT-OFDM using Simulink Model M. Prem Anand 1 Rudrashish Roy 2 1 Assistant Professor 2 M.E Student 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication
Performance Evaluation of Wireless Communication System Employing DWT-OFDM using Simulink Model M. Prem Anand 1 Rudrashish Roy 2 1 Assistant Professor 2 M.E Student 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication
Lab 7: DELTA AND SIGMA-DELTA A/D CONVERTERS
 ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 6 Lab 7: DELTA AND SIGMA-DELTA A/D CONVERTERS Goal The goals of this experiment are: - Verify the operation of a differential ADC; - Find the
ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 6 Lab 7: DELTA AND SIGMA-DELTA A/D CONVERTERS Goal The goals of this experiment are: - Verify the operation of a differential ADC; - Find the
Local Asynchronous Communication. By S.Senthilmurugan Asst.Professor/ICE SRM University. Chennai.
 Local Asynchronous Communication By S.Senthilmurugan Asst.Professor/ICE SRM University. Chennai. Bitwise Data Transmission Data transmission requires: Encoding bits as energy Transmitting energy through
Local Asynchronous Communication By S.Senthilmurugan Asst.Professor/ICE SRM University. Chennai. Bitwise Data Transmission Data transmission requires: Encoding bits as energy Transmitting energy through
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
S.D.M COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 VISHVESHWARAIAH TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY S.D.M COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A seminar report on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Submitted by Sandeep Katakol 2SD06CS085 8th semester
VISHVESHWARAIAH TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY S.D.M COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A seminar report on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Submitted by Sandeep Katakol 2SD06CS085 8th semester
Physical Layer, Part 2. Analog and Digital Transmission
 CS 656 Analog/Digital, Page 1 Physical Layer, Part 2 Analog and Digital Transmission These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at
CS 656 Analog/Digital, Page 1 Physical Layer, Part 2 Analog and Digital Transmission These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at
Chapter Two. Fundamentals of Data and Signals. Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User's Approach Seventh Edition
 Chapter Two Fundamentals of Data and Signals Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User's Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Distinguish between
Chapter Two Fundamentals of Data and Signals Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User's Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Distinguish between
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty Name: S.Kalpana, AP/ECE QUESTION BANK UNIT I ANALOG
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty Name: S.Kalpana, AP/ECE QUESTION BANK UNIT I ANALOG
Performance Analysis Of OFDM Using 4 PSK, 8 PSK And 16 PSK
 Performance Analysis Of OFDM Using 4 PSK, 8 PSK And 16 PSK Virat Bhambhe M.Tech. Student, Electrical and Electronics Engineering Gautam Buddh Technical University (G.B.T.U.), Lucknow (U.P.), India Dr.
Performance Analysis Of OFDM Using 4 PSK, 8 PSK And 16 PSK Virat Bhambhe M.Tech. Student, Electrical and Electronics Engineering Gautam Buddh Technical University (G.B.T.U.), Lucknow (U.P.), India Dr.
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
Channel Concepts CS 571 Fall Kenneth L. Calvert
 Channel Concepts CS 571 Fall 2006 2006 Kenneth L. Calvert What is a Channel? Channel: a means of transmitting information A means of communication or expression Webster s NCD Aside: What is information...?
Channel Concepts CS 571 Fall 2006 2006 Kenneth L. Calvert What is a Channel? Channel: a means of transmitting information A means of communication or expression Webster s NCD Aside: What is information...?
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels
 Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Design and Implementation of Digital Stethoscope using TFT Module and Matlab Visualisation Tool
 World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research, Volume 3, Issue 1 (2018) 297-304 Contents available at WJTER World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research Journal Homepage: www.wjter.com
World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research, Volume 3, Issue 1 (2018) 297-304 Contents available at WJTER World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research Journal Homepage: www.wjter.com
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)
![Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)](/thumbs/96/127341232.jpg) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution
 High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution Raghava Garipelly Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sree Chaitanya College of Engineering, Karimnagar, A.P, INDIA. Abstract: A high speed CMOS comparator
High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution Raghava Garipelly Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sree Chaitanya College of Engineering, Karimnagar, A.P, INDIA. Abstract: A high speed CMOS comparator
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer. Bird s Eye View. Outline. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING
 BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING AIM: To set up a circuit to generate Binary Amplitude Shift keying and to plot the output waveforms. COMPONENTS AND EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: IC CD4016, IC 7474, Resistors, Zener
BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING AIM: To set up a circuit to generate Binary Amplitude Shift keying and to plot the output waveforms. COMPONENTS AND EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: IC CD4016, IC 7474, Resistors, Zener
