HDR, displays & low-level vision
|
|
|
- Everett Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rafał K. Mantiuk HDR, displays & low-level vision SIGGRAPH Asia Course on Cutting-Edge VR/AR Display Technologies
2 These slides are a part of the course Cutting-edge VR/AR Display Technologies (Gaze-, Accommodation-, Motion-aware and HDR-enabled) Presented at SIGGRAPH Asia in Tokyo on the 5 th of December 2018 The latest version of the slides and the slides for the remaining part of the tutorial can be found at: Material is copyright Rafał Mantiuk, 2018, except where otherwise noted. 5 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
3 HDR & VR? Do we need HDR VR headsets? OLED contrast 1,000,000:1 6 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
4 ToC HDR in a nutshell Display technologies in VR Perception & image quality Example: Temporal Resolution Multiplexing 8 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
5 Dynamic range Luminance max L min L (for SNR>3) Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge Slide 9
6 Dynamic range (contrast) As ratio: Usually written as C:1, for example 1000:1. As orders of magnitude or log10 units: As stops: C = L max L min C 2 = log 2 L max L min C 10 = log 10 L max L min One stop is doubling of halving the amount of light 10 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
7 Visible colour gamut The eye can perceive more colours and brightness levels than a display can produce a JPEG file can store The premise of HDR: Visual perception and not the technology should define accuracy and the range of colours The current standards not fully follow to this principle 12 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
8 Standard vs. High Dynamic Range HDR cameras/formats/displays attempt capture/represent/reproduce (almost) all visible colours They represent scene colours and therefore we often call this representation scene-referred SDR cameras/formats/devices attempt to capture/represent/reproduce only colours of a standard srgb colour gamut, mimicking the capabilities of CRTs monitors 13 They represent display colours and therefore we often call this representation display-referred
9 Luminance Luminance measure of light intensity weighted by the sensitivity of the achromatic mechanism. Units: cd/m 2 Luminance 700 L V = න 350 kl λ V λ dλ k = Light spectrum (radiance) Luminous efficiency function (weighting) 14 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
10 From rendering to display 15
11 From rendering to display 16
12 Luminance and Luma Luminance Photometric quantity defined by the spectral luminous efficiency function L R G B Units: cd/m 2 Luma Gray-scale value computed from LDR (gamma corrected) image Y = R G B R prime denotes gamma correction Unitless R' = R 1/g 17 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
13 Sensitivity to luminance Weber-law the just-noticeable difference is proportional to the magnitude of a stimulus The smallest detectable luminance difference Background (adapting) luminance Ernst Heinrich Weber [From wikipedia] Constant Typical stimuli: ΔL L 18 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
14 Consequence of the Weber-law Smallest detectable difference in luminance For k=1% L ΔL 100 cd/m 2 1 cd/m 2 1 cd/m cd/m 2 Adding or subtracting luminance will have different visual impact depending on the background luminance Unlike LDR luma values, luminance values are not perceptually uniform! 19 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
15 How to make luminance (more) perceptually uniform? response - R Using Fechnerian integration Derivative of response dr dl (L) = 1 DL(L) Detection threshold 1 ΔL Luminance transducer: R(L) = L 0 1 L(l) dl luminance - L 20 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
16 Assuming the Weber law and given the luminance transducer R(L) = the response of the visual system to light is: L 0 1 L(l) dl 21 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
17 Fechner law R(L) = aln(l) Response of the visual system to luminance is approximately logarithmic The values of HDR pixel values are much more intuitive when they are plotted / considered / processed in the logarithmic domain Gustav Fechner [From Wikipedia] 22 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
18 ToC HDR in a nutshell Display technologies in VR Perception & image quality Example: Temporal Resolution Multiplexing 23 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
19 VR display technologies TFT-LCD TN, STN, MVA, PVA, IPS AMOLED Contrast: <3000:1 Transmissive Complex temporal response Arbitrary bright Constant power at constant backlight Contrast: >10,000:1 Emmisive Rapid response Brightness affects longevity Power varies with image content 24 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
20 LCD TN LCD color may change with the viewing angle contrast up to 3000:1 higher resolution results in smaller fill-factor color LCD transmits only up to 8% (more often close to 3-5%) light when set to full white 25 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
21 LCD temporal response Experiment on an IPS LCD screen We rapidly switched between two intensity levels at 120Hz Measured luminance integrated over 1s The top plot shows the difference between expected ( I t 1+I t ) and measured luminance 2 The bottom plot: intensity measurement for the full brightness and half-brightness display settings 26 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
22 OLED based on electrophosphorescence large viewing angle the power consumption varies with the brightness of the image fast (< 1 microsec) arbitrary sizes life-span is a concern more difficult to produce 27 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
23 Mate 9 Pro + DayDream HTC Vive Low persistence displays Most VR displays flash an image for a fraction of frame duration This reduces hold-type blur And also reduces the perceived lag of the rendering 28 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
24 Lens in VR displays Aberrations when viewing off-center Chromatic aberration Loss of resolution Difficult to eliminate if the exact eye position is unknown Glare Scattering of the light in the lens From Fresnel fringes Reduces dynamic range Examples from: 29 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
25 Resolution Relevant units: pixels per visual degree [ppd] Nyquist frequency in cycles per degree = ½ of ppd PC & mobile resolution 1981: x ppd 1990: x ppd 2011: x ppd 2016: 31 4K 50 ppd 2018: ppd VR resolution 2016 HTC Vive: 10 ppd 2018 HTC Vive Pro: 13 ppd 32 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
26 ToC HDR in a nutshell Display technologies in VR Perception & image quality Example: Temporal Resolution Multiplexing 33 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
27 (Camera) image reconstruction model Captured image Latent image Y = gx + η Convolution kernel Noise Can we come up with a similar model for visual system? 34 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
28 Modeling visual system Cornea Lens Photoreceptors Retinal ganglion cells LGN Visual Cortex Detection Defocus & Aberrations Glare Adaptation Colour opponency Luminance masking Spectral sensitivity P & M visual pathways Spatial- / orientation- / temporal- Selective channels Integration Contrast masking Contrast Sensitivity Function Excellent visualization of the human eye: 35 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
29 Contrast Spatial frequency [cycles per degree] 36 Campbell & Robson contrast sensitivity chart
30 37
31 Contrast Sensitivity Function Temporal frequency Stimulus size Spatial frequency Eccentricity CSF = S(r,q,w,l,i 2,d,e) Orientation Adapting luminance Viewing distance 38
32 Contrast Sensitivity Function Sensitivity = inverse of the detection threshold S = L b ΔL Detection of barely noticeable luminance difference ΔL on a uniform background L b Varies with luminance HTC Vive iphone 4 Retina display CSF models: Barten, P. G. J. (2004). Mantiuk, R., Kim, K. J., Rempel, A. G., & Heidrich, W. (2011) 39 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
33 Spatio-chromatic CSF 40 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
34 High brightness HDR display [15,000 cd/m 2 ] 41 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
35 Color CSF across the luminance range 42 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
36 Color CSF across the luminance range 43 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
37 Color CSF across the luminance range 44 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
38 Color CSF across the luminance range 45 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
39 Color CSF across the luminance range 46 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
40 Color CSF across the luminance range 47 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
41 Spatio-chromatic CSF Chromatic channels (red-green, blue-yellow) are much less sensitive to high frequencies This is why we can (often) get away with chroma subsampling in image/video compression 48 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
42 Georgeson and Sullivan J. Phsysio Contrast Constancy CSF is NOT MTF of visual system Contrast constancy There is little variation in magnitude of perceived contrast above the detection threshold 49 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
43 50 Contrast constancy No CSF above the detection threshold
44 Modeling visual perception Since visual system is highly non-linear, a linear model Y = gx + η cannot be used. CSF is NOT MTF! Visual processing is an unknown non-linear function: Input image Percept (not an image) Y = f[x] Visual processing 51 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
45 Predicting visible differences with CSF But we can use CSF to find the probability of spotting a difference beween a pair of images X 1 and X 2 : p f[x 1 ] = f[x 2 ] X 1, X 2, CSF X 1 X 2 Wavelet decomposition ΔL / Compute contrast Background luminance ΔL L b X CSF L b L b ΔL thr -1 Psychometric Wavelet function reconstruction P detection (simplified) Visual Difference Predictor Daly, S. (1993). Mantiuk, R., et al. (2011) 52 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
46 Retinal velocity Sensitivity drops rapidly once images start to move The eye tracks moving objects Smooth Pursuit Eye Motion (SPEM) Stabilizes images on the retina But tracking is not perfect Loss of sensitivity mostly caused by imperfect SPEM SPEM worse at high velocities Motion sharpenning 56 Masks the loss of higher frequencies Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge Spatio-velocity contrast sensitivity Kelly s model [1979]
47 Real-world Perfect motion Hold-on blur The eye smoothly follows a moving object But the image on the display is frozen for 1/60 th of a second Physical image + eye motion + temporal integration 57 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
48 60 Hz display Hold-on blur The eye smoothly follows a moving object But the image on the display is frozen for 1/60 th of a second Physical image + eye motion + temporal integration 58 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
49 Black frame insertion Hold-on blur The eye smoothly follows a moving object But the image on the display is frozen for 1/60 th of a second Physical image + eye motion + temporal integration 59 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
50 Flicker Critical Flicker Frequency Strongly depends on luminance big issue for HDR VR headsets Increases with eccentricity and stimulus size It is possible to detect flicker even at 2kHz For saccadic eye motion [Hartmann et al. 1979] 60 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
51 Simulation (cyber) sickness Conflict between vestibular and visual systems When camera motion inconsistent with head motion Frame of reference (e.g. cockpit) helps Worse with larger FOV Worse with high luminance and flicker 61 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
52 ToC HDR in a nutshell Display technologies in VR Perception & image quality Example: Temporal Resolution Multiplexing 62 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
53 VR rendering required bandwidth 2 ( ) GBps 9Gbps 2 eyes resolution refresh rate pixel data
54 TRM: Temporal Resolution Multiplexing Render every second frame at a lower resolution Transfer high- and low-resolution frames When displaying Compensate for the loss of high frequencies Model display and its limitations Handle the limited dynamic range See the demo in the break! [Denes et al. 2019, Temporal Resolution Multiplexing, TCVCG/IEEE VR] 64 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
55 TRM: Why does it work? The eye cannot see high spatio-temporal frequencies The eye cannot see the loss of sharpness for moving objects motion sharpenning Head motion masks higher frequences Spatio-temporal CSF Spatio-velocity CSF No need to render these frequencies 65 Rafał Mantiuk, University of Cambridge
56 Summary VR/AR display technologies must exploit the limitations of the visual system Because the display / rendering bandwidth is becoming too large HDR for VR is a great idea because It gives more realistic experience Better quality with the same number of pixels Additional depth cues HDR for VR is bad idea because Increased flicker visibility Increased simulation sickness Lens glare will reduce the effective dynamic range 66 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
57 References Concise overview of high dynamic range imaging Mantiuk, R. K., Myszkowski, K., & Seidel, H. (2015). High Dynamic Range Imaging. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (pp. 1 42). Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Downloadable PDF: Comprehensive book on display technologies Hainich, R. R., & Bimber, O. (2011). Displays: Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press. Book on HDR Imaging Reinhard, E., Heidrich, W., Debevec, P., Pattanaik, S., Ward, G., & Myszkowski, K. (2010). High Dynamic Range Imaging: Acquisition, Display, and Image-Based Lighting (2nd editio). Morgan Kaufmann. Computational models of visual perception WANDELL, B.A Foundations of vision. Sinauer Associates. 67 Rafał Mantiuk, Univ. of Cambridge
High dynamic range in VR. Rafał Mantiuk Dept. of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge
 High dynamic range in VR Rafał Mantiuk Dept. of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge These slides are a part of the tutorial Cutting-edge VR/AR Display Technologies (Gaze-, Accommodation-,
High dynamic range in VR Rafał Mantiuk Dept. of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge These slides are a part of the tutorial Cutting-edge VR/AR Display Technologies (Gaze-, Accommodation-,
High dynamic range and tone mapping Advanced Graphics
 High dynamic range and tone mapping Advanced Graphics Rafał Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge Cornell Box: need for tone-mapping in graphics Rendering Photograph 2 Real-world scenes
High dynamic range and tone mapping Advanced Graphics Rafał Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge Cornell Box: need for tone-mapping in graphics Rendering Photograph 2 Real-world scenes
25/02/2017. C = L max L min. L max C 10. = log 10. = log 2 C 2. Cornell Box: need for tone-mapping in graphics. Dynamic range
 Cornell Box: need for tone-mapping in graphics High dynamic range and tone mapping Advanced Graphics Rafał Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge Rendering Photograph 2 Real-world scenes
Cornell Box: need for tone-mapping in graphics High dynamic range and tone mapping Advanced Graphics Rafał Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge Rendering Photograph 2 Real-world scenes
Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance
 Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance Sumanta N. Pattanaik 1 Mark D. Fairchild 2 James A. Ferwerda 1 Donald P. Greenberg 1 1 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University,
Multiscale model of Adaptation, Spatial Vision and Color Appearance Sumanta N. Pattanaik 1 Mark D. Fairchild 2 James A. Ferwerda 1 Donald P. Greenberg 1 1 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University,
The Human Visual System!
 an engineering-focused introduction to! The Human Visual System! EE367/CS448I: Computational Imaging and Display! stanford.edu/class/ee367! Lecture 2! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! nautilus eye,
an engineering-focused introduction to! The Human Visual System! EE367/CS448I: Computational Imaging and Display! stanford.edu/class/ee367! Lecture 2! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! nautilus eye,
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
12/02/2017. From light to colour spaces. Electromagnetic spectrum. Colour. Correlated colour temperature. Black body radiation.
 From light to colour spaces Light and colour Advanced Graphics Rafal Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge 1 2 Electromagnetic spectrum Visible light Electromagnetic waves of wavelength
From light to colour spaces Light and colour Advanced Graphics Rafal Mantiuk Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge 1 2 Electromagnetic spectrum Visible light Electromagnetic waves of wavelength
On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model
 On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model Garrett M. Johnson and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester New
On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model Garrett M. Johnson and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester New
Color and perception Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
Color and perception Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 A slight detour We ve spent the whole class talking about how to put images on the screen What happens when we look at those images? Are there any
The Quality of Appearance
 ABSTRACT The Quality of Appearance Garrett M. Johnson Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology 14623-Rochester, NY (USA) Corresponding
ABSTRACT The Quality of Appearance Garrett M. Johnson Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology 14623-Rochester, NY (USA) Corresponding
On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model
 On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model Garrett M. Johnson and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester New
On Contrast Sensitivity in an Image Difference Model Garrett M. Johnson and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester New
icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance
 icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance Jiangtao Kuang, Mark D. Fairchild, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New York Abstract A new image appearance model, designated as icam06, has been developed
icam06, HDR, and Image Appearance Jiangtao Kuang, Mark D. Fairchild, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New York Abstract A new image appearance model, designated as icam06, has been developed
The luminance of pure black: exploring the effect of surround in the context of electronic displays
 The luminance of pure black: exploring the effect of surround in the context of electronic displays Rafa l K. Mantiuk a,b, Scott Daly b and Louis Kerofsky b a Bangor University, School of Computer Science,
The luminance of pure black: exploring the effect of surround in the context of electronic displays Rafa l K. Mantiuk a,b, Scott Daly b and Louis Kerofsky b a Bangor University, School of Computer Science,
Realistic Image Synthesis
 Realistic Image Synthesis - HDR Capture & Tone Mapping - Philipp Slusallek Karol Myszkowski Gurprit Singh Karol Myszkowski LDR vs HDR Comparison Various Dynamic Ranges (1) 10-6 10-4 10-2 100 102 104 106
Realistic Image Synthesis - HDR Capture & Tone Mapping - Philipp Slusallek Karol Myszkowski Gurprit Singh Karol Myszkowski LDR vs HDR Comparison Various Dynamic Ranges (1) 10-6 10-4 10-2 100 102 104 106
Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II
 Lecture 13: Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II Visual Computing Systems Today Finish image processing pipeline Auto-focus / auto-exposure Camera processing elements Smart phone processing elements
Lecture 13: Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II Visual Computing Systems Today Finish image processing pipeline Auto-focus / auto-exposure Camera processing elements Smart phone processing elements
ISSN Vol.03,Issue.29 October-2014, Pages:
 ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.29 October-2014, Pages:5768-5772 www.ijsetr.com Quality Index Assessment for Toned Mapped Images Based on SSIM and NSS Approaches SAMEED SHAIK 1, M. CHAKRAPANI 2 1 PG Scholar,
ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.29 October-2014, Pages:5768-5772 www.ijsetr.com Quality Index Assessment for Toned Mapped Images Based on SSIM and NSS Approaches SAMEED SHAIK 1, M. CHAKRAPANI 2 1 PG Scholar,
PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY. Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist
 PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist INTRODUCTION Virtual reality is an exciting challenging workload for computer graphics Most VR pixels are peripheral
PERCEPTUAL INSIGHTS INTO FOVEATED VIRTUAL REALITY Anjul Patney Senior Research Scientist INTRODUCTION Virtual reality is an exciting challenging workload for computer graphics Most VR pixels are peripheral
Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II
 Lecture 14: Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II Visual Computing Systems Today Finish image processing pipeline Auto-focus / auto-exposure Camera processing elements Smart phone processing elements
Lecture 14: Camera Image Processing Pipeline: Part II Visual Computing Systems Today Finish image processing pipeline Auto-focus / auto-exposure Camera processing elements Smart phone processing elements
Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing
 I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
I22: Digital Image processing Lecture 3: Grey and Color Image Processing Prof. YingLi Tian Sept. 13, 217 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of New York
Visual Perception. human perception display devices. CS Visual Perception
 Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
Visual Perception human perception display devices 1 Reference Chapters 4, 5 Designing with the Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson 2 Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important
COLOR and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 How
Color images C1 C2 C3
 Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
Color imaging Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..) Digital
VU Rendering SS Unit 8: Tone Reproduction
 VU Rendering SS 2012 Unit 8: Tone Reproduction Overview 1. The Problem Image Synthesis Pipeline Different Image Types Human visual system Tone mapping Chromatic Adaptation 2. Tone Reproduction Linear methods
VU Rendering SS 2012 Unit 8: Tone Reproduction Overview 1. The Problem Image Synthesis Pipeline Different Image Types Human visual system Tone mapping Chromatic Adaptation 2. Tone Reproduction Linear methods
Color Science. CS 4620 Lecture 15
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 2013 Steve Marschner 1 [source unknown] 2013 Steve Marschner 2 What light is Light is electromagnetic radiation exists as oscillations of different frequency (or, wavelength)
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016
 Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
Vision Science I Exam 2 31 October 2016 1) Mr. Jack O Lantern, pictured here, had an unfortunate accident that has caused brain damage, resulting in unequal pupil sizes. Specifically, the right eye is
HIGH DYNAMIC RANGE VERSUS STANDARD DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSION EFFICIENCY
 HIGH DYNAMIC RANGE VERSUS STANDARD DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSION EFFICIENCY Ronan Boitard Mahsa T. Pourazad Panos Nasiopoulos University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada TELUS Communications Inc., Vancouver,
HIGH DYNAMIC RANGE VERSUS STANDARD DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSION EFFICIENCY Ronan Boitard Mahsa T. Pourazad Panos Nasiopoulos University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada TELUS Communications Inc., Vancouver,
Frequencies and Color
 Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
Frequencies and Color Alexei Efros, CS280, Spring 2018 Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976 Spatial Frequencies and
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Color image differences, image appearance, image quality, vision modeling 1. INTRODUCTION
 Measuring Images: Differences, Quality, and Appearance Garrett M. Johnson * and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science, Rochester Institute of
Measuring Images: Differences, Quality, and Appearance Garrett M. Johnson * and Mark D. Fairchild Munsell Color Science Laboratory, Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science, Rochester Institute of
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 4: Color Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Chap. 4 of Fundamentals of Multimedia Some reference from http://media.ee.ntu.edu.tw/courses/dvt/15f/ 1 Outline
Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 4: Color Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Chap. 4 of Fundamentals of Multimedia Some reference from http://media.ee.ntu.edu.tw/courses/dvt/15f/ 1 Outline
High Dynamic Range Imaging: Towards the Limits of the Human Visual Perception
 High Dynamic Range Imaging: Towards the Limits of the Human Visual Perception Rafał Mantiuk Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken 1 Introduction Vast majority of digital images and video material
High Dynamic Range Imaging: Towards the Limits of the Human Visual Perception Rafał Mantiuk Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken 1 Introduction Vast majority of digital images and video material
Color appearance in image displays
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Presentations and other scholarship 1-18-25 Color appearance in image displays Mark Fairchild Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/other
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Presentations and other scholarship 1-18-25 Color appearance in image displays Mark Fairchild Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/other
Images. CS 4620 Lecture Kavita Bala w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Fall 2015 Lecture 38
 Images CS 4620 Lecture 38 w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 1 Announcements A7 extended by 24 hours w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Color displays Operating principle: humans are trichromatic match
Images CS 4620 Lecture 38 w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 1 Announcements A7 extended by 24 hours w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Color displays Operating principle: humans are trichromatic match
Virtual Reality I. Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age. Donald P. Greenberg November 9, 2017 Lecture #21
 Virtual Reality I Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Donald P. Greenberg November 9, 2017 Lecture #21 1968: Ivan Sutherland 1990s: HMDs, Henry Fuchs 2013: Google Glass History of Virtual Reality 2016:
Virtual Reality I Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Donald P. Greenberg November 9, 2017 Lecture #21 1968: Ivan Sutherland 1990s: HMDs, Henry Fuchs 2013: Google Glass History of Virtual Reality 2016:
This is due to Purkinje shift. At scotopic conditions, we are more sensitive to blue than to red.
 1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
1. We know that the color of a light/object we see depends on the selective transmission or reflections of some wavelengths more than others. Based on this fact, explain why the sky on earth looks blue,
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso. Color Image Processing
 For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
For a long time I limited myself to one color as a form of discipline. Pablo Picasso Color Image Processing 1 Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification
Compression of High Dynamic Range Video Using the HEVC and H.264/AVC Standards
 Compression of Dynamic Range Video Using the HEVC and H.264/AVC Standards (Invited Paper) Amin Banitalebi-Dehkordi 1,2, Maryam Azimi 1,2, Mahsa T. Pourazad 2,3, and Panos Nasiopoulos 1,2 1 Department of
Compression of Dynamic Range Video Using the HEVC and H.264/AVC Standards (Invited Paper) Amin Banitalebi-Dehkordi 1,2, Maryam Azimi 1,2, Mahsa T. Pourazad 2,3, and Panos Nasiopoulos 1,2 1 Department of
Color Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15
 Color http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 has been posted. - Due Friday March 23 rd (one-week homework!) - Any questions about the
Color http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 has been posted. - Due Friday March 23 rd (one-week homework!) - Any questions about the
High Dynamic Range Displays
 High Dynamic Range Displays Dave Schnuelle Senior Director, Image Technology Dolby Laboratories The Demise of the CRT What was good: Large viewing angle High contrast Consistent EO transfer function Good
High Dynamic Range Displays Dave Schnuelle Senior Director, Image Technology Dolby Laboratories The Demise of the CRT What was good: Large viewing angle High contrast Consistent EO transfer function Good
MODIFICATION OF ADAPTIVE LOGARITHMIC METHOD FOR DISPLAYING HIGH CONTRAST SCENES BY AUTOMATING THE BIAS VALUE PARAMETER
 International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management January-June 2012, Volume 5, No. 1, pp. 73-77 MODIFICATION OF ADAPTIVE LOGARITHMIC METHOD FOR DISPLAYING HIGH CONTRAST SCENES BY
International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management January-June 2012, Volume 5, No. 1, pp. 73-77 MODIFICATION OF ADAPTIVE LOGARITHMIC METHOD FOR DISPLAYING HIGH CONTRAST SCENES BY
Color , , Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7
 Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September 28 th. - Requires camera and
Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 7 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September 28 th. - Requires camera and
Temporal Resolution Multiplexing: Exploiting the limitations of spatio-temporal vision for more efficient VR rendering
 Temporal Resolution Multiplexing: Exploiting the limitations of spatio-temporal vision for more efficient VR rendering Gyorgy Denes Kuba Maruszczyk George Ash Rafał K. Mantiuk University of Cambridge,
Temporal Resolution Multiplexing: Exploiting the limitations of spatio-temporal vision for more efficient VR rendering Gyorgy Denes Kuba Maruszczyk George Ash Rafał K. Mantiuk University of Cambridge,
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Ronald S. Harwerth, OD, PhD Office: Room 2160 Office hours: By appointment Telephone: 713-743-1940 email: rharwerth@uh.edu
COLOR. and the human response to light
 COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
COLOR and the human response to light Contents Introduction: The nature of light The physiology of human vision Color Spaces: Linear Artistic View Standard Distances between colors Color in the TV 2 Amazing
/ Impact of Human Factors for Mixed Reality contents: / # How to improve QoS and QoE? #
 / Impact of Human Factors for Mixed Reality contents: / # How to improve QoS and QoE? # Dr. Jérôme Royan Definitions / 2 Virtual Reality definition «The Virtual reality is a scientific and technical domain
/ Impact of Human Factors for Mixed Reality contents: / # How to improve QoS and QoE? # Dr. Jérôme Royan Definitions / 2 Virtual Reality definition «The Virtual reality is a scientific and technical domain
Visual Perception. Martin Čadík. Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
 Visual Perception Martin Čadík Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Content HVS Visual Illusions, Form, Brightness Adaptation - HDRI Colour Vision Depth, Motion Image Quality Assessment
Visual Perception Martin Čadík Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic Content HVS Visual Illusions, Form, Brightness Adaptation - HDRI Colour Vision Depth, Motion Image Quality Assessment
Tonemapping and bilateral filtering
 Tonemapping and bilateral filtering http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 6 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September
Tonemapping and bilateral filtering http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 6 Course announcements Homework 2 is out. - Due September
A Wavelet-Based Encoding Algorithm for High Dynamic Range Images
 The Open Signal Processing Journal, 2010, 3, 13-19 13 Open Access A Wavelet-Based Encoding Algorithm for High Dynamic Range Images Frank Y. Shih* and Yuan Yuan Department of Computer Science, New Jersey
The Open Signal Processing Journal, 2010, 3, 13-19 13 Open Access A Wavelet-Based Encoding Algorithm for High Dynamic Range Images Frank Y. Shih* and Yuan Yuan Department of Computer Science, New Jersey
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
The Science Seeing of process Digital Media. The Science of Digital Media Introduction
 The Human Science eye of and Digital Displays Media Human Visual System Eye Perception of colour types terminology Human Visual System Eye Brains Camera and HVS HVS and displays Introduction 2 The Science
The Human Science eye of and Digital Displays Media Human Visual System Eye Perception of colour types terminology Human Visual System Eye Brains Camera and HVS HVS and displays Introduction 2 The Science
CSE 332/564: Visualization. Fundamentals of Color. Perception of Light Intensity. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 Perception of Light Intensity CSE 332/564: Visualization Fundamentals of Color Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University How Many Intensity Levels Do We Need? Dynamic Intensity Range
Perception of Light Intensity CSE 332/564: Visualization Fundamentals of Color Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University How Many Intensity Levels Do We Need? Dynamic Intensity Range
High dynamic range imaging and tonemapping
 High dynamic range imaging and tonemapping http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 12 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due
High dynamic range imaging and tonemapping http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 12 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due
ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF LUMINANCE AND DETAILS IN IMAGES UNDER AMBIENT LIGHT
 ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF LUMINANCE AND DETAILS IN IMAGES UNDER AMBIENT LIGHT Haonan Su 1, Cheolkon Jung 1, Shuyao Wang 2, and Yuanjia Du 2 1 School of Electronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi an 710071,
ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF LUMINANCE AND DETAILS IN IMAGES UNDER AMBIENT LIGHT Haonan Su 1, Cheolkon Jung 1, Shuyao Wang 2, and Yuanjia Du 2 1 School of Electronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi an 710071,
Reading. Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Optional. Color. Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995.
 Reading Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Color Optional Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995. Gerald S. Wasserman. Color Vision: An Historical ntroduction.
Reading Foley, Computer graphics, Chapter 13. Color Optional Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA 1995. Gerald S. Wasserman. Color Vision: An Historical ntroduction.
Images and Displays. Lecture Steve Marschner 1
 Images and Displays Lecture 2 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Introduction Computer graphics: The study of creating, manipulating, and using visual images in the computer. What is an image? A photographic print?
Images and Displays Lecture 2 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Introduction Computer graphics: The study of creating, manipulating, and using visual images in the computer. What is an image? A photographic print?
Sunderland, NE England
 Sunderland, NE England Robert Grosseteste (1175-1253) Bishop of Lincoln Teacher of Francis Bacon Exhibit featuring color ideas of Robert Grosseteste Closes Saturday! Exactly 16 colors: (unnamed) White
Sunderland, NE England Robert Grosseteste (1175-1253) Bishop of Lincoln Teacher of Francis Bacon Exhibit featuring color ideas of Robert Grosseteste Closes Saturday! Exactly 16 colors: (unnamed) White
Lecture 26. PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Finalities. Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
IFT3355: Infographie Couleur. Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal
 IFT3355: Infographie Couleur Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal Color Appearance Visual Range Electromagnetic waves (in nanometres) γ rays X rays ultraviolet violet
IFT3355: Infographie Couleur Victor Ostromoukhov, Pierre Poulin Dép. I.R.O. Université de Montréal Color Appearance Visual Range Electromagnetic waves (in nanometres) γ rays X rays ultraviolet violet
Color image processing
 Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
Color image processing Color images C1 C2 C3 Each colored pixel corresponds to a vector of three values {C1,C2,C3} The characteristics of the components depend on the chosen colorspace (RGB, YUV, CIELab,..)
Color Outline. Color appearance. Color opponency. Brightness or value. Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Color appearance
 Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
Color Outline Wavelength encoding (trichromacy) Three cone types with different spectral sensitivities. Each cone outputs only a single number that depends on how many photons were absorbed. If two physically
Photometric Image Processing for High Dynamic Range Displays. Matthew Trentacoste University of British Columbia
 Photometric Image Processing for High Dynamic Range Displays Matthew Trentacoste University of British Columbia Introduction High dynamic range (HDR) imaging Techniques that can store and manipulate images
Photometric Image Processing for High Dynamic Range Displays Matthew Trentacoste University of British Columbia Introduction High dynamic range (HDR) imaging Techniques that can store and manipulate images
Color Science. What light is. Measuring light. CS 4620 Lecture 15. Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD)
 Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Color Science CS 4620 Lecture 15 1 2 What light is Measuring light Light is electromagnetic radiation Salient property is the spectral power distribution (SPD) [Lawrence Berkeley Lab / MicroWorlds] exists
Color , , Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 11
 Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 11 Course announcements Homework 2 grades have been posted on Canvas. - Mean: 81.6% (HW1:
Color http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 11 Course announcements Homework 2 grades have been posted on Canvas. - Mean: 81.6% (HW1:
CS148: Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging. Displays. Topics. Spatial resolution Temporal resolution Tone mapping. Display technologies
 CS148: Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Displays Topics Spatial resolution Temporal resolution Tone mapping Display technologies Resolution World is continuous, digital media is discrete Three
CS148: Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Displays Topics Spatial resolution Temporal resolution Tone mapping Display technologies Resolution World is continuous, digital media is discrete Three
Visualizing High Dynamic Range Images in a Web Browser
 jgt 29/4/2 5:45 page # Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: Visualizing High Dynamic Range Images in a Web Browser Rafal Mantiuk and Wolfgang Heidrich The University of British Columbia Abstract. We present a technique
jgt 29/4/2 5:45 page # Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: Visualizing High Dynamic Range Images in a Web Browser Rafal Mantiuk and Wolfgang Heidrich The University of British Columbia Abstract. We present a technique
High Dynamic Range Imaging
 High Dynamic Range Imaging 1 2 Lecture Topic Discuss the limits of the dynamic range in current imaging and display technology Solutions 1. High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging Able to image a larger dynamic
High Dynamic Range Imaging 1 2 Lecture Topic Discuss the limits of the dynamic range in current imaging and display technology Solutions 1. High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging Able to image a larger dynamic
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2019 1 remaining Chapter 2 stuff 2 Mach Band
We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision.
 LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
LECTURE 4 SENSORY ASPECTS OF VISION We have already discussed retinal structure and organization, as well as the photochemical and electrophysiological basis for vision. At the beginning of the course,
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
IMAGE ENHANCEMENT - POINT PROCESSING
 1 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT - POINT PROCESSING KOM3212 Image Processing in Industrial Systems Some of the contents are adopted from R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, 2nd edition, Prentice
1 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT - POINT PROCESSING KOM3212 Image Processing in Industrial Systems Some of the contents are adopted from R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, 2nd edition, Prentice
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lecture 4: Colour Topics to be covered Motivation for Studying Colour Physical Background Biological Background Technical Colour Spaces Motivation Colour science
Color and Perception
 Color and Perception Why Should We Care? Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Some errors
Color and Perception Why Should We Care? Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Why Should We Care? Human vision is quirky what we render is not what we see Some errors
Visual Perception. Jeff Avery
 Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Visual Perception Jeff Avery Source Chapter 4,5 Designing with Mind in Mind by Jeff Johnson Visual Perception Most user interfaces are visual in nature. So, it is important that we understand the inherent
Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Color Space Mahdi Amiri March 2012 Sharif University of Technology Physics of Color Light Light or visible light is the portion of electromagnetic radiation that
Considerations for Standardization of VR Display. Suk-Ju Kang, Sogang University
 Considerations for Standardization of VR Display Suk-Ju Kang, Sogang University Compliance with IEEE Standards Policies and Procedures Subclause 5.2.1 of the IEEE-SA Standards Board Bylaws states, "While
Considerations for Standardization of VR Display Suk-Ju Kang, Sogang University Compliance with IEEE Standards Policies and Procedures Subclause 5.2.1 of the IEEE-SA Standards Board Bylaws states, "While
Color. Homework 1 is out. Overview of today. color. Why is color useful 2/11/2008. Due on Mon 25 th Feb. Also start looking at ideas for projects
 Homework 1 is out Color Lecture 2 Due on Mon 25 th Feb Also start looking at ideas for projects Suggestions are welcome! Overview of today Physics of color Human encoding of color Color spaces Camera sensor
Homework 1 is out Color Lecture 2 Due on Mon 25 th Feb Also start looking at ideas for projects Suggestions are welcome! Overview of today Physics of color Human encoding of color Color spaces Camera sensor
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Vision 1. Physical Properties of Light. Overview of Topics. Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8
 Vision 1 Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8 1 1 Overview of Topics Physical Properties of Light Physical properties of light Interaction of light with objects Anatomy of the eye 2 3 Light A
Vision 1 Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8 1 1 Overview of Topics Physical Properties of Light Physical properties of light Interaction of light with objects Anatomy of the eye 2 3 Light A
Image Processing: An Overview
 Image Processing: An Overview Sebastiano Battiato, Ph.D. battiato@dmi.unict.it Program Image Representation & Color Spaces Image files format (Compressed/Not compressed) Bayer Pattern & Color Interpolation
Image Processing: An Overview Sebastiano Battiato, Ph.D. battiato@dmi.unict.it Program Image Representation & Color Spaces Image files format (Compressed/Not compressed) Bayer Pattern & Color Interpolation
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Vision and Color. Reading. The lensmaker s formula. Lenses. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
OFFSET AND NOISE COMPENSATION
 OFFSET AND NOISE COMPENSATION AO 10V 8.1 Offset and fixed pattern noise reduction Offset variation - shading AO 10V 8.2 Row Noise AO 10V 8.3 Offset compensation Global offset calibration Dark level is
OFFSET AND NOISE COMPENSATION AO 10V 8.1 Offset and fixed pattern noise reduction Offset variation - shading AO 10V 8.2 Row Noise AO 10V 8.3 Offset compensation Global offset calibration Dark level is
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones.
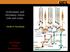 Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Achromatic and chromatic vision, rods and cones. Andrew Stockman NEUR3045 Visual Neuroscience Outline Introduction Rod and cone vision Rod vision is achromatic How do we see colour with cone vision? Vision
Visual Perception. Overview. The Eye. Information Processing by Human Observer
 Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
Visual Perception Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Class Introduction to DIP/DVP applications and examples Image as a function Concepts
Spectral colors. What is colour? 11/23/17. Colour Vision 1 - receptoral. Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision
 Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Colour Vision I: The receptoral basis of colour vision Colour Vision 1 - receptoral What is colour? Relating a physical attribute to sensation Principle of Trichromacy & metamers Prof. Kathy T. Mullen
Raster Graphics. Overview קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' What is an image? What is an image? Image Acquisition. Image display 5/19/2008.
 Overview Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models How do we perceive colors? How can we describe and represent colors? קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים
Overview Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models How do we perceive colors? How can we describe and represent colors? קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים
קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור
 קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models Overview How
קורס גרפיקה ממוחשבת 2008 סמסטר ב' Raster Graphics 1 חלק מהשקפים מעובדים משקפים של פרדו דוראנד, טומס פנקהאוסר ודניאל כהן-אור Images What is an image? How are images displayed? Color models Overview How
IMAGES AND COLOR. N. C. State University. CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking. Fall Lecture # 10
 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 10 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture
IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 10 IMAGES AND COLOR N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Color Image Processing
 Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Color Image Processing Jesus J. Caban Outline Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Color Perception & Analysis 1 Discuss Assignment #1 Project Proposal Due next Monday, Oct 4th Project proposal Submit
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference
 1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
1 Visual computation of surface lightness: Local contrast vs. frames of reference Alan L. Gilchrist 1 & Ana Radonjic 2 1 Rutgers University, Newark, USA 2 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Extended Dynamic Range Imaging: A Spatial Down-Sampling Approach
 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics October 5-8, 2014, San Diego, CA, USA Extended Dynamic Range Imaging: A Spatial Down-Sampling Approach Huei-Yung Lin and Jui-Wen Huang
2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics October 5-8, 2014, San Diego, CA, USA Extended Dynamic Range Imaging: A Spatial Down-Sampling Approach Huei-Yung Lin and Jui-Wen Huang
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital image processing is based on. Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis
 Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Chapter 2: Digital Image Fundamentals Digital image processing is based on Mathematical and probabilistic models Human intuition and analysis 2.1 Visual Perception How images are formed in the eye? Eye
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
To discuss. Color Science Color Models in image. Computer Graphics 2
 Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
Color To discuss Color Science Color Models in image Computer Graphics 2 Color Science Light & Spectra Light is an electromagnetic wave It s color is characterized by its wavelength Laser consists of single
Tone mapping. Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2009 Yung-Yu Chuang. with slides by Fredo Durand, and Alexei Efros
 Tone mapping Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2009 Yung-Yu Chuang 2009/3/5 with slides by Fredo Durand, and Alexei Efros Tone mapping How should we map scene luminances (up to 1:100,000) 000) to display
Tone mapping Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2009 Yung-Yu Chuang 2009/3/5 with slides by Fredo Durand, and Alexei Efros Tone mapping How should we map scene luminances (up to 1:100,000) 000) to display
CS6640 Computational Photography. 6. Color science for digital photography Steve Marschner
 CS6640 Computational Photography 6. Color science for digital photography 2012 Steve Marschner 1 What visible light is One octave of the electromagnetic spectrum (380-760nm) NASA/Wikimedia Commons 2 What
CS6640 Computational Photography 6. Color science for digital photography 2012 Steve Marschner 1 What visible light is One octave of the electromagnetic spectrum (380-760nm) NASA/Wikimedia Commons 2 What
